clutch FORD FIESTA 2007 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2007, Model line: FIESTA, Model: FORD FIESTA 2007Pages: 1226, PDF Size: 61.26 MB
Page 985 of 1226

Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01 -25 Transmission (AW81-40) 307-01 -25
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Item Descriotion
I 1 I From the torque converter I
~l%ansmission input shaft I
1 4 1 Small sun gear I
1 6 1 Planet gear carrier I
1 8 1Short planet gear I
1 9 1 Long planet gear I
10 Annulus and
output wheel of the planetary
/ (gearset
I 11 I Intermediate gear stage I
1 12 1 Differential assembly I
1 13 12nd - 4th gear brake I
1 14 1 2nd gear one-way clutch I
1 15 1 Large sun gear I - --
1 16 14th gear brake I
1 17 1 3rdl4th gear clutch I
~Iianetary gearset, rear I
I B I Planetary gearset, front I
Drive is transmitted from the torque converter (I)
to the transmission input shaft (2) and via the
3rdl4th gear clutch (1 7) to the planet gear carrier
(6).
The large sun gear (15) is held by the 4th gear
brake
(16), the 2nd gear one-way clutch (14) and
the 2nd-4th gear brake
(1 3).
N0TE:The short planet gears (8) and the small
sun gear (4) co-rotate, but they have no influence
on the transmission ratio.
The long planet gears (9) drive the annulus (10) in
the same direction of rotation as the output from
the engine.
The annulus is fixedly connected to the output
wheel of the planetary
gearset and drives the
intermediate gear stage
(11) in the opposite
direction of rotation to the output from the engine.
The intermediate gear stage drives the differential
assembly
(12) in the same direction of rotation as
the output from the engine.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380528en
procarmanuals.com
Page 987 of 1226

Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01 -27 Transmission (AW81-40) 307-01 -27
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Item Description
I 1 I From the torque converter I
1 2 I Transmission input shaft I
1 4 ISmaII sun gear I
11 Planet gear carrier I
1 7 1 Reverse gear brake I
1 8 1Short planet gear I
1 9 1 Long planet gear I
10 Annulus and output wheel
of the planetary
I (gearset
I 11 I Intermediate gear stage I
1 12 1 Differential assembly I
1 15 1 Large sun gear I
1 18 1 Reverse gear clutch I
I A I Planetary gearset, rear I
I B I Planetary gearset, front I
Drive is transmitted from the torque converter (1)
to the transmission input shaft
(2) and via the
r reverse gear clutch (1 8) to the large sun gear (1 5).
The planet gear carrier
(6) is held by the reverse
gear brake
(7).
The large sun gear drives the long planet gears
(9) in the opposite direction of rotation to the output
from the engine.
N0TE:The short planet gears (8) and the small
sun gear (4) co-rotate, but they have no influence
on the transmission ratio.
The long planet gears drive the annulus (1
0) in the
opposite direction of rotation to the output from the
engine.
The annulus is fixedly connected to the output
wheel of the planetary
gearset and drives the
intermediate gear stage (I
I ) in the same direction
of rotation as the output from the engine.
The intermediate gear stage drives the differential
assembly (1 2) in the opposite direction of rotation
to the output from the engine.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380528en
procarmanuals.com
Page 991 of 1226

Automatic TransmissionlTransaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01 -31 Transmission (AW81-40) 307-01 -31
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The transmission control unit determines hill climb
mode or trailer operation from the change in throttle
; valve position supplied by the PCM in relation to
the acceleration of the vehicle.
Depending on the driving resistance, the
transmission control unit chooses between two
gearshift maps which have been specially
programmed for this purpose and in which the shift
timings are again chosen as a function of the
accelerator pedal position and the vehicle speed..
Hill descent mode
The hill descent mode is used to take better
advantage of engine braking during hill descents.
A 'hill descent' situation is recognised by the
transmission control unit if the vehicle is
accelerating without operation of the accelerator
pedal.
If in addition the brake is also depressed then the
transmission control unit automatically shifts back
from 4th into 3rd gear.
