Abs sensor FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 1432 of 2057

E53340
1
2
3
Description
Item
Tuning fork exciter
1
Suspension
2
Measuring side
3
Due to the special way in which it works. the
combined yaw rate sensor and lateral acceleration
sensor/longitudinal acceleration sensor must be
installed the right way up in the designated location
specified by the manufacturer. Any slight deviation
in the installation position and/or installation
location could lead to impaired functionality and
thereby possible failure of the stability assist.
Front wheel sensor
E96823
Active sensors are used to determine the rotational
speeds of the wheels at the hub. After the ignition
is switched on, the ABS module supplies the
sensors with power. The sensors work in
accordance with the Hall effect principle and
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 14
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 14
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1433 of 2057
generate a square wave output signal. The signal
acts in proportion to the rotational speed of the
sensor ring. The ABS sensor rings are built into
the seals in the front wheel bearings. The ABS
module evaluates the signals from all four sensors
to calculate a vehicle speed signal based on the
rotational speeds of all wheels. The road speed is
transmitted on the CAN bus. The powertrain controlmodule (PCM) uses this signal and the
programmed tire size to calculate the vehicle
speed. The calculated vehicle speed is forwarded
on the CAN bus and is requested by other control
units that need this input information.
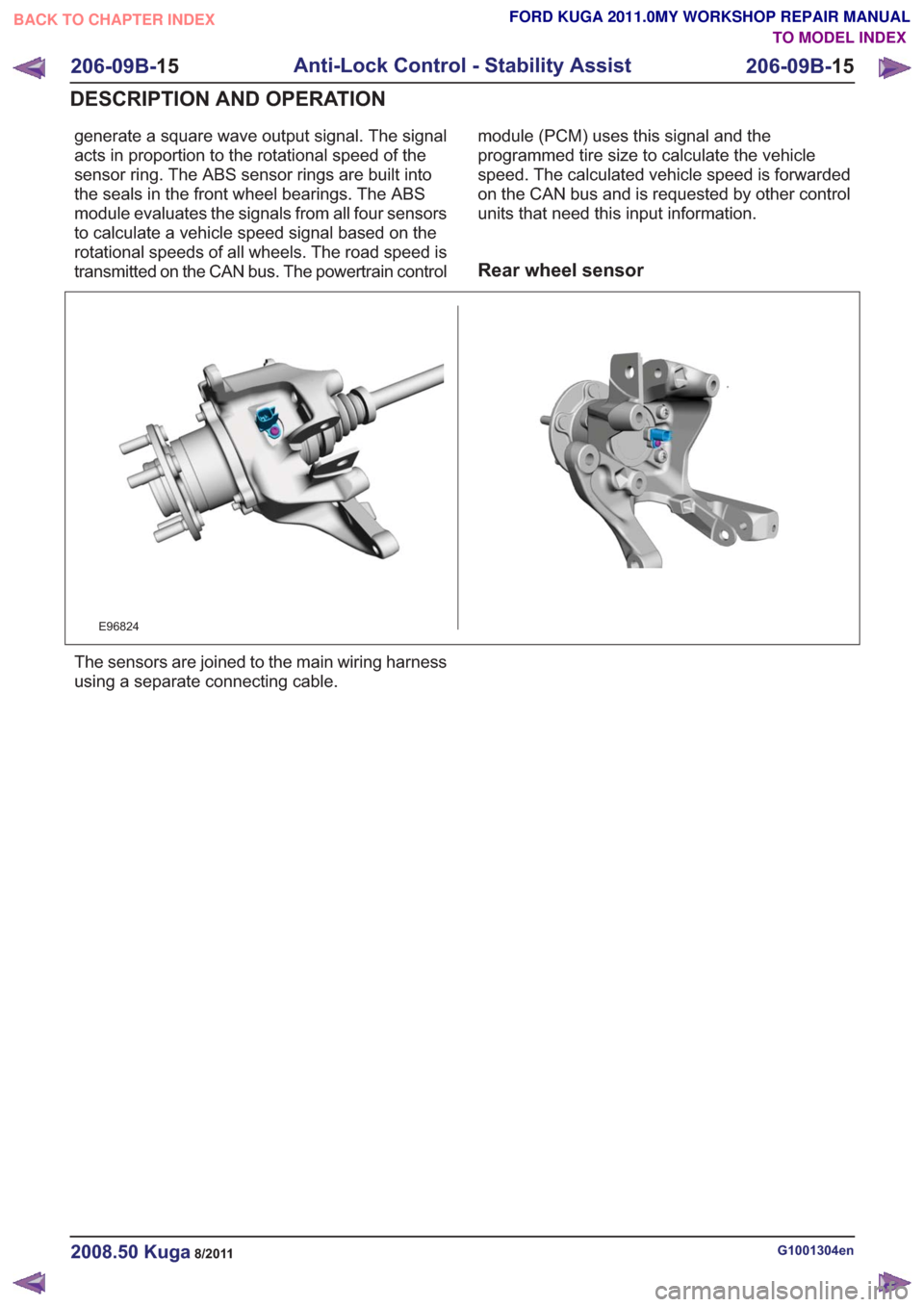
Rear wheel sensor
E96824
The sensors are joined to the main wiring harness
using a separate connecting cable.
