ABS FORD MONDEO 1993 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1993, Model line: MONDEO, Model: FORD MONDEO 1993Pages: 279, PDF Size: 12.71 MB
Page 4 of 279

0•4Introduction
Introduced in March 1993, the Ford
Mondeo models are available in four-door
Saloon, five-door Hatchback and five-door
Estate configurations. All feature a high
standard of equipment, with driver/passenger
safety in accidents being a particularly high
design priority; all models are fitted with
features such as side impact bars in all doors,
“anti-submarine” seats combined with “seatbelt grabbers” and pre-tensioners, and an
airbag fitted to the steering wheel. Vehicle
security is enhanced, with an in-built alarm
system and engine immobiliser being fitted as
standard, as well as double-locking doors
with shielded locks, and security-coded audio
equipment.
The four-cylinder petrol engine is a new
design, available in 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litrecapacities. It is controlled by a sophisticated
engine management system, which combines
multi-point sequential fuel injection and
distributorless ignition systems with
evaporative emissions control, exhaust gas
recirculation and a three-way regulated
catalytic converter (with a pulse-air system for
rapid warm-up) to ensure that the vehicle
complies with the most stringent of the
emissions control standards currently in force,
and yet provides the levels of performance
and fuel economy expected.
The transversely-mounted engine drives
the front roadwheels through either a five-
speed manual transmission with a cable-
operated clutch, or through an electronically-
controlled four-speed automatic transmission.
The fully-independent suspension is by
MacPherson strut on all four roadwheels,
located by transverse lower arms at the front,
and by transverse and trailing arms at the rear;
anti-roll bars are fitted at front and rear. The
Estate rear suspension is of a different design,
to give maximum loadspace inside the
vehicle, with self-levelling suspension units
available as an option. On some models, the
suspension is electronically-controlled
through the Adaptive Damping System.
The steering is power-assisted, the pump
being belt-driven from the engine, and the
rack-and-pinion steering gear mounted
behind the engine.
The vacuum servo-assisted brakes are disc
at the front, with drums at the rear on most
models; disc rear brakes and an
electronically-controlled Anti-lock Braking
System (ABS) are available on some models,
with a Traction Control System (TCS) available
as a further option where ABS is fitted.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to Champion Spark Plug,
who supplied the illustrations showing spark
plug conditions. Certain other illustrations are
the copyright of the Ford Motor Company,
and are used with their permission. Thanks
are also due to Sykes-Pickavant Limited, who
provided some of the workshop tools, and to
all those people at Sparkford who helped in
the production of this manual.
Project vehicles
The main project vehicle used in the
preparation of this manual, and appearing in
many of the photographic sequences, was a
1993-model Ford Mondeo 2.0 Si Hatchback.
Additional work was carried out and
photographed on a 1993-model 2.0 Si Saloon
and a 1993-model 2.0 Ghia Estate (with
automatic transmission).
Introduction to the Ford Mondeo
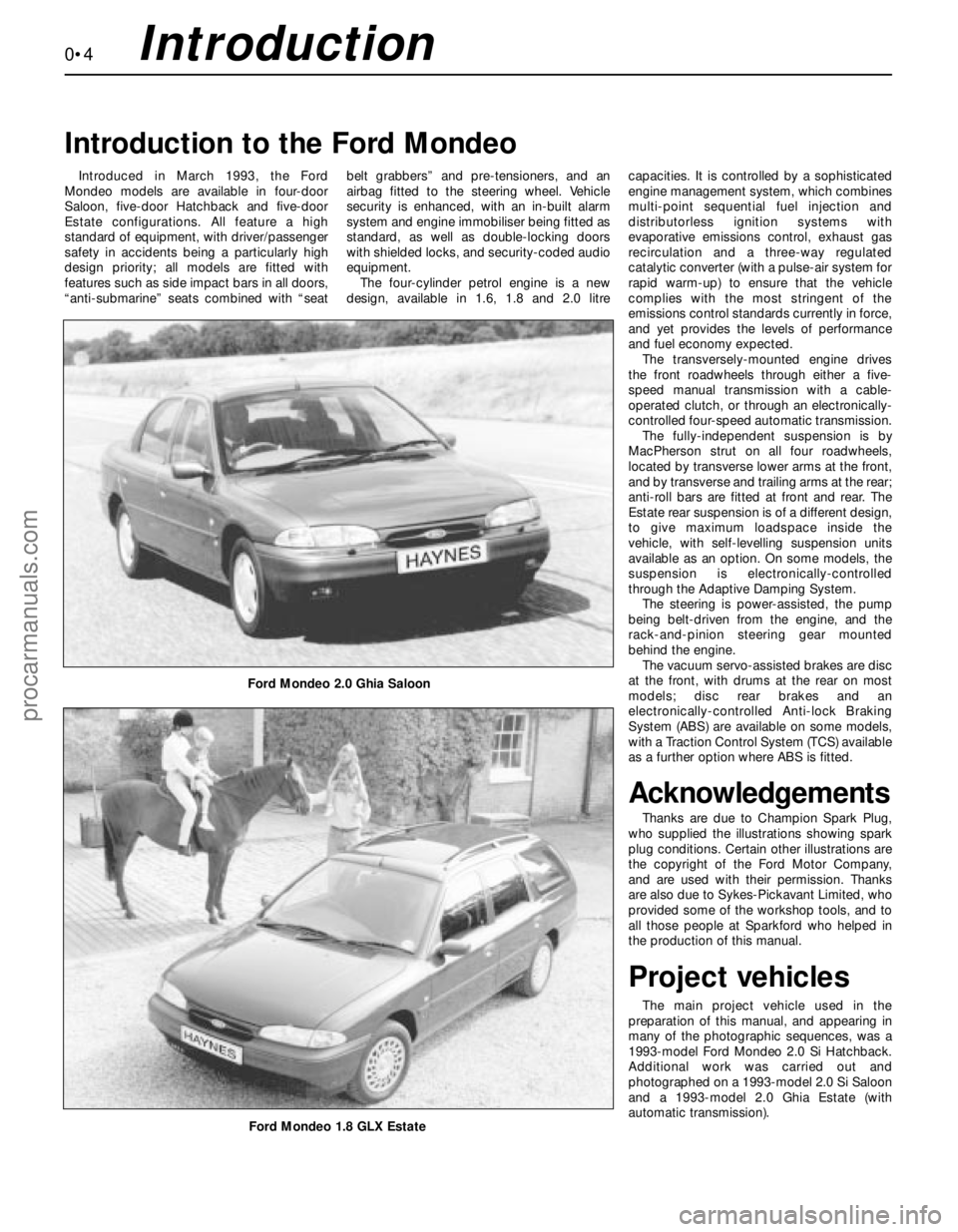
Ford Mondeo 2.0 Ghia Saloon
Ford Mondeo 1.8 GLX Estate
procarmanuals.com
Page 8 of 279
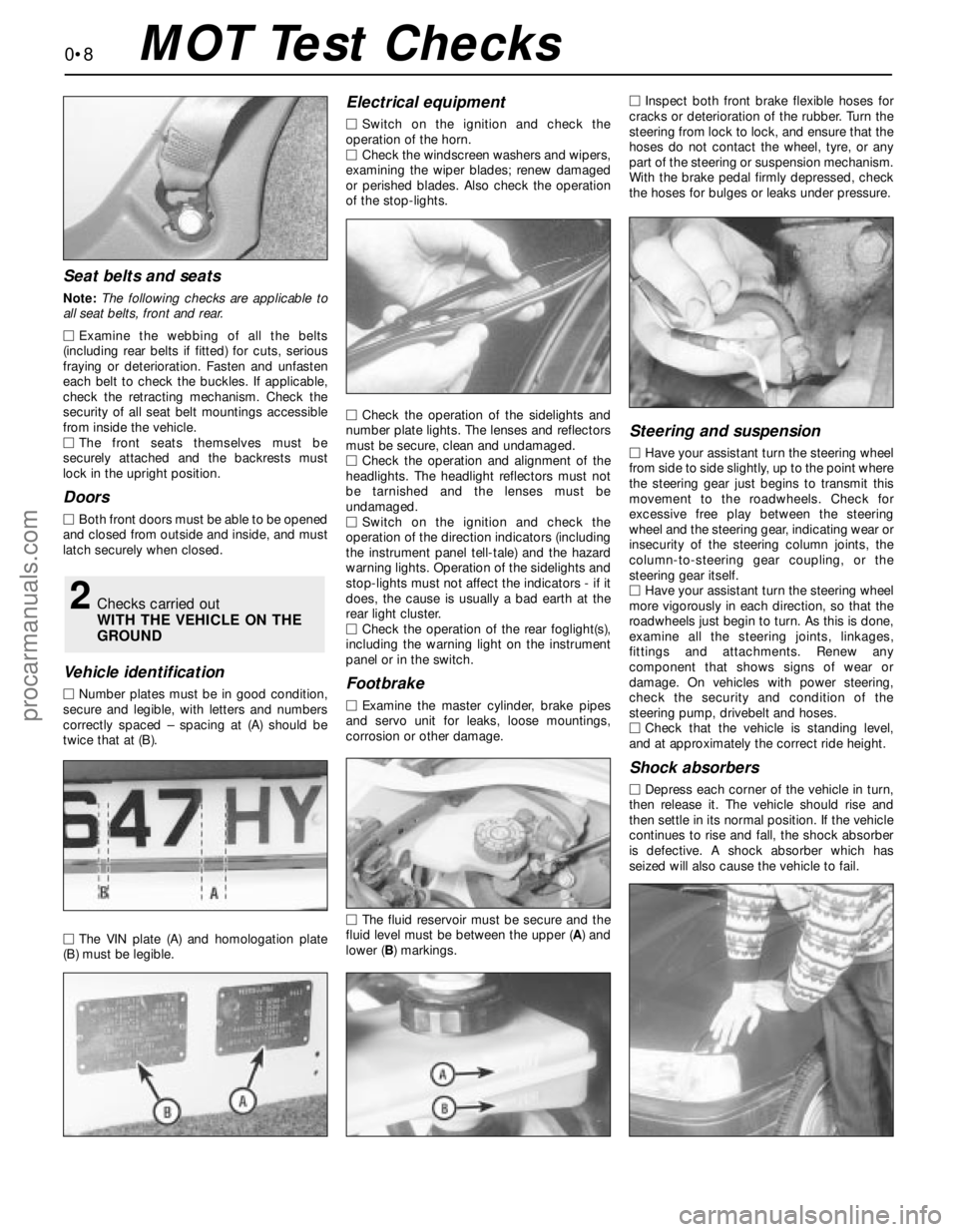
Seat belts and seats
Note: The following checks are applicable to
all seat belts, front and rear.
MExamine the webbing of all the belts
(including rear belts if fitted) for cuts, serious
fraying or deterioration. Fasten and unfasten
each belt to check the buckles. If applicable,
check the retracting mechanism. Check the
security of all seat belt mountings accessible
from inside the vehicle.
MThe front seats themselves must be
securely attached and the backrests must
lock in the upright position.
Doors
MBoth front doors must be able to be opened
and closed from outside and inside, and must
latch securely when closed.
Vehicle identification
MNumber plates must be in good condition,
secure and legible, with letters and numbers
correctly spaced – spacing at (A) should be
twice that at (B).
MThe VIN plate (A) and homologation plate
(B) must be legible.
Electrical equipment
MSwitch on the ignition and check the
operation of the horn.
MCheck the windscreen washers and wipers,
examining the wiper blades; renew damaged
or perished blades. Also check the operation
of the stop-lights.
MCheck the operation of the sidelights and
number plate lights. The lenses and reflectors
must be secure, clean and undamaged.
MCheck the operation and alignment of the
headlights. The headlight reflectors must not
be tarnished and the lenses must be
undamaged.
MSwitch on the ignition and check the
operation of the direction indicators (including
the instrument panel tell-tale) and the hazard
warning lights. Operation of the sidelights and
stop-lights must not affect the indicators - if it
does, the cause is usually a bad earth at the
rear light cluster.
MCheck the operation of the rear foglight(s),
including the warning light on the instrument
panel or in the switch.
Footbrake
MExamine the master cylinder, brake pipes
and servo unit for leaks, loose mountings,
corrosion or other damage.
MThe fluid reservoir must be secure and the
fluid level must be between the upper (A) and
lower (B) markings.MInspect both front brake flexible hoses for
cracks or deterioration of the rubber. Turn the
steering from lock to lock, and ensure that the
hoses do not contact the wheel, tyre, or any
part of the steering or suspension mechanism.
With the brake pedal firmly depressed, check
the hoses for bulges or leaks under pressure.
Steering and suspension
MHave your assistant turn the steering wheel
from side to side slightly, up to the point where
the steering gear just begins to transmit this
movement to the roadwheels. Check for
excessive free play between the steering
wheel and the steering gear, indicating wear or
insecurity of the steering column joints, the
column-to-steering gear coupling, or the
steering gear itself.
MHave your assistant turn the steering wheel
more vigorously in each direction, so that the
roadwheels just begin to turn. As this is done,
examine all the steering joints, linkages,
fittings and attachments. Renew any
component that shows signs of wear or
damage. On vehicles with power steering,
check the security and condition of the
steering pump, drivebelt and hoses.
MCheck that the vehicle is standing level,
and at approximately the correct ride height.
Shock absorbers
MDepress each corner of the vehicle in turn,
then release it. The vehicle should rise and
then settle in its normal position. If the vehicle
continues to rise and fall, the shock absorber
is defective. A shock absorber which has
seized will also cause the vehicle to fail.
2Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE ON THE
GROUND
0•8MOT Test Checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 9 of 279
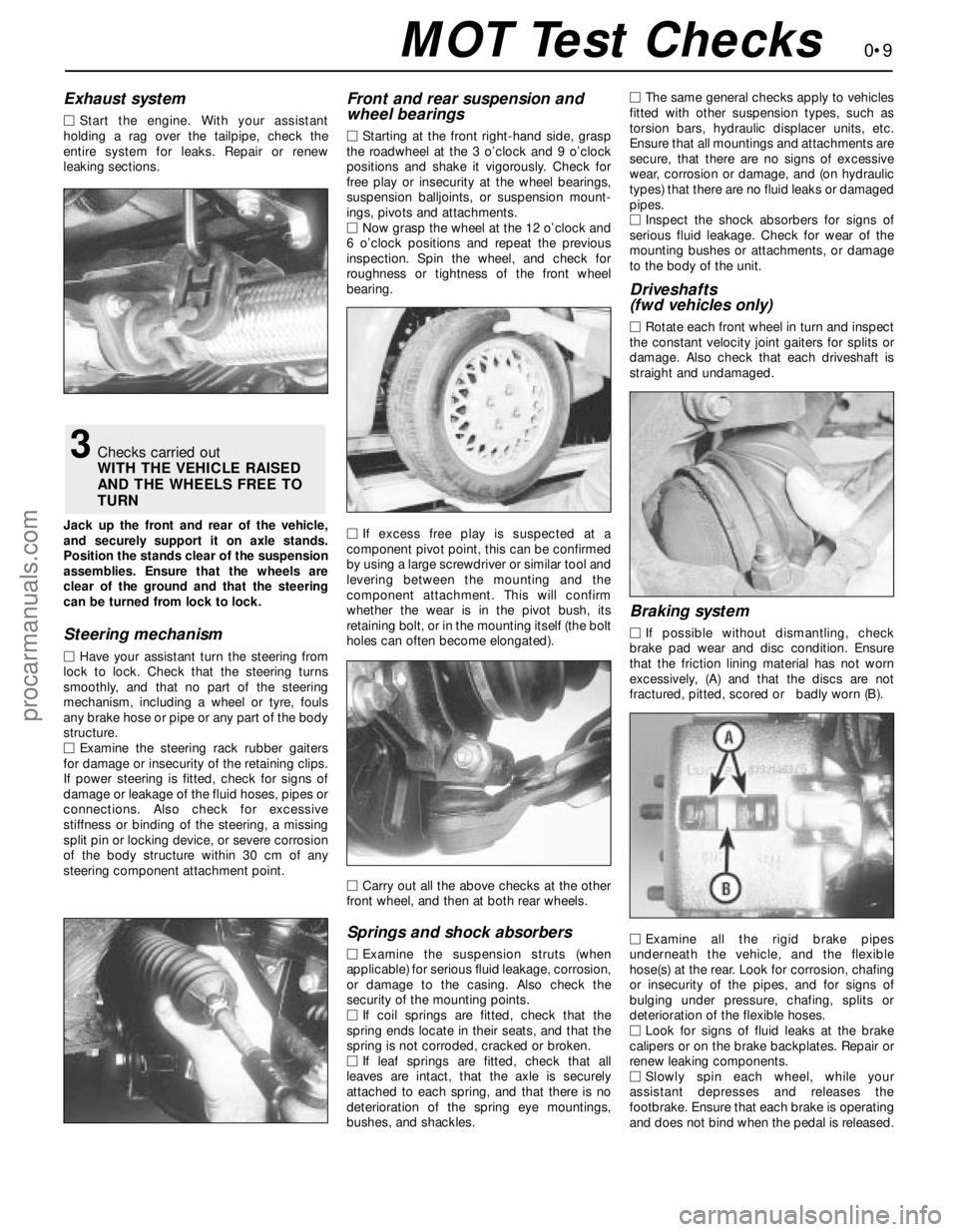
Exhaust system
MStart the engine. With your assistant
holding a rag over the tailpipe, check the
entire system for leaks. Repair or renew
leaking sections.
Jack up the front and rear of the vehicle,
and securely support it on axle stands.
Position the stands clear of the suspension
assemblies. Ensure that the wheels are
clear of the ground and that the steering
can be turned from lock to lock.
Steering mechanism
MHave your assistant turn the steering from
lock to lock. Check that the steering turns
smoothly, and that no part of the steering
mechanism, including a wheel or tyre, fouls
any brake hose or pipe or any part of the body
structure.
MExamine the steering rack rubber gaiters
for damage or insecurity of the retaining clips.
If power steering is fitted, check for signs of
damage or leakage of the fluid hoses, pipes or
connections. Also check for excessive
stiffness or binding of the steering, a missing
split pin or locking device, or severe corrosion
of the body structure within 30 cm of any
steering component attachment point.
Front and rear suspension and
wheel bearings
MStarting at the front right-hand side, grasp
the roadwheel at the 3 o’clock and 9 o’clock
positions and shake it vigorously. Check for
free play or insecurity at the wheel bearings,
suspension balljoints, or suspension mount-
ings, pivots and attachments.
MNow grasp the wheel at the 12 o’clock and
6 o’clock positions and repeat the previous
inspection. Spin the wheel, and check for
roughness or tightness of the front wheel
bearing.
MIf excess free play is suspected at a
component pivot point, this can be confirmed
by using a large screwdriver or similar tool and
levering between the mounting and the
component attachment. This will confirm
whether the wear is in the pivot bush, its
retaining bolt, or in the mounting itself (the bolt
holes can often become elongated).
MCarry out all the above checks at the other
front wheel, and then at both rear wheels.
Springs and shock absorbers
MExamine the suspension struts (when
applicable) for serious fluid leakage, corrosion,
or damage to the casing. Also check the
security of the mounting points.
MIf coil springs are fitted, check that the
spring ends locate in their seats, and that the
spring is not corroded, cracked or broken.
MIf leaf springs are fitted, check that all
leaves are intact, that the axle is securely
attached to each spring, and that there is no
deterioration of the spring eye mountings,
bushes, and shackles.MThe same general checks apply to vehicles
fitted with other suspension types, such as
torsion bars, hydraulic displacer units, etc.
Ensure that all mountings and attachments are
secure, that there are no signs of excessive
wear, corrosion or damage, and (on hydraulic
types) that there are no fluid leaks or damaged
pipes.
MInspect the shock absorbers for signs of
serious fluid leakage. Check for wear of the
mounting bushes or attachments, or damage
to the body of the unit.
Driveshafts
(fwd vehicles only)
MRotate each front wheel in turn and inspect
the constant velocity joint gaiters for splits or
damage. Also check that each driveshaft is
straight and undamaged.
Braking system
MIf possible without dismantling, check
brake pad wear and disc condition. Ensure
that the friction lining material has not worn
excessively, (A) and that the discs are not
fractured, pitted, scored or badly worn (B).
MExamine all the rigid brake pipes
underneath the vehicle, and the flexible
hose(s) at the rear. Look for corrosion, chafing
or insecurity of the pipes, and for signs of
bulging under pressure, chafing, splits or
deterioration of the flexible hoses.
MLook for signs of fluid leaks at the brake
calipers or on the brake backplates. Repair or
renew leaking components.
MSlowly spin each wheel, while your
assistant depresses and releases the
footbrake. Ensure that each brake is operating
and does not bind when the pedal is released.
3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE RAISED
AND THE WHEELS FREE TO
TURN
0•9MOT Test Checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 19 of 279
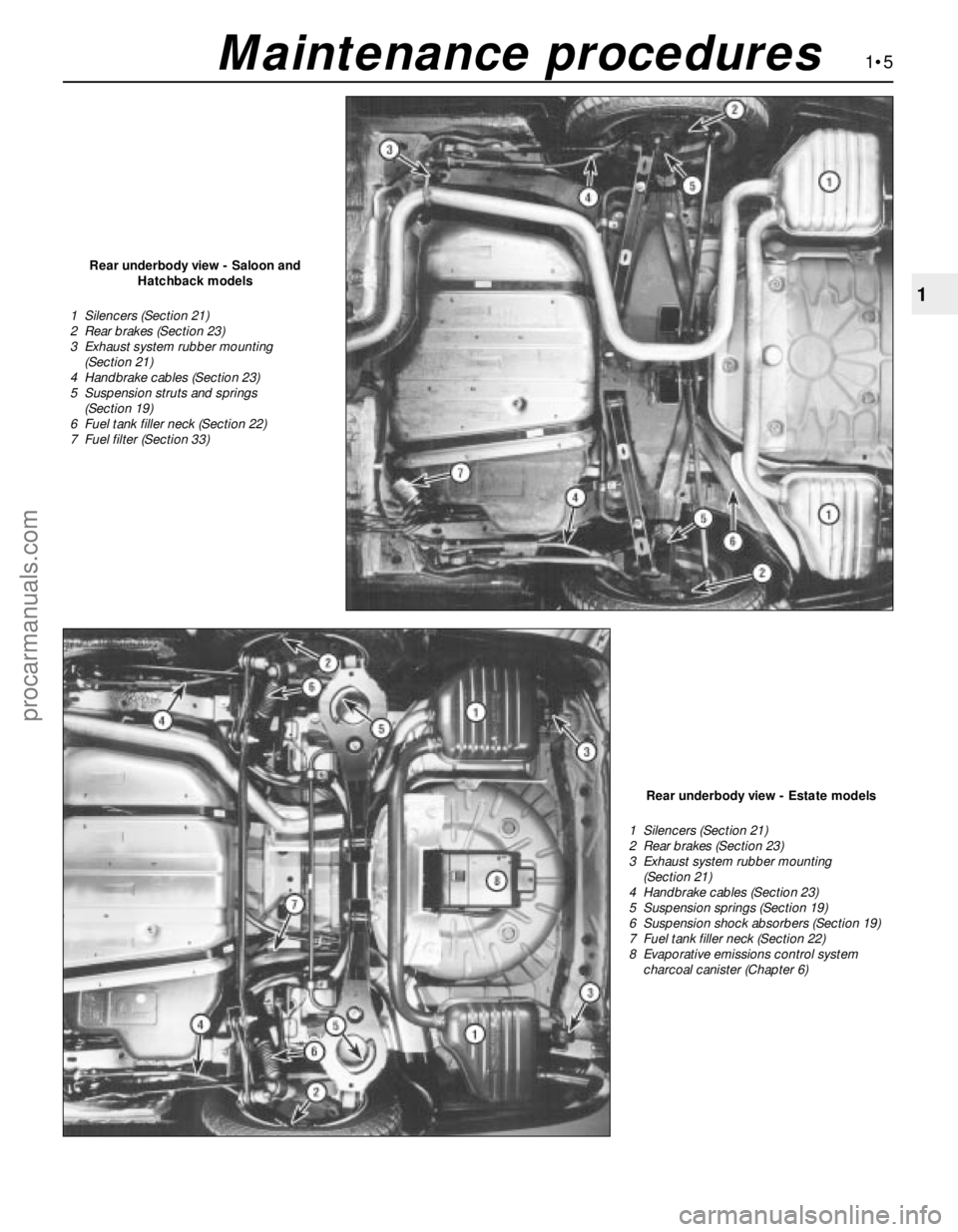
1•5
1
Maintenance procedures
Rear underbody view - Saloon and
Hatchback models
1 Silencers (Section 21)
2 Rear brakes (Section 23)
3 Exhaust system rubber mounting
(Section 21)
4 Handbrake cables (Section 23)
5 Suspension struts and springs
(Section 19)
6 Fuel tank filler neck (Section 22)
7 Fuel filter (Section 33)
Rear underbody view - Estate models
1 Silencers (Section 21)
2 Rear brakes (Section 23)
3 Exhaust system rubber mounting
(Section 21)
4 Handbrake cables (Section 23)
5 Suspension springs (Section 19)
6 Suspension shock absorbers (Section 19)
7 Fuel tank filler neck (Section 22)
8 Evaporative emissions control system
charcoal canister (Chapter 6)
procarmanuals.com
Page 21 of 279
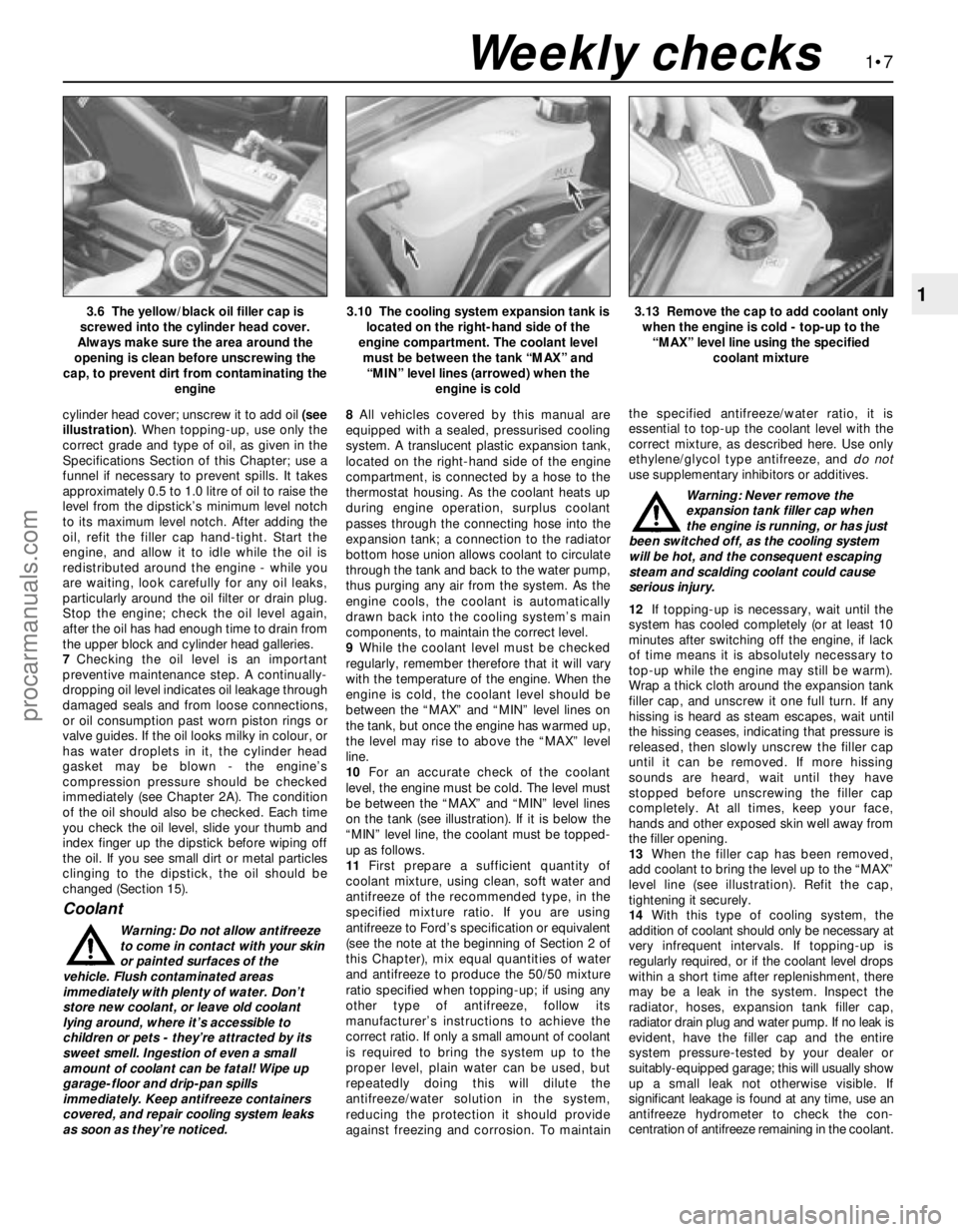

cylinder head cover; unscrew it to add oil (see
illustration). When topping-up, use only the
correct grade and type of oil, as given in the
Specifications Section of this Chapter; use a
funnel if necessary to prevent spills. It takes
approximately 0.5 to 1.0 litre of oil to raise the
level from the dipstick’s minimum level notch
to its maximum level notch. After adding the
oil, refit the filler cap hand-tight. Start the
engine, and allow it to idle while the oil is
redistributed around the engine - while you
are waiting, look carefully for any oil leaks,
particularly around the oil filter or drain plug.
Stop the engine; check the oil level again,
after the oil has had enough time to drain from
the upper block and cylinder head galleries.
7Checking the oil level is an important
preventive maintenance step. A continually-
dropping oil level indicates oil leakage through
damaged seals and from loose connections,
or oil consumption past worn piston rings or
valve guides. If the oil looks milky in colour, or
has water droplets in it, the cylinder head
gasket may be blown - the engine’s
compression pressure should be checked
immediately (see Chapter 2A). The condition
of the oil should also be checked. Each time
you check the oil level, slide your thumb and
index finger up the dipstick before wiping off
the oil. If you see small dirt or metal particles
clinging to the dipstick, the oil should be
changed (Section 15).
Coolant
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin
or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Flush contaminated areas
immediately with plenty of water. Don’t
store new coolant, or leave old coolant
lying around, where it’s accessible to
children or pets - they’re attracted by its
sweet smell. Ingestion of even a small
amount of coolant can be fatal! Wipe up
garage-floor and drip-pan spills
immediately. Keep antifreeze containers
covered, and repair cooling system leaks
as soon as they’re noticed.8All vehicles covered by this manual are
equipped with a sealed, pressurised cooling
system. A translucent plastic expansion tank,
located on the right-hand side of the engine
compartment, is connected by a hose to the
thermostat housing. As the coolant heats up
during engine operation, surplus coolant
passes through the connecting hose into the
expansion tank; a connection to the radiator
bottom hose union allows coolant to circulate
through the tank and back to the water pump,
thus purging any air from the system. As the
engine cools, the coolant is automatically
drawn back into the cooling system’s main
components, to maintain the correct level.
9While the coolant level must be checked
regularly, remember therefore that it will vary
with the temperature of the engine. When the
engine is cold, the coolant level should be
between the “MAX” and “MIN” level lines on
the tank, but once the engine has warmed up,
the level may rise to above the “MAX” level
line.
10For an accurate check of the coolant
level, the engine must be cold. The level must
be between the “MAX” and “MIN” level lines
on the tank (see illustration). If it is below the
“MIN” level line, the coolant must be topped-
up as follows.
11First prepare a sufficient quantity of
coolant mixture, using clean, soft water and
antifreeze of the recommended type, in the
specified mixture ratio. If you are using
antifreeze to Ford’s specification or equivalent
(see the note at the beginning of Section 2 of
this Chapter), mix equal quantities of water
and antifreeze to produce the 50/50 mixture
ratio specified when topping-up; if using any
other type of antifreeze, follow its
manufacturer’s instructions to achieve the
correct ratio. If only a small amount of coolant
is required to bring the system up to the
proper level, plain water can be used, but
repeatedly doing this will dilute the
antifreeze/water solution in the system,
reducing the protection it should provide
against freezing and corrosion. To maintainthe specified antifreeze/water ratio, it is
essential to top-up the coolant level with the
correct mixture, as described here. Use only
ethylene/glycol type antifreeze, and do not
use supplementary inhibitors or additives.
Warning: Never remove the
expansion tank filler cap when
the engine is running, or has just
been switched off, as the cooling system
will be hot, and the consequent escaping
steam and scalding coolant could cause
serious injury.
12If topping-up is necessary, wait until the
system has cooled completely (or at least 10
minutes after switching off the engine, if lack
of time means it is absolutely necessary to
top-up while the engine may still be warm).
Wrap a thick cloth around the expansion tank
filler cap, and unscrew it one full turn. If any
hissing is heard as steam escapes, wait until
the hissing ceases, indicating that pressure is
released, then slowly unscrew the filler cap
until it can be removed. If more hissing
sounds are heard, wait until they have
stopped before unscrewing the filler cap
completely. At all times, keep your face,
hands and other exposed skin well away from
the filler opening.
13When the filler cap has been removed,
add coolant to bring the level up to the “MAX”
level line (see illustration). Refit the cap,
tightening it securely.
14With this type of cooling system, the
addition of coolant should only be necessary at
very infrequent intervals. If topping-up is
regularly required, or if the coolant level drops
within a short time after replenishment, there
may be a leak in the system. Inspect the
radiator, hoses, expansion tank filler cap,
radiator drain plug and water pump. If no leak is
evident, have the filler cap and the entire
system pressure-tested by your dealer or
suitably-equipped garage; this will usually show
up a small leak not otherwise visible. If
significant leakage is found at any time, use an
antifreeze hydrometer to check the con-
centration of antifreeze remaining in the coolant.
1•7
13.13 Remove the cap to add coolant only
when the engine is cold - top-up to the
“MAX” level line using the specified
coolant mixture3.6 The yellow/black oil filler cap is
screwed into the cylinder head cover.
Always make sure the area around the
opening is clean before unscrewing the
cap, to prevent dirt from contaminating the
engine3.10 The cooling system expansion tank is
located on the right-hand side of the
engine compartment. The coolant level
must be between the tank “MAX” and
“MIN” level lines (arrowed) when the
engine is cold
Weekly checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 22 of 279
15Coolant hydrometers are available at
most automotive accessory shops. If the
specific gravity of a sample taken from the
expansion tank (when the engine is switched
off and fully cooled down) is less than that
specified, the coolant mixture strength has
fallen below the minimum. If this is found,
either the coolant strength must be restored
by adding neat antifreeze to Ford’s
specification (if that is what is in the system)
or by draining and flushing the system, then
refilling it with fresh coolant mixture of the
correct ratio (if any other type of antifreeze is
being used).
16When checking the coolant level, always
note its condition; it should be relatively clear.
If it is brown or rust-coloured, the system
should be drained, flushed and refilled. If
antifreeze has been used which does not
meet Ford’s specification, its corrosion
inhibitors will lose their effectiveness with
time; such coolant must be renewed regularly,
even if it appears to be in good condition,
usually at the intervals suggested at the
beginning of Section 2 of this Chapter.
Windscreen/tailgate and
headlight washer fluid
17Fluid for the windscreen/tailgate washer
system (and where applicable the headlight
washer system) is stored in a plastic reservoir,
which is located at the right front corner of the
engine compartment. In milder climates, plain
water can be used to top-up the reservoir, but
the reservoir should be kept no more than
two-thirds full, to allow for expansion should
the water freeze. In colder climates, the use of
a specially-formulated windscreen washer
fluid, available at your dealer or any car
accessory shop, will help lower the freezing
point of the fluid (see illustration). Do notuse
regular (engine) antifreeze - it will damage the
vehicle’s paintwork.
Battery electrolyte
18On models not equipped with a sealed
battery (see Section 9), check the electrolyte
level of all six battery cells. The level must be
approximately 10 mm above the plates; this
may be shown by maximum and minimum
level lines marked on the battery’s casing (seeillustration). If the level is low, use a coin to
release the filler/vent cap, and add distilled
water. Install and securely retighten the cap.
Caution: Overfilling the cells may
cause electrolyte to spill over
during periods of heavy charging,
causing corrosion or damage.
Refer also to the warning at the beginning
of Section 9.
Brake fluid
19The brake fluid reservoir is located on the
top of the brake master cylinder, which is
attached to the front of the vacuum servo unit.
The “MAX” and “MIN” marks are indicated on
the side of the translucent reservoir, and the
fluid level should be maintained between
these marks at all times (see illustration).
20The brake fluid inside the reservoir is
readily visible. With the vehicle on level
ground, the level should normally be on or just
below the “MAX” mark.
21Progressive wear of the brake pads and
brake shoe linings causes the level of the
brake fluid to gradually fall; however, when
the brake pads are renewed, the original level
of the fluid is restored. It is not therefore
necessary to top-up the level to compensate
for this minimal drop, but the level must never
be allowed to fall below the minimum mark.
22If topping-up is necessary, first wipe the
area around the filler cap with a clean rag
before removing the cap. When adding fluid,
pour it carefully into the reservoir, to avoid
spilling it on surrounding painted surfaces
(see illustration). Be sure to use only the
specified hydraulic fluid (see “Lubricants,
fluids and capacities”at the start of this
Chapter) since mixing different types of fluid
can cause damage to the system.
Warning: Brake hydraulic fluid
can harm your eyes and damage
painted surfaces, so use extreme
caution when handling and
pouring it. Wash off spills immediately with
plenty of water. Do not use fluid that has
been standing open for some time, as it
absorbs moisture from the air. Excessmoisture can cause corrosion and a
dangerous loss of braking effectiveness.
23When adding fluid, it is a good idea to
inspect the reservoir for contamination. The
system should be drained and refilled if
deposits, dirt particles or contamination are
seen in the fluid.
24After filling the reservoir to the correct
level, make sure that the cap is refitted
securely, to avoid leaks and the entry of
foreign matter.
25If the reservoir requires repeated
replenishing to maintain the correct level, this
is an indication of an hydraulic leak
somewhere in the system, which should be
investigated immediately.
Power steering fluid
26See Section 5 of this Chapter.
1Periodic inspection of the tyres may spare
you from the inconvenience of being stranded
with a flat tyre. It can also provide you with
vital information regarding possible problems
in the steering and suspension systems
before major damage occurs.
2The original tyres on this vehicle are
equipped with tread wear indicator (TWI)
bands, which will appear when the tread
depth reaches approximately 1.6 mm. Most
tyres have a mark around the tyre at regular
intervals to indicate the location of the tread
4 Tyre and tyre pressure checks
1•8
3.17 Topping-up the windscreen washer
reservoir3.18 On non-sealed batteries, keep the
electrolyte level of all the cells in the
battery between the maximum and
minimum levels (arrowed) - ie, 10 mm
above the plates. Use only distilled water,
and never overfill3.19 Brake fluid reservoir, showing “MAX”
and “MIN” marks
3.22 Topping-up the brake fluid reservoir
Weekly checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 29 of 279
5Check all fluid reservoirs, filler caps, drain
plugs and fittings etc, looking for any signs of
leakage of oil, transmission and/or brake
hydraulic fluid, coolant and power steering
fluid. If the vehicle is regularly parked in the
same place, close inspection of the ground
underneath it will soon show any leaks; ignore
the puddle of water which will be left if the air
conditioning system is in use. As soon as a
leak is detected, its source must be traced
and rectified. Where oil has been leaking for
some time, it is usually necessary to use a
steam cleaner, pressure washer or similar, to
clean away the accumulated dirt, so that the
exact source of the leak can be identified.
Vacuum hoses
6It’s quite common for vacuum hoses,
especially those in the emissions system, to
be colour-coded, or to be identified by
coloured stripes moulded into them. Various
systems require hoses with different wall
thicknesses, collapse resistance and
temperature resistance. When renewing
hoses, be sure the new ones are made of the
same material.
7Often the only effective way to check a
hose is to remove it completely from the
vehicle. If more than one hose is removed, be
sure to label the hoses and fittings to ensure
correct installation.
8When checking vacuum hoses, be sure to
include any plastic T-fittings in the check.
Inspect the fittings for cracks, and check the
hose where it fits over the fitting for distortion,
which could cause leakage.
9A small piece of vacuum hose (quarter-inch
inside diameter) can be used as a
stethoscope to detect vacuum leaks. Hold
one end of the hose to your ear, and probe
around vacuum hoses and fittings, listening
for the “hissing” sound characteristic of a
vacuum leak.
Warning: When probing with the
vacuum hose stethoscope, be
very careful not to come into
contact with moving engine
components such as the auxiliary
drivebelt, radiator electric cooling fan, etc.
Fuel hoses
Warning: There are certain
precautions which must be taken
when inspecting or servicing fuel
system components. Work in a well-
ventilated area, and do not allow open
flames (cigarettes, appliance pilot lights,
etc.) or bare light bulbs near the work
area. Mop up any spills immediately, and
do not store fuel-soaked rags where they
could ignite.
10Check all fuel hoses for deterioration and
chafing. Check especially for cracks in areas
where the hose bends, and also just before
fittings, such as where a hose attaches to the
fuel filter.
11High-quality fuel line, usually identified by
the word “Fluoroelastomer” printed on thehose, should be used for fuel line renewal.
Never, under any circumstances, use
unreinforced vacuum line, clear plastic tubing
or water hose for fuel lines.
12Spring-type clamps are commonly used
on fuel lines. These clamps often lose their
tension over a period of time, and can be
“sprung” during removal. Replace all
spring-type clamps with screw clamps
whenever a hose is replaced.
Metal lines
13Sections of metal piping are often used
for fuel line between the fuel filter and the
engine. Check carefully to be sure the piping
has not been bent or crimped, and that cracks
have not started in the line.
14If a section of metal fuel line must be
renewed, only seamless steel piping should
be used, since copper and aluminium piping
don’t have the strength necessary to
withstand normal engine vibration.
15Check the metal brake lines where they
enter the master cylinder and ABS hydraulic
unit (if used) for cracks in the lines or loose
fittings. Any sign of brake fluid leakage calls
for an immediate and thorough inspection of
the brake system.
1With the vehicle parked on level ground,
apply the handbrake firmly and open the
bonnet. Using an inspection light or a small
electric torch, check all visible wiring within
and beneath the engine compartment.
2What you are looking for is wiring that is
obviously damaged by chafing against sharp
edges, or against moving suspension/
transmission components and/or the auxiliary
drivebelt, by being trapped or crushed
between carelessly-refitted components, or
melted by being forced into contact with the
hot engine castings, coolant pipes, etc. In
almost all cases, damage of this sort is
caused in the first instance by incorrect
routing on reassembly after previous work has
been carried out.
3Depending on the extent of the problem,
damaged wiring may be repaired by rejoining
the break or splicing-in a new length of wire,
using solder to ensure a good connection,
and remaking the insulation with adhesive
insulating tape or heat-shrink tubing, as
appropriate. If the damage is extensive, given
the implications for the vehicle’s future
reliability, the best long-term answer may well
be to renew that entire section of the loom,
however expensive this may appear.
4When the actual damage has been
repaired, ensure that the wiring loom is re-
routed correctly, so that it is clear of other
components, and not stretched or kinked, and
is secured out of harm’s way using the plastic
clips, guides and ties provided.
5Check all electrical connectors, ensuringthat they are clean, securely fastened, and
that each is locked by its plastic tabs or wire
clip, as appropriate. If any connector shows
external signs of corrosion (accumulations of
white or green deposits, or streaks of “rust”),
or if any is thought to be dirty, it must be
unplugged and cleaned using electrical
contact cleaner. If the connector pins are
severely corroded, the connector must be
renewed; note that this may mean the renewal
of that entire section of the loom - see your
local Ford dealer for details.
6If the cleaner completely removes the
corrosion to leave the connector in a
satisfactory condition, it would be wise to
pack the connector with a suitable material
which will exclude dirt and moisture,
preventing the corrosion from occurring
again; a Ford dealer may be able to
recommend a suitable product.
7Check the condition of the battery
connections - remake the connections or
renew the leads if a fault is found (see Chap-
ter 5). Use the same techniques to ensure that
all earth points in the engine compartment
provide good electrical contact through clean,
metal-to-metal joints, and that all are securely
fastened. (In addition to the earth connection
at the engine lifting eye, and that from the
transmission to the body/battery, there are
one or two earth points behind each headlight
assembly, and one below the power steering
fluid reservoir.)
8Refer to Section 31 for details of spark plug
(HT) lead checks.
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any fittings or
remove any components until
after the system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant must be properly
discharged into an approved type of
container, at a dealer service department
or an automotive air conditioning repair
facility capable of handling R134a
refrigerant. Always wear eye protection
when disconnecting air conditioning
system fittings.
1The following maintenance checks should
be performed on a regular basis, to ensure
that the air conditioner continues to operate at
peak efficiency:
(a) Check the auxiliary drivebelt. If it’s worn
or deteriorated, renew it (see Section 11).
(b) Check the system hoses. Look for cracks,
bubbles, hard spots and deterioration.
Inspect the hoses and all fittings for oil
bubbles and seepage. If there’s any
evidence of wear, damage or leaks, renew
the hose(s).
(c) Inspect the condenser fins for leaves,
insects and other debris. Use a “fin
14 Air conditioning system
check
13 Engine compartment wiring
check
1•15
1
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 54 of 279
related components, to remove all traces of
oil. Fit a new belt on reassembly.
2If the timing belt is still clean, slip it off the
toothed pulley, taking care not to twist it too
sharply; use the fingers only to handle the
belt. Do notrotate the crankshaft until the
timing belt is refitted. Cover the belt, and
secure it so that it is clear of the working area
and cannot slip off the remaining toothed
pulley.
3Unfasten the pulley bolt and withdraw the
pulley (see Section 11).
4Unbolt the camshaft right-hand bearing
cap, and withdraw the defective oil seal.
Clean the seal housing, and polish off any
burrs or raised edges, which may have
caused the seal to fail in the first place.
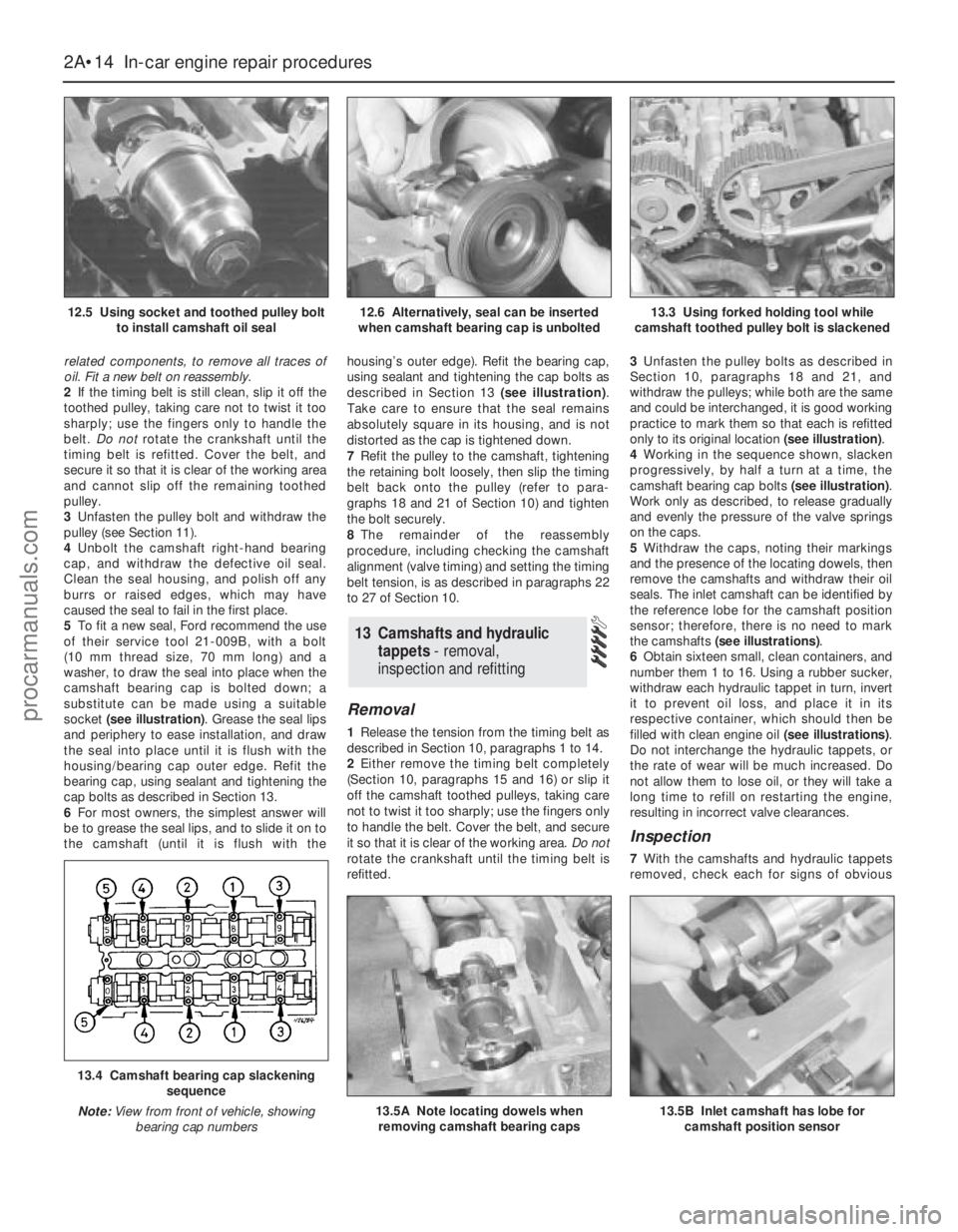
5To fit a new seal, Ford recommend the use
of their service tool 21-009B, with a bolt
(10 mm thread size, 70 mm long) and a
washer, to draw the seal into place when the
camshaft bearing cap is bolted down; a
substitute can be made using a suitable
socket (see illustration). Grease the seal lips
and periphery to ease installation, and draw
the seal into place until it is flush with the
housing/bearing cap outer edge. Refit the
bearing cap, using sealant and tightening the
cap bolts as described in Section 13.
6For most owners, the simplest answer will
be to grease the seal lips, and to slide it on to
the camshaft (until it is flush with thehousing’s outer edge). Refit the bearing cap,
using sealant and tightening the cap bolts as
described in Section 13 (see illustration).
Take care to ensure that the seal remains
absolutely square in its housing, and is not
distorted as the cap is tightened down.
7Refit the pulley to the camshaft, tightening
the retaining bolt loosely, then slip the timing
belt back onto the pulley (refer to para-
graphs 18 and 21 of Section 10) and tighten
the bolt securely.
8The remainder of the reassembly
procedure, including checking the camshaft
alignment (valve timing) and setting the timing
belt tension, is as described in paragraphs 22
to 27 of Section 10.
Removal
1Release the tension from the timing belt as
described in Section 10, paragraphs 1 to 14.
2Either remove the timing belt completely
(Section 10, paragraphs 15 and 16) or slip it
off the camshaft toothed pulleys, taking care
not to twist it too sharply; use the fingers only
to handle the belt. Cover the belt, and secure
it so that it is clear of the working area. Do not
rotate the crankshaft until the timing belt is
refitted.3Unfasten the pulley bolts as described in
Section 10, paragraphs 18 and 21, and
withdraw the pulleys; while both are the same
and could be interchanged, it is good working
practice to mark them so that each is refitted
only to its original location (see illustration).
4Working in the sequence shown, slacken
progressively, by half a turn at a time, the
camshaft bearing cap bolts (see illustration).
Work only as described, to release gradually
and evenly the pressure of the valve springs
on the caps.
5Withdraw the caps, noting their markings
and the presence of the locating dowels, then
remove the camshafts and withdraw their oil
seals. The inlet camshaft can be identified by
the reference lobe for the camshaft position
sensor; therefore, there is no need to mark
the camshafts (see illustrations).
6Obtain sixteen small, clean containers, and
number them 1 to 16. Using a rubber sucker,
withdraw each hydraulic tappet in turn, invert
it to prevent oil loss, and place it in its
respective container, which should then be
filled with clean engine oil (see illustrations).
Do not interchange the hydraulic tappets, or
the rate of wear will be much increased. Do
not allow them to lose oil, or they will take a
long time to refill on restarting the engine,
resulting in incorrect valve clearances.
Inspection
7With the camshafts and hydraulic tappets
removed, check each for signs of obvious
13 Camshafts and hydraulic
tappets - removal,
inspection and refitting
2A•14 In-car engine repair procedures
12.5 Using socket and toothed pulley bolt
to install camshaft oil seal12.6 Alternatively, seal can be inserted
when camshaft bearing cap is unbolted13.3 Using forked holding tool while
camshaft toothed pulley bolt is slackened
13.4 Camshaft bearing cap slackening
sequence
Note:View from front of vehicle, showing
bearing cap numbers
13.5A Note locating dowels when
removing camshaft bearing caps13.5B Inlet camshaft has lobe for
camshaft position sensor
procarmanuals.com
Page 60 of 279

additional lifting eyes where required (see
illustration). Remove completely the
engine/transmission front mounting, unscrew
the rear mounting’s centre bolt, and unbolt
the left-hand mounting from the body.
Unscrew the six nuts securing the right-hand
mounting bracket, and withdraw the bracket.
13Being careful to watch the wiring, coolant
hoses, fluid cooler pipes or gearchange
linkage and transmission support rods (where
appropriate), and the radiator electric cooling
fan, to ensure that nothing is trapped,
stretched or damaged, lift the
engine/transmission unit by 2 to 3 inches and
support it securely.
14Progressively unscrew the sump retaining
bolts. Break the joint by striking the sump
with the palm of the hand, then lower the
sump and withdraw it with the
engine/transmission lower adaptor plate; note
the presence of any shims between the sump
and transmission.
15Remove and discard the sump gasket;
this must be renewed as a matter of course
whenever it is disturbed.
16While the sump is removed, take the
opportunity to remove the oil pump pick-up/
strainer pipe and to clean it (see Section 16).
Refitting
17On reassembly, thoroughly clean and
degrease the mating surfaces of the cylinder
block/crankcase and sump, then use a cleanrag to wipe out the sump and the engine’s
interior. If the oil pump pick-up/strainer pipe
was removed, fit a new gasket and refit the
pipe, tightening its screws to the specified
torque wrench setting. Fit the new gasket to
the sump mating surface so that the gasket
fits into the sump groove (see illustration).
18If the sump is being refitted with the
engine/transmission still connected and in the
vehicle, proceed as follows:
(a) Check that the mating surfaces of the
sump, the cylinder block/crankcase and
the transmission are absolutely clean and
flat. Any shims found on removal of the
sump must be refitted in their original
locations.
(b) Apply a thin film of suitable sealant (Ford
recommend Hylosil 102) to the junctions
of the cylinder block/crankcase with the
oil pump and the crankshaft left-hand oil
seal carrier. Without delay - the sump
bolts must be fully tightened within 10 to
20 minutes of applying the sealant - offer
up the sump and engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate, and refit the bolts,
tightening them lightly at first (see
illustration).
(c) Ensuring that the engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate is correctly located,
firmly press the sump against the
transmission, and tighten the
transmission-to-sump (ie, engine) bolts to
the specified torque wrench setting.(d) Without disturbing the position of the
sump, and working in a diagonal
sequence from the centre outwards,
tighten the sump bolts to the specified
torque wrench setting.
(e) Proceed to paragraph 20.
19If the sump is being refitted with the
engine and transmission separated (in or out
of the vehicle), proceed as follows:
(a) Apply a thin film of suitable sealant (Ford
recommend Hylosil 102) to the junctions
of the cylinder block/crankcase with the
oil pump and the crankshaft left-hand oil
seal carrier (see illustration). Without
delay - the sump bolts must be fully
tightened within 10 to 20 minutes of
applying the sealant - offer up the sump
to the cylinder block/crankcase, and
insert the sump bolts, tightening them
lightly at first.
(b) Using a suitable straight edge to check
alignment across the flat-machined faces
of each, move the sump as necessary so
that its left-hand face - including any
shims found on removal - is flush with
that of the cylinder block/crankcase (see
illustration). Without disturbing the
position of the sump, and working in a
diagonal sequence from the centre
outwards, tighten the sump bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(c) Check again that both faces are flush
before proceeding; if necessary, unbolt
the sump again, clean the mating
surfaces, and repeat the full procedure to
ensure that the sump is correctly aligned.
(d) If it is not possible to achieve exact
alignment by moving the sump, shims are
available in thicknesses of 0.25 mm
(colour-coded yellow) or 0.50 mm (colour-
coded black) to eliminate the discrepancy
(see illustration).
20The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following points.
(a) Tighten all fasteners to the torque wrench
settings specified.
(b) Always renew any self-locking nuts
disturbed on removal.
(c) Lower the engine/transmission unit into
place, and reassemble the rear, left-hand
2A•20 In-car engine repair procedures
15.17 Ensure gasket is located correctly in
sump groove15.18 Engine/transmission lower adaptor
plate (arrowed) must be refitted with sump15.19A Apply sealant (arrowed) as
directed when refitting sump
15.19B Checking alignment of sump with
cylinder block/crankcase15.19C Sump-to-cylinder block/crankcase
alignment shims
1 Fitting points on sump 2 Shim
procarmanuals.com
Page 75 of 279
gear linkage heat shield. Reconnect the
gearchange linkage and transmission support
rods to the transmission, adjusting the linkage
using the marks made on removal (see
Chapter 7, Part A, for details).
56Re-install the remaining components and
fasteners in the reverse order of removal.
57Add coolant, engine oil and transmission
fluids as needed (see Chapter 1).
58Run the engine, and check for proper
operation and the absence of leaks. Shut off
the engine, and recheck the fluid levels.
59Remember that, since the front suspension
subframe and steering gear have been
disturbed, the wheel alignment and steering
angles must be checked fully and carefully as
soon as possible, with any necessary
adjustments being made. This operation is best
carried out by an experienced mechanic, using
proper checking equipment; the vehicle should
therefore be taken to a Ford dealer or similarly-
qualified person for attention.
1It is much easier to dismantle and work on
the engine if it is mounted on a portable engine
stand. These stands can often be hired from a
tool hire shop. Before the engine is mounted
on a stand, the flywheel/driveplate should be
removed (Part A of this Chapter, Section 21)
so that the stand bolts can be tightened into
the end of the cylinder block/crankcase.
2If a stand is not available, it is possible to
dismantle the engine with it mounted on
blocks, on a sturdy workbench or on the floor.
Be extra-careful not to tip or drop the engine
when working without a stand.
3If you are going to obtain a reconditioned
engine, all external components must be
removed first, to be transferred to the
replacement engine (just as they will if you are
doing a complete engine overhaul yourself).
Note:When removing the external
components from the engine, pay close
attention to details that may be helpful or
important during refitting. Note the fitted
position of gaskets, seals, spacers, pins,
washers, bolts and other small items.These
external components include the following:
(a) Alternator and brackets (Chapter 5).
(b) HT leads and spark plugs (Chapter 1).
(c) Thermostat and housing (Chapter 3).
(d) Dipstick tube.
(e) Fuel injection system components
(Chapter 4).
(f) All electrical switches and sensors - refer
to the appropriate Chapter.
(g) Inlet and exhaust manifolds (Part A of this
Chapter).
(h) Oil filter (Chapter 1).
(i) Engine/transmission mounting brackets
(Part A of this Chapter, Section 22).
(j) Flywheel/driveplate (Part A of this
Chapter, Section 21).
4If you are obtaining a “short” engine (whichconsists of the engine cylinder
block/crankcase, crankshaft, pistons and
connecting rods all assembled), then the
cylinder head, sump, oil pump, and timing belt
will have to be removed also.
5If you are planning a complete overhaul, the
engine can be dismantled and the internal
components removed in the following order.
(a) Inlet and exhaust manifolds (Part A of this
Chapter).
(b) Timing belt, toothed pulleys and
tensioner, and timing belt inner cover
(Part A of this Chapter).
(c) Cylinder head (Part A of this Chapter,
Section 14).
(d) Flywheel/driveplate (Part A of this
Chapter, Section 21).
(e) Sump (Part A of this Chapter, Section 15).
(f) Oil pump (Part A of this Chapter, Sec-
tion 16).
(g) Piston/connecting rod assemblies
(Section 9).
(h) Crankshaft (Section 10).
6Before beginning the dismantling andoverhaul procedures, make sure that you have
all of the correct tools necessary. Refer to the
introductory pages at the beginning of this
manual for further information.
Note:New and reconditioned cylinder heads
are available from the manufacturers, and
from engine overhaul specialists. Due to the
fact that some specialist tools are required for
the dismantling and inspection procedures,
and new components may not be readily
available (refer to Section 1 of this Part), it may
be more practical and economical for the
home mechanic to purchase a reconditioned
head, rather than to dismantle, inspect and
recondition the original head.
1Remove the camshafts and hydraulic
tappets (Part A of this Chapter, Section 13),
being careful to store the hydraulic tappets as
described (see illustration).
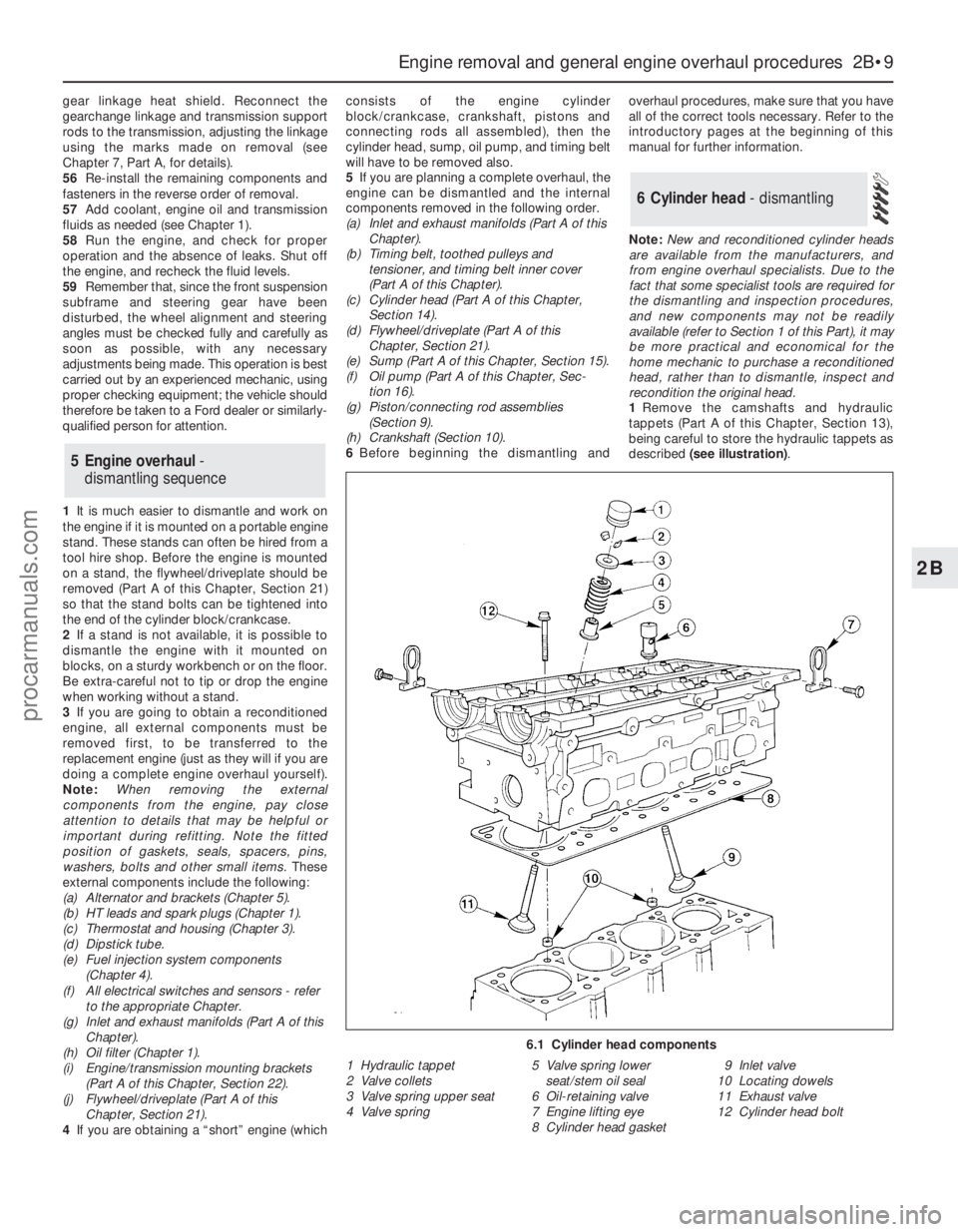
6 Cylinder head - dismantling
5 Engine overhaul-
dismantling sequence
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•9
2B
6.1 Cylinder head components
1 Hydraulic tappet
2 Valve collets
3 Valve spring upper seat
4 Valve spring5 Valve spring lower
seat/stem oil seal
6 Oil-retaining valve
7 Engine lifting eye
8 Cylinder head gasket9 Inlet valve
10 Locating dowels
11 Exhaust valve
12 Cylinder head bolt
procarmanuals.com