( ' Cold start mode
In order to reach operating temperature as quickly
as possible under low ambient temperatures,
gearshifts into 4th gear and engagement of the
torque converter clutch (TCC) are suppressed if
one of the following conditions is met:
Transmission fluid temperature below +20 "C
Coolant temperature below - 40°C
The following are actuated: SSA shift solenoid valve,
SSB shift solenoid valve,
Shift solenoid valve, TCC.
Overheating protection mode
The overheating protection mode serves to protect
the transmission against overheating and the
serious damage that this can cause.
If the transmission fluid temperature reaches a
temperature of around 135
"C, the transmission
control employs a shift pattern designed to prevent
a further increase in the transmission fluid
temperature. When
the transmission fluid temperature drops
back below approx. 125
"C, the transmission
control exits the overheating protection mode.
The MIL warning lamp is actuated by the
transmission control unit if the transmission fluid
temperature reaches approximately 140
"C.
The MIL warning lamp goes out again when the
transmission fluid temperature drops back to below
around 130
"C.
Main line pressure control
In order to ensure the highest possible efficiency
of the automatic transmission and to limit the power
losses from the fluid pump, the main line pressure
is adapted accordingly by the main regulating valve
as a function of the accelerator pedal position
(driver torque demand) and the selector lever
position.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Accelerator pedal position and actuation
Selector lever position
The following are actuated:
Main 'regulating valve
Engagement of the TCC
The TCC is engaged in 3rd and 4th gear depending
on the current driving situation.
Engagement is controlled in accordance with the
shift map stored in the control unit.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Accelerator pedal position and actuation,
Vehicle speed,
Selector lever position,
Transmission fluid temperature,
Coolant temperature.
The following are actuated:
Shift solenoid valve, TCC.
Torque reduction during gearshifts
In order to improve the quality of gearshifts and to
avoid gearshift judder, the engine torque is reduced
by the PCM in response to a request from the
transmission control unit during gearshifts.
The engine torque is also reduced during
engagement and disengagement of the TCC.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380530en
procarmanuals.com
Page 992 of 1226

Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01 -32 Transmission
(AW81-40) 307-01 -32
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
This is influenced by the following variables:
Engine speed,
Engine load,
Transmission input speed,
Vehicle speed.
The following are actuated:
PCM (torque reduction request signal via the
CAN databus).
Pressure control during gearshifts
In order to ensure that the engagement of the
clutches and brakes is as judder-free as possible,
the main line pressure is reduced during gearshifts.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Enginespeed,
Engine load,
Transmission input speed,
Vehicle speed.
The following are actuated:
Main regulating valve.
Shift timing adaptation during upshifts
In order to ensure that the engagement of the
clutches and brakes is as judder-free as possible,
the timing of the gearshift processes is monitored
during upshifts.
In the event of any discrepancy from the target
values, the main line pressure is adapted
accordingly during the next gearshift.
The shift timing adaptation during upshifts is only
active at transmission fluid temperatures between
50
"C and 120 "C.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Engine load,
Accelerator pedal position,
Transmission input speed,
Vehicle speed,
Transmission fluid temperature,
Selector lever position.
The following are actuated:
Main regulating valve.
Shift timing adaptation during shifts from
3rd to 4th gear
The shift from 3rd gear into 4th gear is the only
gearshift during which a clutch is disengaged and
a brake is engaged simultaneously.
In order to control the synchronized switching of
the two components as exactly as possible, the
shifl timing solenoid valve is actuated accordingly.
In order to ensure that this particular gearshift is
performed as judder-free as possible throughout
the service life of the transmission, the gearshift is
monitored by the two rotational speed sensors and
the actuation of the shift timing solenoid valve is
adapted accordingly.
The shift timing adaptation for gearshifts from 3rd
gear into 4th gear is only active at transmission
fluid temperatures between 30
"C and 120 "C.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Engine load,
Accelerator pedal position,
Transmission input speed,
Vehicle speed,
Transmission fluid temperature,
Selector lever position.
The following are actuated:
Shift timing solenoid valve.
Shift timing adaptation during shifts from
4th to 3rd gear
The shift from 4th gear into 3rd gear is the only
gearshift during which a brake is disengaged and
a clutch is engaged simultaneously.
In order to control the engagement of the clutch as
precisely as possible, the main regulating valve is
actuated accordingly in order to build up the
actuating pressure at exactly the right time.
In order to ensure that this particular gearshift is
performed as judder-free as possible throughout
the service life of the transmission, the gearshift is
monitored by the two rotational speed sensors and
the actuation of the main regulating valve is
adapted accordingly.
The shift timing adaptation for gearshifts from 4th
-
gear into 3rd gear is only active at transmission (
fluid temperatures between 20 "C and 120 "C. .
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380530en
procarmanuals.com
Page 993 of 1226

Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4Speed Automatic
307-01 -33 Transmission (AW81-40) 307-01 -33
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
This is influenced by the following variables: Vehicle
speed,
Engine load, Transmission fluid temperature.
Accelerator pedal position, The following are actuated:
Transmission input speed, SSA shift solenoid valve,
Vehicle speed,
Transmission fluid temperature,
Selector lever position.
The
following are actuated:
Main
regulating valve.
Reverse gear safety strategy
SSB shift solenoid valve.
Torque reduction when pulling away
In order to protect the clutches against excessively
high torque when pulling away, the PCM reduces
the engine torque in response to a request from
the transmission
control.
If the accelerator pedal is depressed while the
The transmission control unit prevents shifts into vehicle is pulling away, then the transmission reverse gear while the vehicle is driving forwards, control unit sends a corresponding signal as otherwise serious transmission damage can be requesting a torque reduction via the CAN databus. caused.
The reverse gear safety strategy is active when This
is influenced by the
following variables:
reverse gear is engaged with the selector lever at ' Selector lever position,
vehicle speeds in excess of 11 kmlh. Accelerator pedal position,
In this
case the transmission control unit actuates ' Engine speed,
the shift timing solenoid valve, as a result of which Transmission input speed,
the actuating pressure does not reach the reverse
. Vehicle speed. gear clutch or the reverse gear brake.
The following are actuated:
The reverse gear safety strategy is deactivated
PCM (torque reduction request signal via the
when the vehicle speed is below 9 kmlh. The
actuating pressure can then reach the reverse gear CAN
databus).
clutch and the reverse gear brake and the gearshift
into reverse gear is performed.
Selector lever positions
This is influenced by the following variables:
Vehicle speed,
Selector lever position.
The
following are actuated:
Shift timing solenoid valve.
Selector lever position "P"
No gear is engaged in selector lever position "P".
The parking
pawl is engaged manually via the
selector lever cable and the selector shaft.
Avoidance of gearshift judder during
engagement of a transmission range Selector
lever position "R"
In order to prevent gearshift judder when moving The reverse gear is eWaged in selector lever
the selector lever from N to D, the transmission position "R.
control unit initially shifts into
2nd gear instead of
1 st gear, and then immediately shifts back into I st
gear before the gearshift process is finished. Selector lever position "N"
This reduces the amount of gearshift judder during No gear is engaged in selector lever position WNW. engagement of a forward drive range.
