rod FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 1695 of 2057

Fuel Charging and Controls
General EquipmentFord diagnostic equipment
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern by operating the system.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage. Visual Inspection Chart
Electrical
Mechanical
– Loose or corrodedconnector(s)
– Wiring harness
– Fuel injector(s)
– Fuel leaks
– Blocked or contamin-
ated fuel filter
– Damaged fuel supply manifold
– Damaged fuel line connections
– Damaged vacuum hoses
– Fuel rail pressure sensor
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step.
4. If the concern is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Ford diagnostic
equipment .
Symptom Chart
Action
Possible Sources
Symptom
• CHECK the PATS LED extin-guishes within 3 seconds when
the ignition is turned on.
REFER to: Anti-Theft - Passive
(419-01 Anti-Theft - Passive,
Diagnosis and Testing).
• PAT S .
• Engine does not crank
• REFER to:Starting System
(303-06 Starting System -
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS)
- VI5, Diagnosis and Testing).
• Starting system.
• REFER to the Wiring Diagrams.
• Ignition switch.
• Carry out a full enginediagnosis using the guided
diagnostic menu in the Ford
diagnostic equipment.
• Powertrain control module
(PCM).
• RESET the IFS switch.
• Inertia fuel shutoff (IFS) switch.
• Engine cranks but does not
start
• Check the fuel system pres-sure.
• Low fuel system pressure.
G1183441en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04A-
4
Fuel Charging and Controls
— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) -
VI5
303-04A- 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1720 of 2057

Turbocharger – Overview
Turbocharger(s)
CAUTION: Do not switch off the engine
while it is running at high speed. If the
engine is switched off while it is running
at high speed, the turbocharger will
continue to run after the engine oil
pressure has already dropped to zero. This
will cause premature wear in the
turbocharger bearings.
A TC consists of an exhaust turbine located in the
exhaust gas flow, this turbine is connected to a
compressor by a shaft. The turbine is made to
rotate by the exhaust gas flow from the engine and
thus drives the compressor. The compressor
increases the pressure in the engine intake tract
so that a greater mass of air enters the cylinder
during the intake stroke.
The turbine housing of the TC is integrated into the
exhaust manifold. This construction offers
thermodynamic advantages compared with the
usual construction, the maximum exhaust
temperature is up to 1050°C.
The maximum boost pressure is 0.65 bar.
The exhaust manifold is secured to the exhaust
side of the cylinder head with 12 self-locking nuts.
The exhaust manifold gasket is a multi-layer steel
gasket and cannot be reused. In order to
compensate for the thermal expansion of the
exhaust manifold, the flange of the TC is provided
with two grooves.
The TC and the exhaust manifold are joined by a
hose clip. The hose clip must not be loosened or
removed. The TC and the exhaust manifold are
not available as separate replacement parts,
exchange is only possible as a complete unit.
The turbocharger heat shield is secured to the
exhaust manifold by four bolts. Two of the bolts
have spring washers underneath their heads.
During removal, make a note of the installation
location of the spring washers to refer to during
installation.
The recirculated air valve is built into the TC
housing and cannot be changed.
The Ford diagnostic unit can test the operation of
the wastegate control valve using actuator
diagnosis.
The boost pressure regulator is set in the factory.
Adjustments to the boost pressure regulator must never be attempted. A red colored seal is applied
to the adjustment nut of the operating rod, in order
to monitor the factory setting of the boost pressure.
The bearings of the TC are lubricated with engine
oil. The engine oil passes from the cylinder block
through the oil supply pipe to the TC. The oil is
returned to the oil pan through the oil return pipe,
The TC is cooled by the engine coolant circuit.
When installing hoses and lines, make certain that
their ends are free of oil residues and dirt.
G1032425en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B-
4
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1722 of 2057

Description
Item
PWM (pulse width modulation) signal
Comments:from PCM (powertrain control module)
5
Atmospheric pressure
6
Turbocharger boost pressure.
7
from air filter
8
Intake air
9Description
Item
Recirculated air valveRefertoComponentDescription:(page
7)
10
Vacuum line, recirculated air valve
11
to intake manifold
12
Throttle plate
13
Compressor
14
Turbine
15
System Operation
Turbocharger(s)
The TC consists of a turbine and a compressor.
The turbine is driven by the exhaust gas flow. A
common shaft drives the compressor and this then
compresses the intake air.
Turbocharger boost pressure control
E98942
1
2
3
4
Description
Item
Atmospheric pressure
1
Turbocharger boost pressure.
2
Wastegate control valve
3
Pilot pressure
4
The size of the TC is designed to produce a charge
effect even at medium engine speeds and lower
exhaust gas flows. This means that, when the engine speed is high and there is a large amount
of exhaust gas, either the boost pressure of the
TC will become too high or its speed will be too
high. The TC must therefore be regulated. The
best regulation is achieved by an electronically
controlled wastegate control valve. The wastegate
control valve controls the pressure on the
membrane in the boost pressure regulator.
The wastegate control valve is actuated by the
PCM with a PWM signal according to a map. The
boost pressure is applied to the wastegate control
valve via the pressure line from the compressor.
This pressure is passed to the boost pressure
regulator via the wastegate control valve. This
opens the bypass valve using a linkage. This
channels a portion of the exhaust gases around
the turbine. If the wastegate control valve is
actuated by the PCM, a bypass is opened in the
wastegate control valve. This causes the pressure
which can act on the membrane in the boost
pressure regulator to be reduced. This occurs until
the boost pressure has reached a set value. By
actuation with a PWM signal, it is also possible to
partially open or close the wastegate control valve.
This results in a constant boost pressure and
therefore high torque over a wide range of engine
speeds.
Because the PCM calculates the boost pressure
using the signal from the boost pressure sensor
and the IAT (intake air temperature) sensor, the
atmospheric pressure and the temperature are
automatically compensated for. Because of this
compensation, the engine power is not noticeably
affected by variations in atmospheric temperature
or pressure.
G1032426en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B-
6
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1726 of 2057
Action
Possible Sources
Symptom
• INSPECT the turbocharger forsigns of damage. INSTALL a
new turbocharger as neces-
sary.
REFER to: Turbocharger (303-
04 Fuel Charging and
Controls - Turbocharger -
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS)
- VI5, Removal and Installa-
tion).
• Turbocharger compressor
rubbing on housing walls.
• Turbocharger turbine rubbing on housing walls.
• Turbocharger bearings and oil seal(s).
• Turbocharger oil supply tube blocked or damaged.
• Blue smoke with excessive
turbocharger noise
• Check the oil return tube forblockage or damage, INSTALL
a new oil return tube as neces-
sary.
• Turbocharger oil return tube
blocked or damaged.
• Blue smoke without excessive
turbocharger noise
• CHECK all vacuum line(s) areinstalled and no signs of air
leaks are present. REPAIR as
necessary.
• Vacuum diaphragm unit
vacuum line(s).
• Poor engine performance
• CHECK the charge air cooler,charge air cooler pipes and
charge air cooler hoses for
leaks and obstructions.
REPAIR as necessary.
• Charge air cooler system.
• CHECK the air cleaner intakepipe for obstruction. REPAIR
the necessary.
• Air cleaner intake pipe.
• The turbocharger boost pres-sure is factory set and must not
be adjusted. CHECK the paint
seal on the vacuum diaphragm
unit actuator rod has not been
broken. If the paint seal has
been broken, INSTALL a new
turbocharger.
REFER to: Turbocharger (303-
04 Fuel Charging and
Controls - Turbocharger -
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS)
- VI5, Removal and Installa-
tion).
• Unauthorized adjustment of the
vacuum diaphragm unit actu-
ator rod.
• CHECK the vacuum diaphragmunit actuator rod moves freely,
If the vacuum diaphragm unit
actuator rod does not move
freely. CHECK for signs of
damage or signs of foreign
material. REPAIR as neces-
sary.
• Vacuum diaphragm unit actu-
ator rod.
G1183442en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B- 10
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1799 of 2057

KS
E96327
23
5
4
1
Description
Item
Seismic mass
1
Piezoceramic
2
Housing
3
Piezoceramic contact
4
Electrical connection
5
The KS converts mechanical vibrations of the
cylinder block into electrical pulses which can then
be processed by the PCM.
