Rear FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1998, Model line: PUNTO, Model: FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.GPages: 225, PDF Size: 18.54 MB
Page 31 of 225

1A.12
Every 20 000 miles - petrol models
18.7 Lift up the cover and remove the filter element (18-va!ve engines) 9 Fit a new air (liter element In position, ensuring that the edges are securely seated 10 Refit the air cloaner cover, engage the rear retainers and secure with the three bolts.
19 Spark plug renewal
1 The correct functioning of the spark plugs is vital for the correct running and efficiency of the engine. It is essential that the plugs fitted are appropnate for the engine (a suitable type is specified at the beginning of this Chapter. If this type is used and the engine Is In good condition, the spark plugs should not need attention between scheduled replacement intervals Spark plug cleaning Is rarely necessary, and should not be attempted
19.2a Disconnecting tho HT leads from Iho spark plugs on 8-valve engines ...
19.4 Removing the spark plugs
unless specialised equipment Is available, as damage can easily be caused to the firing ends. 2 To remove the plugs first remove the air cleaner assembly (8-vaive engines) or the a»r cleaner, resonator and inlet air duct (16-valve engines) with reference to Chapter 4A or 4B. if the marks on the original-equipment spark plug (HT) leads cannot be seen, mark the leads 1 to 4, to correspond to the cylinder the lead serves (No 1 cylinder is at the timing belt end of the engine). Pull the leads from the plugs by gripping the end fitting, not the lead, otherwise the lead conneciion may be Iractured (see illustrations) 3 It is advisable to remove the dirt from the spark plug recesses using a clean brush, vacuum cleaner or compressed air before removing the plugs, to prevent dirt dropping into the cylinders. 4 Unscrew the plugs using a spark plug spanner, suitable box spanner or a deep socket and extension bar (see illustration). Keep the socket aligned with the spark plug • If it is forcibly moved to one side, the ceramic insulator may be broken off. As each plug is removed examine 4 as fallows. 5 Examination of the spark plugs will give a good Indication of the condition of the engine. If the Insulator nose of the spark plug Is clean and white, with no deposits, this is Indicative of a weak mixture or too hot a plug (a hot plug transfers heal away from the electrode slowly, a cold plug transfers heat away quickly). 6 If the tip and insulator nose are covered with hard black-looking deposits, this
19.2b ... and on 16-valve engines
19.9 Ad|ustlng a spark plug electrode gap
indicates that the mixture Is too rich. If the plug is black and oily, then It is likely that the engine is fairly worn, as well as the mixture being too rich. 7 If the Insulator nose is covered with light tan to greyish-brown deposits, then the mixture Is correct and it is likely that (he engine Is in good condition. 6 The spark plug electrode gap is of considerable importance as, if it Is too large or too small, the size of the spark and its efficiency will be seriously impaired. The gap should be set to the value given in the Specifications at the beginning of this Chapter. 9 To set the gap. measure it with a feeler blade and then bend open, or closed, the outer plug elect/ode until the correct gap l9 achieved. The centre electrode should never be bent, as this may crack the insulator and cause plug I allure, if nothing worse. If using feeler blades, the gap is correct when the appropriate-size blade is a firm sliding fit (see illustration). 10 Special spark plug electrode gap adjusting tools are available from most motor accessory shops, or from some spark plug manufacturers, 11 Before fitting the spark plugs, check that the threaded connector sleeves are tight, and that the plug exterior surfaces and threads are clean (see Haynes Hint). 12 Remove the rubber hose (If used), and tighten the plug to the specified torque using the spark plug socket and a torque wrench, Refit the remaining spark plugs In the same manner. 13 Connect the HT leads In their correct order, and refit any components removed for access.
It is very often difficult to insert spark plugs into their holes without cross-threading them. To, avoid this possibility, fit a short length of Si 16 Inch Internal diameter rubber hose over the end of the spark plug. The flexible hose acts as a universal Joint to help align the plug with the plug hole. Should the plug beginto cross-thread, the hose will slip on the spark plug, preventing thread damage to the cylinder head
Page 34 of 225

Maintenance procedures - petrol models 1A.15
Every 40 000 miles (60 000 km) or 4 years
29 Rear brake shoe check
1 Chock the front wheels then Jack up the rear of Ihe car and support it on axle stands (see Jacking and Vehicle Support). Remove the rear roadwheels. 2 Using the inspection hole at the edge of the brake drum, check that the linings are not worn below Ihe minimum thickness given in the Specifications (see illustration). If necessary use a torch. 3 If the friction material on any shoe is worn down to the specified minimum thickness or
less,
all four shoes must be renewed as a set. 4 At the same time check for signs of brake
Kutti
leakage. 5 For a comprehensive check, the brake drum should be removed and cleaned. This
will allow the wheel cylinders to be checked, and the condition of the brake drum itself to be fully examined (see Chapter 9). 6 Refit the lubber plugs then lower the car to the ground.