The powertrain is not blocked. This is influenced by the following variables:
Selector lever position,
Accelerator pedal position,
Transmission input speed,
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380530en
procarmanuals.com
Page 997 of 1226
Automatic TransmissionlTransaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01 -37 Transmission
(AW81-40) 307-01 -37
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
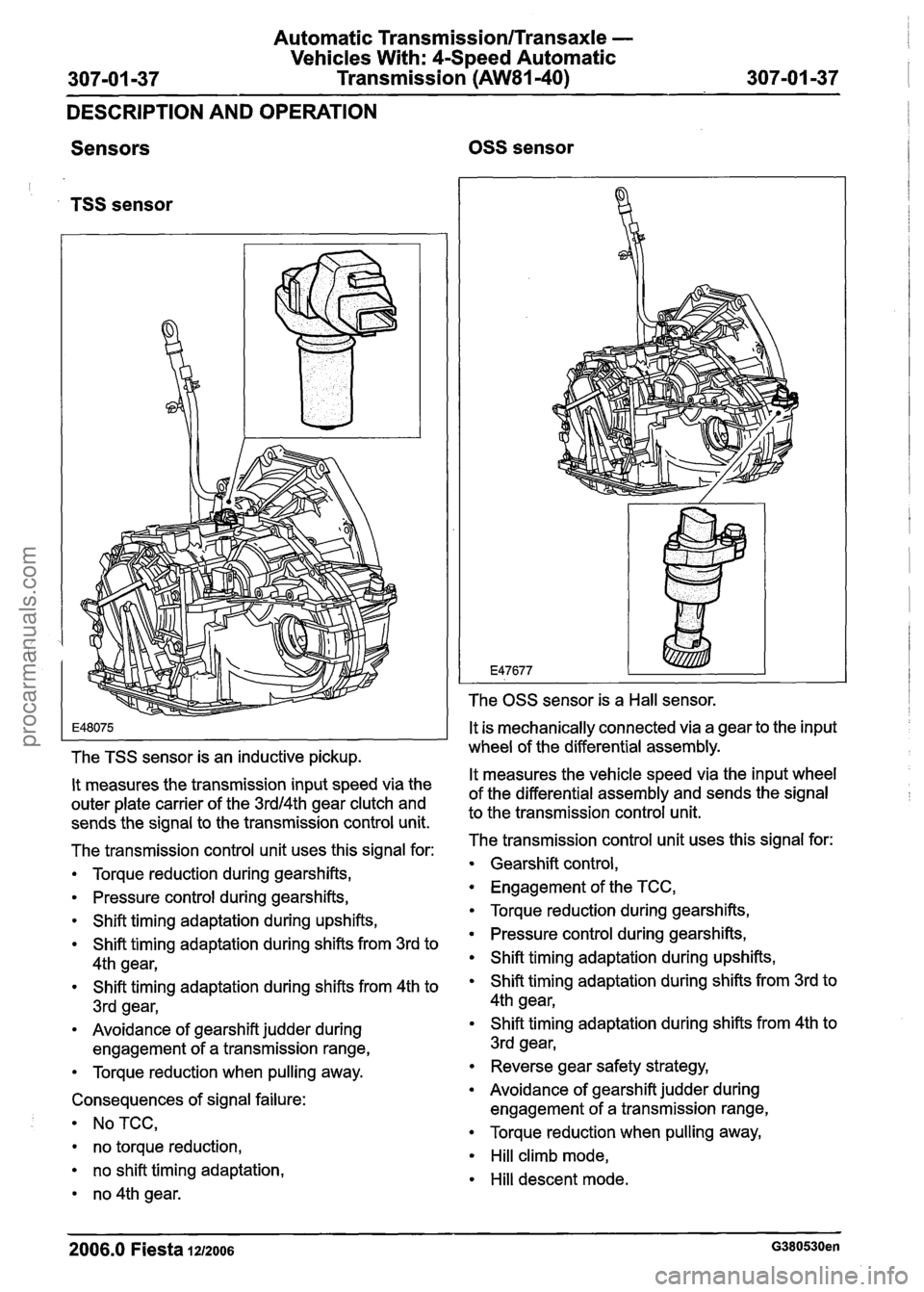
Sensors
OSS sensor
TSS sensor
The TSS sensor is an inductive pickup.
It measures the transmission input speed via the
outer plate carrier of the
3rdl4th gear clutch and
sends the signal to the transmission control unit.
The transmission control unit uses this signal for:
Torque reduction during gearshifts,
Pressure control during gearshifts,
Shift timing adaptation during upshifts,
Shift timing adaptation during shifts from 3rd to
4th gear,
Shift timing adaptation during shifts from 4th to
3rd gear,
Avoidance of gearshift judder during
engagement of a transmission range,
Torque reduction when pulling away.
Consequences of signal failure:
No TCC,
no torque reduction,
no shift timing adaptation,
no 4th gear. The
OSS sensor is a Hall sensor.
It is mechanically connected via a gear to the input
wheel of the differential assembly.
