light FORD MONDEO 1993 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1993, Model line: MONDEO, Model: FORD MONDEO 1993Pages: 279, PDF Size: 12.71 MB
Page 42 of 279

Lubrication
Engine oil type/specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Engine oil capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Oil pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . No information available at time of writing
Oil pump clearances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . No information available at time of writing
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Cylinder head cover bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 1.5
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 5
Camshaft toothed pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68 50
Camshaft bearing cap bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 14
Cylinder head bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 33
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten a further 105°
Timing belt cover fasteners:
Upper-to-middle (outer) cover bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 3
Cover-to-cylinder head or block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 5
Cover studs-to-cylinder head or block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 to 11 6.5 to 8
Timing belt tensioner bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 28
Timing belt tensioner backplate locating peg . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 to 11 6 to 8
Timing belt tensioner spring retaining pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Timing belt guide pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 to 40 26 to 30
Water pump pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Water pump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 3
Auxiliary drivebelt idler pulley . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Inlet manifold nuts and bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 13
Alternator mounting bracket-to-cylinder block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 35
Cylinder head support plates:
Front plate Torx screws - to power steering pump/air conditioning
compressor mounting bracket and cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 35
Rear plate/engine lifting eye - to alternator mounting bracket
and cylinder head bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 35
Front engine lifting eye bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 12
Inlet and exhaust manifold studs-to-cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 maximum 7 maximum
Exhaust manifold heat shield bolts:
Shield-to-cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 5
Shield/dipstick tube . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Shield/coolant pipe-to-manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 17
Exhaust manifold nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 12
Air conditioning refrigerant pipe-to-exhaust manifold bolts . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Crankshaft pulley bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108 to 115 80 to 85
Oil pump-to-cylinder block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Oil pick-up pipe-to-pump screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Oil baffle/pump pick-up pipe nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 14
Oil filter adaptor-to-pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 to 25 13 to 18
Oil pressure warning light switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 20
Oil level sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 20
Sump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 to 22 15 to 16
Coolant pipe-to-sump bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Flywheel/driveplate bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110 to 112 81 to 83
Crankshaft left-hand oil seal carrier bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 16
Transmission-to-engine bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 30
Engine/transmission front mounting:
Mounting bracket-to-transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Not available
Mounting-to-subframe bolts/nuts - stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Mounting-to-subframe bolts/nuts - stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Mounting centre bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120 89
Engine/manual transmission rear mounting:
Mounting bracket-to-transmission 12 mm fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78 to 84 58 to 62
Mounting bracket-to-transmission 10 mm fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Mounting-to-subframe bolts and nut - stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Mounting-to-subframe bolts and nut - stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Mounting centre bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120 89
2A•2 In-car engine repair procedures
procarmanuals.com
Page 45 of 279

The cylinder head is provided with two oil
galleries, one on the inlet side and one on the
exhaust, to ensure constant oil supply to the
camshaft bearings and hydraulic tappets. A
retaining valve (inserted into the cylinder
head’s top surface, in the middle, on the inlet
side) prevents these galleries from being
drained when the engine is switched off. The
valve incorporates a ventilation hole in its
upper end, to allow air bubbles to escape
from the system when the engine is restarted.
While the crankshaft and camshaft
bearings and the hydraulic tappets receive a
pressurised supply, the camshaft lobes and
valves are lubricated by splash, as are all
other engine components.
Valve clearances - general
It is necessary for a clearance to exist
between the tip of each valve stem and the
valve operating mechanism, to allow for the
expansion of the various components as the
engine reaches normal operating
temperature.
On most older engine designs, this meant
that the valve clearances (also known as
“tappet” clearances) had to be checked and
adjusted regularly. If the clearances were
allowed to be too slack, the engine would be
very noisy, its power output would suffer, and
its fuel consumption would increase. If the
clearances were allowed to be too tight, the
engine’s power output would be reduced,
and the valves and their seats could be
severely damaged.
The engines covered in this manual,
however, employ hydraulic tappets which use
the lubricating system’s oil pressure
automatically to take up the clearance
between each camshaft lobe and its
respective valve stem. Therefore, there is no
need for regular checking and adjustment of
the valve clearances, but it is essential that
onlygood-quality oil of the recommended
viscosity and specification is used in the
engine, and that this oil is always changed at
the recommended intervals. If this advice is
not followed, the oilways and tappets may
become clogged with particles of dirt, or
deposits of burnt (inferior) engine oil, so that
the system cannot work properly; ultimately,
one or more of the tappets may fail, and
expensive repairs may be required.
On starting the engine from cold, there will
be a slight delay while full oil pressure builds
up in all parts of the engine, especially in the
tappets; the valve components, therefore,
may well “rattle” for about 10 seconds or so,
and then quieten. This is a normal state of
affairs, and is nothing to worry about,
provided that all tappets quieten quickly and
stay quiet.
After the vehicle has been standing for
several days, the valve components may
“rattle” for longer than usual, as nearly all the
oil will have drained away from the engine’s
top end components and bearing surfaces.
While this is only to be expected, care mustbe taken not to damage the engine under
these circumstances - avoid high speed
running until all the tappets are refilled with oil
and operating normally. With the vehicle
stationary, hold the engine at no more than a
fast idle speed (maximum 2000 to 2500 rpm)
for 10 to 15 seconds, or until the noise
ceases. Do not run the engine at more than
3000 rpm until the tappets are fully recharged
with oil and the noise has ceased.
If the valve components are thought to be
noisy, or if a light rattle persists from the top
end after the engine has warmed up to
normal operating temperature, take the
vehicle to a Ford dealer for expert advice.
Depending on the mileage covered and the
usage to which each vehicle has been put,
some vehicles may be noisier than others;
only a good mechanic experienced in these
engines can tell if the noise level is typical for
the vehicle’s mileage, or if a genuine fault
exists. If any tappet’s operation is faulty, it
must be renewed (Section 13).
The following major repair operations can
be accomplished without removing the
engine from the vehicle. However, owners
should note that any operation involving the
removal of the sump requires careful
forethought, depending on the level of skill
and the tools and facilities available; refer to
the relevant text for details.
(a) Compression pressure - testing.
(b) Cylinder head cover - removal and
refitting.
(c) Timing belt covers - removal and refitting.
(d) Timing belt - renewal.
(e) Timing belt tensioner and toothed pulleys
- removal and refitting.
(f) Camshaft oil seals - renewal.
(g) Camshafts and hydraulic tappets -
removal and refitting.
(h) Cylinder head - removal, overhaul and
refitting.
(i) Cylinder head and pistons -
decarbonising.
(j) Sump - removal and refitting.
(k) Crankshaft oil seals - renewal.
(l) Oil pump - removal and refitting.
(m) Piston/connecting rod assemblies -
removal and refitting (but see note below).
(n) Flywheel/driveplate - removal and
refitting.
(o) Engine/transmission mountings - removal
and refitting.
Clean the engine compartment and the
exterior of the engine with some type of
degreaser before any work is done. It will
make the job easier, and will help to keep dirt
out of the internal areas of the engine.
Depending on the components involved, it
may be helpful to remove the bonnet, to
improve access to the engine as repairs are
performed (refer to Chapter 11 if necessary).Cover the wings to prevent damage to the
paint; special covers are available, but an old
bedspread or blanket will also work.
If vacuum, exhaust, oil or coolant leaks
develop, indicating a need for component/
gasket or seal replacement, the repairs can
generally be made with the engine in the
vehicle. The intake and exhaust manifold
gaskets, sump gasket, crankshaft oil seals
and cylinder head gasket are all accessible
with the engine in place.
Exterior components such as the intake
and exhaust manifolds, the sump, the oil
pump, the water pump, the starter motor, the
alternator and the fuel system components
can be removed for repair with the engine in
place.
Since the cylinder head can be removed
without lifting out the engine, camshaft and
valve component servicing can also be
accomplished with the engine in the vehicle,
as can renewal of the timing belt and toothed
pulleys.
In extreme cases caused by a lack of
necessary equipment, repair or renewal of
piston rings, pistons, connecting rods and
big-end bearings is possible with the engine
in the vehicle. However, this practice is not
recommended, because of the cleaning and
preparation work that must be done to the
components involved, and because of the
amount of preliminary dismantling work
required - these operations are therefore
covered in Part B of this Chapter.
1When engine performance is down, or if
misfiring occurs which cannot be attributed to
the ignition or fuel systems, a compression
test can provide diagnostic clues as to the
engine’s condition. If the test is performed
regularly, it can give warning of trouble before
any other symptoms become apparent.
2The engine must be fully warmed-up to
normal operating temperature, the oil level
must be correct, the battery must be fully
charged, and the spark plugs must be
removed. The aid of an assistant will be
required also.
3Disable the ignition system by unplugging
the ignition coil’s electrical connector, and
remove fuse 14 to disconnect the fuel pump.
4Fit a compression tester to the No 1
cylinder spark plug hole - the type of tester
which screws into the plug thread is to be
preferred.
5Have the assistant hold the throttle wide
open and crank the engine on the starter
motor; after one or two revolutions, the
compression pressure should build up to a
maximum figure, and then stabilise. Record
the highest reading obtained.
6Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders,
recording the pressure developed in each.
7At the time of writing, no compression
3 Compression test -
description and interpretation
2 Repair operations possible with
the engine in the vehicle
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•5
2A
procarmanuals.com
Page 46 of 279

specifications were available from Ford, but a
typical reading would be in excess of 12 bars.
All cylinders should produce very similar
pressures; any difference greater than 10%
indicates the existence of a fault. Note that the
compression should build up quickly in a
healthy engine; low compression on the first
stroke, followed by gradually-increasing
pressure on successive strokes, indicates worn
piston rings. A low compression reading on the
first stroke, which does not build up during
successive strokes, indicates leaking valves or a
blown head gasket (a cracked head could also
be the cause). Deposits on the undersides of the
valve heads can also cause low compression.
8If the pressure in any cylinder is
considerably lower than the others, introduce
a teaspoonful of clean oil into that cylinder
through its spark plug hole, and repeat the
test.
9If the addition of oil temporarily improves
the compression pressure, this indicates that
bore or piston wear is responsible for the
pressure loss. No improvement suggests that
leaking or burnt valves, or a blown head
gasket, may be to blame.
10A low reading from two adjacent cylinders
is almost certainly due to the head gasket
having blown between them; the presence of
coolant in the engine oil will confirm this.
11If one cylinder is about 20 percent lower
than the others and the engine has a slightly
rough idle, a worn camshaft lobe or faulty
hydraulic tappet could be the cause.
12If the compression is unusually high, the
combustion chambers are probably coated
with carbon deposits. If this is the case, the
cylinder head should be removed and
decarbonised.
13On completion of the test, refit the spark
plugs, then reconnect the ignition system and
fuel pump.
General
1Top Dead Centre (TDC) is the highest point
in its travel up-and-down its cylinder bore
that each piston reaches as the crankshaftrotates. While each piston reaches TDC both
at the top of the compression stroke and
again at the top of the exhaust stroke, for the
purpose of timing the engine, TDC refers to
the piston position (usually No 1 piston) at the
top of its compression stroke.
2It is useful for several servicing procedures
to be able to position the engine at TDC.
3No 1 piston and cylinder are at the right-
hand (timing belt) end of the engine (right-
and left-hand are always quoted as seen from
the driver’s seat). Note that the crankshaft
rotates clockwise when viewed from the
right-hand side of the vehicle.
Locating TDC
4Remove all the spark plugs (Chapter 1).
5Disconnect both battery leads - see
Chapter 5, Section 1 - unless the starter
motor is to be used to turn the engine.
6Apply the handbrake and ensure that the
transmission is in neutral, then jack up the
front right-hand side of the vehicle and
support on an axle stand. Remove the
roadwheel.
7Remove the auxiliary drivebelt cover (see
Chapter 1) to expose the crankshaft pulley
and timing marks.
8It is best to rotate the crankshaft using a
spanner applied to the crankshaft pulley bolt;
however, it is possible also to use the starter
motor (switched on either by an assistant
using the ignition key, or by using a remote
starter switch) to bring the engine close to
TDC, then finish with a spanner. If the starter
is used, be sure to disconnect the battery
leads immediately it is no longer required.
9Note the two pairs of notches in the inner
and outer rims of the crankshaft pulley. In the
normal direction of crankshaft rotation
(clockwise, seen from the right-hand side of the
vehicle) the first pair of notches are irrelevant to
the vehicles covered in this manual, while the
second pair indicate TDC when aligned with
the rear edge of the raised mark on the sump.
Rotate the crankshaft clockwise until the
second pair of notches align with the edge of
the sump mark; use a straight edge extended
out from the sump if greater accuracy is
required (see illustrations).10Nos 1 and 4 cylinders are now at TDC,
one of them on the compression stroke.
Remove the oil filler cap; if No 4 cylinder
exhaust cam lobe is pointing to the rear of the
vehicle and slightly downwards, it is No 1
cylinder that is correctly positioned. If the
lobe is pointing horizontally forwards, rotate
the crankshaft one full turn (360°) clockwise
until the pulley notches align again, and the
lobe is pointing to the rear and slightly down.
No 1 cylinder will then be at TDC on the
compression stroke.
11Once No 1 cylinder has been positioned
at TDC on the compression stroke, TDC for
any of the other cylinders can then be located
by rotating the crankshaft clockwise 180° at a
time and following the firing order (see
Specifications).
12An alternative method of locating TDC is
to remove the cylinder head cover (see
Section 5) and to rotate the crankshaft
(clockwise, as described in paragraph 8
above) until the inlet valves for the cylinder
concerned have opened and just closed
again. Insert a length of wooden dowel
(approximately 150 mm/6 in long) or similar
into the spark plug hole until it rests on the
piston crown, and slowly further rotate the
crankshaft (taking care not to allow the dowel
to be trapped in the cylinder) until the dowel
stops rising - the piston is now at the top of
its compression stroke, and the dowel can be
removed.
13There is a “dead” area around TDC (as
the piston stops rising, pauses and then
begins to descend) which makes difficult the
exact location of TDC by this method; if
accuracy is required, either establish carefully
the exact mid-point of the dead area, or refer
to the timing marks (paragraph 9 above).
1Unplug the two electrical connectors and
disconnect the vacuum hose (where fitted),
then remove the air cleaner assembly cover
with the air mass meter, the resonator and the
plenum chamber (see Chapter 4).
2Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
5 Cylinder head cover-
removal and refitting
4 Top Dead Centre (TDC) for
No 1 piston - locating
2A•6 In-car engine repair procedures
4.9A Do not use crankshaft pulley’s first
pair of notches “A” - align second pair of
notches “B” with raised rib on sump “C” . . .4.9B . . . using a straight edge extended
out from the sump (arrowed) if greater
accuracy is required5.4 Disconnecting crankcase breather
hose from cylinder head cover union
procarmanuals.com
Page 47 of 279

throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4.
Where fitted, disconnect also the cruise
control actuator cable (see Chapter 12).
3Remove the timing belt upper cover (see
Section 9).
4Disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the cylinder head cover union (see
illustration).
5Unplug the HT leads from the spark plugs
and withdraw them, unclipping the leads from
the cover.
6Working progressively, unscrew the
cylinder head cover retaining bolts, noting the
spacer sleeve and rubber seal at each, then
withdraw the cover (see illustration).
7Discard the cover gasket; this mustbe
renewed whenever it is disturbed. Check that
the sealing faces are undamaged, and that
the rubber seal at each retaining bolt is
serviceable; renew any worn or damaged
seals.
8On refitting, clean the cover and cylinder
head gasket faces carefully, then fit a new
gasket to the cover, ensuring that it locates
correctly in the cover grooves (see
illustration).
9Refit the cover to the cylinder head, then
insert the rubber seal and spacer sleeve at
each bolt location (see illustration). Start all
bolts finger-tight, ensuring that the gasket
remains seated in its groove.
10Working in a diagonal sequence from the
centre outwards, and in two stages (see
Specifications), tighten the cover bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
11Refit the HT leads, clipping them into
place so that they are correctly routed; each
is numbered, and can also be identified by
the numbering on its respective coil terminal.
12Reconnect the crankcase breather hose,
and refit the timing belt upper cover.
Reconnect and adjust the accelerator cable,
then refit the air cleaner assembly cover with
the air mass meter, the resonator and the
plenum chamber (see Chapter 4).
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when disconnecting
any part of the fuel system. Don’t smoke,
or allow naked flames or bare light bulbs in
or near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas appliance
(such as a clothes dryer or water heater) is
installed. If you spill petrol on your skin,
rinse it off immediately. Have a fire
extinguisher rated for petrol fires handy,
and know how to use it.
Removal
1Park the vehicle on firm, level ground,
apply the handbrake firmly, and slacken the
nuts securing the right-hand front roadwheel.
2Relieve the fuel system pressure (see
Chapter 4).3Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1.
4Unplugging the two electrical connectors
and disconnecting the vacuum hose (where
fitted), remove the air cleaner assembly cover
with the air mass meter, the resonator and the
plenum chamber (see Chapter 4).
5Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4 -
where fitted, disconnect also the cruise
control actuator cable (see Chapter 12).
6Disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the cylinder head cover union.
7Unbolt the upper part of the exhaust
manifold heat shield; unclip the coolant hose
to allow it to be withdrawn. Slacken the
sleeve nut securing the EGR pipe to the
manifold, remove the two screws securing
the pipe to the ignition coil bracket, then
unscrew the sleeve nut securing the pipe to
the EGR valve - see Chapter 6 for full details if
required.
8Remove the two screws securing the wiring
“rail” to the top of the manifold - this is simply
so that it can be moved as required to reach
the manifold bolts. Unplug their electrical
connectors to disconnect the camshaft
position sensor and the coolant temperature
sensor, then unclip the wiring from the ignition
coil bracket, and secure it to the manifold.
9Remove the three screws securing the
wiring “rail” to the rear of the manifold.
Releasing its wire clip, unplug the large
electrical connector (next to the fuel pressure
regulator) to disconnect the wiring of themanifold components from the engine wiring
loom.
10Marking or labelling them as they are
unplugged, disconnect the vacuum hoses as
follows:
(a) One from the rear of the throttle housing
(only the one hose - there is no need to
disconnect the second hose running to
the fuel pressure regulator).
(b) One from the union on the manifold’s left-
hand end.
(c) The braking system vacuum servo unit
hose (see Chapter 9 for details).
(d) One from the Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve.
11Equalise the pressure in the fuel tank by
removing the filler cap, then undo the fuel
feed and return lines connecting the engine to
the chassis (see Chapter 4). Plug or cap all
open fittings.
12Unbolt the power steering high-pressure
pipe and the earth lead from the cylinder
head rear support plate/engine lifting eye,
then unscrew the bolt securing the support
plate/lifting eye to the alternator mounting
bracket.
13Unscrew the six nuts securing the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting
bracket, then withdraw the bracket.
14Remove the alternator (see Chapter 5).
15Unbolt the alternator mounting bracket
from the rear of the cylinder block and
withdraw it, together with the cylinder head
rear support plate/engine lifting eye (see
illustration).
6 Inlet manifold -
removal and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•7
2A
5.8 Ensure gasket is located correctly in
cover groove5.6 Removing cylinder head cover
5.9 Ensure rubber seal is fitted to each
cover bolt spacer, as shown6.15 Alternator mounting bracket must be
unbolted from rear of cylinder block to
permit access to inlet manifold nut
procarmanuals.com
Page 51 of 279
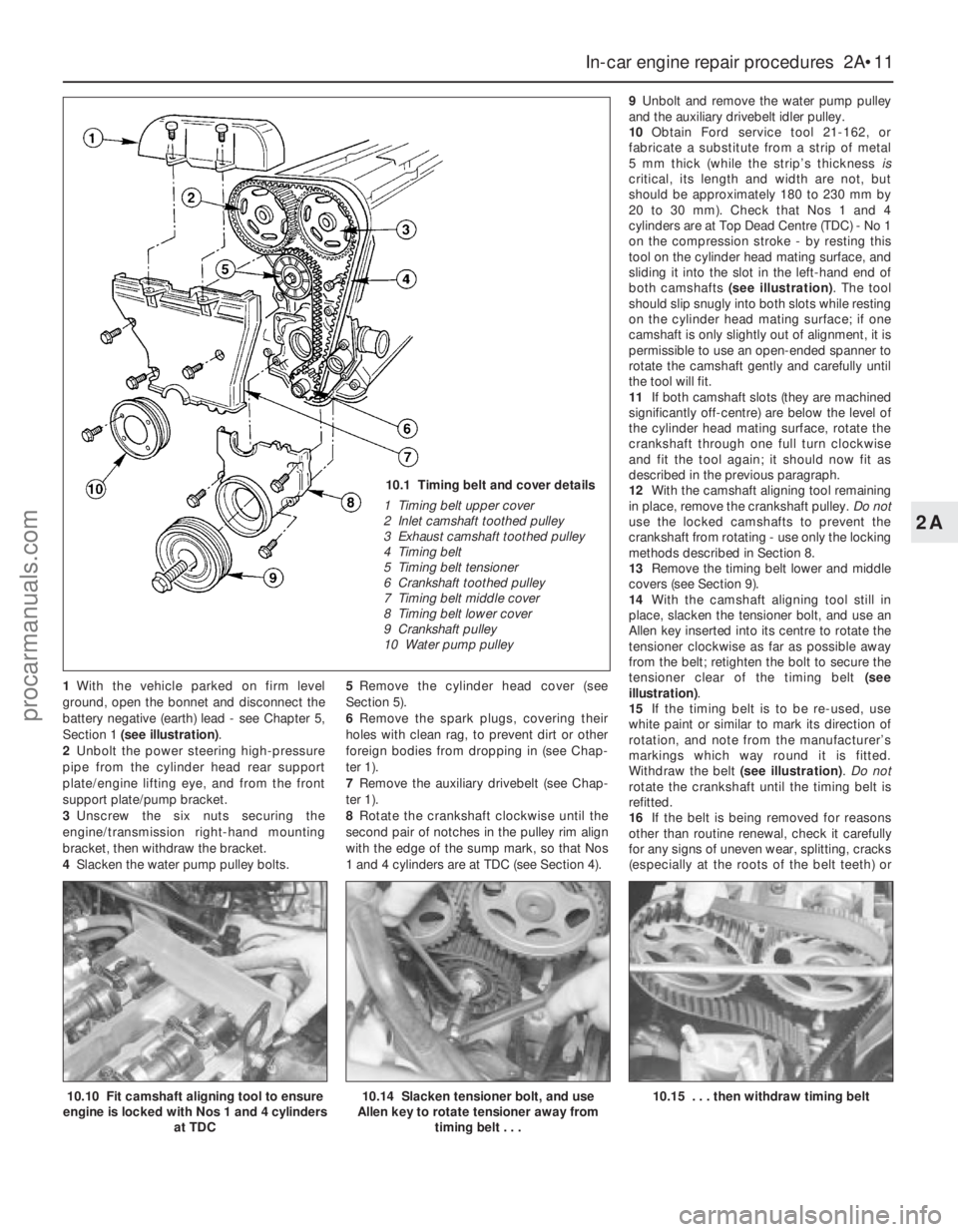
1With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1 (see illustration).
2Unbolt the power steering high-pressure
pipe from the cylinder head rear support
plate/engine lifting eye, and from the front
support plate/pump bracket.
3Unscrew the six nuts securing the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting
bracket, then withdraw the bracket.
4Slacken the water pump pulley bolts.5Remove the cylinder head cover (see
Section 5).
6Remove the spark plugs, covering their
holes with clean rag, to prevent dirt or other
foreign bodies from dropping in (see Chap-
ter 1).
7Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see Chap-
ter 1).
8Rotate the crankshaft clockwise until the
second pair of notches in the pulley rim align
with the edge of the sump mark, so that Nos
1 and 4 cylinders are at TDC (see Section 4).9Unbolt and remove the water pump pulley
and the auxiliary drivebelt idler pulley.
10Obtain Ford service tool 21-162, or
fabricate a substitute from a strip of metal
5 mm thick (while the strip’s thickness is
critical, its length and width are not, but
should be approximately 180 to 230 mm by
20 to 30 mm). Check that Nos 1 and 4
cylinders are at Top Dead Centre (TDC) - No 1
on the compression stroke - by resting this
tool on the cylinder head mating surface, and
sliding it into the slot in the left-hand end of
both camshafts (see illustration). The tool
should slip snugly into both slots while resting
on the cylinder head mating surface; if one
camshaft is only slightly out of alignment, it is
permissible to use an open-ended spanner to
rotate the camshaft gently and carefully until
the tool will fit.
11If both camshaft slots (they are machined
significantly off-centre) are below the level of
the cylinder head mating surface, rotate the
crankshaft through one full turn clockwise
and fit the tool again; it should now fit as
described in the previous paragraph.
12With the camshaft aligning tool remaining
in place, remove the crankshaft pulley. Do not
use the locked camshafts to prevent the
crankshaft from rotating - use only the locking
methods described in Section 8.
13Remove the timing belt lower and middle
covers (see Section 9).
14With the camshaft aligning tool still in
place, slacken the tensioner bolt, and use an
Allen key inserted into its centre to rotate the
tensioner clockwise as far as possible away
from the belt; retighten the bolt to secure the
tensioner clear of the timing belt (see
illustration).
15If the timing belt is to be re-used, use
white paint or similar to mark its direction of
rotation, and note from the manufacturer’s
markings which way round it is fitted.
Withdraw the belt (see illustration). Do not
rotate the crankshaft until the timing belt is
refitted.
16If the belt is being removed for reasons
other than routine renewal, check it carefully
for any signs of uneven wear, splitting, cracks
(especially at the roots of the belt teeth) or
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•11
2A
10.10 Fit camshaft aligning tool to ensure
engine is locked with Nos 1 and 4 cylinders
at TDC10.14 Slacken tensioner bolt, and use
Allen key to rotate tensioner away from
timing belt . . .10.15 . . . then withdraw timing belt
10.1 Timing belt and cover details
1 Timing belt upper cover
2 Inlet camshaft toothed pulley
3 Exhaust camshaft toothed pulley
4 Timing belt
5 Timing belt tensioner
6 Crankshaft toothed pulley
7 Timing belt middle cover
8 Timing belt lower cover
9 Crankshaft pulley
10 Water pump pulley
procarmanuals.com
Page 52 of 279

contamination with oil or coolant. Renew the
belt if there is the slightest doubt about its
condition. As a safety measure, the belt must
be renewed as a matter of course at the
intervals given in Chapter 1; if its history is
unknown, the belt should be renewed
irrespective of its apparent condition
whenever the engine is overhauled. Similarly,
check the tensioner spring (where fitted),
renewing it if there is any doubt about its
condition. Check also the toothed pulleys for
signs of wear or damage, and ensure that the
tensioner and guide pulleys rotate smoothly
on their bearings; renew any worn or
damaged components. If signs of oil or
coolant contamination are found, trace the
source of the leak and rectify it, then wash
down the engine timing belt area and related
components, to remove all traces of oil or
coolant.
17On reassembly, temporarily refit the
crankshaft pulley, to check that the pulley
notches and sump rib are aligned as
described in paragraph 8 above, then ensure
that both camshafts are aligned at TDC by
the special tool (paragraph 10). If the engine
is being reassembled after major dismantling,
both camshaft toothed pulleys should be free
to rotate on their respective camshafts; if the
timing belt alone is being renewed, both
pulleys should still be securely fastened.
18A holding tool will be required to prevent
the camshaft toothed pulleys from rotating
while their bolts are slackened and
retightened; either obtain Ford service tool15-030A, or fabricate a substitute as follows.
Find two lengths of steel strip, one
approximately 600 mm long and the other
about 200 mm, and three bolts with nuts and
washers; one nut and bolt forming the pivot of
a forked tool, with the remaining nuts and
bolts at the tips of the “forks”, to engage with
the pulley spokes as shown in the
accompanying illustrations. Note:Do not use
the camshaft aligning tool (whether genuine
Ford or not) to prevent rotation while the
camshaft toothed pulley bolts are slackened
or tightened; the risk of damage to the
camshaft concerned and to the cylinder head
is far too great. Use only a forked holding tool
applied directly to the pulleys, as described.
19If it is being fitted for the first time, screw
the timing belt tensioner spring retaining pin
into the cylinder head, tightening it to the
specified torque wrench setting. Unbolt the
tensioner, hook the spring on to the pin and
the tensioner backplate, then refit the
tensioner, engaging its backplate on the
locating peg (see illustrations).
20In all cases, slacken the tensioner bolt (if
necessary), and use an Allen key inserted into
its centre to rotate the tensioner clockwise as
far as possible against spring tension, then
retighten the bolt to secure the tensioner (see
illustration).
21Fit the timing belt; if the original is being
refitted, ensure that the marks and notes
made on removal are followed, so that the
belt is refitted the same way round, and to run
in the same direction. Starting at thecrankshaft toothed pulley, work anti-
clockwise around the camshaft toothed
pulleys and tensioner, finishing off at the rear
guide pulley. The front run, between the
crankshaft and the exhaust camshaft toothed
pulleys, mustbe kept taut, without altering
the position either of the crankshaft or of the
camshaft(s) - if necessary, the position of the
camshaft toothed pulleys can be altered by
rotating each on its camshaft (which remains
fixed by the aligning tool). Where the pulley is
still fastened, use the holding tool described
in paragraph 18 above to prevent the pulley
from rotating while its retaining bolt is
slackened - the pulley can then be rotated on
the camshaft until the belt will slip into place;
retighten the pulley bolt.
22When the belt is in place, slacken the
tensioner bolt gently until the spring pulls the
tensioner against the belt; the tensioner
should be retained correctly against the
timing belt inner shield and cylinder head, but
must be just free to respond to changes in
belt tension (see illustration).
23Tighten both camshaft toothed pulley
bolts (or check that they are tight, as
applicable) and remove the camshaft aligning
tool. Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley,
and rotate the crankshaft through two full
turns clockwise to settle and tension the
timing belt, returning the crankshaft (pulley
notches) to the position described in
paragraph 8 above. Refit the camshaft
aligning tool; it should slip into place as
described in paragraph 10. If all is well,
proceed to paragraph 26 below.
24If one camshaft is only just out of line, fit
the forked holding tool to its toothed pulley,
adjust its position as required, and check that
any slack created has been taken up by the
tensioner; rotate the crankshaft through two
further turns clockwise, and refit the camshaft
aligning tool to check that it now fits as it
should. If all is well, proceed to paragraph 26
below.
25If either camshaft is significantly out of
line, use the holding tool described in
paragraph 18 above to prevent its pulley from
rotating while its retaining bolt is slackened -
the camshaft can then be rotated (gently and
carefully, using an open-ended spanner) until
2A•12 In-car engine repair procedures
10.19A Fitting tensioner spring retaining
pin10.19B Hook spring onto tensioner and
refit as shown - engage tensioner
backplate on locating peg (arrowed) . . .10.20 . . . then use Allen key to position
tensioner so that timing belt can be refitted
10.22 Slacken tensioner bolt to give initial
belt tension10.25 Using forked holding tool while
camshaft toothed pulley bolt is tightened
procarmanuals.com
Page 58 of 279

14Unscrew the two nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold (Chapter 4); disconnect the oxygen
sensor wiring, so that it is not strained by the
weight of the exhaust system.
15Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see
Chapter 1).
16Support the weight of the
engine/transmission using a trolley jack, with
a wooden spacer to prevent damage to the
sump.
17Unscrew the six nuts securing the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting
bracket, then withdraw the bracket. Unbolt
the auxiliary drivebelt’s idler pulley (see
illustration).
18Unbolt the cylinder head front and rear
support plates (see illustrations).
19Remove the timing belt and both
camshafts (see Sections 10 and 13); if the
cylinder head is to be dismantled, withdraw
the hydraulic tappets.
20Remove the timing belt inner shield (see
Section 9).
21Working in the reverseof the sequence
shown in illustration 14.32C, slacken the ten
cylinder head bolts progressively and by one
turn at a time; a Torx key (TX 55 size) will be
required. Remove each bolt in turn, and
ensure that new replacements are obtained
for reassembly; these bolts are subjected to
severe stresses and so must be renewed,
regardless of their apparent condition,
whenever they are disturbed.22Lift the cylinder head away; use
assistance if possible, as it is a heavy
assembly (see illustration). Remove the
gasket, noting the two dowels, and discard it.
Refitting
23The mating faces of the cylinder head and
cylinder block must be perfectly clean before
refitting the head. Use a hard plastic or wood
scraper to remove all traces of gasket and
carbon; also clean the piston crowns. Take
particular care, as the soft aluminium alloy is
easily damaged. Also, make sure that the
carbon is not allowed to enter the oil and
water passages - this is particularly important
for the lubrication system, as carbon could
block the oil supply to any of the engine’s
components. Using adhesive tape and paper,
seal the water, oil and bolt holes in the
cylinder block. Clean all the pistons in the
same way.24Check the mating surfaces of the cylinder
block and the cylinder head for nicks, deep
scratches and other damage. If slight, they
may be removed carefully with a file, but if
excessive, machining may be the only
alternative to renewal.
25If warpage of the cylinder head gasket
surface is suspected, use a straight edge to
check it for distortion. Refer to Part B of this
Chapter, Section 7, if necessary.
26Wipe clean the mating surfaces of the
cylinder head and cylinder block. Check that
the two locating dowels are in position in the
cylinder block, and that all cylinder head bolt
holes are free from oil.
27Position a new gasket over the dowels on
the cylinder block surface, so that the
“TOP/OBEN” mark is uppermost, and the
tooth (or teeth, according to engine size)
protruding from one edge point to the front of
the vehicle (see illustration).
28Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley,
and rotate the crankshaft anti-clockwise so
that No 1 cylinder’s piston is lowered to
approximately 20 mm before TDC, thus
avoiding any risk of valve/piston contact and
damage during reassembly.
29As the cylinder head is such a heavy and
awkward assembly to refit with manifolds, it is
helpful to make up a pair of guide studs from
two 10 mm (thread size) studs approximately
90 mm long, with a screwdriver slot cut in one
end - two old cylinder head bolts with their
heads cut off would make a good starting
point. Screw these guide studs, screwdriver
slot upwards to permit removal, into the bolt
holes at diagonally-opposite corners of the
cylinder block surface (or into those where
the locating dowels are fitted, as shown);
ensure that approximately 70 mm of stud
protrudes above the gasket.
30Refit the cylinder head, sliding it down the
guide studs (if used) and locating it on the
dowels (see illustration). Unscrew the guide
studs (if used) when the head is in place.
31Fit the new cylinder head bolts dry (do not
oiltheir threads); carefully enter each into its
hole and screw it in, by hand only, until finger-
tight.
32Working progressively and in the
sequence shown, use first a torque wrench,
2A•18 In-car engine repair procedures
14.17 Unbolt auxiliary drivebelt idler pulley14 18A Remove cylinder head front . . .14.18B . . . and rear support plates
14.22 Using an engine hoist to lift off the
cylinder head complete with manifolds
14.27 Ensuring protruding tooth (or teeth)
“A” are at front and marking “B” is
upwards, locate new cylinder head gasket
on dowels “C”
To prevent carbon entering
the gap between the pistons
and bores, smear a little
grease in the gap. After
cleaning each piston, use a small brush
to remove all traces of grease and
carbon from the gap, then wipe away
the remainder with a clean rag.
procarmanuals.com
Page 60 of 279

additional lifting eyes where required (see
illustration). Remove completely the
engine/transmission front mounting, unscrew
the rear mounting’s centre bolt, and unbolt
the left-hand mounting from the body.
Unscrew the six nuts securing the right-hand
mounting bracket, and withdraw the bracket.
13Being careful to watch the wiring, coolant
hoses, fluid cooler pipes or gearchange
linkage and transmission support rods (where
appropriate), and the radiator electric cooling
fan, to ensure that nothing is trapped,
stretched or damaged, lift the
engine/transmission unit by 2 to 3 inches and
support it securely.
14Progressively unscrew the sump retaining
bolts. Break the joint by striking the sump
with the palm of the hand, then lower the
sump and withdraw it with the
engine/transmission lower adaptor plate; note
the presence of any shims between the sump
and transmission.
15Remove and discard the sump gasket;
this must be renewed as a matter of course
whenever it is disturbed.
16While the sump is removed, take the
opportunity to remove the oil pump pick-up/
strainer pipe and to clean it (see Section 16).
Refitting
17On reassembly, thoroughly clean and
degrease the mating surfaces of the cylinder
block/crankcase and sump, then use a cleanrag to wipe out the sump and the engine’s
interior. If the oil pump pick-up/strainer pipe
was removed, fit a new gasket and refit the
pipe, tightening its screws to the specified
torque wrench setting. Fit the new gasket to
the sump mating surface so that the gasket
fits into the sump groove (see illustration).
18If the sump is being refitted with the
engine/transmission still connected and in the
vehicle, proceed as follows:
(a) Check that the mating surfaces of the
sump, the cylinder block/crankcase and
the transmission are absolutely clean and
flat. Any shims found on removal of the
sump must be refitted in their original
locations.
(b) Apply a thin film of suitable sealant (Ford
recommend Hylosil 102) to the junctions
of the cylinder block/crankcase with the
oil pump and the crankshaft left-hand oil
seal carrier. Without delay - the sump
bolts must be fully tightened within 10 to
20 minutes of applying the sealant - offer
up the sump and engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate, and refit the bolts,
tightening them lightly at first (see
illustration).
(c) Ensuring that the engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate is correctly located,
firmly press the sump against the
transmission, and tighten the
transmission-to-sump (ie, engine) bolts to
the specified torque wrench setting.(d) Without disturbing the position of the
sump, and working in a diagonal
sequence from the centre outwards,
tighten the sump bolts to the specified
torque wrench setting.
(e) Proceed to paragraph 20.
19If the sump is being refitted with the
engine and transmission separated (in or out
of the vehicle), proceed as follows:
(a) Apply a thin film of suitable sealant (Ford
recommend Hylosil 102) to the junctions
of the cylinder block/crankcase with the
oil pump and the crankshaft left-hand oil
seal carrier (see illustration). Without
delay - the sump bolts must be fully
tightened within 10 to 20 minutes of
applying the sealant - offer up the sump
to the cylinder block/crankcase, and
insert the sump bolts, tightening them
lightly at first.
(b) Using a suitable straight edge to check
alignment across the flat-machined faces
of each, move the sump as necessary so
that its left-hand face - including any
shims found on removal - is flush with
that of the cylinder block/crankcase (see
illustration). Without disturbing the
position of the sump, and working in a
diagonal sequence from the centre
outwards, tighten the sump bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(c) Check again that both faces are flush
before proceeding; if necessary, unbolt
the sump again, clean the mating
surfaces, and repeat the full procedure to
ensure that the sump is correctly aligned.
(d) If it is not possible to achieve exact
alignment by moving the sump, shims are
available in thicknesses of 0.25 mm
(colour-coded yellow) or 0.50 mm (colour-
coded black) to eliminate the discrepancy
(see illustration).
20The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following points.
(a) Tighten all fasteners to the torque wrench
settings specified.
(b) Always renew any self-locking nuts
disturbed on removal.
(c) Lower the engine/transmission unit into
place, and reassemble the rear, left-hand
2A•20 In-car engine repair procedures
15.17 Ensure gasket is located correctly in
sump groove15.18 Engine/transmission lower adaptor
plate (arrowed) must be refitted with sump15.19A Apply sealant (arrowed) as
directed when refitting sump
15.19B Checking alignment of sump with
cylinder block/crankcase15.19C Sump-to-cylinder block/crankcase
alignment shims
1 Fitting points on sump 2 Shim
procarmanuals.com
Page 61 of 279
and right-hand mountings. Do not yet
release the hoist; the weight of the
engine/transmission unit must not be
taken by the mountings until all are
correctly aligned.
(d) Fitting the Ford service tool in place of the
front mounting, tighten the
engine/transmission mounting fasteners
to their specified torque wrench settings,
and in the sequence described in Part B
of this Chapter, Section 4, paragraphs 49
and 50.
(e) Refill the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
(f) Refill the engine with oil, remembering
that you are advised to fit a new filter (see
Chapter 1).
(g) Check for signs of oil or coolant leaks
once the engine has been restarted and
warmed-up to normal operating
temperature.
Removal
Note:While this task is theoretically possible
when the engine is in place in the vehicle, in
practice, it requires so much preliminary
dismantling, and is so difficult to carry out due
to the restricted access, that owners are
advised to remove the engine from the vehicle
first. Note, however, that the oil pumppressure relief valve can be removed with the
engine in situ - see paragraph 8.
In addition to the new pump gasket and
other replacement parts required, read
through Section 15, and ensure that the
necessary tools and facilities are available.
1Remove the timing belt (see Section 10).
2Withdraw the crankshaft toothed pulley
and the thrustwasher behind it, noting which
way round the thrustwasher is fitted (see
Section 11).
3Remove the sump (see Section 15).
4Undo the screws securing the oil pump
pick-up/strainer pipe to the pump, then
unscrew the nut and withdraw the oil pump
pick-up/strainer pipe. Discard the gasket.
5Unbolt the pump from the cylinder
block/crankcase (see illustration). Withdraw
and discard the gasket, and remove the
crankshaft right-hand oil seal. Thoroughly
clean and degrease all components,
particularly the mating surfaces of the pump,
the sump, and the cylinder block/crankcase.
Inspection
6Unscrew the Torx screws, and remove the
pump cover plate; noting any identification
marks on the rotors, withdraw the rotors (see
illustration).
7Inspect the rotors for obvious signs of wear
or damage, and renew if necessary; if either
rotor, the pump body, or its cover plate are
scored or damaged, the complete oil pump
assembly must be renewed.
8The oil pressure relief valve can bedismantled, if required, without disturbing the
pump. With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, apply the handbrake securely and
raise its front end, supporting it securely on
axle stands. Remove the front right-hand
roadwheel and auxiliary drivebelt cover (see
Chapter 1) to provide access to the valve.
9Unscrew the threaded plug, and recover
the valve spring and plunger (see
illustrations). If the plug’s sealing O-ring is
worn or damaged, a new one must be
obtained, to be fitted on reassembly.
10Reassembly is the reverse of the
dismantling procedure; ensure the spring and
valve are refitted the correct way round, and
tighten the threaded plug securely.
Refitting
11The oil pump must be primed on
installation, by pouring clean engine oil into it,
and rotating its inner rotor a few turns.
12Using grease to stick the new gasket in
place on the cylinder block/crankcase, and
rotating the pump’s inner rotor to align with
the flats on the crankshaft, refit the pump and
insert the bolts, tightening them lightly at first
(see illustration).
13Using a suitable straight edge and feeler
gauges, check that the pump is both centred
exactlyaround the crankshaft, and aligned
squarely so that its (sump) mating surface is
exactly the same amount - between 0.3 and
0.8 mm - below that of the cylinder block/
crankcase on each side of the crankshaft
(see illustration). Being careful not to disturb
16 Oil pump - removal,
inspection and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•21
2A
16.9B . . . to withdraw oil pressure relief
valve spring and plunger16.12 Use new gasket when refitting oil
pump16.13 Check the oil pump is positioned
correctly
16.5 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to remove
oil pump16.6 Withdrawing oil pump inner rotor16.9A Unscrew threaded plug - seen
through right-hand wheel arch . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 62 of 279

the gasket, move the pump into the correct
position, and tighten its bolts to the specified
torque wrench setting.
14Check that the pump is correctly located;
if necessary, unbolt it again, and repeat the
full procedure to ensure that the pump is
correctly aligned.
15Fit a new crankshaft right-hand oil seal
(see Section 20).
16Using grease to stick the gasket in place
on the pump, refit the pick-up/strainer pipe,
tightening its screws and nut to their specified
torque wrench settings (see illustration).
17The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, referring to
the relevant text for details where required.
1Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
Disconnect the coolant hoses from the oil
cooler.
2Unscrew the oil filter (see Chapter 1) -
catch any escaping oil in a drip tray.
3Unscrew the filter adaptor from the oil
pump, and withdraw the oil cooler; note how
its unions are aligned, and be prepared for oil
loss from the cooler.
4Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:(a) Renew all O-rings and seals disturbed on
removal.
(b) Align the cooler’s unions as noted on
removal, and tighten the adaptor to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(c) Refill the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
(d) Refit the oil filter, then check the engine
oil level, and top-up as necessary (see
Chapter 1).
(e) Check for signs of oil or coolant leaks once
the engine has been restarted and warmed-
up to normal operating temperature.
1With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
2Raise the front of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands.
3Undo the two screws, and remove the
sensor’s cover from the front of the sump
(see illustration).
4Unplug the wiring from the sensor (see
illustration). Where necessary, unplug the
electrical connector to disconnect the sensor
wiring, and unclip the connector to release
the wiring from the vehicle.
5Unscrew the sensor, and quickly plug the
sump aperture to minimise oil loss; note the
sensor’s seal.6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; renew the sensor’s seal if it is
worn or damaged, and tighten the sensor to
the specified torque wrench setting. Check
the engine oil level, and top-up as necessary
(see Chapter 1) - check for signs of oil leaks
once the engine has been restarted and
warmed-up to normal operating temperature.
1The switch is screwed into the rear of the
cylinder block, above the right-hand
driveshaft’s support bearing (see
illustration).
2With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
3Raise the front of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands.
4Unplug the wiring from the switch, and
unscrew it; be prepared for some oil loss.
5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; apply a thin smear of suitable
sealant to the switch threads, and tighten it to
the specified torque wrench setting. Check
the engine oil level, and top-up as necessary
(see Chapter 1). Check for signs of oil leaks
once the engine has been restarted and
warmed-up to normal operating temperature.
Note:Don’t try to prise these seals out
without removing the oil pump or seal carrier -
the seals are too soft, and the amount of
space available is too small, for this to be
possible without considerable risk of damage
to the seal housing and/or the crankshaft
journal. Follow exactly the procedure given
below.
Right-hand seal
1Remove the oil pump (see Section 16).
2Drive the oil seal out of the pump from
behind (see illustration).
20 Crankshaft oil seals -
renewal
19 Oil pressure warning light
switch - removal and refitting
18 Oil level sensor-
removal and refitting
17 Oil cooler -
removal and refitting
2A•22 In-car engine repair procedures
16.16 Use new gasket when refitting oil
pick-up pipe to pump18.3 Remove screws (arrowed) to remove
oil level sensor cover . . .18.4 . . . disconnecting wiring from sensor
19.1 Oil pressure warning light switch
(arrowed) is screwed into rear of cylinder
block, above right-hand driveshaft support
bearing
20.2 Driving out crankshaft right-hand oil
seal
procarmanuals.com