AUX FORD SIERRA 1992 2.G SOHC Engines Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1992, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1992 2.GPages: 24, PDF Size: 1.03 MB
Page 1 of 24

1.3 litre engine
General
Engine type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Four-cylinder, in-line, single overhead camshaft
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3-4-2
Engine code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . JCT
Bore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.02 mm
Stroke . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66.00 mm
Cubic capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1294 cc
Compression ratio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.0:1
Compression pressure at starter motor speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 to 13 bar
Maximum continuous engine speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5800 rpm
Maximum engine power (DIN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 kW at 5700 rpm
Maximum engine torque (DIN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98 Nm at 3100 rpm
Cylinder bore diameter
Standard class 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.000 to 79.010 mm
Standard class 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.010 to 79.020 mm
Standard class 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.020 to 79.030 mm
Standard class 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.030 to 79.040 mm
Oversize class A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.510 to 79.520 mm
Oversize class B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.520 to 79.530 mm
Oversize class C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.530 to 79.540 mm
Standard service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.030 to 79.040 mm
Oversize 0.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79.530 to 79.540 mm
Oversize 1.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80.030 to 80.040 mm
Chapter 2 Part A:
SOHC engines
Auxiliary shaft - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Camshaft and cam followers - removal, inspection and refitting . . . .24
Compression test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Crankcase ventilation system - inspection and maintenance . . . . . . .4
Crankshaft and bearings - examination and renovation . . . . . . . . . .35
Crankshaft and main bearings - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Crankshaft front oil seal - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Crankshaft rear oil seal - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Cylinder block and bores - examination and renovation . . . . . . . . . .36
Cylinder head - dismantling and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Cylinder head - inspection and renovation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Cylinder head - removal and refitting (engine in vehicle) . . . . . . . . . .20
Cylinder head - removal and refitting (engine removed) . . . . . . . . . . .21
Engine - refitting (automatic transmission in vehicle) . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Engine - refitting (manual gearbox in vehicle) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Engine - removal leaving automatic transmission in vehicle . . . . . . .10
Engine - removal leaving manual gearbox in vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Engine/automatic transmission assembly - reconnection and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Engine/automatic transmission assembly - removal and separation .12Engine dismantling,examination, renovation and reassembly - general
information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Engine/manual gearbox - reconnection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Engine/manual gearbox assembly - removal and separation . . . . . .11
Engine mountings - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Engine oil and filter - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Flywheel/driveplate - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . .26
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Initial start-up after overhaul or major repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Major operations possible with the engine in the vehicle . . . . . . . . . . .6
Major operations requiring engine removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Method of engine removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Oil pump - dismantling, inspection and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Oil pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Pistons and connecting rods - examination and renovation . . . . . . .33
Pistons and connecting rods - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Sump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Timing belt and sprockets - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Valve clearances - checking and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
2A¥1
Specifications Contents
2A
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Page 2 of 24

Crankshaft
Endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.08 to 0.28 mm (0.003 to 0.011 in)
Main bearing running clearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.010 to 0.064 mm
Main bearing journal diameter:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56.970 to 56.990 mm
Undersize 0.25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56.720 to 56.740 mm
Undersize 0.50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56.470 to 56.490 mm
Undersize 0.75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56.220 to 56.240 mm
Undersize 1.00 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55.970 to 55.990 mm
Main bearing thrustwasher thickness:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.30 to 2.35 mm
Oversize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.50 to 2.55 mm
Big-end bearing running clearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.006 to 0.060 mm
Big-end bearing journal diameter:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51.980 to 52.000 mm
Undersize 0.25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51.730 to 51.750 mm
Undersize 0.50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51.480 to 51.500 mm
Undersize 0.75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51.230 to 51.250 mm
Undersize 1.00 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50.980 to 51.000 mm
Pistons and piston rings
Piston diameter:
Standard class 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78.965 to 78.975 mm
Standard class 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78.975 to 78.985 mm
Standard class 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78.985 to 78.995 mm
Standard class 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78.995 to 79.005 mm
Standard service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78.990 to 79.015 mm
Service oversize 0.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79.490 to 79.515 mm
Service oversize 1.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79.990 to 80.015 mm
Piston ring end gap:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.300 to 0.500 mm
Centre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.300 to 0.500 mm
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.400 to 1.400 mm
Auxiliary shaft
Endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.050 to 0.204 mm (0.002 to 0.008 in)
Cylinder head
Valve seat angle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44¼ 30Õ to 45¼ 00Õ
Service correction cutter*:
Upper correction angle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30¼
Lower correction angle:
Inlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75¼
Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62.5¼
Valve seat width . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.5 to 2.0 mm
Valve guide bore:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.063 to 8.088 mm
Oversize 0.2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.263 to 8.288 mm
Oversize 0.4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.463 to 8.488 mm
*Not for use with hardened valve seats
Camshaft
Endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.104 to 0.204 mm (0.004 to 0.008 in)
Thrust plate thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.98 to 4.01 mm (0.156 to 0.158 in)
Bearing journal diameter:
