fuel pressure ISUZU TF SERIES 2004 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2004, Model line: TF SERIES, Model: ISUZU TF SERIES 2004Pages: 4264, PDF Size: 72.63 MB
Page 1336 of 4264
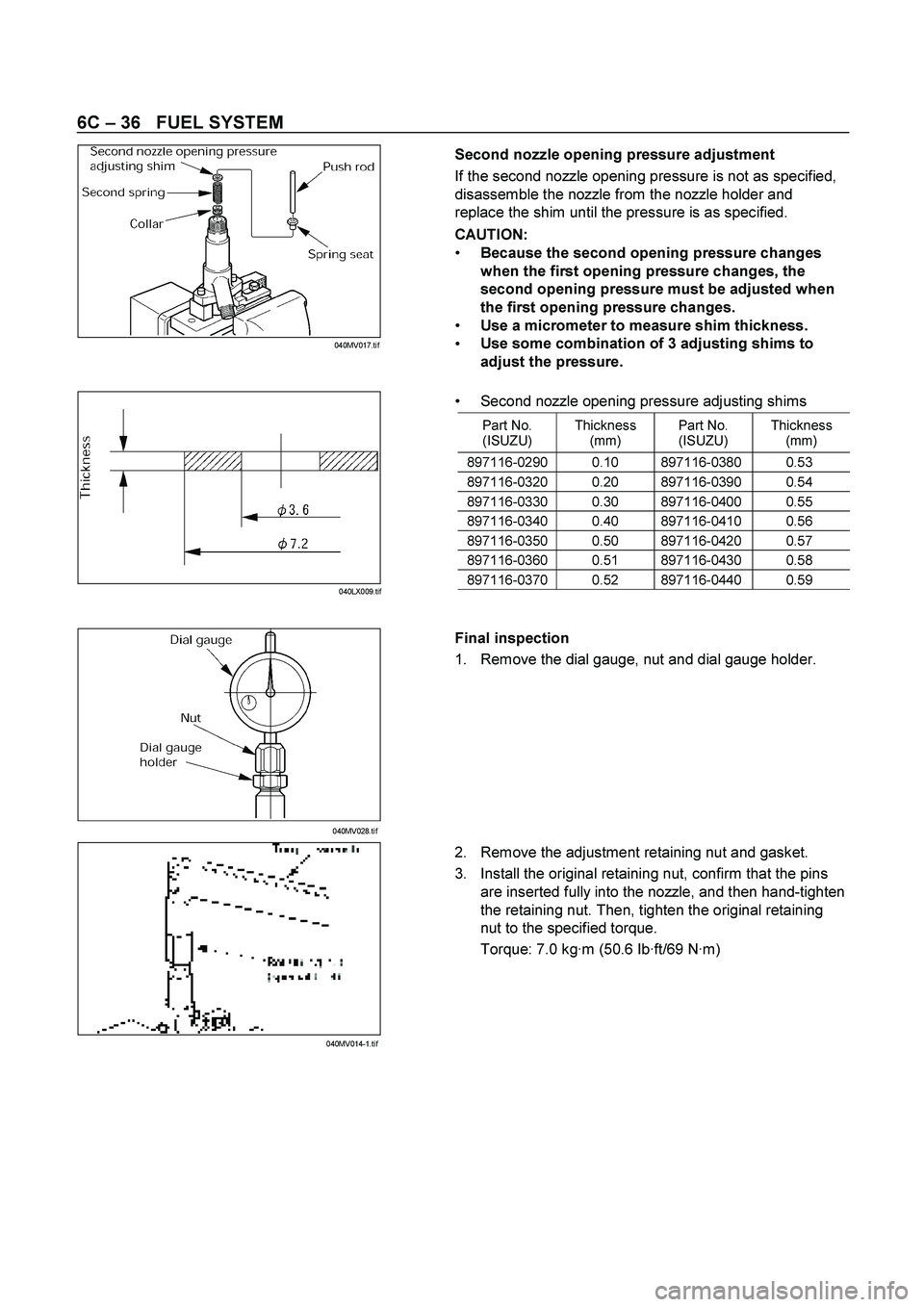
6C – 36 FUEL SYSTEM
Second nozzle opening pressure adjustment
If the second nozzle opening pressure is not as specified,
disassemble the nozzle from the nozzle holder and
replace the shim until the pressure is as specified.
CAUTION:
Because the second opening pressure changes
when the first opening pressure changes, the
second opening pressure must be adjusted when
the first opening pressure changes.
Use a micrometer to measure shim thickness.
Use some combination of 3 adjusting shims to
adjust the pressure.
Second nozzle opening pressure adjusting shims
Part No.
(ISUZU) Thickness
(mm) Part No.
(ISUZU) Thickness
(mm)
897116-0290 0.10 897116-0380 0.53
897116-0320 0.20 897116-0390 0.54
897116-0330 0.30 897116-0400 0.55
897116-0340 0.40 897116-0410 0.56
897116-0350 0.50 897116-0420 0.57
897116-0360 0.51 897116-0430 0.58
897116-0370 0.52 897116-0440 0.59
Final inspection
1. Remove the dial gauge, nut and dial gauge holder.
2. Remove the adjustment retaining nut and gasket.
3. Install the original retaining nut, confirm that the pins
are inserted fully into the nozzle, and then hand-tighten
the retaining nut. Then, tighten the original retaining
nut to the specified torque.
Torque: 7.0 kg·m (50.6 Ib·ft/69 N·m)
040MV017.tif
040LX009.tif
040MV028.tif
040M V014-1.ti
f
Page 1337 of 4264
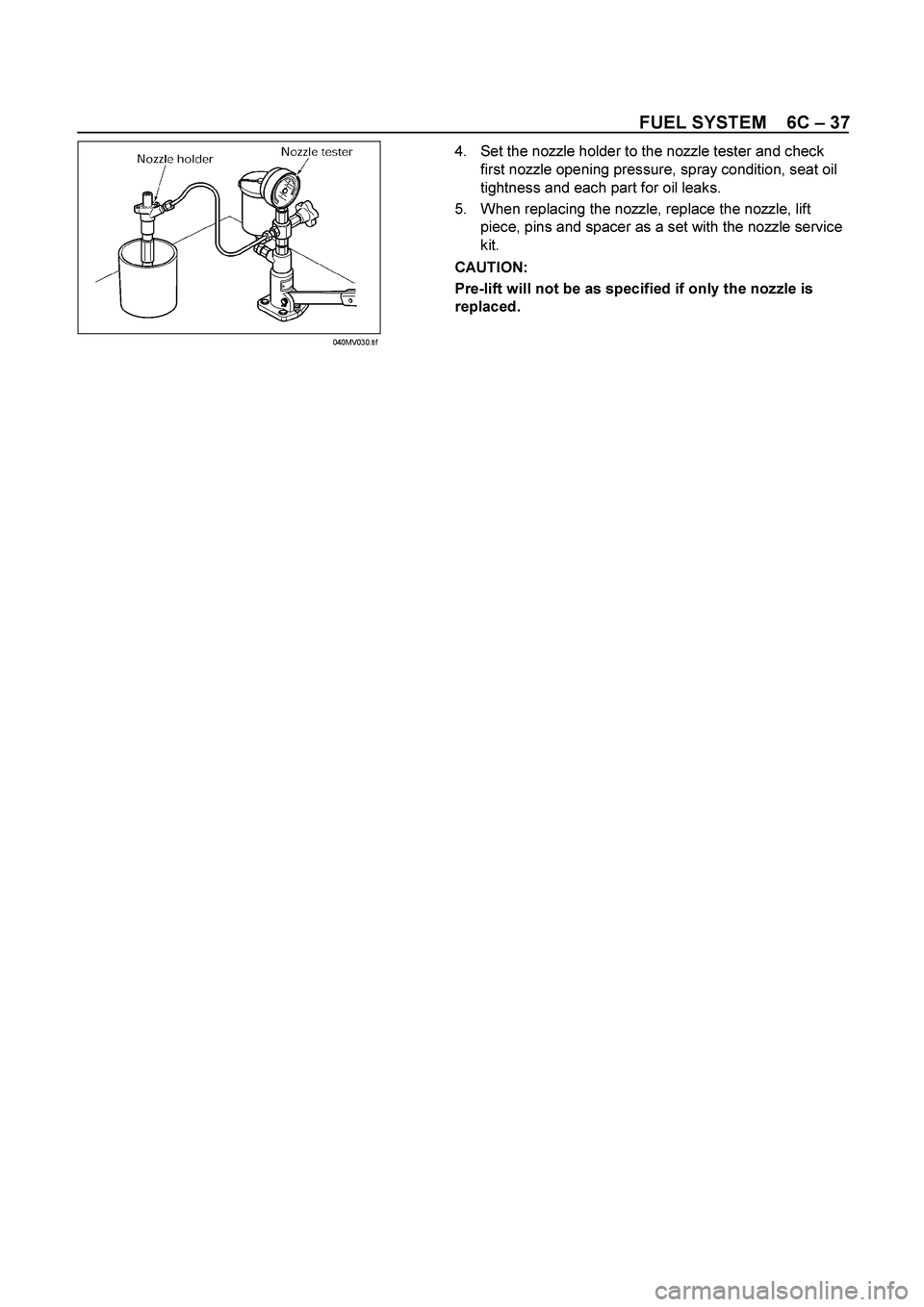
FUEL SYSTEM 6C – 37
4. Set the nozzle holder to the nozzle tester and check
first nozzle opening pressure, spray condition, seat oil
tightness and each part for oil leaks.
5. When replacing the nozzle, replace the nozzle, lift
piece, pins and spacer as a set with the nozzle service
kit.
CAUTION:
Pre-lift will not be as specified if only the nozzle is
replaced.
040MV030.tif
Page 1373 of 4264
4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–1
ENGINE
CONTENTS
4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ABBREVIATION CHARTS ........................ 6E-9
4JA1-TC .................................................... 6E-10
4JH1-TC .................................................... 6E-11
ECM CIRCUIT DIAGRAM (4JA1-TC) ........ 6E-14
ECM CIRCUIT DIAGRAM (4JA1-TC) ........ 6E-15
ECM CIRCUIT DIAGRAM (4JH1-TC) ........ 6E-16
ECM CIRCUIT DIAGRAM (4JH1-TC) ........ 6E-17
GROUND POINT CHART GENERAL EXPORT
(LHD) (1/4) ............................................... 6E-18
LOCATION ................................................ 6E-34
PARTS LOCATION ................................... 6E-39
CONNECTOR LIST ................................... 6E-40
RELAY AND FUSE .................................... 6E-43
RELAY AND FUSE BOX LOCATION
(LHD & RHD) ........................................... 6E-43
RELAY AND FUSE BOX LOCATION
(LHD & RHD) ........................................... 6E-44
FUSE AND RELAY LOCATION (LHD & RHD) 6E-45
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1/7) .................. 6E-46
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (2/7) .................. 6E-47
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (3/7) .................. 6E-48
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (4/7) .................. 6E-49
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (5/7) .................. 6E-50
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (6/7) .................. 6E-51
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (7/7) .................. 6E-52
ECM CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENT &
OUTPUT SIGNAL .................................... 6E-53
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ECM AND
SENSORS ............................................... 6E-64
Engine Control Module (ECM) ................... 6E-64
Pump Control Unit (PSG) & Data Ex change
Between Control Module ......................... 6E-64
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor & Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor ....................... 6E-65
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) .................. 6E-66
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor ............ 6E-66
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E-67
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) .................... 6E-67
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR EGR
(EXHAUST GAS RE-CIRCULATION) ..... 6E-68
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR
INJECTION PUMP .................................. 6E-70Outline ....................................................... 6E-70
Cross-section View .................................... 6E-70
Low Pressure Fuel Circuit .......................... 6E-71
High Pressure Fuel Circuit ......................... 6E-72
Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor ................. 6E-72
High Pressure Solenoid Valve ................... 6E-73
Timing Control Valve (TCV) ....................... 6E-74
ISUZU Strategy Based Diagnostics .............. 6E-76
Overview .................................................... 6E-76
STRATEGY BASED DIAGNOSTICS CHART 6E-76
Diagnostic Thought Process ...................... 6E-77
1. Verify the Complaint .............................. 6E-77
2. Perform Preliminary Checks .................. 6E-77
3. Check Bulletins and Troubleshooting Hints 6E-78
4. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic Checks 6E-78
5a and 5b. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic
Procedures .............................................. 6E-78
5c. Technician Self Diagnoses .................. 6E-78
5d. Intermittent Diagnosis .......................... 6E-79
5e. Vehicle Operates as Designed ............ 6E-80
6. Re-examine the complaint ..................... 6E-81
7. Repair and Verify Fix ............................. 6E-81
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION ....... 6E-82
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) ............. 6E-82
TECH 2 OPERATING FLOW CART
(START UP) ............................................. 6E-86
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS
(ENGINE DATA) ................................... 6E-88
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS
(ENGINE DATA) ................................... 6E-90
MISCELLANEOUS TEST .......................... 6E-92
Plotting Snapshot Graph ............................ 6E-93
Plotting Graph Flow Chart (Plotting graph
after obtaining vehicle information) .......... 6E-94
Flow Chart for Snapshot Replay
(Plotting Graph) ....................................... 6E-95
SNAPSHOT DISPLAY WITH TIS2000 ...... 6E-96
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
CHECK .................................................... 6E-105
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-105
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-105
Test Description ......................................... 6E-105
Page 1378 of 4264

6E–6 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-268
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-268
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0645
(Symptom Code 4) (Flash Code 46) A/C
Compressor Relay Circuit Voltage Low ... 6E-269
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0645
(Symptom Code 8) (Flash Code 46) A/C
Compressor Relay Circuit Voltage High .. 6E-272
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0703
(SYMPTOM CODE A) (FLASH CODE 25)
BRAKE SWITCH CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION 6E-273
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0703
(SYMPTOM CODE B) (FLASH CODE 25)
BRAKE SWITCH CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION 6E-273
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-274
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-274
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0703
(Symptom Code A) (Flash Code 25) Brake
Switch Circuit Malfunction ....................... 6E-274
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0703
(Symptom Code B) (Flash Code 25)
Brake Switch Circuit Malfunction ............. 6E-278
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0704
(SYMPTOM CODE 6) (FLASH CODE 57)
CLUTCH SWITCH INPUT CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION ....................................... 6E-281
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-281
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-281
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0704
(Symptom Code 6) (Flash Code 57)
Clutch Switch Input Circuit Malfunction ... 6E-282
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1105
(SYMPTOM CODE 1) (FLASH CODE 86)
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT ............................ 6E-285
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1105
(SYMPTOM CODE 2) (FLASH CODE 86)
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
CIRCUIT LOW INPUT ............................. 6E-285
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-285
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-285
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1105
(Symptom Code 1) (Flash Code 86) Barometric
Pressure Sensor Circuit High Input ......... 6E-285
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1105
(Symptom Code 2) (Flash Code 86) Barometric
Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Input .......... 6E-285
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1120
(SYMPTOM CODE 1) (FLASH CODE 21)
PEDAL/THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT ............................ 6E-287
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1120
(SYMPTOM CODE 7) (FLASH CODE 21)PEDAL/THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
VOLTAGE SUPPLY CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT 6E-287
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1120
(SYMPTOM CODE 9) (FLASH CODE 21)
PEDAL/THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
VOLTAGE SUPPLY CIRCUIT LOW INPUT 6E-287
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1120
(SYMPTOM CODE D) (FLASH CODE 21)
PEDAL/THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
BRAKE SWITCH ERROR ....................... 6E-287
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1120
(SYMPTOM CODE E) (FLASH CODE 21)
PEDAL/THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
IDLE POSITION SWITCH ERROR ......... 6E-287
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-288
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-288
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1120
(Symptom Code 1) (Flash Code 21)
Pedal/Throttle Position Sensor
Circuit High Input ..................................... 6E-288
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1120
(Symptom Code 7) (Flash Code 21)
Pedal/Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
Supply Circuit High Input ......................... 6E-293
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1120
(Symptom Code 9) (Flash Code 21)
Pedal/Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
Supply Circuit Low Input .......................... 6E-295
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1120
(Symptom Code D) (Flash Code 21)
Pedal/Throttle Position Sensor Brake
Switch Error ............................................. 6E-298
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1120
(Symptom Code E) (Flash Code 21)
Pedal/Throttle Position Sensor Idle
Position Switch Error ............................... 6E-300
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1173
(SYMPTOM CODE 3) (FLASH CODE 22) FUEL
REDUCTION CAUSED BY HIGH COOLANT
TEMPERATURE ...................................... 6E-302
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1173
(SYMPTOM CODE 7) (FLASH CODE 22) FUEL
REDUCTION CAUSED BY HIGH FUEL
TEMPERATURE ...................................... 6E-302
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1173
(SYMPTOM CODE A) (FLASH CODE 22) FUEL
REDUCTION CAUSED BY LOW FUEL
TEMPERATURE ...................................... 6E-302
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-302
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-302
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1173
(Symptom Code 3) (Flash Code 22) Fuel
Reduction Caused By High Coolant
Page 1436 of 4264
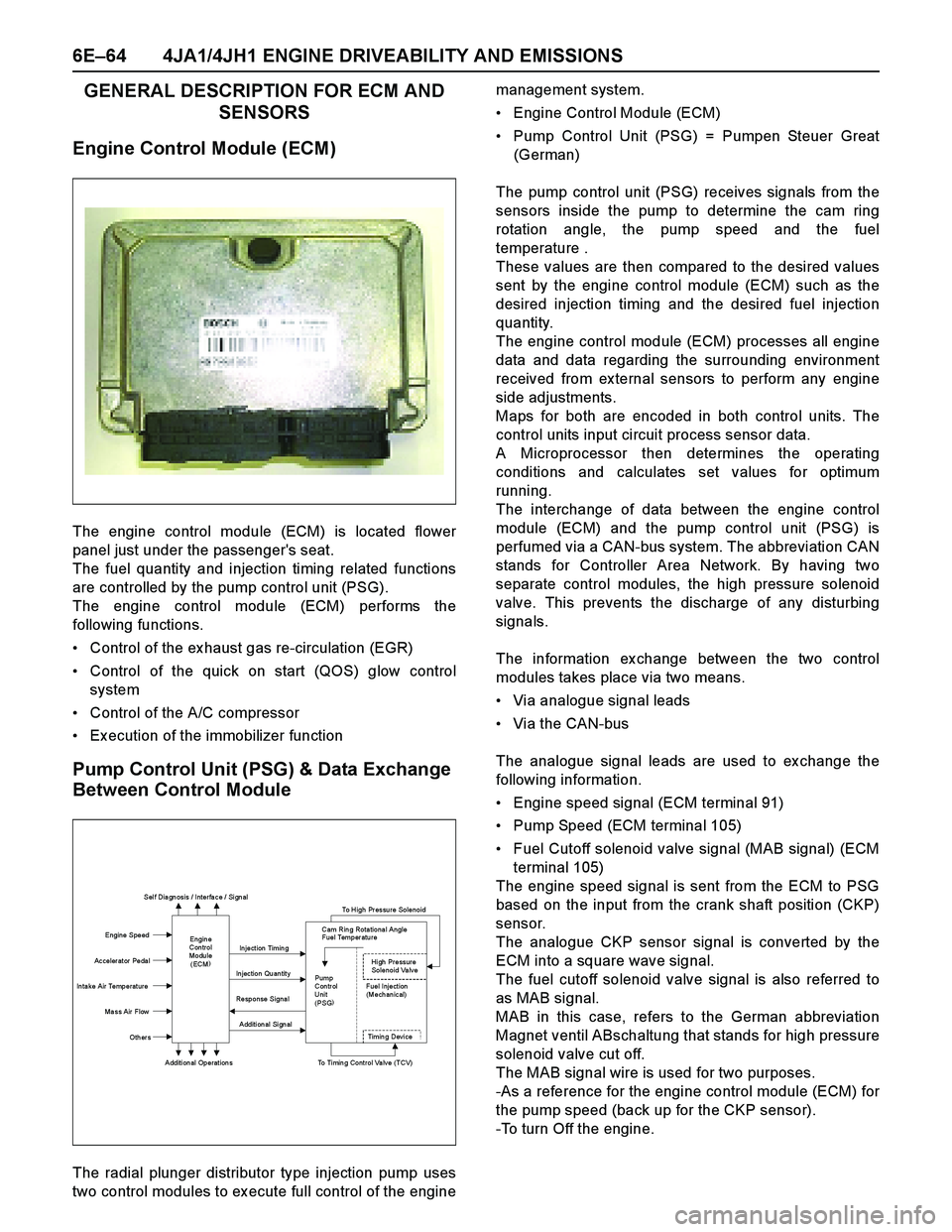
6E–64 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ECM AND
SENSORS
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located flower
panel just under the passenger's seat.
The fuel quantity and injection timing related functions
are controlled by the pump control unit (PSG).
The engine control module (ECM) performs the
following functions.
Control of the ex haust gas re-circulation (EGR)
Control of the quick on start (QOS) glow control
system
Control of the A/C compressor
Ex ecution of the immobilizer function
Pump Control Unit (PSG) & Data Exchange
Between Control Module
The radial plunger distributor type injection pump uses
two control modules to ex ecute full control of the enginemanagement system.
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Pump Control Unit (PSG) = Pumpen Steuer Great
(German)
The pump control unit (PSG) receives signals from the
sensors inside the pump to determine the cam ring
rotation angle, the pump speed and the fuel
temperature .
These values are then compared to the desired values
sent by the engine control module (ECM) such as the
desired injection timing and the desired fuel injection
quantity.
The engine control module (ECM) processes all engine
data and data regarding the surrounding environment
received from ex ternal sensors to perform any engine
side adjustments.
Maps for both are encoded in both control units. The
control units input circuit process sensor data.
A Microprocessor then determines the operating
conditions and calculates set values for optimum
running.
The interchange of data between the engine control
module (ECM) and the pump control unit (PSG) is
perfumed via a CAN-bus system. The abbreviation CAN
stands for Controller Area Network. By having two
separate control modules, the high pressure solenoid
valve. This prevents the discharge of any disturbing
signals.
The information ex change between the two control
modules takes place via two means.
Via analogue signal leads
Via the CAN-bus
The analogue signal leads are used to ex change the
following information.
Engine speed signal (ECM terminal 91)
Pump Speed (ECM terminal 105)
Fuel Cutoff solenoid valve signal (MAB signal) (ECM
terminal 105)
The engine speed signal is sent from the ECM to PSG
based on the input from the crank shaft position (CKP)
sensor.
The analogue CKP sensor signal is converted by the
ECM into a square wave signal.
The fuel cutoff solenoid valve signal is also referred to
as MAB signal.
MAB in this case, refers to the German abbreviation
Magnet ventil ABschaltung that stands for high pressure
solenoid v alv e cut off.
The MAB signal wire is used for two purposes.
-As a reference for the engine control module (ECM) for
the pump speed (back up for the CKP sensor).
-To turn Off the engine.
Sel f Dia gn osis / Interfa ce / Si gn al
To High Pressure Solenoid
Engine Speed
Injection Timing
Accelerator Pedal
Injection Quantity
In ta ke Air Temperat ure
Response Signal
Ma ss Air Flow
Additional Signal
Others
Additional Operations To Timing Control Valve (TCV)
Engin e
Con trol
Modu le
(ECM) Cam Rin g Rota tiona l Angle
Fuel Temper atu re
High Pressure
Solenoid Valve
Pump
Con tr ol Fuel Inject ion
Unit (Mechanical)
(PSG)
Ti m i n
g Devi ce
Page 1442 of 4264
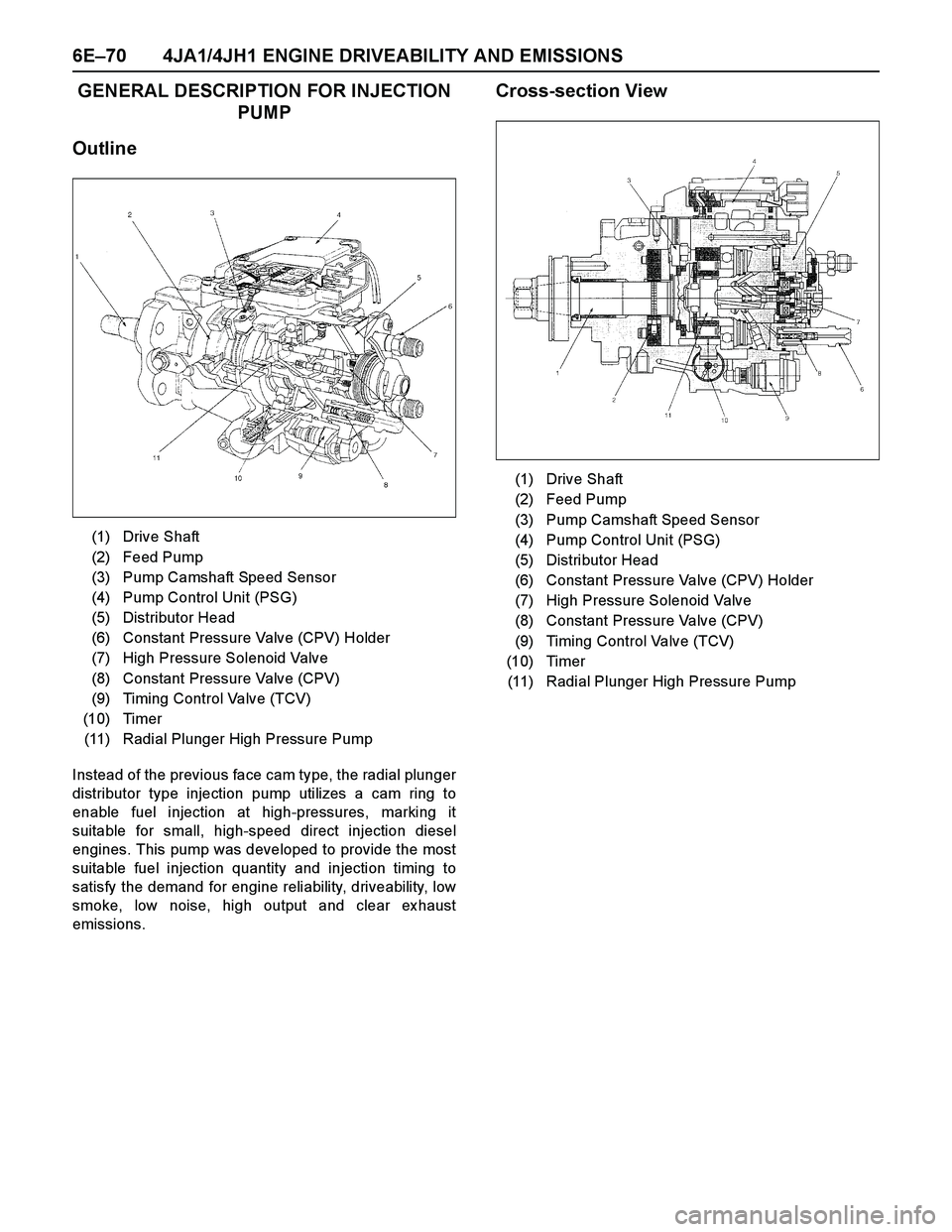
6E–70 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR INJECTION
PUMP
Outline
Instead of the previous face cam type, the radial plunger
distributor type injection pump utilizes a cam ring to
enable fuel injection at high-pressures, marking it
suitable for small, high-speed direct injection diesel
engines. This pump was developed to provide the most
suitable fuel injection quantity and injection timing to
satisfy the demand for engine reliability, driveability, low
smoke, low noise, high output and clear ex haust
emissions.
Cross-section View
(1) Drive Shaft
(2) Feed Pump
(3) Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor
(4) Pump Control Unit (PSG)
(5) Distributor Head
(6) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV) Holder
(7) High Pressure Solenoid Valve
(8) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV)
(9) Timing Control Valve (TCV)
(10) Timer
(11) Radial Plunger High Pressure Pump
(1) Drive Shaft
(2) Feed Pump
(3) Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor
(4) Pump Control Unit (PSG)
(5) Distributor Head
(6) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV) Holder
(7) High Pressure Solenoid Valve
(8) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV)
(9) Timing Control Valve (TCV)
(10) Timer
(11) Radial Plunger High Pressure Pump
Page 1443 of 4264
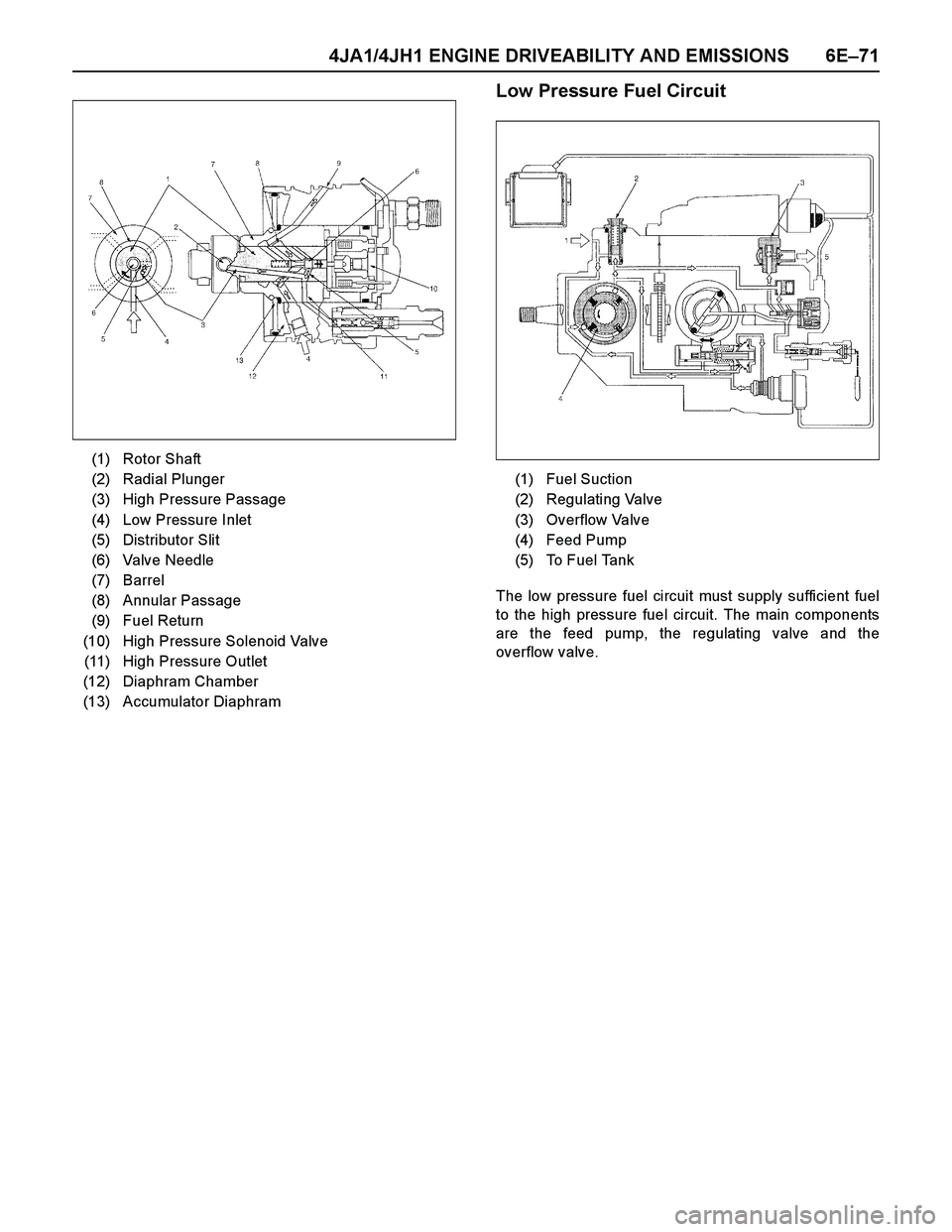
4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–71
Low Pressure Fuel Circuit
The low pressure fuel circuit must supply sufficient fuel
to the high pressure fuel circuit. The main components
are the feed pump, the regulating valve and the
overflow valve. (1) Rotor Shaft
(2) Radial Plunger
(3) High Pressure Passage
(4) Low Pressure Inlet
(5) Distributor Slit
(6) Valve Needle
(7) Barrel
(8) Annular Passage
(9) Fuel Return
(10) High Pressure Solenoid Valve
(11) High Pressure Outlet
(12) Diaphram Chamber
(13) Accumulator Diaphram
(1) Fuel Suction
(2) Regulating Valve
(3) Overflow Valve
(4) Feed Pump
(5) To Fuel Tank
Page 1444 of 4264
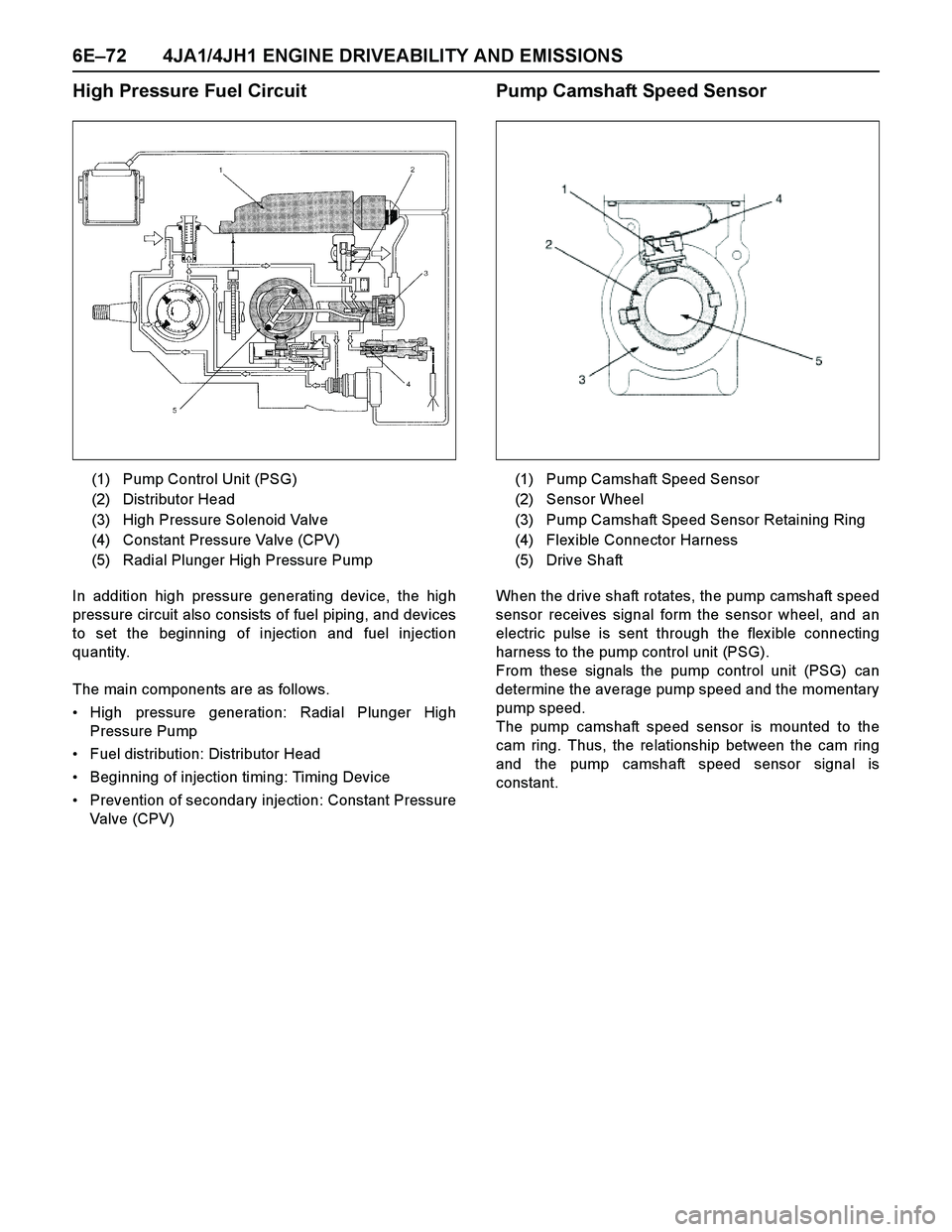
6E–72 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
High Pressure Fuel Circuit
In addition high pressure generating device, the high
pressure circuit also consists of fuel piping, and devices
to set the beginning of injection and fuel injection
quantity.
The main components are as follows.
High pressure generation: Radial Plunger High
Pressure Pump
Fuel distribution: Distributor Head
Beginning of injection timing: Timing Device
Prevention of secondary injection: Constant Pressure
Valve (CPV)
Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor
When the drive shaft rotates, the pump camshaft speed
sensor receives signal form the sensor wheel, and an
electric pulse is sent through the flex ible connecting
harness to the pump control unit (PSG).
From these signals the pump control unit (PSG) can
determine the average pump speed and the momentary
pump speed.
The pump camshaft speed sensor is mounted to the
cam ring. Thus, the relationship between the cam ring
and the pump camshaft speed sensor signal is
constant. (1) Pump Control Unit (PSG)
(2) Distributor Head
(3) High Pressure Solenoid Valve
(4) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV)
(5) Radial Plunger High Pressure Pump
(1) Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor
(2) Sensor Wheel
(3) Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor Retaining Ring
(4) Flex ible Connector Harness
(5) Drive Shaft
Page 1445 of 4264
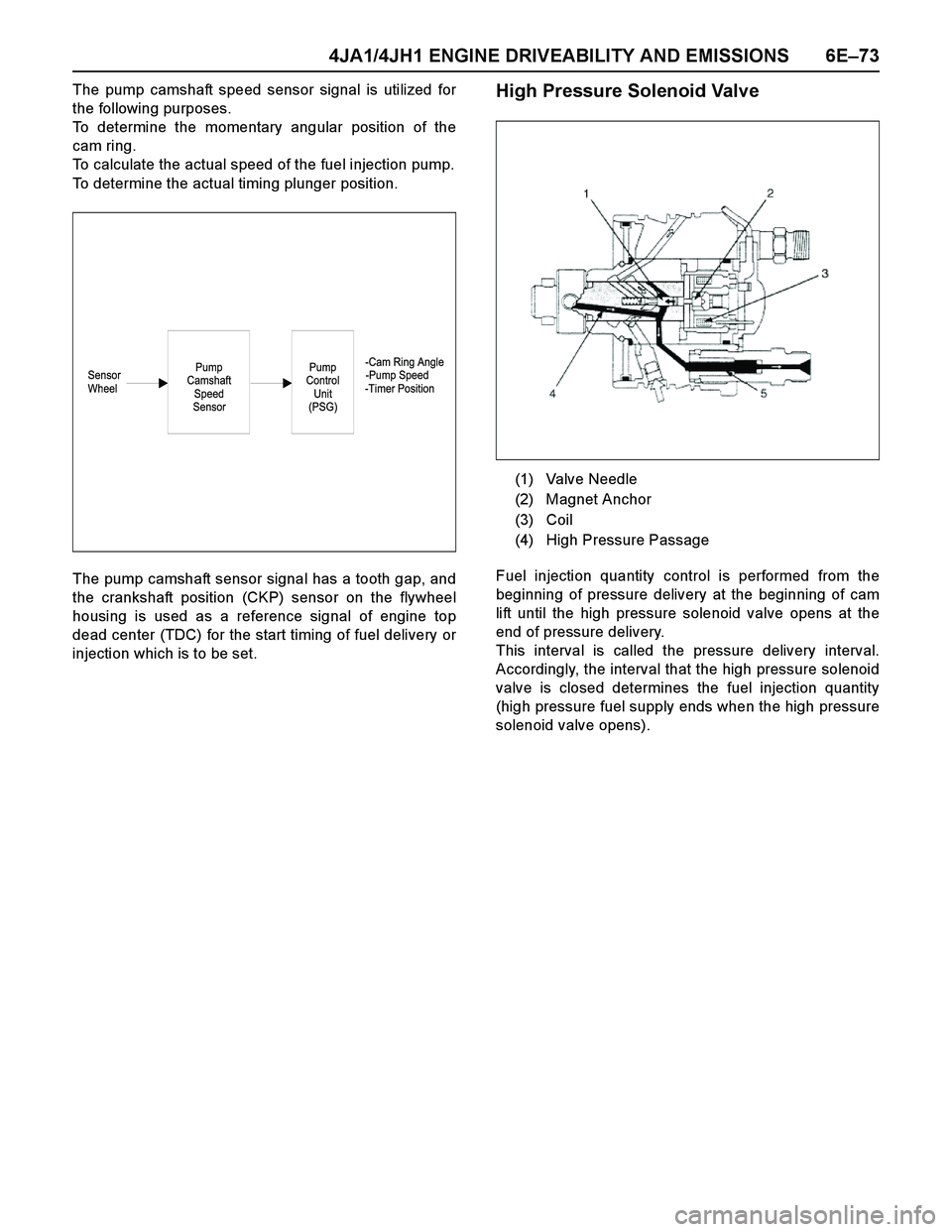
4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–73
The pump camshaft speed sensor signal is utilized for
the following purposes.
To determine the momentary angular position of the
cam ring.
To calculate the actual speed of the fuel injection pump.
To determine the actual timing plunger position.
The pump camshaft sensor signal has a tooth gap, and
the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor on the flywheel
housing is used as a reference signal of engine top
dead center (TDC) for the start timing of fuel delivery or
injection which is to be set.High Pressure Solenoid Valve
Fuel injection quantity control is performed from the
beginning of pressure delivery at the beginning of cam
lift until the high pressure solenoid valve opens at the
end of pressure delivery.
This interval is called the pressure delivery interval.
Accordingly, the interval that the high pressure solenoid
valve is closed determines the fuel injection quantity
(high pressure fuel supply ends when the high pressure
solenoid valve opens).
-Cam Ring Angle
Sensor -Pump Speed
Wheel -Timer PositionPump
Control
Unit
(PSG)Pump
Camshaft
Speed
Sensor
(1) Valve Needle
(2) Magnet Anchor
(3) Coil
(4) High Pressure Passage
Page 1446 of 4264
6E–74 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
When current from the pump control unit (PSG) flows to
the high pressure solenoid valve coil, the magnet
anchor (a movable iron core) pushes the valve needle,
toward the valve seat.
When the valve seat is completely closed by the valve
needle, the way, of the fuel in the high pressure
passage to the low pressure circuit is closed.
The pressure of the fuel in the high pressure passage is
rapidly increased by radial plunger lift, and the high
pressure fuel is delivered through the constant pressure
valve (CPV) to the nozzle holder assembly and is
injected into the engine cylinder.
When the fuel injection quantity demanded by the
engine is reached, the current to the coil is cut and the
valve needle re-opens the valve seat.
As a result of this, a path is opened for the fuel in the
high pressure passage to the low pressure circuit and
the pressure decreases. With a decrease in injection
pressure the nozzle closes and injection ends.Timing Control Valve (TCV)
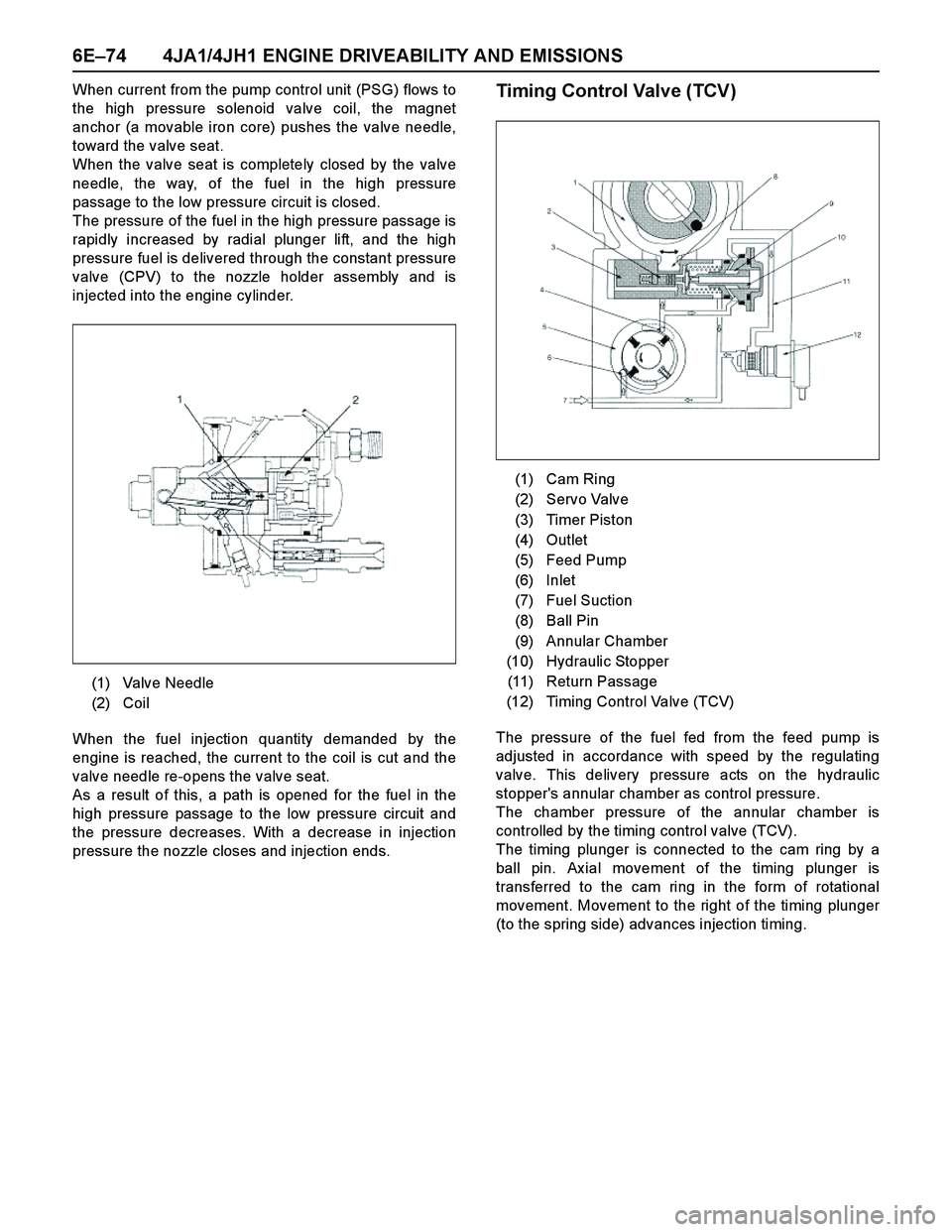
The pressure of the fuel fed from the feed pump is
adjusted in accordance with speed by the regulating
valve. This delivery pressure acts on the hydraulic
stopper's annular chamber as control pressure.
The chamber pressure of the annular chamber is
controlled by the timing control valve (TCV).
The timing plunger is connected to the cam ring by a
ball pin. Ax ial movement of the timing plunger is
transferred to the cam ring in the form of rotational
movement. Movement to the right of the timing plunger
(to the spring side) advances injection timing. (1) Valve Needle
(2) Coil
(1) Cam Ring
(2) Servo Valve
(3) Timer Piston
(4) Outlet
(5) Feed Pump
(6) Inlet
(7) Fuel Suction
(8) Ball Pin
(9) Annular Chamber
(10) Hydraulic Stopper
(11) Return Passage
(12) Timing Control Valve (TCV)