ignition FIAT UNO 1983 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1983, Model line: UNO, Model: FIAT UNO 1983Pages: 303, PDF Size: 10.36 MB
Page 76 of 303

5 Condenser (capacitor)-
removal, testing and refitting
1
The purpose of the condenser (sometimes
known as the capacitor) is to ensure that when
the contact breaker points open there is no
sparking across them which would weaken
the spark and cause rapid deterioration of the
points.
The condenser is fitted in parallel with the
contact breaker points. If it develops a short
circuit it will cause ignition failure as the points
will be prevented from interrupting the low
tension circuit.
1If the engine becomes very difficult to start
(or begins to misfire whilst running) and the
breaker points show signs of excessive
burning, suspect the condenser has failed
with open circuit. A test can be made by
separating the points by hand with the ignition
switched on. If this is accompanied by a
bright spark at the contact points, it is
indicative that the condenser has failed.
2Without special test equipment, the only
sure way to diagnose condenser trouble is to
replace a suspected unit with a new one and
note if there is any improvement.
3To remove the condenser from the
distributor, take out the screw which secures
it to the distributor body and disconnect its
leads from the terminals.
4When fitting the condenser, it is vital to
ensure that the fixing screw is secure. The
lead must be secure on the terminal with no
chance of short circuiting.
6 Distributor-
removal and refitting
3
1Remove the spark plug from No. 4 cylinder
and then turn the crankshaft either by
applying a spanner to the pulley nut or by
jacking up a front wheel, engaging top gear
and turning the wheel in the forward direction
of travel.
2Place a finger over the plug hole and feel
the compression being generated as the
piston rises up the cylinder bore.
3Alternatively, if the rocker cover is off,
check that the valves on No. 1 cylinder are
closed.
4Continue turning the crankshaft until the
flywheel and flywheel housing (BTDC) ignition
timing marks are in alignment. Number 4
piston is now in firing position.
5Remove the distributor cap and place it to
one side complete with high tension leads.
6Disconnect the distributor vacuum hose
and low tension lead (photo).
7Mark the distributor pedestal mounting
plinth in relation to the crankcase. Also mark
the contact end of the rotor in relation to the
rim of the distributor body.8Unbolt the clamp plate and withdraw the
distributor.
9Refit by having No. 4 piston at its firing
position and the distributor rotor and pedestal
marks aligned, then push the distributor into
position, mating it to the splined driveshaft.
10If a new distributor is being fitted then of
course alignment marks will not be available
to facilitate installation in which case, hold the
unit over its mounting hole and observe the
following.
903 cc engine: Distributor cap high tension
lead sockets pointing towards alternator and
at 90º to centre line of rocker cover. Contact
end of rotor arm pointing towards No. 4
contact in distributor cap (when fitted).
1116 cc and 1301 cc engine: Distributor
vacuum unit pointing downwards at 135º to
rear edge of timing belt cover. Contact end of
rotor arm pointing towards No. 4 contact in
distributor cap (when fitted).
11Tighten the distributor clamp bolt,
reconnect the vacuum hose and the low
tension leads. Refit the distributor cap. Screw
in the spark plug.
12Check the ignition timing as described in
Section 4.
7 Distributor (mechanical
breaker type)- overhaul
3
Ducellier
1The cap must have no flaws or cracks and
the HT terminal contacts should not be
severely corroded. The centre spring-loaded
carbon contact is renewable. If in any doubt
about the cap, buy a new one.
2The rotor deteriorates minimally, but with
age the metal conductor tip may corrode. It
should not be cracked or chipped and the
metal conductor must not be loose. If in
doubt, renew it. Always fit a new rotor if fitting
a new cap.
3With the distributor removed as described
in the preceding Section, take off the rotor
and contact breaker.4To remove the contact breaker movable
arm, extract the clip and take off the washer
from the top of the pivot post.
5Extract the screw and remove the fixed
contact arm.
6Carefully record the setting of the advance
toothed segment and then remove the spring
clip and vacuum capsule fixing screws and
withdraw the capsule with link rod.
7Pick out the lubrication pad from the recess
in the top of the distributor shaft. Unscrew the
screw now exposed.
8Mark the relationship of the cam to the
counterweight pins and then remove the cam
assembly.
9There is no way to test the bob weight
springs other than by checking the
performance of the distributor on special test
equipment, so if in doubt, fit new springs
anyway. If the springs are loose where they
loop over the posts, it is more than possible
that the post grooves are worn. In this case,
the various parts which include the shaft will
need renewal. Wear to this extent would mean
that a new distributor is probably the best
solution in the long run. Be sure to make note
of the engine number and any serial number
on the distributor when ordering.
10If the mainshaft is slack in its bushes or
the cam on the spindle, allowing sideways
play, it means that the contact points gap
setting can only be a compromise; the cam
position relative to the cam follower on the
moving point arm is not constant. It is not
practical to re-bush the distributor body
unless you have a friend who can bore and
bush it for you. The shaft can be removed by
driving out the roll pin from the retaining collar
at the bottom. (The collar also acts as an oil
slinger to prevent excess engine oil creeping
up the shaft.)
Marelli
11With the distributor removed from the
engine, take off the spark shield and rotor.
12Remove the contact breaker and carrier
as described in Section 2.
