fuel pump ISUZU TF SERIES 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2004, Model line: TF SERIES, Model: ISUZU TF SERIES 2004Pages: 4264, PDF Size: 72.63 MB
Page 1442 of 4264
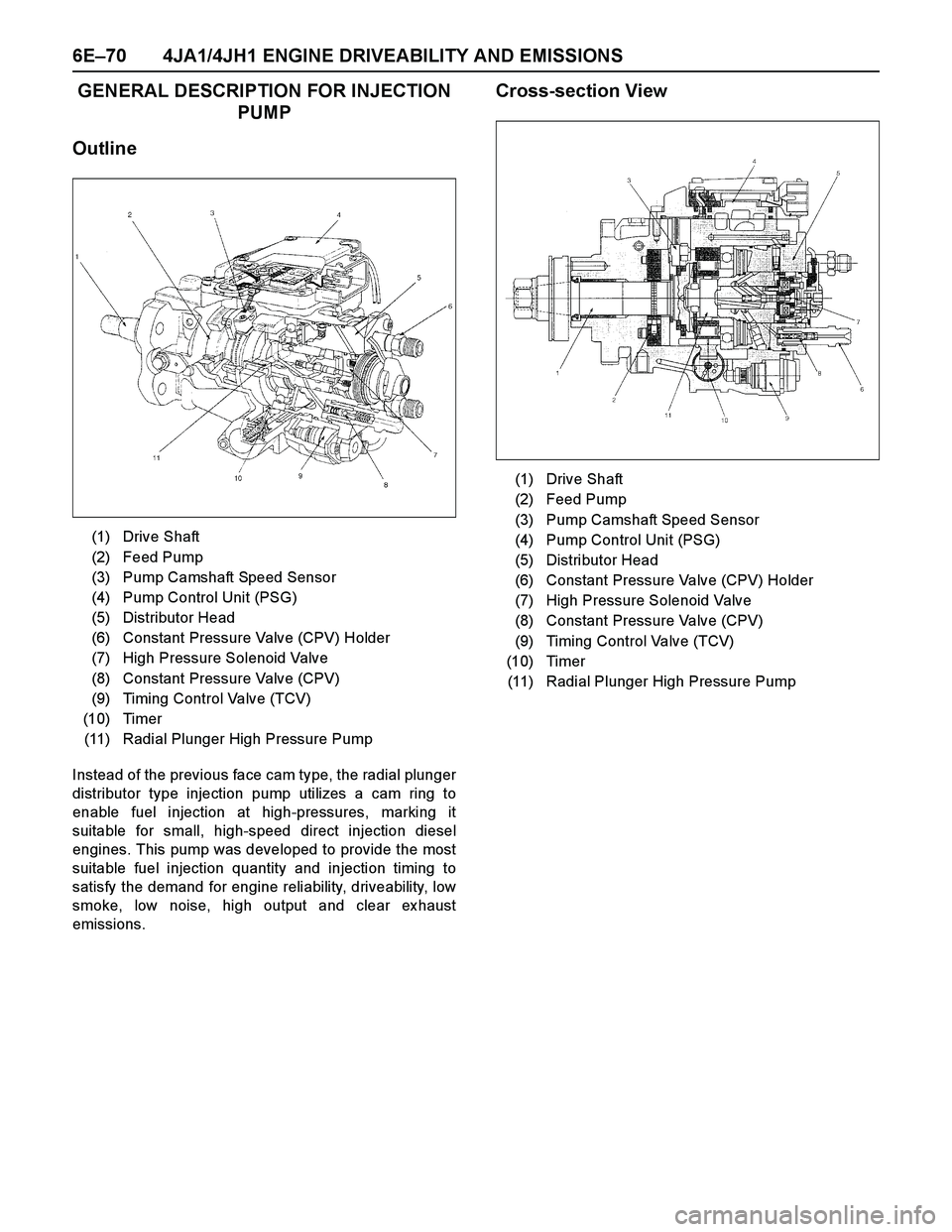
6E–70 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR INJECTION
PUMP
Outline
Instead of the previous face cam type, the radial plunger
distributor type injection pump utilizes a cam ring to
enable fuel injection at high-pressures, marking it
suitable for small, high-speed direct injection diesel
engines. This pump was developed to provide the most
suitable fuel injection quantity and injection timing to
satisfy the demand for engine reliability, driveability, low
smoke, low noise, high output and clear ex haust
emissions.
