ABS FORD GRANADA 1985 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1985, Model line: GRANADA, Model: FORD GRANADA 1985Pages: 255, PDF Size: 14.98 MB
Page 130 of 255

Chapter 10
Braking system
ABS module - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Brake discs - inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Brake hydraulic system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Brake hydraulic system - fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Brake pedal - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Brake pipes and hoses - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . .21
Control module (April 1992 on) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .31
Front brake disc - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Front brake pads - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Front caliper - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Front caliper - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
G (gravity) switch (April 1992 on) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . .33
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Handbrake cable - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Handbrake cable - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Handbrake control lever - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Hydraulic unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Hydraulic unit accumulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .17Hydraulic unit fluid reservoir - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Hydraulic unit hoses - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Hydraulic unit pressure switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . .19
Hydraulic unit pump and motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .18
Master cylinder (April 1992 on) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .27
Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) (April 1992 on) - removal and refitting . .32
Rear brake disc - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Rear brake pads - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Rear caliper - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Rear caliper - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Rear disc splash shield - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Vacuum servo unit (April 1992 on) - testing, removal and refitting .28
Vacuum servo unit check valve (April 1992 on) - removal, testing and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Valve block and pump assembly (April 1992 on) - removal and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Wheel sensors - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
General
System type: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Discs all round, hydraulic operation, anti-lock braking system
(ABS). Handbrake by mechanical operation of rear calipers
System make:
Models up to April 1992 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Teves MK II ABS
Models from April 1992 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Teves MK IV ABS
Hydraulic system
Fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hydraulic fluid to Ford spec SAM-6C9103-A
Operating pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130 to 190 bar (1885 to 2755 lbf/in2)
Pressure warning switch operates at . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 to 110 bar (1450 to 1595 lbf/in2)
Brake pads
Lining minimum thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 mm (0.06 in)
Brake discs
Run-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.15 mm (0.006 in) maximum
Thickness variation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.015 mm (0.0006 in) maximum
Minimum thickness:
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 mm (0.87 in)
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cast into outer rim (typically 8.9 mm/0.35 in)
Rear - Estate models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 mm (0.71 in)
10•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
10
procarmanuals.com
Page 131 of 255
Models covered in this Manual have disc
brakes fitted all round. The footbrake operates
hydraulically on all four wheels, and the
handbrake operates mechanically on the rear
wheels. Both footbrake and handbrake are
self-adjusting in use.
Ford’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) is
fitted to all models. The system monitors the
rotational speed of each roadwheel. When a
wheel begins to lock under heavy braking, the
ABS reduces the hydraulic pressure to that
wheel, so preventing it from locking. When this
happens a pulsating effect will be noticed at
the brake pedal. On some road surfaces the
tyres may squeal when braking hard even
though the wheels are not locked.
The main components of the system are the
hydraulic unit, the calipers, pads and discs,
the wheel sensors and the “brain” or control
module. The hydraulic unit contains the
elements of a traditional master cylinder, plus
an electric motor and pump, a pressure
accumulator and control valves. The pump is
the source of pressure for the system and
does away with the need for a vacuum servo.
The hydraulic circuit is split front and rear,
as is normal practice with rear-wheel drive
vehicles. In the event that the hydraulic pump
fails, unassisted braking effort is still available
on the front calipers only.
Warning lights inform the driver of low brake
fluid level, ABS failure and (on some models)
brake pad wear. The low fluid level light
doubles as a “handbrake on” light; if it
illuminates at the same time as the ABS
warning light, it warns of low hydraulic
pressure.
ABS cannot overturn the laws of physics:
stopping distances will inevitably be greater on
loose or slippery surfaces. However, the system
should allow even inexperienced drivers to
retain directional control under panic braking.
From August 1986 the following
modifications were made to the braking
system.
a)The relays differ from earlier versions.b)The hydraulic pump is constructed of iron
rather than alloy.
c)A new pressure warning switch is used.
d)The earlier high pressure rubber hose is
replaced by a steel pipe.
To overcome the problem of excessive rear
brake pad wear, Ford introduced a differential
valve which is screwed into the ABS valve
block.The valve limits the pressure applied to
the rear brake calipers and so reduces brake
pad wear. From 1988 onwards, the valve has
been fitted during production. The differential
valve can also be fitted to earlier models. Refer
to your Ford dealer for further information.
From April 1992 onwards, the models
covered in this Manual were equipped with a
new Teves MK IV anti-lock braking system
instead of the Teves MK II system fitted to the
earlier models.
The Teves MK IV system differs from the
earlier MK II system in the following ways.
a)The source of hydraulic pressure for the
system is a conventional master cylinder
and vacuum servo assembly.
b)A valve block and pump assembly is used
instead of the hydraulic control unit. The
block contains the inlet and outlet
solenoid valves that control the hydraulic
system. There are three pairs of valves,
one for each brake circuit (paragraph c).
c)The hydraulic braking system consists of
three separate circuits; one for each front
brake (which are totally independent of
each other), and a joint circuit which
operates both rear brakes.
d)A G (gravity) switch is incorporated in the
system. This is an inertia type switch and
informs the control module when the
vehicle is decelerating rapidly.
e)A Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) is fitted to the
vacuum servo unit. The PTS informs the
control module of the position of the brake
pedal when the anti-lock sequence starts
and ensures that a constant pedal height
is maintained during the sequence.
The MK IV system operates as follows.
During normal operation the system
functions in the same way as a non-ABS
system would. During this time the three inlet
valves in the valve block are open and theoutlet valves are closed, allowing full hydraulic
pressure present in the master cylinder to act
on the main braking circuit. If the control
module receives a signal from one of the
wheel sensors and senses that a wheel is
about to lock, it closes the relevant inlet valve
in the valve block which then isolates the
brake caliper on the wheel which is about to
lock from the master cylinder, effectively
sealing in the hydraulic pressure. If the speed
of rotation of the wheel continues to decrease
at an abnormal rate, the control module will
then open the relevant outlet valve in the valve
block; this allows the fluid from the relevant
hydraulic circuit to return to the master
cylinder reservoir, releasing pressure on the
brake caliper so that the brake is released. The
pump in the valve block also operates to assist
in the quick release of pressure. Once the
speed of rotation of the wheel returns to an
acceptable rate the pump stops, the outlet
valve closes and the inlet valve is opened,
allowing the hydraulic master cylinder
pressure to return to the caliper which then
reapplies the brake. This cycle can be carried
many times a second. The solenoid valves
connected to the front calipers operate
independently, but the valve connected to the
rear calipers operates both calipers
simultaneously.
