seat adjustment FORD SIERRA 1983 1.G Engine Electrical Systems Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1983, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1983 1.GPages: 24, PDF Size: 0.93 MB
Page 13 of 24
10The distributor cap (except on 1.6 and 1.8
litre CVH (R6A type) engines) and the HT
leads should be cleaned and checked at the
specified intervals. To test the HT leads,
remove them together with the distributor
cap, then connect an ohmmeter to the end of
each lead and its appropriate terminal within
the cap in turn (see illustration). If the
resistance of any lead is greater than the
maximum given in the Specifications, check
that the lead connection in the cap is good
before renewing the lead.
Refitting
11Before fitting the spark plugs, check that
the threaded connector sleeves are tight and
that the plug exterior surfaces are clean. As
the plugs incorporate taper seats also make
sure that the threads and seats are clean.
12On DOHC models before refitting thespark plugs, coat their threads with suitable
antiseize compound, taking care not to
contaminate the electrodes.
13Screw in the spark plugs by hand, then
tighten them to the specified torque. Do not
exceed the torque figure.
14Push the HT leads firmly onto the spark
plugs, and where applicable refit the air
cleaner and/or inlet hose.Testing
All models except 1.6 and 1.8 litre
CVH (R6A type)
1The coil is located on the left-hand side of
the engine compartment and is retained by a
metal strap (see illustration). It is of high
output type and the HT tower should be kept
clean at all times to prevent possible arcing.
Bosch and Femsa coils are fitted with
protective plastic covers and Polmot coils are
fitted with an internal fusible link.
2To ensure that the correct HT polarity at the
spark plugs, the LT coil leads must always be
connected correctly. The black lead must
always be connected to the terminal marked +
115, and the green lead to the terminal
marked /1. Incorrect connections can cause
poor starting, misfiring, and short spark plug
life.
3To test the coil first disconnect the LT and
HT leads. Connect an ohmmeter betweenboth LT terminals and check that the primary
winding resistance is as given in the
Specifications. Connect the ohmmeter
between the HT terminal and either LT
terminal and check that the secondary
winding resistance is as given in the
Specifications. If either winding resistance is
not as specified, the coil should be renewed.
Reconnect the LT and HT leads on
completion.
1.6 and 1.8 litre (R6A type) CVH
models
4The coil fitted to these models is located
towards the front right-hand side of the
cylinder block (see illustration).
5Testing of the coil should be entrusted to a
Ford dealer or a suitable specialist.
Removal
All models except 1.6 and 1.8 litre
CVH (R6A type)
6Disconnect the battery negative lead,
7Disconnect the LT and HT leads from the
coil (see illustration).
8Remove the securing screw(s) and detach
the coil and strap assembly from the body
panel. Note that on models with the ESC
system, the coil strap is secured by the top
ESC module securing screw. On certain
models with the ESC II or EEC IV systems, an
“octane adjustment” service lead may be
connected to one of the coil securing screws.
On 2.0 litre DOHC fuel-injected models, the
coil/ignition module heat shield must be
removed for access to the coil securing bolts.
The heat shield is secured by two screws.
Note that on certain models, an earthing lead
12Coil - testing, removal and
refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•13
5
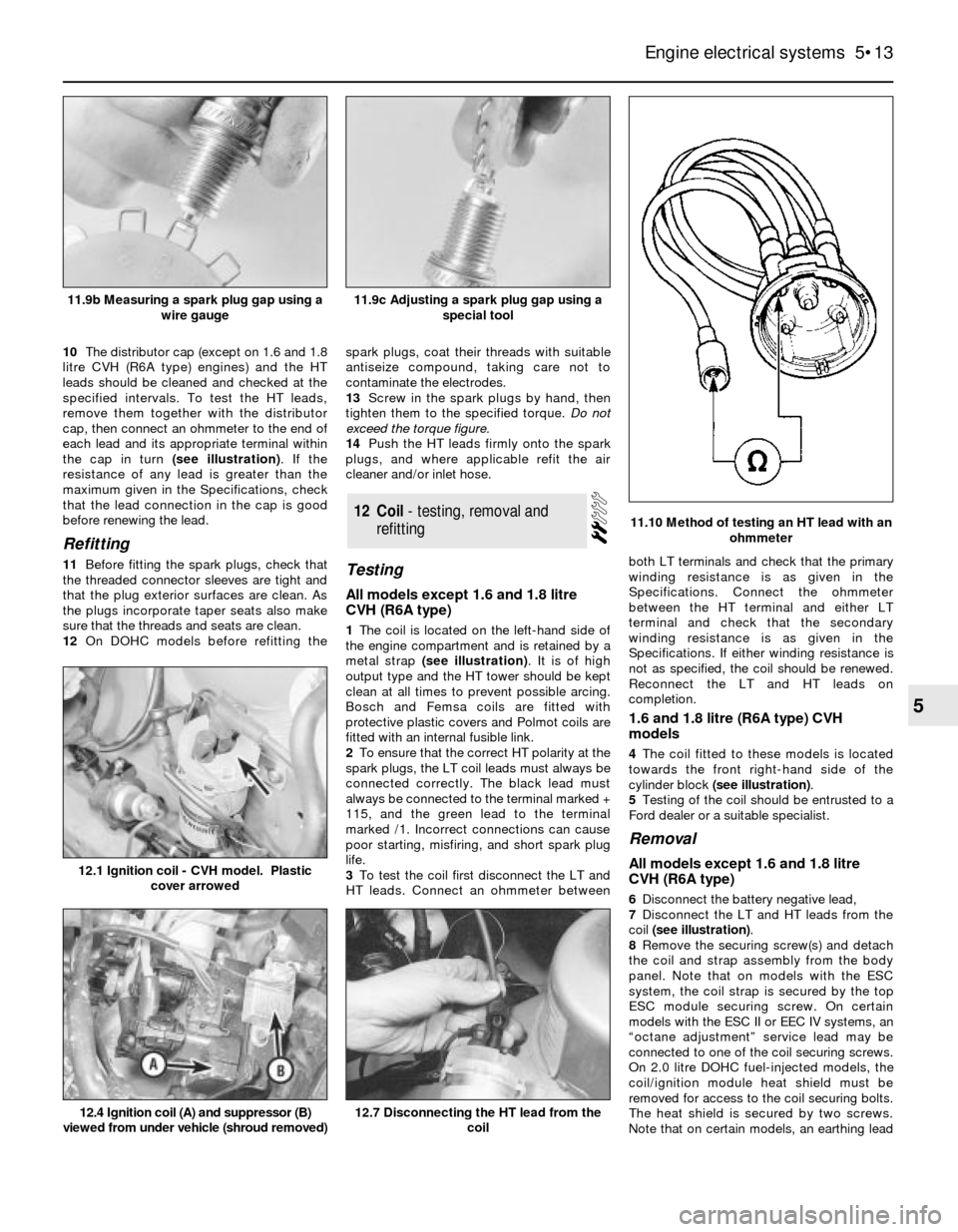
11.10 Method of testing an HT lead with an
ohmmeter
12.4 Ignition coil (A) and suppressor (B)
viewed from under vehicle (shroud removed)12.7 Disconnecting the HT lead from the
coil
12.1 Ignition coil - CVH model. Plastic
cover arrowed
11.9c Adjusting a spark plug gap using a
special tool11.9b Measuring a spark plug gap using a
wire gauge
Page 18 of 24
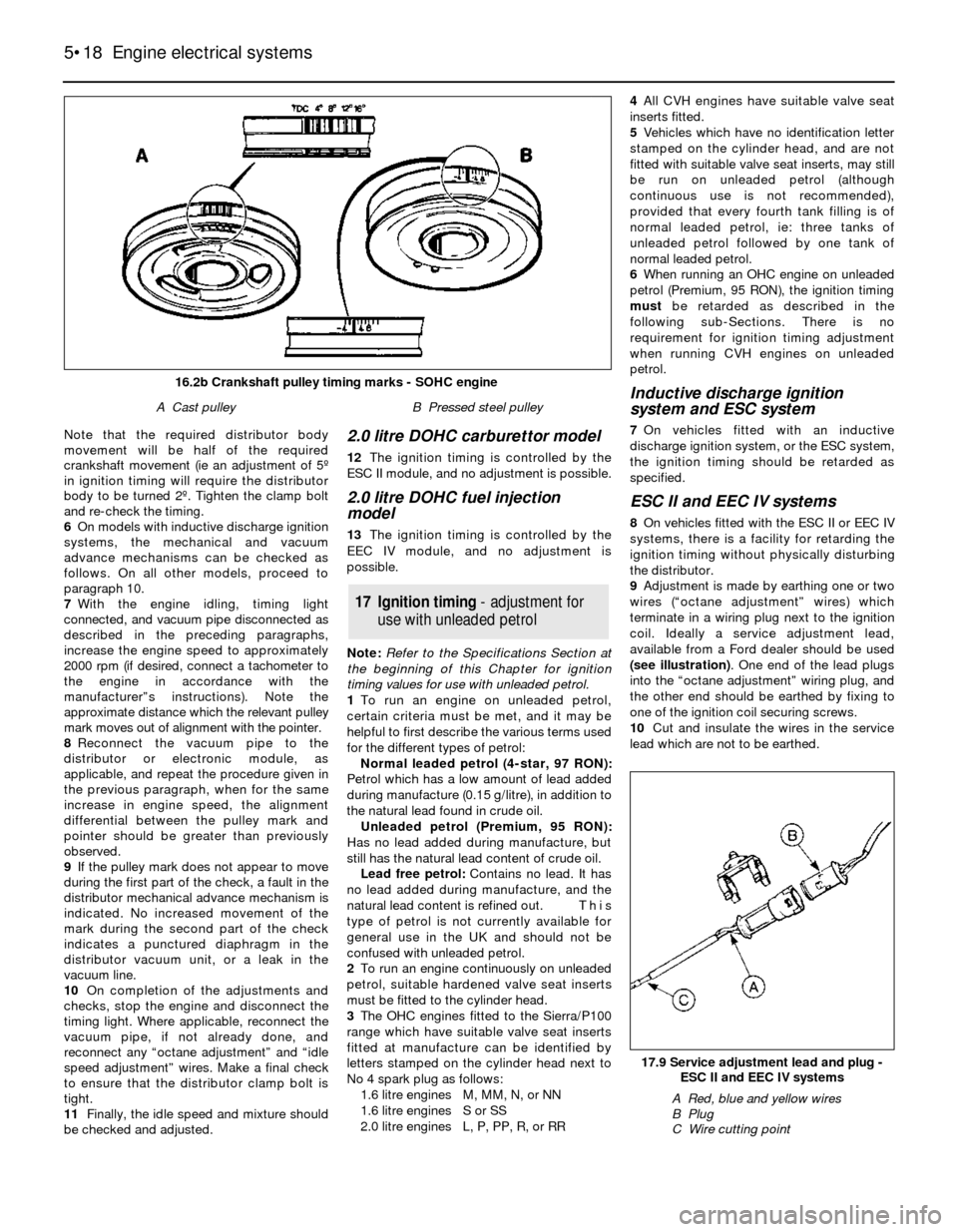
Note that the required distributor body
movement will be half of the required
crankshaft movement (ie an adjustment of 5º
in ignition timing will require the distributor
body to be turned 2º. Tighten the clamp bolt
and re-check the timing.
6On models with inductive discharge ignition
systems, the mechanical and vacuum
advance mechanisms can be checked as
follows. On all other models, proceed to
paragraph 10.
7With the engine idling, timing light
connected, and vacuum pipe disconnected as
described in the preceding paragraphs,
increase the engine speed to approximately
2000 rpm (if desired, connect a tachometer to
the engine in accordance with the
manufacturer”s instructions). Note the
approximate distance which the relevant pulley
mark moves out of alignment with the pointer.
8Reconnect the vacuum pipe to the
distributor or electronic module, as
applicable, and repeat the procedure given in
the previous paragraph, when for the same
increase in engine speed, the alignment
differential between the pulley mark and
pointer should be greater than previously
observed.
9If the pulley mark does not appear to move
during the first part of the check, a fault in the
distributor mechanical advance mechanism is
indicated. No increased movement of the
mark during the second part of the check
indicates a punctured diaphragm in the
distributor vacuum unit, or a leak in the
vacuum line.
10On completion of the adjustments and
checks, stop the engine and disconnect the
timing light. Where applicable, reconnect the
vacuum pipe, if not already done, and
reconnect any “octane adjustment” and “idle
speed adjustment” wires. Make a final check
to ensure that the distributor clamp bolt is
tight.
11Finally, the idle speed and mixture should
be checked and adjusted.2.0 litre DOHC carburettor model
12The ignition timing is controlled by the
ESC II module, and no adjustment is possible.
2.0 litre DOHC fuel injection
model
13The ignition timing is controlled by the
EEC IV module, and no adjustment is
possible.
Note: Refer to the Specifications Section at
the beginning of this Chapter for ignition
timing values for use with unleaded petrol.
1To run an engine on unleaded petrol,
certain criteria must be met, and it may be
helpful to first describe the various terms used
for the different types of petrol:
Normal leaded petrol (4-star, 97 RON):
Petrol which has a low amount of lead added
during manufacture (0.15 g/litre), in addition to
the natural lead found in crude oil.
Unleaded petrol (Premium, 95 RON):
Has no lead added during manufacture, but
still has the natural lead content of crude oil.
Lead free petrol: Contains no lead. It has
no lead added during manufacture, and the
natural lead content is refined out. This
type of petrol is not currently available for
general use in the UK and should not be
confused with unleaded petrol.
2To run an engine continuously on unleaded
petrol, suitable hardened valve seat inserts
must be fitted to the cylinder head.
3The OHC engines fitted to the Sierra/P100
range which have suitable valve seat inserts
fitted at manufacture can be identified by
letters stamped on the cylinder head next to
No 4 spark plug as follows:
1.6 litre enginesM, MM, N, or NN
1.6 litre enginesS or SS
2.0 litre enginesL, P, PP, R, or RR4All CVH engines have suitable valve seat
inserts fitted.
5Vehicles which have no identification letter
stamped on the cylinder head, and are not
fitted with suitable valve seat inserts, may still
be run on unleaded petrol (although
continuous use is not recommended),
provided that every fourth tank filling is of
normal leaded petrol, ie: three tanks of
unleaded petrol followed by one tank of
normal leaded petrol.
6When running an OHC engine on unleaded
petrol (Premium, 95 RON), the ignition timing
must be retarded as described in the
following sub-Sections. There is no
requirement for ignition timing adjustment
when running CVH engines on unleaded
petrol.
Inductive discharge ignition
system and ESC system
7On vehicles fitted with an inductive
discharge ignition system, or the ESC system,
the ignition timing should be retarded as
specified.
ESC II and EEC IV systems
8On vehicles fitted with the ESC II or EEC IV
systems, there is a facility for retarding the
ignition timing without physically disturbing
the distributor.
9Adjustment is made by earthing one or two
wires (“octane adjustment” wires) which
terminate in a wiring plug next to the ignition
coil. Ideally a service adjustment lead,
available from a Ford dealer should be used
(see illustration). One end of the lead plugs
into the “octane adjustment” wiring plug, and
the other end should be earthed by fixing to
one of the ignition coil securing screws.
10Cut and insulate the wires in the service
lead which are not to be earthed.
17Ignition timing -adjustmentfor
usewithunleadedpetrol
5•18Engine electrical systems
17.9 Service adjustment lead and plug -
ESC II and EEC IV systems
A Red, blue and yellow wires
B Plug
C Wire cutting point
16.2b Crankshaft pulley timing marks - SOHC engine
A Cast pulleyB Pressed steel pulley