13Refer to paragraphs 9 and 10 for details of
counterweight springs and shaft bushes
(photo).
Ignition system 4•5
6.6 Distributor LT connection4.5 Distributor clamp plate nut
4
Page 77 of 303

Reassembly
14This is a reversal of dismantling. On
Ducellier distributors, make sure that the
advance toothed segment is returned to its
original setting otherwise the advance curves
for your particular engine will be upset.
8 Ignition coil (mechanical
breaker ignition)
1Coils normally last the life of a car. The
most usual reason for a coil to fail is after
being left with the ignition switched on but the
engine not running. There is then constant
current flowing, instead of the intermittent
flow when the contact breaker is opening. The
coil then overheats, and the insulation is
damaged (photo).
2If the coil seems suspect after fault finding,
the measurement of the resistance of the
primary and secondary windings (usually an
ohmmeter) can establish its condition. If an
ohmmeter is not available, it will be necessary
to try a new coil.
9 Digiplex (electronic) ignition
- location of components and
precautions
1The main components of this system are
located within the engine compartment as
shown.
2On cars equipped with this system, it is
4•6 Ignition system
Fig. 4.7 Main components of Digiplex ignition system (Sec 9)8.1 Ignition coil
Fig. 4.6 Exploded view of typical Ducellier distributor (Sec 7)
1 Cap
2 Rotor
3 Movable breaker arm
4 Vacuum advance link
5 Fixed contact breaker arm
6 Contact breaker baseplate
7 Cam assembly8 Centrifugal advance weight
control springs
9 Driveshaft and plate
10 Body
11 LT insulator
12 Condenser
13 Vacuum capsule14 Cap retaining spring
15 Thrust washer
16 Spacer washer
17 Driving dog
18 Retaining pin
19 Felt pad
7.13 Marelli distributor centrifugal weights
and springs
1 Control unit
2 Cut-out control unit
3 Ignition coil
4 Flywheel (engine
speed) sensor
5 Crankshaft pulley
(TDC) sensor
6 Vacuum hose
Page 78 of 303

important that the following precautions are
observed.
3Never start the engine if the battery leads
are loose.
4Do not stop the engine by pulling off a
battery lead.
5Remove the control unit if ambient
temperature (paint drying oven) is above 80ºC
(176ºF).
6Never connect or disconnect the multi-plug
at the control unit unless the ignition is
switched off.
7Disconnect the battery negative lead before
carrying out electric body welding.10 Digiplex (electronic) ignition
- checks and adjustments
3
1Without special equipment, any work on the
system components should be restricted to
the following.
Engine speed sensor
2The gap between the sensor and the teeth
of the flywheel should be between 0.25 and
1.3 mm (0.0099 to 0.0512 in). Any
deviation will be due to mechanical damage to
the sensor, no adjustment being possible.
TDC sensor
3The gap between the sensor and one of the
TDC reference marks on the crankshaft pulley
should be between 0.4 and 1.0 mm (0.016 to
0.039 in).
4Any deviation will be due to the sensor
plate becoming loose. To reposition it will
necessitate setting No. 1 piston at TDC which
can only be carried out accurately by your
dealer using special tools.
Supply circuit and continuity of
coil primary winding
5Connect a test lamp between contacts 11
and 9 of the multi-plug having first pulled it
from the control unit.
6Switch on the ignition, the test lamp should
come on. If it does not, either the connection
at the positive pole of the control unit or the
coil primary winding is open.
Control unit earth
7Connect a test lamp between contacts 8
and 9 of the multi-plug having first pulled it
from the control unit. Switch on the ignition,
the test lamp should come on. If it does not,
improve the earth connection.
11 Spark plugs
1
1The correct functioning of the spark plugs is
vital for the correct running and efficiency of the
engine. It is essential that the plugs fitted are
appropriate for the engine, and the suitable type
is specified at the beginning of this chapter. If
Ignition system 4•7
Fig. 4.9 Digiplex control unit (Sec 9)
1 Vacuum hose connector
2 Multi-plug socket
1 Control unit
2 Distributor
3 Ignition coil4 TDC sensor
5 Wiring connector plug6 Engine speed sensor
7 Wiring connector plug
Fig. 4.8 Location of Digiplex ignition system components (Sec 9)
Fig. 4.13 Test lamp connected between
terminals 8 and 9 of control unit multi-plug
(Sec 10)Fig. 4.12 Test lamp connected between
terminals 11 and 9 of control unit
multi-plug (Sec 10)
Fig. 4.11 TDC sensor gap (Sec 10)
Fig. 4.10 Engine speed sensor gap
(Sec 10)
4
Page 79 of 303
this type is used and the engine is in good
condition, the spark plugs should not need
attention between scheduled replacement
intervals. Spark plug cleaning is rarely
necessary and should not be attempted unless
specialised equipment is available as damage
can easily be caused to the firing ends.
2At the specified intervals, the plugs should
be renewed. The condition of the spark plug
will also tell much about the overall condition
of the engine.
3If the insulator nose of the spark plug is
clean and white, with no deposits, this is
indicative of a weak mixture, or too hot a plug.
(A hot plug transfers heat away from the
electrode slowly - a cold plug transfers it away
quickly.)