30 Timing belt renewal
Refer to Chapter 2A or 2B. Note: Although the norma/ interval for timing belt renewal is 70 000 miles (105 000 km), it is strongly recommended that the interval Is reduced on vehicles which are subjected to intensive use. ie, mainly short journeys or a lot of stop-start driving. The actual belt renewal interval is therefore very much up to the individuaf owner. That being said, it is highly recommended to err on the side of safety, and
29.2 Check the thickness of the shoe friction material through the hole on the edge of the drum (arrowed)
renew the belt at 40 000 miles (60 000 km), bearing in mind the drastic consequences resulting from belt failure.
Every 60 000 miles (90 000 km) or 6 years
31 Emission control system check
Refer to Chapter 4D. A full check of the emissions control systems must be made by a Fiat dealer.
Every 80 000 miles (120 000 km)
32 Manual transmission all renewal S
1 Park the vehicle on a level surface, if possible over an inspection pit or on a ramp as the filler/level and drain plugs are accessed from order
the
engine compartment. If necessary
Jack
ip the vehicle and support on axle stands (see
Jacking and vehicle
support). 2 Wipe clean the area around the filler/leval And drain plugs, which are on the front and bottom of the transmission (see illustration).
3 Using an Allen key. unscrew the filler/level plug and clean it. 4 Position a suitable container beneath the transmission, then use the Allen key to unscrew the drain plug. Allow the oil to completely drain. 5 Wipe clean the drain plug then refit and tighten It. 6 Fill the transmission with ihe correct grade and quantity of oil, referring to Section 26 when checking the level. Refit and lighten the filler/level plug. 7 Where applicable lower the vehicle to the ground. 32.2 Transmission drain plug location (viewed from under the vehicle)
Every 2 years (regardless of mileage)
33 Coolant renewal
I
Cooling system draining
A
Warning: Walt until the engine Is cold before starting this pro-cedure. Do not allow antifreeze to come In contact with your skin, or with the painted surfaces of the vehicle. Rinse off spills immediately with plenty of water.
Ndver
leave antifreeze lying around In an open container, or fn a puddle In the
driveway or on the garage floor. Children and pets are attracted by its sweet smell, but ant/freeze can be fatal if ingested. 1 With the engine completely cold, cover the expansion tank cap with a wad of rag. and slowly turn the cap anticlockwise to relieve the pressure in the cooling system (a hissing sound will normally be heard). Wait until any pressure remaining in the system is released, then continue to tum the cap until it can be removed. 2 Position a suitable container beneath the radiator bottom hose connection, then release the retaining clip and ease the hose from the radiator stub (see illustration). If the hose 33.2 Disconnecting the radiator bottom hose to drain tho coolant
Page 37 of 225

1B»1
Chapter
1
Part B:
Routine maintenance & servicing - diesel models
Contents
Air filter renewal 13 Auxiliary drivebelt(s) check and renewal 16 Brake fluid renewal 2d Brake warning lamp operation check 5 Clutch adjustment check 17 Coolant renewal 27 Drtv«shaft gaiter check 10 Emissions control systems check 25
Engage
oil and filter renewal 3 Exhaust system check 9 Front brake pad check 6
Fuel
fitter renewal 12 Fuel Filter water draining 4 Headlight beam adjustment 20
Hinge and lock lubrication 19 Hose and fluid leak check 6 Idle speed check and adjustmenl 11 Introduction ... 1 Manual transmission oil level check 22 Manual transmission oil renewal - 26 Pollen filter renewal 14 Rear brake shoe check 23 Regular maintenance 2 Road test 21 Steering and suspension check 15 Timing belt renewal 24 Underbody sealant check 7 Valve clearance check and adjustment 16
^m
Degrees of difficulty
Easy, sutable for % Fairly easy, suitable FaHycifficult, i'. Difficult, suitable fa Very difficult, novice with irttte % for beginner with suitable for competent experienced DIY
1
suitable for expert DIY * or professional jQ experience some experience DIY mechanic mechanic 1
suitable for expert DIY * or professional jQ
Page 39 of 225

Maintenance schedule - diesel models 1B.3
The mamtenance intervals in this manual are provided with the assumption that you. reI ihe dealer, will be carrying out the work.
These
are the minimum maintenance intervals recommended by us for vehicles driven daily.
ff you wish to keep your vehicle In peak condition at all times, you may wish to perform some of these procedures more often. We encourage frequent maintenance, because it enhances the efficiency.
performance and resale value of your vehicle. When the vehicle Is new, it should be serviced by a factory-authorised dealer service department, in order to preserve the factory warranty.
Every 250 miles (400 km) or weekly O Refer to Weekly checks
Every 5000 miles (7500 km) or
6
months - whichever comes first • Renew the engine oil and filter (Section 3) P Drain any water from the fuel filter (Section 4)
Every 10 000 miles (15 000 km) or
12
months - whichever comes first ill addition lo tho Items listed above, cany out the following; D Check the operation of the brake warning lamp J (Section 5) Check the front brake pads for wear (Section 6) :-G Check the underbody and sealant for damage j" (Section 7) n Hose and fluid leak check (Section 8) 0 Check the condition of the exhaust system and its 1 mountings (Section 9) -D Check the condition of the driveshaft gaiters ", (Section 10) O Check and adjust the idle speed (Section 11) ;0 Renew (he fuel filter (Section 12) J] Renew the air filter element (Section 13) L) Renew the pollen filter (Section 14) •• Check the steering and suspension components • for condition and security (Section 15)
Every 20 000 miles (30 000 km) or
2
years - whichever comes first In addition to the Items listed above, cany out the following: (P Check and if necessary adjust the tension of the auxiliary drlvebeltfs) (Section 16) '• Check the freeplay and height of the clutch pedal " (Section 17) D Check and if necessary adjust the valve clearances (Section 18) Lubricate all hinges and locks (Section 19) • Check the headlight beam adjustment (Section 20) O Cany out a road test (Section 21)
Every 30 000 miles (45 000 km) or
3 years - whichever comes first In addition to the Items listed above, cany out the following: • Check and if necessary top-up the manual transmission oil level (Section 22)
Every 40 000 miles (60 000 km) or
4 years - whichever comes first In addition to the items listed above, cany out the following: • Check the rear brake shoes for wear (Section 23) • Renew the timing belt (Section 24)'
•Note: Although the normal interval for timing belt renewal is 70 000 miles (ids 000 km), it is strongly recommended that the belt Is renewed at 40 000 miles (60 000 km) on vehicles which are subjected to intensive use, le. mainly short Journeys or a lot of stop-start driving. The actual bait renewal interval Is therefore very much up to the Individual owner, but bear in mind that sevefe engine damage will result if the belt breaks.
Every 60 000 miles (90 000 km) or
6 years - whichever comes first In addition to the Items listed above, cany out the following: • Check the condition and operation of the emission control system components (Section 25)
Every 80 000 miles (120 000 km) • Renew the manual transmission oil (Section 26)
Every 2 years
(regardless of mileage) • Renew the engine coolant (Section 27) • Renew the brake fluid (Section 28)
Page 40 of 225
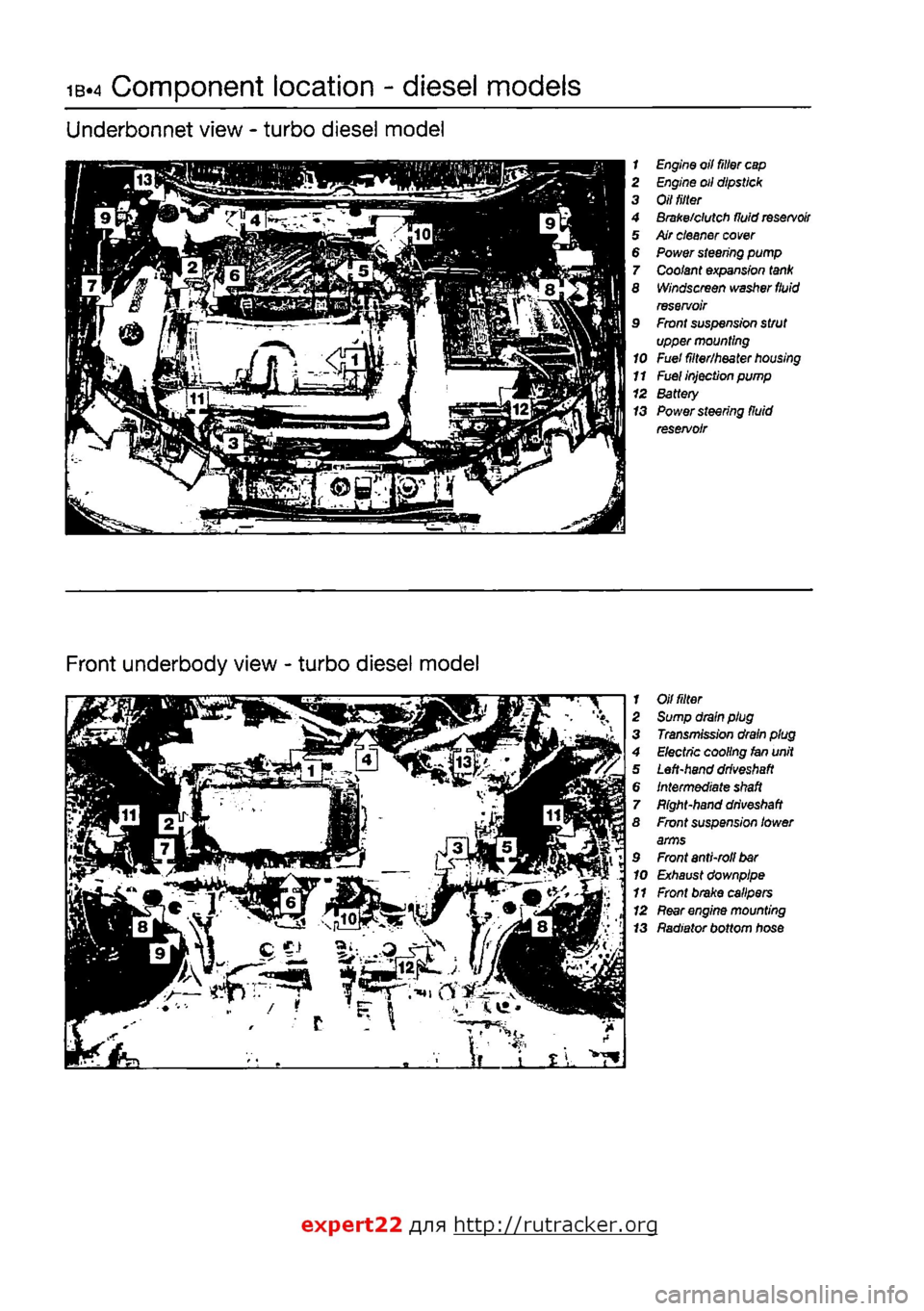
ib-4 Component location - diesel models
Underbonnet view - turbo diesel model
1 Engine oil filter
cap
2 Engine oil dipstick 3 Oil
tilter
4 Brake/clutch fluid
reservoir
5 Air cleaner
cover
6 Power steering pump 7 Coolant expansion
tank
8 Windscreen washer
fluid
reservoir 9 Front suspension strut upper mounting 10 Fuel filter/heater
housing
11
Fuel
injection pump 12 Battery 13 Power steering fluid reservoir
Front underbody view - turbo diesel model
1 Oil
fitter
2 Sump drain plug 3 Transmission drain plug 4 Electric cooling fan unit 5 Left-hand
driveshaft
6 Intermediate
shaft
7 Bight-hand
driveshaft
8 Front suspension lower arms 9 Front anti-roll
bar
10 Exhaust downpipe 11 Front brake calipers 12
Rear
engine mounting 13 Radiator bottom hose
expert22 fl/ia http://rutracker.org
Page 41 of 225

Component location - diesel models ib-s
Rear underbody view - turbo diesel model
1
Fuel tank
2
Exhaust
tailpipe
and
silencer 3 Fear axle 4 Coil springs 5
Rear anti-roll bar
€
Handbrake cables
7
Rear brake pressure regulating valve
8
Rear shock
absorber
lower
mountings
Maintenance procedures
1 Introduction
This Chapter Is designed to help the home mechanic maintain his/her vehicle for safety, economy, long life and peak performance. The Chapter contains a master maintenance schedule, and Sections dealing specifically with each task in the schedule. Visual checks, adjustments, component renewal and other helpful items are included. Refer to the accompanying illustrations of the engine compartment and the underside of the vohicle for the locations of the various components. Servicing your vehicle in accordance with ihe mileage/time maintenance schedule and the following Sections will provide a planned maintenance programme, which should result in a long and reliable service life. This is a comprehensive plan, so maintaining some items but not others at the specified service internals, will not produce the same results. As you service your vehicle, you will ctecover that many of the procedures can. and should, be grouped together, because of the particular procedure being performed, or because of the proximity of two otherwise-unrelated components to one another. For example, if the vehicle is raised for any reason, the exhaust can be inspected at the same time as the suspension and steering components. The first step in this maintenance programme is to prepare yoursetf before the
actual work begins. Read through all the Sections relevant to the work to be carried out. then make a list and gather all the parts and tools required. If a problem is encountered, seek advice from a parts specialist, or a dealer service department.
2 Regular maintenance
1 If, from the time Ihe vehicle is new, the routine maintenance schedule is followed closely, and frequent checks are made of fluid levels and high-wear Items, as suggested throughout this manual, the engine wifl be kept in relatively good running condition, and the need for additional work will be minimised. 2 It is possible that there will be times when the engine is running poorly due to the lack of regular maintenance. This is even more likely if a used vehicle, which has not received regular and frequent maintenance checks, is purchased, in such cases, additions! work may need to be carried out, outside of the regular maintenance intervals. 3 If engine wear is suspected, a compression test {refer to Chapter 2C} will provide valuable information regarding the overall performance of the main internal components. Such a test can be used as a basis to decide on the extent of the work to be carried out. If, for example, a compression test indicates serious Internal engine wear, conventional maintenance as
described in this Chapter will not greatly improve the performance of the engine, and may prove a wa3te of time and money, unless extensive overhaul work Is carried out first. 4 The following series of operations are those usually required to Improve the performance of a generally poor-running engine:
Primary operations a,I Clean, Inspect and test the battery (See Weekly checks). b) Check all the engine-related fluids (See Weekly checks). c) Drain the water from the fuel filter (Section 4) d) Check the condition and tension of the auxiliary dnvebeft(s) (Section 16). e) Check the condition of the air fitter, and renew if necessary (Section 13). f) Check the condition of all hoses, and check for fluid leaks (Section 8). g) Check the engine idle speed setting {Section 11). h) Check the exhaust gas emissions (Section 25). 5 If the above operations do not prove fully effective, carry out the following secondary operations:
Secondary operations All items listed under Pnmary operations, plus the following: a) Check the charging system (Chapter 5A, Section 4). b) Renew the fuel filter (Section 12) and check the fuel system (see Chapter 4Q.
Page 43 of 225

Maintenance procedures - diesel models ib.?
Every 10 000 miles (15 000 km) or 12 months
5 Brake warning lamp operation check 1
1 With Ihe ignition Key inserted and turned to the MAR position, open the bonnet and depress the button on the top of the brake
fluid
reservoir cap (see illustration). I
As
the button is pressed, the brake warning
lamp
on the instrument panel should light. 3 If Ihe lamp fails to illuminate, check the operation of the level switch using a continuity taster, then refer to Chapter t2, Section 5,
and
check the Instrument panel bulb.
6 Front brake pad check ^
I
1 firmly apply Ihe handbrake, then jack up the front of the car and support it securely on arie stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). Remove the front roadwheels. 2 Using a steel rule, measure the thickness of
the
friction material of the brake pads on both brakes. This must not be less than 1.5 mm. Ctefc the thickness of the pad friction material through the hole on the front of the caliper
|see
lustration), 3
For a
comprehensive check, the brake pads should be removed and cleaned. The operation of the caliper can then also bo checked, and the condition of the brake disc iteeil can be fully examined on both sides. Refer to Chapter 9 for further Information. 4 If any pad's friction material Is worn to the specified thickness or less, all lour pads must to renewed as a set. Refer to Chapter 9. 5 On completion refit the roadwheels and lower the car to the ground.
7 Underbody sealant check f^
1 Jack up the front and rear of the car and support on axle stands (see Jacking and
vehicle
support). Alternatively position the car over
an
Inspection pit. 2 Check the complete underbody, wheel housings and side sills for corrosion and/or damage to the underbody sealant. If evident,
rapairi
8
Hose
and fluid leak check
1 Visually inspect the engine Joint faces. g3skets and seals for any signs of water or oil leaks. Pay particular attention to the areas
5.1 Depress tho button on the top of the brake fluid reservoir cap
around the camshaft cover, cylinder head, oil filter and sump joint faces. Bear in mind that, over a period of time, some very slight seepage from these areas is to be expected -what you are really looking for is any indication of a serious leak (see Haynes Hint). Should a teak be found, renew the offending gasket or oil seal by referring to the appropriate Chapters In this manual, 2 Also check the security and condition of all the engine-related pipes and hoses. Ensure thai all cable-ties or securing clips are In place and in good condition. Clips which are broken or missing can lead to chafing of the hoses, pipes or wiring, which could cause more serious problems In the future. 3 Carefully check the radiator hoses and heater hoses along their entire length. Renew any hose which is cracked, swollen or deteriorated. Cracks will show up better If the hose is squeezed. Pay close attention to the hose clips that secure the hoses to the cooling system components. Hose clips can pinch and puncture hoses, resulting in leaks. 4 Inspect all the cooling system components (hoses. )olnt faces etc.) for leaks. A leak in the cooling system will usually show up as white or rust-coloured deposits on the area adjoining the leak, Where any problems of this nature are found on system components, renew the component or gasket with reference to Chapter 3. 5 With the vehicle raised, inspect the fuel tank and filler neck for punctures, cracks and other damage, The connection between the filler neck and tank is especially critical. Sometimes a rubber filler neck or connecting hose will leak due to loose retaining clamps or deteriorated rubber. 6 Carefully check all rubber hoses and metal fuel lines leading away from the fuel tank. Check for loose connections, deteriorated hoses, crimped lines, and other damage. Pay particular attention to the vent pipes and hoses, which often loop up around the filler neck and can become blocked or crimped. Follow the lines to the front of the vehicle, carefully Inspecting them all the way. Renew damaged sections as necessary.
6.2 Check the thickness of the pad friction material through the hote on the front of the caliper
7 With the vehicle raised, check along the length of the underside for leaks from the metal brake lines, caused by damage or corrosion. 8 At each front brake caliper, check the area around the brake pipe unions and the bleed nipples for hydraulic fluid leakage, 9 Remove the front roadwheels and chock for fluid leakage from the area around the caliper piston seal. Check that the tip of the piston dust seal is correctly located in its groove. If it has been displaced, the brake caliper should be removed and overhauled as described in Chapter 9, to check for internal dirt Ingress or corrosion. 10 Check the area surrounding the master cylinder and vacuum servo unit for signs of corrosion, Insecurity or hydraulic fluid leakage. Examine the vacuum hose leading to the servo unit for signs of damage or chafing. 11 From within the engine compartment, check the security of all fuel hose attachments and pipe unions, and Inspect the fuel hoses and vacuum hoses for kinks, chafing and deterioration. 12 Where applicable, check the condition of the power steering fluid hoses and pipes.
A leak in the cooling system will usually show up as white or rust coloured deposits on the area adjoining the leak.
Page 48 of 225

1B«12 Every 20 000 miles - diesel models
21 Road test
Instruments and electrical equipment 1 Check the operation of atl instruments and electrical equipment. 2 Make sure that all instruments read correctly, and switch on all electrical equipment rn turn, to check that It functions properly. Steering and suspension 3 Check for any abnormalities in the steering, suspension, handling or road feel. 4 Drive the vehicle, and check that there are no unusual vibrations or noises. 5 Check that the steering feete positive, with no excessive sloppiness, or roughness, and check for any suspension noises when cornering and driving over bumps. Drivetrain 6 Check (he performance of the engine, clutch, transmission and driveshafts.
7 Listen for any unusual noises from the engine, clutch and transmission. 8 Make sure that the engine runs smoothly when Idling, and that there is no hesitation when accelerating. 9 Check that the clutch action is smooth and progressive, that tho drive is taken up smoothly, and that the pedal travel Is not excessive. Also listen for any noises when the clutch pedal is depressed. 10 Check that all gears can be engaged smoothly without noise, and that the gear lever action Is not abnormally vague or notchy. 11 Listen for a metallic clicking sound from ihe front of the vehicle, as the vehicle « driven slowly In a circle with the steering on full-lock. Carry out this check In both directions, if a clicking noise is heard, this Indicates wear in a driveshaft |oinl, in which case renew the joint if necessary.
Check the braking system 12 Make sure that the vehicle does not pull to one side when braking, and that the wheels do not lock prematurely when braking hard.
13 Check that there Is no vibration through the steering when braking. 14 Check that the handbrake operates correctiy without excessive movement of th« lever, end that it holds the vehicle stationery on a slope. 15 Test the operation of the brake servo unit as follows. With the engine off, depress the footbrake four or five times to exhaust the vacuum. Hold the brake pedal depressed, then start the engine. As the engine starts, there should be a noticeable give In the brake pedal as vacuum builds up. Allow the engine to run for at least two minutes, and then switch it off. If the brake pedal is depressed now, it should be possible to detect a hiss from the servo es the pedal is depressed. After about four or five applications, no fimher hissing should be heard, and the pedal should feel considerably harder. Note: The vacuum for the servo unit is provided by the vacuum pump mounted on the left-hand end of t/ie cylinder head.
Every 30 000 miles (45 000 km) or 3 years
22 Manual transmission oil level check ;5§
1 Park the vehicle on a level surface. If possible over an inspection pit or on a ramp as the filler/level plug is best reached from under Ihe engine compartment. The oil level must be checked before the car Is driven, or at least 5 minutes after the engine has been switched off. If the oil is checked Immediately after driving the car. some of the oil will remain distnbuted around the transmission compo-nents, resulting In an inaccurate level reading. 2 Wipe clean the area around the filler/level plug, which is situated on tho front of the
transmission (see illustration). Using an Allen key. unscrew the plug and clean it. 3 The oil level should reach the lower edge of the filler/level hole. A certain amount of oil will have gathered behind the filler/level plug, and will trickle out when it is removed; this does not necessarily Indicate that the level Is correct. To ensure that a true level Is established, wait until the Initial trickle has stopped, then add oil as necessary until a trickle of new oil can be seen emerging. The level will be correct when the flow ceases; use only good-quality oil of the specified type-Make sure that the vehicle Is completely level when checking the level and do not overfill. 4 When the level is correct refit and tighten the plug and wipe away any spilt oil.
22.2 Transmission filler/level plug location
Every 40 000 miles (60 000 km) or 4 years
23 Rear brake shoe check
1 Chock the front wheels then jack up the rear of the car and support It on axle stands (see Jacking and Vehicle Support), Remove the rear roadwhecla. 2 Using the inspection hole at the edge ot the brake drum, check that the linings are not worn below the minimum thickness given In the Spec ifi cat Ions (see Illustration). If necessary use a torch. 3 If the friction material on any shoe is worn down to the specified minimum thickness or iess. all four shoes must be renewed as a set, 4 At the same time check for signs of brake fluid leakage. 5 For a comprehensive check, the brake
drum should be removed and cleaned. This will allow the wheel cylinders to be checked, and the condition of the brake drum itself to be fully examined (see Chapter 9). 8 Refit the rubber plugs then lower the car to the ground.
24 Timing belt renewal
Refer to Chapter 2C. Note: Although the normal interval for timing belt
ranees/a!
is 70 000
mHes
(105 000
km),
it is strong recommended that the interval is reduced on vehicles which are subjected to intensive use, ie, mainly short journeys or a lot of stop-start driving. The actual belt renewal interval is therefore very much up to tho individual owner.
That being said, it is highly recommended to err on the side of safety, and renew (he belt at
this
earlier interval, bearing in mind the drastic consequences resulting from belt fetfure.
23.2 Check the thickness of the shoe friction material through the hole on the edge of the drum (arrowed)
Page 56 of 225

2A*10 SOHC (8-valve) petrol engine in-car repair procedures
6.3 Camshaft cover gasket
not attempt to lover it ofl • instead free >t by working around the cover and lapping it lightly with a soft-faced mallet, 3 Recover the camshaft covor gasket {see Illustration). Inspect the gasket carefully. And renew It If damage or deterioration is evident. 4 Clean the mating surfaces of the cylinder head and camshaft cover thoroughly, removing all traces of oil and old gasket - take care to avoid damaging the surfaces as you do this.
Refitting 5 Locate a new gasket on the cylinder head and make sure it Is correctly seated. 6 Lower the cover onto the gasket making sure the gasket is not displaced. 7 Insert Ihe mounting bolts and tighten them progressively to the specified torque. 8 Refit the air cleaner assembly and inlet duct with reference to Chapter 4A or 48.
7 Camshaft oil seal • renewal I
1 Remove the timing beft and camshaft sprocket as described in Sections 4 and 5, 2 Using a suitable hooked Instrument, remove the oil seal from the cylinder head taking care not to damage the surface of (he camshaft. 3 Clean the seating in the cylinder head and the end of the camshaft. To prevent damage to the new olf seal as it is being fitted, wrap some adhesive tape around the end of the camshaft and lightly oil it.
4 Dip the new oil seal In oil then locate it over the camshaft making sure that the sealing lips are facing inwards, 5 Using a suitable tubular drift, drive the oil seal squarely Into the cylinder head. Remove the adhesive tape. 8 Refit the camshaft sprocket and liming belt wtth reference to Sections 5 and 4.
8 Crankshaft oil seals - ^ renewal S
Front (right-hand side) oil seal 1 The fronl oil seal is located in tho oil pump on the front of the crankshaft. Remove the timing belt as described in Section 4 and the crankshaft sprocket as described in Section 5. 2 Using a hooked instrument, remove the oil seal from the oil pump casing taking care not to damage the surface of the crankshaft. 3 Clean Ihe seating in the housing and the surface of the crankshaft. To prevent damage to the new oil seal as it is being fitted, wrap some adhesive tape around the end of the crankshaft and lightly oil it. 4 Dtp the new oil seal In oil then offer It up 1o the oil pump casing making sure that tho sealing lips are facing Inwards. G Using a suitable tubular drift, drive the oil seal squarely into the casing. Remove the adhesive tape. 6 Refit the crankshaft sprocket and timing belt with reference to Sections S and 4.
Rear {left-hand side) oil seal Note: The following paragraphs describe renewal of the rear oil seal leaving the housing in position. Refer to Chapter 2D for details of removing the housing. 7 Remove the fiywheel/drlveplate as described in Section 10. 8 Using a suitable hooked instrument, remove the oil seal from the rear oil seat housing taking care not to damage the surface of Ihe crankshaft. 9 Clean the seating In the nousing and the surface of the crankshaft. Check the crankshaft for burrs which may damage the sealing lip of the new seal, and If necessary use a fine file to remove them,
10 Dip the new seal In clean engine oil and carefully locate it over the crankshaft rear flange making sure that It is the correct way round. 11 Progressively tap the oil seal Into the housing keeping It square to prevent distortion. A block of wood is useful for this purpose. 12 Refit the fiywheet/drlvepiate with refer-ence to Section 10.
9 Cylinder head -removal and refitting I
i Removing the timing belt inner covers 9.12 Removing the cylinder head
Removal 1 Disconnect the battery negative termine! (refer to Disconnecting the battery In the Reference Section of this manual). 2 Drain the cooling system as described In Chapter 1A. then remove the air cleaner and ducting as described in Chapter 4A or 48. 3 Disconnect the accelerator cable and controls from the throttle housing. 4 Disconnect the fuel hoses. 5 Disconnect the coolant and vacuum hoses from the cylinder head and inlet manifold. 6 Disconnect all electrical leads noting their location. 7 Remove the Ignition colls with reference to Chapter 58. 8 Remove the timing belt as described in Section 4, then unbolt end remove the timing belt inner covers (see Illustration). 9 Unbolt and remove the Inlet manifold, complete with throttle housing. On MPI models unbolt the fuel rail. 10 Unbolt the exhaust manifold from th» cylinder head, and tie it to the front of tto engine compartment. If preferred remove the manifold completely by unbolting Ihe downpipe. Also disconnect iha downpipe bracket. 11 Unscrew the cylinder head bolts hall a turn at a time in the reverse order to thai shown In illustration 9.24b. When the bolts in free, remove them wtth their washers. 12 Lift the cylinder head from Ihe block (see Illustration), if It is stuck tight Insert pieces
of
wood Into the exhaust or Inlet ports, and use them as levers to rock the head off the block. On no account drive levers into the gasket joint, nor attempt to tap the head sideways,
as
It Is located on positioning dowels. 13 Remove and discard the cylinder heed gasket and the manifold gaskets. 14 The cylinder head can be dismantled after removing the camshaft and cam followers as described in Chapter 2D. 15 If the valves have been ground-in, the valve clearances will require adjusting, as described In Chapter 1A. This should be dons before the cylinder head is refitted to the engine.
Page 58 of 225

2A*10 SOHC (8-valve) petrol engine in-car repair procedures
10.10 Tighten the flywheel bolt to the specified torque However, it may be possible lo have it surface*ground; seek (he advice of a Rat dealer or engine reconditioning specialist, 5 If Ihe ring gear is badly worn or has missing teeth, the flywheel must be renewed. Automatic transmission models 6 Check the driveplate for signs of damage and renew it if necessary. If the ring gear is badly worn or has missing teeth, the driveplate must be renewed.
Refitting 7 Clean the mating surfaces of the flywheel/ drivoplate and crankshoft. Remove any remaining locking compound from the threads of the crankshaft holes, using the correct-size tap. if available.
ft a suitable tap fs not . # | available, cut two slots down jHlNTI
toe
threads of ono of the old bolts with a hacksaw, and use the bolt to remove the locking compound from the throads.
8 If the new retaining bolts are not supplied with their threads already pre-coated, apply a suitable thread-locking compound to the threads of each bolt. 9 Offer up the fiywhee'/drlveplate lo the crankshaft, using the alignment marks made during removal, and fit the new retaining bolts (together with the spacer plate on manual transmission models), 10 Lock the flywheel/dnveplate using Ihe method employed on dismantling, and tighten
the retaining bolts to the specified torque (see illustration), 11 Refit the clutch on manual transmission models as described in Chapter 6. 12 Relit the transmission as described In Chapter 7A or 78.
11 Engine mountings • inspection and renewal
inspection 1 Firmly apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the car and support it securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). 2 Check Ihe mounting rubbers to see if they are cracked, hardened or separated from the metal at any point; renew the mounting if any such damage or deterioration is evident. 3 Check that all the mounting's fasteners are securely tightened; use a torque wrench to check II possible. 4 Using a large screwdriver or a crowbar, check for wear In the mounting by carefuliy levering against It to check for free play. Where this is not possible enlist the
aid
of
an
assistant to move the engina/transmission back
and
forth, or from s»de to side, while you watch the mounting. While some free play rs to bo expected even from new components, excessive wear
should
be obvious. If excessive free play is found, check first that the fasteners are correctly secured, then renew any worn components as described below.
Renewal Right-hand mounting 5 Firmly apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the car and support it securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). 8 Place a trolley jack beneath the right-hand side of Ihe engine, with a block of wood on the jack head. Raise the jack until it is supporting the weight of the engine. 7 Unscrew the nut securing the engine bracket to the mounting. 8 Lower the engine slightly then unboll the mounting from the body. 9 Locate the new mounting on the body, insert the bolts and tighten to the specified torque.
10 Raise tne engine and locate the bracket on the mounting. Refit tho nut and tighten lo the specified torque. 11 Remove the trolley jack and lower the vehicle to the ground. Left-hand mounting 12 Firmly apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the car and support it securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support) 13 Place a trolley |sck beneath the transmission, with a block of wood on the jack head. Raise the jack until it is supporting tne weight of the engine/transmission. 14 Unscrew Ihe bolts securing the left-hand mounting to tho body. 15 Unscrew the nut securing ihe mounting to the transmission bracket and recover the washers. 16 Lower the transmission sufficiently to remove the mounting from the transmission bracket. 17 Locate the new mounting In the trans-mission bracket and refit the nut and washers. Tighten the nut to the specified torque. 18 Raise the engine and refit the mounting-to-body bolts. Tighten the bolts to the specified torque. 19 Remove the Irolloy jack and lower the vehicle lo the ground. Rear mounting 20 Firmly apply the handbrake, then Jack up the front of the car and support It securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). 21 Working beneath Ihe vehicle, unscrew Ihe bolts secunng the rear engine mounting to the underbody. 22 Temporarily support the weight of the engine/transmission using a trolley jack. 23 Unbolt the rear mounting assembly from Ihe transmission and withdraw from under the vehicle. 24 Unscrew the bolt and separate Ihe bracket from tlve mounting. 28 Fitting the new mounting Is a reversal of the removal procedure.
12 Sump -removal and refitting
12.2 Removing the flywheel housing cover plate 12.4 Removing the sump
Removal 1 Firmly apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the car and support it securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). Drain the engine oil as described in Chapter 1 A. 2 Unbolt and remove the cover plate from the lower pari of the llywheel housing (see illustration). 3 Refer to Chapter 4D and unbolt the exhaust Iront pipe from Ihe manifold. Undo Ihe support bracket fastenings and lower the front pipe clear of the sump. 4 Unscrew the sump securing screws and nuts and pull the sump downwards to remove it (see Illustration). The joint sealant will