Engine FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 1847 of 2057
E112322
The TCM adapts the gear changing to ensure that
the correct gear is selected for the style of driving,
the engine load, driver requirements, vehicle speed
etc. This leads to lower fuel consumption together
with improved comfort through smoother gear
changes and lower noise levels.
The TCM receives information on the driver's
desired transmission range and type of driving
mode. In contrast to a transmission which is only
controlled hydraulically, the control module can
calculate the best times to shift gear and activate
torque converter lockup by using the signals from
the sensors in the transmission and the engine
management system.
The control module enables small changes in the
operating conditions to be made and adapts thevarious transmission functions to ensure that the
correct gear is always selected in relation to the
type of driving mode.
The TCM has adaptive capabilities. This ensures
smooth gear changes throughout the whole service
life of the transmission.
To exactly determine the activation points of the
gear shifts and torque converter lockup on the
basis of the type of driving mode chosen, the TCM
receives the following information:
• Transmission range chosen (TR sensor).
• Type of driving mode chosen
(normal/sport/select-shift).
• Transmission input shaft speed (TSS sensor).
• Transmission output shaft speed (OSS sensor).
• Transmission fluid temperature (TFT sensor).
• The engine speed and the torque as well as the throttle plate opening - from the PCM via the
CAN data bus.
• Actuation of the accelerator pedal - from the PCM via the CAN data bus.
• Coolant temperature - from the PCM via the CAN data bus.
• Vehicle speed - from the ABS via the CAN data bus.
• Actuation of the brake pedal - from the ABS via the CAN data bus.
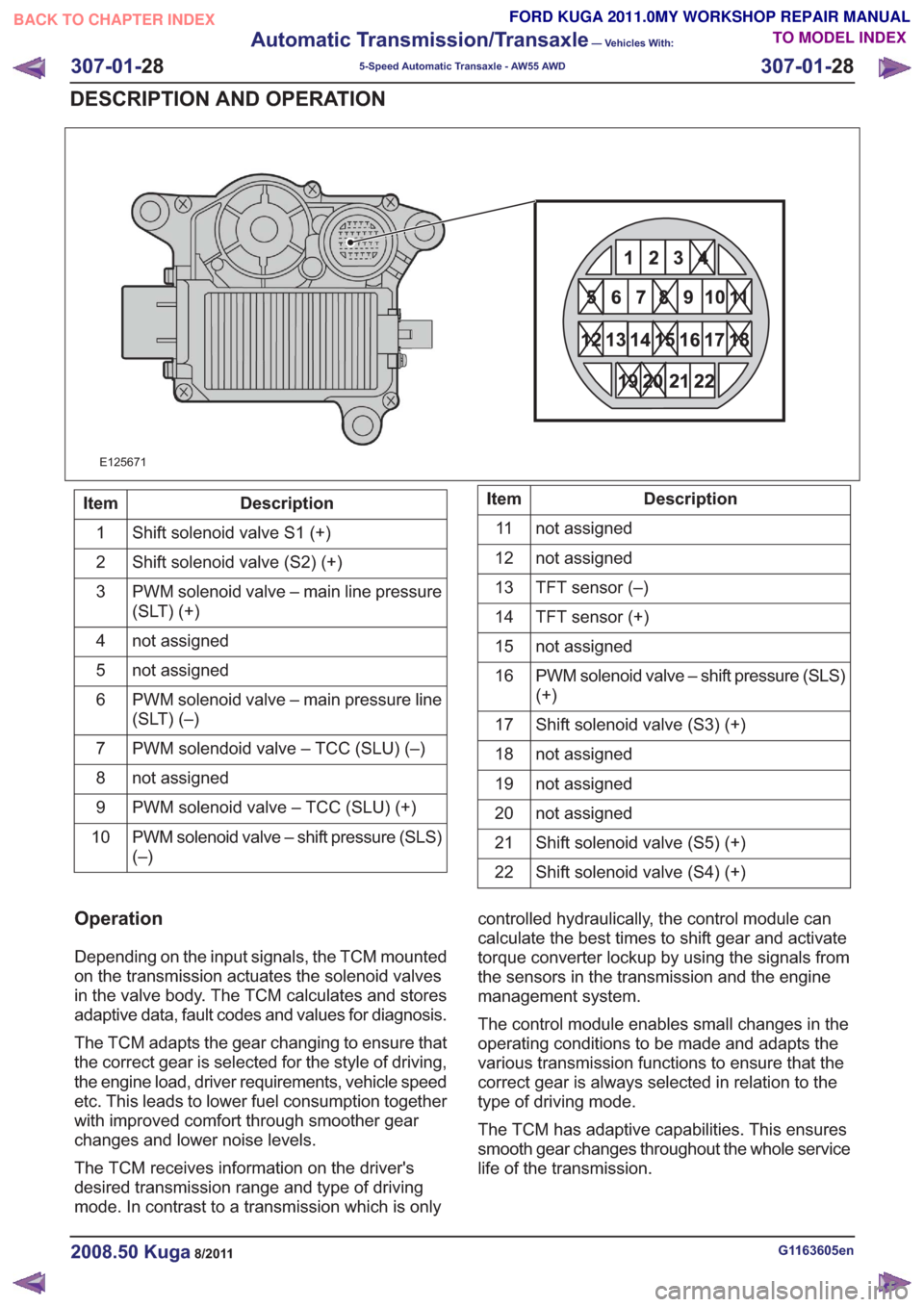
Pin assignment for TCM connector 'A' (connection to vehicle)
11
E125669
Description
Item
Battery (+)
1
not assigned
2Description
Item
not assigned
3
not assigned
4
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 26
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 26
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1849 of 2057
21
22 20 19
15 14 13
161718 12
876
9
10
11 5
3
42121
22 20 19
15 14 13
161718 12
876
9
10
11 5
3
421
E125671
Description
Item
Shift solenoid valve S1 (+)
1
Shift solenoid valve (S2) (+)
2
PWM solenoid valve – main line pressure
(SLT) (+)
3
not assigned
4
not assigned
5
PWM solenoid valve – main pressure line
(SLT) (–)
6
PWM solendoid valve – TCC (SLU) (–)
7
not assigned
8
PWM solenoid valve – TCC (SLU) (+)
9
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
(–)
10Description
Item
not assigned
11
not assigned
12
TFT sensor (–)
13
TFT sensor (+)
14
not assigned
15
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
(+)
16
Shift solenoid valve (S3) (+)
17
not assigned
18
not assigned
19
not assigned
20
Shift solenoid valve (S5) (+)
21
Shift solenoid valve (S4) (+)
22
Operation
Depending on the input signals, the TCM mounted
on the transmission actuates the solenoid valves
in the valve body. The TCM calculates and stores
adaptive data, fault codes and values for diagnosis.
The TCM adapts the gear changing to ensure that
the correct gear is selected for the style of driving,
the engine load, driver requirements, vehicle speed
etc. This leads to lower fuel consumption together
with improved comfort through smoother gear
changes and lower noise levels.
The TCM receives information on the driver's
desired transmission range and type of driving
mode. In contrast to a transmission which is only controlled hydraulically, the control module can
calculate the best times to shift gear and activate
torque converter lockup by using the signals from
the sensors in the transmission and the engine
management system.
The control module enables small changes in the
operating conditions to be made and adapts the
various transmission functions to ensure that the
correct gear is always selected in relation to the
type of driving mode.
The TCM has adaptive capabilities. This ensures
smooth gear changes throughout the whole service
life of the transmission.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
28
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 28
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1850 of 2057

To exactly determine the activation points of the
gear shifts and torque converter lockup on the
basis of the type of driving mode chosen, the TCM
receives the following information:
• Selected transmission range (TR sensor)
• Selected driving mode (normal/sport/select-shift)
• Transmission input shaft speed (TSS sensor)
• Transmission output shaft speed (OSS sensor)
• Transmission fluid temperature (TFT sensor)
• The engine speed and the torque as well as thethrottle plate opening - from the PCM via the
CAN databus
• Actuation of accelerator – from the PCM via the CAN databus
• The coolant temperature – from the PCM via the CAN databus
• Road speed – from the ABS module via the CAN databus
• Actuation of brake pedal – from the PCM via the CAN databus
Gearshift control
Adaptation
The TCM monitors every shift operation in all
driving conditions to make even and smooth gear
shifts possible. This is done by the control module,
which either lowers or increases the hydraulic line
pressure during gearshifts.
The changed pressure values are stored in the
control module memory after the engine is switched
off and retrieved during engine starting. This
improves the shift comfort and extends the service
life.
Full adaptability occurs when the following criteria
are met:
• Throttle plate opening is constant.
• Transmission fluid temperature between 65 °Cand 110 °C.
Shifting from 'P' to another transmission
range
To be able to move the selector lever from 'P' into
another transmission range, the ignition must be
switched on and the brake pedal pressed (stoplamp
switch on). The TCM detects the position of the
brake pedal via the CAN data bus and the engaged
transmission range from the TR sensor. Based on this information, the TCM transmits a
signal to the select-shift switch module. This
activates the brake shift interlock actuator in the
selector lever assembly.
When the brake shift interlock actuator is activated,
the locking pin is retracted so that another
transmission range can be selected.
The brake shift interlock actuator is deactivated
when the ignition is switched off. It is mechanically
locked when the gear selector lever is in 'P'.
Automatic transmission, selector lever in
position "D".
The TCM adapts the shift points to match the
driving conditions. Normally the TCM is in adaptive
mode and gear changes take place adapted to the
driving conditions. If special driving conditions are
detected, the TCM switches to predefined
characteristics.
When driving with normal acceleration, the TCM
uses a preset shift program which is optimized for
economical driving.
This shift program is suitable for "normal" driving
and delivers early upward changes and torque
converter lockup. Furthermore, the transmission
fluid pressure is adapted to make smooth
engagement of the gears possible.
Sport mode, selector lever in position "S"
The transmission switches from automatic
operation into sport mode. In this mode the TCM
switches to another set of characteristic curves.
These characteristic curves for control of the gear
changes are adapted to sporting calculations (e.g.
gear change at higher engine speed).
In the sport mode shift program the shift points are
set so that good performance is offered. Changing
down occurs at lower engine speeds.
Manual gear changes (select-shift mode) can be
made in sport mode by moving the selector lever
in the (+) or (-) direction.
Changing gear in select-shift mode
If you move the selector lever to 'S', the automatic
transaxle remains hydraulically in 'D' position. If
you move the gear selector lever forwards (-), the
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
29
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 29
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1851 of 2057

select-shift switch module transmits a downshift
signal to the TCM.
If you move the gear selector lever backwards (+),
an upshift signal is transmitted to the TCM. In the
instrument cluster, the symbol when the selector
lever is in the 'S' position changes from 'D' to the
current gear, for example 3.
The TCM transmits a signal to the select-shift
switch module to switch on the light emitting diode
for 'S' and to switch off all other light emitting
diodes. The TCM decides whether the shift process
is possible.
If the shift process is permitted, then the various
valves are activated according to the intended
combination for each gear.
In certain situations however, the TCM determines
the gear shifting. The following applies:
• If the vehicle is stationary, only 1st, 2nd and 3rdgears can be selected. 4th gear can be selected
at speeds over 30 km/h and 5th gear at speeds
over 40 km/h.
• The kickdown function is only available in the automatic transmission range 'D'
• Automatic gear changes into the next higher or next lower gear occur at fixed vehicle speeds
and fixed engine speeds
• The permitted engine speed for manual change down agree with that for the kickdown change
up, i.e. an engine speed of approximately 6000
rpm.
• If the temperature inside the transmission rises too high, the TCM takes control of the shift
decisions in order to select a gear in which
activation of torque converter lockup at the
current speed is possible
• Torque converter lockup is possible in 3rd, 4th and 5th gear. (1st and 2nd gears do not have
torque converter lockup)
The signal that specifies the position of the lever
to the select-shift switch module is generated as
follows in the selector lever position 'S': there is a
Hall sensor at the printed circuit board for the
module for each of the three selector lever
positions. A permanent magnet on the cover in the
selector lever affects the output signals to the
control module from the sensors. The control
module recognizes the position of the lever by the
differences in the signal properties.Selector lever from 'N' to 'R' position
The TCM only permits shifting to reverse gear if
the vehicle speed is less than 4.35 mph.
If the vehicle speed is greater than 7 km/h (approx.
4.35 mph), the clutch (C2) and the multi-plate brake
(B3) are not activated and the gearshift is thus
prevented.
Self-test and Diagnosis
The TCM monitors all the transaxle sensors and
electronic components including the PCM. If a fault
occurs, the driver is informed via a warning
indicator and a text message in the instrument
cluster. Faults are stored as DTCs in the fault
memory of the TCM and can be read out and
cleared using the IDS.
Temperature controlled torque converter
lockup
If heavy load and high ambient temperatures cause
an abnormal rise in the transmission temperature,
torque converter lockup is activated as often as
possible (temperature controlled lockup).
This reduces the slip and the heat developed in
the transmission. When the temperature drops
below +20 °C, torque converter lockup is not used.
Slip locking
When changing gear this function makes it possible
for the gears to engage more smoothly with
reduced vibration and less noise. In this mode, the
torque converter clutch is activated but not fully
locked.
The following conditions must be met for the
function to activate:
• Gear selector lever in position D or S.
• Gear 3, 4 or 5.
• The transmission input speed is 1100 rpm or more and the throttle plate opening 20 - 35%.
• The transmission fluid temperature is 40 - 120 °C.
Hill climbing
The TCM can change the shift pattern slightly when
driving uphill to avoid changing gear too often.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 30
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 30
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1852 of 2057

The TCM detects uphill driving by comparing the
engine load transmitted by the PCM with the engine
speed. If the engine load increases and the engine
speed falls, then the TCM causes the transaxle to
shift to a lower transmission range in order to
increase the traction force.
Downhill driving
The TCM detects downhill driving by comparing
the engine load and engine speed values
transmitted by the PCM with the OSS sensor
signal. In order to prevent overloading of the
vehicle brakes, the TCM causes the transaxle to
shift to a lower transmission range.
Hill-hold function
If the vehicle is stopped on an uphill incline, the
TCM detects this through the faster drop in engine
speed compared with the drop in engine speed
when stopping on the flat. In this situation, the
hydraulics are actuated by the TCM in such a way
that the vehicle is prevented from rolling back. This
function is not used on steep inclines.
If the vehicle is parked on an uphill incline (ignition
switched off), the hill-hold function is not active
when pulling away.
Altitude correction
Lower air density results in reduced engine
performance. In order to compensate for this
operating situation, the TCM changes the shift
points.
Selector lever lock
To prevent the selector lever being accidentally
moved from the P or N position, the vehicle also
has an electrically operated selector lever lock.
This blocks the locking pin in the locking segment
and thus locks the selector lever in the P or N
position.
Shifting from P into another transmission
range
To be able to move the selector lever from P into
another transmission range, the ignition must be
switched on and the brake pedal must be
depressed (stop light switch on). The TCM detects
the position of the brake pedal via the CAN data
bus and the engaged transmission range from the
TR sensor.
The signal is then transferred from the TCM to the
select-shift switch module in order to activate the
solenoid valve in the selector mechanism
assembly.
In position P, the solenoid valve is activated and
the locking pin is pulled in so that the lock button
on the selector lever can be pressed as usual to
engage another transmission range.
In the selector mechanism assembly there is a Hall
sensor which is affected by a permanent magnet
on the gate of the selector mechanism assembly.
If the selector lever is moved from the P position,
both the Hall sensor and the selector lever lock
solenoid are simultaneously deactivated, to prevent
the selector from being kept in the N position.
If the ignition is set to "I" or "0" the solenoid valve
is deactivated. When the selector lever is in the P
position, it is mechanically locked because it has
no voltage.
Shifting from N into another transmission
range
The conditions are the same as for shifting from P
into another transmission range.
However, the lock button on the selector lever must
be pressed to be able to select R or P.
Power flow through the transmission
Clutches and brakes
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-31
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 31
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1857 of 2057
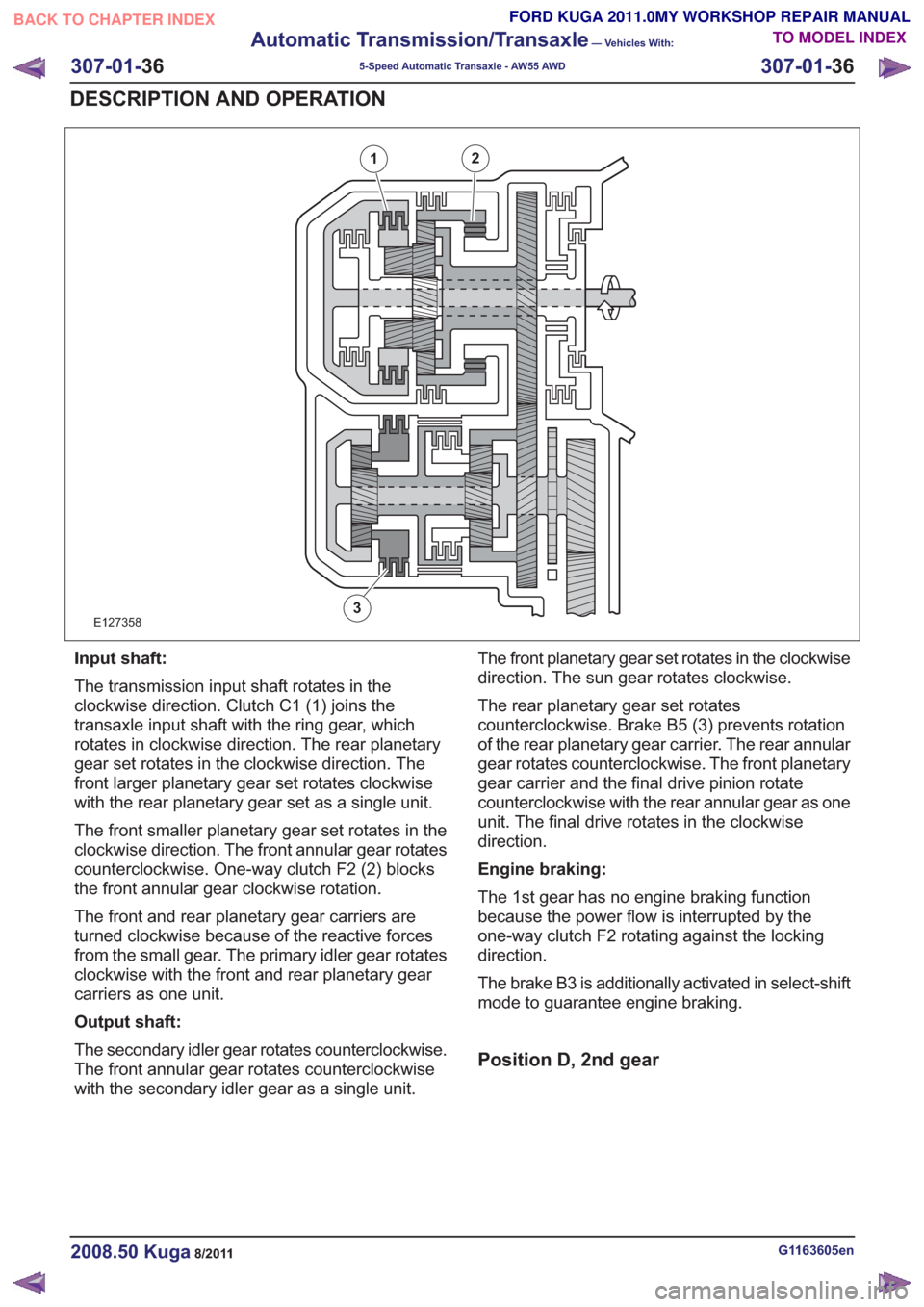
E127358
21
3
Input shaft:
The transmission input shaft rotates in the
clockwise direction. Clutch C1 (1) joins the
transaxle input shaft with the ring gear, which
rotates in clockwise direction. The rear planetary
gear set rotates in the clockwise direction. The
front larger planetary gear set rotates clockwise
with the rear planetary gear set as a single unit.
The front smaller planetary gear set rotates in the
clockwise direction. The front annular gear rotates
counterclockwise. One-way clutch F2 (2) blocks
the front annular gear clockwise rotation.
The front and rear planetary gear carriers are
turned clockwise because of the reactive forces
from the small gear. The primary idler gear rotates
clockwise with the front and rear planetary gear
carriers as one unit.
Output shaft:
The secondary idler gear rotates counterclockwise.
The front annular gear rotates counterclockwise
with the secondary idler gear as a single unit.The front planetary gear set rotates in the clockwise
direction. The sun gear rotates clockwise.
The rear planetary gear set rotates
counterclockwise. Brake B5 (3) prevents rotation
of the rear planetary gear carrier. The rear annular
gear rotates counterclockwise. The front planetary
gear carrier and the final drive pinion rotate
counterclockwise with the rear annular gear as one
unit. The final drive rotates in the clockwise
direction.
Engine braking:
The 1st gear has no engine braking function
because the power flow is interrupted by the
one-way clutch F2 rotating against the locking
direction.
The brake B3 is additionally activated in select-shift
mode to guarantee engine braking.
Position D, 2nd gear
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
36
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 36
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1858 of 2057
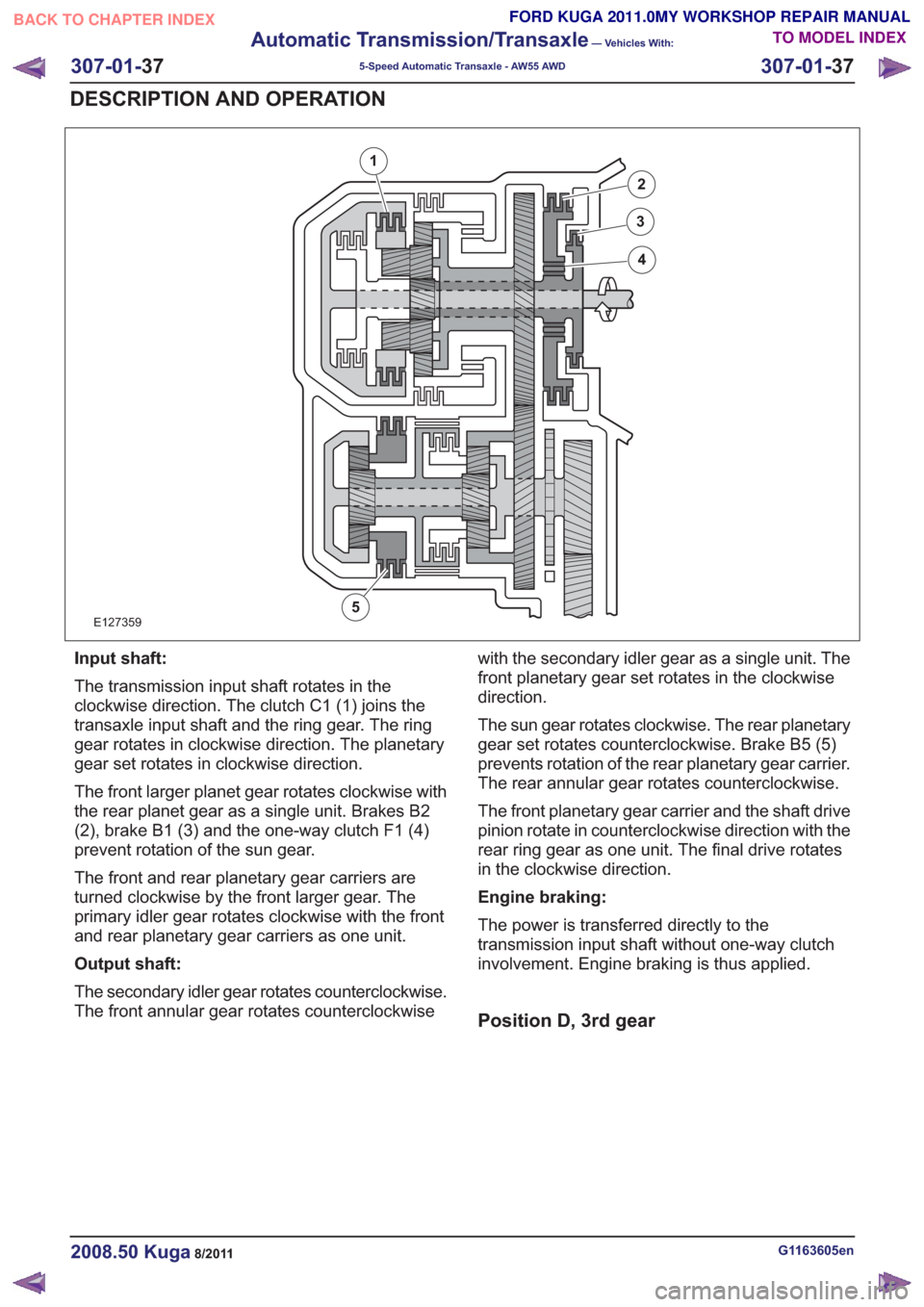
E127359
1
2
3
4
5
Input shaft:
The transmission input shaft rotates in the
clockwise direction. The clutch C1 (1) joins the
transaxle input shaft and the ring gear. The ring
gear rotates in clockwise direction. The planetary
gear set rotates in clockwise direction.
The front larger planet gear rotates clockwise with
the rear planet gear as a single unit. Brakes B2
(2), brake B1 (3) and the one-way clutch F1 (4)
prevent rotation of the sun gear.
The front and rear planetary gear carriers are
