fuel GEELY MK 2008 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GEELY, Model Year: 2008, Model line: MK, Model: GEELY MK 2008Pages: 416, PDF Size: 25.19 MB
Page 34 of 416

2-13For servicing items whose deadlines have expired, they should be maintained at the same intervals as before. The
intervals are recorded in maintenance schedule.
Rubber hoses
Used in cooling and heating system, braking and fuel-feeding systems should be inspected by qualified Geely
technicians according to Geely maintenance schedule.
There are all very important maintenance items. Hoses must be replaced immediately should there be any aging
or damage. Please pay attention, rubber hoses age as time goes by, and they may have problems of inflation, wear,
or crack.
Special Tips
If the vehicle is driven under one or more of the following circumstances, the maintenance items should be
carried out more frequently. See attached maintenance schedule.
A Road condition
1. drive on rough, muddy or skiddy roads
2. drive on dusty roads.
B driving condition
1. Repeat driving within 8km a few times, or when the outdoor temperature is below 0 degree centigrade.
2. Idle the car drive at a low speed for a long time, such as police car, taxi, or door to door delivery vehicles.
3. Continuously drive the car at high speed for more than 2 hours (80% of the max speed).IV. Regular inspections1. weekly schedule
inspect engine oil level and cleanness
inspect engine coolant level
inspect brake fluid level
inspect windshield wash fluid level
inspect power steering fluid level
2. monthly inspections
inspect water pump belt
inspect electrolyte level in battery
inspect tire air pressure and wear
inspect steering wheel
inspect brake
inspect acceleration pedal
3. inspection when driving (low speed)
inspect speed meter and water temperature
check steering wheel power and if vehicle runs off-track
check if the front wheels skid or swing
inspect if brake functions or if the vehicle runs off-track when brake is functioning
4. other inspection items
Eliminate problems immediately when there is anything abnormalUsage and Maintenance of MK Series - Maintenance Category and Content of MK Sedan
Page 35 of 416

2-14
V. Table 1 List of parts to be replaced regularlyThe intervals in the part list are for cars driven under normal condition. If the car is driven in special circumstances,
the replacement can be advanced from the schedule above.SystemParts need to be replaced regularly
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22Brake master cylinder cup valve and dust coverBrake master cylinder cup
Brake hose
Brake caliper valve
Brake booster rubber
Brake booster vacuum hose
Brake fluid
MT Transmission oil
AT Transmission oil
Steering fluid
Air Cleaner
Air c leaner f ilter
Lubricant
Oil filter
Fuel filter
Coolant
All hoses
Canister
Timing beltWedge belt (including the power steering pump,
air conditioner compressor and generator belts)PCV system
Spark plugEvery 2 years (or as required)
Every 2 years (or as required)
Every 2 years (or as required)
Every 4 years (or as required)
Every 2 years (or as required)
Every 4 years (or as required)
Every 2 years,or 40000km (or as required)
Every 2 years,or 40000km (or as required)
Every 2 years,or 40000km (or as required)
Every 2 years,or 40000km (or as required)
To be cleaned every 10,000km and changed
every 30,000km (or as required)
First 2500km or 2 months. Every 7500km or
6 months afterward (or as required)
First 2500km or 2 months. Every 7500km or
6 months afterward (or as required)
Every 5000km (or as required)
Every 40000km (or as required)
Every year (or as required)
Every 2 years (or as required)
Every 60000km (or as required)
Every 120000km (or as required)
Every 50000km (or as required)
Every 20000km or 12 months (or as required)
Every 20000km (or as required)Intervals
DrivelineSteering SystemBraking
SystemEngineA/C System
(API) SG or above(Table 1)Usage and Maintenance of MK Series - Maintenance Category and Content of MK Sedan
Page 39 of 416

2-18Section 3 Daily Maintenance of MK SedanDaily maintenance means operation of vehicle regular inspection, cleaning, fastening, and refilling according to
vehicle usage and condition on the basis of regular maintenance to make sure the vehicle is at good status. Daily
maintenance can be performed by driver or professional automotive mechanics in daily use of vehicle. But some
of the items must be conducted by professional mechanics at service shops.
1. Maintenance of air cleaner
Air cleaner filters the air that is coming into engine for the first time. Dust and other dirt filtered out gathers in the
induction tube. Air cleaner filters a lot of dust and dirty, so it must be cleaned in time.
2. Maintenance of air filter
Air filter does not only filter the dust and dirt in the air, but also keeps smooth ventilation. Its status has great effects
on the fuel economy and power of the engine, so it must be checked and maintained in time.
Before it is time to replace air filter, maintain it. Remove the filter, knock it with hand or stick to get rid of dust
on the filter and remove dirt inside the filter cover according to the cleanness of the road that the vehicle usually
runs on.
ATTENTION: do not clean the filter with wet cloth. Fasten the filter well when installing it back.
3. Maintenance of battery
Battery is used to start the vehicle and supply power to electrical facilities. Its status directly affects the regular
usage of the vehicle, especially for vehicles equipped with electrical controlled facilities. Keeping the battery in
good technical status and connections is especially important. It is necessary to often perform the following
inspections and maintenance in regular usage:
(1) Clean the outside of battery Inspect if the battery case or cover surface is dirty or has dirt, oil, or other dirty
things regularly. Clean it and keep the surface dry to avoid electrical leak caused by cover deformation.
(2) Check battery connections Bad connection between battery electrode and cable results in low engine start
speed which makes it difficult to start the vehicle or the vehicle cannot be started because of low output voltage
from battery. Loose connection at battery end leads to damage of electrical components and loss of trouble code
and other information stored in RAM of the computer system as a result of low voltage. Therefore, it is necessary
to check if the connection of cables on the battery electrode is good. When it is found loose, it must be fastened.
If there is any rust, the cables must be loosened, washed clean and be connected again.
4. Maintenance of tires and wheels
(1) Keeping tires and wheels under good condition is very important to vehicle fuel consumption and driving
safety. Therefore, inspect and maintain the tires regularly. Every 10000 km, the wheels should be adjusted. Follow
the sequence in picture 3:
Judge if there is any hidden problems in vehicle chassis mechanism by observing wear in different places, andfinding out the hidden problems does not only help you to understand
the technical status of the vehicle, but also benefits driving safety.
a. Serious wear on both edges of tire tread, means tires often
work with low tire pressure.
b. Wear of middle of the tire tread is mainly because the tires
are used with high tire pressure.This kind of wear shortens
the useful life of tires, and may result in sudden flat tire
when the vehicle runs on uneven road surface or meets any
obstacles.Usage and Maintenance of MK Series - Daily Maintenance of MK Sedan
Page 46 of 416

Table 3Section 2 Removal of the Engine Assembly from the Vehicle1. Avoid petrol overflowing (Disconnect from the fuel tank).
2. Remove the front wheel.Figure 1-5Engine AssemblyRemoval of the Engine Assembly from the Vehicle3-5CO
Normal
Low
HighHC
High
High
HighProblems
Bad idle speed
Bad idle speed
(HC reading fluctuates)
Bad idle speed
(Black smoke exhausts)Causes
1. Ignition fault:
Incorrect ignition timing;
Dirt, short circuit, or incorrect spark plug gap.
2. Incorrect valve gap.
3. Suction and exhaust valve leak.
4. Cylinder leaks.
1. Vacuum leaks.
PCV pipe . manifold;
Idle speed control valve;
Brake booster pipeline.
2. Spark lacks since the mixed gas is too thin.
1. Air filter is blocked.
2. PCV valve is blocked.
3. EFI system fails.
ECU fails.
Pressure regulator of fuel oil is out of order.
Water temperature sensor does not work.
Suction pressure/temperature sensor fails.
Injector fails.
The throttle position sensor fails.3. Discharge the coolant completely.
4. Remove the air filter assembly with hose (see Figure 1-5).
(1) Disconnect the joint of the temperature sensor and the wire
plug.
(2) Disconnect the vent duct from the hose of the air filter.
(3) Release the wire clip bolt on the air filter.
(4) Disconnect the hose of the air filter from the throttle body.
(5) Remove 3 bolts and the air filter assemblies.
5. Remove the battery.
6. Remove the fuel pipe sub-assembly.
7. Disconnect the water pipe; disconnect the water outlet pipe of the
heater from the air conditioner pipe.
8. Release the nut and remove the accelerator control cable. -
Page 49 of 416

Chapter 2 Engine MechanicalSection 1 Engine ComponentsComponent ViewFigure 2-1Engine MechanicalEngine Components3-8Upside of radiator support
Engine cover lock assembly
Starter assembly
Output pipe of oil cooler
Input pipe of oil coolerTransmission control cable assembly Fuel oil sub-assembly Accelerator control cable assemble
Water inlet pipe of heater
Water outlet pipe of heaterTransmission control cable assemblySuitable for 1.5L/1.6L(Tight coupling)Suitable for 1.3L/1.5L(Non-tight coupling) Radiator assemblyAir filter assembly with hose
Clutch release assembly
Water inlet pipe of radiator
Water outlet pipe of radiator
Battery -
Page 51 of 416
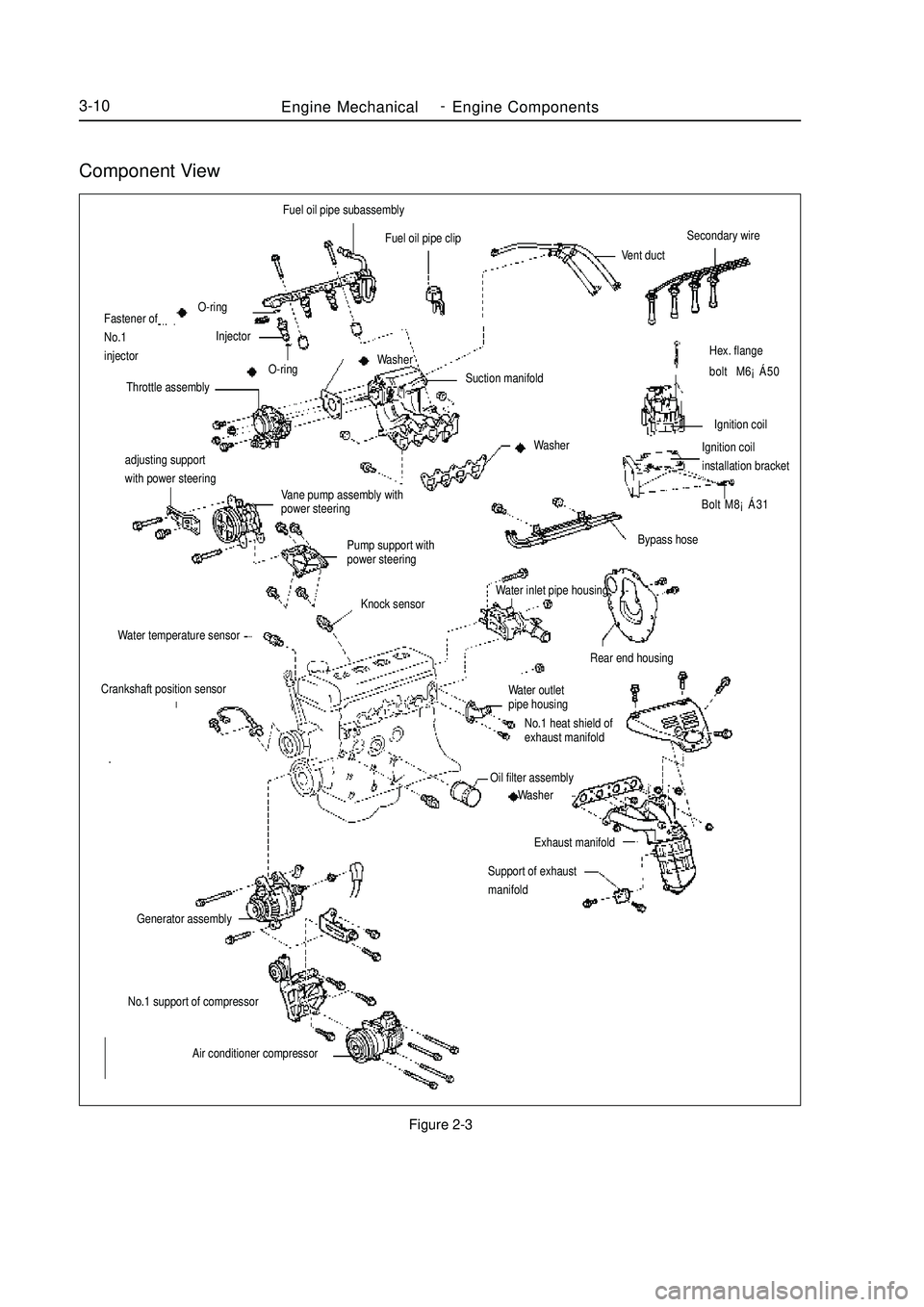
Component ViewFigure 2-3Engine MechanicalEngine Components3-10adjusting support
with power steering
Vane pump assembly with
power steering
Pump support with
power steeringHex. flange
bolt M6¡Á50
Ignition coil
Ignition coilinstallation bracket
Bolt M8¡Á31Fuel oil pipe subassembly
Fuel oil pipe clip
Vent ductSecondary wireBypass hose
Rear end housingWater outlet
pipe housing
No.1 heat shield of
exhaust manifoldOil filter assembly
Washer
Exhaust manifold
Support of exhaust
manifoldO-ring
Fastener of
No.1
injectorInjector
O-ring
Throttle assemblySuction manifold Washer
WasherKnock sensor
Water temperature sensorCrankshaft position sensorGenerator assemblyNo.1 support of compressor
Air conditioner compressorWater inlet pipe housing -
Page 56 of 416
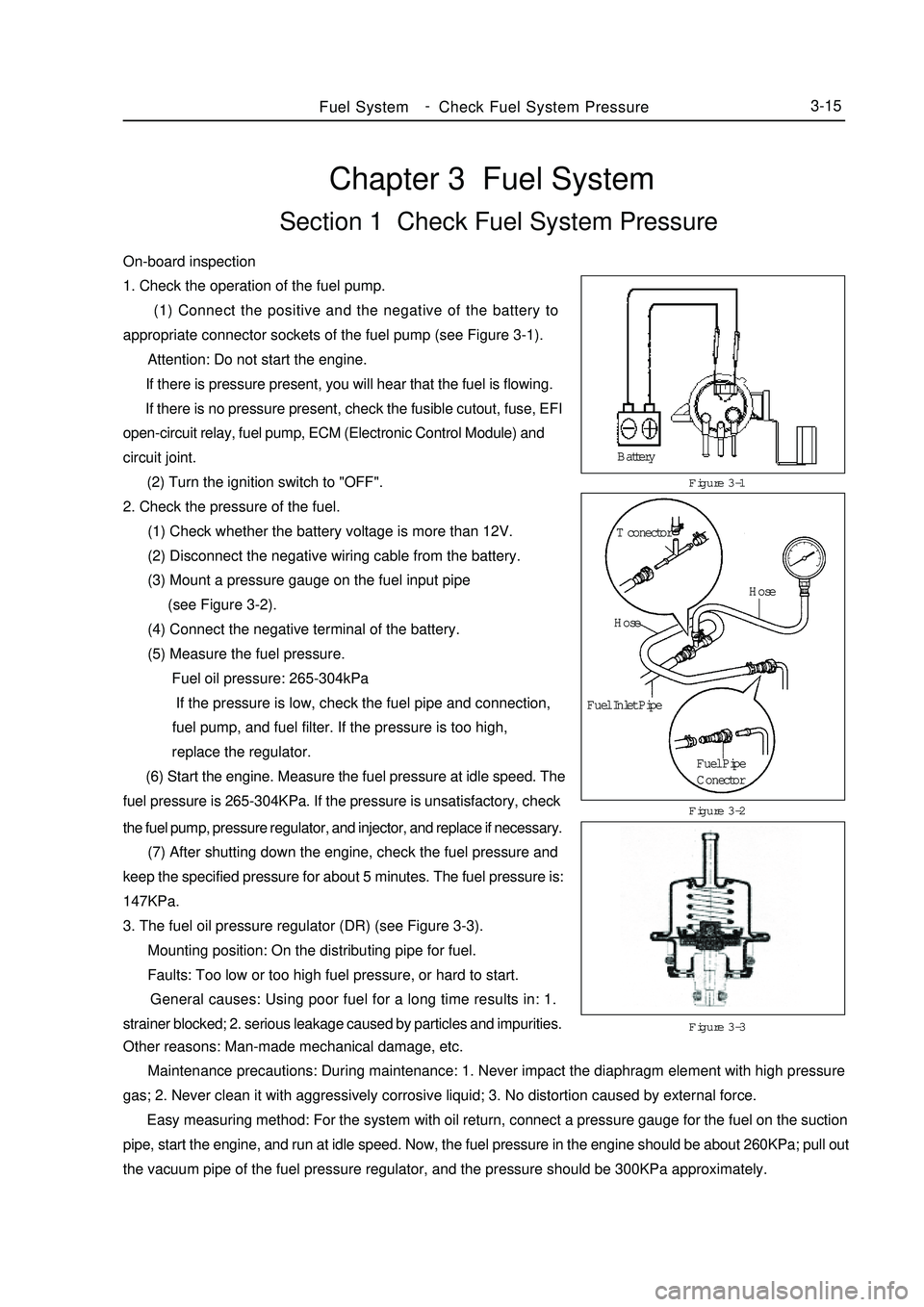
Chapter 3 Fuel SystemSection 1 Check Fuel System PressureOn-board inspection
1. Check the operation of the fuel pump.
(1) Connect the positive and the negative of the battery to
appropriate connector sockets of the fuel pump (see Figure 3-1).
Attention: Do not start the engine.
If there is pressure present, you will hear that the fuel is flowing.
If there is no pressure present, check the fusible cutout, fuse, EFI
open-circuit relay, fuel pump, ECM (Electronic Control Module) and
circuit joint.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to "OFF".
2. Check the pressure of the fuel.
(1) Check whether the battery voltage is more than 12V.
(2) Disconnect the negative wiring cable from the battery.
(3) Mount a pressure gauge on the fuel input pipe
(see Figure 3-2).
(4) Connect the negative terminal of the battery.
(5) Measure the fuel pressure.
Fuel oil pressure: 265-304kPa
If the pressure is low, check the fuel pipe and connection,
fuel pump, and fuel filter. If the pressure is too high,
replace the regulator.
(6) Start the engine. Measure the fuel pressure at idle speed. The
fuel pressure is 265-304KPa. If the pressure is unsatisfactory, checkFigure 3-1
Figure 3-3 Figure 3-2Fuel SystemCheck Fuel System Pressure3-15the fuel pump, pressure regulator, and injector, and replace if necessary.
(7) After shutting down the engine, check the fuel pressure and
keep the specified pressure for about 5 minutes. The fuel pressure is:
147KPa.
3. The fuel oil pressure regulator (DR) (see Figure 3-3).
Mounting position: On the distributing pipe for fuel.
Faults: Too low or too high fuel pressure, or hard to start.
General causes: Using poor fuel for a long time results in: 1.
strainer blocked; 2. serious leakage caused by particles and impurities.
Other reasons: Man-made mechanical damage, etc.
Maintenance precautions: During maintenance: 1. Never impact the diaphragm element with high pressure
gas; 2. Never clean it with aggressively corrosive liquid; 3. No distortion caused by external force.
Easy measuring method: For the system with oil return, connect a pressure gauge for the fuel on the suction
pipe, start the engine, and run at idle speed. Now, the fuel pressure in the engine should be about 260KPa; pull out
the vacuum pipe of the fuel pressure regulator, and the pressure should be 300KPa approximately.Battery
T conector
Hose
Hose
Fuel Inlet Pipe
Fuel Pipe
Conector -
Page 57 of 416
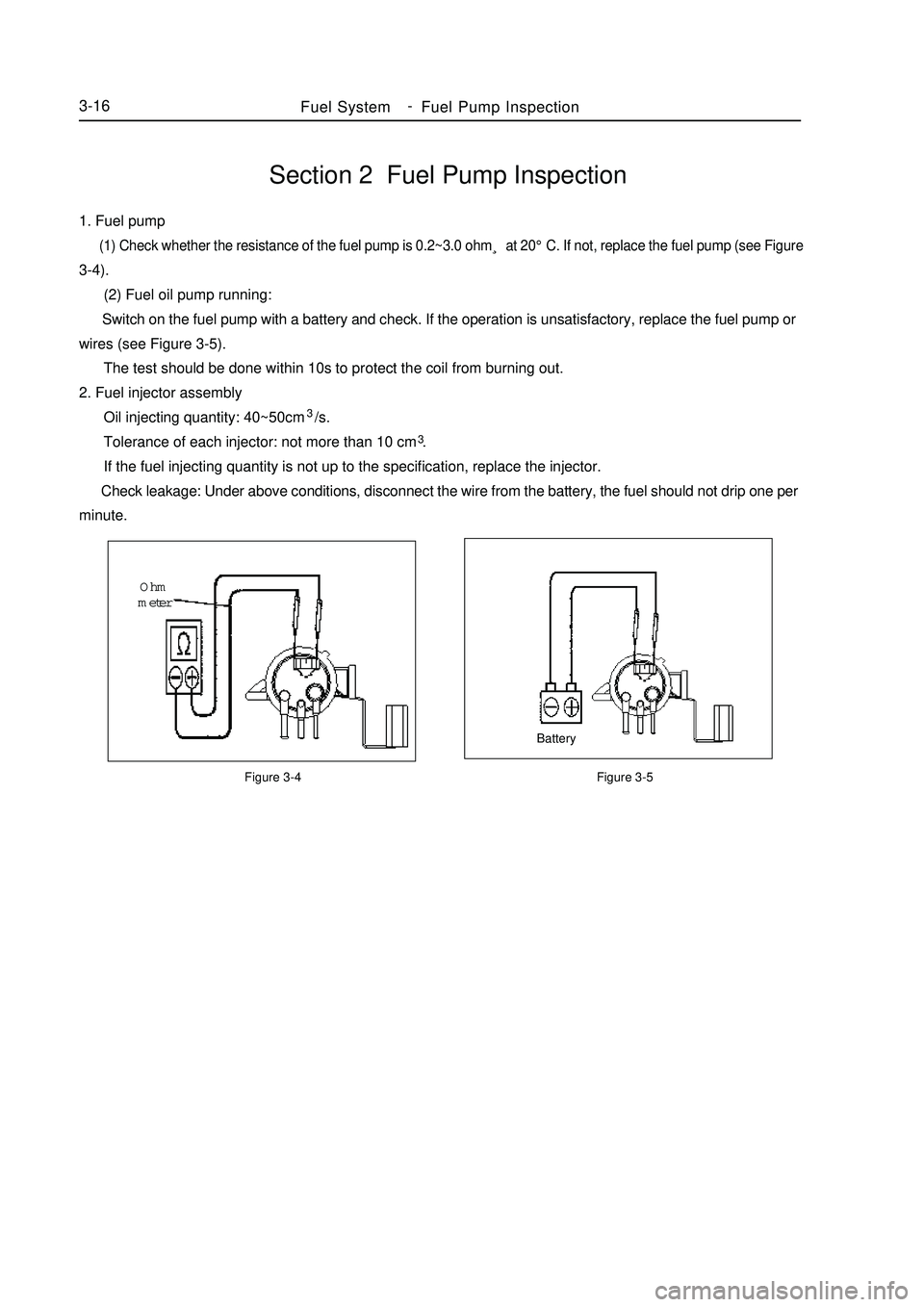
Section 2 Fuel Pump Inspection1. Fuel pump (1) Check whether the resistance of the fuel pump is 0.2~3.0 ohm¸ at 20°C. If not, replace the fuel pump (see Figure3-4).
(2) Fuel oil pump running:
Switch on the fuel pump with a battery and check. If the operation is unsatisfactory, replace the fuel pump or
wires (see Figure 3-5).
The test should be done within 10s to protect the coil from burning out.
2. Fuel injector assembly
Oil injecting quantity: 40~50cm3/s.
Tolerance of each injector: not more than 10 cm3.
If the fuel injecting quantity is not up to the specification, replace the injector.
Check leakage: Under above conditions, disconnect the wire from the battery, the fuel should not drip one per
minute.Figure 3-4 Figure 3-5BatteryOhm
meterFuel SystemFuel Pump Inspection3-16 -
Page 58 of 416
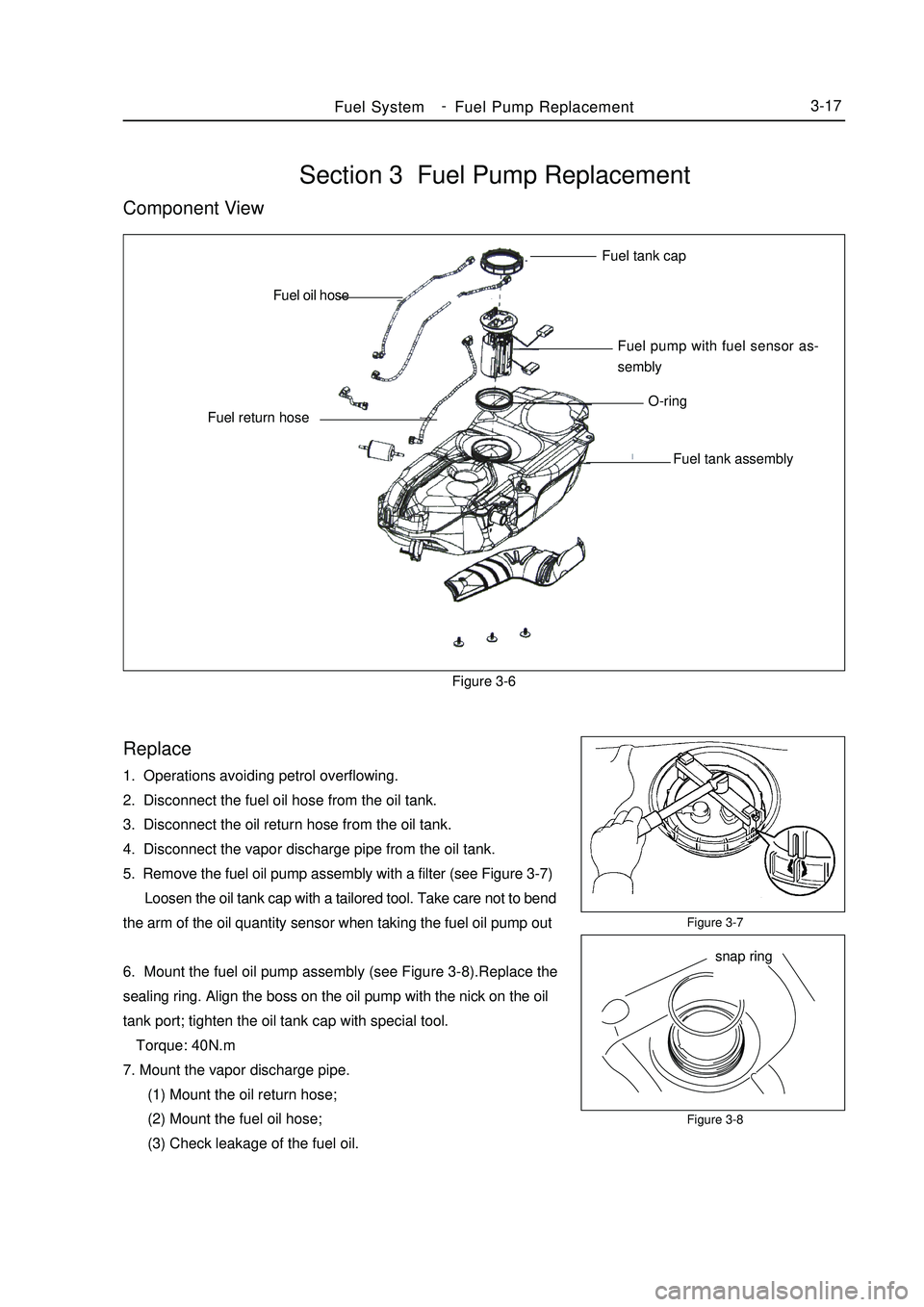
Section 3 Fuel Pump ReplacementComponent ViewFigure 3-6Replace1. Operations avoiding petrol overflowing.
2. Disconnect the fuel oil hose from the oil tank.
3. Disconnect the oil return hose from the oil tank.
4. Disconnect the vapor discharge pipe from the oil tank.
5. Remove the fuel oil pump assembly with a filter (see Figure 3-7)
Loosen the oil tank cap with a tailored tool. Take care not to bend
the arm of the oil quantity sensor when taking the fuel oil pump out
6. Mount the fuel oil pump assembly (see Figure 3-8).Replace the
sealing ring. Align the boss on the oil pump with the nick on the oil
tank port; tighten the oil tank cap with special tool.
Torque: 40N.m
7. Mount the vapor discharge pipe.
(1) Mount the oil return hose;
(2) Mount the fuel oil hose;
(3) Check leakage of the fuel oil.Figure 3-7
Figure 3-8Fuel SystemFuel Pump Replacement3-17Fuel tank cap
Fuel pump with fuel sensor as-
sembly
O-ring
Fuel tank assembly Fuel return hoseFuel oil hose
snap ring -
Page 59 of 416
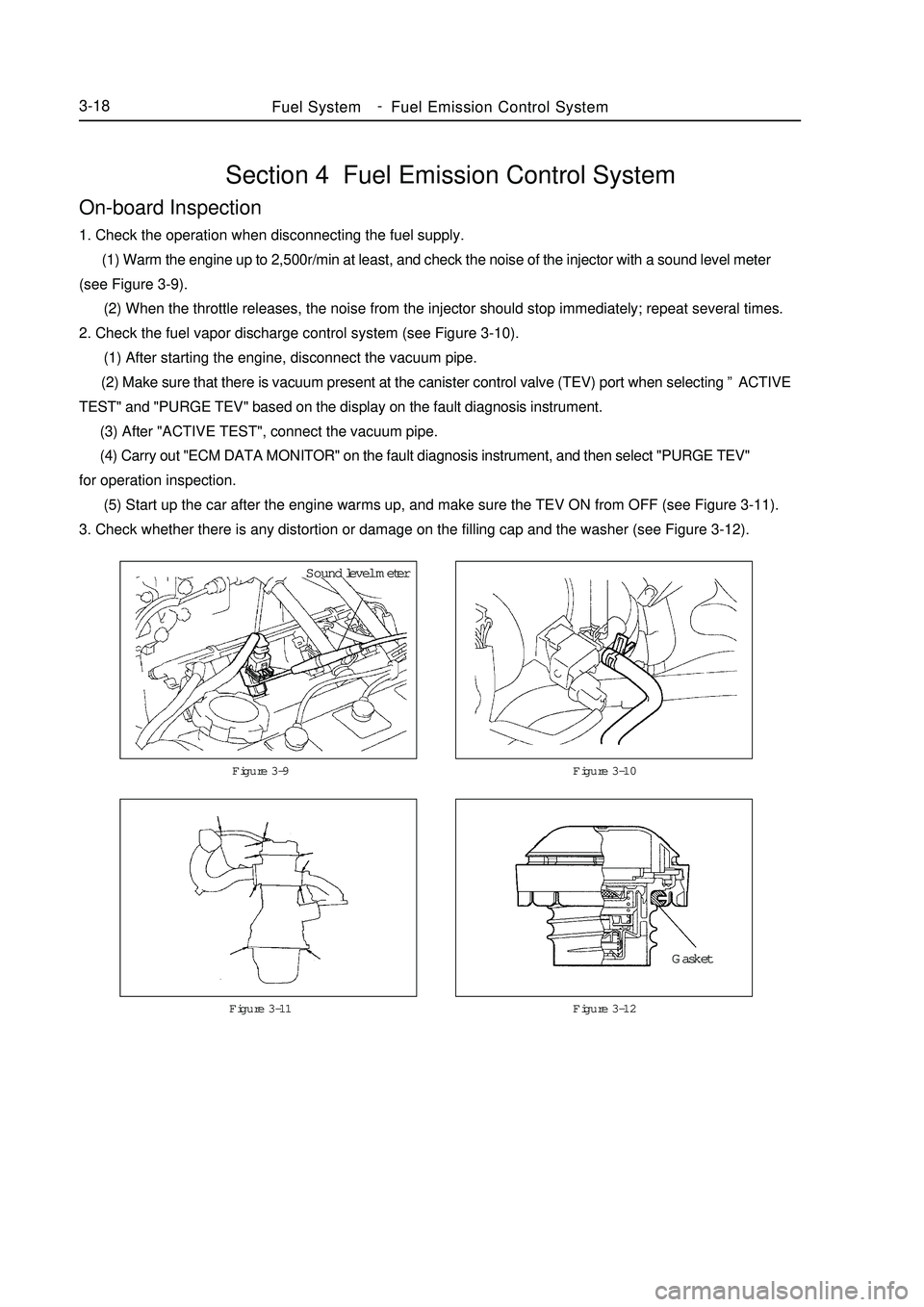
Section 4 Fuel Emission Control SystemOn-board Inspection1. Check the operation when disconnecting the fuel supply.
(1) Warm the engine up to 2,500r/min at least, and check the noise of the injector with a sound level meter
(see Figure 3-9).
(2) When the throttle releases, the noise from the injector should stop immediately; repeat several times.
2. Check the fuel vapor discharge control system (see Figure 3-10).
(1) After starting the engine, disconnect the vacuum pipe.
(2) Make sure that there is vacuum present at the canister control valve (TEV) port when selecting ”ACTIVE
TEST" and "PURGE TEV" based on the display on the fault diagnosis instrument.
(3) After "ACTIVE TEST", connect the vacuum pipe.
(4) Carry out "ECM DATA MONITOR" on the fault diagnosis instrument, and then select "PURGE TEV"
for operation inspection.
(5) Start up the car after the engine warms up, and make sure the TEV ON from OFF (see Figure 3-11).
3. Check whether there is any distortion or damage on the filling cap and the washer (see Figure 3-12).Figure 3-9 Figure 3-10Fuel SystemFuel Emission Control System3-18Figure 3-11 Figure 3-12Sound level meter
Gasket -