It measures the vehicle speed via the input wheel
of the differential assembly and sends the signal
to the transmission control unit.
The transmission control unit uses this signal for:
Gearshift control,
Engagement of the TCC,
Torque reduction during gearshifts,
Pressure control during gearshifts,
Shift timing adaptation during upshifts,
Shift timing adaptation during shifts from 3rd to
4th gear,
Shift timing adaptation during shifts from 4th to
3rd gear,
Reverse gear safety strategy,
Avoidance of gearshift judder during
engagement of a transmission range,
Torque reduction when pulling away,
Hill climb mode,
Hill descent mode.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380530en
procarmanuals.com
Page 1000 of 1226
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01 -40 Transmission (AW81-40)
307-01 -40
DESCRIPTION AND
OPEMION
Driver's side door ajar switch
The door ajar switch is located in the door lock on
the driver's side.
When the door is closed a ground connection is
signalled to the transmission control unit.
When the door is opened this ground connection
is interrupted.
The transmission control unit uses the signal from
the driver's side door ajar switch to warn the driver
if the selector lever is not in position
"P" and the
driver's door is open.
In this case the transmission control unit transmits
the warning tone request via the CAN
databus to
the instrument cluster.
The instrument cluster passes this request on to
the GEM, which then generates a warning tone.
Consequences of signal failure:
no warning tone request.
Actuators
Main regulating valve
Item Description
I 1 I Main regulating valve I
The main regulating valve is a proportional valve
which converts the applied electric current into a
proportional hydraulic pressure.
The currentless state corresponds to maximum
pressure.
/
The main regulating valve is used to determine the
main line pressure and therefore the actuating
pressure for the clutches and brakes.
Consequences of signal failure:
hydraulic emergency running mode.
SSA and SSB shift solenoid valves
Item Description
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380530en
1
2
SSA
SSB
(- t..
procarmanuals.com
Page 1001 of 1226
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01
-41 Transmission (AW81-40) 307-01 -41
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The SSA and SSB shift solenoid valves are used In
their currentless state they are open.
to switch the different hydraulic paths in the main
Consequences of signal failure: control body. hydraulic emergency running mode.
They are actuated by the transmission control unit
according to the required gear.
Actuation of the SSA and SSB shift solenoid valves
Shift timing solenoid valve
gear
I st gear
2nd gear
3rd gear
4th gear
kern Descri~tion
I 1 I Shift timing solenoid valve I
SSA On
On Off
Off
The shift timing solenoid valve is used to precisely SSB
On Off
Off
On
control the timing of the engagement and
disengagement of the
I st3rd gear clutch.
In addition, it is also used to prevent engagement
of reverse gear if the driver moves the selector
lever to "R" while the vehicle is driving forwards at
a speed in excess of
11 kmlh.
It is actuated by the transmission control unit
according to requirements.
In its currentless state the solenoid valve is closed.
Consequences of signal failure: hydraulic emergency running mode.
Shift solenoid valve, TCC
Item Description
I 1 I Shift solenoid valve, TCC I
The TCC shift solenoid valve is used to engage or
disengage the TCC.
It is actuated by the transmission control unit
according to requirements.
In its currentless state the solenoid valve is open
and the TCC is not engaged.