The operation of the ABS system is entirely
dependent on electrical signals. To prevent
the system responding to any inaccurate
signals, a built-in safety circuit monitors all
signals received by the control module. If an
inaccurate signal or low battery voltage is
detected, the ABS system is automatically
shut down and the warning lamp on the
instrument cluster is illuminated to inform the
driver that the ABS system is not operational.
Whilst in this state the system functions in the
same way as a non-ABS system would. If a
fault does develop in the ABS system, the car
must be taken to a Ford dealer for fault
diagnosis and repair. The system is equipped
with a diagnostic plug into which a special
diagnostic (STAR) tester can be plugged. This
allows faults to be easily traced.
1General information
10•2Braking system
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Front caliper:
To stub axle carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51 to 6138 to 45
Slide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Rear caliper:
Bracket to carrier plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51 to 6138 to 45
Slide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31 to 3523 to 26
Hydraulic unit to bulkhead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Accumulator to pump body . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Pump mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 95 to 7
High pressure hose banjo bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 to 2412 to 18
Reservoir mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 to 63 to 4
Wheel sensor fixing bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Vacuum servo unit retaining nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Master cylinder retaining nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Valve block and pump assembly mounting nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . .21 to 2815 to 21
procarmanuals.com
Page 132 of 255

Note: Hydraulic fluid is poisonous; wash off
immediately and thoroughly in the case of skin
contact and seek immediate medical advice if
any fluid is swallowed or gets into the eyes.
Certain types of hydraulic fluid are inflammable
and may ignite when allowed into contact with
hot components; when servicing any hydraulic
system it is safest to assume that the fluid is
inflammable and to take precautions against
the risk of fire as though it is petrol that is
being handled. Finally, it is hygroscopic (it
absorbs moisture from the air) old fluid may be
contaminated and unfit for further use. When
topping-up or renewing the fluid, always use
the recommended type and ensure that it
comes from a freshly-opened sealed container
1Bleeding is necessary whenever air has
entered the hydraulic system - for instance
after component renewal. Because the
hydraulic circuits are split, if only the front or
rear circuit has been disturbed it will normally
only be necessary to bleed the front or rear
calipers. If the hydraulic unit has been
disturbed or the fluid level has been allowed to
fall so low that air has entered the system,
both front and rear circuits must be bled,
starting with the front
2The services of an assistant will be required.
As far as is known, pressure bleeding or other
“one-man” equipment cannot be used. In
addition a supply of fresh brake fluid of the
correct type will be needed, together with a
length of flexible tube to fit the bleed screws
and a clean glass or plastic container.
3Do not allow the hydraulic unit pump motor
to run for more than two minutes at a time. The
motor must be allowed to cool (with the
ignition off) for at least ten minutes after each
two minute spell of running.
4Remember that brake fluid is poisonous and
that the rear brake hydraulic system may be
under considerable pressure. Take care not to
allow hydraulic fluid to spray into the face or
eyes.
5Keep the reservoir topped up to the MAX
mark during bleeding.
6Discard the fluid bled out of the system as it
is unfit for re-use.
Models before April 1992
Front brakes
7Remove the dust cap (if fitted) from the left-
hand caliper bleed screw. Slacken the bleed
screw, then nip it up again. Make sure that the
ignition is off.8Fit the bleed tube over the bleed screw.
Place the other end of the tube in the bleed jar
(glass or plastic container). Pour sufficient
brake fluid into the jar to cover the end of the
tube.
9Open the bleed screw one full turn. Have
the assistant depress the brake pedal as far as
it will go, and hold it depressed. Tighten the
bleed screw, then tell the assistant to release
the pedal.
10Repeat paragraph 9 until clean fluid, free
of air bubbles, flows from the bleed screw
during the downstrokes. Remember to keep
the fluid reservoir topped up.
11Repeat the operations on the right-hand
caliper. Refit the bleed screw dust caps (if
applicable) on completion.
Rear brakes
12Remove the dust cap (if fitted) from the
rear left-hand caliper bleed screw. Open the
bleed screw one full turn.
13Fit the bleed tube over the bleed screw.
Place the other end of the tube in the bleed jar
(see illustration).
14Have the assistant depress the brake
pedal as far as it will go and hold it down.
Switch on the ignition: the hydraulic unit pump
will start and fluid will flow from the bleed
screw.
15When clean fluid, free of air bubbles,
emerges from the bleed screw, tighten the
bleed screw and have the assistant release the
pedal.
16Wait for the hydraulic unit pump to stop,
then top-up the reservoir and repeat the
procedure on the right-hand caliper. This time
the brake pedal should only be depressed
half-way.
17Switch off the ignition, top-up the reservoir
again and refit the reservoir cap. Refit the
bleed screw dust caps (if applicable).
Models from April 1992
18This operation can be carried out using the
information given above inparagraphs 1 to 10,
ignoring the reference to the hydraulic unit
pump and bearing in mind the following.
19Note that if only one circuit is disturbed it
will only be necessary to bleed that relevant
circuit on completion.20If the complete system is to be bled, it
should be done in the following order.
a)Left-hand front caliper.
b)Right-hand front brake caliper.
c)Left-hand rear caliper.
d)Right-hand rear caliper.
See Chapter 1, Section 44.
1Whenever the brake pads are inspected,
also inspect the brake discs for deep
scratches, scores or cracks. Light scoring is
normal and may be ignored. A cracked disc
must be renewed; scratches and scores can
sometimes be machined out, provided that the
thickness of the disc is not reduced below the
specified minimum.
2When the brake pads are renewed, or if
brake judder or snatch is noticed, check the
discs for run-out and thickness variation. (Note
that wheel bearing wear can cause disc run-
out.)
3Position a dial test indicator probe against
the disc wear face, approximately 15 mm (0.6 in)
in from the outer circumference. Zero the
indicator, rotate the disc and read the run-out
from the indicator(see illustration).Maximum
run-out is given in the Specifications. If a dial
test indicator is not available, use a fixed
pointer and feeler blades.
4Measure the thickness of the disc, using a
micrometer, in eight evenly spaced positions
around the disc. Maximum thickness variation
is given in the Specifications. Renew the disc if
the variation is out of limits.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts, raise and
support the vehicle and remove the relevant
front wheel.
2Remove the two bolts which hold the caliper
bracket to the stub axle carrier. Lift the caliper
5Front brake disc - removal and
refitting
4Brake discs - inspection
3Brake hydraulic system - fluid
renewal
2Brake hydraulic system -
bleeding
Braking system 10•3
10
2.13 Bleeding a rear brake caliper
4.3 Measuring brake disc run-out
Hydraulic fluid is an effective
paint stripper and will attack
plastics; if any is spilt, it
should be washed off
immediately using copious quantities of
fresh water.
procarmanuals.com
Page 135 of 255

5Extract the piston seal from the groove in
the bore, using a blunt instrument (see
illustration). Discard the seal and dust boot.
6Clean the piston and bore with methylated
spirit and inspect them for scuffs, scores or
other damage. If the piston is corroded it must
be renewed. Slight imperfections in the bore
can be polished out with wire wool.
7Place the clean component on a clean
surface ready for reassembly. Lubricate the
caliper hose with clean hydraulic fluid.
8Fit the new piston seal to the groove in the
bore, using fingers only to work it into position.
9Lubricate the piston with clean hydraulic
fluid and fit the dust boot over the piston,
making sure it is the right way up. Insert the
piston into the bore and press it home,
engaging the dust boot lip with the groove on
the caliper (see illustration).
10This completes the overhaul of the hydraulic
components. Items such as slide bolts and
bracket can also be renewed if necessary.
11Remove the bleed screw while the caliper
is on the bench and apply a little anti-seize
compound to its threads, to avoid trouble in
undoing it later.
1With the ignition off, pump the brake pedal
at least 20 times (or until it becomes hard) to
depressurise the system.
2Chock the front wheels and release the
handbrake. Slacken the rear wheel nuts, raiseand support the vehicle and remove the
relevant wheel.
3Disconnect the pad wear warning wires,
when fitted.
4Disconnect the flexible hose from the brake
pipe. Plug or cap the open unions to reduce
spillage and to keep dirt out. Unscrew the
flexible hose from the caliper and remove it.
5Remove the two slide bolts. Lift the caliper
off the pads and bracket, at the same time
unhooking the handbrake cable (see
illustrations). Alternatively, the two bracket-
to-hub bolts can be removed and the caliper
and bracket separated on the bench.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations,
but before refitting the wheel, bleed both rear
calipers as described in Section 2.
7When bleeding is complete, pump the brake
pedal several times to bring the pads up to the
disc, then check the operation of the
handbrake.
Note: Complete dismantling of the rear caliper
should not be attempted unless Ford spring
compressor (tool No 12-007) is available. or
unless the problems likely to arise in the absence
of the tool are understood. Renewal of the piston
seal and dust boot requires no special tools.
1Clean the caliper externally and mount it in a
soft-jawed vice.
2Rotate the piston anti-clockwise until it isprotruding from the bore by about 20 mm (0.8 in).
Free the dust boot from the groove in the
piston, then carry on unscrewing the piston
and remove it. Remove and discard the dust
boot.
3The piston and bore may now be cleaned
and examined, and the piston seal and dust
boot renewed, as described for the front
caliper (Section 10).
4The piston adjuster nut seal should also be
renewed. Remove the circlip from the piston,
then extract the thrustwashers, wave washer
and thrust bearing. Note the fitted sequence of
these components. Finally remove the nut
(see illustrations).
5Remove the seal from the nut, noting which
way round it is fitted. Clean the nut with
methylated spirit. Lubricate the new seal with
clean hydraulic fluid and fit it to the nut.
12Rear caliper - overhaul
11Rear caliper - removal and
refitting
10•6Braking system
10.5 Removing the piston seal
12.4a Removing the circlip from a rear
caliper piston . . .12.4b . . . followed by a thrustwasher . . .
11.5b . . . and remove the rear caliper
10.9 Pressing the piston into the bore11.5a Unhook the handbrake cable . . .
12.4c . . . a wave washer and (not shown)
another thrustwasher . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 140 of 255

5Unscrew the hose from its union on the
caliper and remove it (see illustration).
6Refit by reversing the removal operations,
then bleed the appropriate part of the
hydraulic system (Section 2). In the case of the
front hoses, check that they are not kinked or
twisted, and that they do not contact other
components when the steering is moved from
lock to lock. Reposition the hose in the
bracket if necessary.
7To remove a rigid pipe, simply undo the
union nuts at the hydraulic unit, hose bracket
or T-piece (see illustration). Free the pipe
from any retaining clips and remove it.
8New pipes can be bought ready-made, with
the unions attached. Some garages and motor
factors will make up pipes to order, using the
old pipe as a pattern. If purchasing proprietary
pipes made of copper alloy or similar material,
follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully
concerning bending, provision of extra clips
etc.
9Fit and secure the new pipe and tighten the
union nuts, bleed the appropriate part of the
hydraulic system (Section 2).
1The handbrake is normally self-adjusting in
use. Adjustment may be required to
compensate for cable stretch over a long
period, and is also necessary after fitting a
new cable.2Chock the front wheels, release the
handbrake and raise and support the rear of
the vehicle.
3Release the adjuster locknut from the
adjuster nut. Back off the adjuster nut,
slackening the cable until both handbrake
levers on the calipers are resting against their
stops (see illustration).
4Paint alignment marks between each
handbrake lever and the caliper body (see
illustration).
5Tighten the adjuster nut until either
handbrake lever just starts to move - as shown
by the alignment marks.
6Apply the handbrake and release it a few
times to equalise the cable runs.
7Tighten the locknut onto the adjuster nut
finger tight, then tighten a further three to six
clicks using self-locking pliers or a peg
spanner.
1Slacken the rear wheel nuts and chock the
front wheels. Raise and support the rear of the
vehicle and remove both rear wheels. Release
the handbrake.
2Slacken off the handbrake cable adjuster
locknut and adjuster nut.
3Free the cable from the equaliser yoke by
removing the circlip and clevis pin (see
illustration). Beware of self-tapping screws
protruding through the floor in this area.4Unhook the cable inner from the handbrake
levers on the calipers. Free the cable outer
from the caliper brackets (see illustration).
