oil reset ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 880 of 6020
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 75
2. Measure the piston diameter.
Piston Measuring Point mm (in)
4JA1T(L) 4JA1TC 78 (3.07)
4JH1TC 70
(2.76)
Piston Grade (Service Part) mm (in)
AX 92.949 - 92.964
(3.6549 - 3.6600)
4JA1T(L) 4JA1TC CX 92.965 - 92.980
(3.6600 - 3.6606)
AX 95.359 - 95.374
(3.7542 - 3.7548)
4JH1TC
CX 95.375 - 95.390
(3.7548 - 3.7555)
Cylinder Liner and Piston Clearance mm (in)
4JA1T(L) 4JA1TC 0.041-0.071 (0.0016-0.0027)
4JH1TC 0.047-0.065
(0.0019-0.0026)
NOTE:
Cylinder liner kit clearances are preset. However, the
cylinder liner installation procedure may result in
slight decreases in cylinder liner clearances. Always
measure the cylinder liner clearance after installation
to be sure that it is correct.
TAPPET AND PUSH ROD
Visually inspect the tappet contact surfaces for pitting,
cracking, and other abnormal conditions. The tappet must be
replaced if any of these conditions are present.
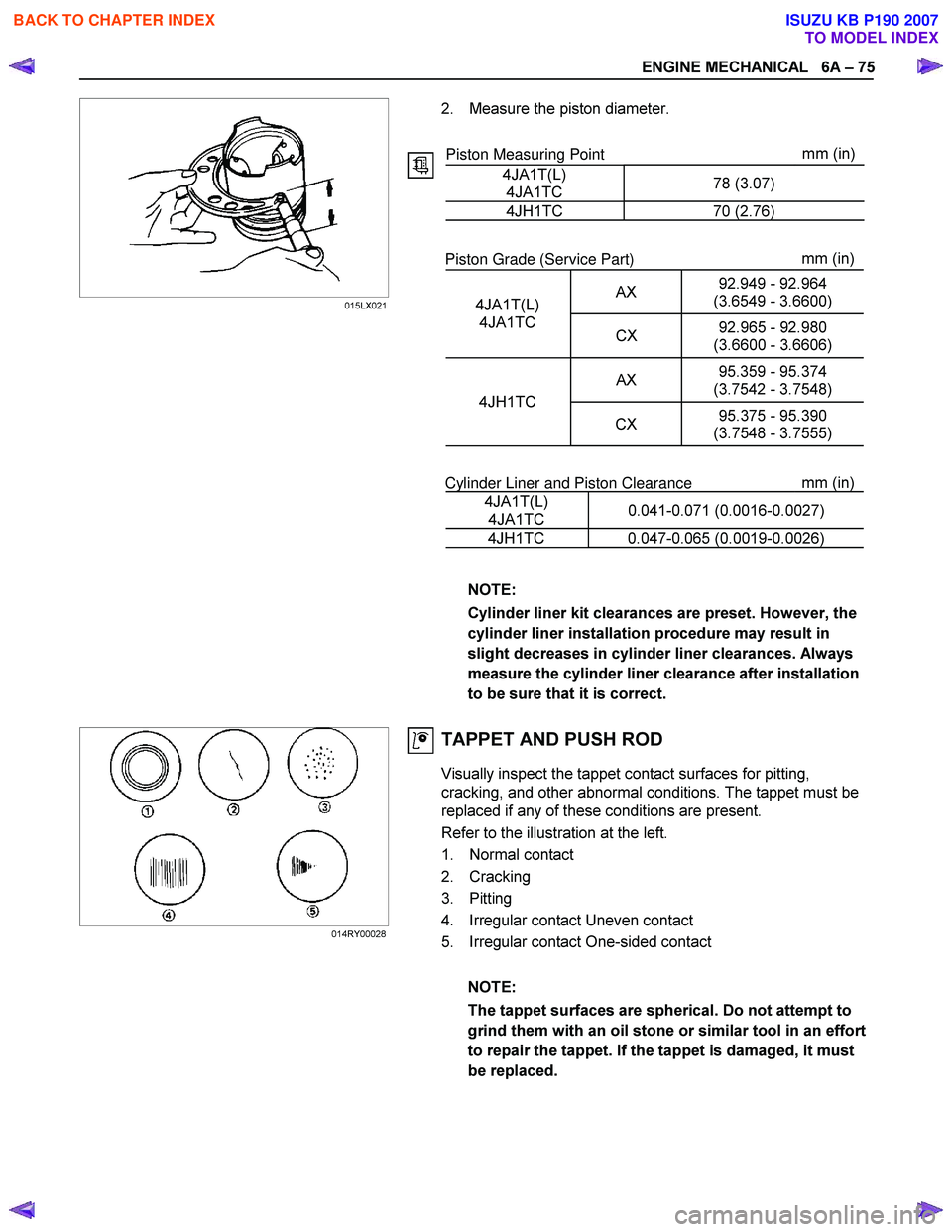
Refer to the illustration at the left.
1. Normal contact
2. Cracking
3. Pitting
4. Irregular contact Uneven contact
5. Irregular contact One-sided contact
NOTE:
The tappet surfaces are spherical. Do not attempt to
grind them with an oil stone or similar tool in an effort
to repair the tappet. If the tappet is damaged, it must
be replaced.
015LX021
014RY00028
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2013 of 6020
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE) 6-13
Fuel Consumption Excessive
Condition Possible cause Correction
Trouble in fuel system Mixture too rich or too lean due to
trouble in fuel injection system Refer to "Abnormal Combustion"
Fuel cut function does not act Refer to "Abnormal Combustion"
Trouble in ignition system Misfiring or abnormal combustion
due to trouble in ignition system Refer to Hard Start or Abnormal
Combustion Troubleshooting
Guide
Others Engine idle speed too high Reset Idle Air Control Valve
Returning of accelerator control
sluggish Correct
Fuel system leakage Correct or replace
Clutch slipping Correct
Brake drag Correct
Selection of transmission gear
incorrect Caution operator of incorrect gear
selection
Oil Problems
Condition Possible cause Correction
Oil pressure too low Wrong oil in use Replace with correct engine oil
Relief valve sticking Replace
Oil pump not operating properly Correct or replace
Oil pump strainer clogged Clean or replace strainer
Oil pump worn Replace
Oil pressure gauge defective Correct or replace
Crankshaft bearing or connecting
rod bearing worn Replace
Oil contamination
Wrong oil in use Replace with new engine oil
Oil filter clogged Replace oil filter
Cylinder head gasket damage Replace gasket
Burned gases leaking Replace piston and piston rings or
rebore cylinders
Oil not reaching valve system Oil passage in cylinder head or cylinder body clogged Clean or correct
Engine Oil Pressure Check
1. Check for dirt, gasoline or water in the engine
oil.
a. Check the viscosity of the oil.
b. Change the oil if the viscosity is outside the specified standard.
c. Refer to the "Maintenance and Lubrication" section of this manual.
2. Check the engine oil level. The level should fall somewhere between the
"ADD" and the "FULL" marks on the oil level
dipstick.
If the oil level does not reach the "ADD" mark on
the oil level dipstick, engine oil must be added.
3. Remove the oil pressure unit.
4. Install an oil pressure gauge.
5. Start the engine and allow the engine to reach normal operating temperature (About 80 °C).
6. Measure the oil pressure.
Oil pressure should be:
150 kPa(21.8 psi) at idle speed.
7. Stop the engine.
8. Remove the oil pressure gauge
9. Install the oil pressure unit.
10. Start the engine and check for leaks.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2219 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–49
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
The TPS is a potentiometer connected to throttle shaft
on the throttle body.
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the voltage
on the signal line and calculates throttle position. As the
throttle valve angle is changed when accelerator pedal
moved. The TPS signal also changed at a moved
throttle valve. As the throttle valve opens, the output
increases so that the output voltage should be high.
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the
amount of the air delivered to the engine.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in
the throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to
prevent icing.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The idle air control valve (IAC) valve is two directional
and gives 2-way control. With power supply to the coils
controlled steps by the engine control module (ECM),
the IAC valve's pintle is moved to adjust idle speed,
raising it for fast idle when cold or there is extra load
from the air conditioning or power steering.
By moving the pintle in (to decrease air flow) or out (to
increase air flow), a controlled amount of the air can
move around the throttle plate. If the engine speed is
too low, the engine control module (ECM) will retract the
IAC pintle, resulting in more air moving past the throttle
plate to increase the engine speed.
If the engine speed is too high, the engine control
module (ECM) will extend the IAC pintle, allowing less
air to move past the throttle plate, decreasing the
engine speed.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small step called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the engine control module (ECM) based
on battery voltage, coolant temperature, engine load,
and engine speed.
If the engine speed drops below a specified value, and
the throttle plate is closed, the engine control module
(ECM) senses a near-stall condition. The engine control
module (ECM) will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve
position to prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with
the engine running, the idle speed will be wrong. In this
case, the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the
key is cycled “On” then “Off”. When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “Off”.
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-
up and the idle characteristic of the vehicle.
If the IAC pintle is fully open, too much air will be
allowed into the manifold. This results in high idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and lean air/
fuel ratio.
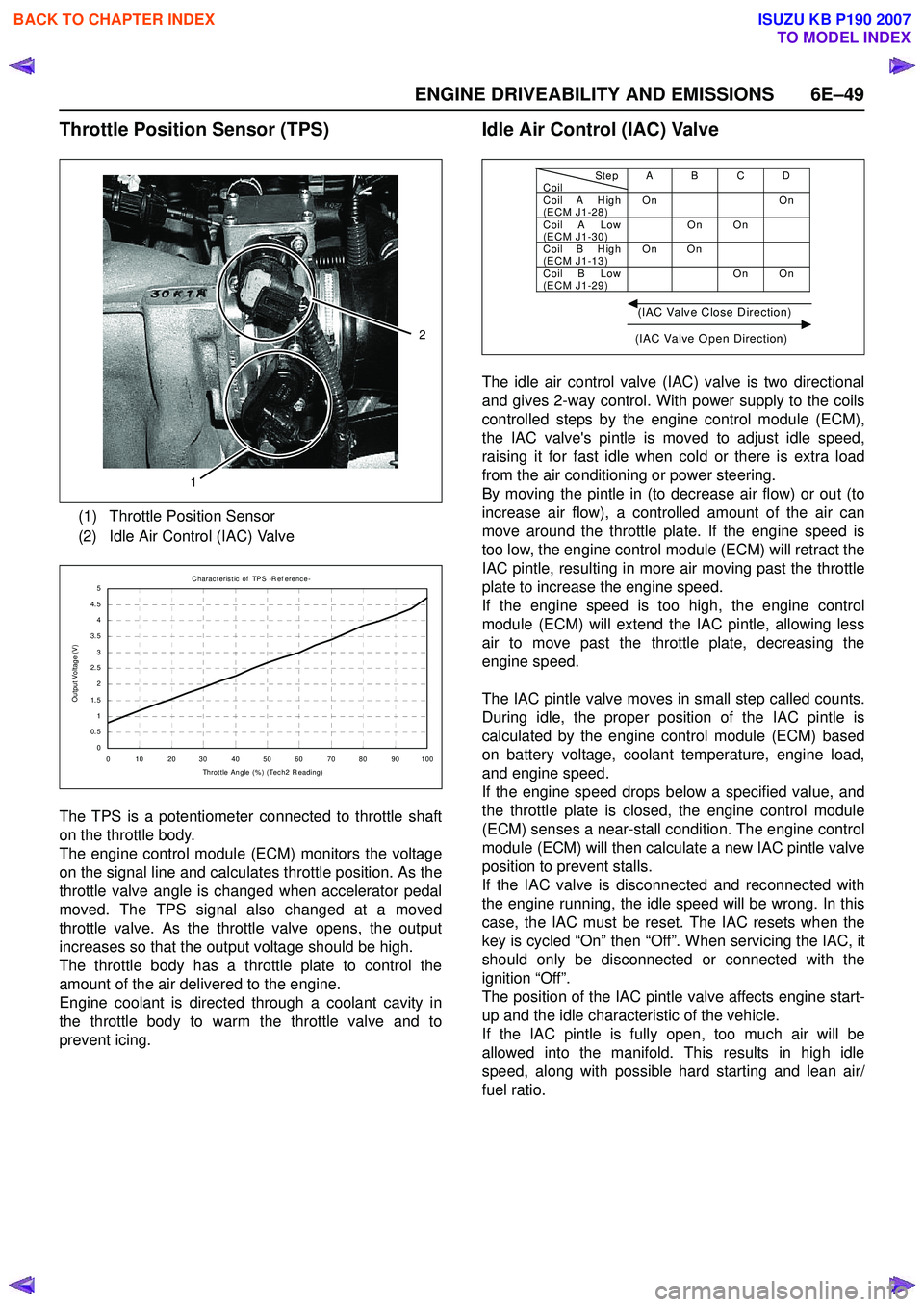
(1) Throttle Position Sensor
(2) Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
1
2
C harac teris t ic of TPS -R ef erenc e-
0
0.5
1
1.5 2
2.5
3
3.5 4
4.5 5
0 10 2030 405060 7080 90100 Throt t le Angle (% ) (Tec h2 R eading)
Output Voltage (V)
StepCoilAB CDCoil A H igh
(ECM J1-28) On On
Coil A Low
(ECM J1-30) On On
Coil B H igh
(ECM J1-13) On On
Coil B Low
(ECM J1-29) On On
(IAC Valve Close Direction)
(IAC Valve Open Direction)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2620 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–141
Reassemble
CAUTION
As there are no serviceable components
within the oil pump, a disassembled oil pump
must be replaced.
Reinstall
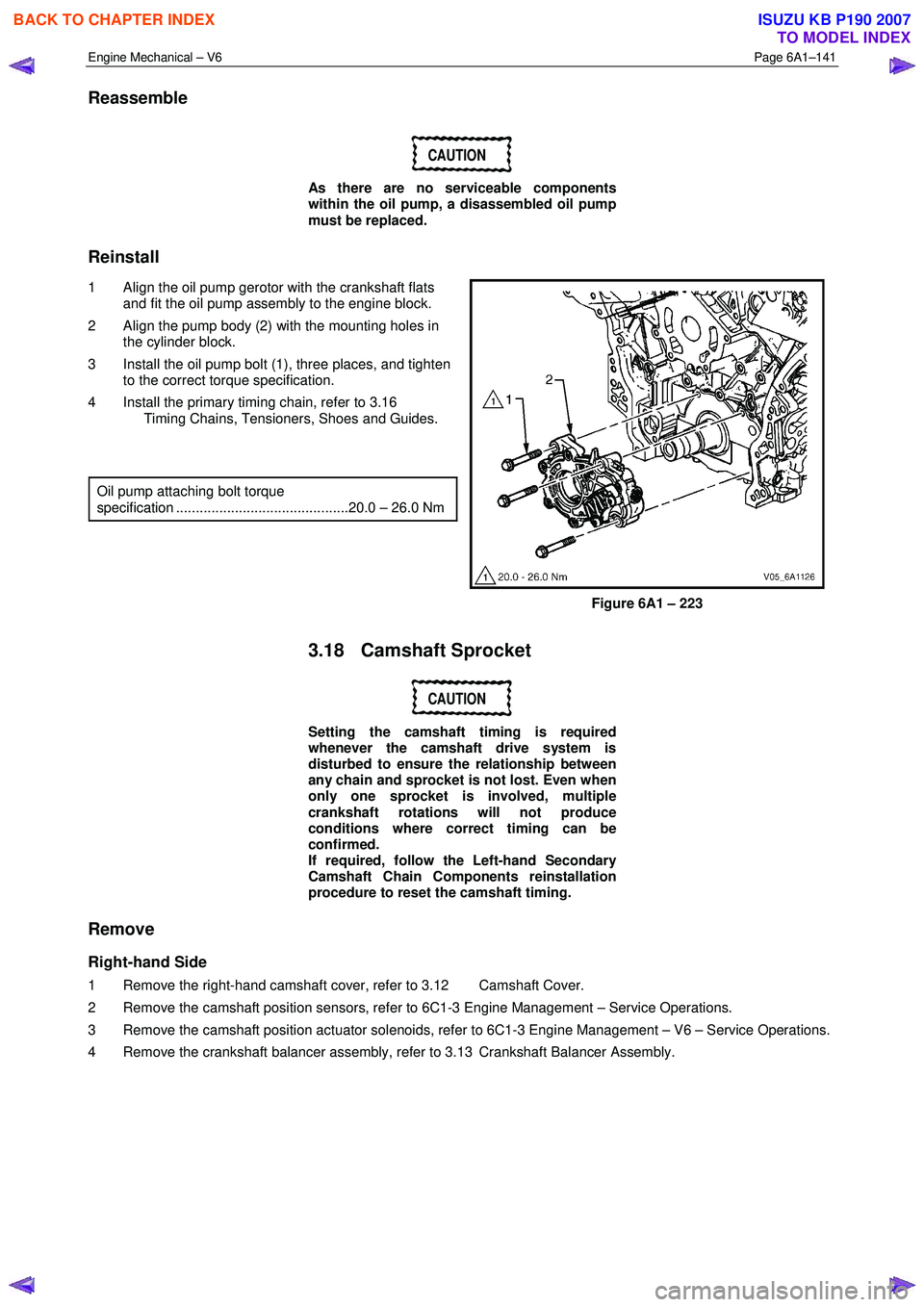
1 Align the oil pump gerotor with the crankshaft flats and fit the oil pump assembly to the engine block.
2 Align the pump body (2) with the mounting holes in the cylinder block.
3 Install the oil pump bolt (1), three places, and tighten to the correct torque specification.
4 Install the primary timing chain, refer to 3.16 Timing Chains, Tensioners, Shoes and Guides.
Oil pump attaching bolt torque
specification ............................................20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Figure 6A1 – 223
3.18 Camshaft Sprocket
CAUTION
Setting the camshaft timing is required
whenever the camshaft drive system is
disturbed to ensure the relationship between
any chain and sprocket is not lost. Even when
only one sprocket is involved, multiple
crankshaft rotations will not produce
conditions where correct timing can be
confirmed.
If required, follow the Left-hand Secondary
Camshaft Chain Components reinstallation
procedure to reset the camshaft timing.
Remove
Right-hand Side
1 Remove the right-hand camshaft cover, refer to 3.12 Camshaft Cover.
2 Remove the camshaft position sensors, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – Service Operations.
3 Remove the camshaft position actuator solenoids, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
4 Remove the crankshaft balancer assembly, refer to 3.13 Crankshaft Balancer Assembly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3325 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–47
6.7 Throttle Body Relearn
A throttle body relearn procedure is performed in one of two ways:
• Engine Control Module initiated throttle body relearn, or
• Tech 2 initiated throttle body relearn.
Engine Control Module Throttle Body Relearn
The engine control module (ECM) will automatically perform a throttle body relearn procedure if either of the following
conditions exist:
• The battery has been disconnected, or
• The ignition switch is in the ON position for greater than 29 seconds, and the following conditions are met:
− Engine speed is less than 40 rpm,
− Vehicle speed is 0 km/h,
− Engine coolant temperature is 5 – 60°C,
− Intake air temperature is 5 – 60°C,
− Accelerator pedal position sensor angle is less than 14.9%, and
− Ignition voltage is greater than 10 V.
Tech 2 Throttle Body Relearn
To perform a throttle body relearn using Tech 2, complete the following procedure:
NOTE
Tech 2 will not initiate a throttle body relearn if
the engine is running.
1 Connect Tech 2 to the data link connector (DLC) and turn the ignition on.
2 On Tech 2 select Engine / Programming / Throttle Body Relearn.
3 W hen Tech 2 displays ‘Do you really want to Reset?’, press the ‘Yes’ soft key.
4 W hen Tech 2 displays ‘Programming Completed’, and the electronic throttle control value displayed by Tech 2 is ‘11’, press the ‘Confirm’ soft key to return to the Tech 2 Programming screen.
5 The throttle body relearn is now complete.
6.8 Electronic Ignition (EI) System Diagnosis
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) controls the ignition coils by pulsing the ignition control (IC) circuits, which triggers an
ignition coil and fires the spark plug. The ECM controls the sequencing and the timing of each ignition coil. The ignition
system consist of the following components:
• The six ignition coils
• The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
• The four camshaft position (CMP) sensors
• The ECM
The ignition coils use the following circuits:
• An IC circuit
• An ignition 1 voltage circuit
• Two ground circuits
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3468 of 6020
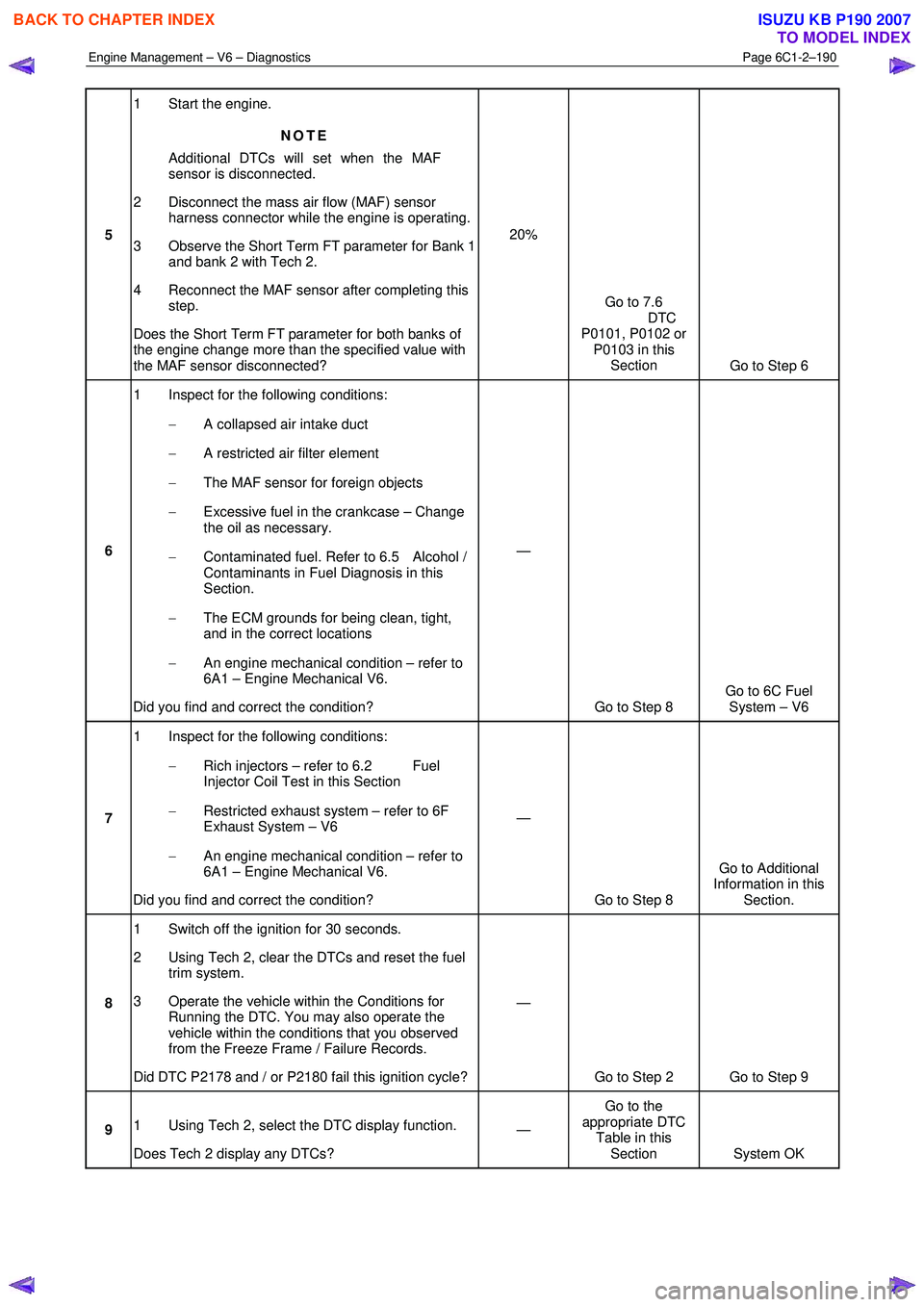
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–190
5 1 Start the engine.
NOTE
Additional DTCs will set when the MAF
sensor is disconnected.
2 Disconnect the mass air flow (MAF) sensor harness connector while the engine is operating.
3 Observe the Short Term FT parameter for Bank 1 and bank 2 with Tech 2.
4 Reconnect the MAF sensor after completing this step.
Does the Short Term FT parameter for both banks of
the engine change more than the specified value with
the MAF sensor disconnected? 20%
Go to 7.6
DTC
P0101, P0102 or P0103 in this Section Go to Step 6
6 1 Inspect for the following conditions:
− A collapsed air intake duct
− A restricted air filter element
− The MAF sensor for foreign objects
− Excessive fuel in the crankcase – Change
the oil as necessary.
− Contaminated fuel. Refer to 6.5 Alcohol /
Contaminants in Fuel Diagnosis in this
Section.
− The ECM grounds for being clean, tight,
and in the correct locations
− An engine mechanical condition – refer to
6A1 – Engine Mechanical V6.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 8 Go to 6C Fuel
System – V6
7 1 Inspect for the following conditions:
− Rich injectors – refer to 6.2 Fuel
Injector Coil Test in this Section
− Restricted exhaust system – refer to 6F
Exhaust System – V6
− An engine mechanical condition – refer to
6A1 – Engine Mechanical V6.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 8 Go to Additional
Information in this Section.
8 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs and reset the fuel trim system.
3 Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running the DTC. You may also operate the
vehicle within the conditions that you observed
from the Freeze Frame / Failure Records.
Did DTC P2178 and / or P2180 fail this ignition cycle? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Step 9
9 1 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? —
Go to the
appropriate DTC Table in this Section System OK
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3503 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–225
F5: EVAP Purge Solenoid
F6: Engine Speed Control
F7: Starter Relay Test
F8: Fuel Injector Balance
F5: Additional Functions
W hen this selection is made from the Tech 2 screen, an additional two choices are provided:
F0: System Identification: In this mode, Tech 2 will display the engine identification screen.
F1: Security Information: W hen selected, this mode displays various engine management data parameters relating to the security system.
F6: Programming
W ithin this selection, there are five programming selections available:
F0: Immobiliser Link to ECM/PIM
F1: Reset ECU
F2: Fuel Trim Reset
F3: Reset Engine Oil Life
F4: Throttle Body Relearn
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3518 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–240
Cruise Control Switch: This parameter displays the state of the cruise control on/off switch input to the control module.
Cruise Control Disengagement Reason: The parameter displays which of a possible 28 causes for the cruise control
to disengage.
CC Disengagement 1 – 8 History (Cruise Control): The parameter displays the last 8 cruise control disengages in
order from 1 to 8, with 8 being the most recent. There are about 28 possible causes for the cruise control to disengage.
Cruise Resume/Acceleration Switch: This parameter displays the state of the cruise control resume/accel switch
position input to the ECM.
Cruise Set / Coast Switch: This parameter displays the state of the cruise controls set/decel. switch position input to
the ECM.
Cycles of Misfire: This parameter displays the number of misfire tests during 200 engine revolutions.
Cylinder 1 – 6 Injector Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fuel injector control circuit. The
parameter displays ‘Fault’ if the fuel injector control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. This
parameter displays ‘Undefined Status’ until the control circuit has been commanded ‘On’.
Dec. Fuel Cutoff (Deceleration): This parameter displays the status of the ECM operating mode, used to turn off the
fuel injectors and the evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge valve during certain deceleration conditions.
Desired Engine Idle Speed: This parameter displays the desired engine idle speed as commanded by the ECM.
Desired Throttle Position: This parameter displays the desired throttle position (TP) angle commanded by the ECM.
Distance Since DTC Cleared: This parameter displays the distance (km) travelled since any diagnostic trouble code
(DTC) has been cleared from the ECM memory.
DTC Set This Ignition: This parameter displays Yes if a DTC set on the current ignition cycle.
ECM Immobilized: This parameter displays ‘Yes’ when an internal control module reset occurs. Tech 2 will display ‘No’
under normal operating conditions.
Electronic Throttle Control Learn Counter: W hen the ECM performs a throttle body relearn procedure, the throttle
plate is commanded to move from the rest position (7% open) to full closed (0%), then to around 10% open.
At the start of this procedure, the Tech 2 ‘TAC Learn Counter’ parameter should display 0, then count up to 11 after the
procedure is completed. If the counter did not start at 0 or if the counter did not end at 11, a fault has occurred and a
DTC should set.
Engine Control Ignition Relay: This parameter displays the state of the control circuit for control module power relay
as commanded by the ECM.
Engine Control Ignition Relay Feedback: This parameter displays the voltage available at the engine control ignition
relay pin of the control module.
Engine Load: This parameter displays the calculated engine load in percent based on inputs to the control module from
various engine sensors.
Engine Oil Life Remaining: This parameter displays the percentage of engine oil life remaining. The controller
calculates the engine oil life by monitoring engine load, collant temperature and engine speed.
Engine Oil Pressure: This parameter displays the oil pressure in kPa from the ECM, developed from the engine oil
pressure (EOP) sensor input.
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor: This parameter displays ‘High’ if the engine oil pressure is within the correct range. If the
ECM detects that the engine oil pressure is not within the correct range, Tech 2 will display ‘Low’.
Engine Runtime: This parameter displays the time elapsed since the engine was started.
Engine Speed: This parameter displays the speed of the engine crankshaft rotation from information received from the
CKP sensor. If there is a CKP sensor DTC, the ECM calculates the engine speed from one of the camshaft position
(CMP) sensors.
EVAP Purge Solenoid (Evaporative Emission): This parameter displays the on-time or duty cycle of the EVAP
canister purge solenoid commanded by the ECM. Zero percent indicates no purge. One hundred percent indicates full
purge.
EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve Circuit Status (Evaporative Emission): This parameter displays the state of the EVAP
purge solenoid control circuit. The parameter displays ‘Fault’ if the EVAP purge solenoid control circuit is open, shorted
to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter displays ‘Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been established as
‘OK’.
Cooling Fan Relay: This parameter displays the control module commanded state of the fan relay control circuit.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3519 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–241
Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fan relay control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the fan relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter displays
‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Level: This parameter displays the amount of fuel in the fuel tank in litres, as calculated by the ECM from data
received from the fuel level sensor.
Fuel Level Sensor: This parameter displays the voltage received from the fuel level sensor in the fuel tank, by the ECM.
Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fuel pump relay control circuit. The
parameter displays ‘Fault’ if the fuel pump relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The
parameter displays ‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Pump Relay: This parameter displays the ECM commanded state of the fuel pump relay control circuit.
Fuel Trim Learn: This parameter displays ‘Enabled’ when conditions are appropriate for enabling long term fuel trim
corrections. This indicates that the long term fuel trim is adapting continuing amounts of short term fuel trim. If Tech 2
displays ‘Disabled’, then long term fuel trim will not respond to changes in short term fuel trim.
Ignition Accessory Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the
ignition ‘ACC’ terminal, X1-4 of the ignition switch.
Ignition On Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the ignition ‘IGN’
terminal X1-3 of the ignition switch.
Initial Brake Apply Signal: This parameter displays the status of the brake lamp switch. Before the cruise control can
be activated, this switch contact must be open circuit when the brake pedal is pressed.
Injection Time Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the amount of fuel injector On-time or pulse width as
commanded by the ECM.
Intake Air Temperature: This parameter displays the temperature of the air entering the air induction system based on
input to the ECM from the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor.
Knock Sensor Signal (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameters displays the voltage input to the control module from the
knock sensor (KS).
Knock Retard: This parameter indicates the amount of spark advance in crankshaft degrees, that the ECM removes
from the ignition control (IC) spark advance in response to the signal from the knock sensors.
Knock Retard Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the knock retard as commanded by the ECM for cylinders 1-6.
Each cylinder is controlled individually based on both knock sensor signal inputs.
Loop Status B1S1 / B2S1 (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1): This parameter displays the state of the fuel control system
as commanded by the ECM. ‘Closed’ Loop operation indicates that the ECM is controlling the fuel delivery based on the
oxygen sensors input signal. In ‘Open’ Loop operation the ECM ignores the oxygen sensor input signal and bases the
amount of fuel to be delivered on other sensor inputs.
LTFT Idle/Deceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for idle and deceleration conditions.
LTFT Cruise/Acceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for cruise and acceleration conditions.
Malfunction Indicator (MI): This parameter displays the commanded (‘On, ‘Off’ or ‘Flashing’) state of the malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) control circuit by the ECM.
Malfunction Indicator (MI) Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the MIL control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the MIL control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. This parameter displays
‘Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Mass Air Flow: This parameter displays the measured quantity (g/s) of air flowing into the engine during all operating
conditions.
Mass Air Flow Sensor: This parameter displays the signal voltage from the mass air flow (MAF) sensor to the ECM.
Misfire Current Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 200 counts. This parameter displays the number of
misfires that have been detected during the last 200 cylinder firing events. The counters may normally display some
activity, but the activity should be nearly equal for all of the cylinders, and in low numbers.
Misfire History Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 65,535 counts. The misfire history counters display the total
level of misfire that has been detected on each cylinder. The misfire history counters will not update or show any activity
until a misfire DTC P0300 has become active. The misfire history counters will update every 200 cylinder firing events.
Oil Level: W hen the ECM receives information from the engine oil level switch, where the engine oil level is within
preset parameters, Tech 2 will display ‘Normal’. If not within preset parameters, the display will show ‘Low’.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3526 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–2
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 20
ECM Reset ...................................................................................................................... ...................................... 20
2.8 Engine Control Module Bracket Assembly......................................................................................... ............... 21
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 21
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 21
2.9 Engine Oil Level and Temperature Sensor ........................................................................................ ................ 22
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 22
Test ....................................................................................................................................................................... 23
Engine Oil Level Sensor Check .................................................................................................. ...................... 23
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 23
2.10 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor..................................................................................................... ........................... 23
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 23
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 24
2.11 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge Valve Quick Connect Fittings ................................................ 24
Disconnect..................................................................................................................... ....................................... 24
Locking Lever Type ............................................................................................................. ............................. 25
Latch Type ....................................................................................................................................................... 25
Connect ............................................................................................................................................................ 25
2.12 Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Valve ...................................................................................... ............... 26
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 26
Test ....................................................................................................................................................................... 27
Resistance Check ............................................................................................................... ............................. 27
Functional Test................................................................................................................................................. 27
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 28
2.13 Fuel Rail Assembly ............................................................................................................. ................................. 28
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 28
Disassemble ......................................................................................................................................................... 30
Fuel Injector ..................................................................................................................................................... 30
Fuel Injector Wiring Harness Assembly.......................................................................................... .................. 32
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 33
2.14 Heated Oxygen Sensor........................................................................................................... ............................. 33
Service Precautions............................................................................................................................................. 33
Six Wire Sensor................................................................................................................................................ 34
Four Wire Sensor ............................................................................................................... .............................. 35
Test ....................................................................................................................................................................... 37
Heater Resistance Check – Six Wire HO2S........................................................................................ ............. 37
Heater Resistance Check – Four Wire HO2S ....................................................................................... ........... 37
2.15 Ignition Coil .......................................................................................................................................................... 38
Ignition Coils ................................................................................................................. ....................................... 38
Remove ............................................................................................................................................................ 38
Disassemble..................................................................................................................................................... 39
Reassemble ..................................................................................................................................................... 39
Test .................................................................................................................................................................. 39
Reinstall ........................................................................................................................................................... 40
2.16 Intake Air Duct Assembly....................................................................................................... ............................. 40
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 40
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 40
2.17 Intake Air Temperature Sensor .................................................................................................. ......................... 41
Test ....................................................................................................................................................................... 41
Resistance Check ............................................................................................................... ............................. 41
2.18 Knock Sensor, Bank 2 (LHS)..................................................................................................... .......................... 42
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 42
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 43
2.19 Knock Sensor, Bank 1 (RHS) ..................................................................................................... ......................... 43
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 43
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 44
2.20 Mass Air Flow Sensor........................................................................................................... ............................... 45
Handling Precautions .......................................................................................................................................... 45
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 45
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 46
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007