turned clockwise by the front larger gear. The
primary idler gear rotates clockwise with the front
and rear planetary gear carriers as one unit.
Output shaft:
The secondary idler gear rotates counterclockwise.
The front annular gear rotates counterclockwisewith the secondary idler gear as a single unit. The
front planetary gear set rotates in the clockwise
direction.
The sun gear rotates clockwise. The rear planetary
gear set rotates counterclockwise. Brake B5 (5)
prevents rotation of the rear planetary gear carrier.
The rear annular gear rotates counterclockwise.
The front planetary gear carrier and the shaft drive
pinion rotate in counterclockwise direction with the
rear ring gear as one unit. The final drive rotates
in the clockwise direction.
Engine braking:
The power is transferred directly to the
transmission input shaft without one-way clutch
involvement. Engine braking is thus applied.
Position D, 3rd gear
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
37
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 37
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1859 of 2057
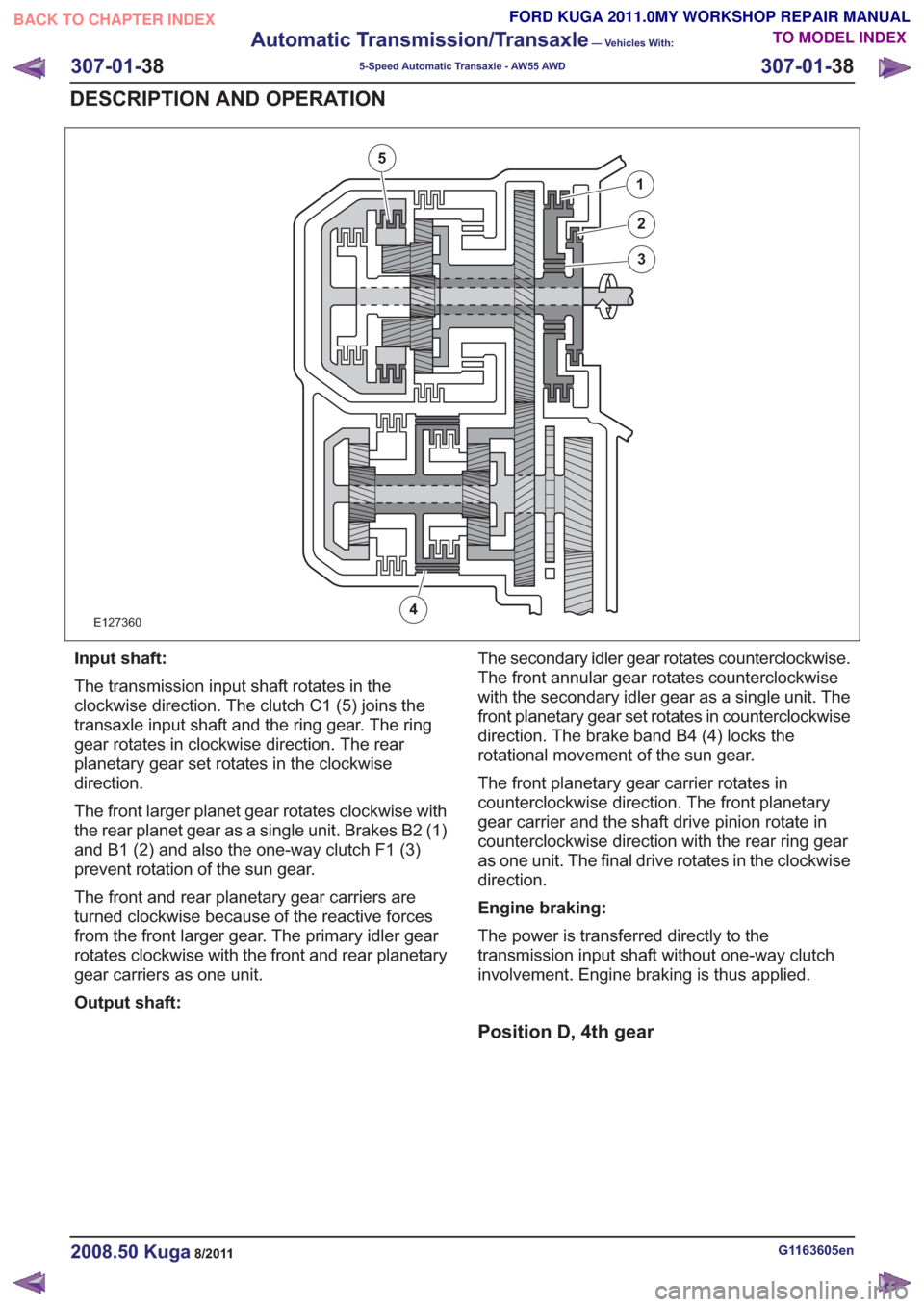
E127360
1
2
3
4
5
Input shaft:
The transmission input shaft rotates in the
clockwise direction. The clutch C1 (5) joins the
transaxle input shaft and the ring gear. The ring
gear rotates in clockwise direction. The rear
planetary gear set rotates in the clockwise
direction.
The front larger planet gear rotates clockwise with
the rear planet gear as a single unit. Brakes B2 (1)
and B1 (2) and also the one-way clutch F1 (3)
prevent rotation of the sun gear.
The front and rear planetary gear carriers are
turned clockwise because of the reactive forces
from the front larger gear. The primary idler gear
rotates clockwise with the front and rear planetary
gear carriers as one unit.
Output shaft:The secondary idler gear rotates counterclockwise.
The front annular gear rotates counterclockwise
with the secondary idler gear as a single unit. The
front planetary gear set rotates in counterclockwise
direction. The brake band B4 (4) locks the
rotational movement of the sun gear.
The front planetary gear carrier rotates in
counterclockwise direction. The front planetary
gear carrier and the shaft drive pinion rotate in
counterclockwise direction with the rear ring gear
as one unit. The final drive rotates in the clockwise
direction.
Engine braking:
The power is transferred directly to the
transmission input shaft without one-way clutch
involvement. Engine braking is thus applied.
Position D, 4th gear
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
38
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 38
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1860 of 2057

E127361
1
2
3
4
5
Input shaft:
The transmission input shaft rotates in the
clockwise direction. The clutch C1 (5) joins the
transaxle input shaft and the ring gear. The ring
gear rotates in clockwise direction. The rear
planetary gear set rotates in the clockwise
direction.
The front larger planet gear rotates clockwise with
the rear planet gear as a single unit. Brake B2 (1),
one-way clutch F1 (3) and brake B1 (2) prevent
rotation of the sun gear.
The front and rear planetary gear carriers are
turned clockwise because of the reactive forces
from the front larger gear. The primary idler gear
rotates clockwise with the front and rear planetary
gear carriers as one unit.
Output shaft:The secondary idler gear rotates clockwise. The
front annular gear rotates counterclockwise with
the secondary idler gear as a single unit. Clutch
C3 (4) connects the sun gear with the front
planetary gear carrier.
The front planetary gear set cannot rotate and the
output shaft rotates counterclockwise as a single
unit. The final drive rotates counterclockwise with
the output shaft as a single unit. The final drive
rotates in the clockwise direction.
Engine braking:
The power is transferred directly to the
transmission input shaft without one-way clutch
involvement. Engine braking is thus applied.
Position D, 5th gear
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
39
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 39
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1861 of 2057
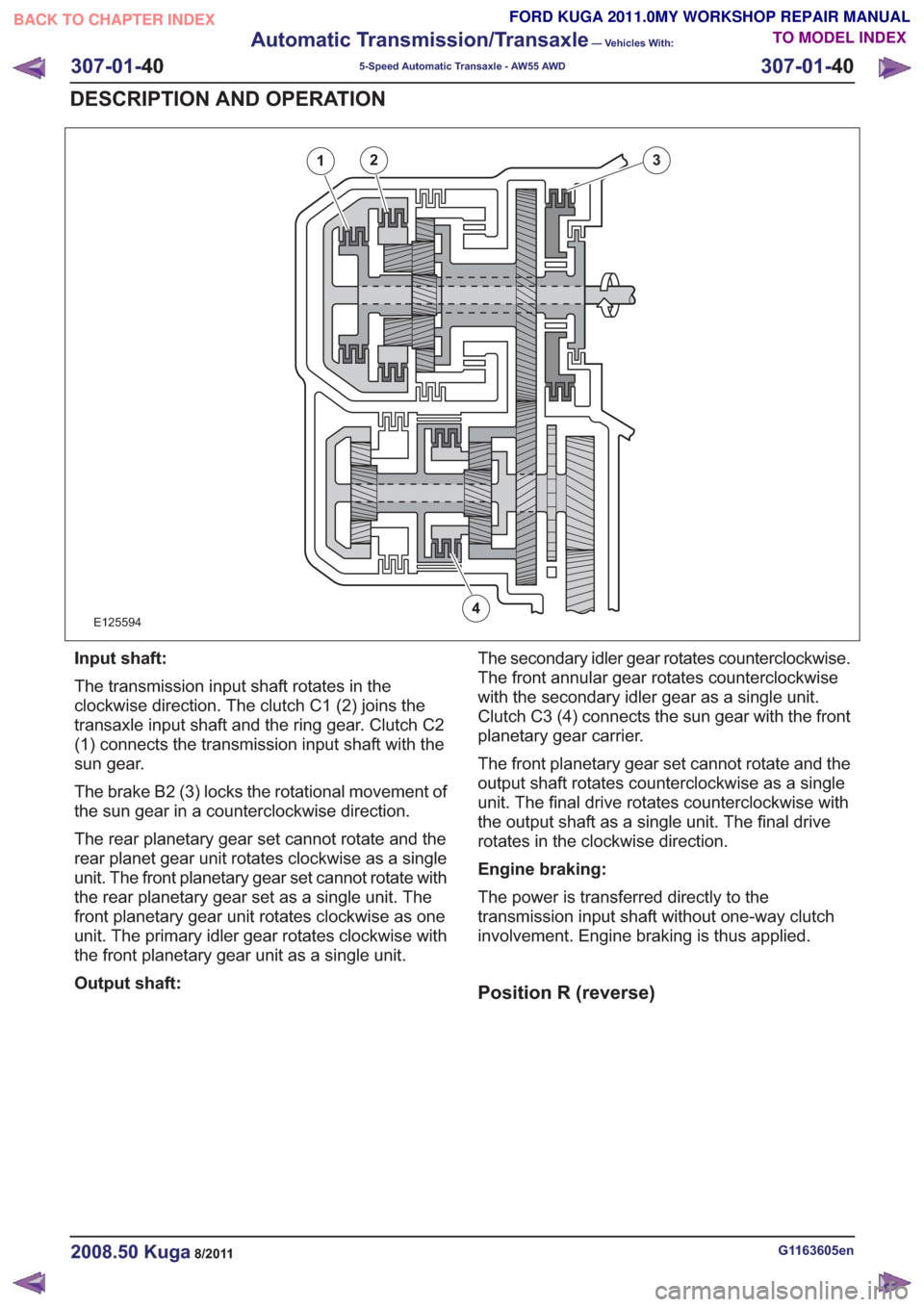
E125594
12
4
3
Input shaft:
The transmission input shaft rotates in the
clockwise direction. The clutch C1 (2) joins the
transaxle input shaft and the ring gear. Clutch C2
(1) connects the transmission input shaft with the
sun gear.
The brake B2 (3) locks the rotational movement of
the sun gear in a counterclockwise direction.
The rear planetary gear set cannot rotate and the
rear planet gear unit rotates clockwise as a single
unit. The front planetary gear set cannot rotate with
the rear planetary gear set as a single unit. The
front planetary gear unit rotates clockwise as one
unit. The primary idler gear rotates clockwise with
the front planetary gear unit as a single unit.
Output shaft:The secondary idler gear rotates counterclockwise.
The front annular gear rotates counterclockwise
with the secondary idler gear as a single unit.
Clutch C3 (4) connects the sun gear with the front
planetary gear carrier.
The front planetary gear set cannot rotate and the
output shaft rotates counterclockwise as a single
unit. The final drive rotates counterclockwise with
the output shaft as a single unit. The final drive
rotates in the clockwise direction.
Engine braking:
The power is transferred directly to the
transmission input shaft without one-way clutch
involvement. Engine braking is thus applied.
Position R (reverse)
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
40
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 40
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL