FORD FREESTAR 2005 1.G Owners Manual
Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2005, Model line: FREESTAR, Model: FORD FREESTAR 2005 1.GPages: 312, PDF Size: 3.96 MB
Page 131 of 312
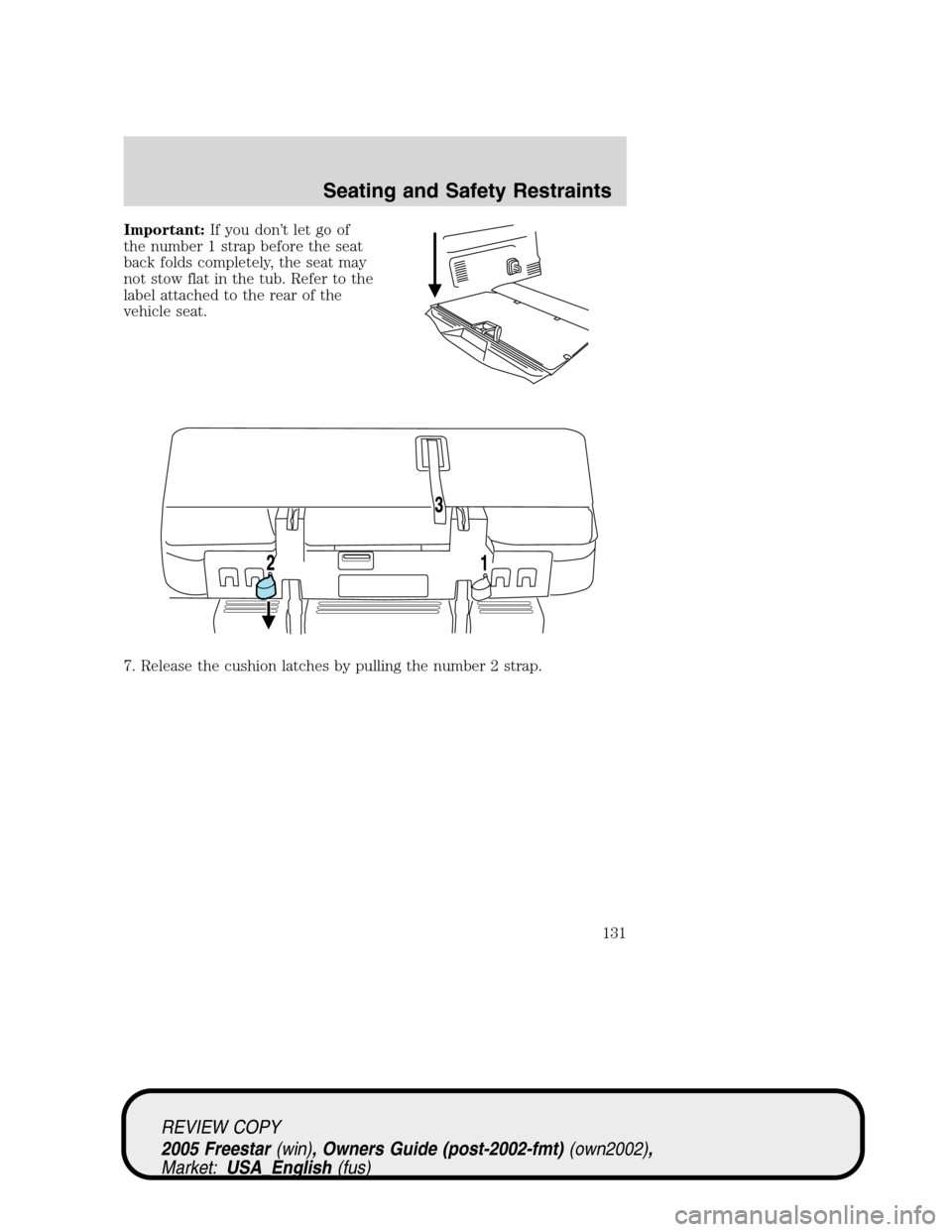
Important:If you don’t let go of
the number 1 strap before the seat
back folds completely, the seat may
not stow flat in the tub. Refer to the
label attached to the rear of the
vehicle seat.