Consequences of signal failure:
Engagement of the TCC.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380530en
procarmanuals.com
Page 1006 of 1226
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4Speed Automatic
307-01 -46 Transmission
(AW81-40) 307101 -46
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
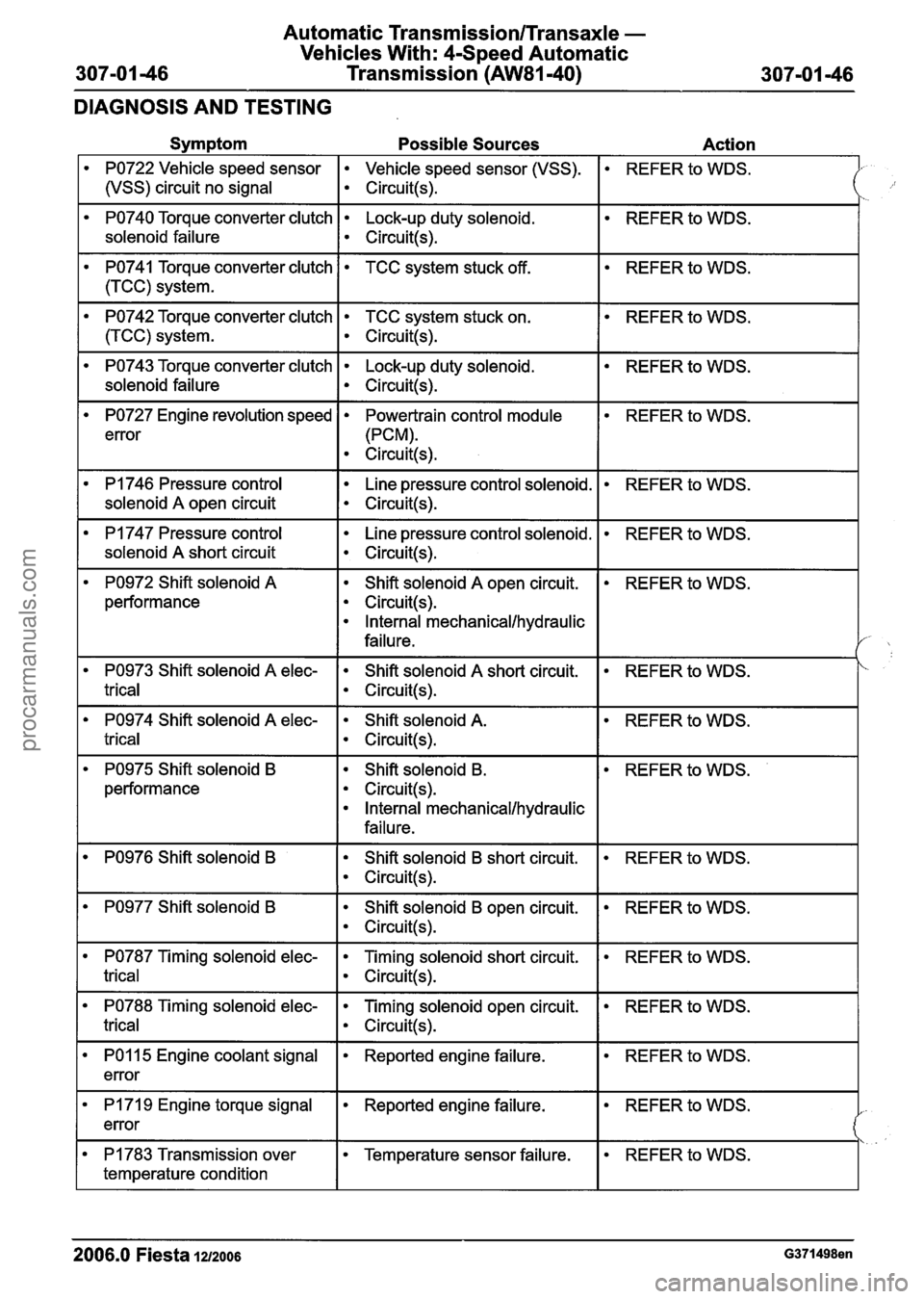
Symptom Possible Sources Action
PO722 Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed sensor (VSS).
1 (vSS) circuit no signal I circuit(+
REFER to WDS.
PO740 Torque converter clutch Lock-up duty solenoid.
solenoid failure
I ~ircuit(s).
REFER to WDS.
REFER to WDS.
PO741 Torque converter clutch
1 (TCC) system.
PO742 Torque converter clutch TCC system stuck on.
I circuit(s).
TCC system stuck off.
REFER to WDS.
PO743 Torque converter clutch Lock-up duty solenoid.
solenoid failure
I circuit(s).
REFER to WDS.
REFER to WDS.
PO727 Engine revolution speed
error
PI 746 Pressure control
I solenoid A open circuit
Powertrain control module
(PCM).
Circuit(s).
I
Line pressure control solenoid.
Circuit(s).
REFER to WDS.
PI 747 Pressure control
solenoid
A short circuit
Line pressure control solenoid.
Circuit(s).
REFER to WDS.
PO972 Shift solenoid A
performance Shift solenoid
A open
circuit.
Circuit(s).
Internal mechanical/hydraulic
failure.
REFER to WDS.
REFER to WDS.
PO974 Shift solenoid A elec- Shift solenoid A.
trical I circuit(!+
PO973 Shift solenoid A elec-
trical
REFER to WDS. Shift solenoid A short circuit.
Circuit(s).
PO975 Shift solenoid B
performance Shift solenoid
B.
Circuit(s).
Internal mechanical/hydraulic
failure.
REFER
to WDS.
PO976 Shift solenoid B Shift solenoid B short circuit.
Circuit(s).
REFER to WDS.
PO977 Shift solenoid B Shift solenoid B open circuit.
Circuit(s).
REFER to WDS.
PO787 Timing solenoid elec- Timing solenoid short circuit.
trical I circuit(s).
REFER to WDS.
REFER to WDS. PO788 Timing solenoid elec-
trical
-- - -
Timing solenoid open circuit.
Circuit(s).
REFER to WDS. PO1 15 Engine coolant signal
error Reported engine failure.
REFER to WDS. I PI 71 9 Engine torque signal
error Reported engine failure.
REFER to WDS. PI 783 Transmission over
temperature condition
2006.0 Fiesta 12/2006 G371498en
Temperature sensor failure.
procarmanuals.com
Page 1008 of 1226
Automatic TransmissionlTransaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01 -48 Transmission (AW81-40) 307-01 -48
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Stall Speed Test
This test checks the operation of the following
components:
1
Test Results
Lower than specification in 'Dl (DRIVE) and 'R'
(REVERSE)
Lower than specification in
'Dl (DRIVE)
Lower than specification in
'R' (REVERSE)
torque converter
forward clutch
low one way clutch assembly
engine performance
Possible Source
Pressure control solenoid inoperative or open wire
harness.
Pressure regulator valve sticking.
Worn oil pump.
Oil strainer blocked.
Fluid leak from each clutch hydraulic circuit.
Drive hydraulic circuit failure.
Forward clutch failure.
Reverse hydraulic circuit failure. Reverse clutch failure.
First and reverse brake failure.
WARNINGS:
A Do not maintain wide open throttle (WOT)
in any range for more than five seconds.
A If the engine speed (rpm) recorded by the
tachometer exceeds maximum specified
rpm, release the accelerator pedal
immediately. Clutch or band slippage is
indicated.
N0TE:The stall speed test should be carried out
with the engine and transaxle at normal operating
temperatures (50°C to 80°C).
A Apply the parking brake firmly while N0TE:Prolonged use of this procedure may set
carrying out each stall test. DTC PO71 2. After carrying out the stall speed test,
A Apply the foot brake firmly while carrying run the OBD test and clear the DTCs.
out each stall test. I. Connect a tachometer to the engine.
CAUTIONS:
A Always carry out the line pressure test
before carrying out the stall speed test. If
the line pressure is low at idle, do not carry
out the stall speed test or further transaxle
damage will occur.
A After testing each of the following ranges
'D'
(DRIVE) and 'R' (REVERSE), move the
selector lever to
'N' (NEUTRAL) and run
the engine at 1000 rpm for approximately
one minute to allow the torque converter
to cool.
2. Press the accelerator pedal to the floor WOT in
each selected range. Record the rpm reached
in each selected range and refer to the stall
speed chart.
3. If the stall speed is not within specification, refer
to the stall speed diagnosis chart.
Stall S~eed Chart
I Engine 1.6L I Speed (rpm) I
I 'Dl (DRIVE) I 2500 2 150 1
'R' (REVERSE) 2420 +, 150 -
Stall
Speed Diagnosis Chart
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G371498en
Test Results
Lower than specification in ID' (DRIVE) and 'R'
(REVERSE)
Possible Source
Low engine power.
Torque converter one-way clutch failure.
procarmanuals.com