heating GEELY MK 2008 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GEELY, Model Year: 2008, Model line: MK, Model: GEELY MK 2008Pages: 416, PDF Size: 25.19 MB
Page 30 of 416

2-9 c. Check levels of braking fluid, engine coolant, engine oil, transmission oil, power steering fluid, and
washing fluid to see if there is any leaking.
d. Inspect if brake pedal, clutch pedal, accelerator pedal, transmission shifter, steering wheel, choke are
loose or stuck. The free travel of clutch pedal is 5~15mm, the free travel of brake pedal is 1~6mm and
the free play of steering wheel is less than 30mm(measurement point at margin of steering wheel). if it
is out of this normal range, the clutch needs to be tuned.
e. Inspect if the connection of battery, lamps and signal lights are normal, and if the wire routing and
position are correct and not loose.
f. Inspect if the tire pressure is correct.
(2) On-road inspection If the inspection result of the above items is good, start the engine and test the car on
road, and perform the following inspections.
a. Acceleration pedal, see if the operation is smooth and if it is loose.
b. Clutch, see if there is any stuck or abnormal noise, and slip when driving.
c. Transmission,check if shifting is smooth,or rough and wrong shifting.Inspect if the display of A/T
shift lever is normal.
d. Steering, check if steering is light and smooth, and if the steering wheel turns back after steering.
e. Brake pedal, apply brake pedal to check if the braking functions well when vehicle speed is at
40km/h and if the vehicle runs off track.
f. Park brake, when parking brake handler is pulled, there should be 6~9 clicking sounds. Pull park brake
when vehicle is running at the speed of 20km/h and transmission is at neutral gear to see if it brakes.
g. Vehicle speed meter, observe the vehicle speed meter while driving. When speed changes, check if the
indicator is moving steadily or shakes.
h. Heating and air-conditioning.Try every control button to see if both heating and cooling system work
well.
i. Abnormal noise, listen carefully to see if there is any abnormal noise from engine, drive line system or
any other parts of the vehicle at a steady speed and during accelerating, and decelerating.
(3) Inspection after test ride check if there is anything abnormal in the vehicle while driving and conduct the
following inspections after the vehicle is parked.
a. Check electrical fan When engine coolant temperature is beyond 92.5°C, the radiator fan should be
running; When A/C is on and the pressure of refrigerant is more than 1.5 cooling ton, air conditioning
cooling fan should be running.
b. Check headlamp, method: park the car 5m away from the inspection surface (inspection board, curtain,
or wall) to the front bumper, and check if the beam from headlamp is good. The upper level if headlamp
should be 540mm above the ground, and the distance between headlamps on the two sides is 900mm.
c. Inspect engine idle speed,idle speed of hot engine is 800r/min±50r/min,when A/C compressor works,
the idle speed should be 900r/min±50r/min. If idle speed is abnormal, adjust the idle speed adjust
ment screw to adjust it.
(4) Usage of new cars in breaking-in period Follow the instructions below in the first 1500~2500km breaking
mileage to avoid wear and abnormal damage in breaking-in period, and to improve vehicle performance, fuel
economy and to extend vehicle useful life.
a. Drive steadily during breaking-in; do not accelerate harshly to avoid running engine at high speed.
Engine should not exceed 4500r/min in any gears. Especially at the early stage of breaking-in, vehicleUsage and Maintenance of MK Series - Usage of MK Series
Page 34 of 416

2-13For servicing items whose deadlines have expired, they should be maintained at the same intervals as before. The
intervals are recorded in maintenance schedule.
Rubber hoses
Used in cooling and heating system, braking and fuel-feeding systems should be inspected by qualified Geely
technicians according to Geely maintenance schedule.
There are all very important maintenance items. Hoses must be replaced immediately should there be any aging
or damage. Please pay attention, rubber hoses age as time goes by, and they may have problems of inflation, wear,
or crack.
Special Tips
If the vehicle is driven under one or more of the following circumstances, the maintenance items should be
carried out more frequently. See attached maintenance schedule.
A Road condition
1. drive on rough, muddy or skiddy roads
2. drive on dusty roads.
B driving condition
1. Repeat driving within 8km a few times, or when the outdoor temperature is below 0 degree centigrade.
2. Idle the car drive at a low speed for a long time, such as police car, taxi, or door to door delivery vehicles.
3. Continuously drive the car at high speed for more than 2 hours (80% of the max speed).IV. Regular inspections1. weekly schedule
inspect engine oil level and cleanness
inspect engine coolant level
inspect brake fluid level
inspect windshield wash fluid level
inspect power steering fluid level
2. monthly inspections
inspect water pump belt
inspect electrolyte level in battery
inspect tire air pressure and wear
inspect steering wheel
inspect brake
inspect acceleration pedal
3. inspection when driving (low speed)
inspect speed meter and water temperature
check steering wheel power and if vehicle runs off-track
check if the front wheels skid or swing
inspect if brake functions or if the vehicle runs off-track when brake is functioning
4. other inspection items
Eliminate problems immediately when there is anything abnormalUsage and Maintenance of MK Series - Maintenance Category and Content of MK Sedan
Page 63 of 416
2. Check the engine coolant quantity in the compensating tank.
The coolant level should be between LOW and FULL.
3. Check the coolant quality.
(1) Remove the radiator cover.
Do not remove the radiator cover when the engine and the radiator are still hot in order to avoid scalding
since the liquid vapor may inject.
(2) Check whether there are excessive deposit and rust or sundries around the radiator cover. The coolant is
not allowed to contact with oil.
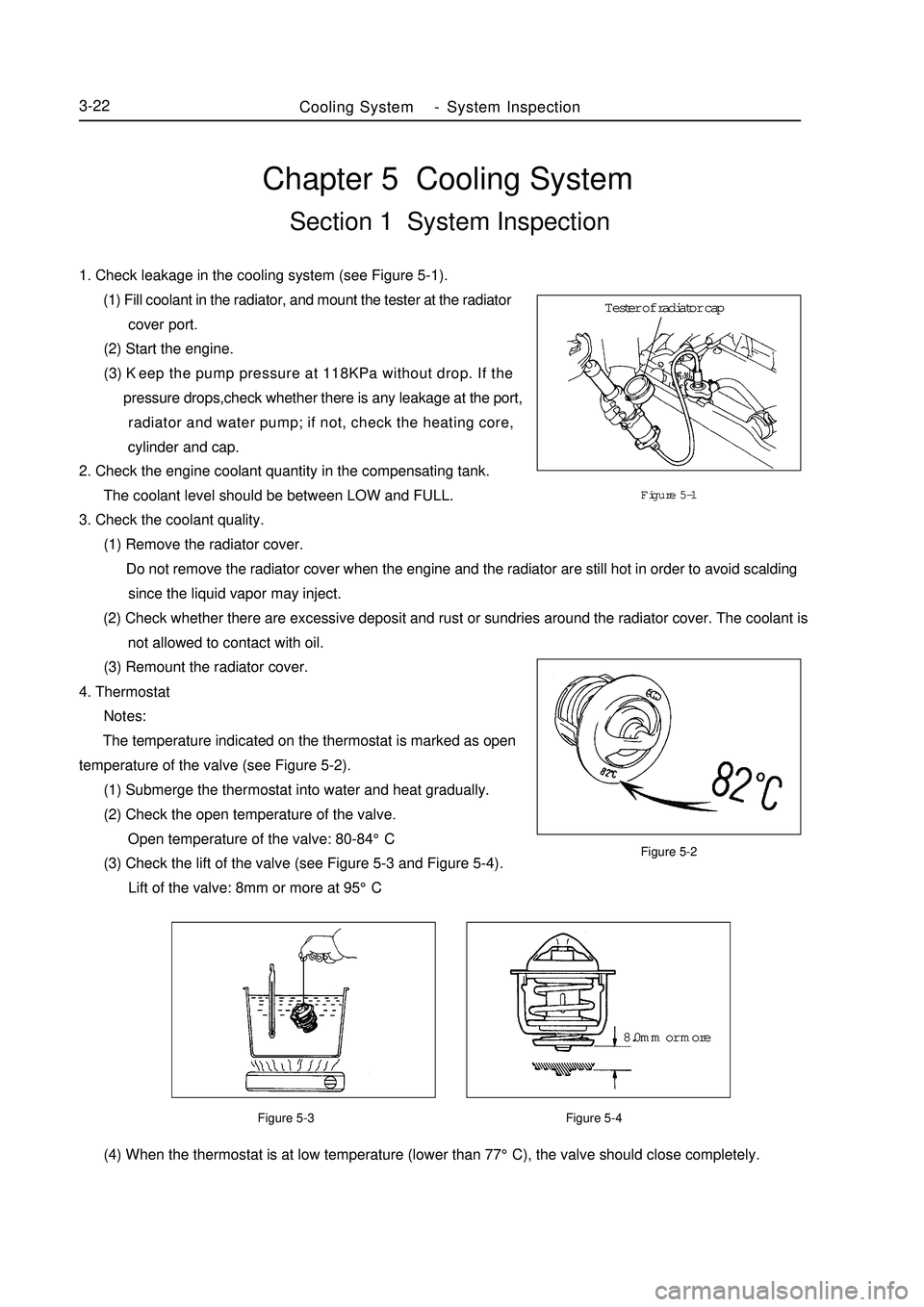
(3) Remount the radiator cover.Chapter 5 Cooling SystemSection 1 System Inspection1. Check leakage in the cooling system (see Figure 5-1).
(1) Fill coolant in the radiator, and mount the tester at the radiator
cover port.
(2) Start the engine.
(3) Keep the pump pressure at 118KPa without drop. If the
pressure drops,check whether there is any leakage at the port,
radiator and water pump; if not, check the heating core,
cylinder and cap.Figure 5-1
Figure 5-2
Figure 5-3 Figure 5-4 (4) When the thermostat is at low temperature (lower than 77°C), the valve should close completely.Cooling SystemSystem Inspection3-224. Thermostat
Notes:
The temperature indicated on the thermostat is marked as open
temperature of the valve (see Figure 5-2).
(1) Submerge the thermostat into water and heat gradually.
(2) Check the open temperature of the valve.
Open temperature of the valve: 80-84°C
(3) Check the lift of the valve (see Figure 5-3 and Figure 5-4).
Lift of the valve: 8mm or more at 95°CTester of radiator cap
8.0mm or more -
Page 259 of 416
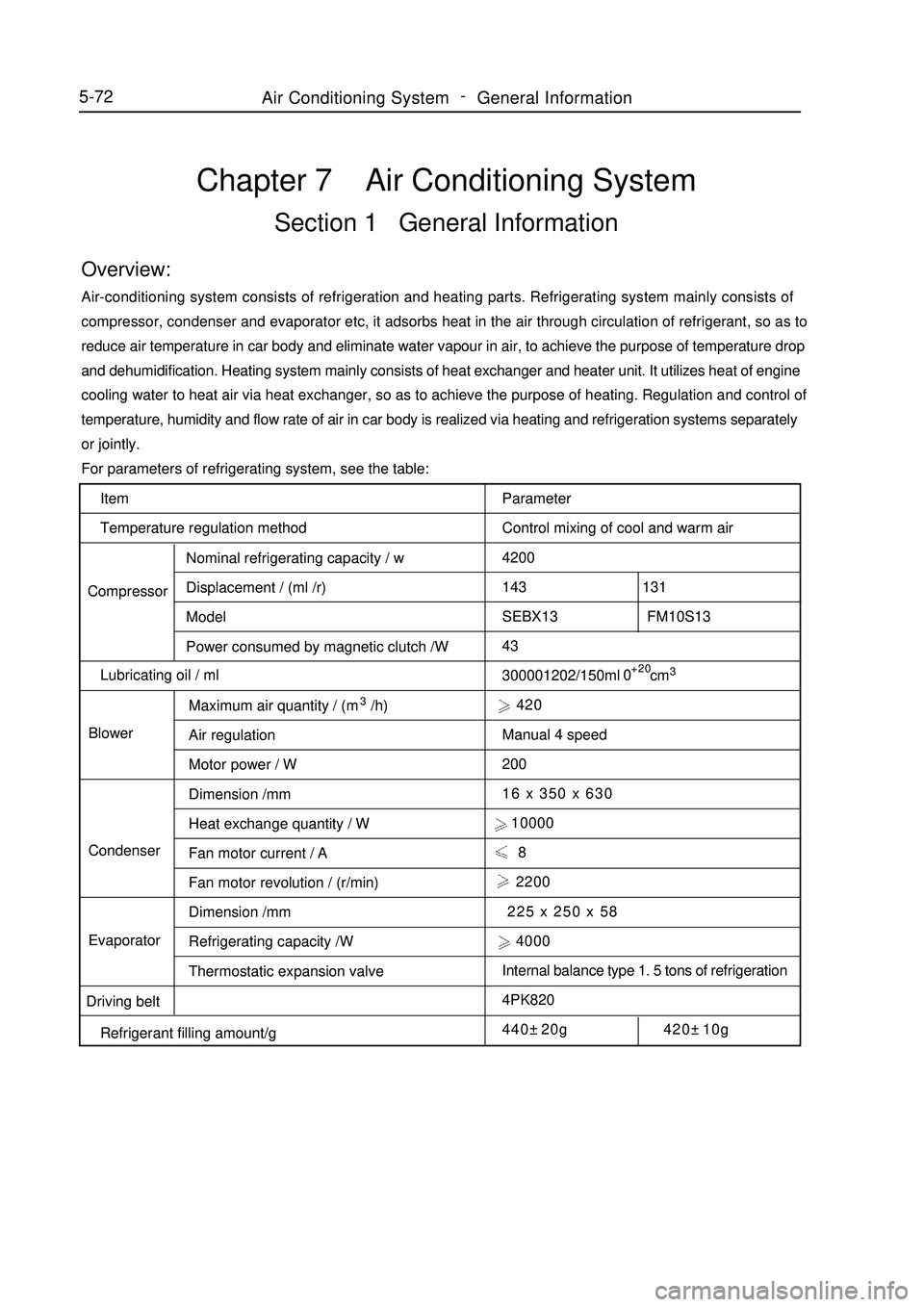
Item
Temperature regulation method
CompressorNominal refrigerating capacity / w
Displacement / (ml /r)
Model
Power consumed by magnetic clutch /W
Lubricating oil / ml
BlowerMaximum air quantity / (m3/h)
Air regulation
Motor power / W
Dimension /mm
Heat exchange quantity / W
Fan motor current / A
Fan motor revolution / (r/min)
Dimension /mm
Refrigerating capacity /W
Thermostatic expansion valve Condenser
Evaporator
Driving belt
Refrigerant filling amount/gChapter 7 Air Conditioning SystemSection 1 General InformationOverview:Air-conditioning system consists of refrigeration and heating parts. Refrigerating system mainly consists of
compressor, condenser and evaporator etc, it adsorbs heat in the air through circulation of refrigerant, so as to
reduce air temperature in car body and eliminate water vapour in air, to achieve the purpose of temperature drop
and dehumidification. Heating system mainly consists of heat exchanger and heater unit. It utilizes heat of engine
cooling water to heat air via heat exchanger, so as to achieve the purpose of heating. Regulation and control of
temperature, humidity and flow rate of air in car body is realized via heating and refrigeration systems separately
or jointly.
For parameters of refrigerating system, see the table:
Parameter
Control mixing of cool and warm air
4200
143 131
SEBX13 FM10S13
43
300001202/150ml cm3 420
Manual 4 speed
200
16 x 350 x 630
10000
8
2200
225 x 250 x 58
4000
Internal balance type 1. 5 tons of refrigeration
4PK820
440±20g 420±10g+20
05-72Air Conditioning System -
General Information
Page 272 of 416

Air Conditioning System -A/C Operating Mechanism5-855. Install the control mechanism assembly
(1) Replace the damaged part, installation is in the reverse order of removal.
(2) Notice:
When installing the warm and cold adjustment damper cable on the head unit of the air conditioner, set
the rocker arm connecting the cable to the maximum travel position of the damper for refrigeration, then
press the cable in the clamp. Do not twist the cable. Check that the temperature control knob on the
rotation panel can stop at both the maximum refrigeration and maximum heating positions and won't
resile.
When installing the inner and outer cycle damper cable on the head unit of the air conditioner, set the
rocker arm connecting the cable to the maximum travel position of the inner cycle, then press the cable
in the clamp. Do not twist the cable. Check that the air intake adjustment rod on the rotation panel can
stop at both the inner and outer cycle maximum positions and won't resile.
When installing the outlet vent adjustment damper cable on the head unit of the air conditioner, set the
rocker arm connecting the cable to the maximum travel position of face mode, then press the cable in
the clamp. Do not twist the cable. Check that the airflow selector knob on the rotation panel can stop
at both the face mode and defroster heating positions and won't resile.4. Remove the inner and outer cycle flipper
Unscrew the retaining buckle and the inner and outer cycle
flipper.Clamp
Page 307 of 416
Fault symptom
Flameout, poor idle speedChapter 9 Engine EFI SystemI. Outline This system includes sensor that detects engine functioning. Engine ECU utilizes sensors installed at differ-
ent parts of engine to measure various working parameters of engine, accurately control oil injection quantity
according to control procedure set in engine electronic control unit, so engine could work in optimum mode
under various operating conditions, i. e. optimal power output, the most economical oil consumption, optimal
exhaust emissions. Engine ECU is capable of start up control, idle speed closed-loop control, air fuel ratio
closed-loop control, canister control, transient operation control, angle of ignition control, knocking control, air
conditioning control, coasting fuel cutoff and overspeed fuel cutoff control, ternary catalyst heating and protec-
tion control, system self-diagnosis etc.II. Inspection of control element1. Manifold intake pressure temperature sensor
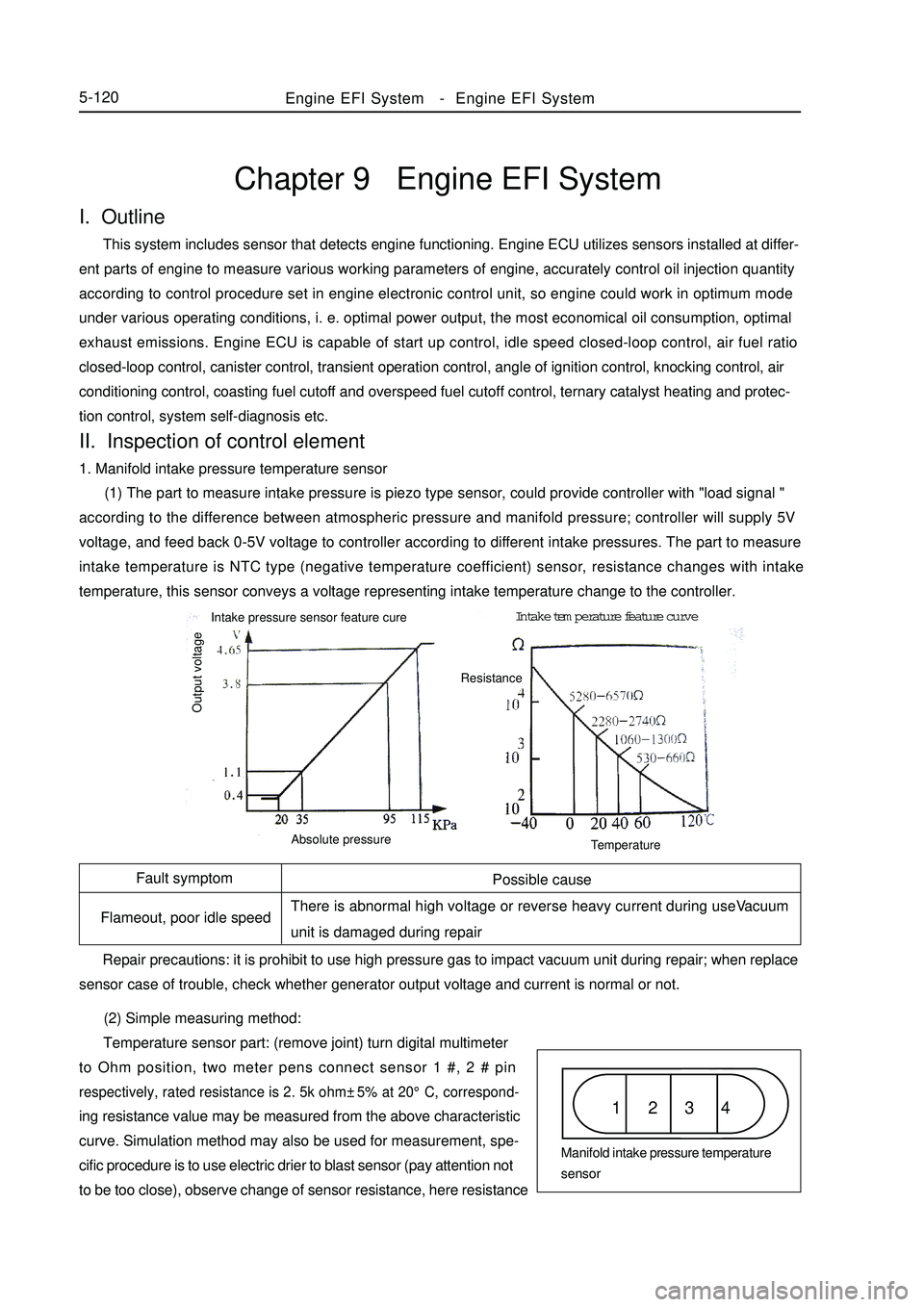
(1) The part to measure intake pressure is piezo type sensor, could provide controller with "load signal "
according to the difference between atmospheric pressure and manifold pressure; controller will supply 5V
voltage, and feed back 0-5V voltage to controller according to different intake pressures. The part to measure
intake temperature is NTC type (negative temperature coefficient) sensor, resistance changes with intake
temperature, this sensor conveys a voltage representing intake temperature change to the controller.
(2) Simple measuring method:
Temperature sensor part: (remove joint) turn digital multimeter
to Ohm position, two meter pens connect sensor 1 #, 2 # pinrespectively, rated resistance is 2. 5k ohm±5% at 20°C, correspond-ing resistance value may be measured from the above characteristic
curve. Simulation method may also be used for measurement, spe-
cific procedure is to use electric drier to blast sensor (pay attention not
to be too close), observe change of sensor resistance, here resistanceEngine EFI System-Engine EFI System5-120Possible cause
There is abnormal high voltage or reverse heavy current during useVacuum
unit is damaged during repair
Repair precautions: it is prohibit to use high pressure gas to impact vacuum unit during repair; when replace
sensor case of trouble, check whether generator output voltage and current is normal or not.1 2 3 4Manifold intake pressure temperature
sensor Intake pressure sensor feature cureIntake temperature feature curve
Output voltageAbsolute pressureTemperatureResistance
Page 367 of 416

I. Removal and installation of door protector Notes:
Installation is basically the reverse of removal and different operation(s) in the process of installation, if any,
will be pointed out specifically.
Installation and removal on the right side is identical with that on the left side.
1. Remove the door protector from the left front door
a. Use a heating lamp or a dedicated electric blower to heat up the door protector to 40~60°C.Chapter 15 Door Protecting StripeCar body40~60°C
Door protector20~30°CInterior & Exterior Trim and Accessory -Door Protecting Stripe6-38 Caution:Do not overheat the door protector.
b. Fasten both ends of the steel wire to the wooden handle.
c. Cut the adhesive tape by pulling the steel wire.
Caution: Make sure not to break the door protector to be
installed later.
Do not cause damage to the car.
d. Remove the door protector.
2. Install the door protector
Caution:Do not overheat the car exterior and the door protector.
c. Rip off the release liner from the door protector;
Caution
Make sure the adhesive tape does not get dusted or stained when a. Rip off the protective tape from the car;
b. Use a heating lamp or a dedicated electric blower to heat up the car exterior and the door protector.
Desired temperature
the release liner is ripped off.
Do not push the door protector too hard; make sure it is attached to the door firmly by pressing it with your
fingers.Protective tapeAdhesive Band
Page 388 of 416

Section 3 Repair After Body Damage The body damage repair includes rectification, reshaping, reinforcing, local change, and complete replacement.
Generally, CO2 welding method is used.I Reshaping Repair1. Rectification
In general, the deformation of body is caused by accident. It can be rectified in a supporting method. In the
rectification process, apply the force in the direction against the force of accident or deformation. In most cases,
cold rectification can be used. Local heating can reduce internal stress, and the corresponding processing shall be
carried out.
For the limousine, it is preferred to rectify it with the dressing machine. All dimensions and tolerances of all
parts shall be returned to the original standard, so the mobility, serviceability and comfortableness can be
guaranteed. (Fig.5-23)Section 2 Typical Technique of Body Panel RepairFig. 5-23 Mounting Bench of Universal Dressing Machine7-16Repair Process Flow:Visual Inspection
& AppraisalRemove Remove Paint Appraise
Platework
RepairAssemble PaintBody Repair -Typical Technique of Body Panel Repair/ Repair After Body Damage
Page 391 of 416

(f). Flatten the edge with hammer or sizing block, and remove the burr with file to make sure that it is aligned
with the both side alternative plates with a clearance not more than 1mm;
(g). Replace the plate, and clamp it with pincers. Carry out the spot welding along the seam at a space of
approximately 50mm;
(h). Make the welding from the center to both sides alternately block by block. Which can reduce the
deformation;
(i). Strike the welding line with the hammer or sizing block to remove the retaining stress. Polish the welding
lien wit the file or manual grinding wheel to make it even and smooth for the painting.
c. Repair for Accidented Damage
(a). Plate work flattening
When the accidented damage occurs on the plate work of the body, it can be repaired by means of beating.
In the repair process, start from Point C as shown in Fig. 5-26. Put the sizing block on the convex point, and beat
it with the hammer and change the block's position correspondingly. When the convex point is flattened, the
concaved part in Point B will rise. Similar wit the original profile of the plate, for the remaining dent, a sizing block
with the same radian can be employed. Press the bottom of the plate with hand, and beat the high point of the dent
with the hammer. (Fig. 5-27)Fig. 5-27 Plate Work Flattening (II)
A. Hammer B. Plate work
C. Sizing block Fig. 5-26 Plate Work Flattening (I)
A. Impact point B. Concaved point after impact
C. Convex point after impactFig. 5-28 Heating & Planishing
Convex Point
1. Heating pointBody Repair -Repair After Body Damage7-19 In the beating process, beat the work piece heavily at the beginning and lightly at the end. Attention shall
be paid to reduce the number of beating as possible as it can. Don't beat the same points repeatedly to prevent the
metal plate extending locally, which can complicate the repair work.
For the larger arc concave, a sizing block can be used under the center of the concave. The area of the sizing
block shall be a little larger. Jack the concaved plate up with a supporting tool. Sometime, heat the concaved part
to wine color to reduce the force. When jacking the plate up, a little excess is acceptable. (Fig. 5-28)
(b) Thermal contraction
When the concave is jacked up, if the plate extends seriously and the area is large, the thermal contraction
method can be used in case that the traditional methods don't work. (Fig. 5-29)
Heat the work piece to cerise color with oxyacetylene flame. The heating scope depends on the degree of extension.
If the extension is serious or the area is large, the heating point shall be larger relatively (diameter: approx.20-
30mm). If the extension is not serious or the area is small, the heating point shall be a little smaller (diameter:
approx.10-15mm). After the heating, beat the heating point immediately. In the beating process, a proper sizing
block is used under the plate. After it is cooled down, beat it lightly with the hammer.
The contraction starts from the highest point to the center, and then to the edge. Heat and flatten the extended
part repeatedly till the plate is flattened fully. If the convex part is too high, compress it to one half of the original
height. After it is cooled down, heat it at the original heating point till the other half of convex part is removed.
Page 392 of 416

Fig. 5-29 Thermal Contraction Method For those parts that are not sure whether they will contract or not, the thermal contraction method shall not
be used to avoiding any side effect. Especially for those thin plates, great attention shall be made to prevent them
from melting down or burning through.
(c) Welding ring
The welding ring method is used to repair the most seriously damaged part of the concave on the plate work
surface. Some rings are welded to connect the rods. (Shown as Fig. 11-30) When the area of the concave is large,
several rings can be welded in a parallel manner, and gets through the rod to make the pulling force act on the plate
surface evenly. The ring can be replaced by the washer. The rod pulls the washer or shaft through a coupling device.
After the concaved plate is flattened by the inertia hammer puller, remove the ring or washer and finish the welding
points.Fig. 5-30 Welding Washer StretchingBody Repair -Repair After Body Damage7-20Washer WasherHeating
Compress
loadCooling
Extend load Plate work
thermal contraction Metal bar thermal
contractionWasherShaft
Shaft Shaft Rod