4If the tip of the insulator nose is covered
with sooty black deposits, then this is
indicative that the mixture is too rich. Should
the plug be black and oily, then it is likely that
the engine is fairly worn, as well as the mixture
being too rich.
5The spark plug gap is of considerable
importance, as, if it is too large or too small
the size of the spark and its efficiency will be
seriously impaired. The spark plug gap should
be set to the gap shown in the Specifications
for the best results.
6To set it, measure the gap with a feeler
gauge, and then bend open, or close, the
outer plug electrode until the correct gap is
achieved. The centre electrode should never
be bent as this may crack the insulation and
cause plug failure, if nothing worse.
7When fitting new plugs, check that the plug
seats in the cylinder head are quite clean.
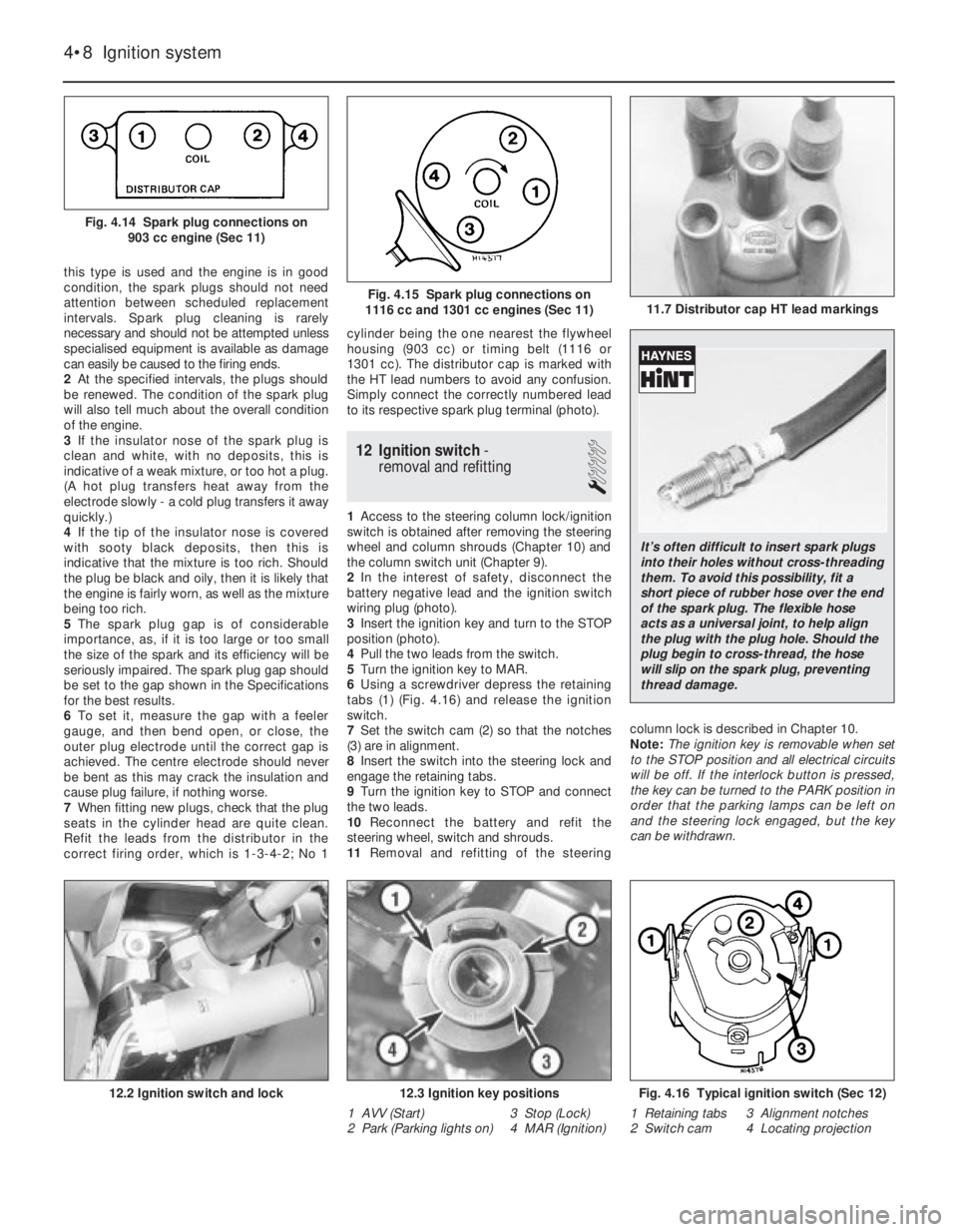
Refit the leads from the distributor in the
correct firing order, which is 1-3-4-2; No 1cylinder being the one nearest the flywheel
housing (903 cc) or timing belt (1116 or
1301 cc). The distributor cap is marked with
the HT lead numbers to avoid any confusion.
Simply connect the correctly numbered lead
to its respective spark plug terminal (photo).
12 Ignition switch-
removal and refitting
1
1Access to the steering column lock/ignition
switch is obtained after removing the steering
wheel and column shrouds (Chapter 10) and
the column switch unit (Chapter 9).
2In the interest of safety, disconnect the
battery negative lead and the ignition switch
wiring plug (photo).
3Insert the ignition key and turn to the STOP
position (photo).
4Pull the two leads from the switch.
5Turn the ignition key to MAR.
