light FORD MONDEO 1993 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1993, Model line: MONDEO, Model: FORD MONDEO 1993Pages: 279, PDF Size: 12.71 MB
Page 63 of 279

3Clean the seal housing and crankshaft,
polishing off any burrs or raised edges, which
may have caused the seal to fail in the first
place.
4Refit the oil pump (see Section 16). Grease
the lips and periphery of the new seal, to ease
installation.
5To fit a new seal, Ford recommend the use
of their service tool 21-093A, with the
crankshaft pulley bolt, to draw the seal into
place; an alternative can be arranged using a
socket of suitable size, with a washer to
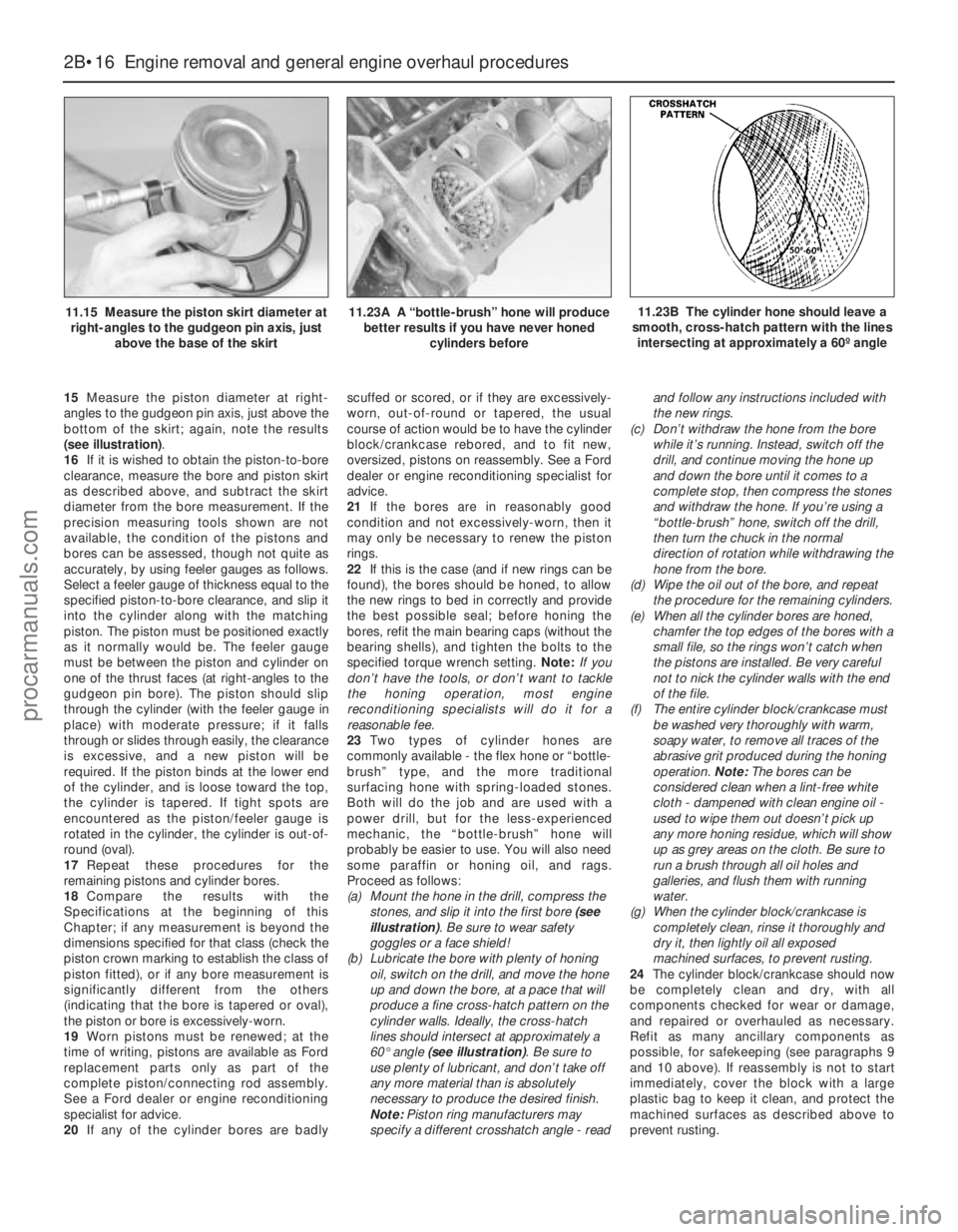
match the crankshaft pulley bolt (see
illustration).
6If such tools are not available, press the
seal squarely into place by hand; tap it in until
it is flush with the pump housing, using a soft-
faced mallet and a socket with an outside
diameter only slightly smaller than the seal’s
(see illustration). This approach requires
great care, to ensure that the seal is fitted
squarely, without distortion or damage.
7Wash off any traces of oil. The remainder of
reassembly is the reverse of the removal
procedure, referring to the relevant text for
details where required. Check for signs of oil
leakage when the engine is restarted.
Left-hand seal
8Remove the transmission (see the relevant
Part of Chapter 7).
9Where appropriate, remove the clutch
(Chapter 8).
10Unbolt the flywheel/driveplate (see
Section 21).11Remove the sump (see Section 15).
12Unbolt the oil seal carrier (see
illustration). Remove and discard its gasket.
13Supporting the carrier evenly on wooden
blocks, drive the oil seal out of the carrier
from behind (see illustration).
14Clean the seal housing and crankshaft,
polishing off any burrs or raised edges, which
may have caused the seal to fail in the first
place. Clean also the mating surfaces of the
cylinder block/crankcase and carrier, using a
scraper to remove all traces of the old gasket
- be careful not to scratch or damage the
material of either - then use a suitable solvent
to degrease them.
15Use grease to stick the new gasket in
place on the cylinder block/crankcase, then
offer up the carrier (see illustration).
16Using a suitable straight edge and feeler
gauges, check that the carrier is both centred
exactlyaround the crankshaft, and aligned
squarely so that its (sump) mating surface is
exactly the same amount - between 0.3 and
0.8 mm - below that of the cylinder
block/crankcase on each side of the
crankshaft. Being careful not to disturb the
gasket, move the carrier into the correct
position, and tighten its bolts to the specified
torque wrench setting (see illustration).
17Check that the carrier is correctly located;
if necessary, unbolt it again, and repeat the
full procedure to ensure that the carrier is
correctly aligned.
18Ford’s recommended method of seal
fitting is to use service tool 21-141, with twoflywheel bolts to draw the seal into place. If
this is not available, make up a guide from a
thin sheet of plastic or similar, lubricate the
lips of the new seal and the crankshaft
shoulder with grease, then offer up the seal,
with the guide feeding the seal’s lips over the
crankshaft shoulder (see illustration). Press
the seal evenly into its housing by hand only,
and use a soft-faced mallet gently to tap it
into place until it is flush with the surrounding
housing.
19Wipe off any surplus oil or grease; the
remainder of the reassembly procedure is the
reverse of dismantling, referring to the
relevant text for details where required.
Check for signs of oil leakage when the
engine is restarted.
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•23
2A
20.15 Use new gasket when refitting left-
hand oil seal carrier20.16 Check the oil seal carrier is correctly
positioned20.18 Using guide made from thin sheet of
plastic to slide oil seal lips over crankshaft
shoulder
20.5 Socket of correct size can be used to
replace Ford service tool, drawing new
seal into place as described20.6 If seal is tapped into place as shown,
exercise great care to prevent seal from
being damaged or distorted20.12 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to remove
crankshaft left-hand oil seal carrier . . .
20.13 . . . and ensure that carrier is
properly supported when driving out used
oil seal - note notches provided in carrier
for drift
procarmanuals.com
Page 64 of 279

Removal
1Remove the transmission (see the relevant
Part of Chapter 7). Now is a good time to
check components such as oil seals and
renew them if necessary.
2Where appropriate, remove the clutch
(Chapter 8). Now is a good time to check or
renew the clutch components and pilot
bearing.
3Use a centre-punch or paint to make
alignment marks on the flywheel/driveplate
and crankshaft, to ensure correct alignment
during refitting.
4Prevent the flywheel/driveplate from
turning by locking the ring gear teeth, or by
bolting a strap between the flywheel/
driveplate and the cylinder block/
crankcase. Slacken the bolts evenly until all
are free.
5Remove each bolt in turn, and ensure that
new replacements are obtained for
reassembly; these bolts are subjected to
severe stresses, and so must be renewed,
regardless of their apparent condition,
whenever they are disturbed.
6Noting the reinforcing plate (automatic
transmission-equipped models only),
withdraw the flywheel/driveplate; do not drop
it - it is very heavy.
Inspection
7Clean the flywheel/driveplate to remove
grease and oil. Inspect the surface for cracks,
rivet grooves, burned areas and score marks.
Light scoring can be removed with emery
cloth. Check for cracked and broken ring gear
teeth. Lay the flywheel/driveplate on a flat
surface, and use a straight edge to check for
warpage.
8Clean and inspect the mating surfaces of
the flywheel/driveplate and the crankshaft. If
the crankshaft left-hand seal is leaking, renew
it (see Section 20) before refitting the
flywheel/driveplate.
9While the flywheel/driveplate is removed,clean carefully its inboard (right-hand) face,
particularly the recesses which serve as the
reference points for the crankshaft
speed/position sensor. Clean the sensor’s tip,
and check that the sensor is securely
fastened.
Refitting
10On refitting, ensure that the
engine/transmission adaptor plate is in place
(where necessary), then fit the
flywheel/driveplate to the crankshaft so that
all bolt holes align - it will fit only one way -
check this using the marks made on removal.
Do not forget the reinforcing plate (where
fitted).
11Lock the flywheel/driveplate by the
method used on dismantling. Working in a
diagonal sequence to tighten them evenly,
and increasing to the final amount in two or
three stages, tighten the new bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting (see
illustration).
12The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, referring to
the relevant text for details where required.
General
1The engine/transmission mountings
seldom require attention, but broken or
deteriorated mountings should be renewed
immediately, or the added strain placed on
the driveline components may cause damage
or wear.
2While separate mountings may be removed
and refitted individually, if more than one is
disturbed at a time - such as if theengine/transmission unit is removed from its
mountings - they must be reassembled and
their fasteners tightened in a strict sequence.
3On reassembly, the weight of the
engine/transmission unit must not be taken
by the mountings until all are correctly
aligned. Fitting the Ford service tool in place
of the front mounting, tighten the
engine/transmission mounting fasteners to
their specified torque wrench settings, and in
the sequence described in Part B of this
Chapter, Section 4, paragraphs 49 and 50.
Inspection
4During the check, the engine/transmission
unit must be raised slightly, to remove its
weight from the mountings.
5Raise the front of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands. Position a jack under
the sump, with a large block of wood
between the jack head and the sump, then
carefully raise the engine/transmission just
enough to take the weight off the mountings.
Warning: DO NOT place any part
of your body under the engine
when it is supported only by a
jack!
6Check the mountings to see if the rubber is
cracked, hardened or separated from the
metal components. Sometimes the rubber
will split right down the centre.
7Check for relative movement between each
mounting’s brackets and the engine/
transmission or body (use a large screwdriver
or lever to attempt to move the mountings). If
movement is noted, lower the engine and
check-tighten the mounting fasteners.
Renewal
Front mounting
8Unbolt the resonator support bracket from
the engine compartment front crossmember,
slacken the two clamp screws securing the
22 Engine/transmission
mountings -
inspection and renewal
21 Flywheel/driveplate -
removal, inspection and refitting
2A•24 In-car engine repair procedures
21.11 Note method used to lock
flywheel/driveplate while (new) bolts are
tightened
22.8 Engine/transmission front mounting - manual transmission shown, automatic
equivalent similar
1 Transmission 3 Mounting 5 Mounting centre bolt
2 Mounting bracket 4 Front suspension subframe
procarmanuals.com
Page 70 of 279

safely and with relative ease, and which may
have to be hired or borrowed, includes (in
addition to the engine hoist) a heavy-duty trolley
jack, a strong pair of axle stands, some wooden
blocks, and an engine dolly (a low, wheeled
platform capable of taking the weight of the
engine/transmission, so that it can be moved
easily when on the ground). A complete set of
spanners and sockets (as described in the front
of this manual) will obviously be needed,
together with plenty of rags and cleaning
solvent for mopping-up spilled oil, coolant and
fuel. If the hoist is to be hired, make sure that
you arrange for it in advance, and perform all of
the operations possible without it beforehand.
This will save you money and time.
Plan for the vehicle to be out of use for
quite a while. A machine shop will be required
to perform some of the work which the do-it-
yourselfer can’t accomplish without special
equipment. These establishments often have
a busy schedule, so it would be a good idea
to consult them before removing the engine,
to accurately estimate the amount of time
required to rebuild or repair components that
may need work.
Always be extremely careful when removing
and installing the engine/transmission.
Serious injury can result from careless
actions. By planning ahead and taking your
time, the job (although a major task) can be
accomplished successfully.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when disconnecting
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow naked flames or bare light
bulbs in or near the work area, and don’t
work in a garage where a natural gas
appliance (such as a clothes dryer or water
heater) is installed. If you spill petrol on
your skin, rinse it off immediately. Have a
fire extinguisher rated for petrol fires
handy, and know how to use it.Note: Read through the entire Section, as well
as reading the advice in the preceding Section,
before beginning this procedure. The engine
and transmission are removed as a unit,
lowered to the ground and removed from
underneath, then separated outside the vehicle.
Removal
1Park the vehicle on firm, level ground, apply
the handbrake firmly, and slacken the nuts
securing both front roadwheels.
2Relieve the fuel system pressure (see
Chapter 4).
3Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1. For better access
the battery may be removed completely (see
Chapter 5).
4Place protective covers on the wings and
engine compartment front crossmember, then
remove the bonnet (see Chapter 11).
5Whenever you disconnect any vacuum
lines, coolant and emissions hoses, wiring
loom connectors, earth straps and fuel lines
as part of the following procedure, always
label them clearly, so that they can be
correctly reassembled.
6Unplug the two electrical connectors,disconnect the vacuum hose (where fitted)
and disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the cylinder head cover, then remove the
complete air cleaner assembly, with the air
mass meter, the resonator and the plenum
chamber (see Chapter 4).
7Equalise the pressure in the fuel tank by
removing the filler cap, then undo the fuel
feed and return lines connecting the engine to
the chassis (see Chapter 4). Plug or cap all
open fittings (see illustration).
8Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4 -
where fitted, also disconnect the cruise
control actuator cable (see Chapter 12).
Secure the cable(s) clear of the
engine/transmission.
9Releasing its wire clip, unplug the power
steering pressure switch electrical connector,
then unbolt the power steering high-pressure
pipe and the earth lead from the cylinder head
rear support plate/engine lifting eye (see
illustrations).
10Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected (see paragraph 5
above), disconnect the vacuum hoses as
follows:
4 Engine/transmission -
removal and refitting
2B•4 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
4.7 Note colour-coding of unions when
disconnecting fuel feed and return lines4.9A Unplug the power steering pressure
switch electrical connector . . .4.9B . . . unbolt the power steering high-
pressure pipe . . .
Whenever any wiring is disconnected, . . . vacuum hoses and pipes should
mark or label it as shown, to ensure be similarly marked
correct reconnection . . .
Masking tape and/or a touch-up paint applicator work well for marking items. Take
instant photos, or sketch the locations of components and brackets.
procarmanuals.com
Page 73 of 279

31Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, disconnect the driveshafts from
the transmission as follows, referring to
Chapter 8 for further details when required:
(a) Unscrew the nuts securing the right-hand
driveshaft support bearing, and withdraw
the heat shield.
(b) Pull the right-hand driveshaft out of the
transmission; be prepared to catch any
spilt oil.
(c) Secure the driveshaft clear of the
engine/transmission - remember that the
unit is to be lowered out of the vehicle -
and ensure that the inner joint is not
turned through more than 18°.
(d) Prise the left-hand driveshaft out of the
transmission - again, be prepared for oil
spillage. Secure the driveshaft clear of the
engine/transmission, and ensure that its
inner joint is not turned through more than
18°.
32Where the vehicle is fitted with automatic
transmission, proceed as follows, referring to
Chapter 7, Part B and to Chapter 8 for further
details when required:
(a) Unscrew its centre bolt, then unbolt the
engine/transmission rear mounting
bracket from the transmission.
(b) Disconnect the fluid cooler pipe from the
rear of the transmission, and secure it
clear of the unit.
(c) Prise the left-hand driveshaft out of the
transmission; be prepared to catch any
spilt oil.
(d) Secure the driveshaft clear of the
engine/transmission - remember that the
unit is to be lowered out of the vehicle -
and ensure that the inner joint is not
turned through more than 18°.
(e) Unscrew the nuts securing the right-hand
driveshaft support bearing, and withdraw
the heat shield.
(f) Pull the right-hand driveshaft out of the
transmission - again, be prepared for oil
spillage. Secure the driveshaft clear of the
engine/transmission, and ensure that its
inner joint is not turned through more than
18°.
(g) Disconnect the fluid cooler pipe from the
front of the transmission, and secure it
clear of the unit.
33The engine/transmission unit should now
be hanging on the right- and left-hand
mountings only, with all components which
connect it to the rest of the vehicle
disconnected or removed and secured well
clear of the unit. Make a final check that this is
the case, then ensure that the body is
securely supported, high enough to permit the
withdrawal of the engine/transmission unit
from underneath; allow for the height of the
engine dolly, if used.
34Take the weight of the engine/
transmission unit, using the lifting eyes
provided on the cylinder head. Unscrew the
six nuts securing the right-hand mounting
bracket, then the three nuts securing the left-
hand bracket. Warning: Do not put any part of
your body under the vehicle, or
under the engine/transmission
unit, when they are supported only by a
hoist or other lifting equipment.
35Lower the engine/transmission to the
ground, and withdraw it from under the
vehicle (see illustration).
36Referring to the relevant part of Chapter 7,
separate the transmission from the engine.
37While the engine/transmission is removed,
check the mountings; renew them if they are
worn or damaged. Similarly, check the
condition of all coolant and vacuum hoses
and pipes (see Chapter 1); components that
are normally hidden can now be checked
properly, and should be renewed if there is
any doubt at all about their condition. Where
the vehicle is fitted with manual transmission,
take the opportunity to overhaul the clutch
components (see Chapter 8). It is regarded by
many as good working practice to renew the
clutch assembly as a matter of course,
whenever major engine overhaul work is
carried out. Check also the condition of all
components (such as the transmission oil
seals) disturbed on removal, and renew any
that are damaged or worn.
Refitting
38Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points.
Tighten all fasteners to the torque wrench
settings given; where settings are not quoted
in the Specifications Sections of the two Parts
of this Chapter, refer to the Specifications
Section of the relevant Chapter of this manual.
39In addition to the points noted in
paragraph 37 above, always renew any
circlips and self-locking nuts disturbed on
removal.
40Where wiring, etc, was secured by cable
ties which had to be cut on removal, ensure
that it is secured with new ties on refitting.
41With all overhaul operations completed,
refit the transmission to the engine as
described in Chapter 7.
42Manoeuvre the engine/transmission unit
under the vehicle, attach the hoist, and lift the
unit into position until the right- and left-hand
mountings can be reassembled; tighten the
(new) nuts only lightly at this stage. Do not yet
release the hoist; the weight of the
engine/transmission unit must not be taken by
the mountings until all are correctly aligned.
43Using new circlips, and ensuring that the
inner joints are not twisted through too great
an angle (see Chapter 8), refit the driveshafts.
Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, the procedure is the reverse of
that outlined in paragraph 31 above. Where
the vehicle is fitted with automatic
transmission, proceed as follows, referring to
Chapter 7, Part B and to Chapter 8 for further
details when required:
(a) Refit the left-hand driveshaft.
(b) Using the clips provided to ensure that
they are correctly routed, and tighteningthe couplings to the specified torque
wrench setting where possible, reconnect
the fluid cooler pipes, first to the rear,
then to the front, of the transmission.
(c) Refit the right-hand driveshaft to the
transmission, refit the heat shield, and
tighten the support bearing nuts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(d) Refit the engine/transmission rear
mounting bracket to the transmission,
tightening the bolts to the torque wrench
setting specified, then refit the mounting,
tightening the centre bolt only lightly at
this stage.
44Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, do not forget to refit the
compressor; tighten the bolts to the specified
torque wrench setting, and plug in its
electrical connector.
45Using the marks and notes made on
removal, refit the cooling system hoses.
Where they are left disconnected or unclipped
for the time being, do not forget to secure
them at the appropriate moment during the
reassembly procedure. Refit the radiator (if
removed), using split pins to secure it in the
raised position.
46Offer up the subframe one side at a time,
and hold it by securing the suspension lower
arm balljoints to the steering knuckle
assemblies. Refit the subframe bolts, ensuring
that the washers are refitted correctly, and
tightening the bolts only lightly at this stage.
47The subframe must now be aligned on the
underbody. Ford specify the use of service
tool 15-097, which is a pair of tapered guides,
with attachments to hold them in the
subframe as it is refitted. However, since the
working diameter of these tools is 20.4 mm,
and since the corresponding aligning holes in
the subframe and underbody are respectively
21 mm and 22 mm in diameter, there is a
significant in-built tolerance possible in the
subframe’s alignment, even if the correct tools
are used. If these tools are not available, you
can align the subframe by eye, centring the
subframe aligning holes on those of the
underbody, and using the marks made on
removal for assistance. Alternatively, you can
align the subframe using a tapered drift (such
as a clutch-aligning tool), or even a deep
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•7
2B
4.35 Lowering the engine/transmission
unit out of the vehicle
procarmanuals.com
Page 74 of 279

socket spanner of suitable size (see
illustrations).
48Once the subframe is aligned as precisely
as possible, tighten its bolts to the specified
torque wrench setting without disturbing its
position. Recheck the alignment once all the
bolts are securely tightened.
49With the subframe aligned and securely
fastened, the engine/transmission unit must
now be positioned precisely, before the
mountings can be reassembled. Ford specify
the use of service tool 21-172; this is a fixture
bolted to the subframe in place of the
engine/transmission front mounting, so that
when the mounting’s centre bolt is refitted, it
is held 60 mm above the subframe’s top
surface, and offset 20 mm to the rear of the
mounting’s subframe bolt holes (centres). DIY
mechanics are advised to obtain the Ford
tool; the only alternative is to have a copy
fabricated (see illustration).
50Fasten the tool to the subframe in place of
the engine/transmission front mounting, and
lightly tighten the mounting’s centre bolt. Refit
the engine/transmission mountings in the
following sequence:
(a) Tighten the left-hand mounting’s nuts to
the specified torque wrench setting - do
not allow the mounting to twist as it is
tightened (see illustration).
(b) Tighten the right-hand mounting’s four
bracket-to-engine nuts to the specified
torque wrench setting.(c) Slowly release the hoist so that the weight
of the engine/transmission unit is taken by
the mountings.
(d) Tighten the right-hand mounting’s two
bracket-to-mounting nuts to the specified
torque wrench setting - do not allow the
mounting to twist as it is tightened (see
illustration).
(e) Reassemble the engine/transmission rear
mounting, tightening the fasteners to the
specified torque wrench settings; tighten
the centre bolt last.
(f) Refit the steering gear to the subframe; if
the Ford service tool is used to tighten the
bolts from underneath the vehicle (see
Chapter 10 for details), note that a torque
wrench which can tighten in an anti-
clockwise direction will be required.
(g) Unbolt the special tool from the front
mounting, refit the mounting - do not
forget the wiring connector bracket - and
tighten first the mounting’s bolts/nuts,
then its centre bolt, to their respective
specified torque wrench settings (see
illustrations).
51Refit the bottom mounting rubbers to the
radiator - ensure that both are the correct way
up - then refit the radiator mounting brackets
to the subframe, ensuring that each is
returned to its correct (marked) location, and
tightening the bolts to the torque wrench
setting specified. Remove the split pins, and
secure the coolant hose connections (where
necessary).
52Refit the air conditioning accumulator/
dehydrator (where appropriate) to the
subframe.
53Tighten the two bolts securing the power
steering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the subframe.
54Fasten each front suspension lower arm
balljoint and track rod end to their respective
steering knuckles, and both anti-roll bar links
to their respective suspension strut. Note the
flexible brake hose bracket attached to each
link stud (see Chapter 10 for details).
55Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, swivel the linkage around to the
front, tighten its rear fasteners, then refit the
2B•8 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
4.47A Tighten subframe mounting
bolts (A) while ensuring that alignment
remains correct - Ford service tools (B)
shown in use here . . .4.47B . . . but alternative methods using
ordinary hand tools can achieve
acceptable alignment, with care4.49 Special tool required to hold
engine/transmission unit precisely, so that
mountings can be tightened into correct
position
4.50B Tighten the right-hand mounting’s
four bracket-to-engine nuts (A), release
the hoist, then tighten the two bracket-to-
mounting nuts (B). Do not allow mounting
to twist
4.50A Do not allow the left-hand mounting
to twist as its nuts (arrowed) are tightened
4.50C Unbolt special tool . . .
4.50D . . . then refit front mounting - do
not forget wiring connector bracket -
tighten the mounting’s nuts first, then its
centre bolt
procarmanuals.com
Page 76 of 279

2Remove the cylinder head (Part A of this
Chapter, Section 14).
3Using a valve spring compressor, compress
each valve spring in turn until the split collets
can be removed. A special valve spring
compressor will be required, to reach into the
deep wells in the cylinder head without risk of
damaging the hydraulic tappet bores; such
compressors are now widely available from
most good motor accessory shops. Release
the compressor, and lift off the spring upper
seat and spring (see illustrations).
4If, when the valve spring compressor is
screwed down, the spring upper seat refuses
to free and expose the split collets, gently tap
the top of the tool, directly over the upper
seat, with a light hammer. This will free the
seat.
5Withdraw the valve through the combustionchamber. If it binds in the guide (won’t pull
through), push it back in, and de-burr the area
around the collet groove with a fine file or
whetstone; take care not to mark the
hydraulic tappet bores.
6Ford recommend the use of their service
tool 21-160 to extract the valve spring lower
seat/stem oil seals; while this is almost
indispensable if the seals are to be removed
without risk of (extremely expensive) damage
to the cylinder head, we found that a
serviceable substitute can be made from a
strong spring of suitable size. Screw on the
tool or spring so that it bites into the seal, then
draw the seal off the valve guide (see
illustrations).
7It is essential that the valves are kept
together with their collets, spring seats and
springs, and in their correct sequence (unless
they are so badly worn that they are to be
renewed). If they are going to be kept and
used again, place them in a labelled polythene
bag or similar small container (see
illustration). Note that No 1 valve is nearest to
the timing belt end of the engine.
8If the oil-retaining valve is to be removed (to
flush out the cylinder head oil galleries
thoroughly), seek the advice of a Ford dealer
as to how it can be extracted; it may be that
the only course of action involves destroying
the valve as follows. Screw a self-tapping
screw into its ventilation hole, and use the
screw to provide purchase with which the
valve can be drawn out; a new valve must be
purchased and pressed into place on
reassembly (see illustration).Note:Always check first what replacement
parts are available before planning any
overhaul operation; refer to Section 1 of this
Part. A Ford dealer, or a good engine
reconditioning specialist/automotive parts
supplier, may be able to suggest alternatives
which will enable you to overcome the lack of
replacement parts.
1Thorough cleaning of the cylinder head and
valve components, followed by a detailed
inspection, will enable you to decide how
much valve service work must be carried out
during the engine overhaul. Note:If the
engine has been severely overheated, it is best
to assume that the cylinder head is warped,
and to check carefully for signs of this.
Cleaning
2Scrape away all traces of old gasket
material and sealing compound from the
cylinder head (see Part A of this Chapter,
Section 14 for details).
3Scrape away the carbon from the
combustion chambers and ports, then wash
the cylinder head thoroughly with paraffin or a
suitable solvent.
7 Cylinder head and valve
components-
cleaning and inspection
2B•10 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
6.3A Standard valve spring compressor
modified as shown . . .6.3B . . . or purpose-built special version,
is required to compress valve springs
without damaging cylinder head . . .
6.3C . . . so that both valve split collets
can be removed from the valve’s stem -
small magnetic pick-up tool prevents loss
of small metal components on removal
and refitting
6.6B . . . can be replaced by home-made
tool if suitable spring can be found
6.6A Ford service tool in use to remove
valve spring lower seat/stem oil seals . . .
6.7 Use clearly-marked containers to
identify components and to keep matched
assemblies together6.8 Cylinder head oil-retaining valve
(arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 77 of 279
4Scrape off any heavy carbon deposits that
may have formed on the valves, then use a
power-operated wire brush to remove
deposits from the valve heads and stems.
Inspection
Note:Be sure to perform all the following
inspection procedures before concluding that
the services of a machine shop or engine
overhaul specialist are required. Make a list of
all items that require attention.
Cylinder head
5Inspect the head very carefully for cracks,
evidence of coolant leakage, and other
damage. If cracks are found, a new cylinder
head should be obtained.
6Use a straight edge and feeler blade to
check that the cylinder head gasket surface is
not distorted (see illustration). If it is, it may
be possible to re-surface it.
7Examine the valve seats in each of the
combustion chambers. If they are severely
pitted, cracked or burned, then they will need
to be renewed or re-cut by an engine overhaul
specialist. If they are only slightly pitted, this
can be removed by grinding-in the valve
heads and seats with fine valve-grinding
compound, as described below.
8If the valve guides are worn, indicated by a
side-to-side motion of the valve, new guidesmust be fitted. Measure the diameter of the
existing valve stems (see below) and the bore
of the guides, then calculate the clearance,
and compare the result with the specified
value; if the clearance is excessive, renew the
valves or guides as necessary.
9The renewal of valve guides is best carried
out by an engine overhaul specialist.
10If the valve seats are to be re-cut, this
must be done only afterthe guides have been
renewed.
Valves
11Examine the head of each valve for
pitting, burning, cracks and general wear, and
check the valve stem for scoring and wear
ridges. Rotate the valve, and check for any
obvious indication that it is bent. Look for pits
and excessive wear on the tip of each valve
stem. Renew any valve that shows any such
signs of wear or damage.
12If the valve appears satisfactory at this
stage, measure the valve stem diameter at
several points, using a micrometer (see
illustration). Any significant difference in the
readings obtained indicates wear of the valve
stem. Should any of these conditions be
apparent, the valve(s) must be renewed.
13If the valves are in satisfactory condition,
they should be ground (lapped) into their
respective seats, to ensure a smooth gas-
tight seal. If the seat is only lightly pitted, or if
it has been re-cut, fine grinding compound
onlyshould be used to produce the required
finish. Coarse valve-grinding compound
should notbe used unless a seat is badly
burned or deeply pitted; if this is the case, the
cylinder head and valves should be inspected
by an expert, to decide whether seat re-
cutting, or even the renewal of the valve or
seat insert, is required.
14Valve grinding is carried out as follows.
Place the cylinder head upside-down on a
bench, with a block of wood at each end to
give clearance for the valve stems.
15Smear a trace of (the appropriate grade
of) valve-grinding compound on the seat face,
and press a suction grinding tool onto the
valve head. With a semi-rotary action, grind
the valve head to its seat, lifting the valve
occasionally to redistribute the grindingcompound (see illustration). A light spring
placed under the valve head will greatly ease
this operation.
16If coarse grinding compound is being
used, work only until a dull, matt even surface
is produced on both the valve seat and the
valve, then wipe off the used compound, and
repeat the process with fine compound. When
a smooth unbroken ring of light grey matt
finish is produced on both the valve and seat,
the grinding operation is complete. Do not
grind in the valves any further than absolutely
necessary, or the seat will be prematurely
sunk into the cylinder head.
17When all the valves have been ground-in,
carefully wash off alltraces of grinding
compound, using paraffin or a suitable
solvent, before reassembly of the cylinder
head.
Valve components
18Examine the valve springs for signs of
damage and discolouration, and also measure
their free length by comparing each of the
existing springs with a new component.
19Stand each spring on a flat surface, and
check it for squareness (see illustration). If
any of the springs are damaged, distorted, or
have lost their tension, obtain a complete set
of new springs.
20Check the spring upper seats and collets
for obvious wear and cracks. Any
questionable parts should be renewed, as
extensive damage will occur if they fail during
engine operation. Any damaged or
excessively-worn parts must be renewed; the
valve spring lower seat/stem oil seals must be
renewed as a matter of course whenever they
are disturbed.
21Check the hydraulic tappets as described
in Part A of this Chapter, Section 13.
1Regardless of whether or not the head was
sent away for repair work of any sort, make
sure that it is clean before beginning
reassembly. Be sure to remove any metal
particles and abrasive grit that may still be
present from operations such as valve
8 Cylinder head - reassembly
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•11
2B
7.12 Measuring the diameter of a valve
stem - if any significant difference is found
in the readings obtained, excessive valve
stem wear is indicated7.15 Grinding-in a valve seat - do not grind
in the valves any more than absolutely
necessary, or their seats will be
prematurely sunk into the cylinder head
7.19 Check each valve spring for
squareness
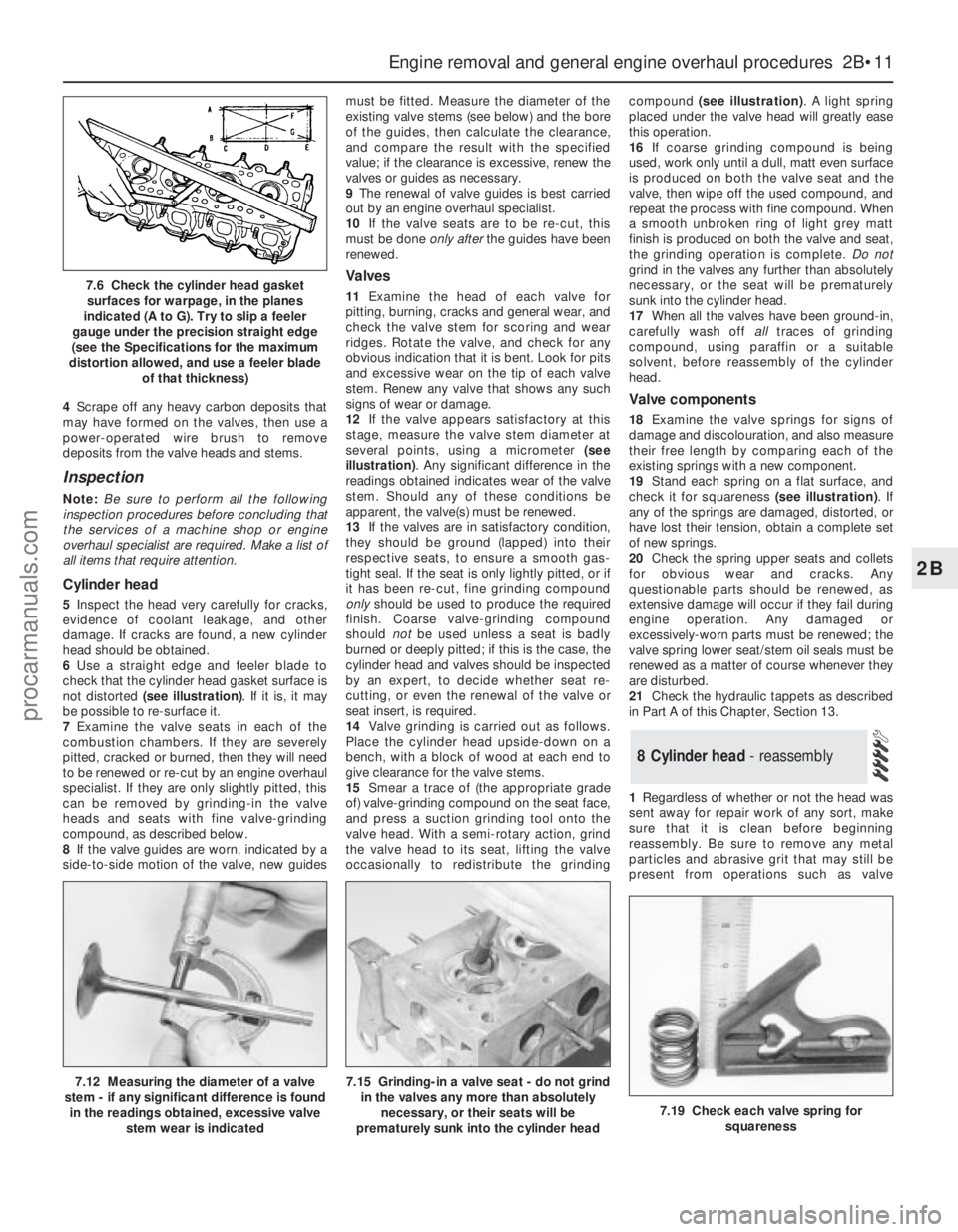
7.6 Check the cylinder head gasket
surfaces for warpage, in the planes
indicated (A to G). Try to slip a feeler
gauge under the precision straight edge
(see the Specifications for the maximum
distortion allowed, and use a feeler blade
of that thickness)
procarmanuals.com
Page 80 of 279

applicable); note that Ford state that the
piston-cooling oil jets (where fitted) must be
renewed whenever the engine is dismantled
for full overhaul (see illustrations).
2Remove the main bearing caps, and
separate the bearing shells from the caps and
the cylinder block/crankcase. Mark or label
the shells, indicating which bearing they were
removed from, and whether they were in the
cap or the block, then set them aside (see
illustration). Wipe clean the block and cap
bearing recesses, and inspect them for nicks,
gouges and scratches.
3Scrape all traces of gasket from the cylinderblock/crankcase, taking care not to damage
the sealing surfaces.
4Remove all oil gallery plugs (where fitted).
The plugs are usually very tight - they may
have to be drilled out and the holes re-tapped.
Use new plugs when the engine is
reassembled. Drill a small hole in the centre of
each core plug, and pull them out with a car
bodywork dent puller (see illustration).
Caution: The core plugs (also
known as freeze or soft plugs)
may be difficult or impossible to
retrieve if they are driven into the
block coolant passages.5If any of the castings are extremely dirty, all
should be steam-cleaned.
6After the castings are returned from steam-
cleaning, clean all oil holes and oil galleries
one more time. Flush all internal passages
with warm water until the water runs clear,
then dry thoroughly, and apply a light film of
oil to all machined surfaces, to prevent
rusting. If you have access to compressed air,
use it to speed the drying process, and to
blow out all the oil holes and galleries.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
7If the castings are not very dirty, you can do
an adequate cleaning job with hot soapy
water (as hot as you can stand!) and a stiff
brush. Take plenty of time, and do a thorough
job. Regardless of the cleaning method used,
be sure to clean all oil holes and galleries very
thoroughly, and to dry all components
completely; protect the machined surfaces as
described above, to prevent rusting.
8All threaded holes must be clean and dry,
to ensure accurate torque readings during
reassembly; now is also a good time to clean
and check the threads of all principal bolts -
however, note that some, such as the cylinder
head and flywheel/driveplate bolts, are to be
renewed as a matter of course whenever they
are disturbed. Run the proper-size tap into
2B•14 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
11.1A Remove water pump . . .11.1B . . . crankcase breather pipe and
PCV valve . . .11.1C . . . unbolt crankcase ventilation
system oil separator . . .
11.1F . . . but note that piston-cooling oil
jets (where fitted) must be renewed as a
matter of course whenever engine is
overhauled11.2 Felt marker pens can be used as
shown to identify bearing shells without
damaging them
11.1D . . . remove electrical
switches/sensors such as crankshaft
speed/position sensor . . .11.1E . . . unbolt blanking plugs (where
fitted) to clean out oilways . . .
11.4 The core plugs should be removed
with a puller - if they’re driven into the
block, they may be impossible to
retrieve
procarmanuals.com
Page 82 of 279
15Measure the piston diameter at right-
angles to the gudgeon pin axis, just above the
bottom of the skirt; again, note the results
(see illustration).
16If it is wished to obtain the piston-to-bore
clearance, measure the bore and piston skirt
as described above, and subtract the skirt
diameter from the bore measurement. If the
precision measuring tools shown are not
available, the condition of the pistons and
bores can be assessed, though not quite as
accurately, by using feeler gauges as follows.
Select a feeler gauge of thickness equal to the
specified piston-to-bore clearance, and slip it
into the cylinder along with the matching
piston. The piston must be positioned exactly
as it normally would be. The feeler gauge
must be between the piston and cylinder on
one of the thrust faces (at right-angles to the
gudgeon pin bore). The piston should slip
through the cylinder (with the feeler gauge in
place) with moderate pressure; if it falls
through or slides through easily, the clearance
is excessive, and a new piston will be
required. If the piston binds at the lower end
of the cylinder, and is loose toward the top,
the cylinder is tapered. If tight spots are
encountered as the piston/feeler gauge is
rotated in the cylinder, the cylinder is out-of-
round (oval).
17Repeat these procedures for the
remaining pistons and cylinder bores.
18Compare the results with the
Specifications at the beginning of this
Chapter; if any measurement is beyond the
dimensions specified for that class (check the
piston crown marking to establish the class of
piston fitted), or if any bore measurement is
significantly different from the others
(indicating that the bore is tapered or oval),
the piston or bore is excessively-worn.
19Worn pistons must be renewed; at the
time of writing, pistons are available as Ford
replacement parts only as part of the
complete piston/connecting rod assembly.
See a Ford dealer or engine reconditioning
specialist for advice.
20If any of the cylinder bores are badlyscuffed or scored, or if they are excessively-
worn, out-of-round or tapered, the usual
course of action would be to have the cylinder
block/crankcase rebored, and to fit new,
oversized, pistons on reassembly. See a Ford
dealer or engine reconditioning specialist for
advice.
21If the bores are in reasonably good
condition and not excessively-worn, then it
may only be necessary to renew the piston
rings.
22If this is the case (and if new rings can be
found), the bores should be honed, to allow
the new rings to bed in correctly and provide
the best possible seal; before honing the
bores, refit the main bearing caps (without the
bearing shells), and tighten the bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting. Note:If you
don’t have the tools, or don’t want to tackle
the honing operation, most engine
reconditioning specialists will do it for a
reasonable fee.
23Two types of cylinder hones are
commonly available - the flex hone or “bottle-
brush” type, and the more traditional
surfacing hone with spring-loaded stones.
Both will do the job and are used with a
power drill, but for the less-experienced
mechanic, the “bottle-brush” hone will
probably be easier to use. You will also need
some paraffin or honing oil, and rags.
Proceed as follows:
(a) Mount the hone in the drill, compress the
stones, and slip it into the first bore (see
illustration). Be sure to wear safety
goggles or a face shield!
(b) Lubricate the bore with plenty of honing
oil, switch on the drill, and move the hone
up and down the bore, at a pace that will
produce a fine cross-hatch pattern on the
cylinder walls. Ideally, the cross-hatch
lines should intersect at approximately a
60° angle (see illustration). Be sure to
use plenty of lubricant, and don’t take off
any more material than is absolutely
necessary to produce the desired finish.
Note:Piston ring manufacturers may
specify a different crosshatch angle - readand follow any instructions included with
the new rings.
(c) Don’t withdraw the hone from the bore
while it’s running. Instead, switch off the
drill, and continue moving the hone up
and down the bore until it comes to a
complete stop, then compress the stones
and withdraw the hone. If you’re using a
“bottle-brush” hone, switch off the drill,
then turn the chuck in the normal
direction of rotation while withdrawing the
hone from the bore.
(d) Wipe the oil out of the bore, and repeat
the procedure for the remaining cylinders.
(e) When all the cylinder bores are honed,
chamfer the top edges of the bores with a
small file, so the rings won’t catch when
the pistons are installed. Be very careful
not to nick the cylinder walls with the end
of the file.
(f) The entire cylinder block/crankcase must
be washed very thoroughly with warm,
soapy water, to remove all traces of the
abrasive grit produced during the honing
operation. Note:The bores can be
considered clean when a lint-free white
cloth - dampened with clean engine oil -
used to wipe them out doesn’t pick up
any more honing residue, which will show
up as grey areas on the cloth. Be sure to
run a brush through all oil holes and
galleries, and flush them with running
water.
(g) When the cylinder block/crankcase is
completely clean, rinse it thoroughly and
dry it, then lightly oil all exposed
machined surfaces, to prevent rusting.
24The cylinder block/crankcase should now
be completely clean and dry, with all
components checked for wear or damage,
and repaired or overhauled as necessary.
Refit as many ancillary components as
possible, for safekeeping (see paragraphs 9
and 10 above). If reassembly is not to start
immediately, cover the block with a large
plastic bag to keep it clean, and protect the
machined surfaces as described above to
prevent rusting.
2B•16 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
11.15 Measure the piston skirt diameter at
right-angles to the gudgeon pin axis, just
above the base of the skirt11.23A A “bottle-brush” hone will produce
better results if you have never honed
cylinders before11.23B The cylinder hone should leave a
smooth, cross-hatch pattern with the lines
intersecting at approximately a 60º angle
procarmanuals.com
Page 83 of 279

Note:Always check first what replacement
parts are available before planning any
overhaul operation; refer to Section 1 of this
Part. A Ford dealer, or a good engine
reconditioning specialist/automotive parts
supplier may be able to suggest alternatives
which will enable you to overcome the lack of
replacement parts.
1Before the inspection process can be
carried out, the piston/connecting rod
assemblies must be cleaned, and the original
piston rings removed from the pistons. The
rings should have smooth, polished working
surfaces, with no dull or carbon-coated
sections (showing that the ring is not sealing
correctly against the bore wall, so allowing
combustion gases to blow by) and no traces
of wear on their top and bottom surfaces. The
end gaps should be clear of carbon, but not
polished (indicating a too-small end gap), and
all the rings (including the elements of the oil
control ring) should be free to rotate in their
grooves, but without excessive up-and-down
movement. If the rings appear to be in good
condition, they are probably fit for further use;
check the end gaps (in an unworn part of the
bore) as described in Section 16. If any of the
rings appears to be worn or damaged, or has
an end gap significantly different from the
specified value, the usual course of action is
to renew all of them as a set. Note:While it is
usual always to renew piston rings when an
engine is overhauled, this of course assumes
that rings are available separately - if not, it
follows that great care must be taken not to
break or damage any of the rings during the
following procedures, and to ensure that each
ring is marked on removal so that it is refitted
onlythe original way up, and onlyto the same
groove.
2Using a piston ring renoval tool, carefully
remove the rings from the pistons. Be careful
not to nick or gouge the pistons in the
process, and mark or label each ring as it is
removed, so that its original top surface canbe identified on reassembly, and so that it can
be returned to its original groove. Take care
also with your hands - piston rings are sharp!
3Scrape all traces of carbon from the top of
the piston. A hand-held wire brush or a piece
of fine emery cloth can be used, once the
majority of the deposits have been scraped
away. Do not, under any circumstances, use a
wire brush mounted in a drill motor to remove
deposits from the pistons - the piston material
is soft, and may be eroded away by the wire
brush.
4Use a piston ring groove-cleaning tool to
remove carbon deposits from the ring
grooves. If a tool isn’t available, but
replacement rings have been found, a piece
broken off the old ring will do the job. Be very
careful to remove only the carbon deposits -
don’t remove any metal, and do not nick or
scratch the sides of the ring grooves (see
illustrations). Protect your fingers - piston
rings are sharp!
5Once the deposits have been removed,
clean the piston/rod assemblies with solvent,
and dry them with compressed air (if
available). Make sure the oil return holes in the
back sides of the ring grooves, and the oilhole in the lower end of each rod, are clear.
6If the pistons and cylinder walls aren’t
damaged or worn excessively - refer to
Section 11 for details of inspection and
measurement procedures - and if the cylinder
block/crankcase is not rebored, new pistons
won’t be necessary. Normal piston wear
appears as even vertical wear on the piston
thrust surfaces, and slight looseness of the
top ring in its groove.
7Carefully inspect each piston for cracks
around the skirt, at the pin bosses, and at the
ring lands (between the ring grooves).
8Look for scoring and scuffing on the thrust
faces of the skirt, holes in the piston crown,
and burned areas at the edge of the crown. If
the skirt is scored or scuffed, the engine may
have been suffering from overheating and/or
abnormal combustion, which caused
excessively-high operating temperatures. The
cooling and lubrication systems should be
checked thoroughly. A hole in the piston
crown is an indication that abnormal
combustion (pre-ignition) was occurring.
Burned areas at the edge of the piston crown
are usually evidence of spark knock
(detonation). If any of the above problems
exist, the causes must be corrected, or the
damage will occur again. The causes may
include intake air leaks, incorrect fuel/air
mixture, incorrect ignition timing, or EGR
system malfunctions.
9Corrosion of the piston, in the form of small
pits, indicates that coolant is leaking into the
combustion chamber and/or the crankcase.
Again, the cause must be corrected, or the
problem may persist in the rebuilt engine.
10Check the piston-to-rod clearance by
twisting the piston and rod in opposite
directions. Any noticeable play indicates
excessive wear, which must be corrected. The
piston/connecting rod assemblies should be
taken to a Ford dealer or engine recondition-
ing specialist to have the pistons, gudgeon
pins and rods checked, and new components
fitted as required.
11Don’tattempt to separate the pistons
from the connecting rods (even if non-genuine
replacements are found elsewhere). This is a
task for a Ford dealer or similar engine
reconditioning specialist, due to the special
heating equipment, press, mandrels and
supports required to do the job. If the
piston/connecting rod assemblies do require
this sort of work, have the connecting rods
checked for bend and twist, since only such
engine repair specialists will have the facilities
for this purpose.
12Check the connecting rods for cracks and
other damage. Temporarily remove the big-
end bearing caps and the old bearing shells,
wipe clean the rod and cap bearing recesses,
and inspect them for nicks, gouges and
scratches. After checking the rods, replace
the old shells, slip the caps into place, and
tighten the bolts finger-tight.
12 Piston/connecting rod
assemblies - inspection
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•17
2B
12.4A The piston ring grooves can be
cleaned with a special tool, as shown
here . . .12.4B . . . or a section of a broken ring, if
available
If a piston ring removal tool is not
available, the rings can be removed by
hand, expanding them over the top of
the pistons. The use of two or three old
feeler blades will be helpful in
preventing the rings dropping into
empty grooves.
procarmanuals.com