The KS consists of piezo-ceramic crystals that
generate a voltage when subjected to a mechanical
load.
When fastening the KS, make sure the specified
torque is adhered to. In this way a defined initial
tension is applied to the crystals which exerts an
influence on the operation of the KS.
When the engine is running, the pressure
fluctuations arising due to the combustion process
cause vibrations in the cylinder block. These act
on the crystals in the KS, causing the sensors to
produce an output signal. The stronger the
vibrations, the higher the frequency and the AC
voltage. These signals are evaluated by the PCM
and compared with stored data.
TIE42093
1
2
A
B1
2
Description
Item
Normal combustion
A
Knocking combustion
B
Pressure characteristic in cylinder
1
Output signal from KS
2
Broadband HO2S
TIE42061
The planar broadband HO2S also allows
measurements of the exhaust gas which deviates
from the stoichiometric ratio (lambda = 1). The
measuring range extends from lambda 0.7 to 2.8,
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 25
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
25
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1800 of 2057

whereby the broadband HO2S emits a clear,
constant signal.
The broadband HO2S consists of a Nernst
concentration cell and an oxygen pump cell, which
transports the oxygen ions.
TIE42098
5
7
9
12
86
4
3
Description
Item
Nernst concentration cell
1
Oxygen pump cell
2
Measuring area
3
Pump current
4
Regulating switch
5
Reference voltage
6
Heater
7
Heating voltage
8
Reference air duct
9
Between the oxygen pump cell and the Nernst
measuring electrode, there is a diffusion gap which
acts as the measuring area and is connected to
the exhaust gas. The Nernst concentration cell is
connected via a duct with the ambient reference
air and the measuring area. It detects the mixture
composition in the measuring area. A concentration
of lambda = 1 is set in the measuring area using
the oxygen ion flow. This is done by applying a
reference voltage which results in a pump current.
When the exhaust gas is lean, the oxygen pump
cell is actuated in such a way that oxygen ions are
pumped out of the measuring area. This is detected
by the regulating switch, so that the flow can move
(positive direction).
If the exhaust gas is rich, then the current direction
is reversed, i.e. the cell pumps oxygen ions into
the measuring area. The regulating switch detects
this, so the flow is reversed (negative direction).
TIE42062
1
2
Description
Item
Pump current in mA
Ip
positive pump current
1
negative pump current
2
The pump current represents a direct measurement
of the mixture composition. With lambda 1 (14.7
kg air/1 kg fuel), the pump current is 0 mA. The
relatively small measured current is converted into
a voltage signal in the PCM using an evaluation
circuit. The heating of the broadband HO2S is
supplied with a reference voltage of 11 to 14V. The
operating temperature of the broadband HO2S is
650 - 900 °C.
The characteristic curve of the broadband HO2S
is constant (linear), without a lambda jump.
VCT (variable camshaft timing) solenoids
The camshaft adjustment solenoids are multi-way
solenoid valves that are actuated with a PWM
signal, thereby allowing the valve plungers to be
steplessly adjusted.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 26
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
26
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1802 of 2057
voltage signal to the PCM corresponding to the
aspirated air mass.
This analogue voltage signal is between 0.5V and
5V. Low mass of intake air produces a low voltage
signal. A high mass of intake air produces a
correspondingly high voltage signal.