6Using a screwdriver depress the retaining
tabs (1) (Fig. 4.16) and release the ignition
switch.
7Set the switch cam (2) so that the notches
(3) are in alignment.
8Insert the switch into the steering lock and
engage the retaining tabs.
9Turn the ignition key to STOP and connect
the two leads.
10Reconnect the battery and refit the
steering wheel, switch and shrouds.
11Removal and refitting of the steeringcolumn lock is described in Chapter 10.
Note: The ignition key is removable when set
to the STOP position and all electrical circuits
will be off. If the interlock button is pressed,
the key can be turned to the PARK position in
order that the parking lamps can be left on
and the steering lock engaged, but the key
can be withdrawn.
4•8 Ignition system
Fig. 4.16 Typical ignition switch (Sec 12)
1 Retaining tabs 3 Alignment notches
2 Switch cam 4 Locating projection12.3 Ignition key positions
1 AVV (Start) 3 Stop (Lock)
2 Park (Parking lights on) 4 MAR (Ignition)12.2 Ignition switch and lock
11.7 Distributor cap HT lead markingsFig. 4.15 Spark plug connections on
1116 cc and 1301 cc engines (Sec 11)
Fig. 4.14 Spark plug connections on
903 cc engine (Sec 11)
It’s often difficult to insert spark plugs
into their holes without cross-threading
them. To avoid this possibility, fit a
short piece of rubber hose over the end
of the spark plug. The flexible hose
acts as a universal joint, to help align
the plug with the plug hole. Should the
plug begin to cross-thread, the hose
will slip on the spark plug, preventing
thread damage.
Page 80 of 303

Fault finding - mechanical breaker ignition system
Ignition system 4•9
4
Engine fails to start
m mLoose battery connections
m mDischarged battery
m mOil in contact points
m mDisconnected ignition leads
m mFaulty condenser
Engine overheats, lacks power
m
mSeized distributor weights
m mPerforated vacuum pipe
m mIncorrect ignition timing
Engine starts and runs but misfires
m
mFaulty spark plug
m mCracked distributor cap
m mCracked rotor arm
m mWorn advance mechanism
m mIncorrect spark plug gap
m mIncorrect contact points gap
m mFaulty condenser
m mFaulty coil
m mIncorrect timing
m mPoor engine/transmission earth connections
Fault finding - Digiplex (electronic) ignition system
Engine fails to start
m
mExcessive gap on TDC sensor
m mTDC or engine speed sensor short circuited or earthed
m mDefective ignition control unit
m mControl unit multi-plug contacts corroded
m mDefective coil
Engine lacks power, high fuel consumption
m
mIncorrect ignition advance
m mTDC sensor incorrectly set
m mDistributor vacuum hose blocked
Page 88 of 303

20By connecting a pressurised container to
the master cylinder fluid reservoir, bleeding is
then carried out by simply opening each bleed
screw in turn and allowing the fluid to run out,
rather like turning on a tap, until no air is
visible in the expelled fluid.
21By using this method, the large reserve of
hydraulic fluid provides a safeguard against
air being drawn into the master cylinder
during bleeding which often occurs if the fluid
level in the reservoir is not maintained.
22Pressure bleeding is particularly effective
when bleeding “difficult” systems or when
bleeding the complete system at time of
routine fluid renewal.
All methods
23When bleeding is completed, check and
top up the fluid level in the master cylinder
reservoir.
24Check the feel of the brake pedal. If it
feels at all spongy, air must still be present in
the system and further bleeding is indicated.
Failure to bleed satisfactorily after a
reasonable period of the bleeding operation,
may be due to worn master cylinder seals.
25Discard brake fluid which has been
expelled. lt is almost certain to be
contaminated with moisture, air and dirt
making it unsuitable for further use. Clean
fluid should always be stored in an airtight
container as it absorbs moisture readily
(hygroscopic) which lowers its boiling point
and could affect braking performance under
severe conditions.
13 Vacuum servo unit-
description
A vacuum servo unit is fitted into the brake
hydraulic circuit on 55 and 70 models in series
with the master cylinder, to provide assistance
to the driver when the brake pedal is
depressed. This reduces the effort required by
the driver to operate the brakes under all
braking conditions.
The unit operates by vacuum obtained from
the induction manifold and comprises basically
a booster diaphragm and non-return valve. The
servo unit and hydraulic master cylinder are
connected together so that the servo unit
piston rod acts as the master cylinder pushrod.
The driver’s braking effort is transmitted
through another pushrod to the servo unit
piston and its built-in control system. The servo
unit piston does not fit tightly into the cylinder,
but has a strong diaphragm to keep its edges
in constant contact with the cylinder wall, so
assuring an air tight seal between the two
parts. The forward chamber is held under
vacuum conditions created in the inlet manifold
of the engine and, during periods when the
brake pedal is not in use, the controls open a
passage to the rear chamber so placing it
under vacuum conditions as well. When the
brake pedal is depressed, the vacuum passageto the rear chamber is cut off and the chamber
opened to atmospheric pressure. The
consequent rush of air pushes the servo piston
forward in the vacuum chamber and operates
the main pushrod to the master cylinder.
The controls are designed so that
assistance is given under all conditions and,
when the brakes are not required, vacuum in
the rear chamber is established when the
brake pedal is released. All air from the
atmosphere entering the rear chamber is
passed through a small air filter.
