wheel INFINITI QX4 2001 Factory Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: INFINITI, Model Year: 2001, Model line: QX4, Model: INFINITI QX4 2001Pages: 2395, PDF Size: 43.2 MB
Page 1189 of 2395

Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ªAIR
BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº
NBEL0001The Supplemental Restraint System such as ªAIR BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº used along with
a seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front passenger for certain types of
collision. The SRS system composition which is available to INFINITI QX4 is as follows:
IFor a frontal collision
The Supplemental Restraint System consists of driver air bag module (located in the center of the steer-
ing wheel), front passenger air bag module (located on the instrument panel on passenger side), seat belt
pre-tensioners, a diagnosis sensor unit, warning lamp, wiring harness and spiral cable.
IFor a side collision
The Supplemental Restraint System consists of side air bag module (located in the outer side of front seat),
satellite sensor, diagnosis sensor unit (one of components of air bags for a frontal collision), wiring harness,
warning lamp (one of components of air bags for a frontal collision).
Information necessary to service the system safely is included in theRS sectionof this Service Manual.
WARNING:
ITo avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death
in the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be performed
by an authorized INFINITI dealer.
IImproper maintenance, including incorrect removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to per-
sonal injury caused by unintentional activation of the system. For removal of Spiral Cable and Air
Bag Module, see the RS section.
IDo not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. Spiral cable and wiring harnesses covered with yellow insulation tape either just
before the harness connectors or for the complete harness are related to the SRS.
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble DiagnosisNBEL0002When you read wiring diagrams, refer to the following:
IGI-11, ªHOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMSº
IEL-9, ªPOWER SUPPLY ROUTINGº for power distribution circuit
When you perform trouble diagnosis, refer to the following:
IGI-35, ªHOW TO FOLLOW TEST GROUPS IN TROUBLE DIAGNOSESº
IGI-24, ªHOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENTº
Check for any Service bulletins before servicing the vehicle.
PRECAUTIONS
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ªAIR BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº
EL-4
Page 1214 of 2395

MEL304D
ReplacementNBEL0010For removal and installation of spiral cable, refer to RS-18,
ªInstallation Ð Air Bag Module and Spiral Cableº.
IEach switch can be replaced without removing combination
switch base.
MEL326G
ITo remove combination switch base, remove base attaching
screw.
SEL151V
IBefore installing the steering wheel, align the steering wheel
guide pins with the screws which secure the combination
switch as shown in the left figure.
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
IDX
COMBINATION SWITCH
Replacement
EL-29
Page 1241 of 2395

Trouble DiagnosesNBEL0193DAYTIME LIGHT CONTROL UNIT INSPECTION TABLENBEL0193S01
Terminal
No.Wire
colorItem ConditionVoltage
(Approximate values)
1 Y/B Alternator
When turning ignition switch to ªONº Less than 1V
When engine is running Battery voltage
When turning ignition switch to ªOFFº Less than 1V
2 Y/R Start signal
When turning ignition switch to ªSTº Battery voltage
When turning ignition switch to ªONº from ªSTº Less than 1V
When turning ignition switch to ªOFFº Less than 1V
3 G Power source
When turning ignition switch to ªONº Battery voltage
When turning ignition switch to ªSTº Battery voltage
When turning ignition switch to ªOFFº Less than 1V
4 R/L Power source
When turning ignition switch to ªONº Battery voltage
When turning ignition switch to ªOFFº Battery voltage
5 R/W Power source
When turning ignition switch to ªONº Battery voltage
When turning ignition switch to ªOFFº Battery voltage
6 R LH hi beam When lighting switch is turned to the 2ND position with
ªHI BEAMº positionBattery voltage
When releasing parking brake with engine running and
turning lighting switch to ªOFFº (daytime light operation)
CAUTION:
Block wheels and ensure selector lever is in N or P
position.Approx. half battery
voltage
HEADLAMP (FOR CANADA) Ð DAYTIME LIGHT SYSTEM Ð
Trouble Diagnoses
EL-56
Page 1242 of 2395

Terminal
No.Wire
colorItem ConditionVoltage
(Approximate values)
7 L/R RH hi beam When lighting switch is turned to the 2ND position with
ªHI BEAMº positionBattery voltage
When releasing parking brake with engine running and
turning lighting switch to ªOFFº (daytime light operation)
CAUTION:
Block wheels and ensure selector lever is in N or P
position.Approx. half battery
voltage
9 PU RH hi beam
(ground)When lighting switch is turned to the 2ND position with
ªHI BEAMº positionLess than 1V
When releasing parking brake with engine running and
turning lighting switch to ªOFFº (daytime light operation)
CAUTION:
Block wheels and ensure selector lever is in N or P
position.Approx. half battery
voltage
10 GY LH hi beam
(ground)When lighting switch is turned to the 2ND position with
ªHI BEAMº positionLess than 1V
When releasing parking brake with engine running and
turning lighting switch to ªOFFº (daytime light operation)
CAUTION:
Block wheels and ensure selector lever is in N or P
position.Approx. half battery
voltage
13
14L/W
W/RLighting switch
(Hi beam)When turning lighting switch to ªHI BEAMº Battery voltage
When turning lighting switch to ªFLASH TO PASSº Battery voltage
16 B Ground Ð Ð
17 L/G Parking brake
switch
When parking brake is released Battery voltage
When parking brake is set Less than 1.5V
BATTERY SAVER CONTROL UNIT INSPECTION TABLENBEL0193S02Refer to ªHEADLAMP (FOR USA)º, EL-42.
Bulb ReplacementNBEL0194Refer to ªHEADLAMP (FOR USA)º (EL-43).
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
IDX
HEADLAMP (FOR CANADA) Ð DAYTIME LIGHT SYSTEM Ð
Trouble Diagnoses (Cont'd)
EL-57
Page 1420 of 2395

VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR CHECK=NBEL0218S06
1 CHECK SPEEDOMETER OPERATION
Does speedometer operate normally?
Ye s©GO TO 2.
No©Check speedometer and vehicle speed sensor circuit. Refer to wiring diagram in EL-228.
2 CHECK VEHICLE SPEED INPUT
1. Apply wheel chocks and jack up drive wheel.
2. Disconnect ASCD control unit harness connector.
3. Check voltage between control unit terminal 22 and ground with turning drive wheel slowly by hand.
SEL263WB
Refer to wiring diagram in EL-227.
Ye s©Vehicle speed sensor is OK.
No©Check harness for open or short between ASCD control unit terminal 22 and combination
meter terminal 13.
ASCD PUMP CIRCUIT CHECKNBEL0218S07
1 CHECK ASCD PUMP
1. Disconnect ASCD pump connector.
2. Measure resistance between ASCD pump terminals 1 and 2, 3, 4.
SEL262WB
Refer to wiring diagram in EL-227.
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 2.
NG©Replace ASCD pump.
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
IDX
AUTOMATIC SPEED CONTROL DEVICE (ASCD)
Trouble Diagnoses (Cont'd)
EL-235
Page 1421 of 2395

2 CHECK ASCD PUMP CIRCUIT
1. Disconnect ASCD control unit harness connector.
2. Check harness for open or short between ASCD control unit and ASCD pump.
SEL269WB
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 3.
NG©Repair harness.
3 CHECK ASCD PUMP POWER SUPPLY
1. Jack-up the drive wheels.
2. Maintain the conditions below.
IVehicle speed is more than 40 km/h (25 MPH).
IMain switch (CRUISE lamp) is ON.
ISet/coast switch (SET lamp) is ON.
Check voltage between ASCD control unit harness connector terminal 12 and ground.
SEL381WB
OK or NG
OK©ASCD pump power supply is OK.
NG©Replace ASCD control unit.
AUTOMATIC SPEED CONTROL DEVICE (ASCD)
Trouble Diagnoses (Cont'd)
EL-236
Page 1571 of 2395

SEL683V
System Description=NBEL0228OUTLINENBEL0228S01The Navigation System (Multi-AV System) relies upon three sens-
ing devices in order to determine vehicle location at regular time
intervals.
1. Vehicle speed sensor: Determines the distance the vehicle has
traveled.
2. Gyro (Angular velocity sensor): Determines vehicle steering
angle and directional change.
3. GPS antenna (GPS data): Determines vehicle forward move-
ment and direction.
The data provided by the three sensing functions together with a
comparison of the mapping information read from the CD-ROM
drive permit accurate determination of the vehicle's current location
and subsequent course (map matching). The information appears
on a liquid crystal display.
This comparison of GPS data (vehicle position sensing) and map
matching permits precise determination of vehicle location.
SEL684V
Position Sensor Operating PrinciplesNBEL0228S0101The sensor determines current vehicle location by calculating the
previously sensed position, the distance traveled from this position,
and the directional changes occurring during this travel.
1. Distance traveled
The distance traveled is calculated using signals received from
the vehicle speed sensor. The sensor automatically compen-
sates for the slightly reduced wheel and tire diameter resulting
from tire wear.
2. Forward movement (Direction)
Changes in the direction of forward movement are calculated
by the gyro (angular velocity sensor) and the GPS antenna
(GPS data). Each of these functions has its advantage and
disadvantages. Depending upon conditions, one function takes
precedence over the other to accurately determine the direc-
tion of forward movement.
Function type Advantage Disadvantage
Gyro (Angular
velocity sen-
sor)IAble to accurately detect
minute changes in steering
angle and direction.ICalculation errors may
accumulate over a long
period of continuous
vehicle travel.
GPS antenna
(GPS data)IAble to sense vehicle travel
in four general directions
(North, South, East, and
West)IUnable to detect direction
of vehicle travel at low
vehicle speeds.
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
System Description
EL-386
Page 1582 of 2395
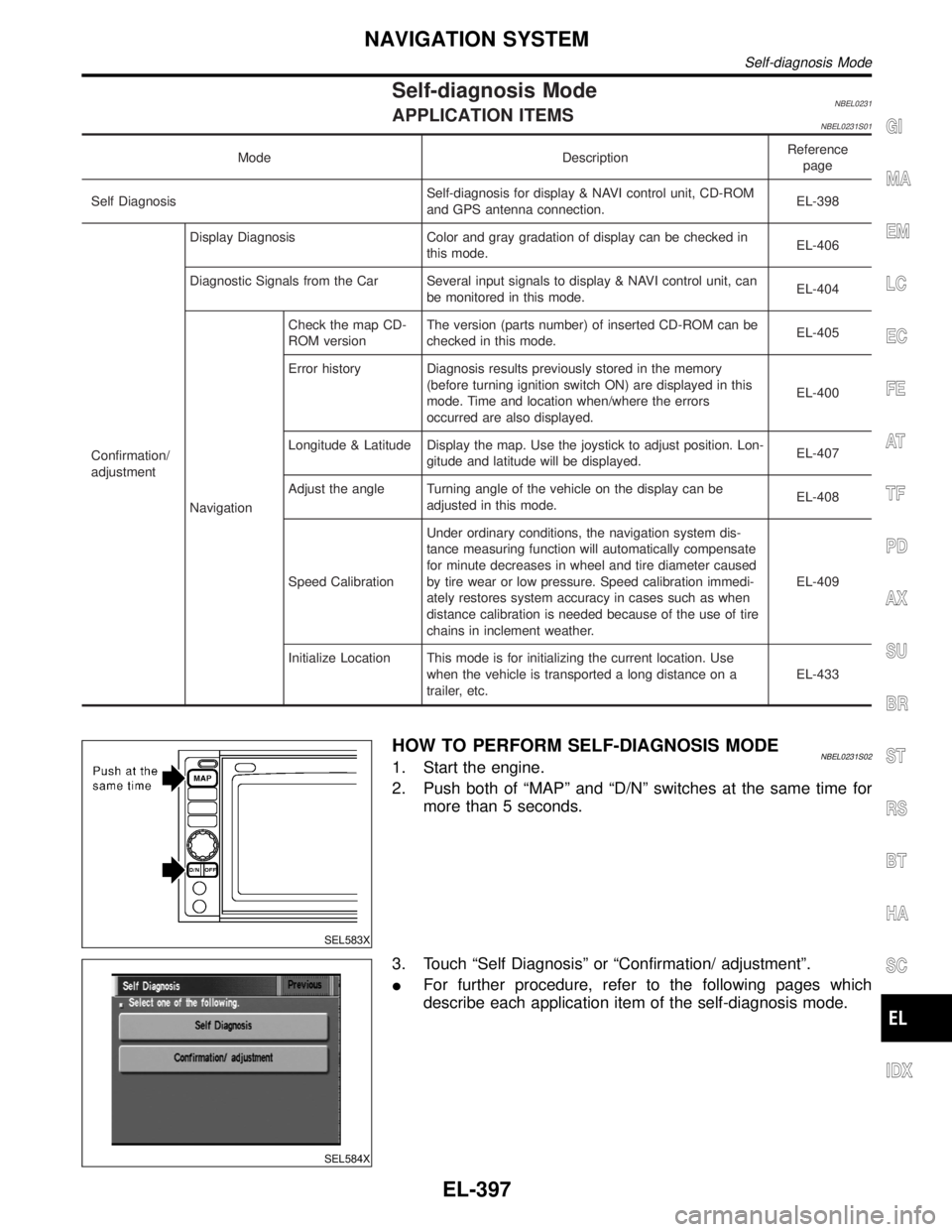
Self-diagnosis ModeNBEL0231APPLICATION ITEMSNBEL0231S01
Mode DescriptionReference
page
Self DiagnosisSelf-diagnosis for display & NAVI control unit, CD-ROM
and GPS antenna connection.EL-398
Confirmation/
adjustmentDisplay Diagnosis Color and gray gradation of display can be checked in
this mode.EL-406
Diagnostic Signals from the Car Several input signals to display & NAVI control unit, can
be monitored in this mode.EL-404
NavigationCheck the map CD-
ROM versionThe version (parts number) of inserted CD-ROM can be
checked in this mode.EL-405
Error history Diagnosis results previously stored in the memory
(before turning ignition switch ON) are displayed in this
mode. Time and location when/where the errors
occurred are also displayed.EL-400
Longitude & Latitude Display the map. Use the joystick to adjust position. Lon-
gitude and latitude will be displayed.EL-407
Adjust the angle Turning angle of the vehicle on the display can be
adjusted in this mode.EL-408
Speed CalibrationUnder ordinary conditions, the navigation system dis-
tance measuring function will automatically compensate
for minute decreases in wheel and tire diameter caused
by tire wear or low pressure. Speed calibration immedi-
ately restores system accuracy in cases such as when
distance calibration is needed because of the use of tire
chains in inclement weather.EL-409
Initialize Location This mode is for initializing the current location. Use
when the vehicle is transported a long distance on a
trailer, etc.EL-433
SEL583X
HOW TO PERFORM SELF-DIAGNOSIS MODENBEL0231S021. Start the engine.
2. Push both of ªMAPº and ªD/Nº switches at the same time for
more than 5 seconds.
SEL584X
3. Touch ªSelf Diagnosisº or ªConfirmation/ adjustmentº.
IFor further procedure, refer to the following pages which
describe each application item of the self-diagnosis mode.
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
IDX
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
Self-diagnosis Mode
EL-397
Page 1610 of 2395

Possible cause Drive condition Service procedure
AreaSlippery road surfaceOn wet, icy, or gravel road where
frequent wheel slippage occurs, dis-
tance calculations may be errone-
ous. The position marker may show
the vehicle to be in inaccurate posi-
tion.
If the position marker does not
move to the correct position
even after the vehicle has been
driven approximately 10 km (6
miles), perform ªADJUST CUR-
RENT LOCATIONº (EL-411). If
necessary, perform ªSPEED
CALIBRATIONº (EL-409). Slanted areaHilly areas where the road has
banked curves. When the vehicle
enters these banked curves, there
may be an error in steering angle
measurement. The position marker
may show the vehicle to be in inac-
curate position.
Map
dataMap display for a given road does not appear.
SEL699V
When the vehicle is driven on a
newly constructed road that does
not appear on the existing map.
Map marking and calibration are not
possible. The position marker may
indicate inaccurate position in close
proximity to the actual position.
Subsequently, when the vehicle is
driven on a road which is available
as map data, the position marker
may still indicate an inaccurate posi-
tion.
The vehicle is driven on a road whose course
has been altered (usually to improve the road or
to eliminate some hazard).
SEL700V
When the map data shown on the
display and the actual conditions are
different. Map matching will not be
possible. The position marker may
indicate inaccurate position in close
proximity to the actual position. If
the vehicle is driven on the indicated
road, further errors may occur.
Vehicle Use of tire chains (Stormy weather)Tire chains will affect distance sens-
ing. The position marker may indi-
cate inaccurate position.If the position marker does not
move to the correct position
even after the vehicle has been
driven approximately 10 km (6
miles), perform ªSPEED CALI-
BRATIONº (EL-409). After
removing the tire chains, sens-
ing accuracy may recover by
itself.
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
IDX
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
This Condition is Not Abnormal (Cont'd)
EL-425
Page 1611 of 2395

Possible cause Drive condition Service procedure
Opera-
tionDriving immediately after starting engine.The gyro (angular velocity sensor)
needs about 15 seconds after the
engine is started to precisely sense
the angular velocity. Directional
sensing errors will occur if the
vehicle is moved immediately after
starting the engine. The position
marker may indicate inaccurate
position.Wait a few moments between
starting the engine and actually
driving the vehicle.
Continuous driving for long distances (non-stop)When the vehicle is driven continu-
ously without stopping over a long
distance, errors in directional sens-
ing may occur. The position marker
may indicate inaccurate position.Stop the vehicle. Perform
ªSPEED CALIBRATIONº (EL-
409).
Rough or violent drivingWheel spinning (peeling out) or simi-
lar rough driving techniques can
adversely affect sensing accuracy.
The position marker may indicate
inaccurate position.If the position marker does not
move to the correct position
even after the vehicle has been
driven approximately 10 km (6
miles), perform ªADJUST CUR-
RENT LOCATIONº (EL-411).
Posi-
tional
calibra-
tion pro-
ceduresPositional calibration precision
SEL701V
If current vehicle location is roughly
set, the system may be unable to
locate the road that the vehicle is
traveling on. (This is especially true
in an area where there are many
roads.)Perform ªADJUST CURRENT
LOCATIONº (EL-411) within a
precision standard of 1 mm
(0.04 in) on the display.
Note: During calibration, use
the most detailed map pos-
sible.
Position calibration direction
SEL702V
When calibrating the position, check
the vehicle direction. If the vehicle
direction is not correct, subsequent
precision of current location will be
affected.Perform ªADJUST CURRENT
LOCATIONº, refer to EL-411.
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
This Condition is Not Abnormal (Cont'd)
EL-426