ABS GREAT WALL FLORID 2008 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GREAT WALL, Model Year: 2008, Model line: FLORID, Model: GREAT WALL FLORID 2008Pages: 281, PDF Size: 43.97 MB
Page 80 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 73Suspension System
Steering knuckle assembly removal
1. Preparation
First, remove the front wheel, the front shock absorber with
coil spring assembly, and the steering knuckle coupling
bolt in turn. For detailed steps, please refer to the removal
of the wheel and the front shock absorber with coil spring
assembly.
2. Remove propeller shaft nuts
(a) First, pry the flattened areas of the propeller shaft's nuts
into a circle with a chisel.
(b) Half-insert a long bolt or metal bar into the brake disc
holes to loosen the nuts (shown on the left).
Tightening torque: 225±20 N·m
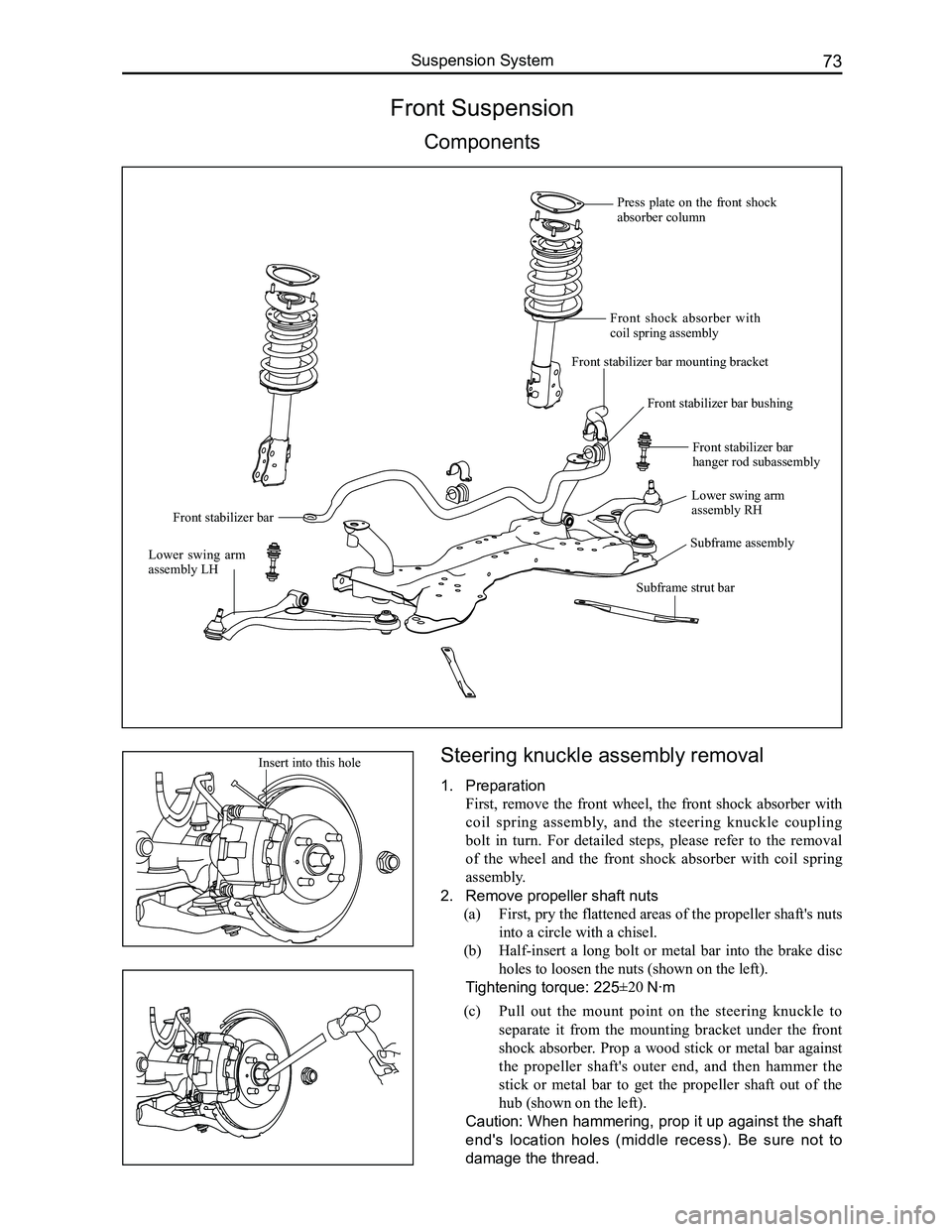
Front Suspension
Components
(c) Pull out the mount point on the steering knuckle to
separate it from the mounting bracket under the front
shock absorber. Prop a wood stick or metal bar against
the propeller shaft's outer end, and then hammer the
stick or metal bar to get the propeller shaft out of the
hub (shown on the left).
Caution: When hammering, prop it up against the shaft
end's location holes (middle recess). Be sure not to
damage the thread.
Insert into this hole
Press plate on the front shock absorber column
Front shock absorber with coil spring assembly
Front stabilizer bar mounting bracket
Front stabilizer bar bushing
Front stabilizer bar
Lower swing arm assembly RH
Lower swing arm assembly LH
Subframe assembly
Front stabilizer bar hanger rod subassembly
Subframe strut bar
Page 82 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 75Suspension System
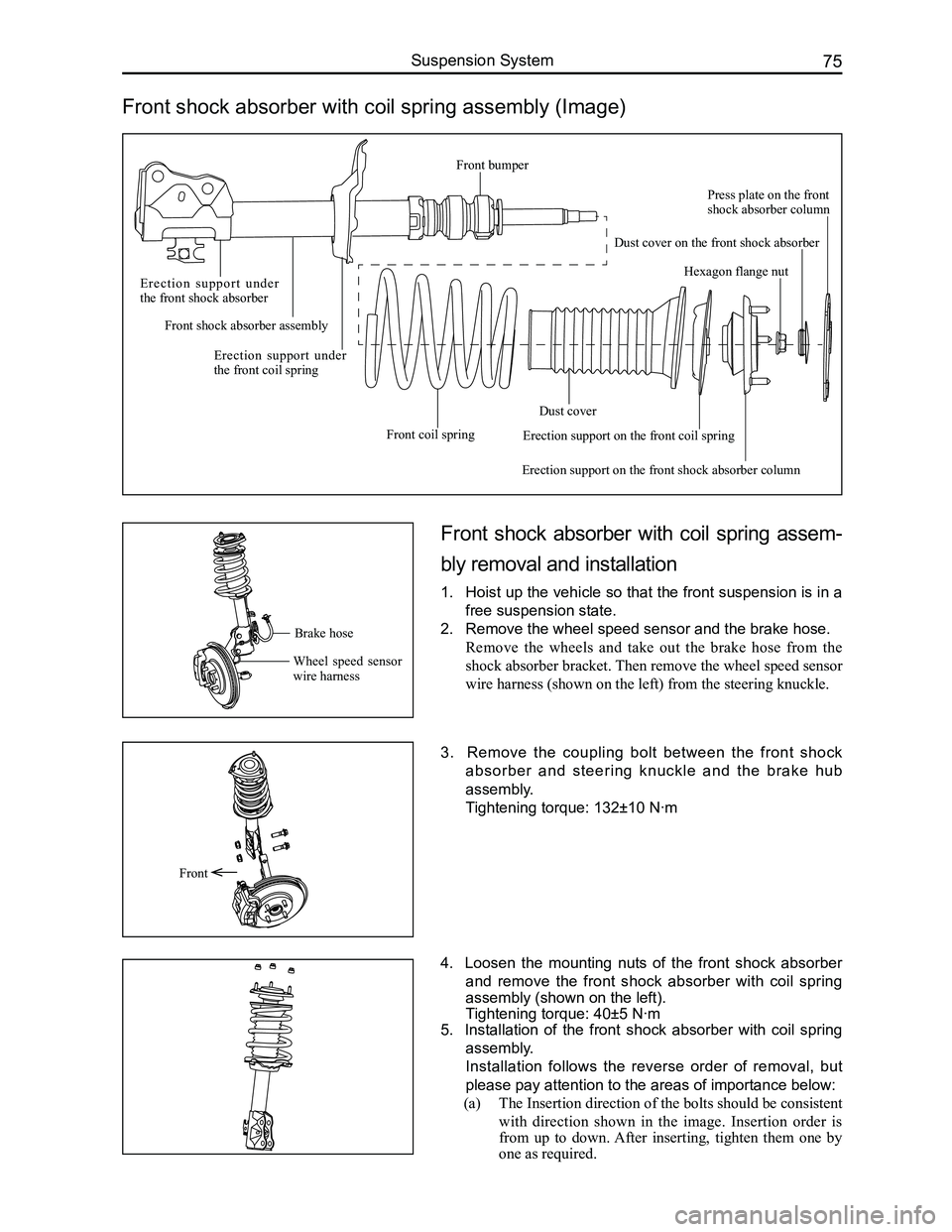
Front shock absorber with coil spring assembly (Image)
Front shock absorber with coil spring assem-
bly removal and installation
1. Hoist up the vehicle so that the front suspension is in a
free suspension state.
2. Remove the wheel speed sensor and the brake hose.
Remove the wheels and take out the brake hose from the
shock absorber bracket. Then remove the wheel speed sensor
wire harness (shown on the left) from the steering knuckle.
3. Remove the coupling bolt between the front shock
absorber and steering knuckle and the brake hub
assembly.
Tightening torque: 132±10 N·m
4. Loosen the mounting nuts of the front shock absorber
and remove the front shock absorber with coil spring
assembly (shown on the left).
Tightening torque: 40±5 N·m
5. Installation of the front shock absorber with coil spring
assembly.
Installation follows the reverse order of removal, but
please pay attention to the areas of importance below:
(a) The Insertion direction of the bolts should be consistent
with direction shown in the image. Insertion order is
from up to down. After inserting, tighten them one by
one as required.
Front
Brake hose
Wheel speed sensor wire harness
E r e c t i o n s u p p o r t u n d e r the front shock absorber
Front shock absorber assembly
Erection support under the front coil spring
Front coil spring
Dust cover
Erection support on the front shock absorber column
Hexagon flange nut
Press plate on the front shock absorber column
Dust cover on the front shock absorber
Erection support on the front coil spring
Front bumper
Page 83 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual76
Front shock absorber with coil spring assem-
bly disassembly and installation
1. Compression spring
Use SST to grasp the spring, separated by adhesive tape
at the contact area. Alternately rotate the bolts on the SST
until there is no tension on the spring seat from the spring.
The front coil spring rotating means that the spring has been
compressed (shown on the left).
2. Disassemble the front shock absorber with coil spring
assembly
Remove the dust cover of the front shock absorber. Remove
the nuts on top using a ratchet wrench and M21 sleeve. Re-
move the erection support on the front shock absorber col-
umn, support bearing, the front coil spring's erection support,
front coil spring, dust cover, and the bumper in turn.
Tightening torque: 40-60 N·m
3. Retracting spring
Alternately reversing, rotate the bolts on the SST until all the
spring tension is released, then remove the tool.
4. Change any component that needs to be replaced
5. Installation of the front shock absorber with coil spring
assembly
Installation is in the reverse order of disassembly,
please pay attention to items below:
(a) Use SST to compact the spring.
(b) Steps for the installation of each component of the
front shock absorber with coil spring assembly is the
opposite of the steps for its disassembly.
(c) Pull up the strut piston rod as hard as possible and
make sure not to let it draw back into the strut.
(b) All of the fastening pieces must be tightened to the
required torque, and comply to the standard gluing re-
quirements in this chapter.
Page 91 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual84
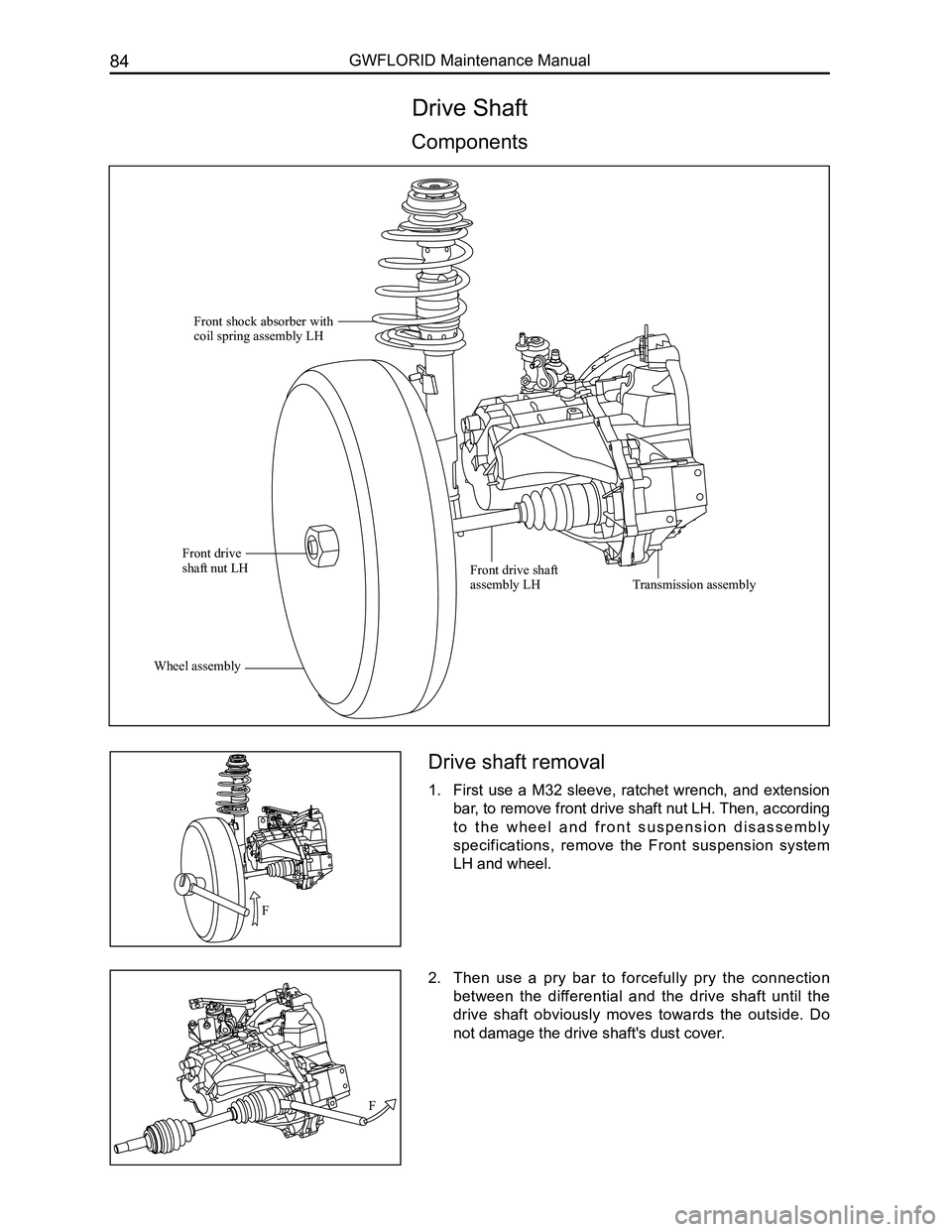
Drive Shaft
Components
Drive shaft removal
1. First use a M32 sleeve, ratchet wrench, and extension
bar, to remove front drive shaft nut LH. Then, according
t o t h e w h e e l a n d f r o n t s u s p e n s i o n d i s a s s e m b l y
specifications, remove the Front suspension system
LH and wheel.
2. Then use a pry bar to forcefully pry the connection
between the differential and the drive shaft until the
drive shaft obviously moves towards the outside. Do
not damage the drive shaft's dust cover.
Front shock absorber with coil spring assembly LH
Front drive shaft nut LH
Wheel assembly
Front drive shaft assembly LHTransmission assembly
F
F
Page 92 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 85Suspension System
Drive shaft installation
1. Insert the drive shaft.
First, align the inner end of the drive shaft and differential
spline. Keep the drive shaft axes and the differential axes
bases uniform, then hammer towards the direction of the
differential drive shaft's outer end until a clear and sharp
clicking sound is heard. Here, the drive shaft and the
transmission should have a clearance of about 1 mm.
2. According to the front suspension and wheel assembly
installation specifications, properly install the front
shock absorber with coil spring assembly LH and
wheel.
3. Use an M32 sleeve, ratchet wrench, and extension bar
to tighten front drive shaft nut LH.
Tightening torque: 225±20 N·m
F
F
Page 93 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual86
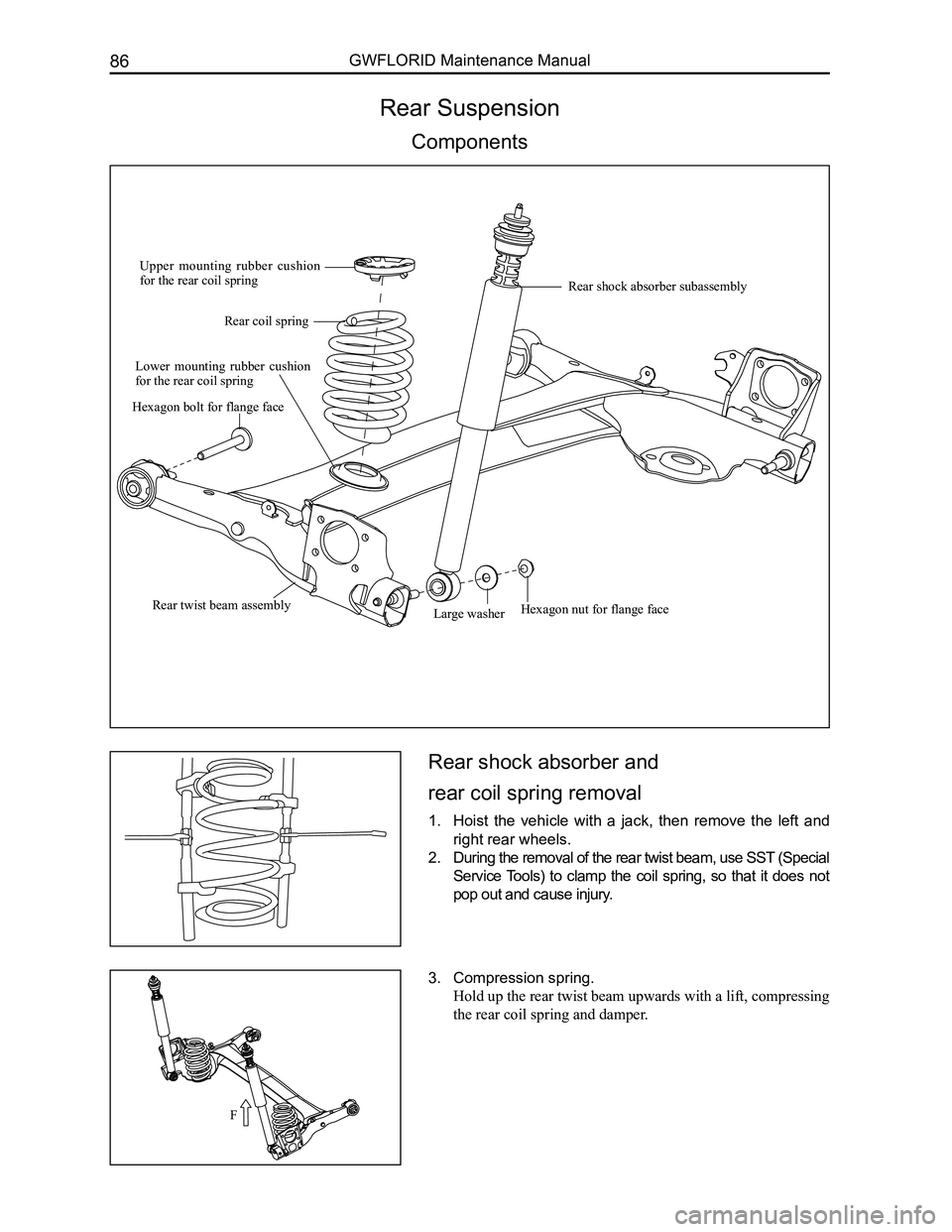
Rear Suspension
Components
Rear shock absorber and
rear coil spring removal
1. Hoist the vehicle with a jack, then remove the left and
right rear wheels.
2. During the removal of the rear twist beam, use SST (Special
Service Tools) to clamp the coil spring, so that it does not
pop out and cause injury.
3. Compression spring.
Hold up the rear twist beam upwards with a lift, compressing
the rear coil spring and damper.
Upper mounting rubber cushion for the rear coil spring
Rear coil spring
Lower mounting rubber cushion for the rear coil spring
Large washerRear twist beam assembly
Rear shock absorber subassembly
Hexagon bolt for flange face
Hexagon nut for flange face
F
Page 94 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 87Suspension System
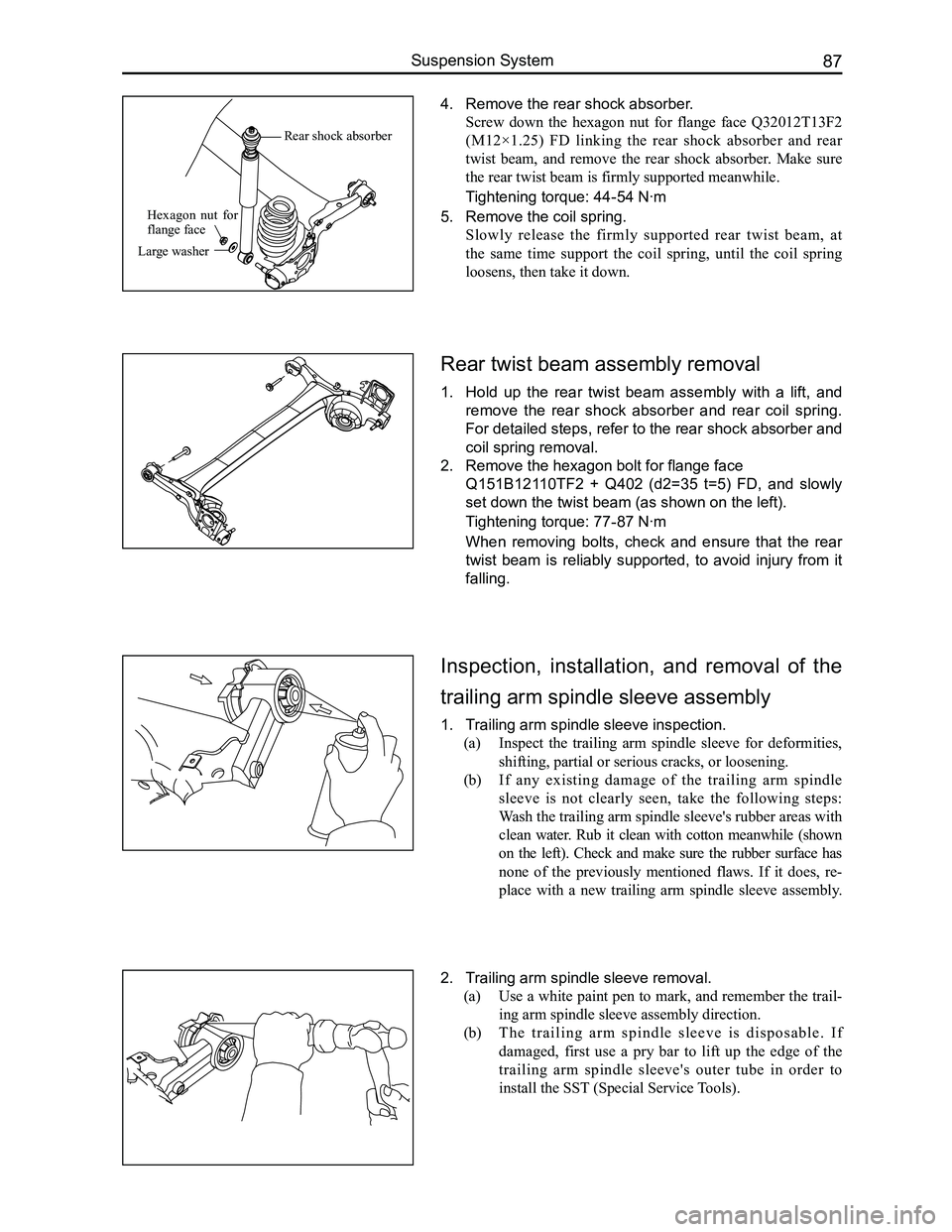
Inspection, installation, and removal of the
trailing arm spindle sleeve assembly
1. Trailing arm spindle sleeve inspection.
(a) Inspect the trailing arm spindle sleeve for deformities,
shifting, partial or serious cracks, or loosening.
(b) If any existing damage of the trailing arm spindle
sleeve is not clearly seen, take the following steps:
Wash the trailing arm spindle sleeve's rubber areas with
clean water. Rub it clean with cotton meanwhile (shown
on the left). Check and make sure the rubber surface has
none of the previously mentioned flaws. If it does, re-
place with a new trailing arm spindle sleeve assembly.
2. Trailing arm spindle sleeve removal.
(a) Use a white paint pen to mark, and remember the trail-
ing arm spindle sleeve assembly direction.
(b) T h e t r a i l i n g a r m s p i n d l e s l e e v e i s d i s p o s a b l e . I f
damaged, first use a pry bar to lift up the edge of the
trailing arm spindle sleeve's outer tube in order to
install the SST (Special Service Tools).
Rear twist beam assembly removal
1. Hold up the rear twist beam assembly with a lift, and
remove the rear shock absorber and rear coil spring.
For detailed steps, refer to the rear shock absorber and
coil spring removal.
2. Remove the hexagon bolt for flange face
Q151B12110TF2 + Q402 (d2=35 t=5) FD, and slowly
set down the twist beam (as shown on the left).
Tightening torque: 77-87 N·m
When removing bolts, check and ensure that the rear
twist beam is reliably supported, to avoid injury from it
falling.
4. Remove the rear shock absorber.
Screw down the hexagon nut for flange face Q32012T13F2
(M12×1.25) FD linking the rear shock absorber and rear
twist beam, and remove the rear shock absorber. Make sure
the rear twist beam is firmly supported meanwhile.
Tightening torque: 44-54 N·m
5. Remove the coil spring.
Slowly release the firmly supported rear twist beam, at
the same time support the coil spring, until the coil spring
loosens, then take it down.
Rear shock absorber
Large washer
Hexagon nut for flange face
Page 96 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 89Suspension System
Wheel and Tire
Tire
Remark
This vehicle's tire is of the tubeless type. The optimal design condition is met when the inflation pressure is at
the recommended value, and the tire is under full load. Maintaining suitable tire pressure and proper driving
habits greatly influence the tire's use life. For the vehicle, it improves riding comfort, stability, and handling. For
the tire, it reduces tread wear, damage to the tire and extends tire life. Overloading, speeding, and unnecessary
emergency braking will all add to the tire's wear and tear.
Tire pressure measurements should be taken under normal temperature. If the tire pressure rises due to motion
generated heat when driving, cooling it will return to the normal temperature. Therefore, do not deflate the tire
when the air pressure has risen to this point. The tire's air pressure will naturally and slowly decrease when used
under normal conditions. Hence please inspect the air pressure regularly (suggested once a month). The spare
tire should be kept in a useable condition at all times.
Inspect the tire pressure when it is cool monthly or before a long drive. Adjust the tire pressure to the recom-
mended level. The air pressure will normally rise because the tire warms up due to movement. Therefore, after
driving, you absolutely must not deflate or reduce the tire's air pressure, as deflating could reduce the cool tire's
air pressure.
Tire inflation
During a new tire's initial stage of use, warning due to bending motions will cause the tire to swell, and thus
reduce the corresponding air pressure. After 24 hours or 2000-3000 km worth of drive, charge the air pressure.
After inflating, check if the air nozzle core is leaking air with soapy \
water, then lock on the cap.
Possible problems caused by tire pressure
Exceeding the recommended air
pressure
Below the recommended air pressureSame vehicle axle, different
air pressure
Possible problems it
can create
1. Bumpy ride
2. The tear or rupturing of the tire
3. Rapid wear of the tire tread's center
1. Noisy turns
2. Uneasy turns
3. Tread edge wear is accelerated and uneven
4. The tire's rim is damaged or ruptured
5. The tire cord ruptures
6. High tire temperature
7. Steering failure
8. Large oil consumption
1. Uneven braking
2. Over steering
3. Steering failure
4. Deviation while accelerating
Tire and wheel (steel wheel) installation instructions
When installing the tire and wheel, the tire's radial hardware components, also called "high spot", should be at
the same level of the wheel's minimum radius or so called "low spot".
The "high spot" of the tire is initially marked by the paint spot on the side of the tire's surface. This paint will
eventually be washed away.
The "low spot" of the wheel is initially marked by a paint spot on the wheel flange. Whenever the tire is
removed from the wheel, the tire and wheel need re-balancing to make sure the vehicle runs smoothly. If no
paint spot is found on the tire, draw a line on the tire and the wheel before they are removed, in order to make
sure that the tire and the wheel will be re-assembled at the same place.\
Tire replacement
When a tire needs to be replaced, make sure to use a tire with the same specification as the original one. A new
tire used for replacement must be of the same dimension, load area, and structure as the original one. Using tires
that are different in dimension or type will influence the vehicle's riding comfort, handling, speedometer and
odometer calibration, vehicle ground clearance, and the clearance between the tire or the tire's snow chain and
the vehicle body or chassis.
It is suggested to use a new pair of tires on the same axle. If only one tire is needed to be replaced, make sure to
use a tire with a tread most similar to the original, so as to keep brak\
e power and traction balanced.
Warning: Do not mix radial tires, bias tires, bias belted tires, etc., which are of different structure on the
same vehicle unless it is an emergency. Mixing different tires would seriously influence the vehicle's
handling and stability, and even possibly lead to losing control of the vehicle.
Page 100 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 93Suspension System
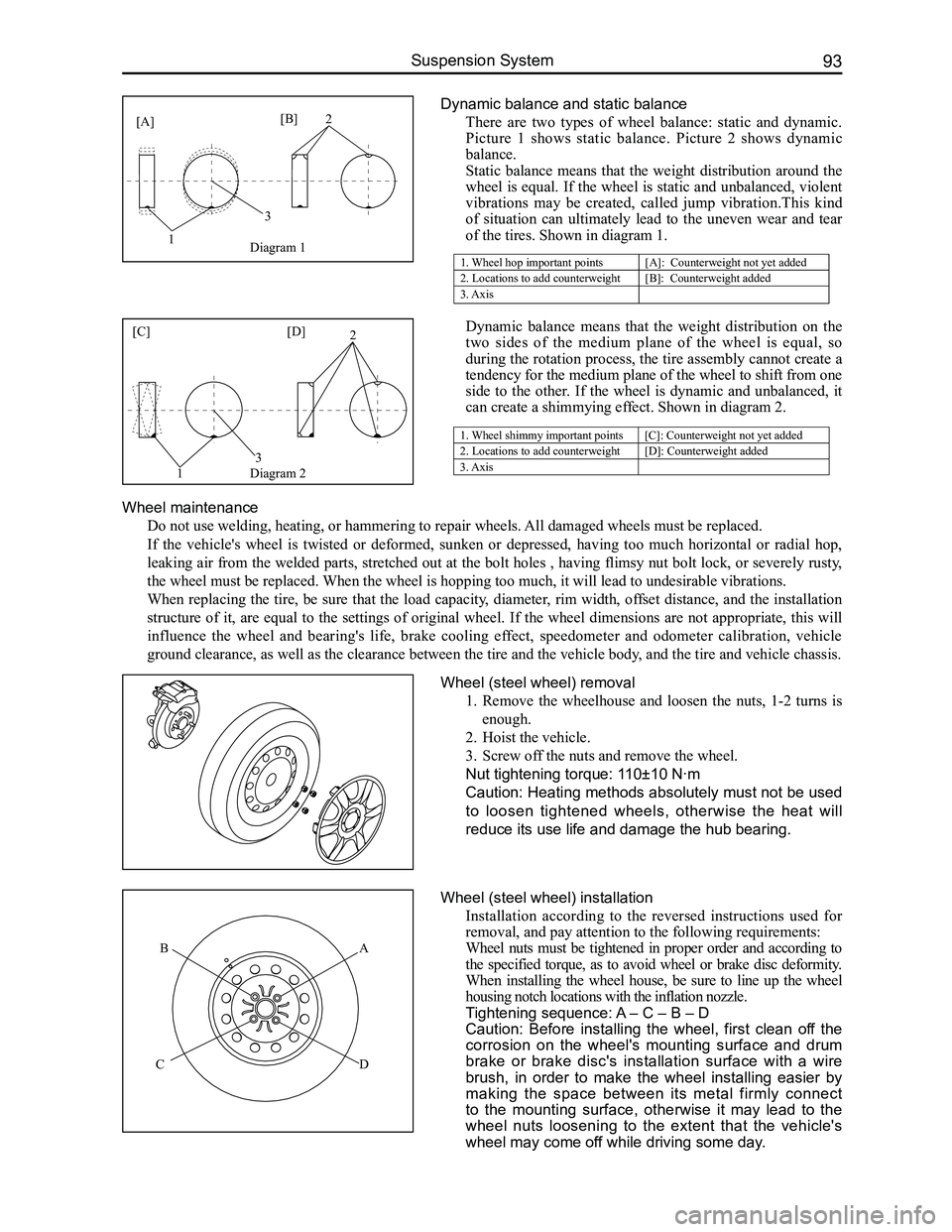
Dynamic balance and static balance
There are two types of wheel balance: static and dynamic.
Picture 1 shows static balance. Picture 2 shows dynamic
balance.
Static balance means that the weight distribution around the
wheel is equal. If the wheel is static and unbalanced, violent
vibrations may be created, called jump vibration.This kind
of situation can ultimately lead to the uneven wear and tear
of the tires. Shown in diagram 1.
Dynamic balance means that the weight distribution on the
two sides of the medium plane of the wheel is equal, so
during the rotation process, the tire assembly cannot create a
tendency for the medium plane of the wheel to shift from one
side to the other. If the wheel is dynamic and unbalanced, it
can create a shimmying effect. Shown in diagram 2.
1. Wheel shimmy important points[C]: Counterweight not yet added
2. Locations to add counterweight[D]: Counterweight added
3. Axis
Wheel maintenance
Do not use welding, heating, or hammering to repair wheels. All damaged wheels must be replaced.
If the vehicle's wheel is twisted or deformed, sunken or depressed, having too much horizontal or radial hop,
leaking air from the welded parts, stretched out at the bolt holes , having flimsy nut bolt lock, or severely rusty,
the wheel must be replaced. When the wheel is hopping too much, it will lead to undesirable vibratio\
ns.
When replacing the tire, be sure that the load capacity, diameter, rim width, offset distance, and the installation
structure of it, are equal to the settings of original wheel. If the wheel dimensions are not appropriate, this will
influence the wheel and bearing's life, brake cooling effect, speedometer and odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance, as well as the clearance between the tire and the vehi\
cle body, and the tire and vehicle chassis.
Wheel (steel wheel) removal
1. Remove the wheelhouse and loosen the nuts, 1-2 turns is
enough.
2. Hoist the vehicle.
3. Screw off the nuts and remove the wheel.
Nut tightening torque: 110±10 N·m
Caution: Heating methods absolutely must not be used
to loosen tightened wheels, otherwise the heat will
reduce its use life and damage the hub bearing.
Wheel (steel wheel) installation
Installation according to the reversed instructions used for
removal, and pay attention to the following requirements:
Wheel nuts must be tightened in proper order and according to
the specified torque, as to avoid wheel or brake disc deformity.
When installing the wheel house, be sure to line up the wheel
housing notch locations with the inflation nozzle.
Tightening sequence: A – C – B – D
Caution: Before installing the wheel, first clean off the
corrosion on the wheel's mounting surface and drum
brake or brake disc's installation surface with a wire
brush, in order to make the wheel installing easier by
making the space between its metal firmly connect
to the mounting surface, otherwise it may lead to the
wheel nuts loosening to the extent that the vehicle's
wheel may come off while driving some day.
1
3
2[A][B]
1. Wheel hop important points[A]: Counterweight not yet added
2. Locations to add counterweight[B]: Counterweight added
3. Axis
Diagram 1
Diagram 2
[C][D]
1
3
2
AB
CD
Page 101 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual94
Brake System
Brake System Components Arrangement Schematics.......95
Brake System Maintenance................................................96
Brake Pedal ........................................................................\
98
Parking Brake Control Mechanism Assembly...................102
Vacuum Booster with Brake Cylinder Assembly ...............103
Anti-lock Brake System ....................................................107
ABS General Problem Maintenance and
Areas of Importance .........................................................109
Steering Knuckle and Hub Brake Assembly .....................112
Front Brake Caliper ..........................................................118
Rear Brake .......................................................................124
Rear Support Axle ............................................................131