Under normal operating conditions, the
vacuum servo unit is very reliable and does
not require overhaul except at very high
mileages. In this case, it is far better to obtain
a service exchange unit, rather than repair the
original unit.
It is emphasised that the servo unit assists
in reducing the braking effort required at the
foot pedal and in the event of its failure, the
hydraulic braking system is in no way affected
except that the need for higher pressures will
be noticed.
14 Vacuum servo unit-
servicing and testing
1Regularly, check that the vacuum hose
which runs between the servo unit and the
inlet manifold is in good condition and is a
tight fit at both ends.
2If broken or badly clogged, renew the air
filter which is located around the brake pedal
push rod. Access to this is obtained by
disconnecting the pushrod from the
cross-shaft or pedal arm, withdrawing the
pushrod, dust excluding boot and end cap.
3If the new filter is cut diagonally from its
centre hole, future renewal can be carried out
without the need for disconnection of the
pushrod.
4If the efficiency of the servo unit is suspect,
it can be checked out in the following way.
5Run the engine, then switch off the ignition.
Depress the footbrake pedal; the distinctive
in-rush of air into the servo should be clearly
heard. It should be possible to repeat this
operation several times before the vacuum in
the system is exhausted.
6Start the engine and have an assistant
apply the footbrake pedal and hold it down.
Disconnect the vacuuum hose from the servo.
There should not be any in-rush of air into the
servo through the connecting stub. lf there is,
the servo diaphragm is probably faulty. During
this test, expect the engine to idle roughly,
unless the open end of the hose to the inlet
manifold is plugged. Reconnect the hose.
7With the engine off, depress the brake
pedal fully. Start the engine with the brake
pedal still depressed; the pedal should be felt
to go down fractionally.
8If the results of these tests are not
satisfactory, remove the unit and fit a new one
as described in the next Section.
15 Vacuum servo unit-
removal and refitting
3
1Syphon as much fluid as possible out of the
master cylinder reservolr.
2Disconnect electrical leads from the
terminals in the reservoir cap then uncouple
the rigid pipelines from the master cylinder
body. Be prepared to catch leaking fluid and
plug the open ends of the pipelines.
3The master cylinder can be unbolted now
from the servo unit, or detached later when
the complete assembly is withdrawn.
4Working inside the car, disconnect the
servo pushrod from the pedal then remove the
servo mounting nuts.
5Withdraw the servo assembly into the
engine compartment, then remove it to the
bench. lf the master cylinder is still attached,
cover the wings with protective sheeting, in
case brake fluid is spilled during removal.
6Refitting is a reversal of the removal
process, but adjust the pushrod clearance as
described in Section 9. On completion of
refitting, bleed the complete hydraulic system
as described in Section 12. Note: Where the
help of an assistant is available, the servo
pushrod need not be disconnected from the
pedal. The rod is a sliding fit in the servo and
the servo can be simply pulled off the rod.
Refitting without having disconnected the rod
from the pedal can be difficult unless the help
of an assistant is available.
16 Handbrake- adjustment
1
Adjustment is normally automatic, by the
movement of the rear brake shoes on their
automatic adjusters.
However, owing to cable stretch,
supplementary adjustment is occasionally
required at the control lever adjuster nut. The
need for this adjustment is usually indicated
by excessive movement of the control lever
when fully applied.
1The rear brakes should be fully applied
when the handbrake control lever has been
pulled over four or five notches.
2If adjustment is required, release the
8•8 Braking system
16.2 Handbrake adjuster nuts
Page 93 of 303

ease the holder out of the alternator. Inspect
the brushes and if worn below the specified
minimum length, they must be renewed.
7Disconnect the brush leads by unsoldering
or carefully cutting them.
8When soldering the new brush leads, do
not allow solder to run down them or their
flexibility will be ruined.
9When inspecting or renewing brushes,
check the surface of the slip rings. Clean them
with solvent or if they are very discoloured,
use very fine glasspaper.
6 Voltage regulator
1This is of integral type and is part of the
brushholder assembly.
2No provision is made for adjustment or
overhaul.
7 Starter motor-
description and testing
2
1The starter motor may be one of two
different makes. Both are of pre-engaged
type.
2This type of starter motor incorporates a
solenoid mounted on top of the starter motor
body. When the ignition switch is operated,
the solenoid moves the starter drive pinion,
through the medium of the shift lever, into
engagement with the flywheel starter ring
gear. As the solenoid reaches the end of its
stroke, and with the pinion by now partially
engaged with the flywheel ring gear, the main
fixed and moving contacts close and engage
the starter motor to rotate the engine.
3This pre-engagement of the starter drive
does much to reduce the wear on the flywheel
ring gear associated with inertia type starter
motors.
4If the starter fails, some fault-finding can be
done with it still on the car. Check the ignition
warning light comes on, and does not go out
when the starter is switched on. If it goes out,
the fault is probably in the battery. If it stays
bright, get an assistant to work the switch,whilst listening to the starter. Listen to find out
if the solenoid clicks into position. If it does
not, pull off the solenoid wire, and check it
with a test bulb. If the wire is live when the key
is turned, but the solenoid does not move,
take off the starter and remove it to the bench
for overhaul.
8 Starter motor-
removal and refitting
1
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the lead from the starter motor
(photo).
3Unscrew the fixing bolts and withdraw the
starter motor, downwards on 1116 cc and
1301 cc models (photo).
4Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
9 Starter motor- overhaul
3
1As with the alternator, the operations
should normally be limited to renewal of the
brushes. If the unit has covered a high
mileage it will usually be more economical to
purchase a new or factory-reconditioned one
rather than renew several components of the
original unit.
2Owing to the possibility that a fault can
develop in the starter motor solenoid or drive
assembly, full dismantling procedures are
given later in this Section.
Brush - renewal
3Slide off the cover band.
4Using a hooked piece of wire, pull up the
springs so that the brushes can be withdrawn
and their lengths checked for wear. If they
have worn below the specified minimum
length, renew them by extracting the brush
lead connecting screws (photo).
Solenoid
5Disconnect the field connecting wire from
the solenoid.
6Unscrew the bolts which hold the solenoid
to the end-frame.
7Unscrew the yoke tie-rod nuts.
9•4 Electrical system
9.4 Starter motor brush partly withdrawn
8.2 Starter motor connections8.3 Removing starter motor
Fig. 9.2 Exploded view of typical starter motor (Sec 9)
1 Armature
2 Drive pinion/clutch3 Drive end bracket
4 Shift lever5 Solenoid
6 Brush endplate7 Brush
8 Field windings
Gripping the brush leads with
a pair of pliers to act as a
heat sink will prevent heat
transfer to the internal
components of the alternator.
Page 99 of 303

27 Tailgate wiper motor-
removal and refitting
1
1Remove the blade and arm as previously
described. Unscrew the drive spindle bezel
nut.
2Open the tailgate fully.
3Unclip and remove the wiper motor cover.
4Unscrew the mounting screws, withdraw
the motor and disconnect the wiring plug
(photo).
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
28 Washer system
1
1The washer system for the windscreen and
the tailgate operates from a bag type fluid
reservoir within the engine compartment
(photo).
2The reservoir bag is fitted with two pumps,
one for each system (photo).
3Use screen cleaning fluid mixed in the
recommended proportion in the washer fluid
reservoir and in very cold weather add a small
quantity of methylated spirit.
4To clear a blocked washer jet nozzle or to
adjust the wash jet glass-striking pattern,
insert a pin part way into the jet nozzle.
29 Heated tailgate window-
precautions and repair
2
1The heater element inside the tailgate glass
should be treated with care.
2Clean only with a damp cloth and wipe in
the direction in which the filaments run. Avoid
scratching with rings on the fingers, or by
allowing luggage to rub on the glass. Never
stick adhesive labels over the heater element.
3Should one of the heater filaments be
broken it can be repaired using one of the
special silver paints available, but follow the
manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
30 Radio/cassette- fitting
2
1In-car entertainment equipment is not
provided as standard on the models covered
by this Manual.
2However, the centre console is designed to
receive a radio set after removing the blanking
plate behind which a power lead is already
provided.
3The ignition system and other electrical
components are suppressed during
production of the car and further suppression
should not be required other than earthing the
wiper motor.
Receiver
4Fit the radio/cassette using the installation
kit supplied with the equipment.
5On Comfort models, fit an in-line fuse in the
power feed. On Super models the radio
supply is protected by fuse number 12.
6Make sure that the radio is well earthed to a
metal body component.
Aerial
7The recommended locations for the aerial
are towards the rear of the right-hand front
wing or on the windscreen pillar.
8Fitting instructions for Fiat aerials are
supplied with them, but the following general
advice will help if using non-Fiat equipment.9Motorised automatic aerials rise when the
equipment is switched on and retract at
switch-off. They require more fitting space
and supply leads, and can be a source of
trouble.
10There is no merit in choosing a very long
aerial as, for example, the type about three
metres in length which hooks or clips on to
the rear of the car, since part of this aerial will
inevitably be located in an interference field.
For VHF/FM radios the best length of aerial is
about one metre. Active aerials have a
transistor amplifier mounted at the base and
this serves to boost the received signal. The
aerial rod is sometimes rather shorter than
normal passive types.
11A large loss of signal can occur in the
aerial feeder cable, especially over the Very
High Frequency (VHF) bands. The design of
feeder cable is invariably in the co-axial form,
ie a centre conductor surrounded by a flexible
copper braid forming the outer (earth)
conductor. Between the inner and outer
conductors is an insulator material which can
be in solid or stranded form. Apart from
insulation, its purpose is to maintain the
correct spacing and concentricity. Loss of
signal occurs in this insulator, the loss usually
being greater in a poor quality cable. The
quality of cable used is reflected in the price
of the aerial with the attached feeder cable.
12The capacitance of the feeder should be
within the range 65 to 75 picofarads (pF)
approximately (95 to 100 pF for Japanese and
American equipment), otherwise the
adjustment of the car radio aerial trimmer may
not be possible. An extension cable is
necessary for a long run between aerial and
receiver. If this adds capacitance in excess of
the above limits, a connector containing a
series capacitor will be required, or an
extension which is labelled as
“capacity-compensated”.
13Fitting the aerial will normally involve
making a 7/8 in (22 mm) diameter hole in the
bodywork, but read the instructions that come
with the aerial kit. Once the hole position has
been selected, use a centre punch to guide
the drill. Use sticky masking tape around the
area for this helps with marking out and drill
location, and gives protection to the
9•10 Electrical system
Fig. 9.8 Radio housing and power lead (A)
(Sec 30)
28.2 Washer pumps28.1 Washer fluid reservoir27.4 Tailgate wiper motor
Page 101 of 303

3The centralised door locking system can
operate independently of the key.
4To gain access to the lock solenoid and
linkage, remove the front door trim panel as
described in Chapter 12.
5Disconnect the battery negative lead.
6Disconnect the electrical wiring plugs from
the solenoid within the door cavity.
7Disconnect the solenoid from the lock lever
by removing the clip.
8Unscrew the two bolts which secure the
solenoid to the door and remove it.
9Renew the solenoid or switch as necessary.
10Refitting is a reversal of removal.
11Refer to Section 10 for details of system
fuses and relays.
33 Economy gauge
(Econometer)
2
1This device is fitted to ES (energy saving)
models and indicates to the driver the fuel
consumption (in litres per 100 km) coupled
with a needle which moves over coloured
sections of a dial to make the driver aware
that his method of driving is either conducive
to high or low fuel consumption. Refer to
Chapter 3, Section 16.
2The device is essentially a vacuum gauge
which also incorporates a warning lamp to
indicate to the driver when a change of gear is
required.
3A fuel cut-out valve (see Chapter 3, Sec-
tion 11) is used in conjunction with the
economy gauge so that when the accelerator
pedal is released during a pre-determined
engine speed range, fuel supply to the engine
is stopped, but resumes when the engine
speed falls below the specified range.
LED (light emitter diode)
4The gearchange indicator will only light up
at engine speeds in excess of 2000 rev/min
for vacuum pressures up to 600 mm Hg in 1st,
2nd and 3rd speed gears and for vacuum
pressures up to 676 mm Hg in 4th speedgear. The light will not come on if 5th speed
gear is engaged or if the coolant temperature
is below 55ºC.
5There is a two second delay in the light
coming on to prevent it operating during rapid
acceleration in a low gear.
6If the LED light comes on during
deceleration it should be ignored.
Fault finding
7A faulty economy gauge should be checked
in the following way.
8Refer to Section 21 and remove the
instrument panel.
9Disconnect the economy gauge L
connector and then connect a test lamp
between the BN cable contact and earth. If
the lamp comes on then the gauge supply
circuit is not open. If the lamp does not come
on, check all connections in the supply cable
which comes from the interconnecting unit of
the electrical system, also Fuse No 12.
10Now connect a voltmeter between the
white cable and earth. Check the voltage with
the engine not running, but the ignition
switched on. It should be between 0.7 and
0.9 volt. If the reading varies considerably
from that specified, check the connections
between the economy gauge and the fuel
cut-out device control unit. If the fault cannot
be rectified, renew the ignition control unit
(Digiplex system, see Chapter 4).
11Now check the closed throttle valve plate
switch by connecting a voltmeter between the
brown and BN cables of the L connector. With
the valve plate open, there should be no
reading, but with it open, voltage should be
indicated.
12Failure to conform as described will be
due to a faulty earth in the switch or a faulty
fuel cut-out device control unit.
13A further test of the throttle valve plate
switch may be carried out by disconnecting
the multi-plug from the fuel cut-out device
control unit.
14Connect a test lamp to contact 4 (positive
battery terminal). The lamp should come on,
when the engine is idling or the accelerator
released. If it does not, renew the throttle
valve plate switch.15Connect a tachometer to the brown/white
cable contact in the L connector and record
the engine speed with the engine running. If
no reading is obtained, renew the Digiplex
ignition control unit which must be faulty.
34 Check control (warning
module) system
2
1This is fitted into the instrument panel of
certain models to provide a means of
checking the operation of many electrical
circuits and other systems in the interest of
safety. Sensors are used where appropriate.
2The following components are not
monitored by the system, but have separate
warning lamps:
Handbrake “on”
Choke in use
Low engine oil pressure
Battery charge indicator
3The multi-functional electronic device
automatically checks the following functions
whether the engine is running or not:
Coolant level
Disc pad wear
Door closure
Engine oil level
Front parking lamps
Rear foglamps
Stop lamps
4The check information is stored by the
system monitor until the engine is started
when the display panel then indicates the
situation by means of the LEDs (light emitter
diodes) and the general lamp.
5If all functions are in order, the green panel
lamp will come on when the ignition key is
turned and will go out after two to three
seconds.
6If some functions are not in order, then the
red panel lamp will come on also the
appropriate LED.
Sensors - checking
7If a fault signal occurs which is
subsequently found to be incorrect, first
check the wiring connections between the
9•12 Electrical system
Fig. 9.15 Check system control panel (Sec 34)
A Parking lamps
B Coolant levelC Engine oil level
D Door closureE Brake fluid level
F Disc pad wearFig. 9.14 Location of control units (Sec 33)
A Digiplex ignition system control unit
B Fuel cut-out valve control unit
Page 102 of 303
sensors, lamp circuits and the control unit.
Corrosion at the terminals may also be a
contributory cause.
8Never short circuit a sensor supply wire or
the electronic module will be damaged.
Check control unit and monitor -
removal and refitting
9Remove the instrument panel as described
in Section 21.
10Unbolt the control unit housing from the
instrument panel.
11Access to the monitor can only be
obtained after removing the tachometer andthe red and green general warning lamps.
Unscrew the two monitor fixing bolts.
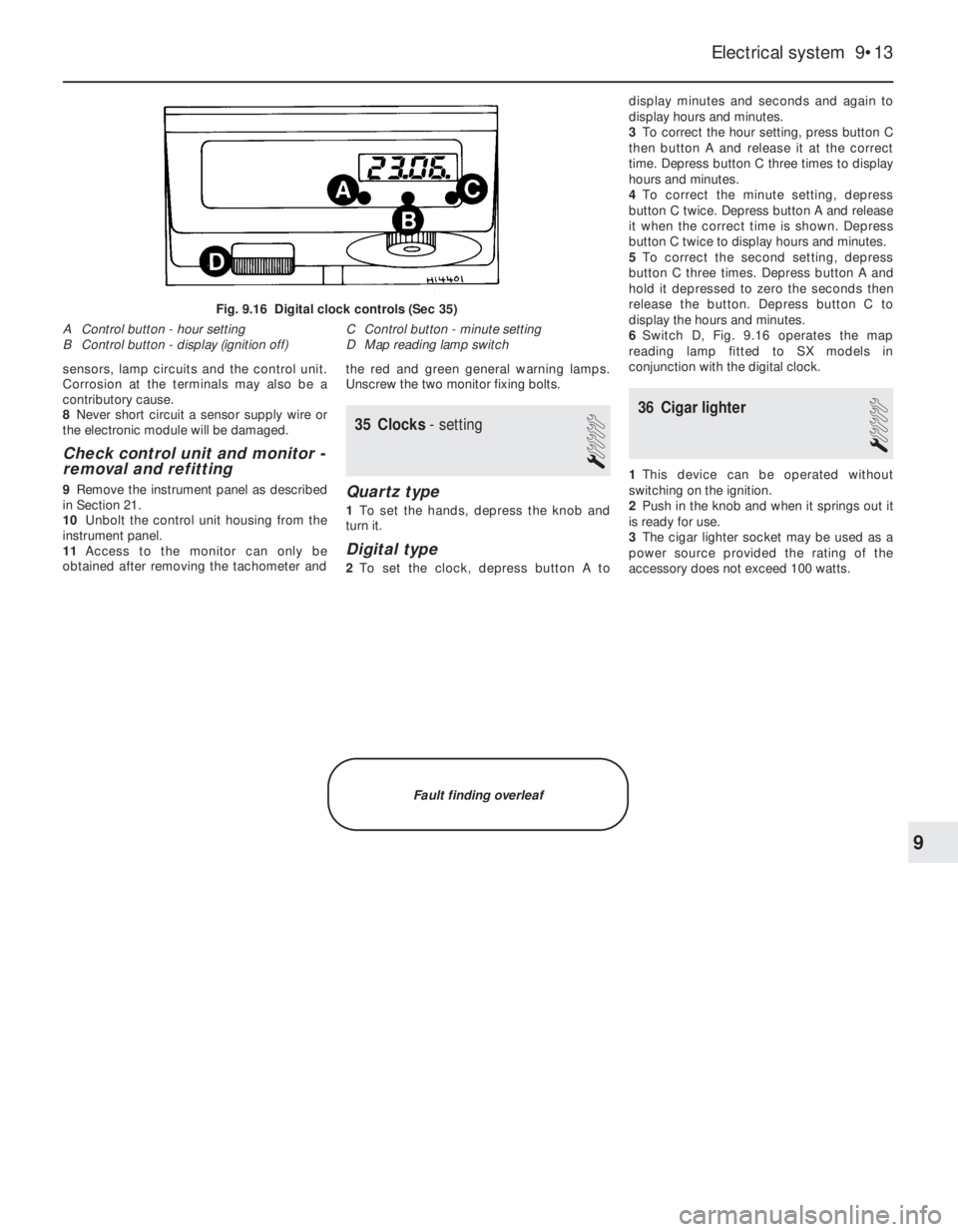
35 Clocks- setting
1
Quartz type
1To set the hands, depress the knob and
turn it.
Digital type
2To set the clock, depress button A todisplay minutes and seconds and again to
display hours and minutes.
3To correct the hour setting, press button C
then button A and release it at the correct
time. Depress button C three times to display
hours and minutes.
4To correct the minute setting, depress
button C twice. Depress button A and release
it when the correct time is shown. Depress
button C twice to display hours and minutes.
5To correct the second setting, depress
button C three times. Depress button A and
hold it depressed to zero the seconds then
release the button. Depress button C to
display the hours and minutes.
6Switch D, Fig. 9.16 operates the map
reading lamp fitted to SX models in
conjunction with the digital clock.
36 Cigar lighter
1
1This device can be operated without
switching on the ignition.
2Push in the knob and when it springs out it
is ready for use.
3The cigar lighter socket may be used as a
power source provided the rating of the
accessory does not exceed 100 watts.
Electrical system 9•13
Fig. 9.16 Digital clock controls (Sec 35)
A Control button - hour setting C Control button - minute setting
B Control button - display (ignition off) D Map reading lamp switch
9
Fault finding overleaf