5Free the cable from the lower arm and
underbody brackets and remove it.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations,
but before refitting the rear wheels, adjust the
cable as described in the previous Section.
1Chock the front wheels and release the
handbrake. Raise and support the rear of the
vehicle.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Disconnect the handbrake cable equaliser
yoke by removing the circlip and clevis pin.
4Remove the centre console (Chapter 12).
5Remove the handbrake control lever boot.
6Disconnect the wiring from the handbrake
warning switch.
7Unbolt the handbrake lever and remove it,
complete with switch. Remove the switch if
necessary.
8Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Remove the under-dash trim on the
passenger’s side.
2Push the module upwards and then swing it
forwards to release it from its clip.
25ABS module - removal and
refitting
24Handbrake control lever -
removal and refitting
23Handbrake cable - removal
and refitting
22Handbrake cable - adjustment
Braking system 10•11
10
21.5 Disconnecting the hose from the
caliper21.7 Brake pipe union T-piece (arrowed)22.3 Handbrake cable adjuster
Locknut previously backed off adjuster nut
22.4 Alignment marks painted on lever and
body23.3 Circlip (arrowed) on equaliser yoke
Note protruding screws in transmission tunnel23.4 Handbrake cable outer attached to
caliper bracket
procarmanuals.com
Page 141 of 255

3Press the multi-plug locking lever,
disconnect the multi-plug and unhook it from
the module. Remove the module.
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the multi-plug is properly
engaged before refitting the module.
Front
1Ensure that the handbrake is applied. Raise
and support the front of the vehicle.
2From under the bonnet disconnect the
wheel sensor wiring multi-plug. Unclip the
wiring, working towards the sensor.
3Remove the securing bolt and withdraw the
sensor from the stub axle carrier (see
illustration).
4Unclip the wire from the bracket on the
strut. Remove the sensor and its wiring (see
illustration).
5Clean any rust or debris from the sensor
bore in the stub axle carrier. Pack the bore
with clean wheel bearing grease.
6Renew the O-ring on the sensor and smear
it with grease.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Rear
8Chock the front wheels and release the
handbrake. Slacken the rear wheel nuts, raiseand support the rear of the vehicle and remove
the rear wheel.
9Fold the rear seat cushion forwards, remove
the side kick panel and roll back the carpet to
gain access to the sensor multi-plug (see
illustration).
10Disconnect the multi-plug, release the
floor grommet and pass the cable through the
floor.
11Unclip the handbrake cable from the
suspension lower arm.
12Remove the caliper front slide bolt and
pivot the caliper rearwards to gain access to
the sensor.
13Remove the sensor securing bolt and
withdraw the sensor.
14Clean up the sensor bore, pack it with
grease and renew the sensor O-ring.
15Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2Disconnect the wiring plug then remove the
master cylinder reservoir cap; do not invert the
cap as hydraulic fluid could enter and damage
the reservoir level switch. Syphon the
hydraulic fluid from the reservoir. Note: Do not
syphon the fluid by mouth, as it is poisonous;
use a syringe or an old poultry baster.
Alternatively, open any convenient bleed
screw in the system and gently pump the
brake pedal to expel the fluid through a plastic
tube connected to the screw.
3Wipe clean the area around the brake pipe
unions on the right-hand side of the master
cylinder and place absorbent rags beneath the
pipe unions to catch any surplus fluid.
4To disconnect the plastic low pressure
hoses, use a small flat bladed screwdriver to
carefully press the flange of the collet into the
master cylinder then pull the hoses out from
the reservoir(see illustration).Unscrew the
two union nuts and disconnect the brake
pipes from master cylinder. Plug or tape over
the pipe/hose ends and master cylinder
orifices to minimise the loss of brake fluid and
to prevent the entry of dirt into the system.
Wash off any spilt fluid immediately with cold
water.5Slacken and remove the two nuts securing
the master cylinder to the vacuum servo unit
then withdraw the unit from the engine
compartment. Remove the O-ring from the
rear of master cylinder and discard it.
6If necessary remove the reservoir from the
master cylinder and withdraw the mounting
bush seals and O-rings. Note that the master
cylinder is a sealed unit with no spare parts
available separately. Therefore if it is faulty it
must be renewed as a unit.
7Fit new mounting bush seals and O-rings to
the master cylinder and refit the reservoir (if
removed). Remove all traces of dirt from the
master cylinder and servo unit mating surfaces
and fit a new O-ring onto the master cylinder
body.
8Fit the master cylinder to the servo unit
ensuring that the pushrod enters the servo unit
bore centrally. Refit the master cylinder
mounting nuts and tighten them to the
specified torque.
9Wipe clean the brake pipe/hose unions and
the master cylinder ports. Refit the pipes to
the master cylinder ports and tighten them
securely. Push the low pressure hoses into
position and check they are securely held by
their retaining collets.
10Refill the master cylinder reservoir with
new fluid and bleed the hydraulic system
1To test the operation of the servo unit
depress the footbrake several times to
exhaust the vacuum then start the engine
whilst keeping the pedal firmly depressed. As
the engine starts there should be a noticeable
“give” in the brake pedal as the vacuum builds
up. Allow the engine to run for at least two
minutes then switch it off. If the brake pedal is
now depressed it should feel normal, but
further applications should result in the pedal
feeling firmer, with the pedal stroke decreasing
with each application.
2If the servo does not operate as described,
inspect the servo unit check valve as
describedin paragraph 3 of Section 29.28Vacuum servo unit (April 1992
on) - testing, removal and
refitting
27Master cylinder (April 1992
on) - removal and refitting
26Wheel sensors - removal and
refitting
10•12Braking system
26.3 Removing a front sensor
27.4 Disconnecting the master cylinder low
pressure hoses (A) and brake pipes (B) -
models from April 1992
26.4 Unclipping the sensor wire from the
strut26.9 Rear wheel sensor multi-plug
(arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 142 of 255

3If the servo unit still fails to operate
satisfactorily the fault lies within the unit itself.
Repairs to the unit are not possible.
4Remove the master cylinder (Section 27).
5Disconnect the vacuum hose from the servo
unit taking care not to displace the rubber
sealing grommet. Disconnect the wiring plug
from the Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) which is
situated on the front of the servo.
6Working from inside the vehicle, remove the
servo pushrod retaining clip from the brake
pedal. If necessary, to improve access to the
brake pedal remove the right-hand lower facia
panel .
7Slacken and remove the four nuts securing
the servo unit to the bulkhead, then return to
the engine compartment and remove the
servo unit from the vehicle. Remove the
gasket from the rear of the unit and discard it.
8Note that the vacuum servo unit is a sealed
assembly with no spare parts available
separately. Therefore if it is faulty it must be
renewed as a unit. Inspect the vacuum servo
vacuum hose sealing grommet for damage or
deterioration and renew if necessary.
9Remove all traces of dirt from the servo unit
and bulkhead mating surfaces and fit a new
gasket onto the rear of the servo.
10Manoeuvre the servo unit into position,
ensuring that the servo unit pushrod is
correctly located with the hole in the pedal.
Refit the servo unit retaining nuts and tighten
them to the specified torque setting. Secure
the pushrod in position with the retaining clip
11Carefully refit the vacuum hose to the servo
unit taking great care not to damage or displace
the sealing grommet. Reconnect the wiring
connector to the Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS).
12Refit the master cylinder as described
above. On completion start the engine and
check the operation of the servo unit.
1Disconnect the vacuum hose from the servo
unit taking care not to displace the rubber
sealing grommet.
2To disconnect the hose from the inlet
manifold, use a small flat-bladed screwdriver
to carefully press the flange of the collet into
the manifold then pull the hose out and
remove it from the vehicle (see illustration).
3Examine the vacuum hose and sealing
grommet for damage, splits, cracks or general
deterioration and renew as necessary. Make
sure that the check valve is working correctly
by blowing through the hose from the servo
unit end. Air should flow in this direction, but
not when blown through from the inlet
manifold hose end. Renew the check valve if it
is at all suspect.
4Ensure that the check valve is fitted the
correct way around then push the connector
into the manifold and check that it is securely
held by the retaining collet.5Carefully refit the vacuum hose to the servo
unit taking great care not to damage or
displace the sealing grommet.
6On completion start the engine and check
the operation of the servo unit.
1Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2Carry out the operations described in
paragraphs 2 to 4 of Section 27.
3Remove all traces of dirt from the exterior of
the block then disconnect the motor and valve
block wiring plugs and free the diagnostic test
wiring plug from the mounting bracket.
4Position some absorbent rag beneath the
valve block then unscrew the three brake pipe
outlet unions whilst avoiding getting surplus
brake fluid in the wiring plugs. Plug the block
ports and pipe ends to minimise the loss of
fluid and prevent the entry of dirt into the
system. Wash off any spilt fluid immediately
with cold water.
5Slacken and remove the three valve block
and pump assembly mounting nuts and
remove the unit from the engine compartment.
6Note that the valve block and pump
assembly is a sealed unit and cannot be
overhauled. If it is faulty it must be renewed.
Note that if the low pressure hoses are
disconnected from the assembly, great care
must be taken when reconnecting them to
ensure that the valve block filter is not
damaged.
7Manoeuvre the assembly into position then
refit the mounting nuts and tighten them by
hand only. Taking into account the amount of
movement in the mounting rubbers, position
the assembly so that it will not contact the
mounting bracket then tighten the mounting
nuts to the specified torque setting.
8Remove the plugs then reconnect the outlet
pipes to the assembly and tighten the union
nuts securely.
9Ensure that the wiring is correctly routed
and reconnect the wiring plugs to the valve
block and pump assembly. Refit thediagnostic test wiring connector to the
mounting bracket.
10Wipe clean the brake pipe/hose unions
and the master cylinder ports. Refit the pipes
to the master cylinder ports and securely
tighten the union nuts. Push the low pressure
hoses into position and check they are
securely held by their retaining collets.
11Reconnect the battery negative terminal,
then fill the master cylinder and bleed the
complete hydraulic system using the
information given earlier in this Section.
1The anti-lock braking control module is
located behind the glovebox. To remove the
module first disconnect the battery negative
terminal.
2Open up the glovebox then, using a small
flat-bladed screwdriver, carefully prise up the
retaining clip and disconnect the glovebox
hinge arms. Withdraw the glovebox assembly
from the facia noting the plastic bushes which
are fitted to the glovebox pivot points.
3Lift the wiring plug retaining clip and
disconnect the plug to the control module. The
ABS module is the upper of the two control
modules mounted horizontally.
4Release the retaining clips and slide the
module out of the mounting bracket (see
illustration).
5Commence refitting by sliding the module
into the mounting bracket until it clips into
position.
6Connect the wiring connector to the
module, ensuring that the wiring is correctly
routed, and secure it in position with the
retaining clip.
7Ensure that the plastic bushes are correctly
fitted to the glovebox then refit the glovebox
assembly, locating the pivots in the correct
locations on the facia panel. Clip the hinge
arms onto the glovebox and check that it
opens and closes smoothly.
8Reconnect the battery negative terminal.
31Control module (April 1992
on) - removal and refitting
30Valve block and pump
assembly (April 1992 on) -
removal and refitting
29 Vacuum servo unit check
valve (April 1992 on) -
removal, testing and refitting
Braking system 10•13
10
29.2 Disconnecting brake servo vacuum
hose from the inlet manifold (DOHC engine
shown)31.4 Removing the ABS control module -
models from April 1992
procarmanuals.com
Page 144 of 255

Chapter 11
Steering and suspension
Front anti-roll bar - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Front anti-roll bar bushes - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Front stub axle carrier - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Front suspension crossmember - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . .15
Front suspension lower arm - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . .18
Front suspension strut - dismantling and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . .22
Front suspension strut - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Front wheel alignment - checking and adjusting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Front wheel bearings - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Power steering fluid - level check and bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Power steering hoses - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Power steering pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Power steering pump drivebelt - removal, refitting and tensioning .10
Rear anti-roll bar - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Rear crossmember insulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Rear hub - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Rear shock absorber - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31Rear spring - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Rear suspension and final drive assembly - removal and refitting . .23
Rear suspension lower arm - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Rear wheel bearings - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Ride height control compressor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .33
Ride height control sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Ride height control system - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Steering column - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Steering column lock - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Steering gear - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Steering intermediate shaft and flexible coupling - removal and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Steering rack bellows - renewal in vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Steering wheel - centralising . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Steering wheel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Track rod end - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Wheel stud - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
General
Suspension type:
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Independent, MacPherson struts and anti-roll bar
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Independent, semi-trailing arms and anti-roll bar; ride height
control optionally available
Steering type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Rack and pinion, power-assisted on some models
Front wheel alignment
Toe:
Setting value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 ± 1 mm (0.08 ± 0.04 in) toe-in
Tolerance in service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 mm (0.02 in) toe-out to 4.5 mm (0.18 in) toe-in
Castor :
SOHC and 2.8 litre models:
Standard, without ride height control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . + 1°51’ ± 1°00’
Standard, with ride height control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . + 1°58’ ± 1°00’
Heavy duty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . + 1°46’ ± 1°00’
DOHC carburettor and low series fuel-injection models . . . . . . . . . . + 2°27’ ± 1°00’
DOHC high series models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . + 2°26’± 1°00’
2.4 litre:
low series models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . + 2°17’ ± 1°00’
high series models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . + 2°50’ ± 1°00’
2.9 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . + 2°22’ ± 1°00’
11•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
11
procarmanuals.com
Page 146 of 255

The steering gear is of rack-and-pinion type.
Power assistance is standard on V6 models
and optional on others. The power-assisted
steering gear has a “variable ratio” effect
which increases the steering ratio about the
straight-ahead position: this provides quick
lock-to-lock action without the penalty of
over-responsiveness in open road driving.
The steering wheel is adjustable both up-
and-down and fore-and-aft. Both steering
column and shaft are designed to collapse
under impact. The steering shaft is connected
to the pinion by an intermediate shaft, which
has a universal joint at its upper end and a
flexible coupling at the lower end.
Front suspension is independent, of the
MacPherson strut type, with coil springs and
concentric telescopic shock absorbers. The
struts are attached to the tops of the stub axle
carriers, which are located at their lower ends
by balljoints incorporated in the lower
suspension arms. The lower suspension arms
pivot at their inner ends, where they are
attached to a central crossmember. The anti-
roll bar is attached to the rear of the arms and
serves to control fore-and-aft movement as
well as reducing roll.
Suspension geometry has been designed to
give good steering “feel”, resistance to pulling
caused by uneven braking effort or tyre
deflation, and (in the case of manual steering)
acceptably low steering wheel effort at parking
speeds. Only toe is adjustable in service.
The rear suspension is also independent. It
is of the semi-trailing arm type, with coil
springs and separate telescopic shock
absorbers. An optionally-available ride height
control system keeps the rear suspension
height constant, regardless of vehicle load.
Both front and rear wheel bearings are of a
special taper-roller type and require no
periodic adjustment in service.1Refer to Chapter 1, Section 35, to check the
power steering fluid level.
2If the fluid level falls so low that air enters
the pump, or after component renewal, the
system must be bled as follows.
3Remove the reservoir filler cap. Top-up with
clean fluid to the appropriate “cold” level. It is
important that the fluid is free of air bubbles,
so do not shake the container when topping-
up, and pour the fluid slowly.
4Disconnect the negative LT lead from the
ignition coil. Have an assistant crank the
engine on the starter in two second bursts, at
the same time turning the steering wheel from
lock to lock. Keep the reservoir topped up
whilst this is going on.
5When air bubbles no longer appear in the
fluid, stop the cranking. Reconnect the coil
negative lead and run the engine for a few
seconds, then stop it and check the level
again. Refit the filler cap.
6Run the vehicle for a few miles to warm up
the fluid and expel any remaining air, then stop
the engine and make a final fluid level check.
Manual steering
1Position the steering in the straight-ahead
position, then remove the ignition key so that
the steering is locked.
2Slacken the front wheel nuts. Raise and
support the front of the vehicle and remove
the front wheels.
3Remove the pinch-bolt and nut which
secure the intermediate shaft flexible coupling
to the pinion shaft (see illustration).
4Slacken the track rod end locknuts by half a
turn each (see illustration).
5Remove the split pin from the track rod
balljoint nuts. Unscrew the nuts, break the
balljoint tapers using a separator tool anddisengage the track rod ends from the
steering arms.
6Remove the two bolts which secure the
steering gear to the crossmember. Lift out the
steering gear.
7Mark the positions of the track rod ends on
the track rods, using paint or sticky tape, so
that they can be refitted in approximately the
same positions. Unscrew the track rod ends
and locknuts.
8Commence refitting by screwing on the
locknuts and track rod ends, observing the
previously made position marks when
applicable.
9Bring the rack to the straight-ahead
position. Do this by counting the number of
turns of the pinion needed to go from lock to
lock, then applying half that number of turns
from full lock on one side.
10Offer the steering gear to the vehicle,
engaging the flexible coupling and loosely
fitting the securing bolts. Note that the master
spline on the pinion shaft mates with the
corresponding groove in the flexible coupling.
11Tighten the two steering gear-to-
crossmember bolts to the specified Stage 1
torque. Slacken the bolts and retighten to the
Stage 2 torque. Finally tighten the bolts
through the angle specified for Stage 3.
12Make sure that the flexible coupling and
pinion shaft are properly engaged, then fit the
pinch-bolt and nut. Tighten the pinch-bolt to
the specified torque.
3Steering gear - removal and
refitting
2Power steering fluid - level
check and bleeding1General information
Steering and suspension 11•3
11
3.3 Master spline and groove on pinion
shaft and coupling
Torque wrench settings (continued)Nmlbf ft
Rear suspension
Driveshaft stub axle nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .250 to 290180 to 210
Final drive mounting to floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Final drive mounting to rear cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 to 5030 to 37
Guide plate-to-floor bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Guide plate insulator bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69 to 8851 to 65
Lower arm to crossmember . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 9559 to 70
Brake anchor plate to lower arm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52 to 6438 to 47
Anti-roll bar bracket bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Shock absorber mountings:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73 to 9754 to 72
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68 to 9250 to 68
Rear hub bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 10059 to 74
Wheels
Wheel nuts (steel or alloy wheels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 10052 to 74
procarmanuals.com
Page 151 of 255
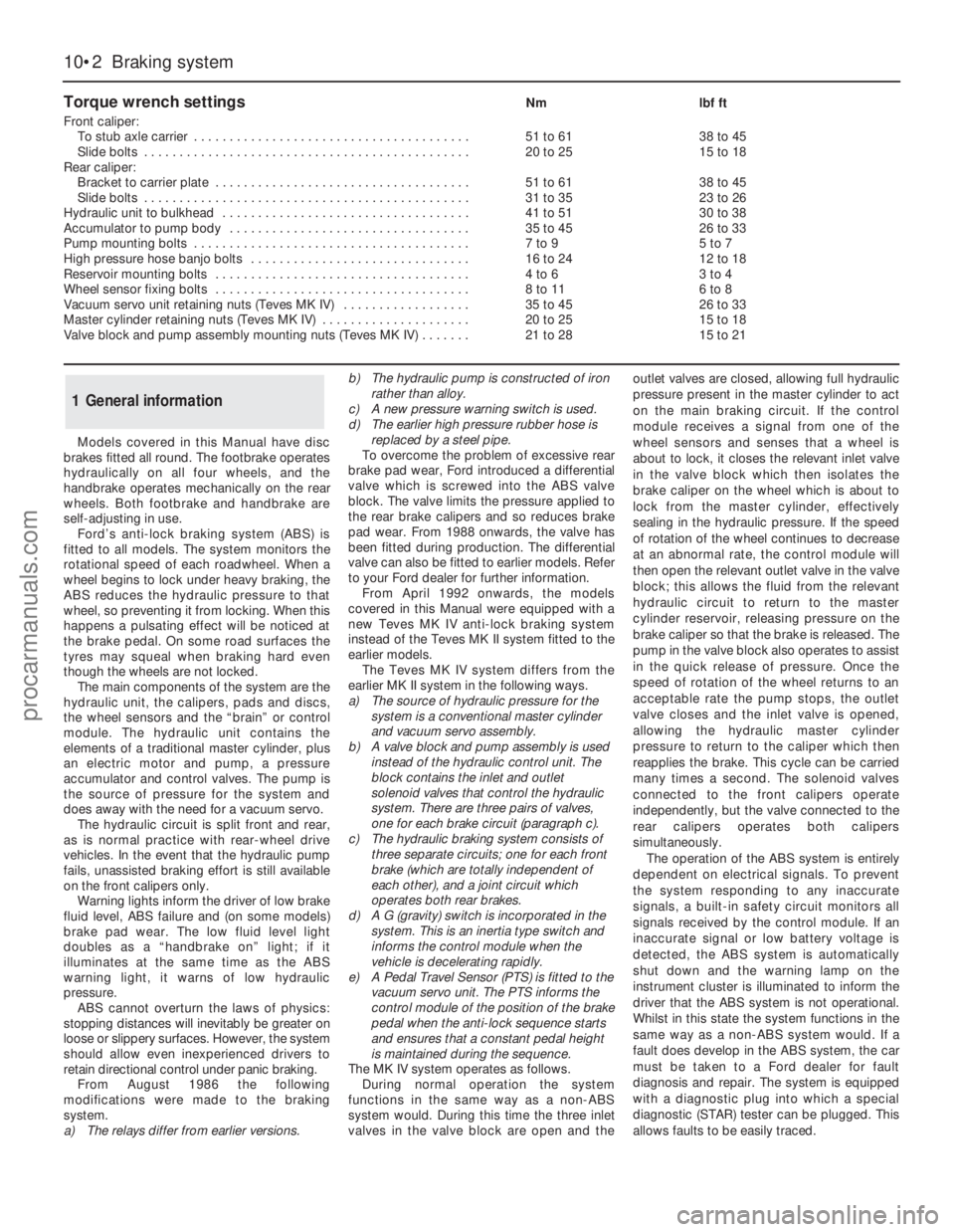
times, then use a proprietary balljoint
separator to break the taper (see illustration).
5Use a stout piece of wood to lever the lower
arm downwards and free the balljoint from the
stub axle carrier.
6Remove the ABS wheel sensor from its
hole.
7Remove the spring clip from one of the
wheel studs and pull the brake disc off the
hub.
8Remove the stub axle carrier pinch-bolt.
Spread the stub axle carrier by carefully
introducing a chisel or blunt instrument into its
slot. Draw the stub axle carrier off the
suspension strut and remove it.
9Refit by reversing the removal operations,
noting the following points:
a)Tighten all fastenings to the specified
torque
b)Use new split pins, when applicable
c)Renew the wheel sensor O-ring if
necessary; clean the sensor and its bore,
and smear them with wheel bearing
grease
Models before August 1989
1Remove the stub axle carrier as described
in the previous Section.
2Screw the wheel nuts onto the studs to
protect the threads. Clamp the stub axle
carrier in a vice by means of the studs and
nuts; do not overtighten.
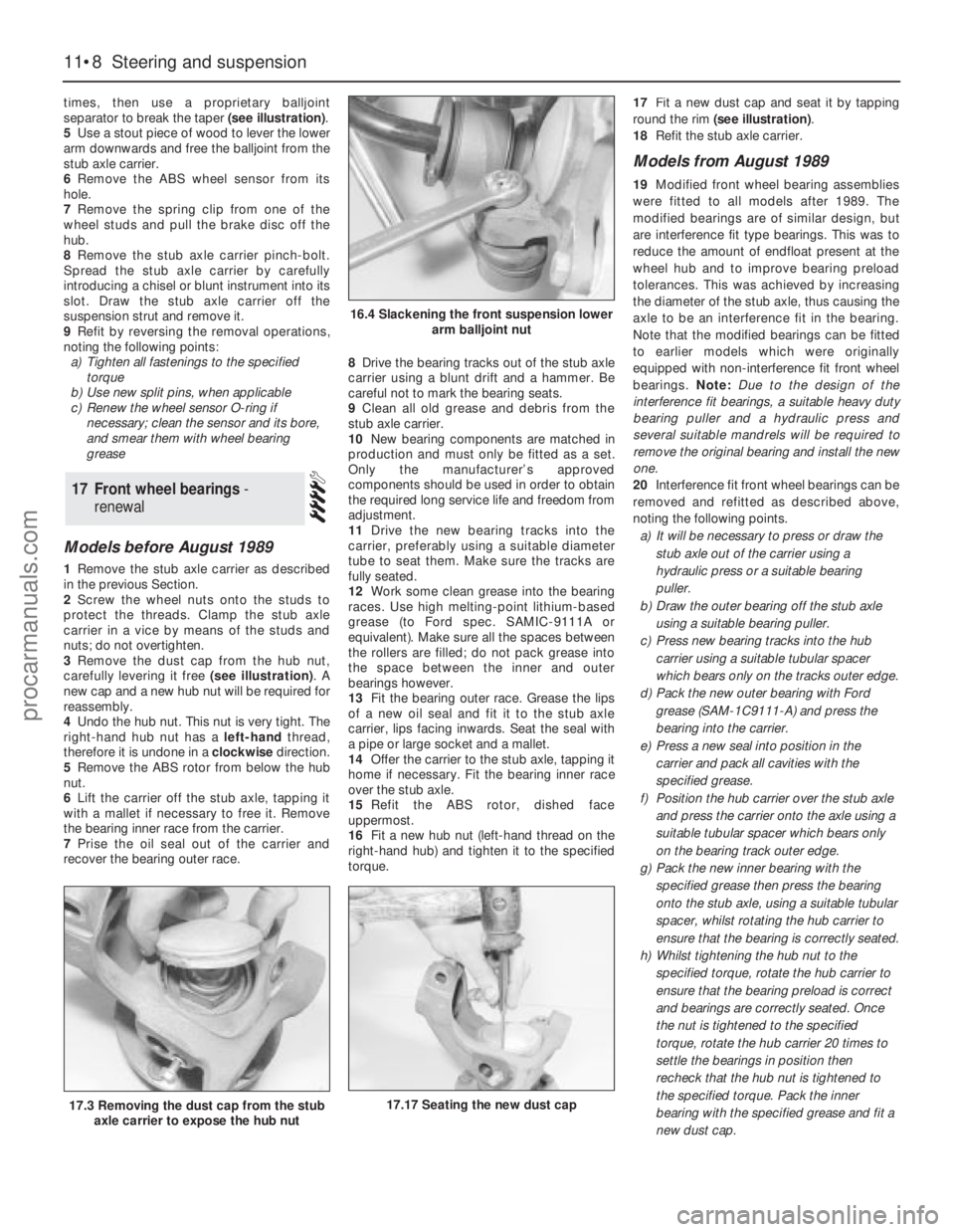
3Remove the dust cap from the hub nut,
carefully levering it free (see illustration). A
new cap and a new hub nut will be required for
reassembly.
4Undo the hub nut. This nut is very tight. The
right-hand hub nut has a left-handthread,
therefore it is undone in a clockwisedirection.
5Remove the ABS rotor from below the hub
nut.
6Lift the carrier off the stub axle, tapping it
with a mallet if necessary to free it. Remove
the bearing inner race from the carrier.
7Prise the oil seal out of the carrier and
recover the bearing outer race.8Drive the bearing tracks out of the stub axle
carrier using a blunt drift and a hammer. Be
careful not to mark the bearing seats.
9Clean all old grease and debris from the
stub axle carrier.
10New bearing components are matched in
production and must only be fitted as a set.
Only the manufacturer’s approved
components should be used in order to obtain
the required long service life and freedom from
adjustment.
11Drive the new bearing tracks into the
carrier, preferably using a suitable diameter
tube to seat them. Make sure the tracks are
fully seated.
12Work some clean grease into the bearing
races. Use high melting-point lithium-based
grease (to Ford spec. SAMIC-9111A or
equivalent). Make sure all the spaces between
the rollers are filled; do not pack grease into
the space between the inner and outer
bearings however.
13Fit the bearing outer race. Grease the lips
of a new oil seal and fit it to the stub axle
carrier, lips facing inwards. Seat the seal with
a pipe or large socket and a mallet.
14Offer the carrier to the stub axle, tapping it
home if necessary. Fit the bearing inner race
over the stub axle.
15Refit the ABS rotor, dished face
uppermost.
16Fit a new hub nut (left-hand thread on the
right-hand hub) and tighten it to the specified
torque.17Fit a new dust cap and seat it by tapping
round the rim (see illustration).
18Refit the stub axle carrier.
Models from August 1989
19Modified front wheel bearing assemblies
were fitted to all models after 1989. The
modified bearings are of similar design, but
are interference fit type bearings. This was to
reduce the amount of endfloat present at the
wheel hub and to improve bearing preload
tolerances. This was achieved by increasing
the diameter of the stub axle, thus causing the
axle to be an interference fit in the bearing.
Note that the modified bearings can be fitted
to earlier models which were originally
equipped with non-interference fit front wheel
bearings. Note: Due to the design of the
interference fit bearings, a suitable heavy duty
bearing puller and a hydraulic press and
several suitable mandrels will be required to
remove the originalbearing and install the new
one.
20Interference fit front wheel bearings can be
removed and refitted as described above,
noting the following points.
a)It will be necessary to press or draw the
stub axle out of the carrier using a
hydraulic press or a suitable bearing
puller.
b)Draw the outer bearing off the stub axle
using a suitable bearing puller.
c)Press new bearing tracks into the hub
carrier using a suitable tubular spacer
which bears only on the tracks outer edge.
d)Pack the new outer bearing with Ford
grease (SAM-1C9111-A) and press the
bearing into the carrier.
e)Press a new seal into position in the
carrier and pack all cavities with the
specified grease.
f)Position the hub carrier over the stub axle
and press the carrier onto the axle using a
suitable tubular spacer which bears only
on the bearing track outer edge.
g)Pack the new inner bearing with the
specified grease then press the bearing
onto the stub axle, using a suitable tubular
spacer, whilst rotating the hub carrier to
ensure that the bearing is correctly seated.
h)Whilst tightening the hub nut to the
specified torque, rotate the hub carrier to
ensure that the bearing preload is correct
and bearings are correctly seated. Once
the nut is tightened to the specified
torque, rotate the hub carrier 20 times to
settle the bearings in position then
recheck that the hub nut is tightened to
the specified torque. Pack the inner
bearing with the specified grease and fit a
new dust cap.
17Front wheel bearings -
renewal
11•8Steering and suspension
16.4 Slackening the front suspension lower
arm balljoint nut
17.17 Seating the new dust cap17.3 Removing the dust cap from the stub
axle carrier to expose the hub nut
procarmanuals.com