7. Release the cushion latches by pulling the number 2 strap.
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
131
Page 132 of 312
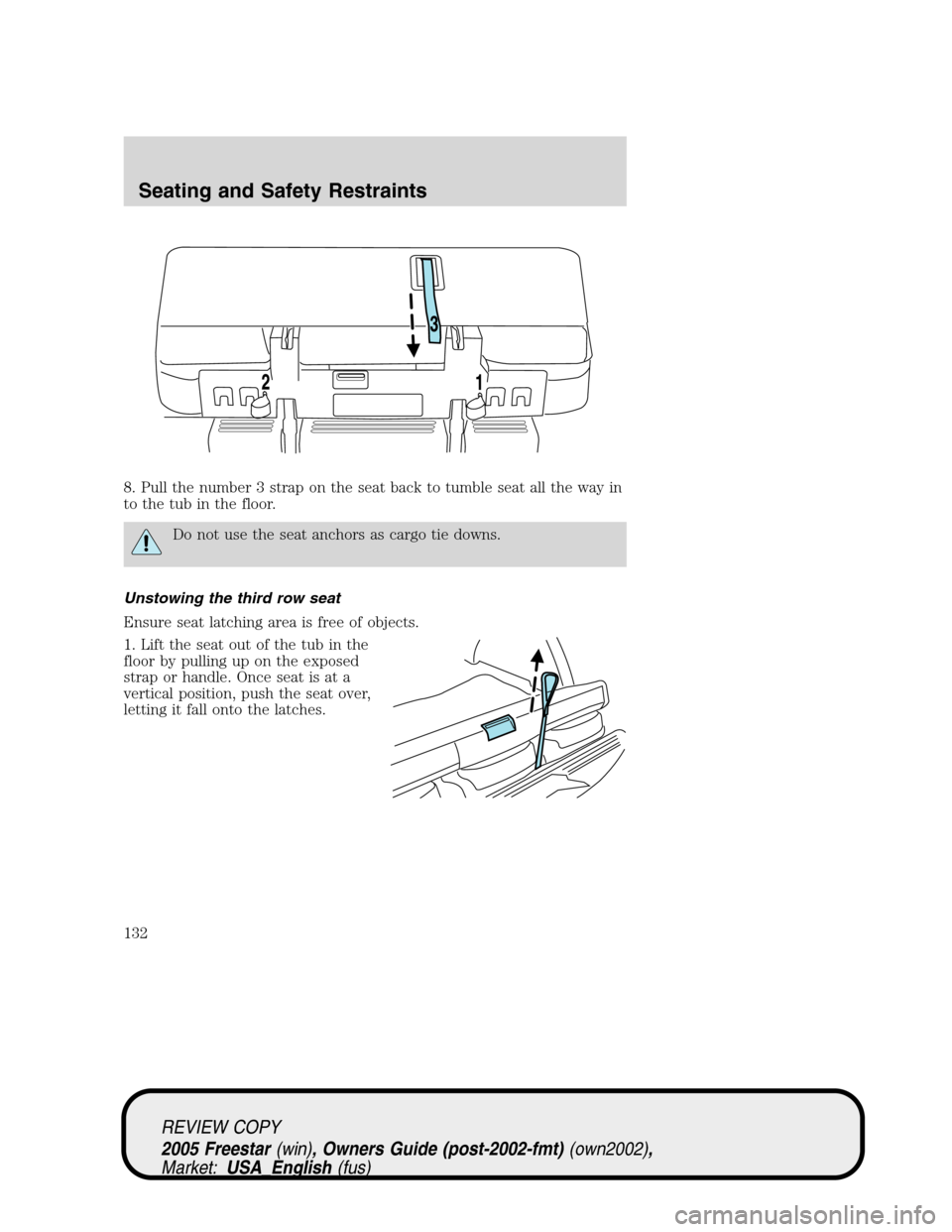
8. Pull the number 3 strap on the seat back to tumble seat all the way in
to the tub in the floor.
