automatic FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 44 of 2057
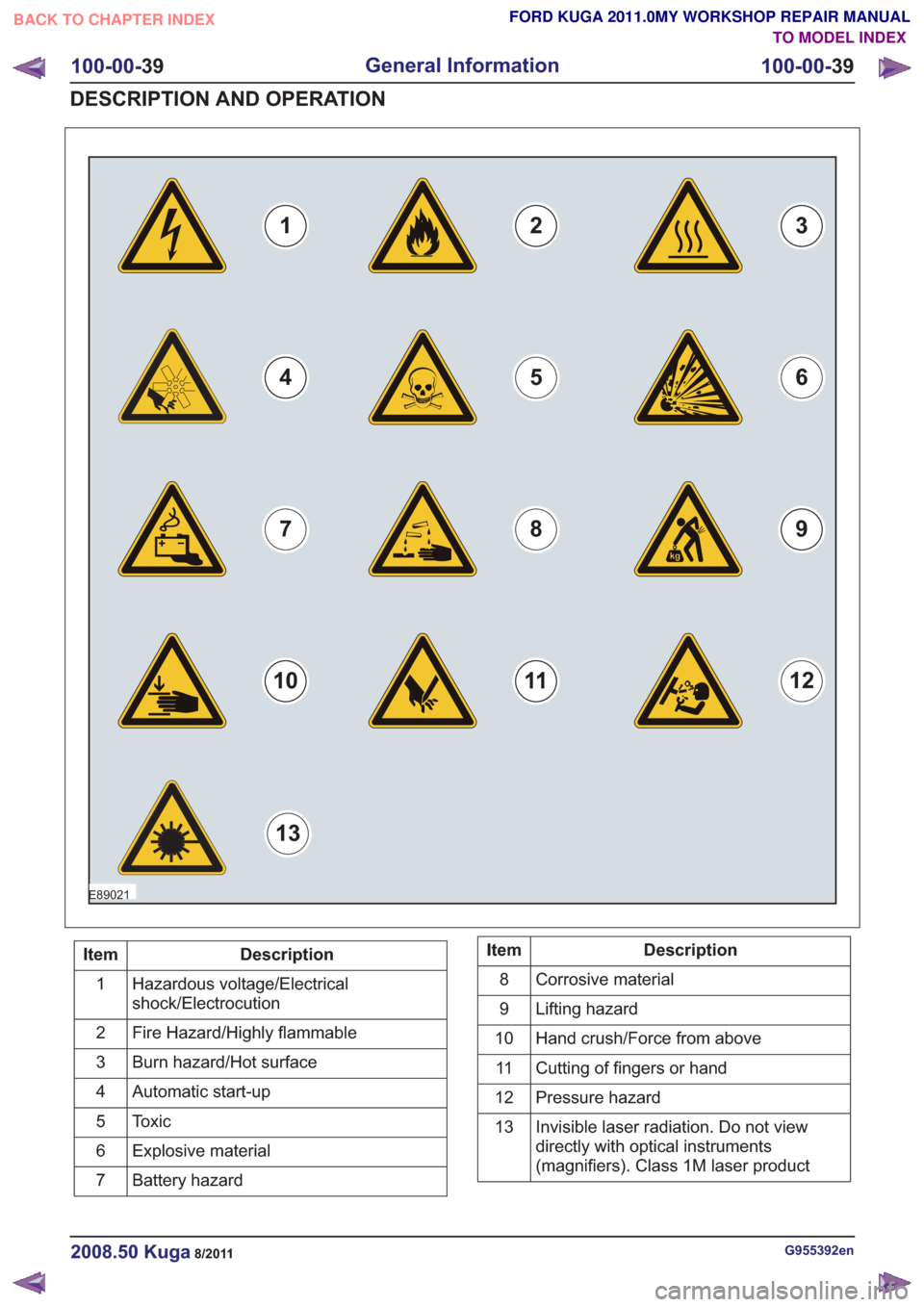
E89021
123
56
798
12
4
13
Description
Item
Hazardous voltage/Electrical
shock/Electrocution
1
Fire Hazard/Highly flammable
2
Burn hazard/Hot surface
3
Automatic start-up
4
Toxic
5
Explosive material
6
Battery hazard
7Description
Item
Corrosive material
8
Lifting hazard
9
Hand crush/Force from above
10
Cutting of fingers or hand
11
Pressure hazard
12
Invisible laser radiation. Do not view
directly with optical instruments
(magnifiers). Class 1M laser product
13
G955392en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
100-00-
39
General Information
100-00- 39
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 60 of 2057

Standard Workshop Practices
Vehicle in Workshop
When working on a vehicle in the workshop always
make sure that:
– the parking brake is applied or the wheels aresecurely chocked to prevent the vehicle moving
forwards or backwards.
– the key is removed from key operated hood locks before any work is carried out around the
front of the vehicle.
– if the engine is to be run, there is adequate ventilation, or an extraction hose to remove
exhaust fumes.
– there is adequate room to raise the vehicle and remove the wheels, if necessary.
– fender covers are always fitted if any work is to be carried out in the engine compartment.
– the battery is disconnected if working on the engine, underneath the vehicle, or if the vehicle
is raised.
CAUTION: When electric arc welding on a
vehicle, always disconnect the generator
wiring to prevent the possibility of a surge
of current causing damage to the internal
components of the generator.
– if using welding equipment on the vehicle, a suitable fire extinguisher is readily available.
Towing the Vehicle
WARNING: When the vehicle is being
towed, the ignition switch must be in
position II (steering lock released and
warning lamps illuminated). Only then will
the steering, turn signal lamps, horn and
stop lamps be operational. Failure to follow
these instructions may result in personal
injury.
NOTE: The removable towing eye (if equipped),
has a left-hand thread and must be fully tightened
before towing can commence.
When towing is necessary, the vehicle towing eyes
should be used. The rope must be securely
fastened to the towing eyes and must also be
attached to the other vehicle such that the rope will
not foul the bodywork.
When a vehicle with automatic transmission is
towed, the gear selector must be in position N (Neutral). Never tow a vehicle with automatic
transmission at a speed greater than 30 mph (50
km/h) or for a distance greater than 30 miles (50
km). If it is necessary to tow the vehicle a greater
distance, the drive wheels must be lifted clear off
the ground.
Alternatively the vehicle can be transported on a
low loader or a trailer.
Connecting a Slave Battery Using
Jumper Cables
WARNING: If the slave battery has recently
been charged and is gassing, cover the
vent plugs or covers with a damp cloth to
reduce the risk of explosion should arcing
occur when connecting the jumper cables.
Failure to follow these instructions may
result in personal injury.
CAUTIONS:
A discharged battery condition may have
been caused by an electrical short circuit.
If this condition exists there will be an
apparently live circuit on the vehicle even
when all normal circuits are switched off.
This can cause arcing when the jumper
cables are connected.
While it is not recommended that the
vehicle is jump started, it is recognized
that this may occasionally be the only
practical way to mobilize a vehicle. In such
an instance, the discharged battery must
be recharged immediately after jump
starting to avoid permanent damage.
– Always make sure that the jumper cables are adequate for the task. Heavy duty cables must
be used.
– Always make sure that the slave battery is of the same voltage as the vehicle battery. The
batteries must be connected in parallel.
– Always make sure that switched electric circuits are switched off before connecting jumper
cables. This reduces the risk of arcing occurring
when the final connection is made.
G17373en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
100-00- 54
General Information
100-00- 54
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 81 of 2057

Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH)
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanicalor electrical damage.
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step.
4. If the concern is not visually evident, verify the symptom and REFER to the Symptom Chart.
How to Use this Diagnostic Procedure
Section
• Noise, vibration and harshness (NVH) concernshave become more important as vehicles have
become more sensitive to these vibrations. This
section is designed to aid in identifying these
concerns.
• The section provides diagnostic procedures based on symptom. If the condition occurs at
high speed, for instance, the most likely place
to start is under Shake and Vibration While
Driving.
• The road test procedure will tell how to sort the conditions into categories and how to tell a
vibration from a shake.
• A series of Road Test Quick Checks are provided to make sure that a cause is either
pinpointed or eliminated.
• Name the condition, proceed to the appropriate section and locate the correct diagnosis. When
the condition is identified, the job is partly done.
• Follow the diagnostic procedure as outlined.
• Quick Checks are described within the step, while more involved tests and adjustments are
outlined in General Procedures.
• Always follow each step exactly and make notes to recall important findings later.
Customer Interview
The road test and customer interview (if available)
provide information that will help identify the
concern and will provide direction to the correct
starting point for diagnosis.
Identify the Condition
NVH usually occur in four areas:
• tires
• engine accessories
• suspension
• driveline
It is important, therefore, that an NVH concern be
isolated into its specific area(s) as soon as
possible. The easiest and quickest way to do this
is to carry out the Road Test as outlined. To assist
in the diagnosis and testing procedure(s), use a
suitable approved NVH diagnosis tester.
Noise Diagnostic Procedure
Non-Axle Noise
The five most common sources of non-axle noise
are exhaust, tires, roof racks, trim panels and
transmission.
Therefore, make sure that none of the following
conditions are the cause of the noise before
proceeding with a driveline teardown and
diagnosis.
• In certain conditions, the pitch of the exhaustmay sound very much like gear noise. At other
times, it can be mistaken for a wheel bearing
rumble.
• Tires, especially snow tires, can have a high pitched tread whine or roar, similar to gear
noise. Radial tires may have this characteristic.
Also, any non-standard tire with an unusual
tread construction may emit a roar or whine
noise.
• Trim panels can also cause whistling or whining noise.
• Clunk may be a metallic noise heard when the automatic transaxle is engaged in "R"
(REVERSE) or "D" (DRIVE) or it may occur
when the throttle is applied or released. It is
caused by backlash somewhere in the driveline.
• Bearing rumble sounds like marbles being tumbled. This condition is usually caused by a
damaged wheel bearing.
G37349en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
100-04- 2
Noise, Vibration and Harshness
100-04- 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 82 of 2057

sometimes noticed in the steering wheel/column,
seats, front floor panel, front door trim panel or
front end sheet metal. It is a low frequency
vibration (around 9-15 cycles per second). It
may or may not be increased by applying the
brakes lightly. REFER to Idle
Boom/Shake/Vibration in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
3. High Speed: A vibration is felt in the front floor panel or seats with no visible shake, but with
an accompanying sound or rumble, buzz, hum,
drone or booming noise. Coast with the clutch
pedal depressed (manual transmission) or shift
control selector lever in "N" (NEUTRAL)
(automatic transmission) and engine idling. If
vibration is still evident, it may be related to
wheels, tires, front brake discs, wheel hubs or
front wheel bearings. REFER to Shake and
Vibration While Driving in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
4. Engine rpm Sensitive: A vibration is felt whenever the engine reaches a particular rpm.
It will disappear in neutral coasts. The vibration
can be duplicated by operating the engine at
the problem rpm while the vehicle is stationary.
It can be caused by any component, from the
accessory drive belt to the clutch or torque
converter which turns at engine speed when the
vehicle is stopped. REFER to Shake and
Vibration While Driving in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
5. Noise and Vibration While Turning: Clicking, popping or grinding noises may be due to the
following:
• worn, damaged or incorrectly installed front wheel bearing.
• damaged powertrain/drivetrain mounts.
Road Conditions
An experienced technician will always establish a
route that will be used for all NVH diagnosis road
tests. The road selected should be reasonably
smooth, level and free of undulations (unless a
particular condition needs to be identified). A
smooth asphalt road that allows driving over a
range of speeds is best. Gravel or bumpy roads
are unsuitable because of the additional road noise
produced. Once the route is established and consistently used, the road noise variable is
eliminated from the test results.
NOTE:
Some concerns may be apparent only on
smooth asphalt roads.
If a customer complains of a noise or vibration on
a particular road and only on a particular road, the
source of the concern may be the road surface. If
possible, try to test the vehicle on the same type
of road.
Vehicle Preparation
Carry out a thorough visual inspection of the
vehicle before carrying out the road test. Note
anything which is unusual. Do not repair or adjust
any condition until the road test is carried out,
unless the vehicle is inoperative or the condition
could pose a hazard to the technician. After
verifying that the condition has been corrected,
make sure all components removed have been
installed.
Power Steering Conditions
Check for the noise in the following conditions to
verify the customer concern.
• Check for the noise in several temperature conditions.
• Is the noise from when the vehicle was new?
• Can the noise be repeated constantly or is it random?
• Check the condition of the vehicle age, mileage and service record.
• Interview the customer to find the operating condition in which the noise will occur. Test the
vehicle based on the detail(s) from the customer
interview.
• Follow the power steering operation noise condition tables below, to find which condition
the noise will occur.
Power Steering Operation Noise Check
Step 1: Check for NVH concerns from non-steering
components, which may sound like noises coming
from the steering system.
G37349en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
100-04- 4
Noise, Vibration and Harshness
100-04- 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 89 of 2057
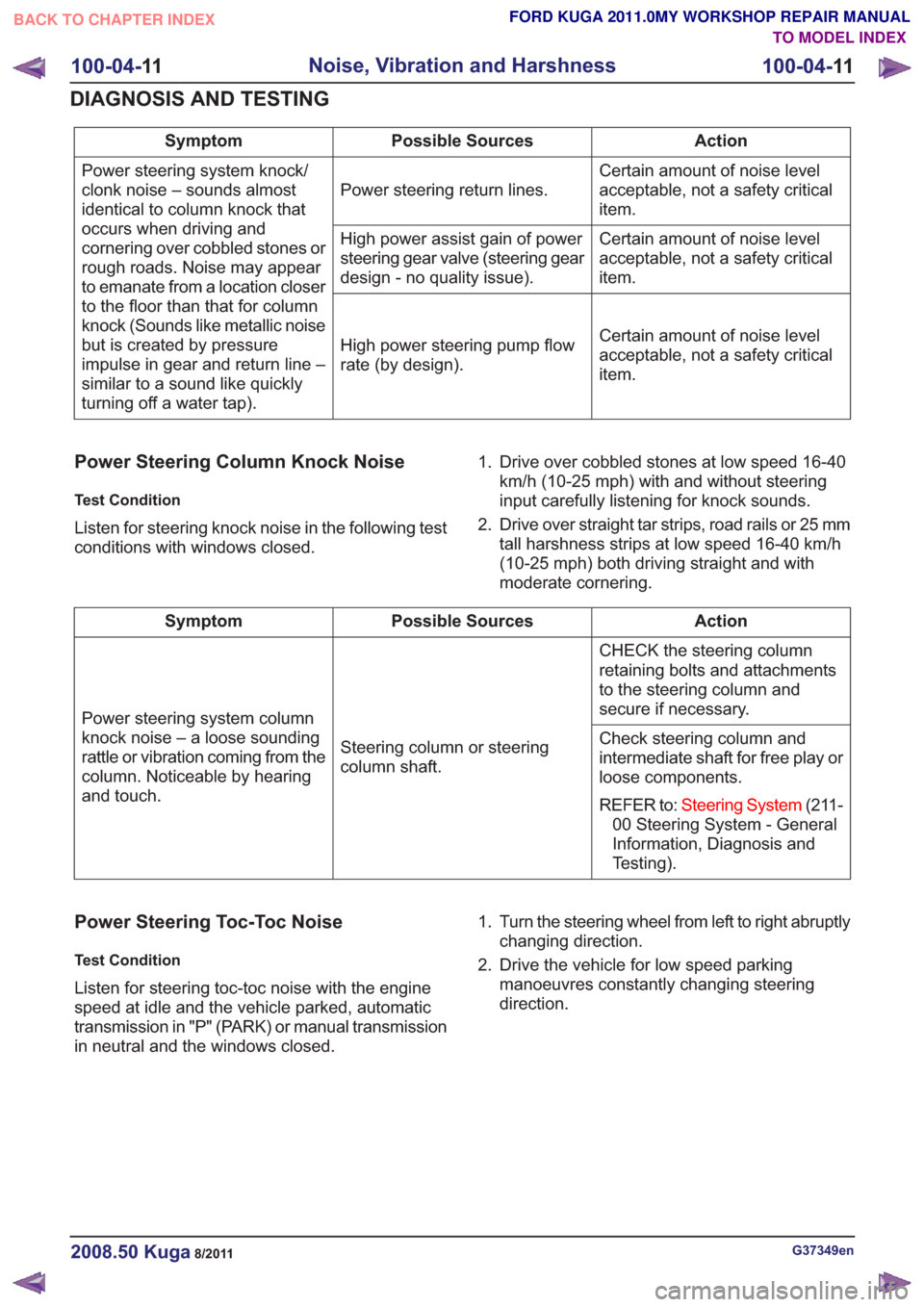
Action
Possible Sources
Symptom
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Power steering return lines.
Power steering system knock/
clonk noise – sounds almost
identical to column knock that
occurs when driving and
cornering over cobbled stones or
rough roads. Noise may appear
to emanate from a location closer
to the floor than that for column
knock (Sounds like metallic noise
but is created by pressure
impulse in gear and return line –
similar to a sound like quickly
turning off a water tap). Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
High power assist gain of power
steering gear valve (steering gear
design - no quality issue).
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
High power steering pump flow
rate (by design).
Power Steering Column Knock Noise
Test Condition
Listen for steering knock noise in the following test
conditions with windows closed. 1. Drive over cobbled stones at low speed 16-40
km/h (10-25 mph) with and without steering
input carefully listening for knock sounds.
2. Drive over straight tar strips, road rails or 25 mm tall harshness strips at low speed 16-40 km/h
(10-25 mph) both driving straight and with
moderate cornering.
Action
Possible Sources
Symptom
CHECK the steering column
retaining bolts and attachments
to the steering column and
secure if necessary.
Steering column or steering
column shaft.
Power steering system column
knock noise – a loose sounding
rattle or vibration coming from the
column. Noticeable by hearing
and touch. Check steering column and
intermediate shaft for free play or
loose components.
REFER to:
Steering System (211-
00 Steering System - General
Information, Diagnosis and
Testing).
Power Steering Toc-Toc Noise
Test Condition
Listen for steering toc-toc noise with the engine
speed at idle and the vehicle parked, automatic
transmission in "P" (PARK) or manual transmission
in neutral and the windows closed. 1. Turn the steering wheel from left to right abruptly
changing direction.
2. Drive the vehicle for low speed parking manoeuvres constantly changing steering
direction.
G37349en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
100-04- 11
Noise, Vibration and Harshness
100-04- 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 90 of 2057
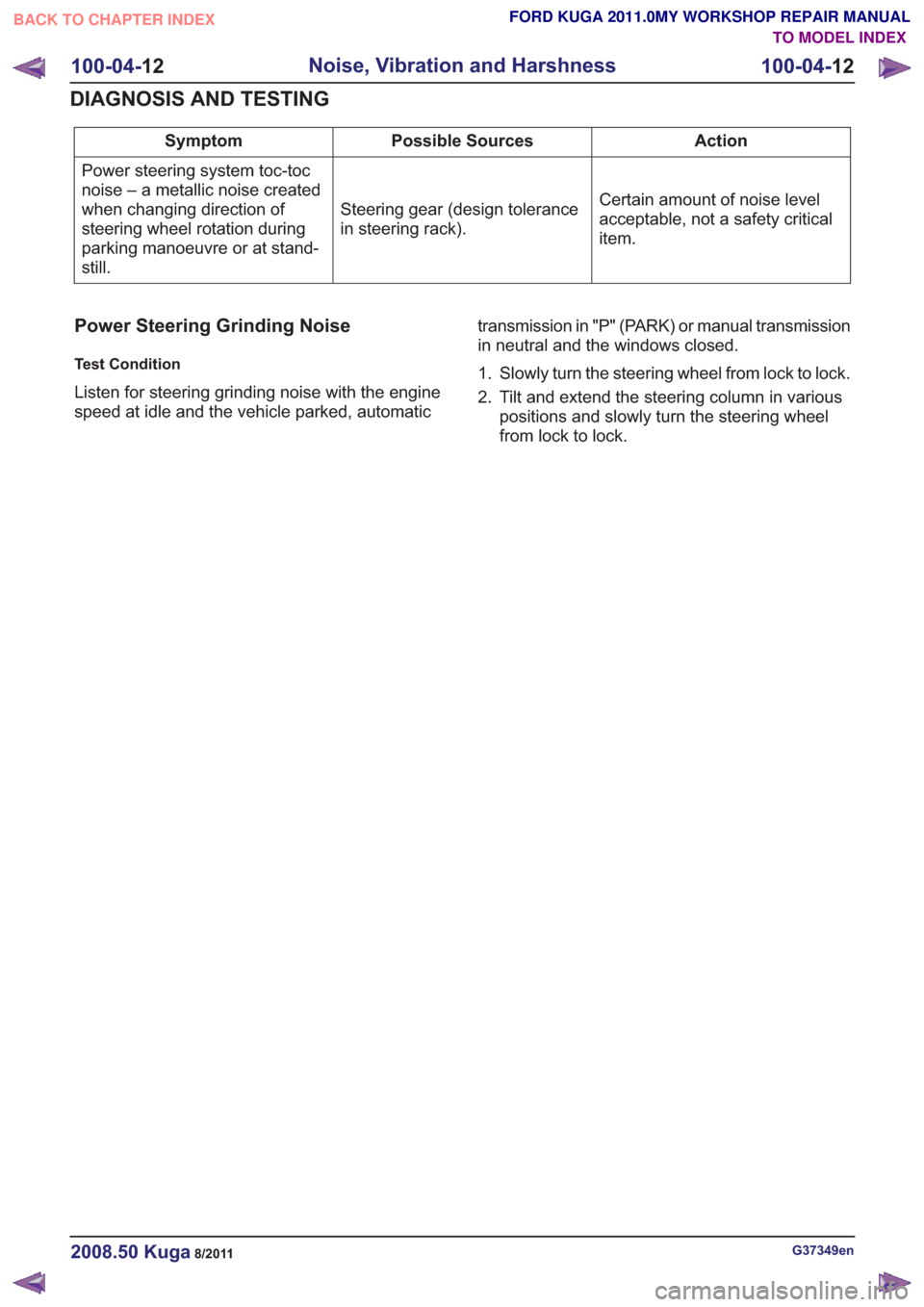
Action
Possible Sources
Symptom
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Steering gear (design tolerance
in steering rack).
Power steering system toc-toc
noise – a metallic noise created
when changing direction of
steering wheel rotation during
parking manoeuvre or at stand-
still.
Power Steering Grinding Noise
Test Condition
Listen for steering grinding noise with the engine
speed at idle and the vehicle parked, automatic transmission in "P" (PARK) or manual transmission
in neutral and the windows closed.
1. Slowly turn the steering wheel from lock to lock.
2. Tilt and extend the steering column in various
positions and slowly turn the steering wheel
from lock to lock.
G37349en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
100-04- 12
Noise, Vibration and Harshness
100-04- 12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 102 of 2057
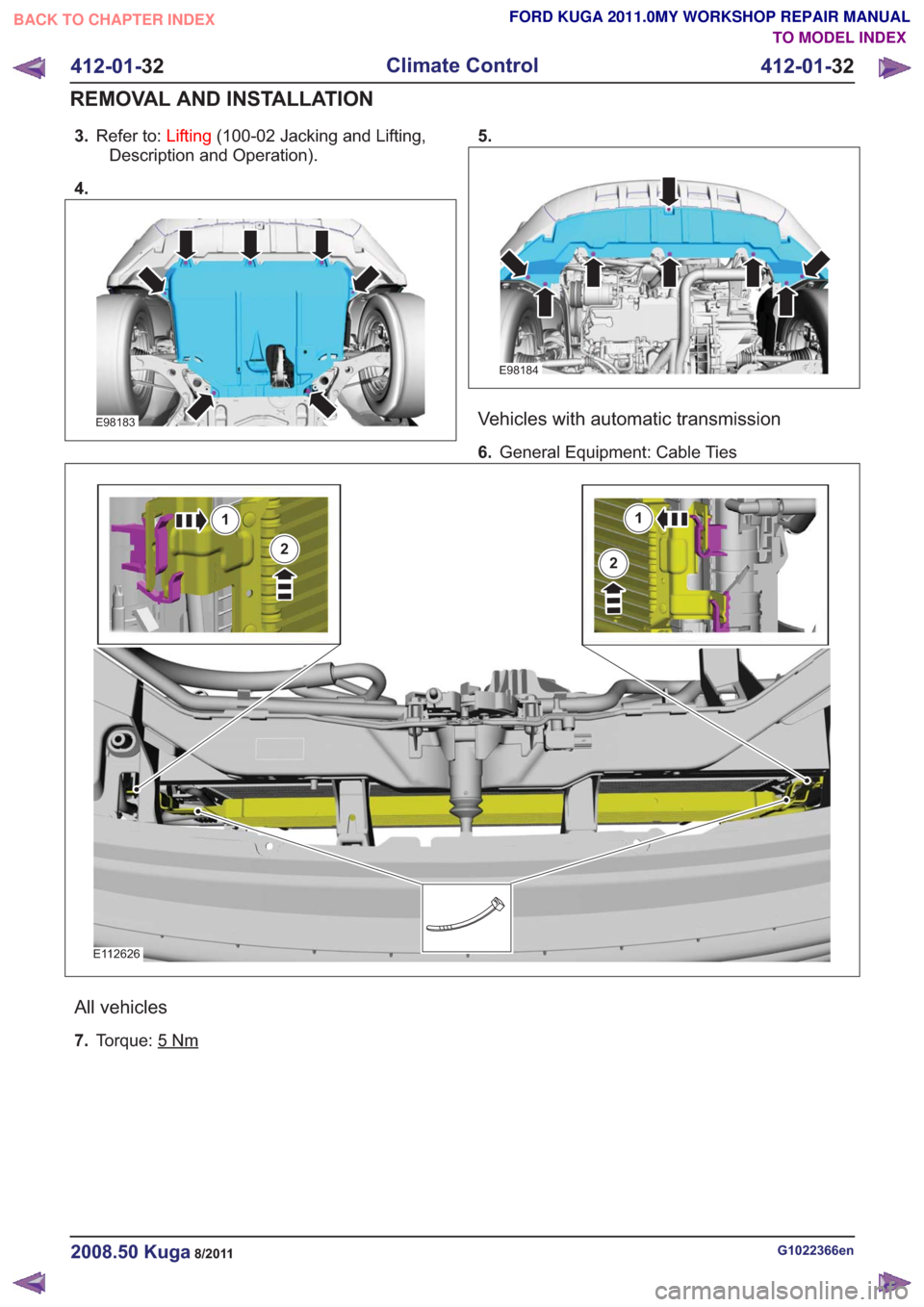
3.Refer to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
4.
E98183
5.
E98184
Vehicles with automatic transmission
6. General Equipment: Cable Ties
E112626
1
2
1
2
All vehicles
7.Torque: 5Nm
G1022366en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
412-01- 32
Climate Control
412-01- 32
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 111 of 2057

Blower Motor Resistor — Vehicles With: Dual AutomaticTemperature Control(34 382 0)
Removal
1.Refer to: In-Vehicle Crossbeam (501-12
Instrument Panel and Console, Removal and
Installation).
2.
E82113
x2
Installation
1. To install, reverse the removal procedure.
G1072295en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
412-01- 41
Climate Control
412-01- 41
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 171 of 2057

Electric Booster Heater
Removal
NOTE:
Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Floor Console (501-12 Instrument
Panel and Console, Removal and Installation).
2. Torque: 9 Nm 3.
Refer to: Climate Control Assembly - Vehicles
With: Manual Temperature Control (412-01
Climate Control, Removal and Installation).
Refer to: Climate Control Assembly - Vehicles
With: Automatic Temperature Control (412-01
Climate Control, Removal and Installation).
4. Torque: 10 Nm1.
2. Torque: 25
Nm
G1074270en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 412-02-18
Auxiliary Climate Control
412-02-18
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUALx4E101619
Page 198 of 2057

Safety Belt Minder Deactivating/Activating
Preparation
1. Apply the parking brake.
2. Place the transmission selector lever in P
(Park) - vehicles with automatic transmission
or the neutral position - vehicles with manual
transmission.
3. Turn the ignition switch to the 0 position.
4. Close all the vehicle doors from the inside of the vehicle.
Deactivating/Activating
NOTE: Deactivation of the belt minder may also
be carried out using IDS. Follow the instructions
on the screen.
1. Unbuckle the drivers safety belt.
2. Turn the ignition switch to position II. (Do not start the engine).
3. Wait at least 15 seconds.
4. NOTE: This step must be completed within 60 seconds or the procedure must be
repeated.
Buckle then unbuckle the safety belt nine
times, ending with the safety belt unbuckled.
Release the red unbuckle switch completely
every cycle.
5. The safety belt warning indicator flashes three times to confirm the belt minder status
change.
6. Turn the ignition switch to position 0. The deactivation/activation procedure is now
complete. G167271en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 413-09-3
Warning Devices
413-09-3
GENERAL PROCEDURESTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL