lock INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: INFINITI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: FX35, Model: INFINITI FX35 2008Pages: 3924, PDF Size: 81.37 MB
Page 2876 of 3924

GI-14
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
Connector symbols shown from the terminal side are enclosed bya single line and followed by the direction mark.
Connector symbols shown from the harness side are enclosed by
a double line and followed by the direction mark.
Certain systems and components, especially those related to OBD, may use a new style slide-locking type harness connector.
For description and how to disconnect, refer to PG section,
“Description”, “HARNESS CONNECTOR”.
Male and female terminals Connector guides for male terminals are shown in black and
female terminals in white in wiring diagrams.
SAMPLE/WIRING DIAGRAM - EXAMPL -
SAIA0257E
SGI363
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2886 of 3924
GI-24
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
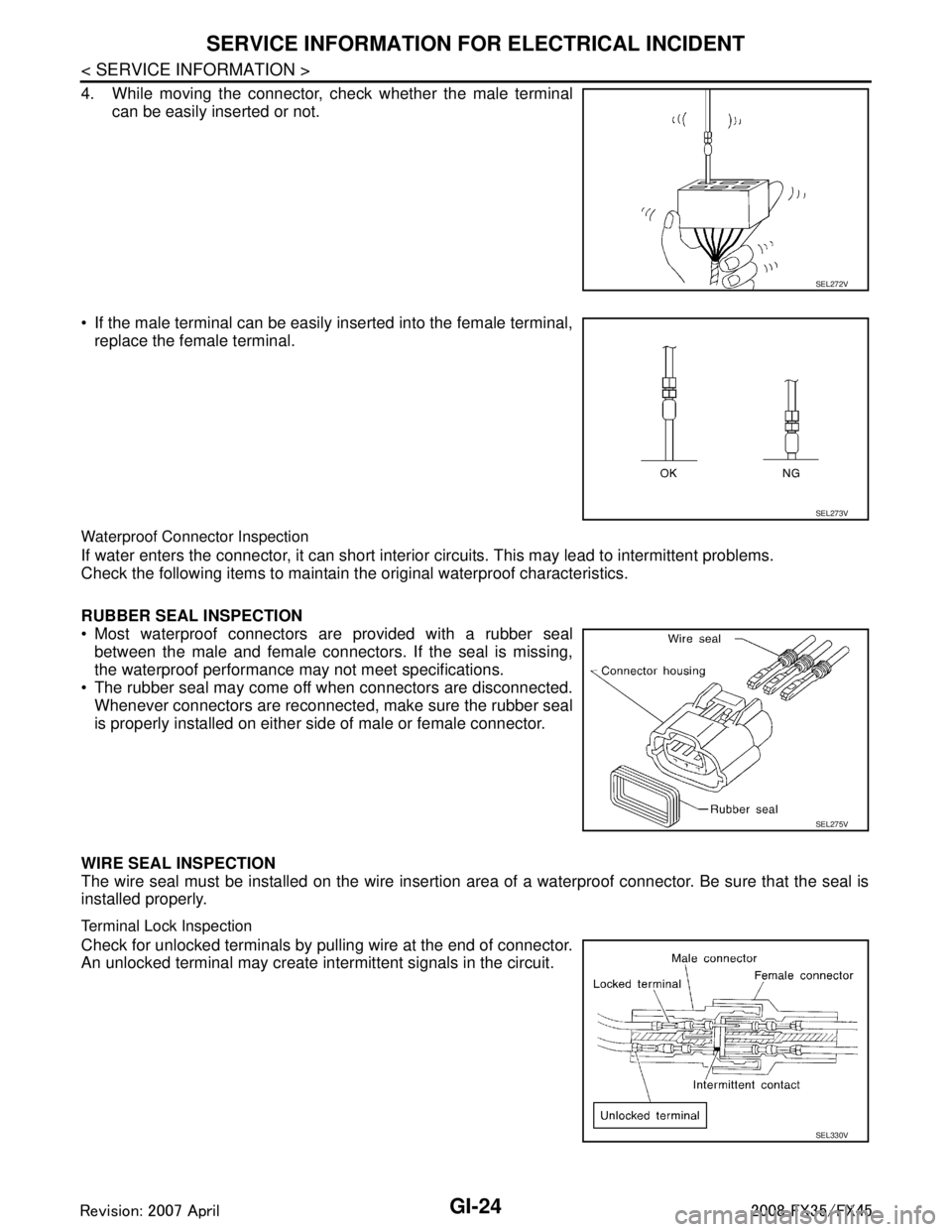
4. While moving the connector, check whether the male terminalcan be easily inserted or not.
If the male terminal can be easily inserted into the female terminal, replace the female terminal.
Waterproof Connector Inspection
If water enters the connector, it can short interior circuits. This may lead to intermittent problems.
Check the following items to maintain the original waterproof characteristics.
RUBBER SEAL INSPECTION
Most waterproof connectors are provided with a rubber seal between the male and female connectors. If the seal is missing,
the waterproof performance may not meet specifications.
The rubber seal may come off when connectors are disconnected. Whenever connectors are reconnected, make sure the rubber seal
is properly installed on either side of male or female connector.
WIRE SEAL INSPECTION
The wire seal must be installed on the wire insertion area of a waterproof connector. Be sure that the seal is
installed properly.
Terminal Lock Inspection
Check for unlocked terminals by pulling wire at the end of connector.
An unlocked terminal may create intermittent signals in the circuit.
SEL272V
SEL273V
SEL275V
SEL330V
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2890 of 3924

GI-28
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
ough understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while test ing electrical components. Gently shake the wiring har-
ness or electrical component to do this.
NOTE:
Refer to “How to Check Terminal” to probe or check terminal.
Testing for “Opens” in the Circuit
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
CONTINUITY CHECK METHOD
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circ uit. The digital multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbo\
l). Make sure to always start
with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circui ts, please refer to the previous schematic.
Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that por-
tion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over
limit or infinite resistance condition. (point A)
Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit
has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, t he DMM would indicate an over limit or infinite resis-
tance condition. (point B)
Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the
circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the ci rcuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or infi-
nite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circui ts please refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodica lly checking the system for the presence of voltage.
This is done by switching the DMM to the voltage function.
Connect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
Begin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end.
With SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
Close SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
OPEN A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORT There are two types of shorts.
SHORT CIRCUIT
When a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the normal resistance to
change.
SHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the circuit.
SGI846-A
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2891 of 3924

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENTGI-29
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
Close the relay and probe at the solenoid. voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the fuse.
Connect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good ground.
Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wir e. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a
known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i .e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Veri fy battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse ter-
minal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and t he DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for
voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper oper ation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted re sistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
Remove the ground bolt or screw.
Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
SGI847-A
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2902 of 3924
GI-40
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TOW TRUCK TOWING
TOW TRUCK TOWING
Tow Truck TowingINFOID:0000000001325684
CAUTION:
All applicable state or Provincial (in Canada) laws and local laws regarding the towing operation
must be obeyed.
It is necessary to use proper towi ng equipment to avoid possible damage to the vehicle during tow-
ing operation. To wing is in accordance with Towing Procedure Manual at dealer.
Always attach safety chains before towing.
When towing, make sure that the transmission, steering system and powertrain are in good order. If
any unit is damaged, dollies must be used.
Never tow an automatic transmission model from the rear (that is backward) with four wheels on the
ground. This may cause serious and exp ensive damage to the transmission.
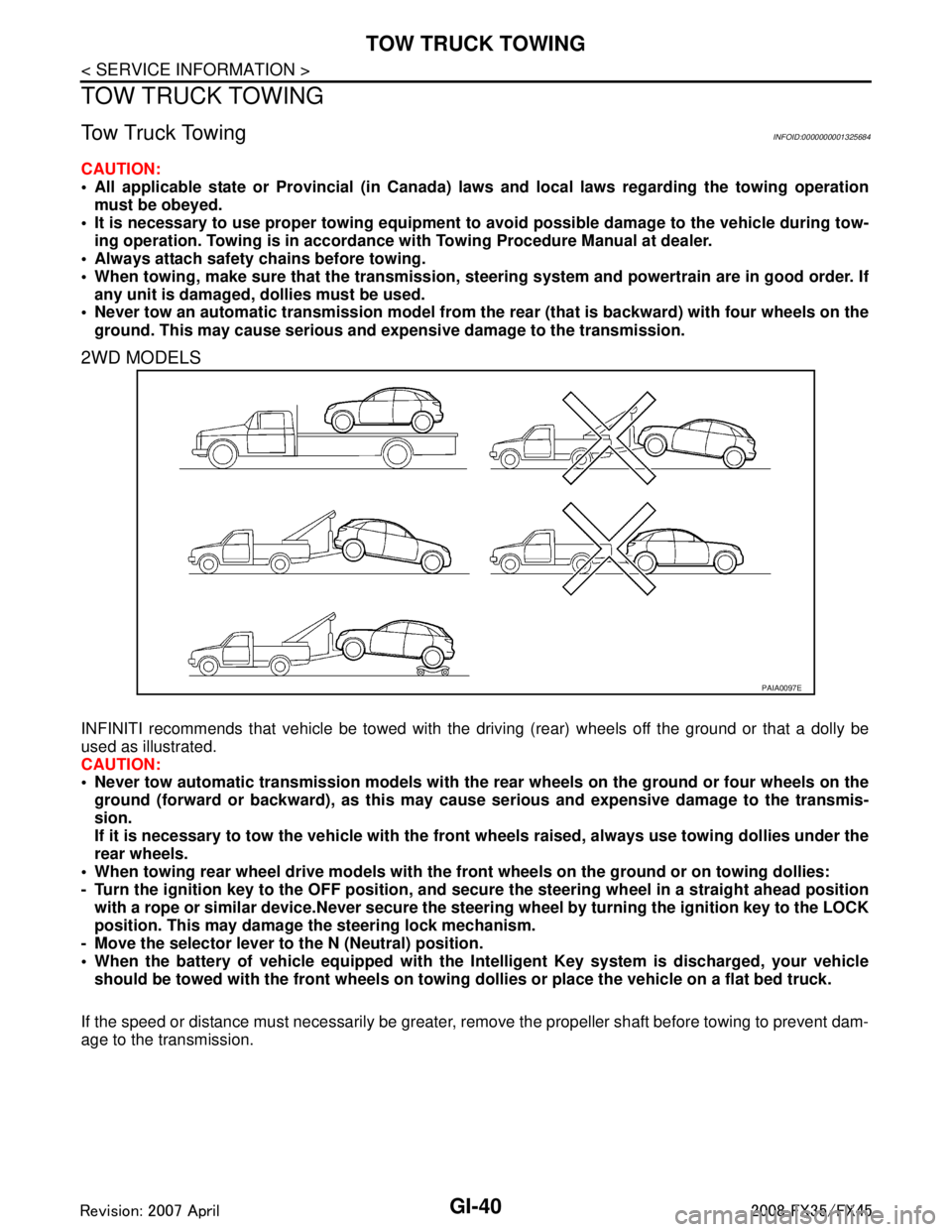
2WD MODELS
INFINITI recommends that vehicle be towed with the dr iving (rear) wheels off the ground or that a dolly be
used as illustrated.
CAUTION:
Never tow automatic transmission models with the r ear wheels on the ground or four wheels on the
ground (forward or backward), as this may cause serious and expensive damage to the transmis-
sion.
If it is necessary to tow the vehicle with the fron t wheels raised, always use towing dollies under the
rear wheels.
When towing rear wheel drive mo dels with the front wheels on the ground or on towing dollies:
- Turn the ignition key to the OFF position, and secure the steering wh eel in a straight ahead position
with a rope or similar device.Never secure the st eering wheel by turning the ignition key to the LOCK
position. This may damage the steering lock mechanism.
- Move the selector lever to the N (Neutral) position.
When the battery of vehicle equipped with the Intelligent Key system is discharged, your vehicle
should be towed with the front wh eels on towing dollies or place the vehicle on a flat bed truck.
If the speed or distance must necessarily be greater, re move the propeller shaft before towing to prevent dam-
age to the transmission.
PAIA0097E
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2906 of 3924
GI-44
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
RECOMMENDED CHEMICAL PRODUCTS AND SEALANTS
RECOMMENDED CHEMICAL PRODUCTS AND SEALANTS
Recommended Chemical Product and SealantINFOID:0000000001325687
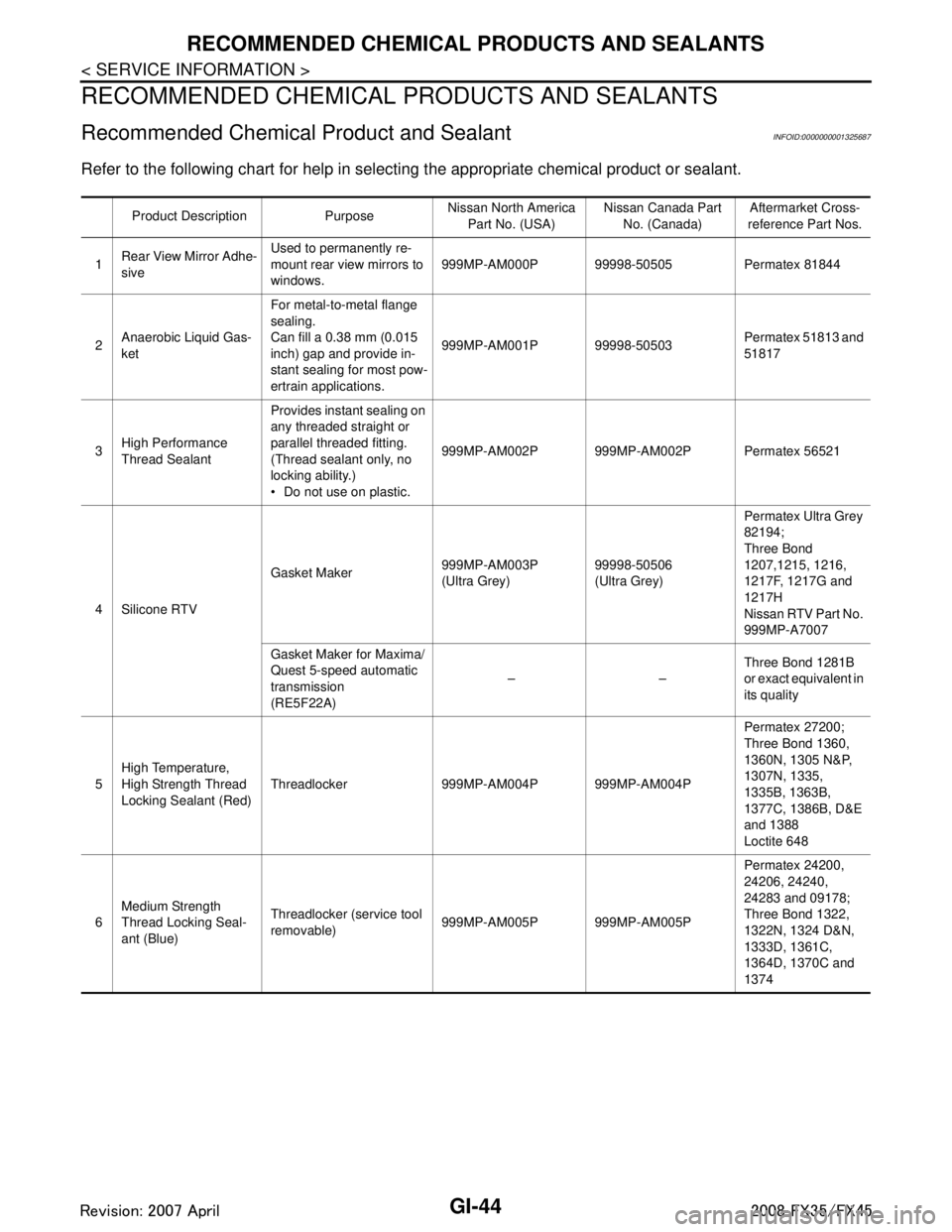
Refer to the following chart for help in selecting the appropriate chemical product or sealant.
Product Description Purpose Nissan North America
Part No. (USA) Nissan Canada Part
No. (Canada) Aftermarket Cross-
reference Part Nos.
1 Rear View Mirror Adhe-
sive Used to permanently re-
mount rear view mirrors to
windows.
999MP-AM000P 99998-50505 Permatex 81844
2 Anaerobic Liquid Gas-
ket For metal-to-metal flange
sealing.
Can fill a 0.38 mm (0.015
inch) gap and provide in-
stant sealing for most pow-
ertrain applications.
999MP-AM001P 99998-50503
Permatex 51813 and
51817
3 High Performance
Thread Sealant Provides instant sealing on
any threaded straight or
parallel threaded fitting.
(Thread sealant only, no
locking ability.)
Do not use on plastic.
999MP-AM002P 999MP-AM002P Permatex 56521
4 Silicone RTV Gasket Maker
999MP-AM003P
(Ultra Grey)99998-50506
(Ultra Grey)Permatex Ultra Grey
82194;
Three Bond
1207,1215, 1216,
1217F, 1217G and
1217H
Nissan RTV Part No.
999MP-A7007
Gasket Maker for Maxima/
Quest 5-speed automatic
transmission
(RE5F22A) ––
Three Bond 1281B
or exact equivalent in
its quality
5 High Temperature,
High Strength Thread
Locking Sealant (Red)
Threadlocker 999MP-AM004P 999MP-AM004P Permatex 27200;
Three Bond 1360,
1360N, 1305 N&P,
1307N, 1335,
1335B, 1363B,
1377C, 1386B, D&E
and 1388
Loctite 648
6 Medium Strength
Thread Locking Seal-
ant (Blue) Threadlocker (service tool
removable)
999MP-AM005P 999MP-AM005P Permatex 24200,
24206, 24240,
24283 and 09178;
Three Bond 1322,
1322N, 1324 D&N,
1333D, 1361C,
1364D, 1370C and
1374
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2912 of 3924

GI-50
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TERMINOLOGY
Nonvolatile random access memory NVRAM ***
On board diagnostic system OBD system Self-diagnosis
Open loop OL Open loop
Oxidation catalyst OC Catalyst
Oxidation catalytic converter system OC system ***
Oxygen sensor O2S Exhaust gas sensor
Park position switch *** Park switch
Park/neutral position switch PNP switchPark/neutral switch
Inhibitor switch
Neutral position switch
Periodic trap oxidizer system PTOX system ***
Positive crankcase ventilation PCV Positive crankcase ventilation
Positive crankcase ventilation valve PCV valve PCV valve
Powertrain cont rol module PCM ***
Programmable read only memory PROM ***
Pulsed secondary air injection control sole-
noid valve PAIRC solenoid valve AIV control solenoid valve
Pulsed secondary air injection system PAIR system Air induction valve (AIV) control
Pulsed secondary air injection valve PAIR valve Air induction valve
Random access memory RAM ***
Read only memory ROM ***
Scan tool ST ***
Secondary air injection pump AIR pump ***
Secondary air injection system AIR system ***
Sequential multiport fuel injection system SFI system Sequential fuel injection
Service reminder indicator SRI ***
Simultaneous multiport fuel injection sys-
tem *** Simultaneous fuel injection
Smoke puff limiter system SPL system ***
Supercharger SC ***
Supercharger bypass SCB ***
System readiness test SRT ***
Thermal vacuum valve TVV Thermal vacuum valve
Three way catalyst TWC Catalyst
Three way catalytic converter system TWC system ***
Three way + oxidation catalyst TWC + OC Catalyst
Three way + oxidation catalytic converter
system TWC + OC system ***
Throttle body TB Throttle chamber
SPI body
Throttle body fuel injection system TBI system Fuel injection control
Throttle position TP Throttle position
Throttle position sensor TPS Throttle sensor
Throttle position switch TP switch Throttle switch
Torque converter clutch solenoid valve TCC solenoid valve Lock-up cancel solenoid
Lock-up solenoid
NEW TERM
NEW ACRONYM /
ABBREVIATION OLD TERM
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2914 of 3924

GW-1
BODY
C
DE
F
G H
J
K L
M
SECTION GW
A
B
GW
N
O P
CONTENTS
GLASSES, WINDOW SYSTEM & MIRRORS
SERVICE INFORMATION .. ..........................3
PRECAUTIONS .............................................. .....3
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT PRE-TEN-
SIONER" ............................................................. ......
3
Precaution for Procedure without Cowl Top Cover ......3
Handling for Adhesive and Primer ............................3
PREPARATION ...................................................4
Special Service Tool ........................................... ......4
Commercial Service Tool ..........................................4
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAG-
NOSES ................................................................
5
Work Flow ........................................................... ......5
Generic Squeak and Rattle Troubleshooting ............7
Diagnostic Worksheet ...............................................9
WINDSHIELD GLASS ........................................11
Removal and Installation ..................................... ....11
BACK DOOR WINDOW GLASS ........................13
Removal and Installation ..................................... ....13
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM ..............................15
Component Parts and Harness Connector Loca-
tion ...................................................................... ....
15
System Description .................................................15
CAN Communication System Description ...............18
CAN Communication Unit .......................................19
Schematic ...............................................................19
Wiring Diagram - WINDOW - ..................................20
Terminal and Reference Value for BCM .................23
Terminal and Reference Value for Power Window
Main Switch .............................................................
24
Terminal and Reference Value for Front Power
Window Switch (Passenger Side) ...........................
25
CONSULT-III Function ............................................26
Work Flow ...............................................................27
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart .........................27
Check BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit .......28
Check Power Window Main Switch Power Supply
Circuit .................................................................. ....
28
Check Front Power Window Switch (Passenger
Side) Power Supply and Ground Circuit ..................
30
Check Front Power Window Motor (Driver Side)
Circuit ......................................................................
30
Check Front Power Window Motor (Passenger
Side) Circuit .............................................................
31
Check rear Power Window Motor (LH) Circuit .........32
Check Rear Power Window Motor (RH) Circuit .......34
Check Limit Switch Circuit (Driver Side) .............. ....36
Check Limit Switch Circuit (Passenger Side) ..........37
Check Encoder Circuit (Driver Side) ........................39
Check Encoder Circuit (Passenger Side) ................40
Check Door Switch ..................................................42
Check Front Door Key Cylinder Switch ...................43
Check Power Window Serial Link (Passenger
Side) ........................................................................
45
Check Power Window Lock Switch .........................46
SIDE WINDOW GLASS ....................................48
Removal and Installation .........................................48
FRONT DOOR GLASS AND REGULATOR .....50
Removal and Installation .........................................50
Disassembly and assembly .....................................52
Inspection after Installation ......................................52
REAR DOOR GLASS AND REGULATOR .......54
Removal and Installation .........................................54
Disassembly and assembly .....................................56
Fitting Inspection .....................................................56
INSIDE MIRROR ...............................................57
Wiring Diagram - I/MIRR - .......................................57
Removal and Installation .........................................58
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER ..........................60
Component Parts and Harness Connector Loca-
tion ...........................................................................
60
System Description ..................................................60
CAN Communication System Description ...............61
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2918 of 3924

SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESGW-5
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
J
K L
M A
B
GW
N
O P
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Work FlowINFOID:0000000001327957
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions thatexist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interviewto document t he facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer'scomments; refer to GW-9, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that existwhen the noise occurs.
The customer may not be able to provide a detailed descriptionor the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain all the facts and conditionsthat exist w hen the noise occurs (or does not occur).
If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnoseand repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplishedby test driving the vehicle with the customer.
After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fa st movement/broughton by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=l owerpitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow mo vement/twisting witha rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contac t/vibration orsimilar movement/loose parts/missing clip
or fastener/incorrect clearance.
Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/some times repeating/oftenbrought on by driver action.
Tick—(Like a clock second hand) Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of li ght materials/loosecomponents/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise) Thump characteristics include softer k nock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary dependingupon the person. A noise that you may judge as acceptable may be very irritatingto the customer.
Weather conditions, especially humidity and temper ature, may havea great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise isduplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regardingthe conditions or location of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicatethe same conditions when you confirm the repair.
SBT842
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2919 of 3924
GW-6
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
If the noise can be duplicated easily during the test drive, to helpidentify the source of the noise, try to dupli-
cate the noise with the vehiclestopped by doing one or all of the following:
1) Close a door.
2) Tap or push/pull around the area where the noise appears tobe coming from.
3) Rev the engine.
4) Use a floor jack to recreate vehicle “twist”.
5) At idle, apply engine load (electrical load, half-cl utch on M/T models, drive position on A/T models).
6) Raise the vehicle on a hoist and hit a tire with a rubber hammer.
Drive the vehicle and attempt to duplicate the conditi ons thecustomer states exist when the noise occurs.
If it is difficult to duplicate the noise, drive the v ehicle slowlyon an undulating or rough road to stress the vehi-
cle body.
CHECK RELATED SERVICE BULLETINS
After verifying the customer concern or symptom, check ASIST for Technica lService Bulletins (TSBs) related
to that concern or symptom.
If a TSB relates to the symptom, fo llow the procedure to repair thenoise.
LOCATE THE NOISE AND IDENTIFY THE ROOT CAUSE
1. Narrow down the noise to a general area. To help pi npoint the source of the noise, use a listening tool
(Chassis Ear: J39570, Engine Ear and mechanics stethoscope).
2. Narrow down the noise to a more specific area and identify the causeof the noise by:
removing the components in the area that you suspect the noiseis coming from. Do not use too much force when removing clips and fasteners, otherwiseclips and fastener can be broken or
lost during the repair, resulting in thecreation of new noise.
tapping or pushing/pulling the component t hat you suspect is causingthe noise.
Do not tap or push/pull the component with excessive force, otherwisethe noise will be eliminated only tem-
porarily.
feeling for a vibration with your hand by touching t he component(s)that you suspect is (are) causing the
noise.
placing a piece of paper between components that you suspect arecausing the noise.
looking for loose components and contact marks. Refer to GW-7, "
Generic Squeak and Rattle Troubleshooting".
REPAIR THE CAUSE
If the cause is a loose component, tighten the component securely.
If the cause is insufficient clearance between components:
- separate components by repositioning or l oosening and retighteningthe component, if possible.
- insulate components with a suitable insulator such as urethane pads, foam blocks, felt cloth tape or urethane
tape. A Nissan Squeak and Rattle Kit (J43980) is av ailable through your authorized Nissan Parts Depart-
ment.
CAUTION:
Do not use excessive force as many components are constructed of plasticand may be damaged.
NOTE:
Always check with the Parts Departm ent for the latest parts information.
The following materials are contained in the Nissan Squeak and Rattle Kit (J43980). Each item can be ordered
separately as needed.
URETHANE PADS [1.5 mm (0.059 in) thick]
Insulates connectors, harness, etc.
76268-9E005: 100 ×135 mm (3.94 ×5.31 in)/76884-71L01: 60 ×85 mm (2.36 ×3.35 in)/76884-
71L02: 15 ×25 mm (0.59 ×0.98 in)
INSULATOR (Foam blocks)
Insulates components from contact. Can be used to fill space behind a panel.
73982-9E000: 45 mm (1.77 in) thick, 50 ×50 mm (1.97 ×1.97 in)/73982-
50Y00: 10 mm (0.39 in) thick, 50 ×50 mm (1.97 ×1.97 in)
INSULATOR (Light foam block)
80845-71L00: 30 mm (1.18 in) thick, 30 ×50 mm (1.18 ×1.97 in)
FELT CLOTHTAPE
Used to insulate where movement does not occu r. Ideal for instrument panel applications.
68370-4B000: 15 ×25 mm (0.59 ×0.98 in) pad/68239-13E00: 5 mm (0.20 in) wide tape roll. The following
materials, not found in the kit, can al so be used to repair squeaks and rattles.
UHMW (TEFLON) TAPE
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C