Face HONDA CIVIC 1997 6.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1997, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 1997 6.GPages: 2189, PDF Size: 69.39 MB
Page 865 of 2189
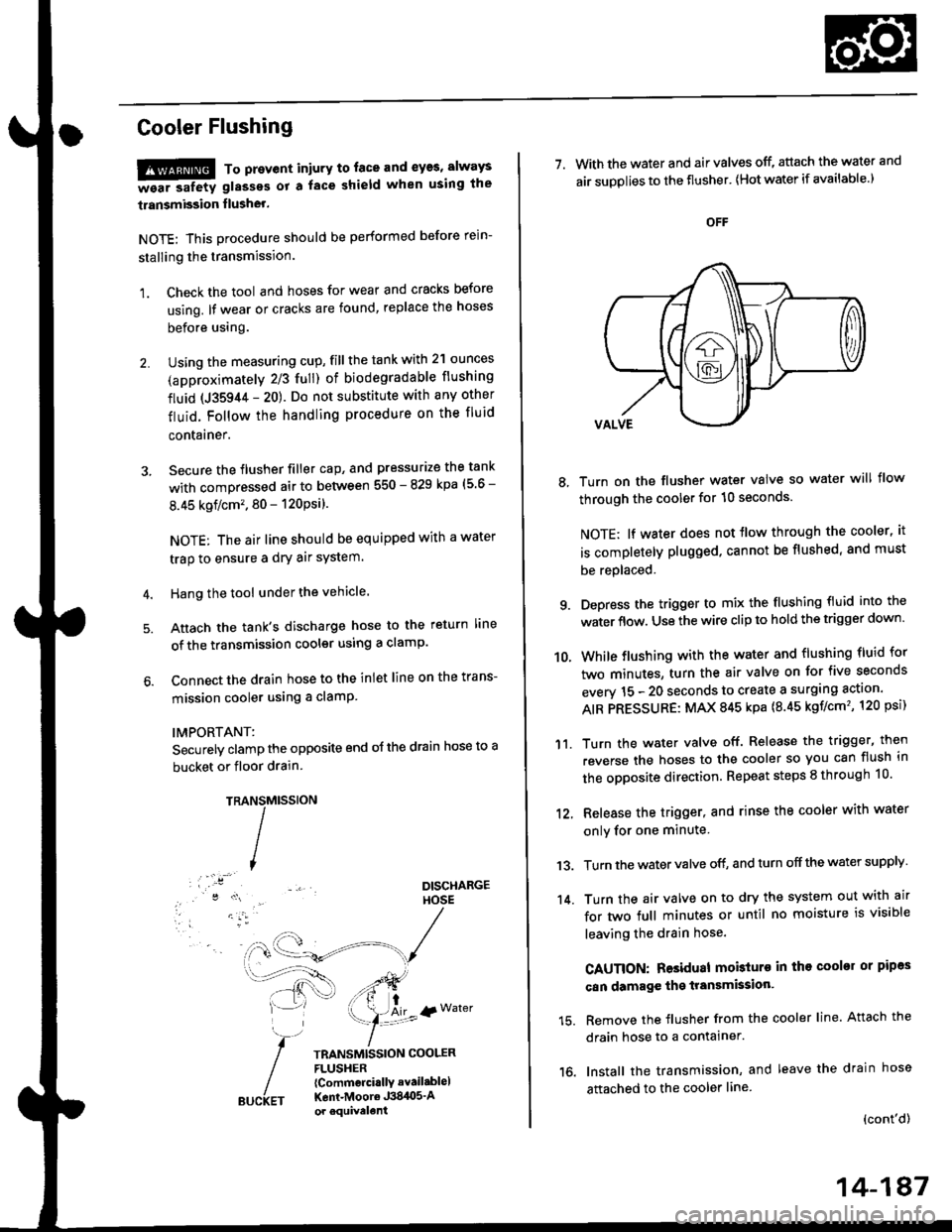
Cooler Flushing
!!!@ To prevent iniury to. face and eyas, always
-ea. safetv glasses ot a face shield when using the
transmission flusher.
NOTE: This procedure should be performed before rein-
stalling the transmission.
1. Check the tool and hoses for wear and cracks before
using. lf wear or cracks are found, replace the hoses
before using.
Using the measuring cup, fill the tank with 2'l ounces
(approximately 2/3 full) of biodegradable flushing
fluid (J35944 - 20). Do not substitute with any other
fluid. Follow the handling procedure on the fluid
contarner.
Secure the flusher filler cap, and pressurize the tank
with compressed air to between 550 - 829 kpa (5 6 -
8.45 kgflcm'�. 80 - 120Psi).
NOTE: The air line should be equipped with a water
trap to ensure a dry air system.
Hang the tool under the vehicle.
Attach the tank's discharge hose to the return line
of the transmission cooler using a clamp.
Connect the drain hose to the inlet line on the trans-
mission cooler using a clamP
IMPORTANT:
Securely clamp the opposite end oJ the drain hose to a
bucket or floor drain.
TRAMtssroN
TRANSMISSION COOLERFLUSHER{Commcrci.llY avail.blel
Kent-Moore J384O5'Aor equivelent
NS
I
{r Water
7. With the water and air valves off, attach the water and
air suDolies to the flusher' lHot water if available.)
8, Turn on the flusher water valve so water will flow
through the cooler for 10 seconds.
NOTE; lf water does not tlow through the cooler, it
is completely plugged. cannot be flushed, and must
be replaced.
9. Depress the trigger to mix the flushing fluid into the
water flow. Use the wire clip to hold the trigger down'
While flushing with the water and flushing fluid for
two minutes, turn the air valve on for five seconds
everv 15 - 20 seconds to create a surging action'
AIR PRESSURE: MAX 845 kpa {8.45 kgf/cm'�, 120 psi)
Turn the water valve off. Release the trigger, then
reverse the hoses to the cooler so you can flush in
the opposite direction. Repeat steps 8 through 10'
12, Release the trigger, and rinse the cooler with water
onlv for one minute
13. Turn the water valve off, and turn off the water supply
14. Turn the air valve on to dry the system out with air
for two full minutes or until no moisture is visible
leaving the drain hose.
CAUTION: Residual mobturo in tho cooler or pipas
can damage the transmksion'
15. Remove the flusher from the cooler line. Attach the
drain hose to a contalner.
16. Install the transmission, and leave the drain hose
attached to the cooler line
{cont'd)
10.
'11.
14-187
Page 873 of 2189

Description
The Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is an electronically controlled automatic transmission with drive and driv
en Oullevs, and a steel belt. The CVT provides non stage speeds forward and one reverse. The entire unit is positioned in
line with the engine.
Transmission
Around the outside of the flywheel is a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being staned.
The transmission has four parallel shafts: the input shaft, the drive pulley shaft. the driven pulley shaft, and the secondary
gear shaft. The input shaft is in line with the engine crankshaft. The drive pulley shaft and the driven pulley shaft consist of
movable and fixed face pulleys. Both pulleys are linked by the steel belt.
The input shaft includes the sun gear. The drive pulley shaft includes the forward clutch which mounts the carrier assem-
bly on the forward clutch drum. The carrier assembly includes the pinion gears which mesh with the sun gear and the ring
gear. The ring gear has a hub-mounted reverse brake disc.
The driven pulley shaft includes the start clutch and the secondary drive gear which is integral with the park gear' The sec-
ondary gear shaft is positioned between the secondary drive gear and the final driven gear. The secondary gear shaft
includes the secondary driven gear which serves to change the rotation direction. because the drive pulley shaft and the
driven oullev shaft rotate the same direction. When certain combinations of planetary gears in the transmission are
engaged by the clutches and the reverse brake, power is transmitted from the drive pulley shaft to the driven pulley shaft
to provide E, E, E, and El.
Electronic Control'96 - 98 Models:
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, three linear solenoids, and a
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions'
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the kick panel on the driver's side.'99 - 00 Models:
The electronic control svstem consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, three linear solenoids and an
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions. A Grade Logic Control System to control shift-
ing in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope.
The PCM is located below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the Pressure Low (PL) reguiator valve body, the shift valve
body, the start clutch control valve body, and the secondary valve body. They are positioned on the lower part of the
transmission housing.
The main valve body contains the Pressure High (PH) control valve, the lubrication valve, and the pitot regulator valve.
The secondary valve body contains the PH regulator valve, the clutch reducing valve, the start clutch valve accumulator,
and the shift inhibitor valve. The PL regulator valve body contains the PL regulator valve and the PH-PL control valve
which is ioined to the PH,PL control linear solenoid. The inhibitor solenoid valve is bolted on the PL regulator valve body.
The shift valve body contains the shift valve and the shift control valve. which is joined to the shift control linear solenoid.
The start clutch control valve body contains the start clutch control valve, which is joined to the start clutch control linear
solenoid. The linear solenoids and the inhibitor solenoid are controlled by the TCM or PCM. The manual valve body which
contains the manual valve and the reverse inhibitor valve, is bolted on the intermediate housing.
The ATF pump assembly is located on the transmission housing, and is linked with the input shaft by the sprockets and
the sprocket chain. The pulleys and the clutch receive fluid from their respective feed pipes, and the reverse brake receives
fluid from internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which linear solenoid the TCM or PCM will activate.
Activating the shift control linear solenoid changes the shift control valve pressure, causing the shift valve to move. This
pressurizes the drive pulley pressure to the drive pulley and the driven pulley pressure to the driven pulley and changes
their effective pulley ratio. Activating the start clutch control linear solenoid moves the start clutch control valve. The start
clutch control valve uncovers the port, providing pressure to the start clutch to engage it(cont'd)
14-195
,!
Page 876 of 2189

Description
Clutches/Reverse Brake/Planetary Gear/Pulleys
Clulches/Reverse Brake
The CVT uses the hydraulically-actuated clutches and brake to engage or disengage the transmission gears. When
hydraulic pressure is introduced into the clutch drum and the reverse brake piston cavity, the clutch piston and the reverse
brake piston move. This presses the friction djscs and the steel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is
then transmitted through the engaged clutch pack to its hub-mounted gear. and through engaged ring gear to pinion
gears.
Likewise, when the hydraulic pressure is bled from the clutch pack and the reverse brake piston cavity, the piston releases
the friction discs and the steel plates, and they are free to slide past each. This allows the gear to spin independently on its
shaft, transmitting no power.
Start Clutch
The start clutch, which is located at the end of the driven pulley shaft, engages/disengages the secondary drive gear.
The start clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipes within the driven pulley shaft.
Forward Clutch
The forward clutch, which is located at the end of the drive pulley shaft, engages/disengages the sun gear.
The forward clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the drive pulley shaft.
Reverse Brake
The reverse brake, which is located inside the inte.mediate housing around the ring gear, locks the ring gear in E posi-
tion. The reverse brake discs are mounted to the ring gear and the reverse brake plates are mounted to the intermediate
housing. The reverse brake is supplied hydraulic pressure by a circuit connected to the internal hydraulic circuit.
Planetary Gear
The planetary gear consists of a sun gear, a carrier assembly, and a ring gear. The sun gear is connected to the input shaft
with splines. The pinion gears are mounted to the carrier which is mounted to the fo.ward clutch drum. The sun gear
inputs the engine power via the input shaft to the planetary gear, and the carrier outputs the engine power. The ring gear
is only used for switching the rotation direction of the pullev shafts,
In E. E, and E positions (forward range), the pinion gears don't rotate and revolve with the sun gear, so the carrier
rotates. In E] positjon {reverse range), the reverse brake locks the ring gear and the sun gear drives the pinion gears to
rotate. The pinion gears rotate and revolve in the opposite direction from the rotation direction of the sun gear, and the
carrier rotates with pinion gear revolution.
Pulleys
Each pulley consists of a movable face and a fixed face, and the effective pulley .atio changes with engine speed. The
drive pulley and the driven pulley are linked by the steel belt.
To achieve a low pulley ratio, high hydraulic pressure works on the movable face of the driven pulley and reduces the
effective diameter of the drive pulley. and a lower hydraulic pressure works on the movable face of the drive pulley to
eliminate the steel belt slippage. To achieve a high pulley ratio, high hydraulic pressure works on the movable face of the
drive pulley and reduces the eifective diameter of the driven pulley, and a lower hydraulic pressure works on the movable
face of the driven pulley to eliminate the steel belt slippage.
b
14-198
Page 879 of 2189
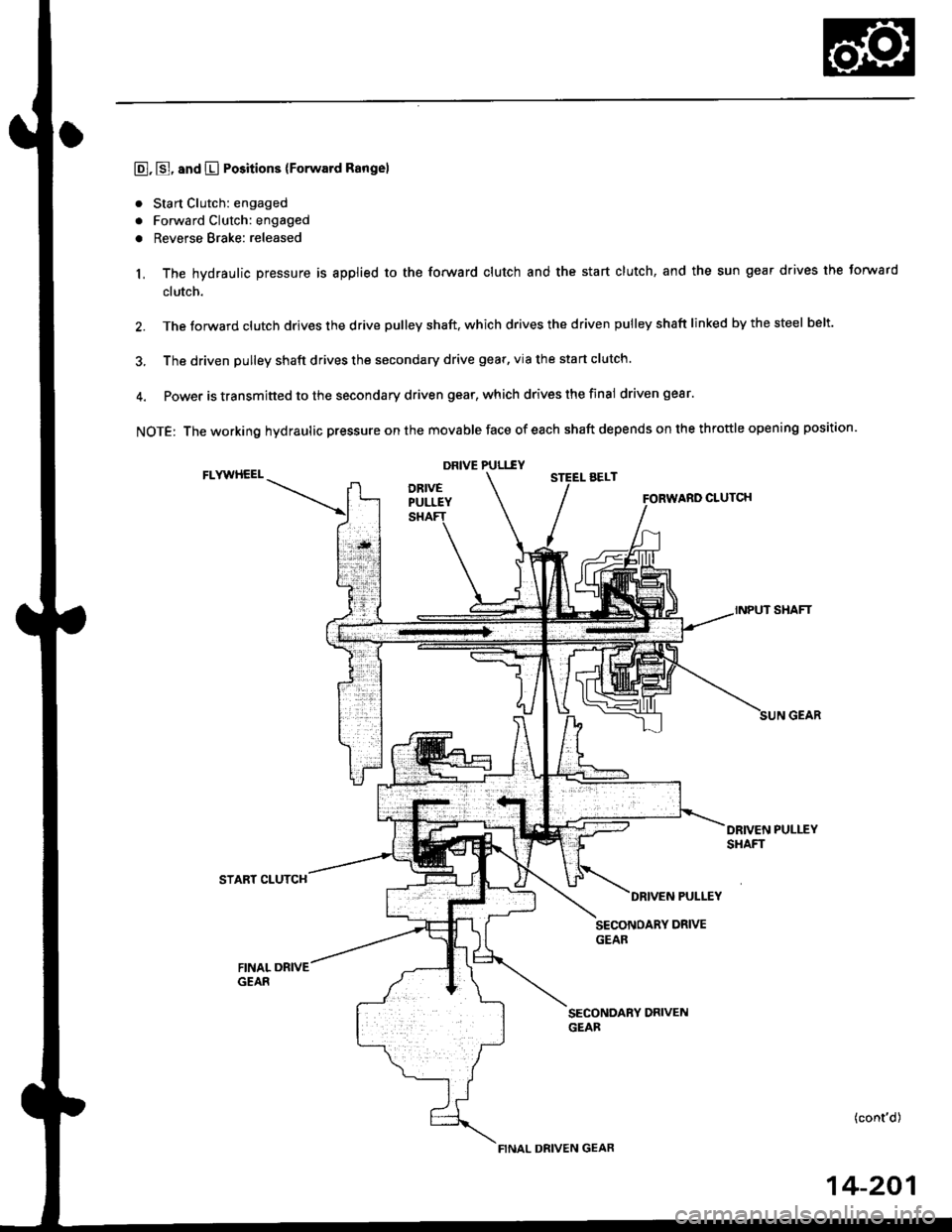
E, E, and E Positions {Forward Rangel
. Sta rt Clutch: engaged
. Forward Clutch: engaged
o Reverse Brake: released
1, The hydraulic pressure is applied to the forward clutch and the start clutch, and the sun gear drives the torward
clutch.
2. The torward clutch drives the drive pulleV shaft. which drives the driven pulley shaft linked by the steel belt.
3, The driven pulley shaft drives the secondary drive gear, via the start clutch.
4. Power is transmitted to the secondary driven gear, which drives the final driven gear.
NOTE: The working hydraulic pressure on the movable face of each shaft depends on the throttle opening position.
DRIVE PULI.f YFLYWHEELSTEEL AELT
CLUTCH
INPUT SHAFT
START CLUTCH
SECONDARY DRIVENGEAR
(cont'd)
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
14-201
Page 891 of 2189
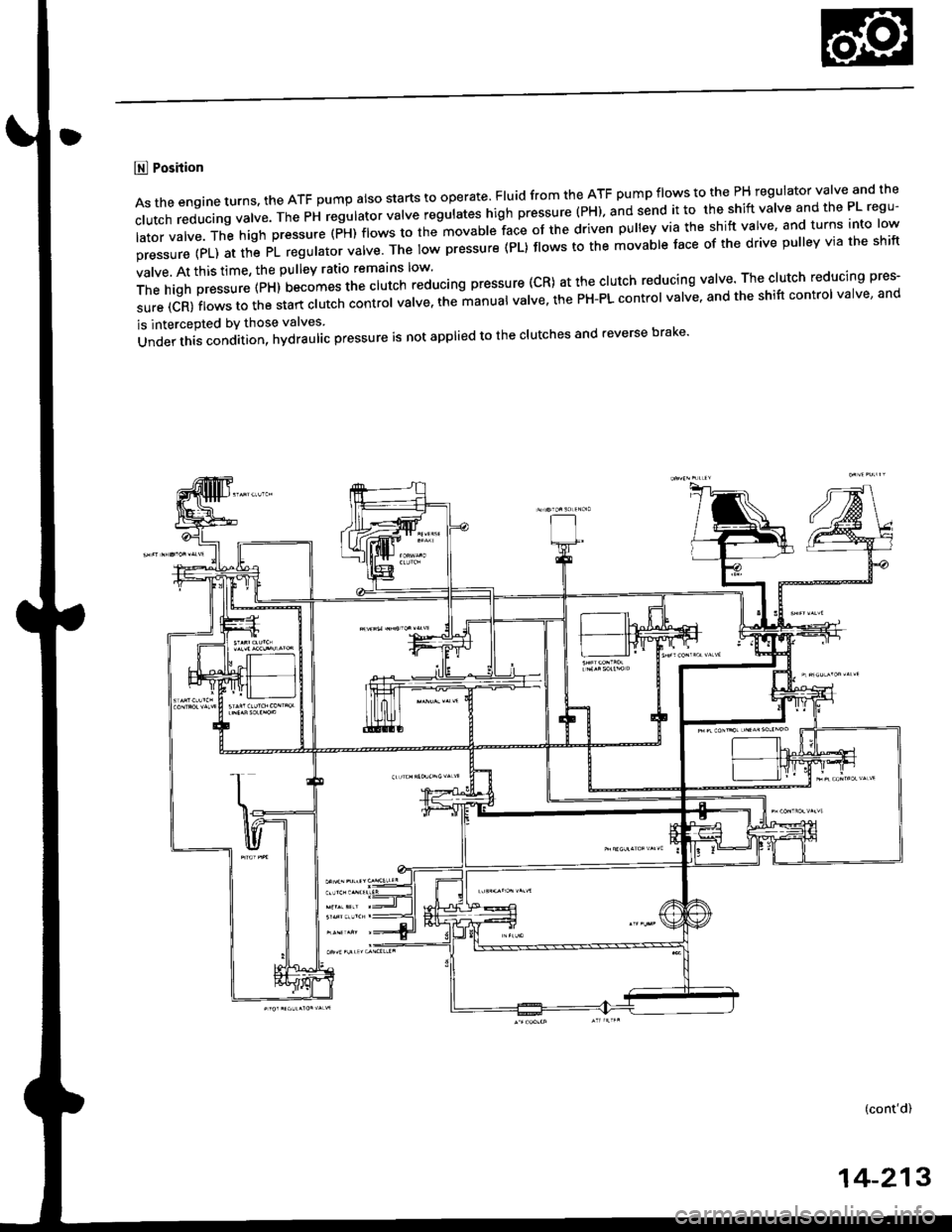
E Position
Astheengineturns.theATFpumpa|sostartstooperate.F|uidfromtheATFpumpf|owstothePHregu|atorva|veandthe
c|Utchreducingva|ve.ThePHregu|atorva|veregu|ateshighpressure(PH).andsendittotheshiftVa|veandthePLregU'
latorvalve.Thehighpressure(PH)flowstothemovablefaceofthedrivenpulleyviatheshiftvalve'andturnsintolow
pressure(PL)atthePLregu|atorva|ve.Thelowpressure(PL}f|owstothemovab|e'aceofthedrivepu||eYviatheshift
valve. At this time, the pulley ratio remarns low'
Thehighpressure(px)uecomesttrectutchreducingpressure(CR)atthec|utchreducingva|Ve.Thec|utchreducingpres.
sure (CR) flows to the start clutch cont'oi uatt". tn"lt"n'al valve' the PH-PL control valve' and the shift control valve' and
is intercepted bY those valves
Under this condition, hydraulac pressure is not applied to the clutches and reverse brake'
(cont'd)
14-213
Page 981 of 2189
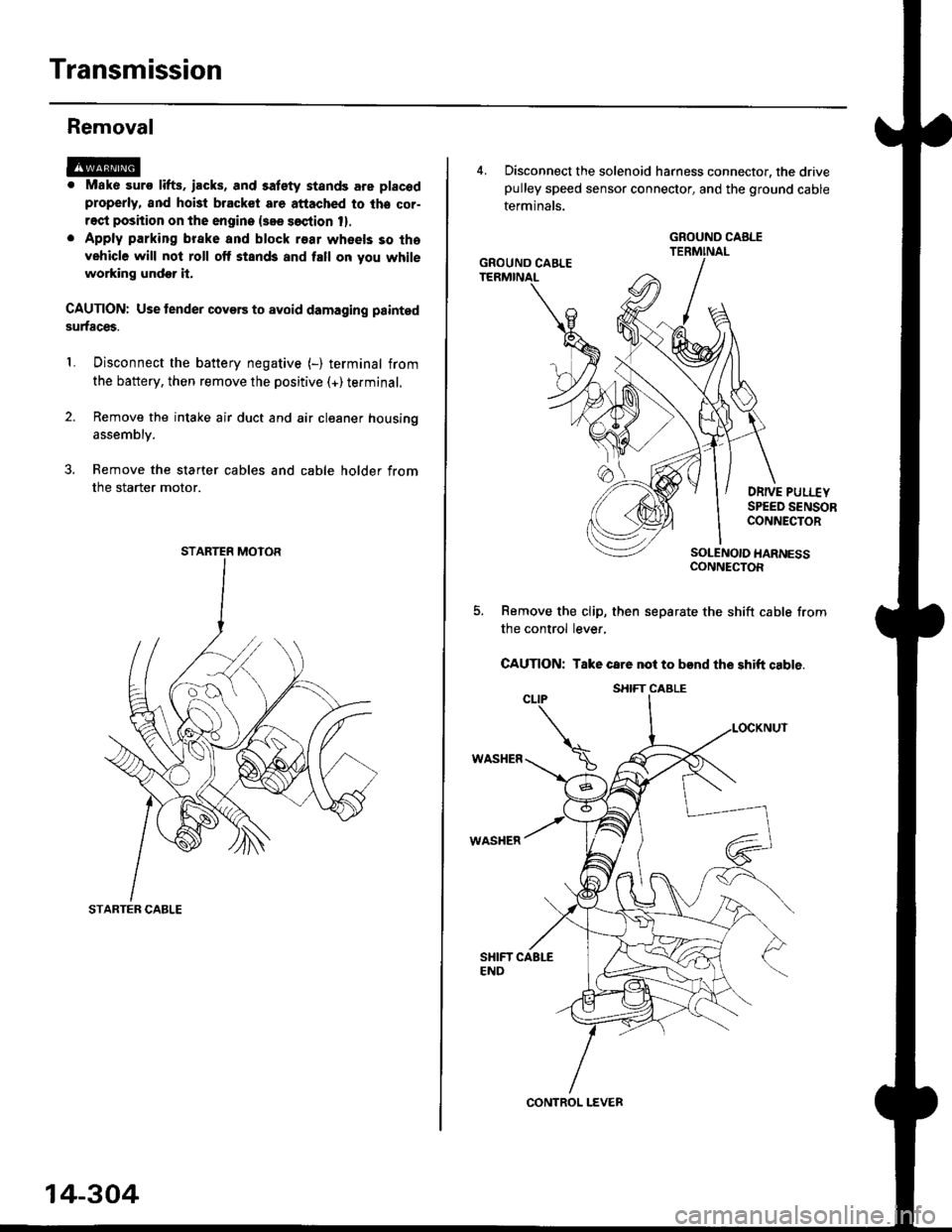
Transmission
Removal
@. Mako suro lifts. iacks, and satety stands are placod
properly, and hoi3t bracket are attached to lhe cor-
rect position on the engine {see soction 1}.
. Apply parking brake and block r€ar wheels so tha
vehicle will not roll off stands and fall on you while
working undor it.
CAUTION: Use tender covers to avoid damaging painted
surfaces.
Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal from
the battery, then remove the positive (+)terminal.
Remove the intake air duct and air cleaner housing
1.
assembly.
3. Remove the starter cables and cable holder from
the starter motor.
STARTER CABLE
STARTER MOTOR
14-304
4, Disconnect the solenoid harness connector, the drivepulley speed sensor connector, and the ground cable
terminals.
DRIVE PULI.-EYSPEED SENSORCONNECTOR
SOLENOIO HARNESSCONNECTOR
Remove the clip, then separate the shift cable from
the control lever,
CAUTION: Take care not to bend the shift cable.
WASHER
WASHER
GROUND CABLE
GROUND CAELE
CONTROL LEVER
S}IIFT CABLE
Page 983 of 2189
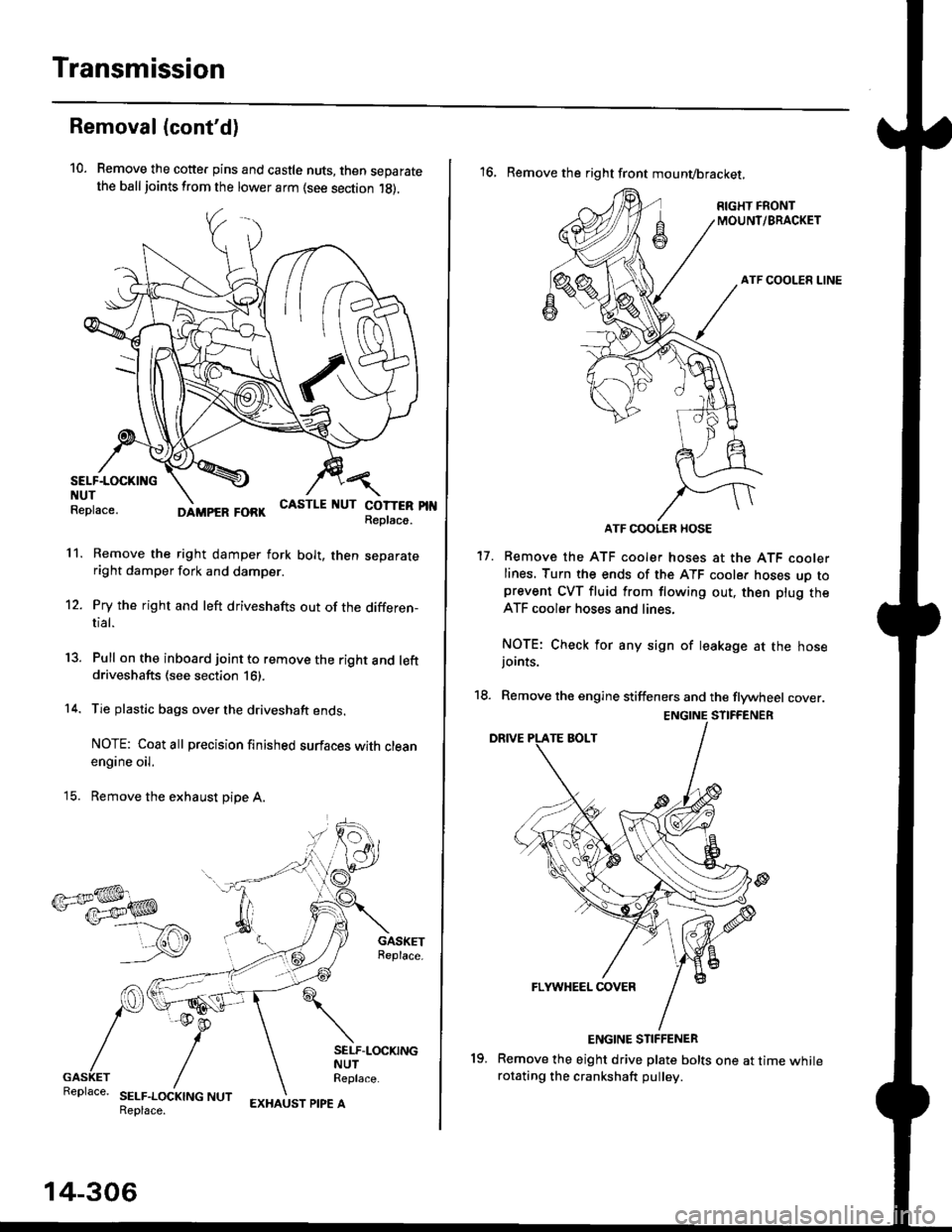
Transmission
Removal (cont'd)
10. Remove the cotte. pins and castle nuts, then separatethe ball joints from the lower arm (see section 1g).
SELF-LOCKING -=V,
NUT \Replace. oitupea rOax
Remove the right damper fork bolt, then separateright damper fork and damper.
Pry the right and left driveshafts out of the differen-tial.
Pull on the inboard joint to remove the right and leftdriveshafts (see section 16).
Tie plastic bags over the driveshaft ends.
NOTE: Coat all precision finished surfaces with cleanengine oil.
Remove the exhaust pipe A.
/\<,\CASTLE I{UT COTTERReplac6.
't 1.
't2.
tJ.
14.
q.
SELF.LOCKINGNUTReplace.
SELF.LOCKING NUTReplace.
14-306
EXHAUST PIPE A
19.
'16, Remove the right front mounvbracket,
ATF COOLER HOSE
17. Remove the ATF cooler hoses at the ATF coolerlines. Turn the ends of the ATF cooler hoses uo toprevent CVT fluid from flowing out, then plug theATF cooler hoses and lines,
NOTE: Check for any sign of leakage at the hosejoints.
18. Remove the engine stiffeners and the flywheel cover.
Remove the eight drive plate bolts one at time whilerotating the crankshaft pullev.
ENGINE STIFFENER
Page 1005 of 2189
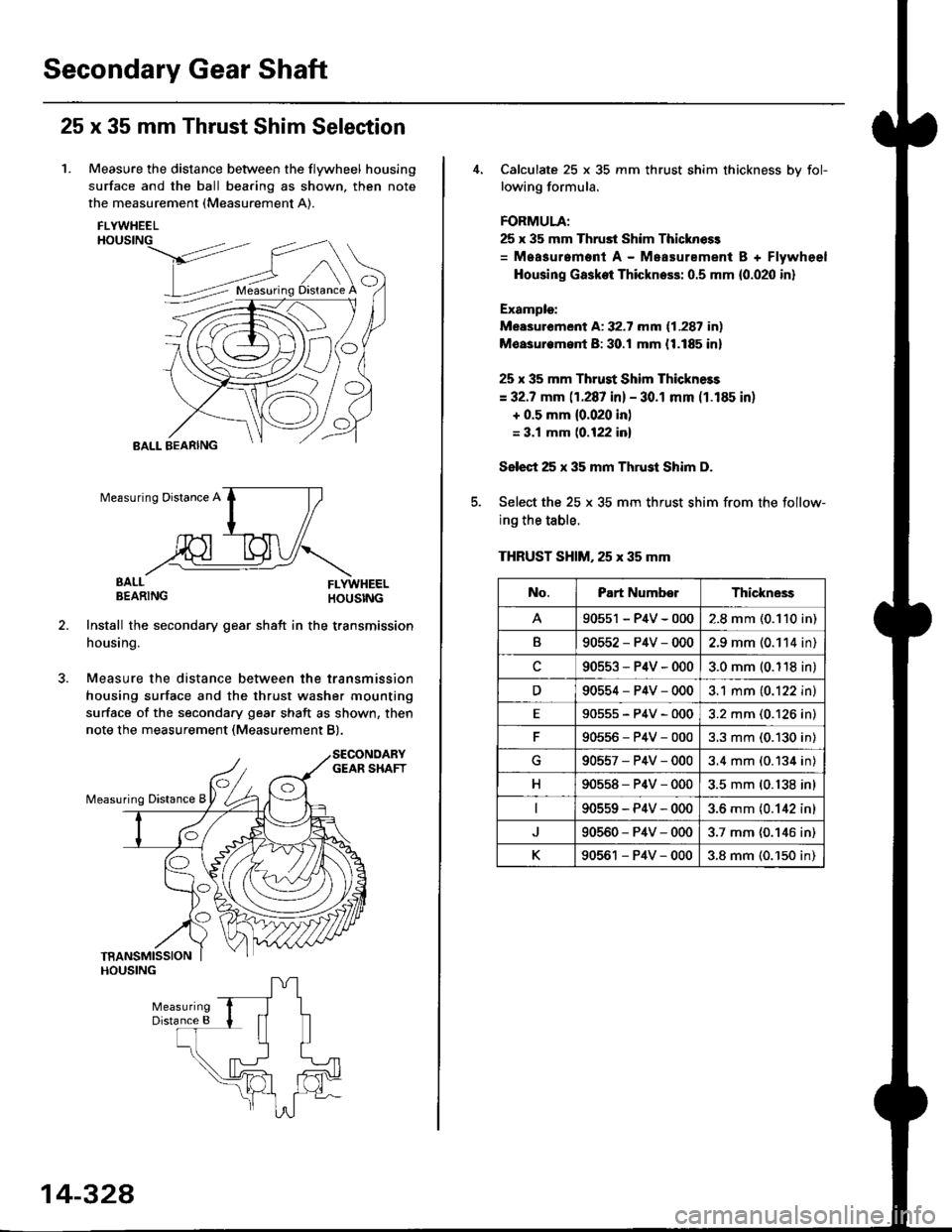
Secondary Gear Shaft
25 x 35 mm Thrust Shim Selection
1. Measure the distance between the flywheel housing
surface and the ball bearing as shown, then note
the measurement (Measurement A).
FLYWHEELHOUSING
>dt?'
BALL BEARING
EALL FLYWHEELBEARING HOUSTNG
Install the secondary gear shatt in the transmission
housing.
Measure the distance between the transmission
housing surface and the thrust washer mounting
surface of the secondary gear shaft as shown, then
note the measurement (Measurement B).
O
Measuring Distance A
BALL
14-328
Calculate 25 x 35 mm thrust shim thickness bv fol-
lowing formula.
FORMULA;
25 x 35 mm Thrust Shim Thicknoss
= Measurement A - Measurement B + Flywheel
Housing Gasket Thickness: 0.5 mm {0.020 in}
Example:
Measurement A: 32.7 mm (1.287 in)
Moasurem.nt B: 30.! mm {1.185 in}
25 x 35 mm Thrust Shim Thickness
= 32.7 mm (1.287 in) - 30.1 mm (1.185 in)
+ 0.5 mm {0.020 in)
= 3.1 mm (0.122 inl
Select 25 x 35 mm Thrust Shim D.
Select the 25 x 35 mm thrust shim from the follow-
ing the table.
THRUST SHIM, 25 x 35 mm
No.Part NumberThickne3s
90551 - P4V - 0002.8 mm (0.110 in)
B90552-P4V-0002.9 mm (0.114 in)
c90553-P4V-0003.0 mm (0.118 in)
D90554-P4V-0003.1 mm (0.122 in)
E90555-P4V-0003.2 mm (0.126 in)
90556-P4V-0003.3 mm (0.130 in)
G90557-P4V-0003.4 mm (0.134 in)
H90558-P4V-0003.5 mm (0.138 in)
90559-P4V-0003.6 mm {0.142 in)
90560-P4V-0003.7 mm (0.146 in)
K90561 - P4V - 0003.8 mm (0.'150 in)
Page 1028 of 2189

Transmission
Gooler Flushing
@ To prevent iniury to face and eyes, alwayswear safety glasses or a tace shield when using thetransmission flusher.
NOTE: This procedure should be performed before rein-stalling the transmission.
'1. Check the tools and hoses for wear and cracks before
using. lf wear or cracks are found, reDlace the hoses
before using.
4.
Using the measuring cup. fill the tank with 2,1 ounces(approximately 2/3 full) of biodegradable flushingfluid (J35944 - 20). Do not substitute with any otherfluid. Follow the handling procedure on the fluidcontatner.
Secure the flusher filler cap, and pressurize the tankwith compressed air to between 5S0 - 829 kpa (5.6 -
8.45 kgf/cm'�, 80 - 120 psi).
NOTE: The air line should be equipped with a watertrap to ensure a dry air system,
Hang the tool under the vehicle.
Attach the tank's discharge hose to the return lineoi the transmission cooler using a clamp.
Connect the drain hose to the inlet line on the trans-mission cooler using a clamp.
IMPORTANT:
Securely clamp the opposite end ofthe drain hose to abucket or floor drain,
t
TRANSMISSION COOLERFLUSHER{Commercially available)Kent-Moore J384O5-Aor oouivalent
TRANSMISSION
14-352
7. With the water and air valves off, attach the water andair supplies to the flusher. (Hot water if available.)
8. Turn on the flusher water valve so water will flowthrough the cooler for 10 seconds.
NOTE: lf water does not flow through the cooler, itis completely plugged, cannot be flushed, and mustbe replsced.
9. Depress the trigger to mix the flushing fluid into thewater flow. Use the wire clip to hold the trigger down.
'10. While flushing with the water and flushing fluid fortwo minutes. turn the air valve on for five secondsevery 15 - 20 seconds to create a surging action.AIR PRESSURE: MAX 845 kpa (8.45 kgflcmr, 120 psi)
11. Turn the water valve off. Release the trigger, thenreverse the hoses to the cooler so you can flush inthe opposite direction. Repeat steps 8 through 10.
12. Release the trigger. and rinse the cooler with wateronly for one minute.
13, Turn the water valve off, and turn off the water supply.
'14. Turn the air valve on to dry the system out with airfor two full minutes or until no moisture is visibleleaving the drain hose.
CAUTION: Rosidual mobturo in the qooler or linescln damage the transmission,
15. Remove the flusher from the cooler line. Attach thedrain hose to a container.
16. Install the transmission. and leave the drain hoseattached to the cooler line.
Page 1044 of 2189
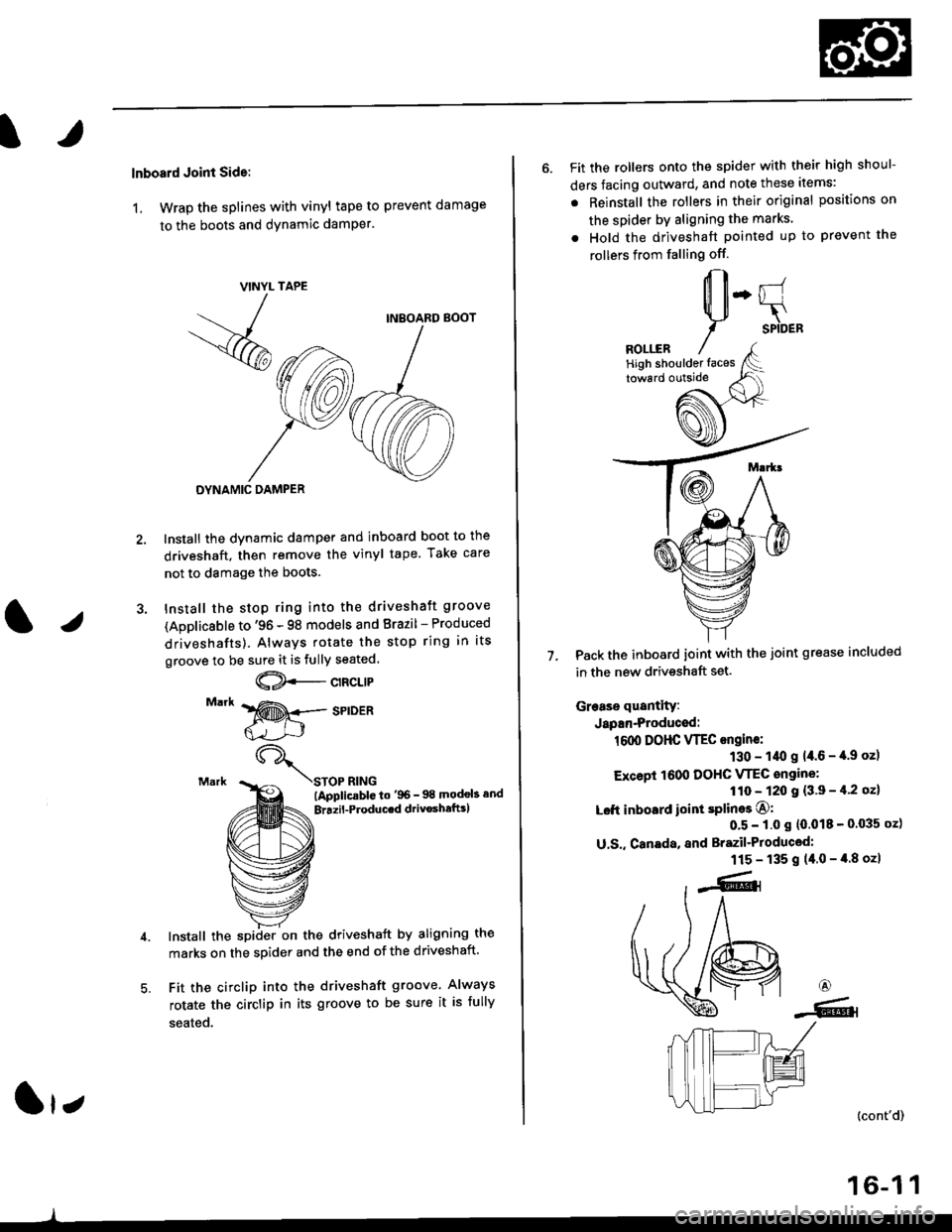
lnboard Joint Side:
1, Wrap the splines with vinyl tape to prevent damage
to the boots and dynamic damPer.
TAPE
INBOARD BOOT
DYNAMIC DAMPER
Install the dynamic damper and inboard boot to the
driveshaft, then remove the vinyl tape. Take care
not to damage the boots.
Install the stop ring into the driveshaft groove
(Applicsble to '96 - 98 models and Brazil - Produced
driveshafts). Always rotate the stop ring in its
groove to be sure it is fully seated.
@--c't"t't
STOP RING(ApplicablG to'96- 98 modob and
Brrzil-Producrd drivoshaftrl
Install the spiiler on the driveshaft by aligning the
marks on the sDider and the end of the driveshaft.
Fit the circlip into the driveshaft groove. Always
rotate the circlip in its groove to be sure it is fully
seated.
VINYL
- -
/
-<@
lr;
6. Fit the rollers onto the spider with their high shoul-
ders facing outward, and note these items:
. Reinstall the rollers in their original positions on
the spider by aligning the marks
. Hold the driveshaft pointed up to prevent the
rollers from falling off.
Pack the inboard joint with the joint grease included
in the new driveshaft set.
Grease quantity:
Japan-Produced:
1600 DOHC VTEC ongine:
130 - 1/t0 g 14.6 - '[.9 oz)
Except 1600 DOHC VTEC angine:
110 - 120 I {3'9 - il'2 oz}
Left inboard ioint splines O:
0'5 - 1.0 s (0.018 - 0'035 oz)
U.S,, Canada, and Brazil'Produced:
115 - 135 g (40-4.8ozl
7.
6
-6.l
(cont'd)
16-1 1
High shoulder faces