Do not use the seat anchors as cargo tie downs.
Unstowing the third row seat
Ensure seat latching area is free of objects.
1. Lift the seat out of the tub in the
floor by pulling up on the exposed
strap or handle. Once seat is at a
vertical position, push the seat over,
letting it fall onto the latches.
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
132
Page 133 of 312
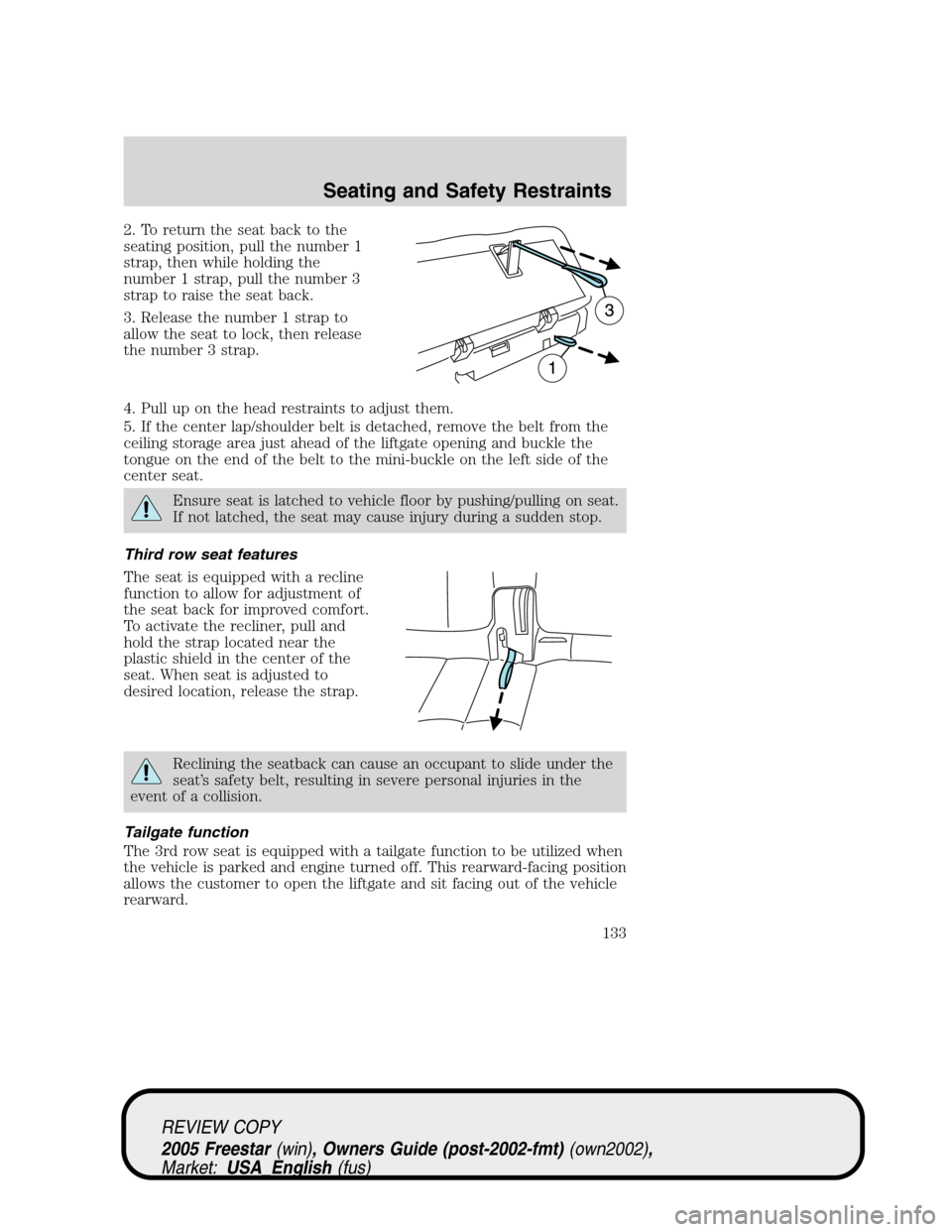
2. To return the seat back to the
seating position, pull the number 1
strap, then while holding the
number 1 strap, pull the number 3
strap to raise the seat back.
3. Release the number 1 strap to
allow the seat to lock, then release
the number 3 strap.
4. Pull up on the head restraints to adjust them.
5. If the center lap/shoulder belt is detached, remove the belt from the
ceiling storage area just ahead of the liftgate opening and buckle the
tongue on the end of the belt to the mini-buckle on the left side of the
center seat.
Ensure seat is latched to vehicle floor by pushing/pulling on seat.
If not latched, the seat may cause injury during a sudden stop.
Third row seat features
The seat is equipped with a recline
function to allow for adjustment of
the seat back for improved comfort.
To activate the recliner, pull and
hold the strap located near the
plastic shield in the center of the
seat. When seat is adjusted to
desired location, release the strap.
Reclining the seatback can cause an occupant to slide under the
seat’s safety belt, resulting in severe personal injuries in the
event of a collision.
Tailgate function
The 3rd row seat is equipped with a tailgate function to be utilized when
the vehicle is parked and engine turned off. This rearward-facing position
allows the customer to open the liftgate and sit facing out of the vehicle
rearward.
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
133
Page 134 of 312

This is not a position suitable for driving. Do not drive the
vehicle with the seat in this position. The safety belts are not
functional when the seat is in the tailgate position.
Ensure head restraints are moved to their full down position, all seat
belts are released from the seat, seat and stowage tub are free of objects.
1. Push the head restraint release buttons and move all head restraints
fully down.
2. To access the tailgate function,
the seat must be in the seating
position. If the seat is not in the
seating position, follow all the steps
of the‘Unstowing Seat Section’.
Once the seat is in the seating
position, release the cushion latches
by pulling the number 2 strap.
Then, pull the seat rearward by the
number 3 strap and set the seat on
the liftgate scuff plate. The number
1 strap is not used to access this
position.
Do not sit on the head restraints.
2
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
134
Page 135 of 312

3. To return the seat, ensure seat
latching area is free of objects.
Then, raise the seat off the liftgate
scuff plate and push at the top of
the seat back to rotate the seat back
onto the latches. Pull up on the
head restraints to raise them.
Ensure seat is latched to vehicle floor by pushing/pulling on seat.
If not latched, the seat may cause injury during a sudden stop.
SAFETY RESTRAINTS
Personal Safety System
The Personal Safety System provides an improved overall level of frontal
crash protection to front seat occupants and is designed to help further
reduce the risk of air bag-related injuries. The system is able to analyze
different occupant conditions and crash severity before activating the
appropriate safety devices to help better protect a range of occupants in
a variety of frontal crash situations.
Your vehicle’s Personal Safety System consists of:
•Driver and passenger dual-stage air bag supplemental restraints.
•Front safety belts with pretensioners, energy management retractors
(first row only), and safety belt usage sensors.
•Driver’s seat position sensor.
•Passenger occupant classification sensor
•Front crash severity sensor.
•Restraints Control Module (RCM) with impact and safing sensors.
•Restraint system warning light and back-up tone.
•The electrical wiring for the air bags, crash sensor(s), safety belt
pretensioners, front safety belt usage sensors, driver seat position
sensor, passenger occupant classification sensor, and indicator lights.
How does the Personal Safety System work?
The Personal Safety System can adapt the deployment strategy of your
vehicle’s safety devices according to crash severity and occupant
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
135
Page 136 of 312

conditions. A collection of crash and occupant sensors provides
information to the Restraints Control Module (RCM). During a crash, the
RCM activates the safety belt pretensioners and/or either one or both
stages of the dual-stage air bag supplemental restraints based on crash
severity and occupant conditions.
The fact that the pretensioners or air bags did not activate for both front
seat occupants in a collision does not mean that something is wrong with
the system. Rather, it means the Personal Safety System determined the
accident conditions (crash severity, belt usage, etc.) were not
appropriate to activate these safety devices. Front air bags are designed
to activate only in frontal and near-frontal collisions (not rollovers, side
impacts or rear impacts) unless the collision causes sufficient
longitudinal deceleration. The pretensioners are designed to activate in
frontal and side collisions, and rollovers.
Driver and passenger dual-stage air bag supplemental restraints
The dual-stage air bags offer the capability to tailor the level of air bag
inflation energy. A lower, less forceful energy level is provided for more
common, moderate-severity impacts. A higher energy level is used for
the most severe impacts. Refer toAir bag supplemental restraints
section in this chapter.
Front crash severity sensor
The front crash severity sensor enhances the ability to detect the
severity of an impact. Positioned up front, it provides valuable
information early in the crash event on the severity of the impact. This
allows your Personal Safety System to distinguish between different
levels of crash severity and modify the deployment strategy of the
dual-stage air bags and safety belt pretensioners.
Driver’s seat position sensor
The driver’s seat position sensor allows your Personal Safety System to
tailor the deployment level of the driver dual-stage air bag based on seat
position. The system is designed to help protect smaller drivers sitting
close to the driver air bag by providing a lower air bag output level.
Front passenger sensing system
For air bags to do their job they must inflate with great force, and this
force can pose a potentially deadly risk to occupants that are very close
to the air bag when it begins to inflate. For some occupants, this occurs
because they are initially sitting very close to the air bag. For other
occupants, this occurs when the occupant is not properly restrained by
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
136
Page 137 of 312

seat belts or child safety seats and they move forward during pre-crash
braking. The most effective way to reduce the risk of unnecessary
injuries is to make sure all occupants are properly restrained. Accident
statistics suggest that children are much safer when properly restrained
in the rear seating positions than in the front.
Air bags can kill or injure a child in a child seat.NEVERplace a
rear-facing child seat in front of an active air bag. If you must
use a forward-facing child seat in the front seat, move the seat all the
way back.
Always transport children 12 years old and under in the back
seat and always properly use appropriate child restraints.
The passenger occupant classification sensor can automatically turn off
the passenger front air bag. The system is designed to help protect small
(child size) occupants from air bag deployments when they are
improperly seated or restrained in the front passenger seat contrary to
proper child-seating or restraint usage recommendations. Even with this
technology, parents areSTRONGLYencouraged to always properly
restrain children in the rear seat. The sensor also turns off the air bag
when the passenger seat is empty to prevent unnecessary replacement of
the air bag after a collision.
Front safety belt usage sensors
The front safety belt usage sensors detect whether or not the driver and
front outboard passenger safety belts are fastened. This information
allows your Personal Safety System to tailor the air bag deployment and
safety belt pretensioner activation depending upon safety belt usage.
Refer toSafety beltsection in this chapter.
Front safety belt pretensioners
The safety belt pretensioners at the front outboard seating positions are
designed to tighten the safety belts firmly against the occupant’s body
during frontal and side collisions, and rollovers. This maximizes the
effectiveness of the safety belts. In frontal collisions, the safety belt
pretensioners can be activated alone or, if the collision is of sufficient
severity, together with the front air bags.
Front safety belt energy management retractors
The front outboard safety belt energy management retractors allow
webbing to be pulled out of the retractor in a gradual and controlled
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
137
Page 138 of 312

manner in response to the occupant’s forward momentum. This helps
reduce the risk of force-related injuries to the occupant’s chest by
limiting the load on the occupant. Refer toEnergy management feature
section in this chapter.
Determining if the Personal Safety System is operational
The Personal Safety System uses a warning light in the instrument
cluster or a back-up tone to indicate the condition of the system. Refer
to theWarning lightsection in theInstrument clusterchapter. Routine
maintenance of the Personal Safety System is not required.
The Restraints Control Module (RCM) monitors its own internal circuits
and the circuits for the air bag supplemental restraints, crash sensor(s),
safety belt pretensioners, front safety belt buckle sensors, driver seat
position sensor, and passenger occupant classification sensor. In addition,
the RCM also monitors the restraints warning light in the instrument
cluster. A difficulty with the system is indicated by one or more of the
following.
•The warning light will either flash or stay lit.
•The warning light will not illuminate immediately after ignition is
turned on.
•A series of five beeps will be heard. The tone pattern will repeat
periodically until the problem and warning light are repaired.
If any of these things happen, even intermittently, have the Personal
Safety System serviced at your dealership or by a qualified technician
immediately. Unless serviced, the system may not function properly in
the event of a collision.
Safety belt precautions
Always drive and ride with your seatback upright and the lap
belt snug and low across the hips.
To reduce the risk of injury, make sure children sit where they
can be properly restrained.
Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the
vehicle is moving. The passenger cannot protect the child from
injury in a collision.
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
138
Page 139 of 312

All occupants of the vehicle, including the driver, should always
properly wear their safety belts, even when an air bag
supplemental restraint system (SRS) is provided.
It is extremely dangerous to ride in a cargo area, inside or
outside of a vehicle. In a collision, people riding in these areas
are more likely to be seriously injured or killed. Do not allow people to
ride in any area of your vehicle that is not equipped with seats and
safety belts. Be sure everyone in your vehicle is in a seat and using a
safety belt properly.
In a rollover crash, an unbelted person is significantly more likely
to die than a person wearing a seat belt.
Each seating position in your vehicle has a specific safety belt
assembly which is made up of one buckle and one tongue that
are designed to be used as a pair. 1) Use the shoulder belt on the
outside shoulder only. Never wear the shoulder belt under the arm.
2) Never swing the safety belt around your neck over the inside
shoulder. 3) Never use a single belt for more than one person.
Always transport children 12 years old and under in the back
seat and always properly use appropriate child restraints.
Combination lap and shoulder belts
1. Insert the belt tongue into the
proper buckle (the buckle closest to
the direction the tongue is coming
from) until you hear a snap and feel
it latch. Make sure the tongue is
securely fastened in the buckle.
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
139
Page 140 of 312

2. To unfasten, push the release
button and remove the tongue from
the buckle.
All restraints in the vehicle are combination lap and shoulder belts.
While you are fastened in the seat belt, the combination lap/shoulder belt
adjusts to your movement. However, if you brake hard, turn hard, or if
your vehicle receives an impact of 5 mph (8 km/h) or more, the safety
belt will become locked and help reduce your forward movement.
Energy Management Feature — Outboard
•This vehicle has a safety belt system with an energy management
feature at the front seats to help further reduce the risk of injury in
the event of a head-on collision.
•This safety belt system has a retractor assembly that is designed to
extend the seat belt webbing in a controlled manner. This helps
reduce the belt force acting on the user’s chest.
Failure to inspect and replace if necessary the Belt and
Retractor assembly after an accident could increase the risk of
injury in a collision.
Vehicle sensitive mode
This is the normal retractor mode, which allows free shoulder belt length
adjustment to your movements and locking in response to vehicle
movement. For example, if the driver brakes suddenly or turns a corner
sharply, or the vehicle receives an impact of approximately 5 mph (8
km/h) or more, the combination safety belts will lock to help reduce
forward movement of the driver and passengers.
Automatic locking mode
The automatic locking mode is not available on the driver safety belt.
When to use the automatic locking mode
In this mode, the shoulder belt is automatically pre-locked. The belt will
still retract to remove any slack in the shoulder belt. The automatic
locking mode is not available on the driver safety belt.
REVIEW COPY
2005 Freestar(win), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)(own2002),
Market:USA_English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
140