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41.987 to 42.013 mm
Centre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44.607 to 44.633 mm
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44.987 to 45.013 mm
Valves
Valve clearance (cold engine):
Inlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.20 ±0.03 mm (0.008 ±0.001 in)
Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.25 ±0.03 mm (0.010 ±0.001 in)
Valve timing:
Inlet opens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22¼ BTDC
Inlet closes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54¼ ABDC
Exhaust opens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64¼ BBDC
Exhaust closes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12¼ ATDC
Valve spring free length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47.00 mm (1.85 in)
2A¥2SOHC engines
Page 3 of 24

Inlet valve stem diameter:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.025 to 8.043 mm
Oversize 0.2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.225 to 8.243 mm
Oversize 0.4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.425 to 8.443 mm
Oversize 0.6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.625 to 8.643 mm
Oversize 0.8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.825 to 8.843 mm
Exhaust valve stem diameter:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7.999 to 8.017 mm
Oversize 0.2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.199 to 8.217 mm
Oversize 0.4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.399 to 8.417 mm
Oversize 0.6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.599 to 8.617 mm
Oversize 0.8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.799 to 8.817 mm
Lubrication system
Oil type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Multigrade engine oil, viscosity range SAE 10W/30 to 20W/50 to API
SG/CD or better
Oil capacity:
With filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.75 litres (6.6 pints)
Without filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.25 litres (5.7 pints)
Oil filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion C102
Oil pump clearances:
Outer rotor to body . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.153 to 0.304 mm (0.006 to 0.012 in)
Inner rotor to outer rotor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.050 to 0.200 mm (0.002 to 0.008 in)
Rotor endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.039 to 0.104 mm (0.002 to 0.004 in)
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Main bearing cap bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88 to 10265 to 75
Big-end bearing cap nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 to 4730 to 35
Crankshaft pulley bolt:
Strength class 8.8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55 to 6041 to 44
Strength class 10.9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100 to 11574 to 85
Camshaft sprocket bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45 to 5033 to 37
Auxiliary shaft sprocket bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45 to 5033 to 37
Flywheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64 to 7047 to 52
Oil pump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2113 to 15
Oil pump cover bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 137 to 10
Sump bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1 to 20.7 to 1.5
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6 to 84 to 6
Stage 3 (after running engine for 20 minutes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 106 to 7
Sump drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2815 to 21
Oil pressure warning lamp switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12 to 159 to 11
Valve adjustment ball-pin locknuts:
7 mm thick nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45 to 5033 to 37
8 mm thick nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50 to 5537 to 41
Cylinder head bolts:
Splined type bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 to 5530 to 41
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50 to 7037 to 52
Stage 3 (after 20 minutes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73 to 8354 to 61
Stage 4 (after running engine for 15 minutes at 1000 rpm) . . . . . .95 to 11570 to 85
Torx type bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4026 to 30
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 7552 to 55
Stage 3 (after 5 minutes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Tighten through a further 90¼
Camshaft cover bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6 to 84 to 6
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 to 31.5 to 2
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6 to 84 to 6
Stage 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6 to 84 to 6
Timing cover bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13 to 1710 to 13
Timing belt tensioner bolts:
Models with tensioner spring:
Spring bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2113 to 15
Pivot bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Models without tensioner spring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Oil pick-up tube/strainer-to-oil pump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11 to 148 to 10
Oil pick-up tube/strainer-to-cylinder block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2113 to 15
SOHC engines 2A¥3
2A
Page 4 of 24

1.6 litre engine
General
Engine type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Four-cylinder, in-line, single overhead camshaft
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3-4-2
Engine codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .LCS, LCT, LSD and LSE
LCS and LCTLSD and LSE
Bore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.67 mm81.32 mm
Stroke . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66.00 mm76.95 mm
Cubic capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1593 cc1597 cc
Compression ratio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9.2 : 19.5 : 1
Compression pressure at starter motor speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11 to 13 bar11 to 13 bar
Maximum continuous engine speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5800 rpm5950 rpm
Maximum engine power (DIN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55 kW at 5300 rpm55 kW at 4900 rpm
Maximum engine torque (DIN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120 Nm at 2900 rpm123 Nm at 2900 rpm
Cylinder bore diameterLCS and LCTLSD and LSE
Standard class 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.650 to 87.660 mm81.300 to 81.310 mm
Standard class 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.660 to 87.670 mm81.310 to 81.320 mm
Standard class 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.670 to 87.680 mm81.320 to 81.330 mm
Standard class 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.680 to 87.690 mm81.330 to 81.340 mm
Oversize class A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88.160 to 88.170 mm81.810 to 81.820 mm
Oversize class B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88.170 to 88.180 mm81.820 to 81.830 mm
Oversize class C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88.180 to 88.190 mm81.830 to 81.840 mm
Standard service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.680 to 87.690 mm81.330 to 81.340 mm
Oversize 0.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88.180 to 88.190 mm81.830 to 81.840 mm
Oversize 1.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88.680 to 88.690 mm82.330 to 82.340 mm
Crankshaft
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine except for the following:
Main bearing thrustwasher thickness from 1987:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.28 to 2.33 mm
Oversize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.48 to 2.53 mm
Pistons and piston rings
Piston diameter:LCS and LCTLSD and LSE
Standard class 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.615 to 87.625 mm81.265 to 81.275 mm
Standard class 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.625 to 87.635 mm81.275 to 81.285 mm
Standard class 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.635 to 87.645 mm81.285 to 81.295 mm
Standard class 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.645 to 87.655 mm81.295 to 81.305 mm
Standard service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.640 to 87.665 mm81.290 to 81.315 mm
Service oversize 0.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88.140 to 88.165 mm81.790 to 81.815 mm
Service oversize 1.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88.640 to 88.665 mm82.290 to 82.315 mm
Piston ring end gap:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.300 to 0.500 mm0.300 to 0.500 mm
Centre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.300 to 0.500 mm0.300 to 0.500 mm
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.400 to 1.400 mm0.400 to 1.400 mm
Auxiliary shaft
Endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.050 to 0.204 mm (0.002 to 0.008 in)
Cylinder head
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine
Camshaft
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine except for the following:
Endfloat:
Engine codes LCS, LCT and LSE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.104 to 0.204 mm (0.004 to 0.008 in)
Engine code LSD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.090 to 0.170 mm (0.003 to 0.007 in)
Valves
Specification as for 1.3 litre engine
Lubrication system
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine
Torque wrench settings
Specification as for 1.3 litre engine
2A¥4SOHC engines
Page 5 of 24

1.8 litre engine
General
Engine type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Four-cylinder, in line, single overhead camshaft
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3-4-2
Engine codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REB and RED
Bore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.20 mm
Stroke . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76.95 mm
Cubic capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1796 cc
Compression ratio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9.5:1
Compression pressure at starter motor speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11 to 13 bar
Maximum continuous engine speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5850 rpm
Maximum engine power (DIN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66kW at 5400 rpm
Maximum engine torque (DIN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .140 Nm at 3500 rpm
Cylinder bore diameter
Standard class 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.180 to 86.190 mm
Standard class 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.190 to 86.200 mm
Standard class 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.200 to 86.210 mm
Standard class 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.210 to 86.220 mm
Oversize class A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.690 to 86.700 mm
Oversize class B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.700 to 86.710 mm
Oversize class C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.710 to 86.720 mm
Standard service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.210 to 86.220 mm
Oversize 0.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.710 to 86.720 mm
Oversize 1.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87.210 to 87.220 mm
Crankshaft
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine except for the following:
Main bearing thrustwasher thickness from 1987:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.28 to 2.33 mm
Oversize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.48 to 2.53 mm
Pistons and piston rings
Piston diameter:
Standard class 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.145 to 86.155 mm
Standard class 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.155 to 86.165 mm
Standard class 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.165 to 86.175 mm
Standard class 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.175 to 86.185 mm
Standard service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.170 to 86.195 mm
Service oversize 0.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.670 to 86.695 mm
Service oversize 1.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86.170 to 86.195 mm
Piston ring end gap:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.300 to 0.500 mm
Centre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.300 to 0.500 mm
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.400 to 1.400 mm
Auxiliary shaft
Endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.050 to 0.204 mm (0.002 to 0.008 in)
Cylinder head and camshaft
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine
Valves
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine except for the following:
Valve clearance (cold engine):
Inlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.20 ±0.03 mm (0.008 ±0.001 in)
Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.25 ±0.03 mm (0.010 ±0.001 in)
Valve timing:
Inlet opens. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24¼ BTDC
Inlet closes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64¼ ABDC
Exhaust opens. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70¼ BBDC
Exhaust closes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18¼ ATDC
Lubrication system
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine
Torque wrench settings
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine
SOHC engines 2A¥5
2A
Page 7 of 24
Piston ring end gap:
Top:
Up to 1985 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.038 to 0.048 mm
From 1985 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.400 to 0.600 mm
Centre:
Up to 1985 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.038 to 0.048 mm
From 1985 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.400 to 0.600 mm
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.400 to 1.400 mm
Auxiliary shaft
Endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.050 to 0.204 mm (0.002 to 0.008 in)
Cylinder head
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine
Valves
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine except for the following:
Valve clearance (cold engine):
Inlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.20 ±0.03 mm (0.008 ±0.001 in)
Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.25 ±0.003 mm (0.010 ±0.001 in)
Valve timing:All except code NAEEngine code NAE
Inlet opens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24¼ BTDC18¼ BTDC
Inlet closes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64¼ ABDC58¼ ABDC
Exhaust opens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70¼ BBDC70¼ BBDC
Exhaust closes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18¼ ATDC6¼ ATDC
Lubrication system
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Specifications as for 1.3 litre engine except for the following:
Crankshaft pulley bolt:
Fuel injection models up to 1987 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115 to 13085 to 96
Fuel injection models from 1987 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100 to 11574 to 85
SOHC engines 2A¥7
2A
The engine is of a four-cylinder, in-line,
single overhead camshaft type, mounted at
the front of the vehicle and available in 1.3,
1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litre versions.
The crankshaft incorporates five main
bearings. Thrustwashers are fitted to the
centre main bearing in order to control
crankshaft endfloat.
The camshaft is driven by a toothed belt
and operates the slightly angled valves via
cam followers which pivot on ball-pins.
The auxiliary shaft which is also driven by
the toothed belt, drives the distributor, oil
pump and fuel pump.
The cylinder head is of crossflow design
with the inlet manifold mounted on the left-
hand side and the exhaust manifold mounted
on the right-hand side.
Lubrication is by means of a bi-rotor pump
which draws oil through a strainer located
inside the sump, and forces it through a full-
flow filter into the engine oil galleries where it
is distributed to the crankshaft, camshaft and
auxiliary shaft. The big-end bearings are
supplied with oil via internal drillings in the
crankshaft. The undersides of the pistons are
supplied with oil from drillings in the big-ends.
The distributor shaft is intermittently supplied
with oil from the drilled auxiliary shaft. The
camshaft followers are supplied with oil via adrilled spray tube from the centre camshaft
bearing.
A semi-closed crankcase ventilation system
is employed whereby piston blow-by gases
are drawn into the inlet manifold via an oil
separator and control valve.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 8.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 23.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 35.
1When engine performance is poor, or if
misfiring occurs which cannot be attributed to
the ignition or fuel system, a compression test
can provide diagnostic clues. If the test is
performed regularly it can give warning of
trouble before any other symptoms become
apparent.2The engine must be at operating
temperature, the battery must be fully
charged and the spark plugs must be
removed. The services of an assistant will also
be required.
3Disable the ignition system by
disconnecting the coil LT feed. Fit the
compression tester to No 1 spark plug hole.
(The type of tester which screws into the
spark plug hole is to be preferred.)
4Have the assistant hold the throttle wide
open and crank the engine on the starter.
Record the highest reading obtained on the
compression tester.
5Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders,
recording the pressure developed in each.
6Desired pressures are given in the
Specifications. If the pressure in any cylinder
is low, introduce a teaspoonful of clean
engine oil into the spark plug hole and repeat
the test.
7If the addition of oil temporarily improves
the compression pressure, this indicates that
bore, piston or piston ring wear was
responsible for the pressure loss. No
improvement suggests that leaking or burnt
valves, or a blown head gasket, may be to
blame.
8A low reading from the two adjacent
cylinders is almost certainly due to the head
gasket between them having blown.
9On completion of the test, refit the spark
plugs and reconnect the coil LT feed.
5Compression test
4Crankcase ventilation system -
inspection and maintenance
3Valve clearances - checking and
adjustment
2Engine oil and filter - renewal
1General information
Page 8 of 24

The following operations can be carried out
without removing the engine from the vehicle:
a)Removal and servicing of the cylinder
head
b)Removal of the camshaft after removal of
the cylinder head
c)Removal of the timing belt and sprockets
d)Removal of the sump
e)Removal of the oil pump
f)Removal of the pistons and connecting
rods
g)Removal of the big-end bearings
h)Removal of the engine mountings
i)Removal of the clutch and flywheel
j)Removal of crankshaft front and rear oil
seals
k)Removal of the auxiliary shaft
The following operations can only be carried
out after removing the engine from the
vehicle:
a)Removal of the crankshaft main bearings
b)Removal of the crankshaft
The engine may be lifted out either on its
own, or together with the manual
gearbox/automatic transmission. Unless work
is to be carried out on the manual
gearbox/automatic transmission, it is
recommended that the engine is removed on
its own. Where automatic transmission is
fitted, the engine should where possible be
removed on its own due to the additional
weight of the transmission. Note: The air conditioning system should
always be discharged by a Ford dealer or air
conditioning specialist.
Note: Refer to the warning in Section 8 before
proceeding. A suitable hoist and lifting tackle
will be required for this operation.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the bonnet.
3On carburettor models remove the air cleaner.
4On fuel injection models, disconnect the
crankcase ventilation hose from the air inlet
hose, then disconnect the air inlet hose from
the throttle body. Depress the locking clip on
the airflow meter wiring plug and disconnect
the plug (pulling on the plug, not the wiring)
then release the four securing clips and lift off
the air cleaner lid with the airflow meter and
air inlet hose.
5Remove the four retaining clips and
unscrew the two retaining screws, then
withdraw the upper section of the cooling fan
shroud from the radiator. Unclip and remove
the lower section of the shroud.
6Remove the thermo-viscous cooling fan as
described in Chapter 3.
7Drain the cooling system.
8Disconnect the upper radiator hose and
where applicable, the expansion tank hose
from the thermostat housing.
9Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
coolant pump, and where applicable from the
inlet manifold and automatic choke. Unclip
the coolant hose from the bracket on the
exhaust manifold hot air shroud/heat shield,
or the camshaft cover, as applicable.
10On carburettor models, where applicable
disconnect the vacuum pipe from the engine
management module.
11Disconnect the brake servo vacuum pipe
from the inlet manifold.
12On carburettor models, disconnect the fuel
hoses from the carburettor and where
applicable the mechanical fuel pump and plug
the ends of the hoses to minimise petrol
spillage. Remember to take adequate fire
precautions.
13On fuel injection models, disconnect the
fuel feed line from the fuel pressure regulator,
then disconnect the fuel supply hose from thefuel rail. Position a suitable container beneath
the pressure regulator, then slowly loosen the
fuel feed union to relieve the pressure in the
fuel lines before disconnecting the union.
Take adequate fire precautions. Plug the ends
of the hoses to minimise petrol spillage.
14Disconnect the throttle cable, and where
applicable remove its bracket.
15Disconnect the HT lead from the ignition
coil.
16Disconnect the wiring from the following
components as applicable depending on
model:
Alternator
Starter motor
Distributor
Oil pressure warning lamp switch
Temperature gauge sender
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Automatic choke
Automatic choke pull-down solenoid
Carburettor anti-dieselling valve
Inlet manifold heater
Carburettor stepper motor
Fuel injection harness
Dipstick
17Where applicable, detach the power
steering pump from the cylinder block and
move it to one side.
18Unscrew and remove the top engine-to-
gearbox bolts which are accessible from the
engine compartment. Note the location of the
earth strap on one of the bolts.
19Note the location of the earth strap on the
rear inlet manifold stud, then remove the nut
and disconnect the strap.
20Apply the handbrake (if not already done),
jack up the front of the vehicle and support on
axle stands (see ÒJacking and Vehicle SupportÓ).
21Drain the engine oil into a suitable
container.
22Remove the starter motor.
23Remove the exhaust downpipe.
24Unscrew the nuts or bolts, as applicable,
securing the engine mountings to the
crossmember. Recover the washers.
25Unscrew and remove the remaining
engine-to-gearbox bolts, and remove the bolt
from the engine adapter plate (see
illustration).
26Remove the two securing bolts and
disconnect the engine-to-gearbox brace from
the engine and gearbox.
27Working inside the vehicle, place a
wooden block under the clutch pedal to raise
it fully against its stop which will hold the
automatic adjuster pawl clear of the toothed
quadrant.
28Disconnect the clutch cable from the
clutch release arm, and pass the cable
through the bellhousing. Where applicable,
remove the clip securing the clutch cable to
the right-hand engine mounting bracket. Note
the cable routing for use when refitting.
29Lower the vehicle to the ground, and
support the gearbox with a trolley jack, using
a block of wood between the jack and the
gearbox to spread the load.
30Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant wires, pipes and hoses have been
disconnected to facilitate engine removal.
9Engine - removal leaving
manual gearbox in vehicle
8Method of engine removal
7Major operations requiring
engine removal
6Major operations possible with
the engine in the vehicle
2A¥8SOHC engines
9.25 Engine adapter plate bolt (A) and
engine-to-gearbox brace (B)
Warning: Vehicles equipped
with air conditioning:
Components of the air
conditioning system may
obstruct work being undertaken on the
engine, and it is not always possible to
unbolt and move them aside sufficiently,
within the limits of their flexible
connecting pipes. In such a case, the
system should be discharged by a Ford
dealer or air conditioning specialist. The
refrigerant is harmless under normal
conditions, but in the presence of a naked
flame (or a lighted cigarette) it forms a
highly toxic gas. Liquid refrigerant spilled
on the skin will cause frostbite. If
refrigerant enters the eyes, rinse them
with a diluted solution of boric acid and
seek medical advice immediately.
Page 12 of 24
Examination and renovation
11With the engine completely stripped,
clean all the components and examine them
for wear. Each part should be checked, and
where necessary renewed or renovated as
described in the relevant Sections. Renew
main and big end shell bearings as a matter of
course, unless it is known that they have had
little wear and are in perfect condition.
12If in doubt as to whether to renew a
component which is still just serviceable,
consider the time and effort which will be
incurred should it fail at an early date.
Obviously the age and expected life of the
vehicle must influence the standards applied.
13Gaskets, oil seals and O-rings must all be
renewed as a matter of routine. Flywheel and
Torx type cylinder head bolts must be
renewed because of the high stresses to
which they are subjected.
14Take the opportunity to renew the engine
core plugs while they are easily accessible.
Knock out the old plugs with a hammer and
chisel or punch. Clean the plug seats, smear
the new plugs with sealant and tap them
squarely into position.
Reassembly
15To ensure maximum life with minimum
trouble from a rebuilt engine, not only must
everything be correctly assembled, but it must
also be spotlessly clean. All oilways must be
clear, and locking washers and spring
washers must be fitted where indicated. Oil all
bearings and other working surfaces
thoroughly with clean engine oil during
assembly.
16Before assembly begins, renew any bolts
or studs with damaged threads.
17Gather together a torque wrench, oil can,
clean rag, and a set of engine gaskets and oil
seals, together with a new oil filter.
18If they have been removed, new Torx type
cylinder head bolts and new flywheel bolts will
be required.
19After reassembling the main engine
components, refit the ancillary components
listed, referring to the appropriate Chapters
where necessary. Delicate items such as the
alternator and distributor may be left until after
the engine has been refitted if preferred.20If the crankcase ventilation oil separator
was removed, apply a liquid sealing agent to
its tube before pressing it into the cylinder
block.
Note: Refer to the warning in Section 8 before
proceeding. On models from mid-1985
(without a timing belt tensioner spring) the belt
tension should be checked using Ford special
tool No 21-113 after refitting. On models up to
mid-1985 (with a tensioner spring), a suitable
splined socket will be required for the
tensioner spring bolt. A suitable puller may be
required to remove the sprockets.
Removal
1If the engine is in the vehicle, carry out the
following operations:
a)Disconnect the battery negative lead
b)Remove the thermo-viscous cooling fan
c)Remove the coolant
pump/alternator/power-steering pump
drivebelt(s)
d)For improved access, remove the radiator
and disconnect the radiator top hose from
the thermostat housing
2Unscrew the three securing bolts and
washers and withdraw the timing cover. Note
the position of the fourth bolt above the
crankshaft pulley which can be left in place.
3Using a socket on the crankshaft pulley
bolt, turn the engine clockwise until the TDC
(top dead centre) mark on the crankshaft
pulley is aligned with the pointer on the
crankshaft front oil seal housing (see
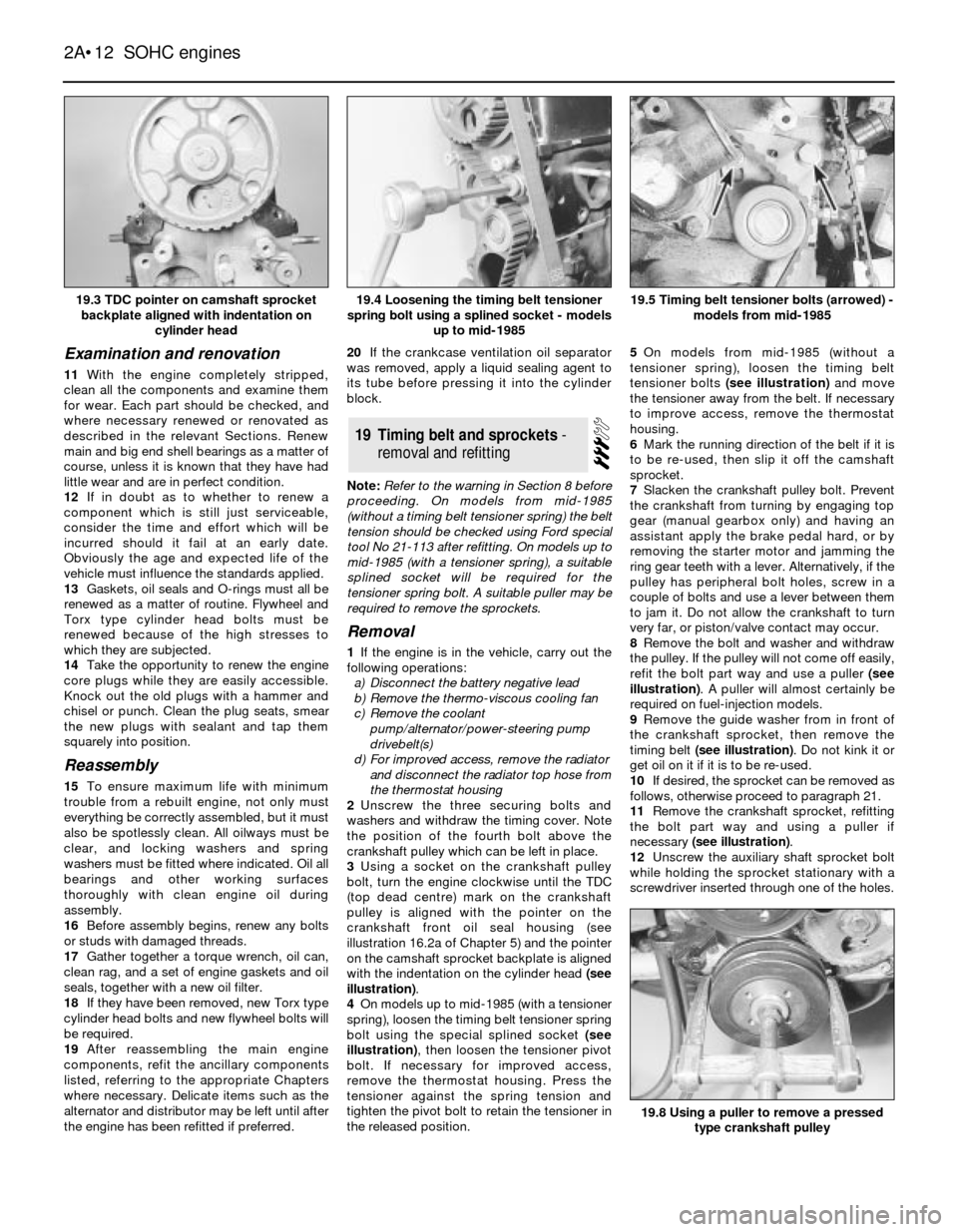
illustration 16.2a of Chapter 5) and the pointer
on the camshaft sprocket backplate is aligned
with the indentation on the cylinder head (see
illustration).
4On models up to mid-1985 (with a tensioner
spring), loosen the timing belt tensioner spring
bolt using the special splined socket (see
illustration), then loosen the tensioner pivot
bolt. If necessary for improved access,
remove the thermostat housing. Press the
tensioner against the spring tension and
tighten the pivot bolt to retain the tensioner in
the released position.5On models from mid-1985 (without a
tensioner spring), loosen the timing belt
tensioner bolts (see illustration)and move
the tensioner away from the belt. If necessary
to improve access, remove the thermostat
housing.
6Mark the running direction of the belt if it is
to be re-used, then slip it off the camshaft
sprocket.
7Slacken the crankshaft pulley bolt. Prevent
the crankshaft from turning by engaging top
gear (manual gearbox only) and having an
assistant apply the brake pedal hard, or by
removing the starter motor and jamming the
ring gear teeth with a lever. Alternatively, if the
pulley has peripheral bolt holes, screw in a
couple of bolts and use a lever between them
to jam it. Do not allow the crankshaft to turn
very far, or piston/valve contact may occur.
8Remove the bolt and washer and withdraw
the pulley. If the pulley will not come off easily,
refit the bolt part way and use a puller (see
illustration). A puller will almost certainly be
required on fuel-injection models.
9Remove the guide washer from in front of
the crankshaft sprocket, then remove the
timing belt (see illustration). Do not kink it or
get oil on it if it is to be re-used.
10If desired, the sprocket can be removed as
follows, otherwise proceed to paragraph 21.
11Remove the crankshaft sprocket, refitting
the bolt part way and using a puller if
necessary (see illustration).
12Unscrew the auxiliary shaft sprocket bolt
while holding the sprocket stationary with a
screwdriver inserted through one of the holes.
19Timing belt and sprockets -
removal and refitting
2A¥12SOHC engines
19.3 TDC pointer on camshaft sprocket
backplate aligned with indentation on
cylinder head19.5 Timing belt tensioner bolts (arrowed) -
models from mid-1985
19.8 Using a puller to remove a pressed
type crankshaft pulley
19.4 Loosening the timing belt tensioner
spring bolt using a splined socket - models
up to mid-1985
Page 13 of 24
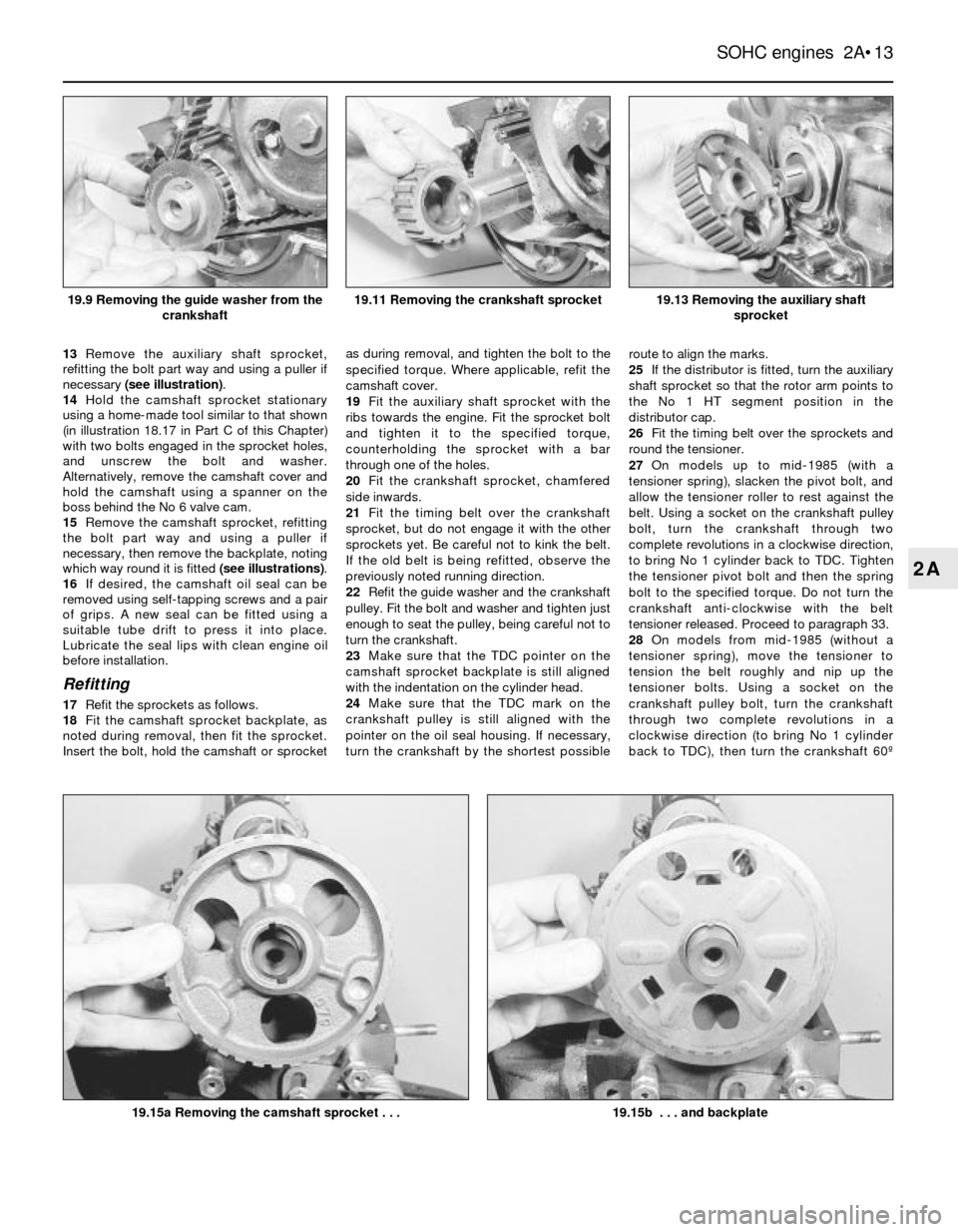
13Remove the auxiliary shaft sprocket,
refitting the bolt part way and using a puller if
necessary (see illustration).
14Hold the camshaft sprocket stationary
using a home-made tool similar to that shown
(in illustration 18.17 in Part C of this Chapter)
with two bolts engaged in the sprocket holes,
and unscrew the bolt and washer.
Alternatively, remove the camshaft cover and
hold the camshaft using a spanner on the
boss behind the No 6 valve cam.
15Remove the camshaft sprocket, refitting
the bolt part way and using a puller if
necessary, then remove the backplate, noting
which way round it is fitted (see illustrations).
16If desired, the camshaft oil seal can be
removed using self-tapping screws and a pair
of grips. A new seal can be fitted using a
suitable tube drift to press it into place.
Lubricate the seal lips with clean engine oil
before installation.
Refitting
17Refit the sprockets as follows.
18Fit the camshaft sprocket backplate, as
noted during removal, then fit the sprocket.
Insert the bolt, hold the camshaft or sprocketas during removal, and tighten the bolt to the
specified torque. Where applicable, refit the
camshaft cover.
19Fit the auxiliary shaft sprocket with the
ribs towards the engine. Fit the sprocket bolt
and tighten it to the specified torque,
counterholding the sprocket with a bar
through one of the holes.
20Fit the crankshaft sprocket, chamfered
side inwards.
21Fit the timing belt over the crankshaft
sprocket, but do not engage it with the other
sprockets yet. Be careful not to kink the belt.
If the old belt is being refitted, observe the
previously noted running direction.
22Refit the guide washer and the crankshaft
pulley. Fit the bolt and washer and tighten just
enough to seat the pulley, being careful not to
turn the crankshaft.
23Make sure that the TDC pointer on the
camshaft sprocket backplate is still aligned
with the indentation on the cylinder head.
24Make sure that the TDC mark on the
crankshaft pulley is still aligned with the
pointer on the oil seal housing. If necessary,
turn the crankshaft by the shortest possibleroute to align the marks.
25If the distributor is fitted, turn the auxiliary
shaft sprocket so that the rotor arm points to
the No 1 HT segment position in the
distributor cap.
26Fit the timing belt over the sprockets and
round the tensioner.
27On models up to mid-1985 (with a
tensioner spring), slacken the pivot bolt, and
allow the tensioner roller to rest against the
belt. Using a socket on the crankshaft pulley
bolt, turn the crankshaft through two
complete revolutions in a clockwise direction,
to bring No 1 cylinder back to TDC. Tighten
the tensioner pivot bolt and then the spring
bolt to the specified torque. Do not turn the
crankshaft anti-clockwise with the belt
tensioner released. Proceed to paragraph 33.
28On models from mid-1985 (without a
tensioner spring), move the tensioner to
tension the belt roughly and nip up the
tensioner bolts. Using a socket on the
crankshaft pulley bolt, turn the crankshaft
through two complete revolutions in a
clockwise direction (to bring No 1 cylinder
back to TDC), then turn the crankshaft 60¼
SOHC engines 2A¥13
2A
19.13 Removing the auxiliary shaft
sprocket
19.15b . . . and backplate19.15a Removing the camshaft sprocket . . .
19.11 Removing the crankshaft sprocket19.9 Removing the guide washer from the
crankshaft
Page 18 of 24

Note: A new gasket should be used when
refitting the auxiliary shaft cover (see text).
Removal
1Remove the timing belt and the auxiliary
shaft sprocket.
2Remove the distributor.
3Remove the mechanical fuel pump and
operating pushrod (where applicable).
4Unscrew the three securing bolts and
remove the auxiliary shaft cover (see
illustration).
5Unscrew the cross-head screws, using an
impact screwdriver if necessary, remove the
thrustplate and withdraw the auxiliary shaft
from the cylinder block (see illustrations).
6Cut the cover gasket along the top of the
crankshaft front oil seal housing and scrape
off the gasket.
Inspection
7Examine the shaft for wear and damage,
and renew it if necessary.
8If desired, the oil seal in the cover can be
renewed as follows.
9Support the cover on blocks of wood and
drive out the old oil seal. Drive the new seal
into place using a suitable metal tube or
socket (see illustrations). The sealing lip
must face towards the cylinder block. Smear
the sealing lip with clean engine oil before
installation.
Refitting
10Commence refitting by lubricating the
auxiliary shaft journals with clean engine oil,
then insert the shaft into the cylinder block.
11Locate the thrustplate in the shaft groove,
then insert the crosshead screws and tighten
them with an impact screwdriver.
12Using a dial test indicator (if available), or
feelerblades, check that the auxiliary shaft
endfloat is within the limits given in the
Specifications. If not, renew the thrustplate
and re-check. If this does not bring the
endfloat within limits, the auxiliary shaft must
be renewed.
13Cut out the relevant section of a new
gasket, and locate it on the cylinder block,
then refit the auxiliary shaft cover and tighten
the securing bolts.
14Where applicable, refit the fuel pump.
15Refit the distributor.
16Refit the auxiliary shaft sprocket and the
timing belt.
Note: The manufacturers recommend that the
flywheel/driveplate securing bolts are renewed
after slackening. Suitable thread-locking agent
will be required to coat the bolt threads.
Removal
1If the engine is in the vehicle, remove the
clutch or the automatic transmission, as
applicable.2Prevent the flywheel/driveplate from turning
by jamming the ring gear teeth or by bolting a
strap between the flywheel/driveplate and the
cylinder block.
3Make alignment marks on the
flywheel/driveplate and the end of the
crankshaft, so that the flywheel/driveplate can
be refitted in its original position.
4Unscrew the securing bolts and withdraw
the flywheel/driveplate. Do not drop it, it is
very heavy. Note that on models with A4LD
type automatic transmission, the driveplate
may be secured with one or two reinforcing
plates depending on model.
5The engine adapter plate may now be
withdrawn from the dowels if required (see
illustration).
Inspection
6With the flywheel/driveplate removed, the
ring gear can be examined for wear and
damage.
7If the ring gear is badly worn or has missing
teeth it should be renewed. The old ring can
be removed from the flywheel/driveplate by
cutting a notch between two teeth with a
hacksaw and then splitting it with a cold
chisel. Wear eye protection when doing this.
8Fitting of a new ring gear requires heating
the ring to 400¼F (204¼C). This can be done by
polishing four equally spaced sections of the
gear, laying it on a heat resistant surface (such
as fire bricks) and heating it evenly with a blow
lamp or torch until the polished areas turn a
light yellow tinge. Do not overheat, or the hard
wearing properties will be lost. The gear has a
26Flywheel/driveplate - removal,
inspection and refitting
25Auxiliary shaft - removal,
inspection and refitting
2A¥18SOHC engines
25.4 Unscrew the auxiliary shaft cover
securing bolts and remove the cover25.5b Withdraw the auxiliary shaft
26.5 Withdrawing the engine adaptor plate25.9b Using a socket to fit a new auxiliary
shaft cover oil seal25.9a Driving out the auxiliary shaft cover
oil seal
25.5a Unscrew the auxiliary shaft
thrustplate securing screws and remove
the thrustplate