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B-
15
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 15
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1465 of 2057

Description
Item
Electro-hydraulic power steering pump
with integrated power steering moduleRefer to Component Description:
Electro-hydraulic power steering pump
(page5)
1
Ignition switch
2
Generic electronic module (GEM)
3
Data link connector (DLC)
4
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
5
ABS module or ESP module
6Description
Item
Steering gear
7
Integrated steering angle sensor - vehicles
built up to 09/2009RefertoComponentDescription:(page
10)
8
High pressure pipe
9
Fluid Return Line
10
Battery junction box (BJB)
11
Battery
12
System Operation
Electronic principle of operation
The power steering module requires the following
information in order to ensure precise steering
behavior in all driving situations:
• Steering wheel position
• Rate of turn of the steering wheel
• Vehicle speed
• Information about the vehicle configuration
• Information about the ignition switch position
• Instantaneous engine operating status
The required information is made available to the
power steering module via direct connections and
via the CAN bus (refer to the flow chart).
The steering wheel position and the rate of turn of
the steering wheel are transmitted to the power
steering module as PWM signals from the steering
angle sensor. The steering angle sensor receives
its voltage and ground supply from the power
steering module and operates inductively with an
input voltage of 5 V.
The vehicle speed is made available to the power
steering module as a CAN bus signal from the ABS
module or ESP module. The engine operating status is made available to
the power steering module as a CAN bus signal
from the PCM.
The power steering module obtains the vehicle
configuration information via the CAN bus from the
GEM. This information is required by the power
steering module in order to define the internal
characteristics of the power steering.
The power steering module obtains information
about the current ignition switch position via the
voltage input (terminal 15) of the ignition switch.
Whilst constantly monitoring the relevant input
signals the power steering module accesses stored
maps. With the aid of this information the pump
speed is matched to the current driving situation.
An electronic diagnosis of the electro-hydraulic
power steering can be performed with the aid of a
diagnostic tester via the DLC of the vehicle. For
additional information please refer to "Diagnosis
and Testing" in this section.
G1001270en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-02-
8
Power Steering
211-02- 8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1767 of 2057
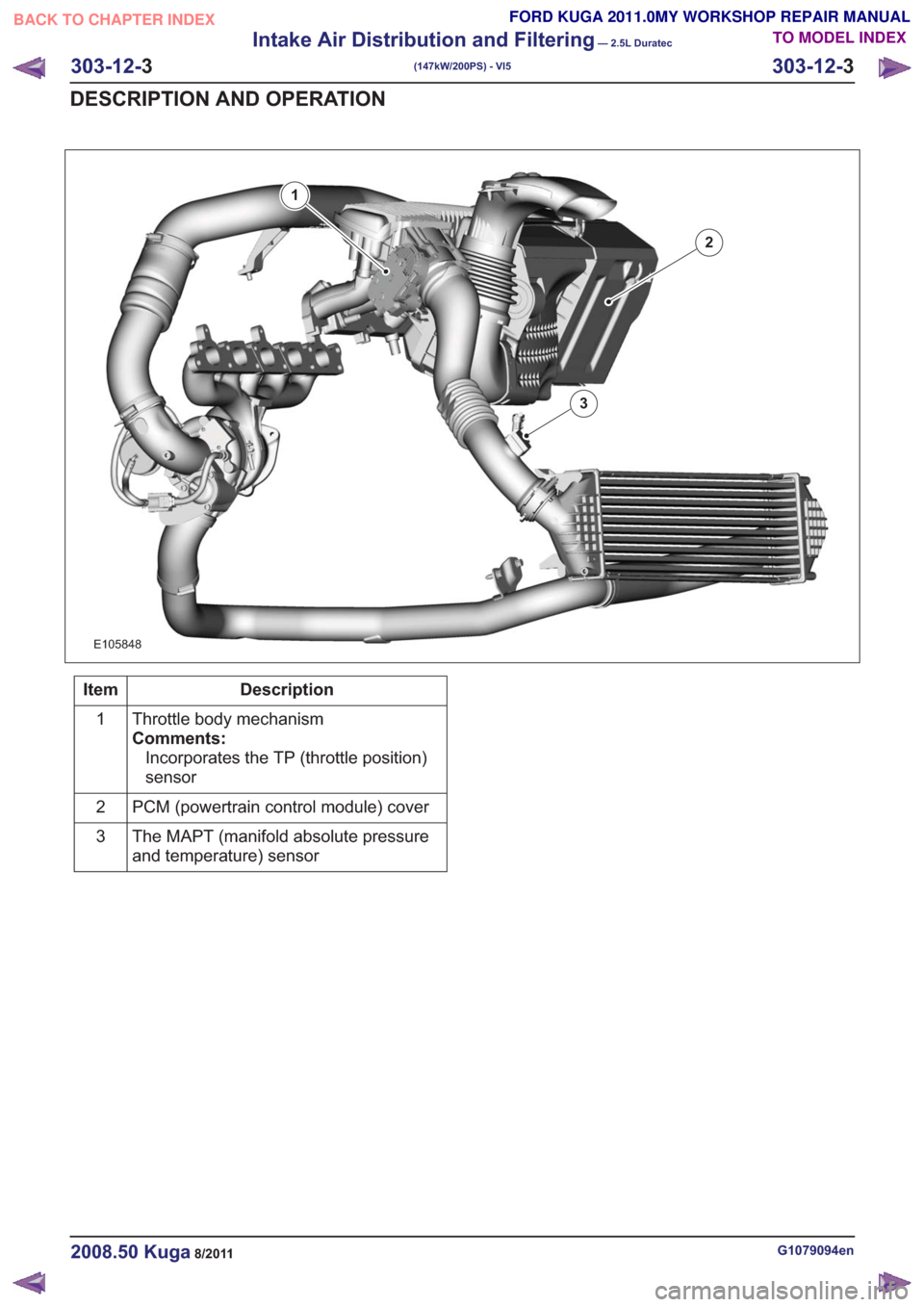
E105848
1
2
3
Description
Item
Throttle body mechanism
Comments:Incorporates the TP (throttle position)
sensor
1
PCM (powertrain control module) cover
2
The MAPT (manifold absolute pressure
and temperature) sensor
3
G1079094en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-12-
3
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering
— 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-12- 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1768 of 2057
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanicalor electrical damage.
Visual Inspection Chart
Electrical
Mechanical
– Mass air flow (MAF)sensor
– Manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
sensor
– Electrical connector(s)
– Air cleaner element
– Air cleaner intake
pipe
– Air cleaner outlet pipe
– Charge air cooler
– Charge air cooler intake pipe
– Charge air cooler outlet pipe 3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported
concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart.
Symptom Chart
Action
Possible Sources
Symptom
• CHECK the pipe(s) for securityand leaks to atmosphere.
INSTALL new intake air
components as necessary.
TEST the system for normal
operation.
• Detached air cleaner pipe(s).
• Detached turbocharger pipe(s).
• Detached charge air cooler
pipe(s).
• Excessive intake air noise
• REFER to:Engine Emission
Control (303-08 Engine
Emission Control - 2.5L
Duratec (147kW/200PS) -
VI5, Diagnosis and Testing).
• Blocked or damaged PCV
pipe(s)/hose(s).
• Blocked or damaged crankcase vent oil separator.
• Oil in the air intake system
• REFER to:Turbocharger(303-
04 Fuel Charging and
Controls - Turbocharger -
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS)
- VI5, Diagnosis and Testing).
• Turbocharger.
• CHECK the air intake pipesplash shield for correct install-
ation and alignment.
REPAIR/INSTALL the air intake
pipe splash shield as neces-
sary. TEST the system for
normal operation.
• Air intake pipe splash shield.
• Water in the air cleaner
G1183447en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-12- 4
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering
— 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-12- 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1775 of 2057

SECTION 303-14 Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5
VEHICLE APPLICATION: 2008.50 Kuga
PA G E
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
303-14-3
Electronic Engine Controls (Component Location) .............................................................
303-14-7
Electronic Engine Controls (Overview) ........................................................................\
.......
303-14-7
General overview ........................................................................\
........................................
303-14-8
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) ........................................................................\
..............
303-14-8
Knock Sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-8
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor ........................................................................\
...............
303-14-9
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor ........................................................................\
..............
303-14-9
Camshaft adjuster solenoid valve........................................................................\
...............
303-14-9
Manifold absolute pressure and temperature sensor .........................................................
303-14-9
Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor ........................................................................\
....
303-14-10
Throttle control unit ........................................................................\
.....................................
303-14-10
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.......................................................................
303-14-10
Ignition coil-on-plug ........................................................................\
....................................
303-14-12
Electronic Engine Controls (System Operation and Component Description) ...................
303-14-12
System Diagram ........................................................................\
.........................................
303-14-16
System Operation ........................................................................\
.......................................
303-14-18
Speed and TDC recording ........................................................................\
......................
303-14-19
Calculation of the ignition angle ........................................................................\
..............
303-14-20
Engine fueling ........................................................................\
.........................................
303-14-22
Engine speed control ........................................................................\
..............................
303-14-22
Oil monitoring ........................................................................\
..........................................
303-14-23
Calculation of valve timing adjustment angle..................................................................
303-14-23
Boost pressure control ........................................................................\
............................
303-14-24
Starting process ........................................................................\
......................................
303-14-24
Alternator control (Smart Charge) ........................................................................\
...........
303-14-24
Component Description ........................................................................\
..............................
303-14-24
CKP sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-25
Broadband HO2S ........................................................................\
...................................
303-14-26
VCT (variable camshaft timing) solenoids ......................................................................
303-14-27
MAF sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-28
APP sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-29
CPP sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-29
BPP switches ........................................................................\
..........................................
303-14-30
Air conditioning (A/C) pressure sensor ........................................................................\
...
303-14-30
Throttle
control unit ........................................................................\
.................................
303-14-31
ECT sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-31
Cooling fan module ........................................................................\
.................................
303-14-32
injectors........................................................................\
...................................................
303-14-32
Ignition coil-on-plug ........................................................................\
.................................
303-14-33
Fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor ........................................................................\
...
303-14-33
Wastegate control valve ........................................................................\
..........................
303-14-34
Engine oil level, temperature and quality sensor ............................................................
303-14-1
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
1
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
PAGE 1 OF 2
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1778 of 2057
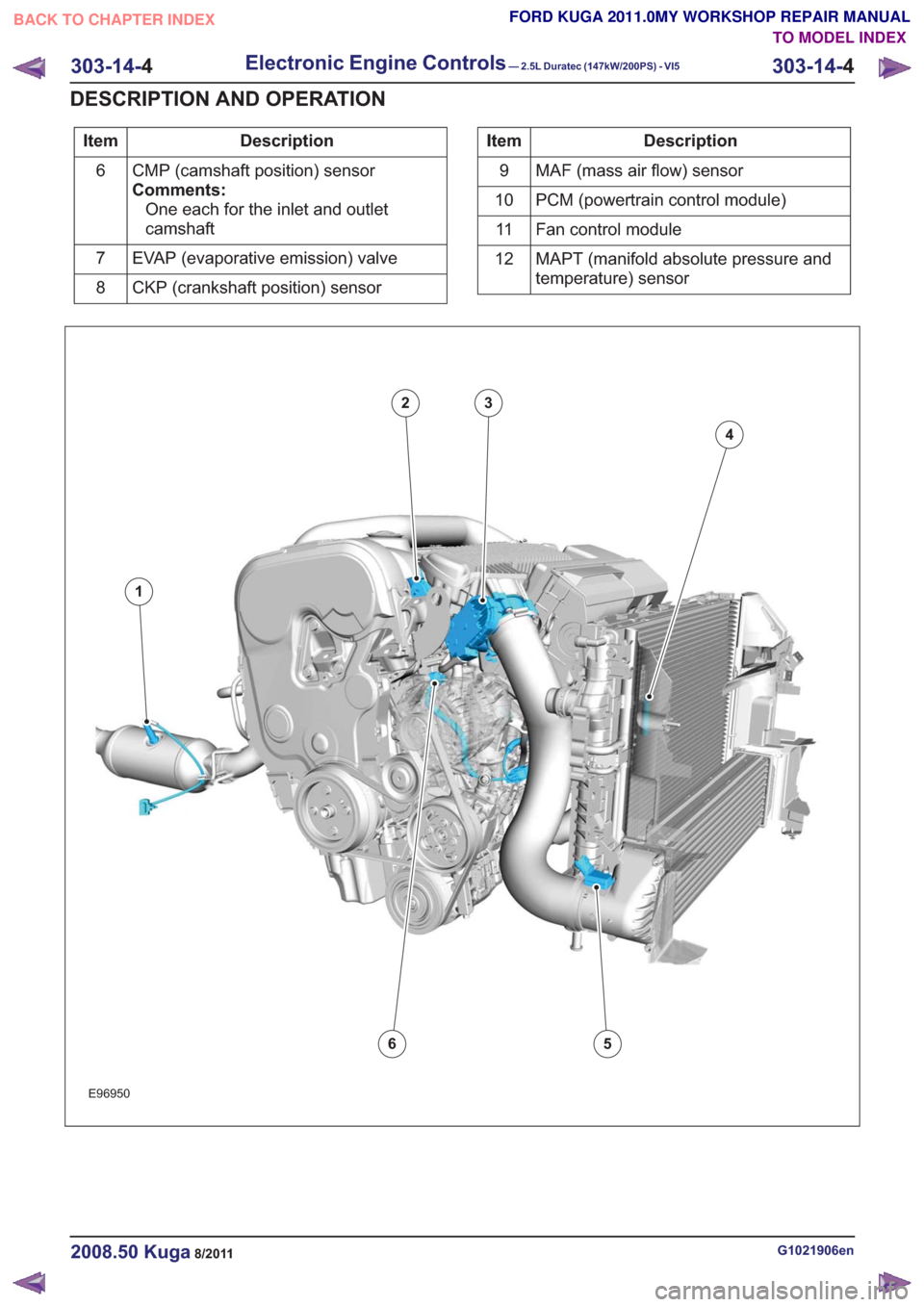
Description
Item
CMP (camshaft position) sensor
Comments:One each for the inlet and outlet
camshaft
6
EVAP (evaporative emission) valve
7
CKP (crankshaft position) sensor
8Description
Item
MAF (mass air flow) sensor
9
PCM (powertrain control module)
10
Fan control module
11
MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and
temperature) sensor
12
E96950
1
23
4
56
G1021906en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
4
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1782 of 2057
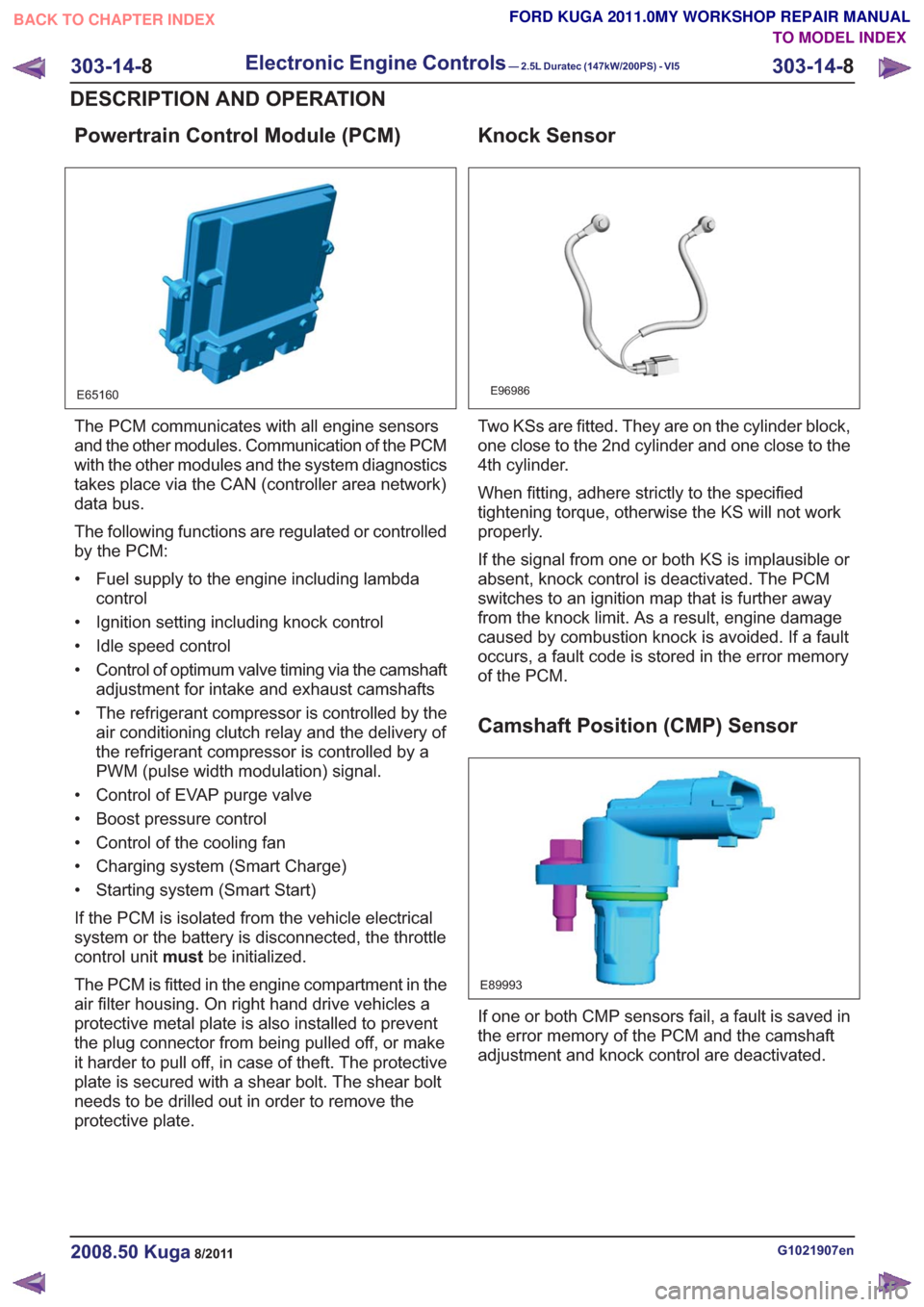
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
E65160
The PCM communicates with all engine sensors
and the other modules. Communication of the PCM
with the other modules and the system diagnostics
takes place via the CAN (controller area network)
data bus.
The following functions are regulated or controlled
by the PCM:
• Fuel supply to the engine including lambdacontrol
• Ignition setting including knock control
• Idle speed control
• Control of optimum valve timing via the camshaft adjustment for intake and exhaust camshafts
• The refrigerant compressor is controlled by the air conditioning clutch relay and the delivery of
the refrigerant compressor is controlled by a
PWM (pulse width modulation) signal.
• Control of EVAP purge valve
• Boost pressure control
• Control of the cooling fan
• Charging system (Smart Charge)
• Starting system (Smart Start)
If the PCM is isolated from the vehicle electrical
system or the battery is disconnected, the throttle
control unit mustbe initialized.
The PCM is fitted in the engine compartment in the
air filter housing. On right hand drive vehicles a
protective metal plate is also installed to prevent
the plug connector from being pulled off, or make
it harder to pull off, in case of theft. The protective
plate is secured with a shear bolt. The shear bolt
needs to be drilled out in order to remove the
protective plate.
Knock Sensor
E96986
Two KSs are fitted. They are on the cylinder block,
one close to the 2nd cylinder and one close to the
4th cylinder.
When fitting, adhere strictly to the specified
tightening torque, otherwise the KS will not work
properly.
If the signal from one or both KS is implausible or
absent, knock control is deactivated. The PCM
switches to an ignition map that is further away
from the knock limit. As a result, engine damage
caused by combustion knock is avoided. If a fault
occurs, a fault code is stored in the error memory
of the PCM.
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
E89993
If one or both CMP sensors fail, a fault is saved in
the error memory of the PCM and the camshaft
adjustment and knock control are deactivated.
G1021907en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 8
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1783 of 2057
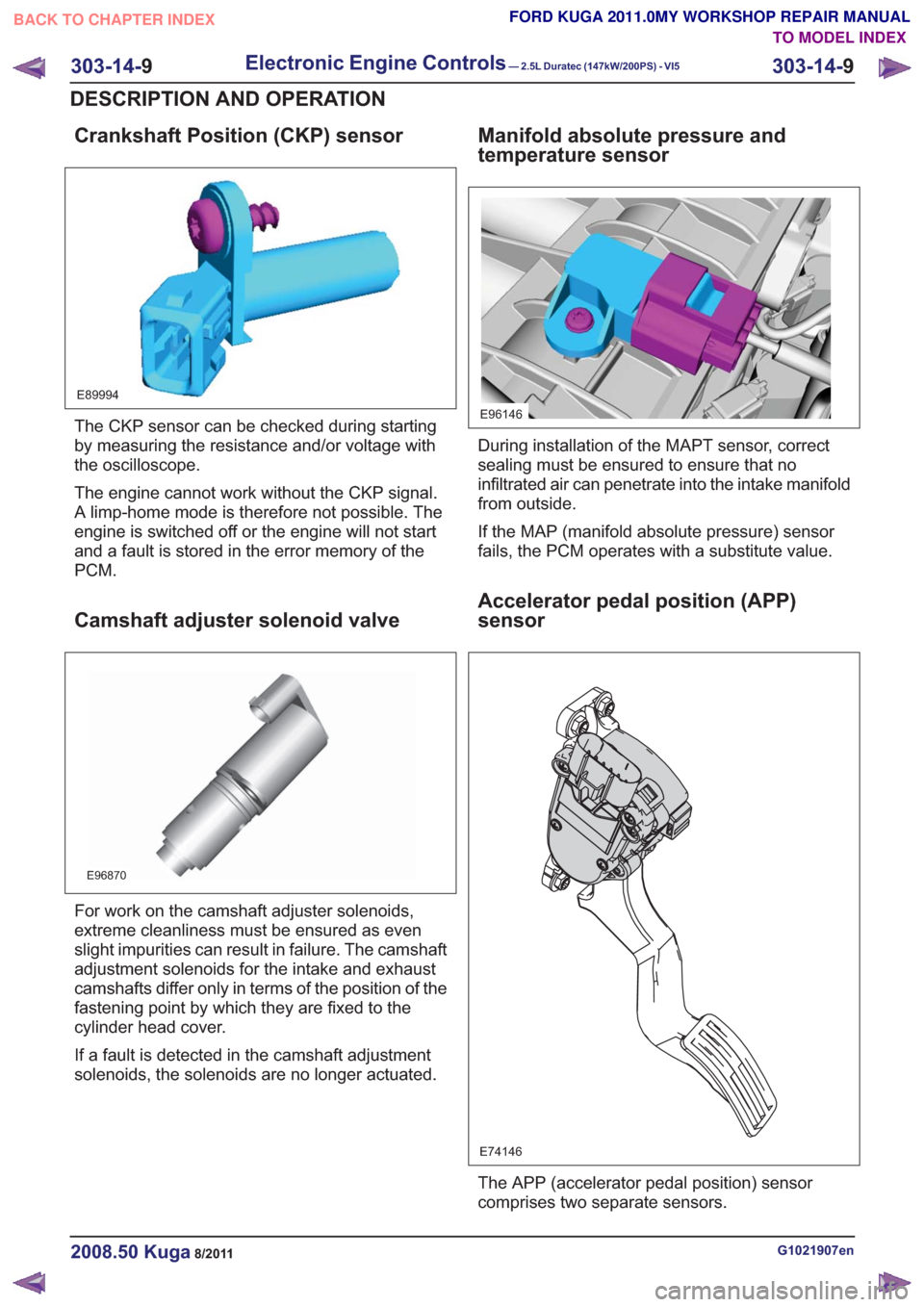
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
E89994
The CKP sensor can be checked during starting
by measuring the resistance and/or voltage with
the oscilloscope.
The engine cannot work without the CKP signal.
A limp-home mode is therefore not possible. The
engine is switched off or the engine will not start
and a fault is stored in the error memory of the
PCM.
Camshaft adjuster solenoid valve
E96870
For work on the camshaft adjuster solenoids,
extreme cleanliness must be ensured as even
slight impurities can result in failure. The camshaft
adjustment solenoids for the intake and exhaust
camshafts differ only in terms of the position of the
fastening point by which they are fixed to the
cylinder head cover.
If a fault is detected in the camshaft adjustment
solenoids, the solenoids are no longer actuated.
Manifold absolute pressure and
temperature sensor
E96146
During installation of the MAPT sensor, correct
sealing must be ensured to ensure that no
infiltrated air can penetrate into the intake manifold
from outside.
If the MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor
fails, the PCM operates with a substitute value.
Accelerator pedal position (APP)
sensor
E74146
The APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor
comprises two separate sensors.
G1021907en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-9
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1795 of 2057

actuated) or opened (actuated). Each cylinder has
its own injector. The injection is accurately dosed
and takes place at a time determined by the PCM.
Injection takes place immediately in front of the
intake valves of the cylinder. The injectors are
actuated ground side via end-stages integrated
into the PCM and using the signal calculated by
the engine management system. Power is supplied
via the Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB.
The injected fuel quantity depends on the opening
time, the fuel pressure and the diameter of the
nozzle holes.
The fuel metering is determined via open or
closed-loop control.
The open control loop differs from the closed
control loop in that the lambda control is
deactivated.
The PCM switches from closed to open-loop control
if the HO2S cools down to below 600°C or fails, as
well as when accelerating, coasting and at full load.
Regulation of injected fuel quantity via the PCM
involves:
• controlling the fuel pump,
• calculating the required quantity of fuel forengine starting,
• observance of the desired air/fuel ratio,
• calculating air mass,
• and calculating the fuel quantity for the different operating states and corresponding fuel
adjustment measures.
Open loop control
Open loop control is used primarily for fuel
injection, as long as the signals of the HO2S are
not involved in the calculation of the PCM.
The two most important reasons that make it
absolutely essential to run the engine without
lambda control (open-loop control) are the following
operating conditions:
• Cold engine (starting, warm-up phase)
• Full-load operation (WOT (wide open throttle))
Under these operating conditions the engine needs
a rich air/fuel mixture with lambda values below λ
= 1 in order to achieve optimum running or
optimum performance.
It is possible to keep this unregulated range very
small by using a broadband HO2S.
Closed-loop control
Closed loop control ensures strict control of
exhaust emissions in conjunction with the TWC (three-way catalytic converter) and economical fuel
consumption. With closed loop control, the signals
from the HO2S are analyzed by the PCM and the
engine always runs in the optimum range of λ = 1.
In addition to the normal HO2S, the signal from the
monitoring sensor for the catalytic converter is also
included in the control. The lambda control is
optimized on the basis of this data.
Certain factors such as wear, component
tolerances or more minor defects such as air leaks
in the intake system are compensated for by
lambda control. If the deviation occurs for a longer
period of time, this is recorded by the adaptive
(self-learning) function of lambda control. In this
instance, the entire map is shifted by the
corresponding amount, to enable control to
commence once again from the virtual baseline.
These adaptive settings are stored in the PCM and
are also used in open-loop control conditions.
If the adaptive value is too high or too low, an error
is stored in the fault memory of the PCM.
Oxygen sensor (HO2S) and catalyst monitor
sensor
A broadband HO2S is used as the HO2S. The
HO2S is located in front of the TWC. The catalyst
monitor sensor is located in the center of the TWC
so that it can detect any deterioration in the
cleaning performance of the TWC more quickly.
The HO2S measures the residual amount of
oxygen in the exhaust before the TWC.
The catalyst monitor sensor measures the amount
of oxygen in the exhaust gas after or in the TWC.
Both the HO2S and the catalyst monitor sensor
transmit these data to the PCM.
The broadband HO2S works at temperatures of
between 650°C and 900 °C. If the temperature
rises above 1000°C, the oxygen sensor will be
irreparably damaged.
To reach optimum operating temperature as quickly
as possible, an electrically-heated oxygen sensor
is installed. The heating also serves to maintain a
suitable operating temperature while coasting, for
example, when no hot gases are flowing past the
oxygen sensor.
The heating element in the HO2S is a PTC
(positive temperature coefficient) resistor. The
heating element is supplied with battery voltage as
soon as the Powertrain Control Module relay
engages. The HO2S is earthed via the PCM. As
the heating current is high when the element is
cold, it is limited via PWM in the PCM until a certain
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
21
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
21
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL