engine FIAT MAREA 2000 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 2000, Model line: MAREA, Model: FIAT MAREA 2000 1.GPages: 330
Page 83 of 330
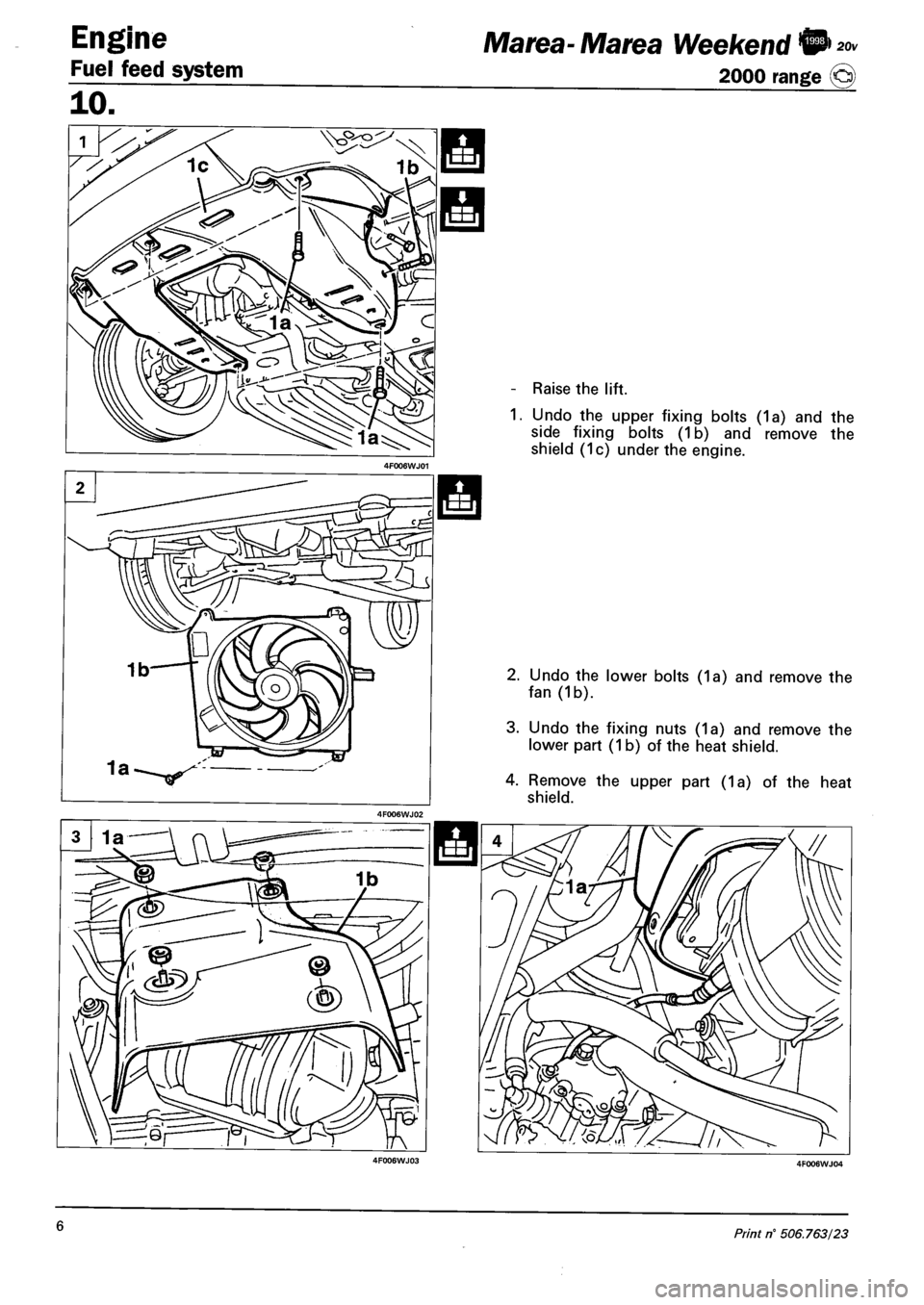
Engine
Fuel feed system
20v Marea- Marea Weekend •
2000 range @
Raise the lift.
Undo the upper fixing bolts (1a) and the
side fixing bolts (1b) and remove the
shield (1c) under the engine.
2. Undo the lower bolts (1a) and remove the
fan (1b).
3. Undo the fixing nuts (1a) and remove the
lower part (1 b) of the heat shield.
4. Remove the upper part (1a) of the heat
shield.
6 Print n° 506.763/23
Page 84 of 330
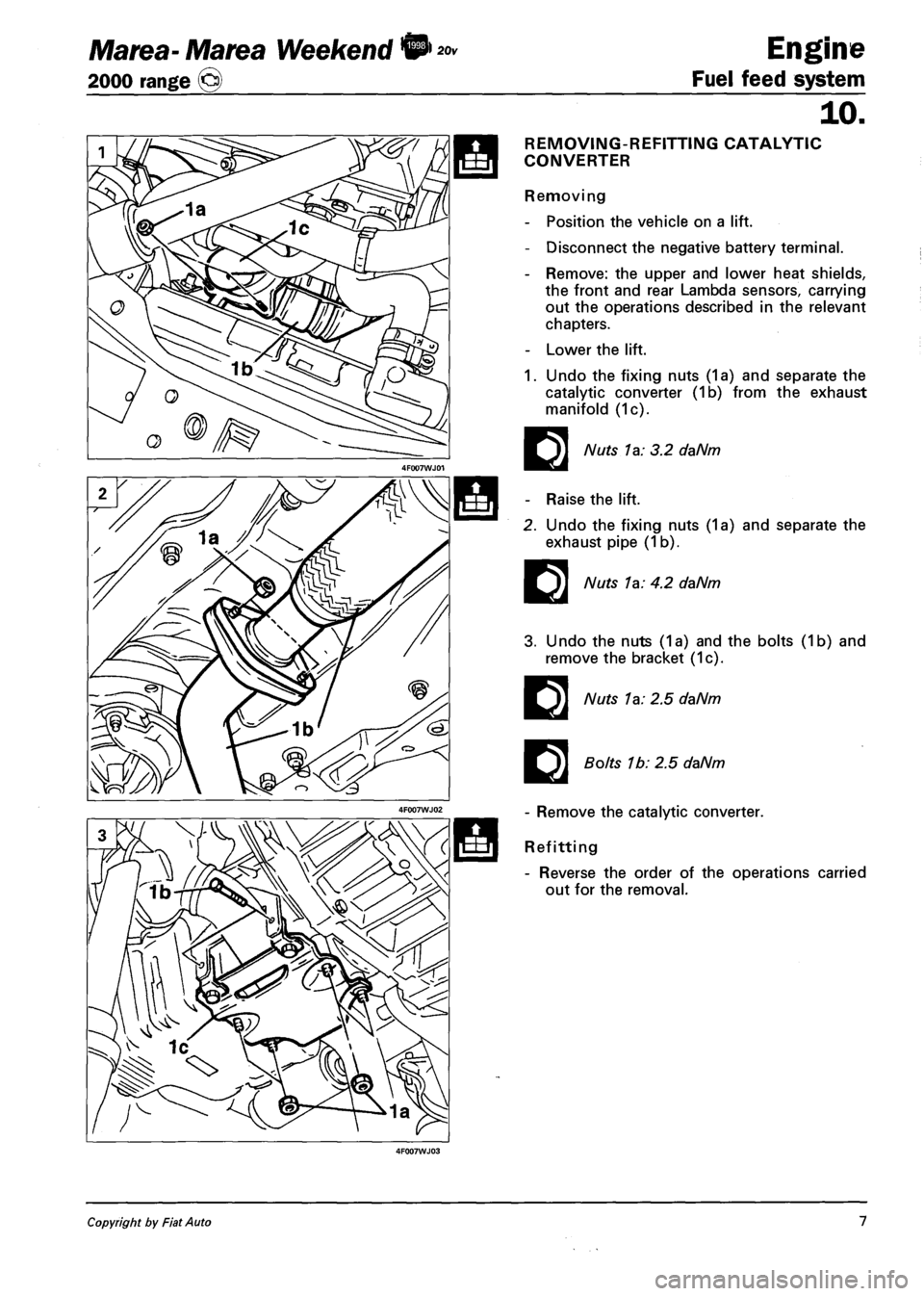
Marea- Marea Weekend 9
2000 range ©
Engine
Fuel feed system
10.
REMOVING-REFITTING CATALYTIC
CONVERTER
Removing
- Position the vehicle on a lift.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Remove: the upper and lower heat shields,
the front and rear Lambda sensors, carrying
out the operations described in the relevant
chapters.
- Lower the lift.
1. Undo the fixing nuts (1a) and separate the
catalytic converter (1b) from the exhaust
manifold (1c).
E
Nuts la: 3.2 daNm
- Raise the lift.
2. Undo the fixing nuts (1a) and separate the
exhaust pipe (1 b).
EI
Nuts 1a: 4.2 daNm
3. Undo the nuts (1a) and the bolts (1b) and
remove the bracket (1c).
E
E
Nuts 1a: 2.5 daNm
Bolts 1b: 2.5 daNm
- Remove the catalytic converter.
Refitting
- Reverse the order of the operations carried
out for the removal.
Copyright by Fiat Auto 7
Page 86 of 330

Marea- Marea Weekend 9 \) JTD
2000 range O
Engine
Index
FUEL SYSTEM
- Introduction
- System management strategies
- Fuel system functional diagram
- Diagram showing information ente
ring/leaving the control unit and
sensors/actuators
INJECTION SYSTEM WIRING DIA
GRAM
- Injection electronic control unit
- Rpm sensor
- Timing sensor
- Air flow meter
- Injectors
- Engine coolant temperature sensor
- Fuel temperature sensor
- Fuel pressure sensor
- Heater plugs control unit
- Accelerator pedal potentiometer
- Brake pedal switch
- Clutch pedal switch
- Excess pressure sensor
- Atmospheric pressure sensor
page
1
1
1
2
8
10
12
13
13
14
15
15
15
16
16
17
17
17
17
THROTTLE CASING
- Removing-refitting
E.G.R. VALVE
- Removing-refitting
E.G.R. VALVE SELF-ADJUSTMENT
MOTOR
- Removing-refitting
E.G.R. VALVE HEAT EXCHANGER
- Removing-refitting
SOLENOID VALVE ON VACUUM
RESERVOIR FOR THROTTLE CA
SING PNEUMATIC VALVE
- Removing-refitting
VACUUM RESERVOIR
- Removing-refitting
10.
page
30
31
32
32
34
34
FUEL SUPPLY CIRCUIT 18
- Immersed (auxiliary) pump and fuel
gauge assembly 19
- Fuel filter 19
- Pressure pump 20
- Fuel pressure regulator 20
- Multifunction valve 21
- Supply manifold (rail) 21
- Inertia safety switch 22
AIR SUPPLY CIRCUIT 23
- Throttle case 24
- Turbocharger 25
SUPERCHARGING PRESSURE
CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE
- Removing-refitting 35
FUEL FILTER
- Removing-refitting 35
PRESSURE REGULATOR
- Removing-refitting 36
EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES 27
- Oxidizing catalytic converter 27
- Exhaust gas recirculation circuit
(EGR) 27
- Recirculation circuit for crankcase
vapours (blow-by) 29
Copyright by Fiat Auto VI 01 Cancels anil replaces
Page 87 of 330

Marea- Marea Weekend © ™ Engine
2000 range Q Fuel feed system
10.
FUEL SYSTEM
INTRODUCTION
Marea and Marea Weekend 1.9 JTD cars are equipped with a 4 cylinder in line, 1910 cc turbodiesel en
gine with two valves per cylinder, an overhead camshaft, turbocharger and intercooler and electronic in
jection.
The fuel system ensures correct engine operation and can be divided into the following subsystems:
- Fuel feed circuit with common rail injection;
- air feed circuit;
- exhaust circuit;
- blow by vapour recirculation circuit;
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) circuit
Operation of the various circuits making up the fuel system is optimised by an electronic control system
managed by a special control unit.
The main feature of the fuel system is common rail fuel injection. Common rail is a higher pressure elec
tronic injection system for fast direct injection diesel engines.
The main features of the common rail system are as follows:
- availability of high injection pressures (up to 1350 bars);
- possibility of modulating these pressures (from a minimum of 150 bars to a maximum of 1350 bars)
independently of engine speed (rpm) and engine load;
- ability to operate at high engine speeds (up to 6000 rpm);
- precise injection control (injection advance and duration);
- reduced fuel consumption;
- reduced emissions.
FUEL SYSTEM MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
The management program (software) is stored inside the control unit memory and consists of a series of
strategies, each of which manages a precise system control function.
Through the use of information providd by the various sensors (input), each strategy processes a set of
parameters based on data stored in special control unit memory areas. It then controls system actuators
(output), i.e. the devices that allow the engine to operate.
The main purpose of these management strategies is to determine the exact amount of fuel to be injected
into the cylinders with timing (injection advance) and pressure designed to achieve the best possible en
gine performance in terms of power, fuel consumption, fumes, emissions and handling.
The main system management strategies are essentially as follows:
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
of injected fuel quantity;
of injection advance;
of injection pressure;
of auxiliary fuel pump;
of injection during over-run (cut-off);
of idle speed;
of maximum speed limitation;
of maximum torque limitation;
of fuel temperature;
of engine coolant temperature;
of air turbocharging pressure;
of glow plugs;
of exhaust fumes;
of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR);
of climate control system activation;
control of engine immobiliser operation (Fiat
CODE);
self-diagnosis
Copyright by Fiat Auto 1
Page 88 of 330
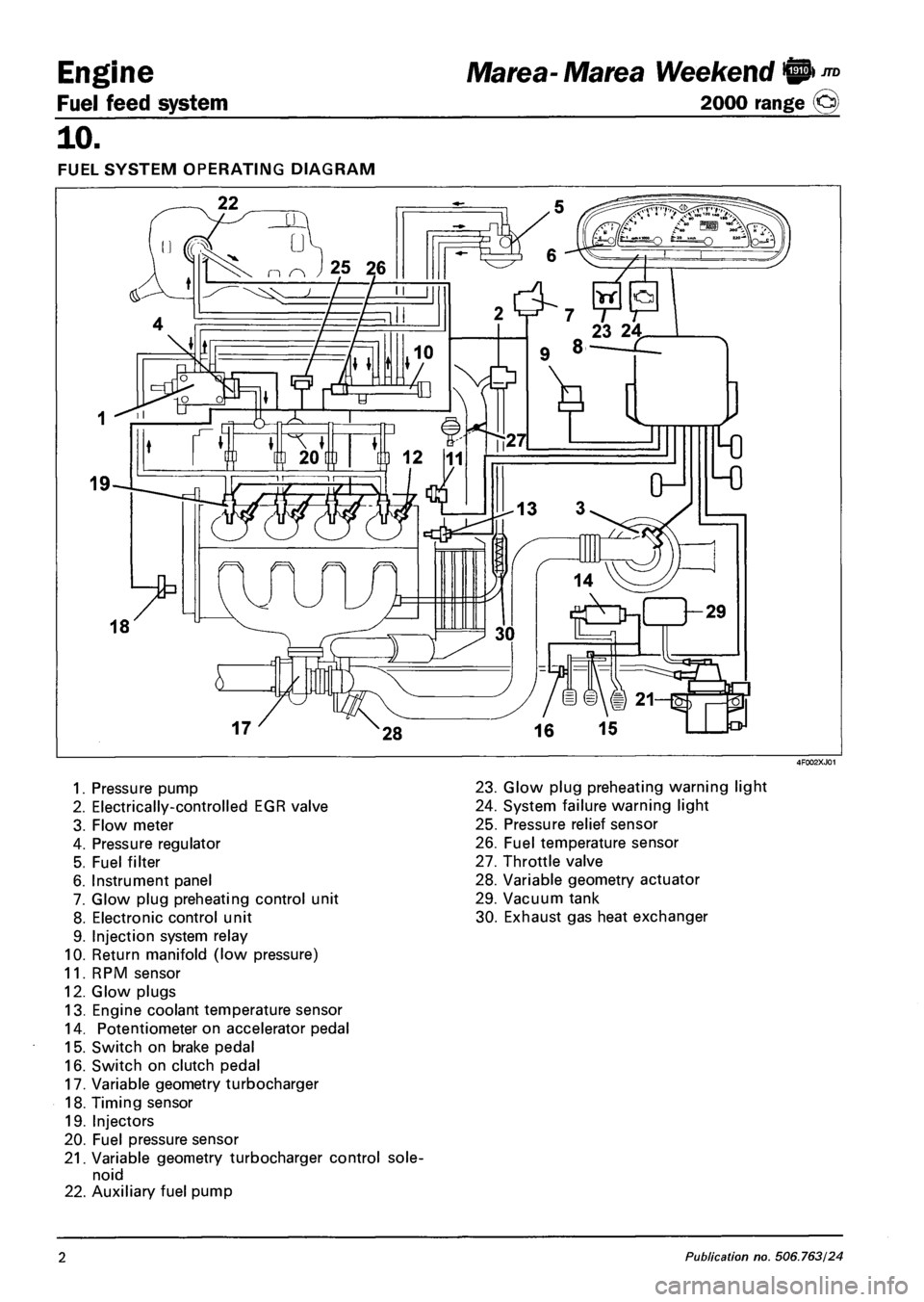
Engine
Fuel feed system
Marea- Marea Weekend © ™
2000 range ©
10.
FUEL SYSTEM OPERATING DIAGRAM
1. Pressure pump
2. Electrically-controlled EGR valve
3. Flow meter
4. Pressure regulator
5. Fuel filter
6. Instrument panel
7. Glow plug preheating control unit
8. Electronic control unit
9. Injection system relay
10. Return manifold (low pressure)
11. RPM sensor
12. Glow plugs
13. Engine coolant temperature sensor
14. Potentiometer on accelerator pedal
15. Switch on brake pedal
16. Switch on clutch pedal
17. Variable geometry turbocharger
18. Timing sensor
19. Injectors
20. Fuel pressure sensor
21. Variable geometry turbocharger control sole
noid
22. Auxiliary fuel pump
23. Glow plug preheating warning light
24. System failure warning light
25. Pressure relief sensor
26. Fuel temperature sensor
27. Throttle valve
28. Variable geometry actuator
29. Vacuum tank
30. Exhaust gas heat exchanger
2 Publication no. 506.763/24
Page 89 of 330

Ma tea- Marea Weekend 9 ™
2000 range (Q) Fuel feed system
Engine
10.
Control of injected fuel quantity
The control unit controls the fuel pressure regulator and injectors on the basis of output signals from the
accelerator pedal potentiometer, flow meter and rpm sensor.
The timing and thus the injection sequence are determined when the engine is started up using signals
from the rpm and timing sensor (synchronisation stage); injection timing is then implemented using the
rpm sensor signal alone and considering a injection sequence of 1 -3-4-2.
The control unit inhibits injection in the following cases:
- fuel pressure level greater than 1500 bars;
- fuel pressure level lower than 120 bars;
- engine speed higher than 6000 rpm.
When the engine has warmed up, maximum injection duration (injector opening time) is 1500 ns, but it
can reach 3000 ns during the start-up stage.
Control of injection advance
The electronic control unit determines injection advance mainly on the basis of the quantity of fuel to be
injected.
The injection advance is then corrected on the basis of coolant temperature and speed in order to com
pensate for ignition delays due to low temperatures in the combustion chamber during warm-up.
The optimum injection point is also processed to ensure driving comfort and emission limits laid down by
Euro 3 legislation.
Control of injection pressure
This control is of particular importance because injection pressure influences the following parameters:
- amount of fuel taken into the cylinders for the same injection time duration;
- injected fuel nebulation;
- spray penetration;
- lag between electrical control to injection and actual injection start and end times.
The above parameters engine behaviour significantly, particularly in terms of power output, exhaust emis
sions, noise levels and handling.
The injection control unit controls the pressure governor on the basis of engine load to obtain an optimal
line pressure at all times.
When the engine is cold, injection pressure is corrected on the basis of engine speed and engine coolant
temperature to meet engine needs at different operating temperatures.
Control of auxiliary fuel pump
The auxiliary fuel pump submerged in the tank is supplied by the injection control unit by means of a relay
when the ignition key is turned on.
Fuel supply to the pump is inhibited when one of the following condition occurs:
- when the ignition has been turned on for a certain length of time without the engine running;
- if the inertia switch cuts in.
Control of injection during over-run (cut-off)
The fuel cut-off strategy is implemented when the injection control unit receives information that the ac
celerator pedal has been released from the potentiometer.
Under these conditions, the control unit cuts off the fuel supply to the injectors and restores it before idle
speed is reached.
Copyright by Fiat Auto 3
Page 90 of 330

Fuel feed system
Engine Marea- Marea Weekend 9 ™
2000 range (Q)
10.
Control of idle speed
On the basis of signals from the rpm sensor and engine coolant temperature sensor, the injection control
unit controls the pressure governor and alters the injector control times to maintain idle speed stable at all
times.
Under certain conditions, the idle speed control unit also considers battery voltage.
Control of maximum speed limitation
According to rpm level, the injection control unit limits maximum speed by means of two types of inter
vention:
- as maximum speed approaches, it reduces the amount of fuel injected to reduce line pressure;
- when maximum speed is exceeded, it inhibits operation of the auxiliary pump and injectors.
Control of maximum torque limitation
On the basis of rpm level, the injection control unit computes limit torque and maximum permitted fume
index parameters on the basis of predefined, stored maps.
It then corrects the above parameters using engine coolant temperature and car speed data. The resulting
values are then used to modulate the amount of fuel to be injected by adjusting the pressure regulator and
injectors.
Control of fuel temperature
The injection control uint is kept constantly informed of fuel temperature by a sensor on the return mani
fold.
If fuel temperature exceeds a set value (about 110 °C), the control unit reduces line pressure by adjusting
the pressure governor, leaving injection times unaltered.
Control of coolant temperature
The injection control unit is constantly informed of coolant temperature by a sensor on the thermostat.
If engine coolant temperature or air conditioning fluid pressure exceeds certain levels, the control unit
performs the following actions:
- It reduces the amount of fuel injected by adjusting the pressure governor and injectors (power reduc
tion);
- it controls the engine radiator cooling fan.
Control of glow plugs
The injection control unit controls operation of the glow plug preheating control unit to bring the tem
perature in the combution chambers up to levels that promote fuel self-ignition and thus make start-up
easier.
The control unit controls the operation of the glow plug control unit for a certain time both before (pre
heating) and after (postheating) engine start-up and also controls activation of the warning light on the
control panel.
Preheating, postheating and glow plug warning light activation times vary according to engine coolant
temperature.
4 Publication no. 506.763/24
Page 91 of 330
![FIAT MAREA 2000 1.G Repair Manual Marea-Marea Weekend 9]
2000 range (j§)
I) JTD
Fuel feed system
Engine
10.
Exhaust fumes control
Through this function the injection control unit limits any exhaust fumes that could be produce FIAT MAREA 2000 1.G Repair Manual Marea-Marea Weekend 9]
2000 range (j§)
I) JTD
Fuel feed system
Engine
10.
Exhaust fumes control
Through this function the injection control unit limits any exhaust fumes that could be produce](/img/10/4653/w960_4653-90.png)
Marea-Marea Weekend 9]
2000 range (j§)
I) JTD
Fuel feed system
Engine
10.
Exhaust fumes control
Through this function the injection control unit limits any exhaust fumes that could be produced during
transition speeds.
To satisy these requirements the control unit processes the signals supplied by the accelerator pedal po
tentiometer, the rpm sensor and the air flow meter and controls the fuel pressure regulator and the injec
tors to meter the correct amount of fuel to inject.
Exhaust gas recirculation control
On the basis of the signals supplied by the rpm sensor, intake air quantity sensor, engine coolant tempe
rature sensor and accelerator pedal position sensor, the control unit calculates the operating times for the
EGR valve so that the exhaust gases are partly recirculated in certain engine operating conditions in line
with Euro 3 pollution control standards.
Air conditioning system engagement control
The injection control unit manages the operation of the air conditioning system compressor electro
magnet coupling following a logic aimed at preventing operating conditions that would adversely affect
engine performance.
- When the compressor is switched on the injection control unit increases the quantity of fuel during
idling to allow the engine to adjust to the increased power requirements and momentarily interrupts the
supply to the compressor in high engine power requirement conditions (strong acceleration).
Engine immobilizer function control
The system is equipped with an engine immobilizer function. This function is achieved through the pre
sence of a specific control unit (Fiat CODE), capable of conversing with the injection control unit and an
electronic key with a special transmitter for sending a recognition code.
Each time the key is turned to the OFF position, the Fiat CODE system completely deactivates the injecti
on control unit.
When the key is turned to the ON position the following operations take place, in order:
1. the injection control unit (whose memory contains a secret code) sends the Fiat CODE control unit a
request to send the secret code to deactivate the immobilizer functions;
2. the Fiat CODE control unit responds by only sending the secret code after, in turn, having received the
recognition code transmitted by the ignition key;
3. the recognition of the secret code allows the deactivation of the injection control unit immobilizer func
tion and its normal operation.
Autodiagnosis
The complete electronic fault diagnosis of the injection system is carried out by connecting the special
equipment (EXAMINER or EXAMINER PLUS) to the standardized diagnostic socket (EOBD).
The system is also equipped with a self-diagnostic function which recognizes, memorizes and signals any
faults.
If a fault is detected in the sensors or actuators, the recovery strategy is immediately activated in order to
ensure that the engine functions at an acceptable level. The vehicle can be driven to a service centre for
the appropriate repairs to be carried out.
Copyright by Fiat Auto 5
Page 92 of 330

Fuel feed system
Engine Marea- Marea Weekend © ™
2000 range @
10.
The control unit autodiagnostic system checks the signals coming from the sensors and compares them
with the figures allowed:
- signalling faults during starting
- warning light on for 4 seconds indicates test stage
- warning light off after 4 seconds indicates no fault with components that could alter the pollution con
trol standard figures
- warning light on after 4 seconds indicates fault.
- signalling faults during operation
- warning light on indicates fault
- warning light off indicates no fault with components that could alter the pollution control standard fig
ures.
- recovery
- from time to time, the control unit defines the type of recovery according to the components which are
faulty
- the recovery parameters are managed by components which are not faulty.
Control of cylinder balancing during idling
According to the signals coming from the sensors, the injection control unit controls the idle speed torque,
altering the injector operating times.
Control of irregular operation
Depending on the signals coming from the sensors, the injection control unit corrects the amount of fuel
to be injected in order to improve driveability and reduce jerking whilst driving.
The correction is achieved through the fuel pressure regulator and by varying the injector operating times.
Control of electrical balance
According to the battery voltage, the injection control unit alters the idle speed, to guarantee a sufficient
current supply from the alternator in situations where the consumers are absorbing a great deal of power.
The variation in the idle speed is achived by regulating the fuel pressure and altering the injector operat
ing times.
VGT variable geometry turbocharger control (1910 JTD 110 CV)
The injection control unit processes the signal coming from the supercharging sensor, at the various en
gine operating speeds, and determines the quantity of fuel to be injected, acting on the fuel pressure
regulator and the injector opening times.
In addition, through the solenoid valve, the control unit regulates the geometry of the turbine in order to
ensure optimum performance in all operating conditions.
Turbocharger waste gate valve control (1910 JTD 100 CV)
At the various engine operating speeds, the injection control unit processes the signal coming from the
supercharging sensor and determines the amount of fuel to inject, acting on the fuel pressure regulator
and the injector opening times.
In addition, the control unit controls the opening of the turbocharger waste gate valve, via the solenoid
valve, in order to ensure excellent performance in all operating conditions.
Control of throttle closing when engine is switched off
When the engine is switched off (ignition key in OFF position) the injection control unit closes the throt
tle valve located on the air intake duct via the special solenoid valve.
This action makes it possible to limit the tiresome shuddering of the engine whilst it is switching off.
6 .i. V!-01-.Cancelftand replaces Print n° 506.763/25
Page 93 of 330
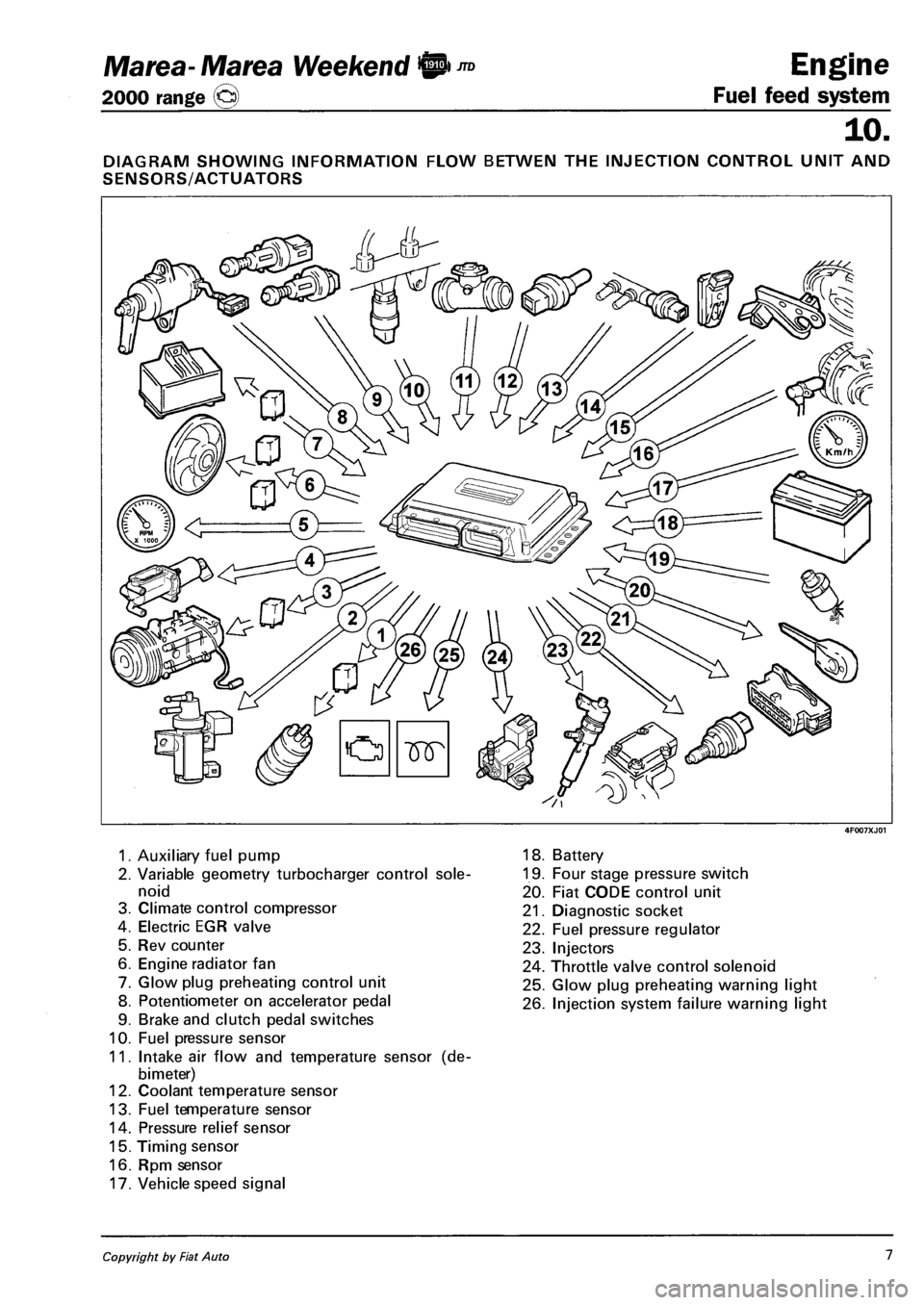
Marea- Marea Weekend 9 ™
2000 range ©
Engine
Fuel feed system
10.
DIAGRAM SHOWING INFORMATION FLOW BETWEN THE INJECTION CONTROL UNIT AND
SENSORS/ACTUATORS
1. Auxiliary fuel pump
2. Variable geometry turbocharger control sole
noid
3. Climate control compressor
4. Electric EGR valve
5. Rev counter
6. Engine radiator fan
7. Glow plug preheating control unit
8. Potentiometer on accelerator pedal
9. Brake and clutch pedal switches
10. Fuel pressure sensor
11. Intake air flow and temperature sensor (de-
bimeter)
12. Coolant temperature sensor
13. Fuel temperature sensor
14. Pressure relief sensor
15. Timing sensor
16. Rpm sensor
17. Vehicle speed signal
18. Battery
19. Four stage pressure switch
20. Fiat CODE control unit
21. Diagnostic socket
22. Fuel pressure regulator
23. Injectors
24. Throttle valve control solenoid
25. Glow plug preheating warning light
26. Injection system failure warning light
Copyright by Fiat Auto 1