The MAF sensor is also capable of detecting the
backflow of the intake air. A sensor element is
heated electrically on the integrated chip and then
cooled by the air flowing through. The regulating
switch supplies the heating current in such a way
that it attains a constant excess temperature in
comparison to the intake air. The mass air flow and
the direction of flow can be derived from this
heating current (given in the form of a signal
voltage). Below a certain voltage value there is a
return flow. The direction is flow is registered by
two sensors pointing in different directions. The
measurement does not require a great deal of
software processing effort, even with a strongly
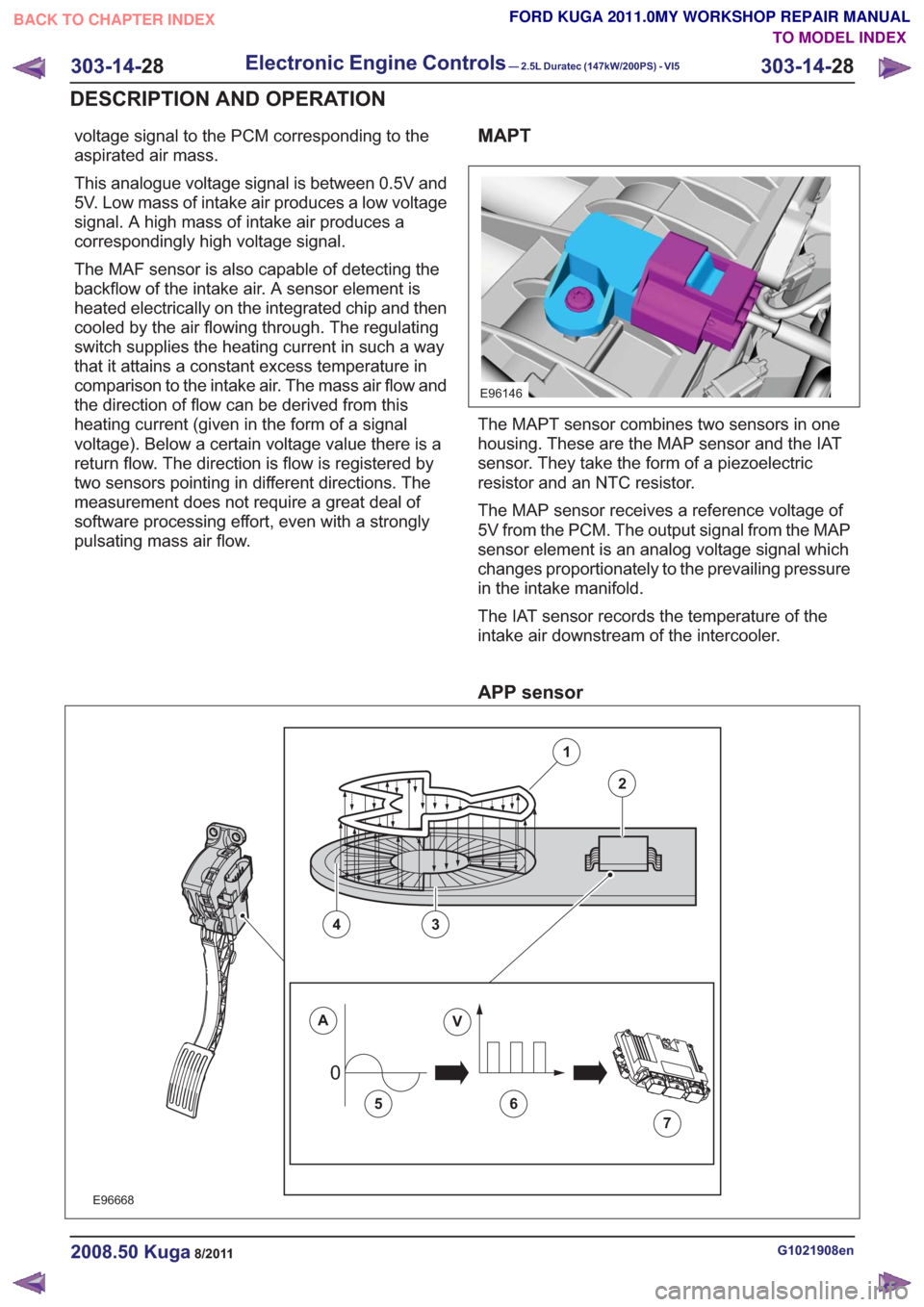
pulsating mass air flow.MAPT
E96146
The MAPT sensor combines two sensors in one
housing. These are the MAP sensor and the IAT
sensor. They take the form of a piezoelectric
resistor and an NTC resistor.
The MAP sensor receives a reference voltage of
5V from the PCM. The output signal from the MAP
sensor element is an analog voltage signal which
changes proportionately to the prevailing pressure
in the intake manifold.
The IAT sensor records the temperature of the
intake air downstream of the intercooler.
APP sensor
00
E96668
1
2
43
AV
56
7
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-28
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
28
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1835 of 2057

Description
Item
ABS (anti-lock brake system)
5
Speed control
6
Select-shift switch module
7
PCM
8
Selector lever lock
9
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
10
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure
(SLT)
11
PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU)
12Description
Item
Shift solenoid S1 (open when dormant)
13
Shift solenoid S2 (closed when dormant)
14
Shift solenoid S3 (closed when dormant)
15
Shift solenoid S4 (open when dormant)
16
Shift solenoid S5 (closed when dormant)
17
The TSS sensor
18
The OSS sensor
19
The TFT sensor
20
TR sensor in TCM
21
Knowing and Understanding Customer
Concerns
Knowing and understanding customer concerns is
necessary in order to perform diagnosis.
First of all, ask the customer under which operating
conditions the problem occurs. If possible, try to
reproduce the concern by road testing the vehicle
with the customer.
You should be familiar with the following operating
conditions:
• Engine operating state
– Cold, warm-up phase, or at operatingtemperature
• Ambient temperature – Below 0 °C (32 °F), 0 to 20 °C (32 to 68 °F),or above 20 °C (68 °F)
• Road conditions – Good, poor, or off-road
• Vehicle load status – Unloaded, loaded, or fully loaded
• Transaxle status in manual mode – Upshift, downshift, overrun or acceleration
Testing Possible Causes of Transmission
Control Faults
Before performing a symptom-based diagnosis,
first carry out checks to eliminate various other
potential causes of the fault.
These situations include:
• Battery state of charge
• Defective fuses • Loose or corroded cables or electrical
connectors
• Ground connections to the transmission
• Retrofitted add-on units which are not approved by Ford, such as air conditioning, car telephone,
cruise control
• Unapproved tire sizes
• Incorrect tire size programmed with IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System)
• Engine tuning
IDS Diagnosis
NOTE: Customer concerns relating to the transaxle
can also be caused by engine-related faults.
The transmission control system of the AW55 is
closely linked to the engine management system.
Faults in the engine management system may
affect the transmission control system.
Before repairing the transaxle, it should be ensured
that the fault is not caused by the engine
management system or other non-transaxle
components.
The diagnosis can be performed on the AW55 with
the aid of von IDS.
visual inspection
A thorough visual inspection of the transaxle is
necessary for successful diagnosis.
A visual inspection is made of the following
components:
• Connectors and plug connections
• Ease of operation of the selector lever
G1163604en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 14
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 14
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1846 of 2057
Serial number of the transmission
Example:09HV70001
• 09: year of manufacture, 2009 •
H: code letter for the month of manufacture,
August
• V7: automatic transaxle type 55-51SN
• 00001 : Production number for the specified
month
Identification letter coding
January
A
February
B
March
C
April
D
May
E
June
F
July
G
August
H.
September
J
October
K
November
left-hand
December
Ground
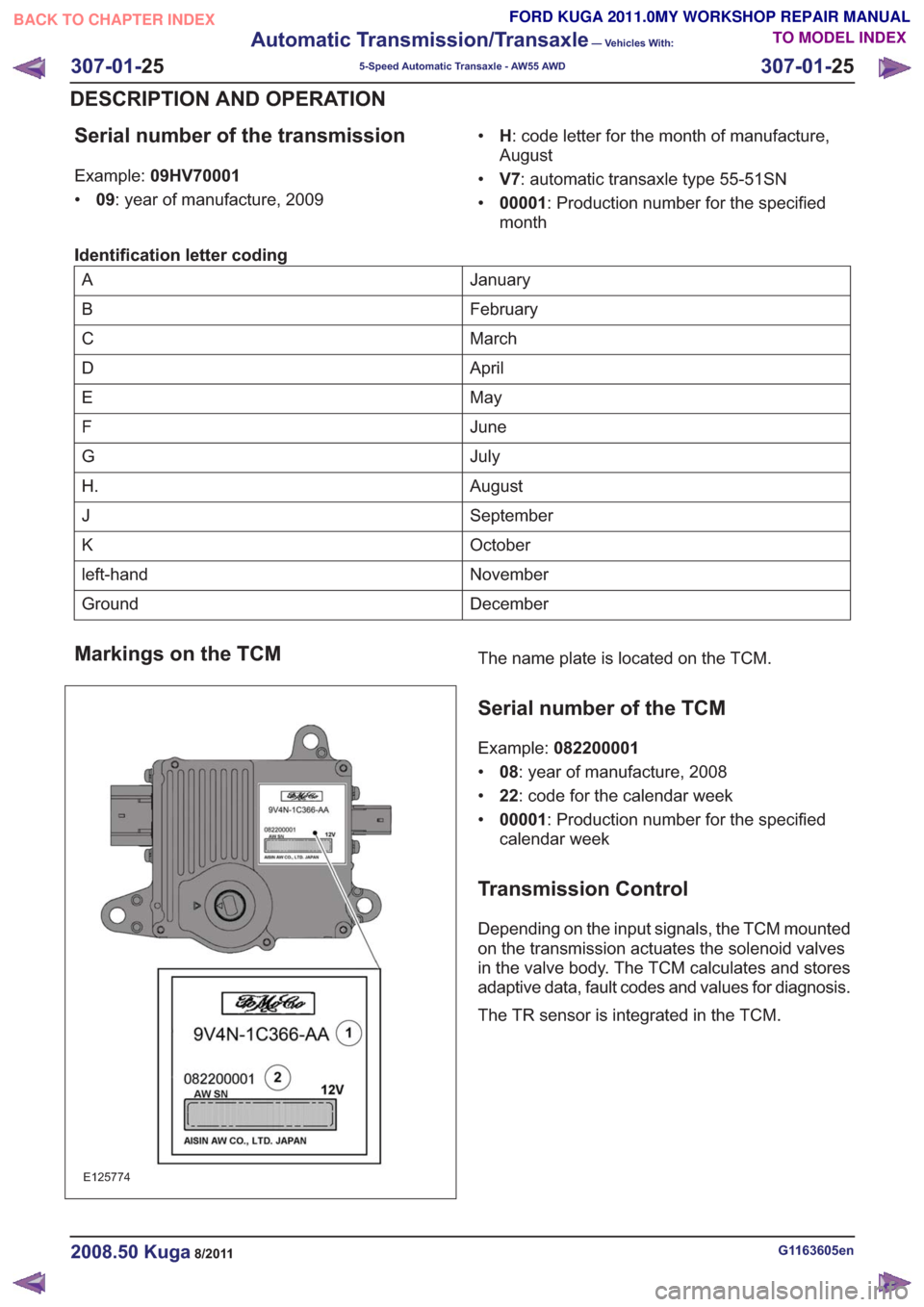
Markings on the TCM
E125774
The name plate is located on the TCM.
Serial number of the TCM
Example: 082200001
• 08: year of manufacture, 2008
• 22: code for the calendar week
• 00001 : Production number for the specified
calendar week
Transmission Control
Depending on the input signals, the TCM mounted
on the transmission actuates the solenoid valves
in the valve body. The TCM calculates and stores
adaptive data, fault codes and values for diagnosis.
The TR sensor is integrated in the TCM.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 25
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 25
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1881 of 2057

The TR sensor
E125819
The TR sensor and the TCM form one unit. This
unit is located at the top of the transmission casing,
on the gear linkage.
Function
The TR sensor has three separate functions:
• Transmit a signal to the TCM about the selectedtransmission range.
• To transmit the signal to switch on the reversing lamps to the GEM when the selector lever is in
the 'R' position.
• To transmit the start enable signal to the PCM when the selector lever is in the 'P' or 'N'
position.
The TR sensor contains a permanent magnet and
a linear Hall detector. It produces a signal voltage
between 0 and 5 V. This signal voltage
corresponds to the selector lever position currently
chosen.
Voltage values for the different gears:
• P approximately 0.65 V
• R approximately 1.64 V
• N approximately 2.12 V
• D approximately 2.49 V
Consequences of signal failure
If the TR sensor fails, the MIL is activated and the
vehicle can be driven in emergency mode 4. The
vehicle can no longer be started for safety reasons
after the ignition is switched off because the TCM
does not detect the current transmission range.
If a shift solenoid valve fails, the MIL is activated
and the vehicle can be driven in the appropriate
emergency mode.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 60
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 60
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL