air bleeding FORD SIERRA 1993 2.G Braking System Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1993, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1993 2.GPages: 22, PDF Size: 1.11 MB
Page 1 of 22

System type
Conventional braking system (except P100 models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Front discs and rear drums with vacuum servo assistance, dual
hydraulic circuit split front/rear, deceleration sensitive pressure relief
valve in rear hydraulic circuit. Cable-operated handbrake on rear
wheels.
ABS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Front and rear discs operated via electrically-driven hydraulic pump,
dual hydraulic circuit split front/rear, pressure regulating valve in rear
hydraulic circuit. Cable-operated handbrake on rear wheels
P100 models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Front discs and rear drums with vacuum servo assistance, dual
hydraulic circuit split front/rear, load apportioning valve in rear
hydraulic circuit. Cable-operated handbrake on rear wheels
Front discs
Type:
1.3 and 1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Solid
1.8 and 2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ventilated
Diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240.0 mm (9.46 in)
Maximum disc run-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.15 mm (0.006 in)
Minimum pad friction material thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 mm (0.06 in)
Rear discs
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Solid
Diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252.7 mm (9.96 in)
Maximum disc run-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.15 mm (0.006 in)
Minimum pad friction material thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 mm (0.06 in)
Rear drums
Internal diameter:
1.3 and 1.6 litre Saloon and Hatchback models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203.2 mm (8.0 in)
1.8 and 2.0 litre Saloon and Hatchback models and all Estate models .228.6 mm (9.0 in)
P100 models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256.0 mm (10.1 in)
Minimum shoe friction material thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 mm (0.04 in)
Chapter 10
Braking system
Brake disc - examination, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Brake drum - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Brake fluid pipes and hoses - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Brake hydraulic system (ABS) - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Brake hydraulic system (conventional braking system) - bleeding . . .2
Brake pedal - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Computer module (ABS) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Deceleration sensitive valve (Saloon, Hatchback and Estate models
with conventional braking system) - removal and refitting . . . . . . .23
Disc pads - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Fluid reservoir (ABS) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Front disc caliper - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
General information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Handbrake cable - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Handbrake cable - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Handbrake lever - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29Hydraulic unit (ABS) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Hydraulic unit accumulator (ABS) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . .17
Hydraulic unit pressure switch (ABS) - removal and refitting . . . . . . .19
Hydraulic unit pump and motor (ABS) - removal and refitting . . . . . .18
Load apportioning valve (P100 models) - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Load apportioning valve (P100 models) - removal and refitting . . . . .24
Master cylinder (conventional braking system) - removal, overhaul and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Rear brake backplate (drum brakes) - removal and refitting . . . . . . .11
Rear drum brake shoes - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Rear disc caliper - removal overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Rear disc splash shield - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Rear wheel cylinder (drum brakes) - removal, overhaul and refitting .10
Vacuum servo (conventional braking system) - removal and refitting .14
Valve block (ABS) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Wheel sensor (ABS) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
10•1
Specifications Contents
10
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Page 2 of 22
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Caliper carrier bracket-to-hub carrier bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51 to 6138 to 45
Front caliper guide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Rear caliper guide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31 to 3523 to 26
Rear brake backplate nuts - P100 models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45 to 5433 to 40
Servo-to-bulkhead nuts (conventional braking system) . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Master cylinder-to-servo nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Hydraulic unit-to-bulkhead nuts (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Hydraulic unit accumulator (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34 to 4625 to 34
Pump mounting bolt (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 95 to 7
High pressure hose-to-pump union (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 125 to 9
Wheel sensor mounting bolts (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
General information
The braking system is of the dual circuit
hydraulic type. The front and rear circuits are
operated independently from a tandem
master cylinder, so that in the event of a
hydraulic failure in one circuit, full braking
force will still be available to two wheels
through the remaining circuit.
A deceleration sensitive valve on Saloon,
Hatchback and Estate models not fitted with
an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), and a load
apportioning valve on P100 models, is
incorporated in the rear brake hydraulic
circuit. The valve regulates the pressure
applied to the rear brakes and reduces the
possibility of the rear wheels locking under
heavy braking.
All models are fitted with front disc brakes,
with solid or ventilated discs depending on
model. The calipers are of single piston sliding
type, which ensures that equal pressure is
applied to each disc pad.
Non-ABS models are fitted with rear disc
brakes or rear drum brakes, incorporating
leading and trailing shoes operated by
double-acting wheel cylinders. A self-adjuster
mechanism is fitted which consists of a
toothed quadrant which is kept in contact with
a toothed pin attached to the shoe strut by
means of a spring. The quadrant incorporates
an arm which locates in a slot in the leading
shoe. As the shoe linings wear the quadrant is
pulled from the pin when the footbrake is
operated, and automatically repositioned to
effectively lengthen the shoe strut.
ABS is available as an option for all models
except the P100. The system comprises an
electronic control unit, roadwheel sensors,
hydraulic actuator with electrically-driven
hydraulic pump, and the necessary valves and
switches. Disc brakes are fitted to all four
wheels. The front disc brakes are similar to
those fitted to non-ABS models, but the rear
brakes incorporate a self-adjusting
mechanism, and a mechanical handbrake
mechanism. The purpose of the system is to
prevent wheel(s) locking during heavy brake
applications. This is achieved by automatic
release of the brake on the locked wheel,followed by reapplication of the brake. This
procedure is carried out four times per second
by the control valves in the valve block. The
valves are controlled by the electronic control
unit which itself receives signals from the
wheel sensors, which monitor the locked or
unlocked state of the wheels. A pressure
regulating valve is incorporated in the rear
hydraulic circuit to maintain the desired
pressure ratio between the front and rear
circuits.
Precautions
Note: Hydraulic fluid is poisonous; wash off
immediately and thoroughly in the case of skin
contact and seek immediate medical advice if
any fluid is swallowed or gets into the eyes.
Certain types of hydraulic fluid are
inflammable and may ignite when allowed into
contact with hot components; when servicing
any hydraulic system it is safest to assume
that the fluid is inflammable and to take
precautions against the risk of fire as though it
is petrol that is being handled. Hydraulic fluid
is also an effective paint stripper and will
attack plastics; if any is spilt, it should be
washed off immediately using copious
quantities of fresh water. Finally, it is
hygroscopic (it absorbs moisture from the air)
old fluid may be contaminated and unfit for
further use. When topping-up or renewing the
fluid, always use the recommended type and
ensure that it comes from a freshly-opened
sealed container
Note: When working on the brake
components, take care not to disperse brake
dust into the air, or to inhale it, since it may
contain asbestos which is injurious to health.
General
1If any of the hydraulic components in the
braking system have been removed or
disconnected, or if the fluid level in the
reservoir has been allowed to fall appreciably,
it is inevitable that air will have been
introduced into the system. The removal of all
this air from the hydraulic system is essential
if the brakes are to function correctly, and the
process of removing it is known as bleeding.
2Where an operation has only affected one
circuit (front or rear) of the hydraulic system,
then it will only be necessary to bleed the
relevant circuit. If the master cylinder has
been disconnected and reconnected, or the
fluid level has been allowed to fall
appreciably, then the complete system must
be bled.
3One of three methods can be used to bleed
the system.
Bleeding
Two-man method
4Gather together a clean jar and a length of
rubber or plastic bleed tubing which will fit the
bleed screws tightly. The help of an assistant
will be required.
5Remove the dust cap where fitted, and
clean around the bleed screw on the relevant
caliper or wheel cylinder, then attach the
bleed tube to the screw (see illustration). If
the complete system is being bled, start at the
front left-hand caliper.
6Check that the fluid reservoir is topped up
and then destroy the vacuum in the brake
servo by giving several applications of the
brake pedal.
7Immerse the open end of the bleed tube in
the jar which should contain two or three
inches of hydraulic fluid. The jar should be
positioned about 300 mm (12.0 in) above the
bleedscrew to prevent any possibility of air
entering the system down the threads of the
bleed screw when it is slackened.
2Brake hydraulic system
(conventional braking system)
- bleeding1General information and
precautions
10•2Braking system
2.5 Removing the dust cap from a wheel
cylinder bleed screw
Caution: Refer to the
precautions in Section 1.
Page 3 of 22
8Open the bleed screw half a turn and have
your assistant depress the brake pedal slowly
to the floor and then, after the bleed screw is
retightened, quickly remove his foot to allow
the pedal to return unimpeded. Repeat the
procedure.
9Observe the submerged end of the tube in
the jar. When air bubbles cease to appear,
tighten the bleed screw when the pedal is
being held fully down by your assistant.
10Top-up the fluid reservoir. It must be kept
topped up throughout the bleeding
operations. If the connecting holes to the
master cylinder are exposed at any time due
to low fluid level, then air will be drawn into
the system and work will have to start all over
again.
11Assuming that the complete system is
being bled, the procedure described in the
preceding paragraphs should be repeated on
the front right-hand caliper followed by the
rear right-hand and left-hand wheel cylinders.
12On completion, remove the bleed tube,
and discard the fluid which has been bled
from the system unless it is required for bleed
jar purposes. Never re-use old fluid.
13On completion of bleeding, top-up the
fluid level in the reservoir. Check the action of
the brake pedal, which should be firm and free
from any “sponginess” which would indicate
that air is still present in the system.
With one-way valve
14There are a number of one-man brake
bleeding kits currently available from motor
accessory shops. It is recommended that one
of these kits should be used whenever
possible, as they greatly simplify the bleeding
operation and also reduce the risk of expelled
air or fluid being drawn back into the system.
15Proceed as described in paragraphs 5
and 6.
16Open the bleed screw half a turn then
depress the brake pedal to the floor and
slowly release it. The one-way valve in the
bleeder device will prevent expelled air from
returning to the system at the completion of
each stroke. Repeat this operation until clear
hydraulic fluid, free from air bubbles, can be
seen coming through the tube. Tighten the
bleed screw.
17Proceed as shown in paragraphs 11 to 13.
With pressure bleeding kit
18These too are available from motor
accessory shops and are usually operated by
air pressure from the spare tyre.
19By connecting a pressurised container to
the master cylinder fluid reservoir, bleeding is
then carried out by simply opening each bleed
screw in turn and allowing the fluid to run out,
rather like turning on a tap, until no air bubbles
are visible in the fluid being expelled.
20Using this system, the large reserve of
fluid provides a safeguard against air being
drawn into the master cylinder during the
bleeding operations.21This method is particularly effective when
bleeding “difficult” systems or when bleeding
the entire system at time of routine fluid
renewal.
22Begin bleeding with reference to
paragraphs 5 and 6 and proceed as described
in paragraphs 11 to 13.
1Keep the fluid reservoir replenished
throughout the bleeding operations.
2Remove the dust cap where fitted, and
clean around the bleed screw on the left-hand
front caliper. Fit a bleed tube to the screw and
immerse the open end in a jar containing
clean hydraulic fluid.
3Open the bleed valve one full turn and have
an assistant depress the brake pedal fully and
hold it down.
4Close the bleed valve and release the brake
pedal. Repeat the procedure until fluid ejected
from the end of the tube is free from air
bubbles.
5Repeat the operations on the right-hand
front caliper.
6Fit the bleed tube to the left-hand rear
caliper and open the bleed valve one full turn.
7Have an assistant depress the brake pedal
fully and hold it down.
8Switch on the ignition to position ll.
9Allow the fluid to bleed from the tube for at
least 15 seconds, when the fluid should be
free from air bubbles.
10Close the bleed valve.
11Release the brake pedal and wait for the
hydraulic pump to stop.
12Fit the bleed tube to the right-hand rear
caliper and open the bleed valve one full turn.
13Have your assistant depress the brake
pedal through half its travel and hold it there.
Allow the fluid to bleed from the tube for at
least 15 seconds, when the fluid should be
free from air bubbles.
14Close the bleed valve.
15Release the brake pedal and wait for the
hydraulic pump to stop then switch off the
ignition.
16Top-up the reservoir with clean fluid.
17When the hydraulic system is being bled
for the purpose of renewing the fluid at the
specified interval, as each caliper is bled,
operate the brake pedal continuously until
clean fluid is seen to enter the jar.
18When the hydraulic pump is running its
note will be heard to change once fluid has
purged through it. Do not allow the pump torun continuously for more than two minutes. If
it does run for a longer period, switch off the
ignition and allow the motor to cool for ten
minutes.
19On completion, discard the fluid which
has been bled from the system unless it is
required for bleed jar purposes. Never re-use
old fluid.
20Check the action of the brake pedal,
which should be firm and free from any
“sponginess”, which would indicate that air is
still present in the system.
Front disc pads
1The disc pad friction material can be
inspected for wear without removing the
roadwheels. Working beneath the vehicle,
insert a mirror between the caliper and the
roadwheel and check that the friction material
thickness is not less than the minimum given
in the Specifications.
2If any one of the pads has worn below the
specified limit, the front pads must be
renewed as an axle set (4 pads).
3To renew the pads, slacken the front
roadwheel nuts, apply the handbrake, then
jack up the front of the vehicle and support on
axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”). Remove the roadwheels. On P100
models, mark the position of the roadwheels
in relation to the wheel studs before removal.
4Proceed as follows according to model:
Girling caliper (1.3 and early 1.6 litre
models)
5Where applicable, disconnect the wiring to
the disc pad wear sensor.
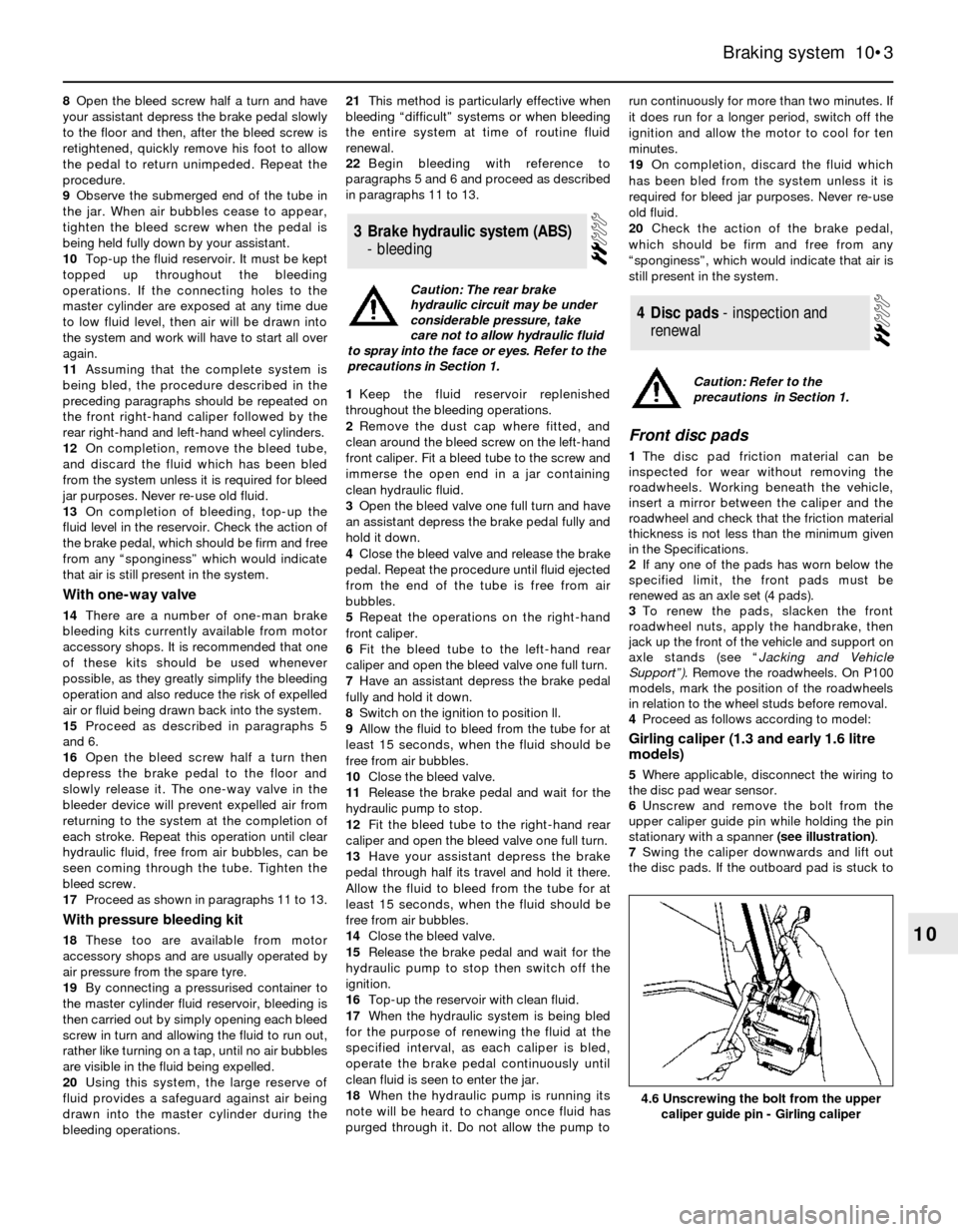
6Unscrew and remove the bolt from the
upper caliper guide pin while holding the pin
stationary with a spanner (see illustration).
7Swing the caliper downwards and lift out
the disc pads. If the outboard pad is stuck to
4Disc pads -inspectionand
renewal
3Brake hydraulic system (ABS)
- bleeding
Braking system 10•3
10
4.6 Unscrewing the bolt from the upper
caliper guide pin - Girling caliper
Caution: Refer to the
precautions in Section 1.
Caution: The rear brake
hydraulic circuit may be under
considerable pressure, take
care not to allow hydraulic fluid
to spray into the face or eyes. Refer to the
precautions in Section 1.