Engine control HONDA CIVIC 1996 6.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1996, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 1996 6.GPages: 2189, PDF Size: 69.39 MB
Page 802 of 2189
Transmission
Removal(cont'd)
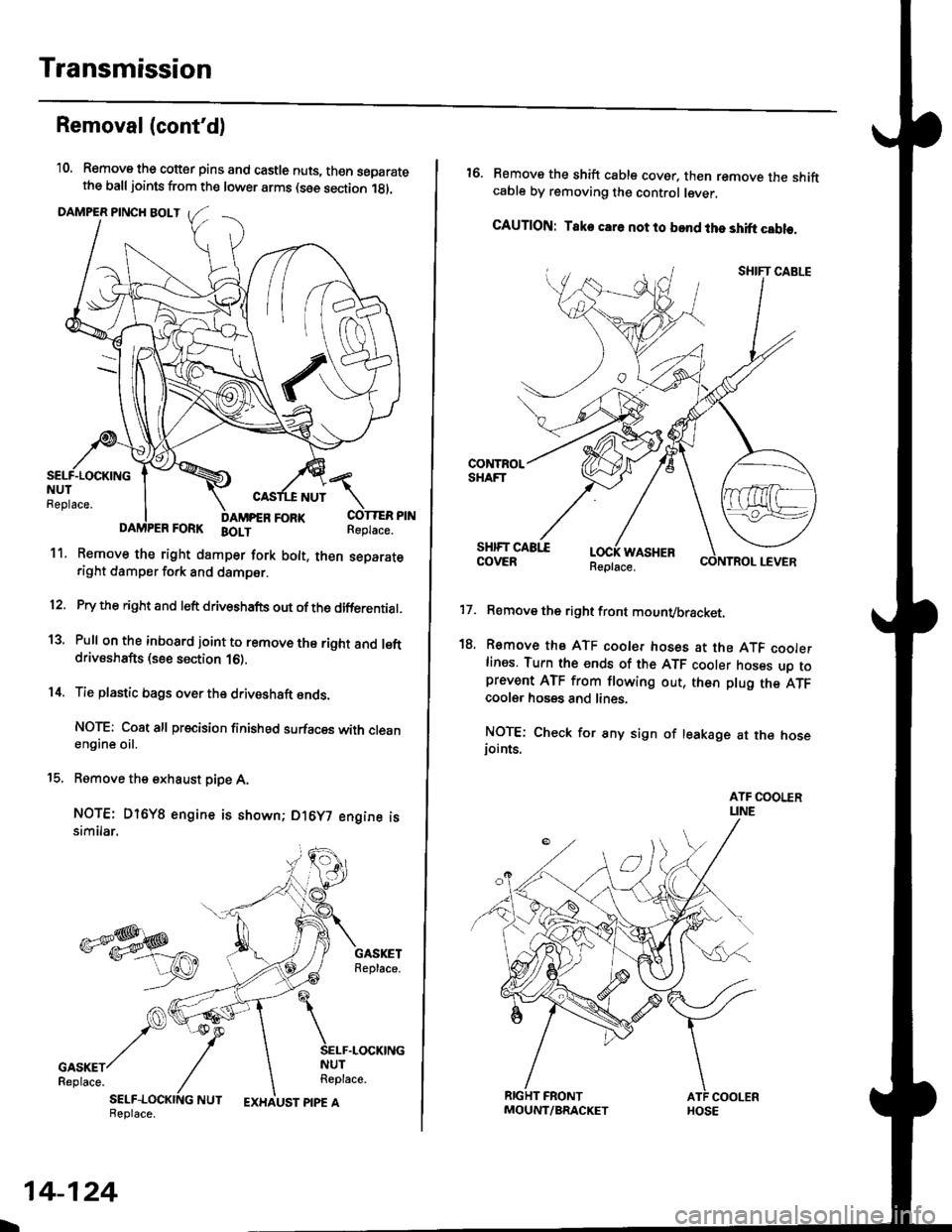
'10. Remove the cotter pins and castle nuts, th€n separatethe balljoints from the lower arms (see section 1gl.
DAMPER PINCH BOLT
NUT
FORI(FORK BOLT
11. Remove the right damper fork bolt. th€nright damper fork and dampor.
COTTER PINReplace.
separate
12.
1a
14.
Pry the right and left driveshafts out ofthe differential.
Pull on the inboard joint to remove the right and leftdrivsshafts (see section 16).
Tie plastic bags over the driveshaft onds.
NOTE: Coat all precision finished surfaces with cleanengine oil.
Remove the exhaust pipe A,
NOTE: Dl6YB engine is shown; D16y7 engine issimilar.
t9.
SELF-LOCKING NUTReplace.
L
14-124
EXHAUST PIPE AMOUNT/BRACKET
17.
18.
16. Remove the shift cable cover. then remove the shiftcable by removing the control lever,
CAUTION: Take car6 not to bond the shift cable.
Remove the right front mounvbracket.
Remove the ATF cooler hoses at the ATF coolerlines. Tufn the ends of the ATF cooler hoses uo toprevent ATF from flowing out, then plug the ATFcooler hosgs and lines.
NOTE: Check for any sign of leakage at the hoseioints.
WASHER
Page 862 of 2189
Transmission
Installation (cont'dl
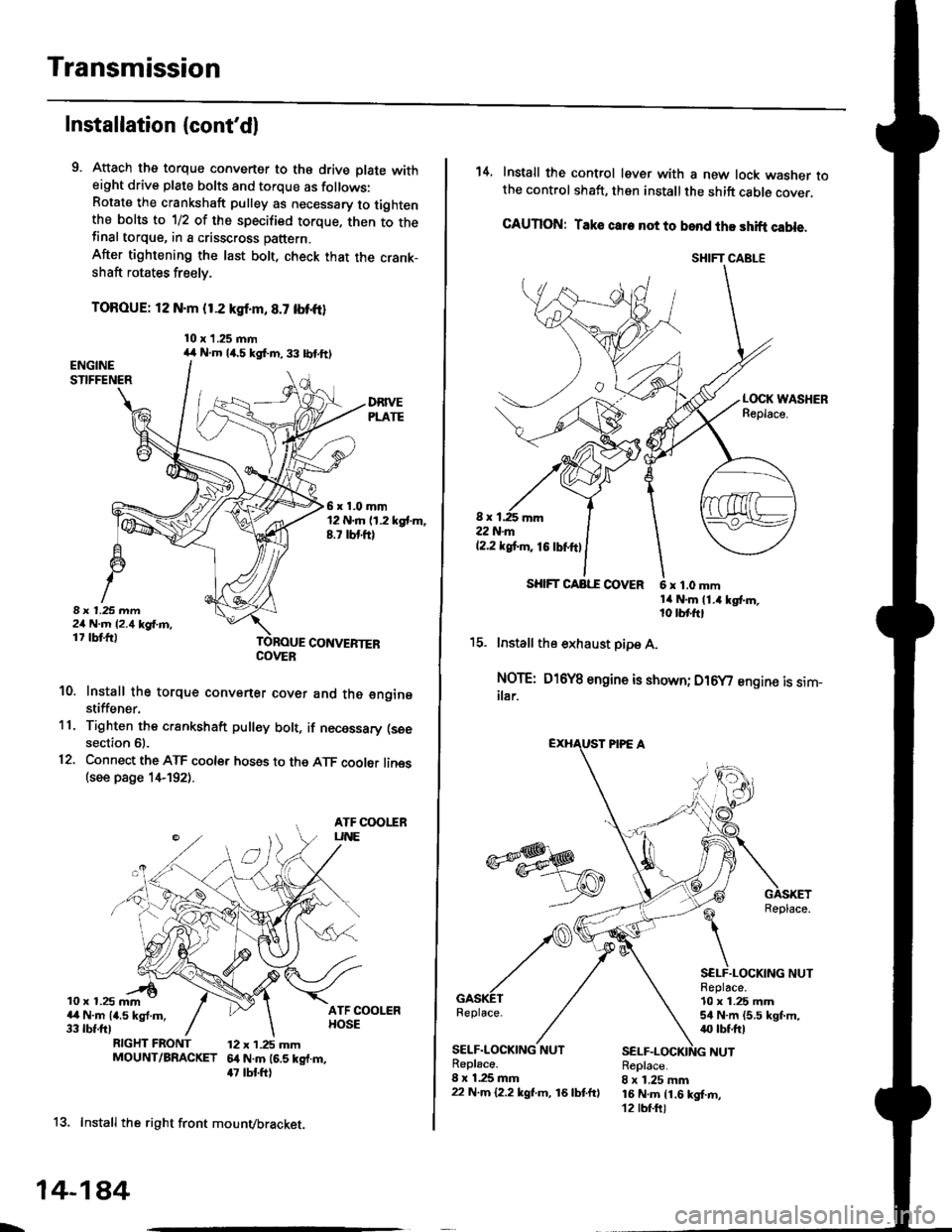
9. Attach the torque converter to the drive plate witheight drive plate bolts and torque as follows:Rotate the crankshaft pulley as necessary to tightenthe bolts to 1/2 of the specified torque. then to thefinal torque, in a crisscross pattern.
After tightening the last bolt, check that the crank-shaft rotates freely.
TOROUE: 12 N.m {1.2 kgl.m, 8.7 tbt{r}
10 x 1.25 mm
6x1.0mm12 N.m (1.2 kgt m,8.7 rbt ft)
I 1.25 mm2/t N.m {2.4 kg{.m,17 tbt ftlCONVERTEB
10. Install the torque convener cover and the €nginestiffener.'11. Tighten the crsnkshaft pull€y bolt, if necessary (see
section 61.
12. Connect the ATF cooler hoses to the ATF cooler lines(see page 1,t192).
ATF COOIIRUNE
10 x 1.25 mma,l N.m {4.5 kgl.m,33 rbt.fttRIGHT FRONT 12 x 1.25 mmMOUNT/BRACKET 6.t N.m (6.5 kg{.m,47 tbt ftl
13. Install the right front mounvbracket.
4,r N.m 14.5 kgf.m,33 lbtft)
COVER
L,
14-1A4
SHIFT CABLE
SHIFT CAAE COVER
14. Install the control lever with a new lock washer tothe control shaft, then install the shift cable cover.
CAUION: Taks care not to bend the shift cable.
L(rcK WASHERReplace.
8 x 1,25 r'|m22N-m12.2 tgt m. 16lbnftl
x 1.0 mmtit N.m 11.4 kgt m,10 tbr,ft,
15. lnstall the exhaust pipe A.
NOTE: D16Y8 engine is shown; D16y/ engine is sim_ilar.
Replace.
GASKETReplace.
SELF.LOCKING NUTReplace.10 x 1.25 mm54 N.m (5.5 lgf.m,40 tbt ftl
NUTSELF.LOCKING NUTReplace.8 x 1.25 mm22 N.m {2.2 kgl.m, 16lbtfrl
Replace.8 x 1.25 mm16 N.m {1.6 kgI.m,12 tbf.ft)
Page 864 of 2189
Transmission
Installation {cont'd)
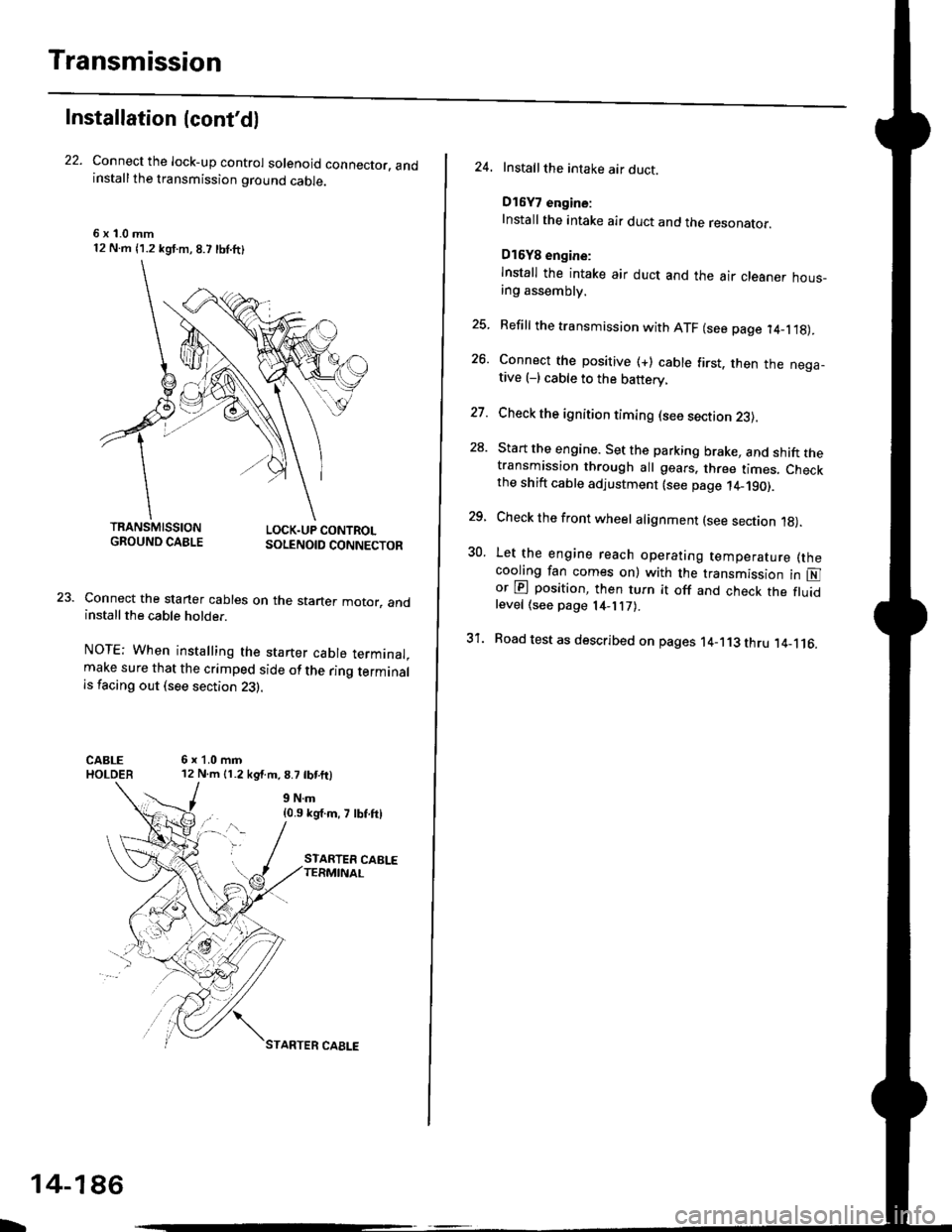
Connect the lock-up control solenoid connector. andinstall the transmission ground cable.
6 x '1.0 mm12 N.m {1.2 kgf.m, 8.7 lbl.ft}
LOCK.UP CONTROLSOLENOID CONNECTOR
Connect the staner cables on the staner motor. andinstall the cable holder.
NOTE; When installing the starter cable terminal.make sure that the crimped side of the ring terminalis facing out (see section 23).
6x1.0mm12 N.m 11.2 kg{.m.8.7 tbtftl
{0.9 kg'f.m, 7 lbf.ftl
TRANSMISSIONGROUND CABLE
b
14-186
STARTER CAELE
24. Installthe intake air duct.
D16Y7 engine:
Install the intake air duct and the resonaror.
D16Y8 engine:
lnstall the intake air duct and the air cleaner hous_ang assembly.
25. Refill the transmission with ATF (see page 14_1.18).
26. Connect the positive (+) cable first. then the nega-tive (-) cable to the battery.
27. Check the ignition timing (see section 23).
28. Start the engine. Set the parking brake, and shift thetransmission through all gears. three times. Checkthe shift cable adjustment (see page 14_190).
29, Check the front wheel alignment (see section 1g).
30. Let the engine reach operating temperature (thecooling fan comes on) with the transmission in Nor @ position, then turn it off and check the fluidlevel (see page 14- 7).
31. Road test as described on pages 14-113 thru ,14_116.
Page 873 of 2189

Description
The Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is an electronically controlled automatic transmission with drive and driv
en Oullevs, and a steel belt. The CVT provides non stage speeds forward and one reverse. The entire unit is positioned in
line with the engine.
Transmission
Around the outside of the flywheel is a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being staned.
The transmission has four parallel shafts: the input shaft, the drive pulley shaft. the driven pulley shaft, and the secondary
gear shaft. The input shaft is in line with the engine crankshaft. The drive pulley shaft and the driven pulley shaft consist of
movable and fixed face pulleys. Both pulleys are linked by the steel belt.
The input shaft includes the sun gear. The drive pulley shaft includes the forward clutch which mounts the carrier assem-
bly on the forward clutch drum. The carrier assembly includes the pinion gears which mesh with the sun gear and the ring
gear. The ring gear has a hub-mounted reverse brake disc.
The driven pulley shaft includes the start clutch and the secondary drive gear which is integral with the park gear' The sec-
ondary gear shaft is positioned between the secondary drive gear and the final driven gear. The secondary gear shaft
includes the secondary driven gear which serves to change the rotation direction. because the drive pulley shaft and the
driven oullev shaft rotate the same direction. When certain combinations of planetary gears in the transmission are
engaged by the clutches and the reverse brake, power is transmitted from the drive pulley shaft to the driven pulley shaft
to provide E, E, E, and El.
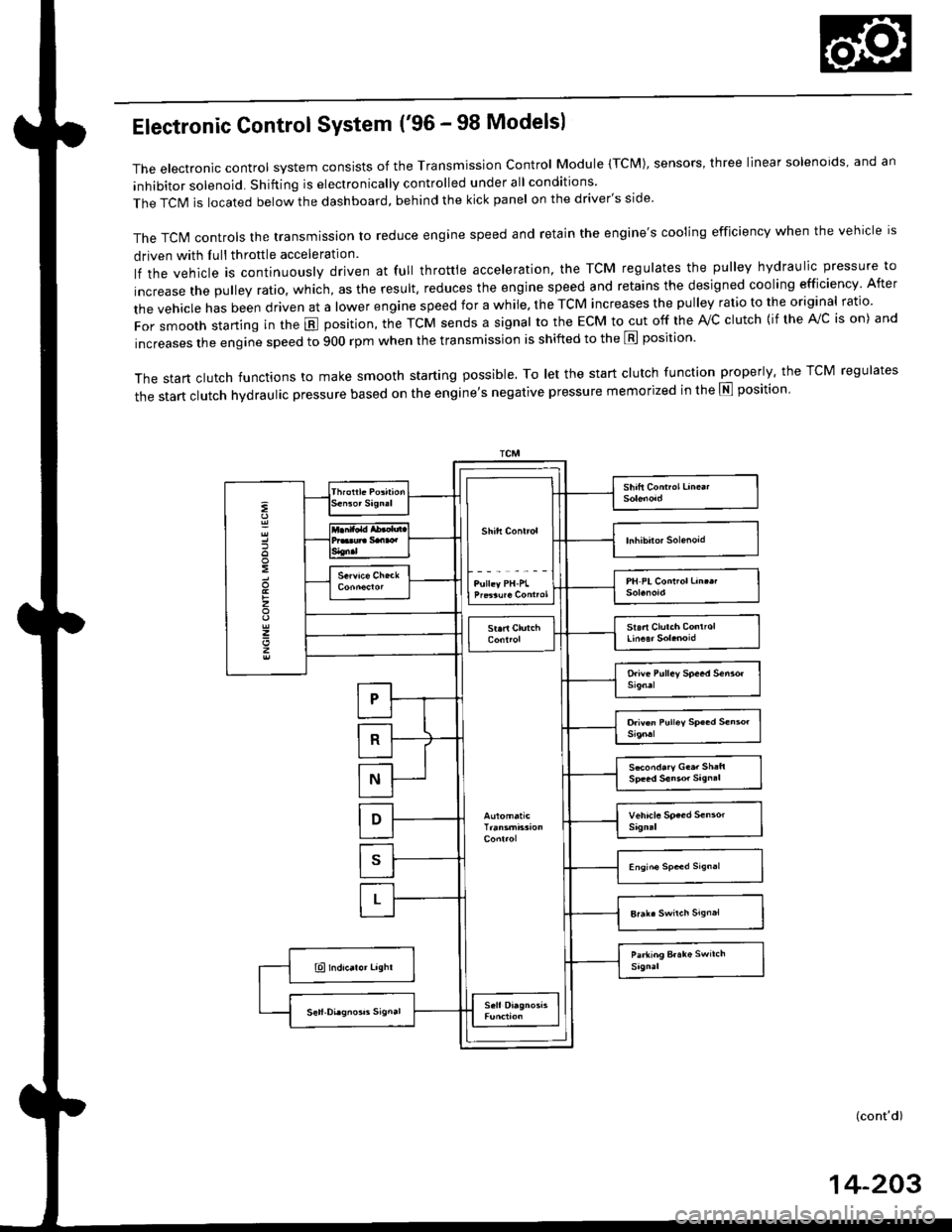
Electronic Control'96 - 98 Models:
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, three linear solenoids, and a
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions'
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the kick panel on the driver's side.'99 - 00 Models:
The electronic control svstem consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, three linear solenoids and an
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions. A Grade Logic Control System to control shift-
ing in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope.
The PCM is located below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the Pressure Low (PL) reguiator valve body, the shift valve
body, the start clutch control valve body, and the secondary valve body. They are positioned on the lower part of the
transmission housing.
The main valve body contains the Pressure High (PH) control valve, the lubrication valve, and the pitot regulator valve.
The secondary valve body contains the PH regulator valve, the clutch reducing valve, the start clutch valve accumulator,
and the shift inhibitor valve. The PL regulator valve body contains the PL regulator valve and the PH-PL control valve
which is ioined to the PH,PL control linear solenoid. The inhibitor solenoid valve is bolted on the PL regulator valve body.
The shift valve body contains the shift valve and the shift control valve. which is joined to the shift control linear solenoid.
The start clutch control valve body contains the start clutch control valve, which is joined to the start clutch control linear
solenoid. The linear solenoids and the inhibitor solenoid are controlled by the TCM or PCM. The manual valve body which
contains the manual valve and the reverse inhibitor valve, is bolted on the intermediate housing.
The ATF pump assembly is located on the transmission housing, and is linked with the input shaft by the sprockets and
the sprocket chain. The pulleys and the clutch receive fluid from their respective feed pipes, and the reverse brake receives
fluid from internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which linear solenoid the TCM or PCM will activate.
Activating the shift control linear solenoid changes the shift control valve pressure, causing the shift valve to move. This
pressurizes the drive pulley pressure to the drive pulley and the driven pulley pressure to the driven pulley and changes
their effective pulley ratio. Activating the start clutch control linear solenoid moves the start clutch control valve. The start
clutch control valve uncovers the port, providing pressure to the start clutch to engage it(cont'd)
14-195
,!
Page 881 of 2189
Electronic Control System ('96 - 98 Modelsl
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission control Module (TcM), sensors, three linear solenoids, and an
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions
The TCIM is located below the dashboard, behind the kick panel on the driver's side'
The TcN4 controls the transmission to reduce engine speed and retain the engine's cooling efficiency when the vehicle is
driven with Iull throttle acceleration
lf the vehicle is continuously driven at full throttle acceleration, the TCM regulates the pulley hydraulic pressure to
increase the pulley ratio, which, as the result. reduces the engine speed and retains the designed cooling efficiency After
the vehicle has been driven at a lower engine speed for a while, the TCM increases the pulley ratio to the original ratio.
For smooth starting in the E position, the TcM sends a signal to the EcM to cut off the rvc clutch {if the A!/c is on) and
increases the engine speed to 900 rpm when the transmission is shifted to the E position'
The start clutch functions to make smooth starting possible. To let the start clutch function properly. the TCM regulates
the start clutch hydraulic pressure based on the entine's negative pressure memorized in the E position'
:
:
z
z
z
S*ond.ry G..r Sh:ft
(cont'd)
14-203
Page 883 of 2189
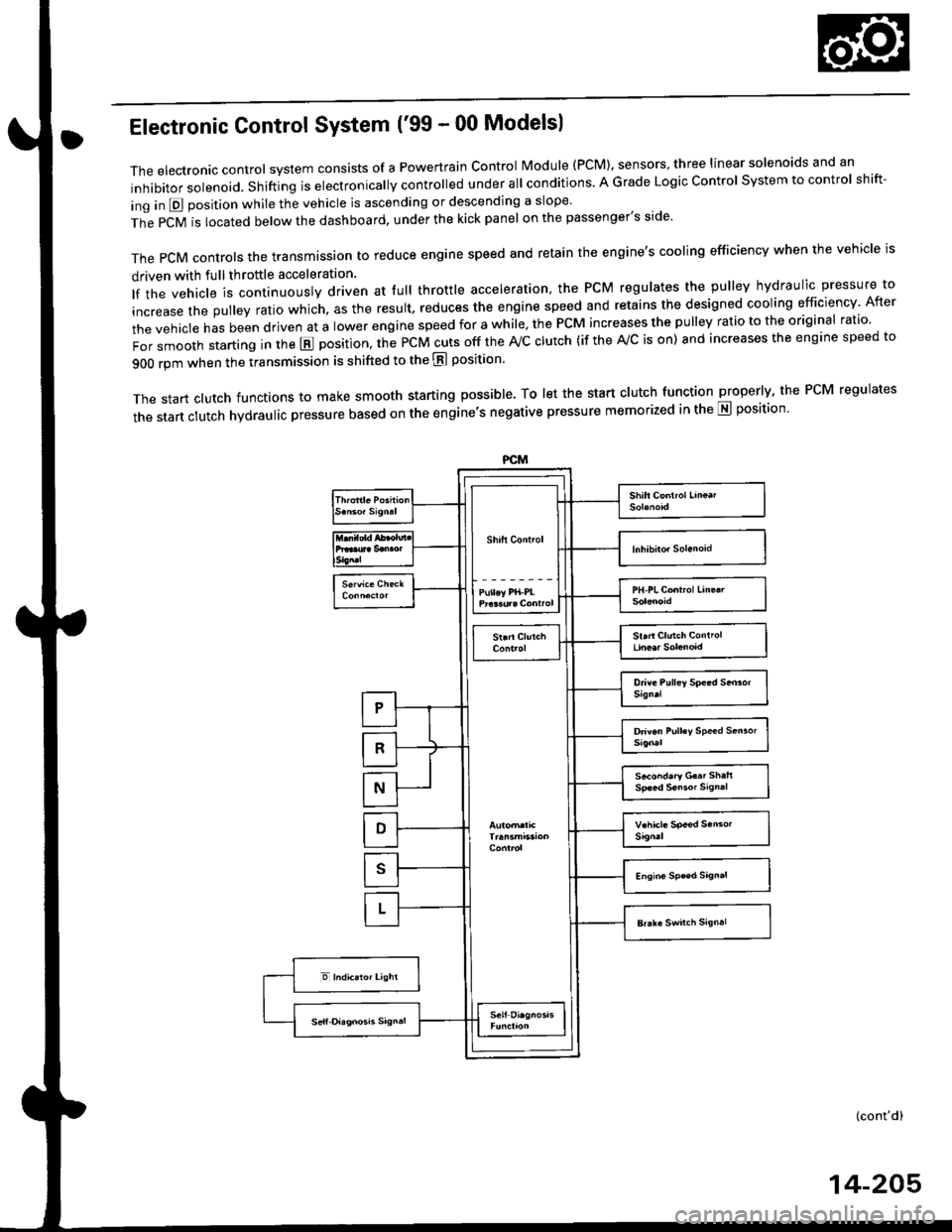
Electronic Gontrol System ('99 - 00 Modelsl
The electronic controt system conststs of a Powertrain control Module (PCM). sensors, three linear solenoids and an
inhibitor solenoid. shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions A Grade Logic control system to control shift-
ing in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope'
fn"pCVirlocatedbelowthedashboard,underthekickpanelonthepassenger'sside'
The pCM controls the transmassion to reduce engine speed and retain the engine's cooling efficiency when the vehicle is
driven with full throftle acceleration
lf the vehicle is continuously driven at lull throttle acceleration, the PCM regulates the pulley hydraulic pressure to
increase the pulley ratio which. as the result, reduces the engine speed and retains the designed cooling efficiency After
the vehicle has been driven at a lower engine speed for a while, the PCM increases the pulley ratio to the original ratio'
i"i ".nl",rr starting in the E position, the PcM cuts off the ,Vc clutch (if the A/c is on) and increases the engine speed to
900 rpm when the transmission is shifted to the E position'
The start clutch functions to make smooth starting possible. To let the start clutch function properly, the PcM regulates
the start clutch hydraulic pressure based on the engine's negative pressure memorized in the E position'
FCM
s*o.d.ry G..t Sh.h
(cont'd)
14-205
Page 884 of 2189

Description
Electronic Control System ('99 - 00 Modelsl (cont'dl
Grade Logic Control System
How it works:
The PcM compares actual driving conditions with memorized driving conditions. based on the input from the vehiclespeed sensor, the throttle position sensor, the manifold absolute pressure sensor, the engine coolant temperature sensor,the brake switch signal, and the shift lever position signal, to control shifting while the vehicle is ascending or descendinga slope.
Ascending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in E position, the system selects the most suitable shiftschedule (pulley ratio) according to the magnitude of a gradient. so the vehicle can run smooth and have more powerwhen needed. There are three ascending modes with different shift schedules according to the magnitude ot a gradient inthe PCM.
Descending Control
when the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hill in E position. the system selects the most suitable shiftschedule (pulley ratio) according to the magnitude of a gradient. This, in combinstion with engine braking, achievessmooth driving when the vehicle is descending, There are three descending modes with different shift schedules accord-ing to the magnitude of a gradient in the PCM.
L
14-206
Page 886 of 2189
Description
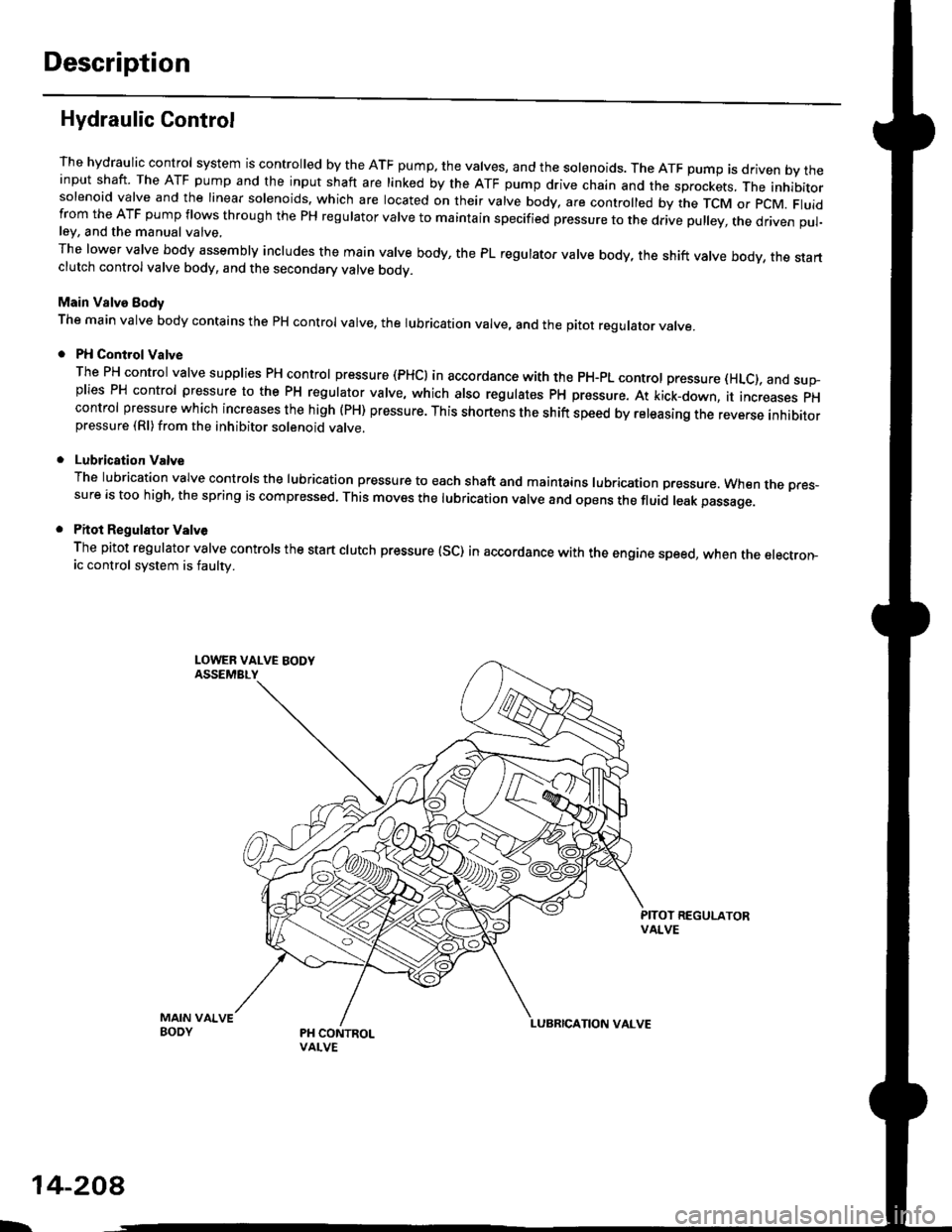
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump. the valves, and the solenoids. The ATF pump is driven by theinput shaft. The ATF pump and the input shaft are linked by the ATF pump drive chain and the sprockets, The inhibitorsolenoid valve and the linear solenoids. which are located on their valve body, are controlled by the TCM or pcM. Fluidfrom the ATF pump flows through the PH regulator valve to maintain specified pressure to the drive pulley, the driven pul-ley, and the manual valve,
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the PL regulator valve body, the shift valve body, the startclutch control valve body, and the secondary valve bodv.
Main Valve Eody
The main valve body contains the pH control valve, the rubrication valve, and the pitot regulator valve.
PH Control Valve
The PH control valve supplies PH control pressure (PHCI in accordance with the pH-pL control pressure (HLc), and sup-plies PH control pressure to the PH regulator valve, which also regulatss PH pressure. At kick-down, it increases pHcontrol pressure which increases the high (PH) pressure. This shortens the shift speed by releasing the reverse inhibitorpressure (Rl)from the inhibitor solenoid valve.
Lubrication Valve
The lubrication valve controls the lubrication pressure to each shaft and maintains lubrication pressure. When rne pres-sure is too high, the spring is compressed. This moves the lubrication valve and opens the fluid leak passage.
Pitot Regulalor Valv6
The pitot regulator valve controls the start clutch pressure (SC) in accordance with the engine speed, when the electron-ic control system is faulw.
MAIN VAIVEBODY
L.
14-208
Page 888 of 2189

Description
Hydraulic Control {cont'dl
PL Regulator Valve Body
The PL regulator valve body contains the PL regulator valve and the PH-PL control valve. which is joined wirh the pH-pL
control linear solenoid. The inhibitor solenoid is bolted on the pL regulator valve body.
. PL Regulator Valve
The PL regulator valve supplies low p.essure (pL) to the pulley to eliminate steel belt slippage.The PL pressure is controlled by the pH-pL control pressure (HLC).
. PH-PL Control Valve
The PH-PL control valve controls the PL regulator valve according to engine torque. The PH-PL control valve suooliesPH-PL control pressure (HLC) to the PH control valve to regulate PH pressure higher than pL pressure. The pH-pL con-trol valve is controlled by the PH-PL control linear solenoid. which is controlled by the TcM or pcM,
. Inhibitor Solenoid
The inhibitor solenoid controls the reverse inhibitor valve by turning on and off. Also, the inhibitor solenoad controls pH
control pressure (PHC) by applying reverse inhibitor pressure (Rl) to the PH control valve. The inhibitor solenoid is con-trolled by the TCM or Pclvl.
Start Clutch Control Valv€ Body
The start clutch control valve body contains the start clutch control valve. Both are joined to the stan clutch control linearsolenoid.
. Start Clutch Control Valve
The start clutch control valve controls start clutch engagement according to the throttle opening. The start clutch con,trol valve is controlled by the stan clutch control linear solenoid, which is controlled bv the TCM o. pCM.
START CLUTCH CONTROLvAt-vE
LOWER VALVE BODYASSEMBI-Y
PH.PL CONTROLLINEAR SOLENOID
I.
14-210
Page 891 of 2189
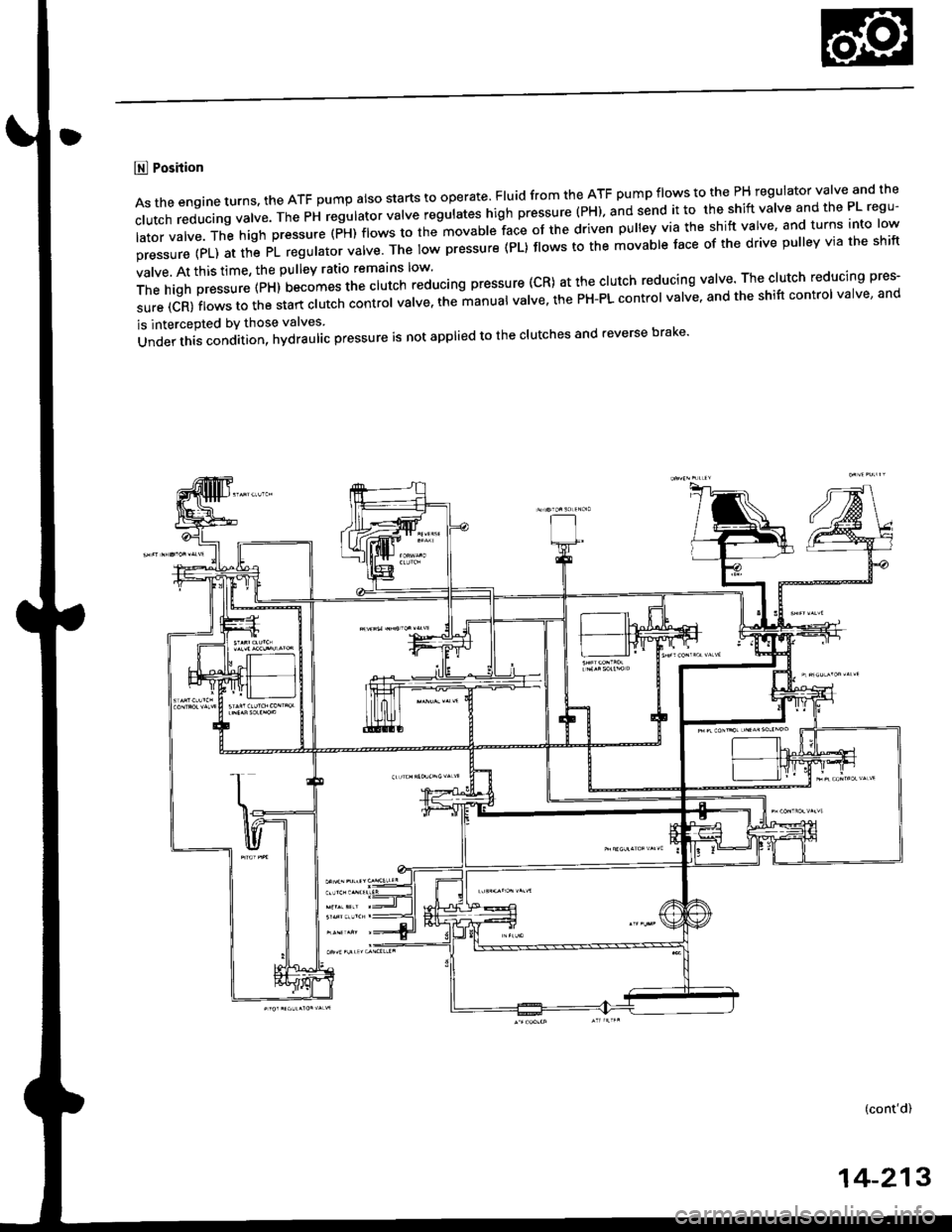
E Position
Astheengineturns.theATFpumpa|sostartstooperate.F|uidfromtheATFpumpf|owstothePHregu|atorva|veandthe
c|Utchreducingva|ve.ThePHregu|atorva|veregu|ateshighpressure(PH).andsendittotheshiftVa|veandthePLregU'
latorvalve.Thehighpressure(PH)flowstothemovablefaceofthedrivenpulleyviatheshiftvalve'andturnsintolow
pressure(PL)atthePLregu|atorva|ve.Thelowpressure(PL}f|owstothemovab|e'aceofthedrivepu||eYviatheshift
valve. At this time, the pulley ratio remarns low'
Thehighpressure(px)uecomesttrectutchreducingpressure(CR)atthec|utchreducingva|Ve.Thec|utchreducingpres.
sure (CR) flows to the start clutch cont'oi uatt". tn"lt"n'al valve' the PH-PL control valve' and the shift control valve' and
is intercepted bY those valves
Under this condition, hydraulac pressure is not applied to the clutches and reverse brake'
(cont'd)
14-213