Cross-section View
(1) Drive Shaft
(2) Feed Pump
(3) Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor
(4) Pump Control Unit (PSG)
(5) Distributor Head
(6) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV) Holder
(7) High Pressure Solenoid Valve
(8) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV)
(9) Timing Control Valve (TCV)
(10) Timer
(11) Radial Plunger High Pressure Pump
(1) Drive Shaft
(2) Feed Pump
(3) Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor
(4) Pump Control Unit (PSG)
(5) Distributor Head
(6) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV) Holder
(7) High Pressure Solenoid Valve
(8) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV)
(9) Timing Control Valve (TCV)
(10) Timer
(11) Radial Plunger High Pressure Pump
Page 1443 of 4264
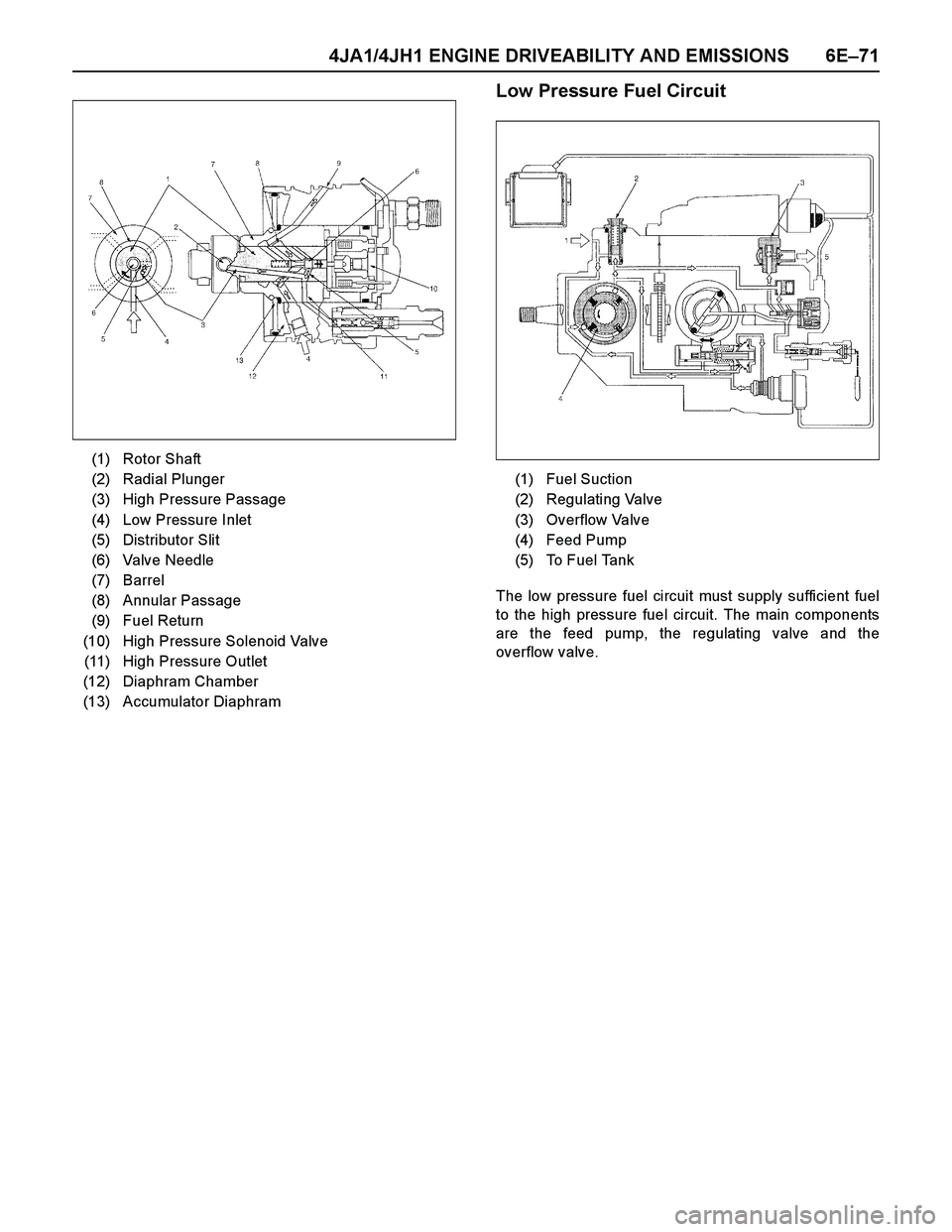
4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–71
Low Pressure Fuel Circuit
The low pressure fuel circuit must supply sufficient fuel
to the high pressure fuel circuit. The main components
are the feed pump, the regulating valve and the
overflow valve. (1) Rotor Shaft
(2) Radial Plunger
(3) High Pressure Passage
(4) Low Pressure Inlet
(5) Distributor Slit
(6) Valve Needle
(7) Barrel
(8) Annular Passage
(9) Fuel Return
(10) High Pressure Solenoid Valve
(11) High Pressure Outlet
(12) Diaphram Chamber
(13) Accumulator Diaphram
(1) Fuel Suction
(2) Regulating Valve
(3) Overflow Valve
(4) Feed Pump
(5) To Fuel Tank
Page 1444 of 4264
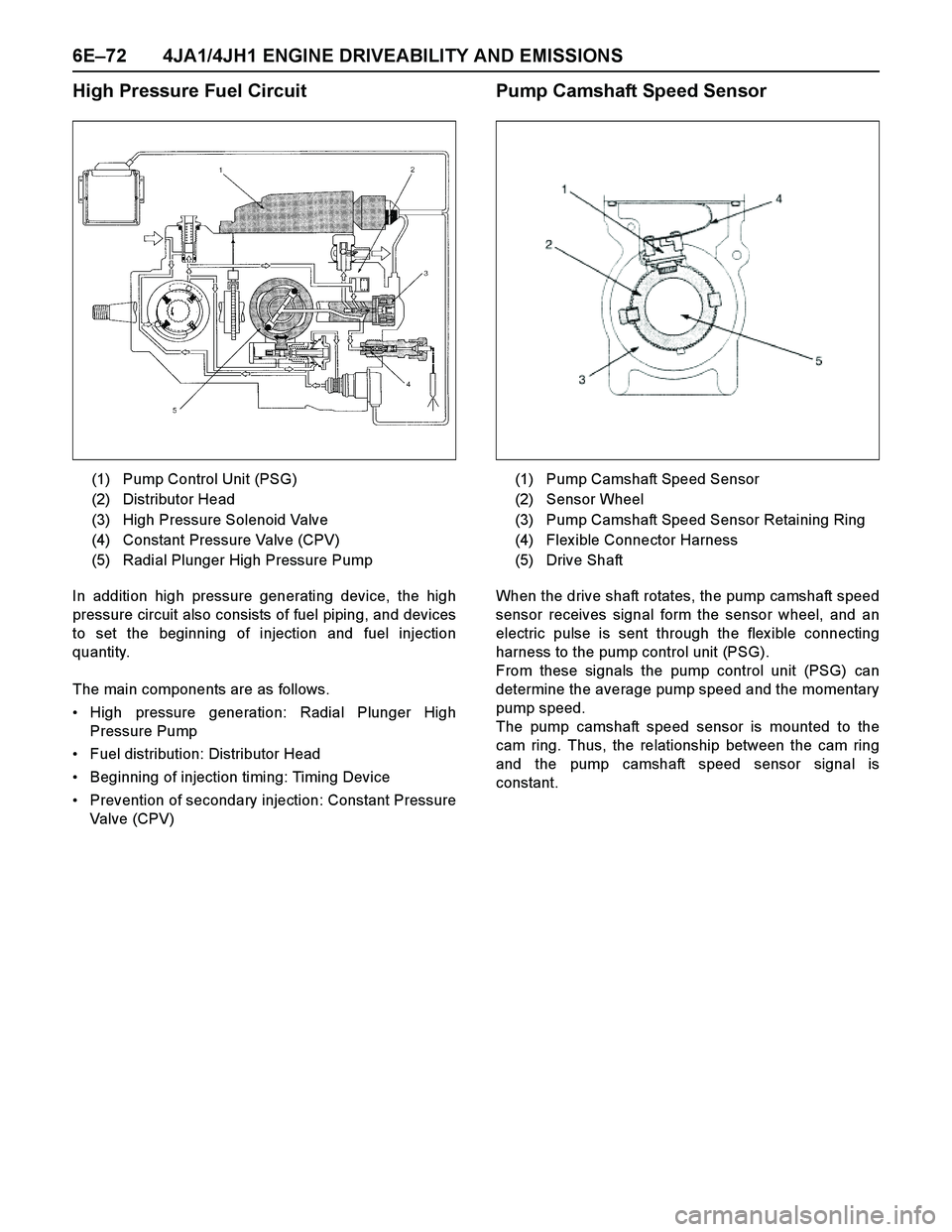
6E–72 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
High Pressure Fuel Circuit
In addition high pressure generating device, the high
pressure circuit also consists of fuel piping, and devices
to set the beginning of injection and fuel injection
quantity.
The main components are as follows.
High pressure generation: Radial Plunger High
Pressure Pump
Fuel distribution: Distributor Head
Beginning of injection timing: Timing Device
Prevention of secondary injection: Constant Pressure
Valve (CPV)
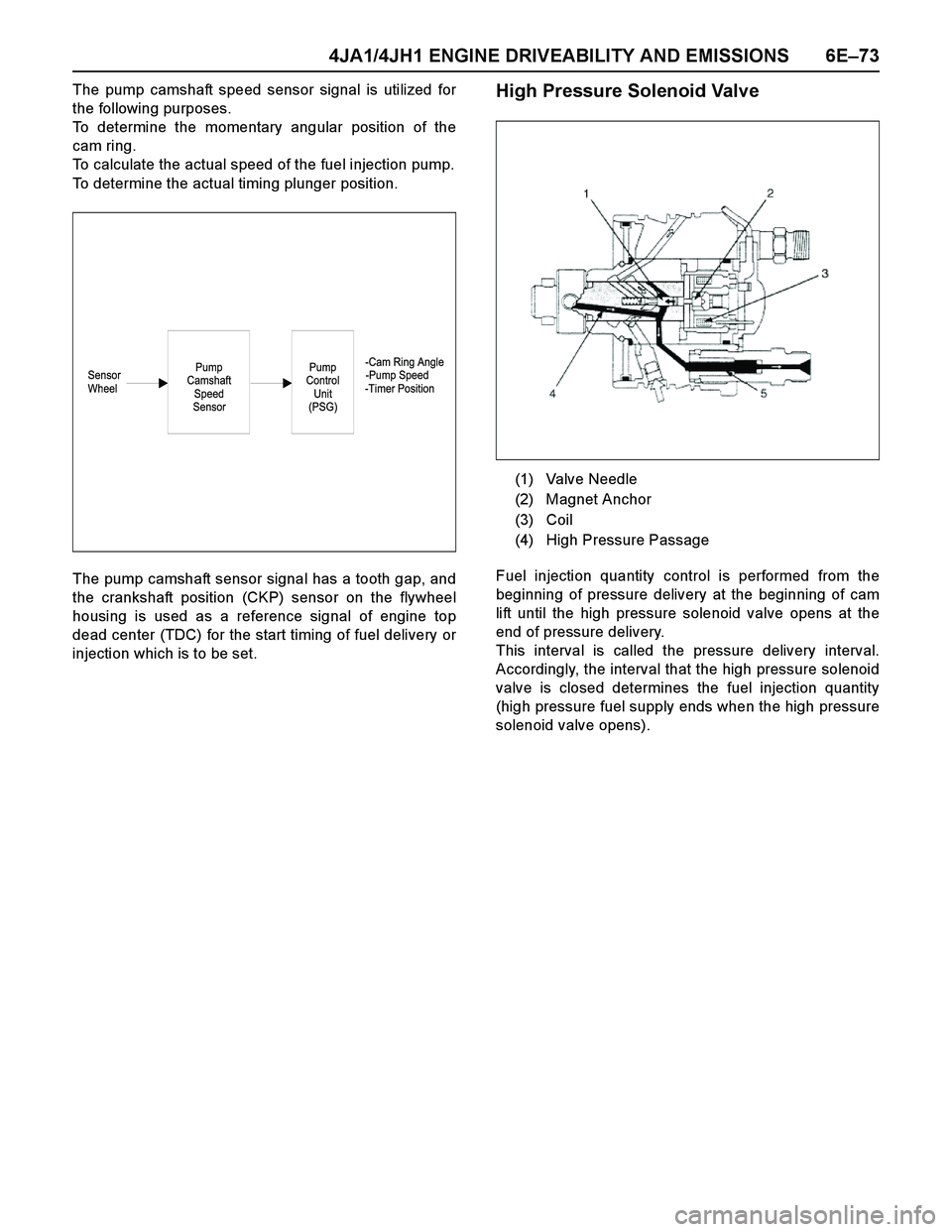
Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor
When the drive shaft rotates, the pump camshaft speed
sensor receives signal form the sensor wheel, and an
electric pulse is sent through the flex ible connecting
harness to the pump control unit (PSG).
From these signals the pump control unit (PSG) can
determine the average pump speed and the momentary
pump speed.
The pump camshaft speed sensor is mounted to the
cam ring. Thus, the relationship between the cam ring
and the pump camshaft speed sensor signal is
constant. (1) Pump Control Unit (PSG)
(2) Distributor Head
(3) High Pressure Solenoid Valve
(4) Constant Pressure Valve (CPV)
(5) Radial Plunger High Pressure Pump
(1) Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor
(2) Sensor Wheel
(3) Pump Camshaft Speed Sensor Retaining Ring
(4) Flex ible Connector Harness
(5) Drive Shaft
Page 1445 of 4264
4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–73
The pump camshaft speed sensor signal is utilized for
the following purposes.
To determine the momentary angular position of the
cam ring.
To calculate the actual speed of the fuel injection pump.
To determine the actual timing plunger position.
The pump camshaft sensor signal has a tooth gap, and
the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor on the flywheel
housing is used as a reference signal of engine top
dead center (TDC) for the start timing of fuel delivery or
injection which is to be set.High Pressure Solenoid Valve
Fuel injection quantity control is performed from the
beginning of pressure delivery at the beginning of cam
lift until the high pressure solenoid valve opens at the
end of pressure delivery.
This interval is called the pressure delivery interval.
Accordingly, the interval that the high pressure solenoid
valve is closed determines the fuel injection quantity
(high pressure fuel supply ends when the high pressure
solenoid valve opens).
-Cam Ring Angle
Sensor -Pump Speed
Wheel -Timer PositionPump
Control
Unit
(PSG)Pump
Camshaft
Speed
Sensor
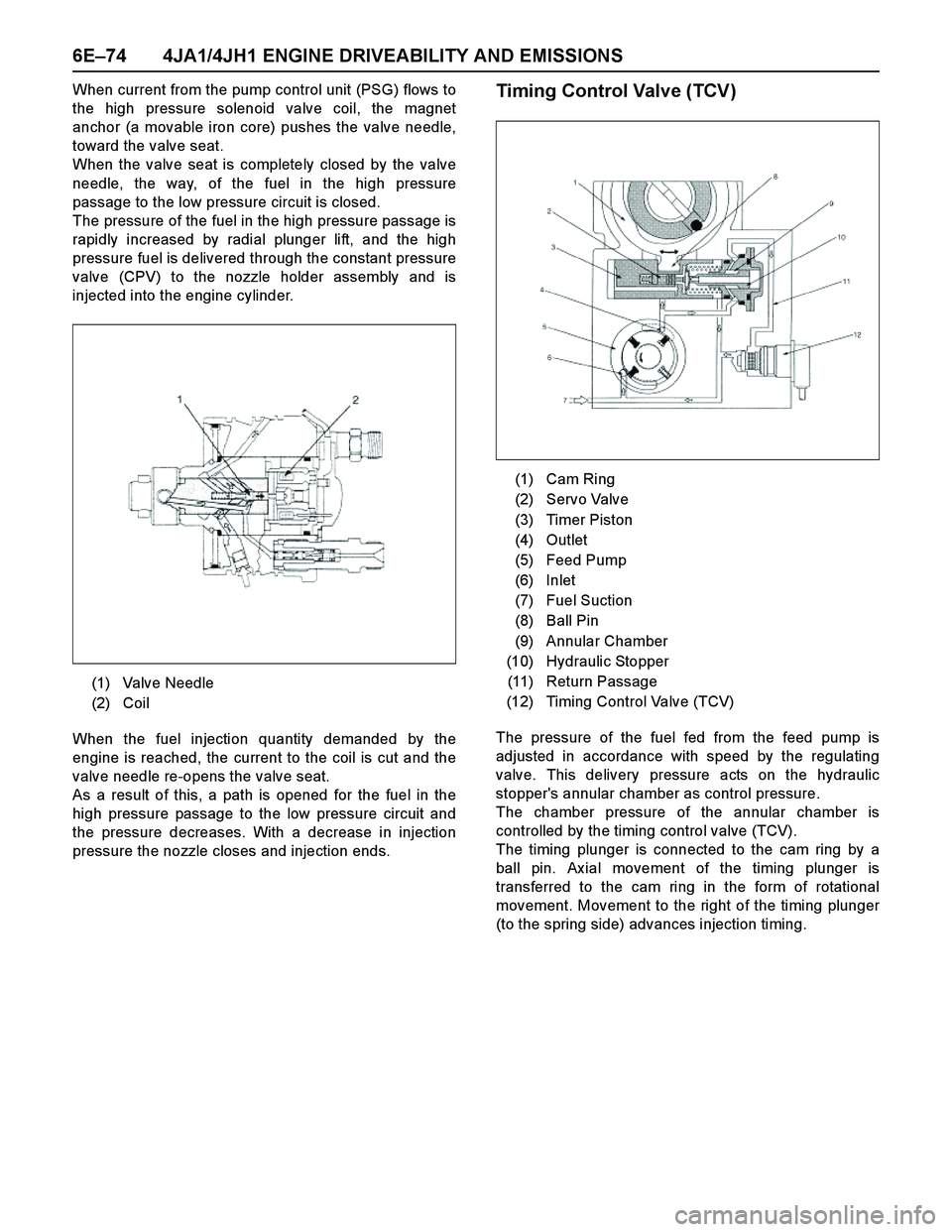
(1) Valve Needle
(2) Magnet Anchor
(3) Coil
(4) High Pressure Passage
Page 1446 of 4264
6E–74 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
When current from the pump control unit (PSG) flows to
the high pressure solenoid valve coil, the magnet
anchor (a movable iron core) pushes the valve needle,
toward the valve seat.
When the valve seat is completely closed by the valve
needle, the way, of the fuel in the high pressure
passage to the low pressure circuit is closed.
The pressure of the fuel in the high pressure passage is
rapidly increased by radial plunger lift, and the high
pressure fuel is delivered through the constant pressure
valve (CPV) to the nozzle holder assembly and is
injected into the engine cylinder.
When the fuel injection quantity demanded by the
engine is reached, the current to the coil is cut and the
valve needle re-opens the valve seat.
As a result of this, a path is opened for the fuel in the
high pressure passage to the low pressure circuit and
the pressure decreases. With a decrease in injection
pressure the nozzle closes and injection ends.Timing Control Valve (TCV)
The pressure of the fuel fed from the feed pump is
adjusted in accordance with speed by the regulating
valve. This delivery pressure acts on the hydraulic
stopper's annular chamber as control pressure.
The chamber pressure of the annular chamber is
controlled by the timing control valve (TCV).
The timing plunger is connected to the cam ring by a
ball pin. Ax ial movement of the timing plunger is
transferred to the cam ring in the form of rotational
movement. Movement to the right of the timing plunger
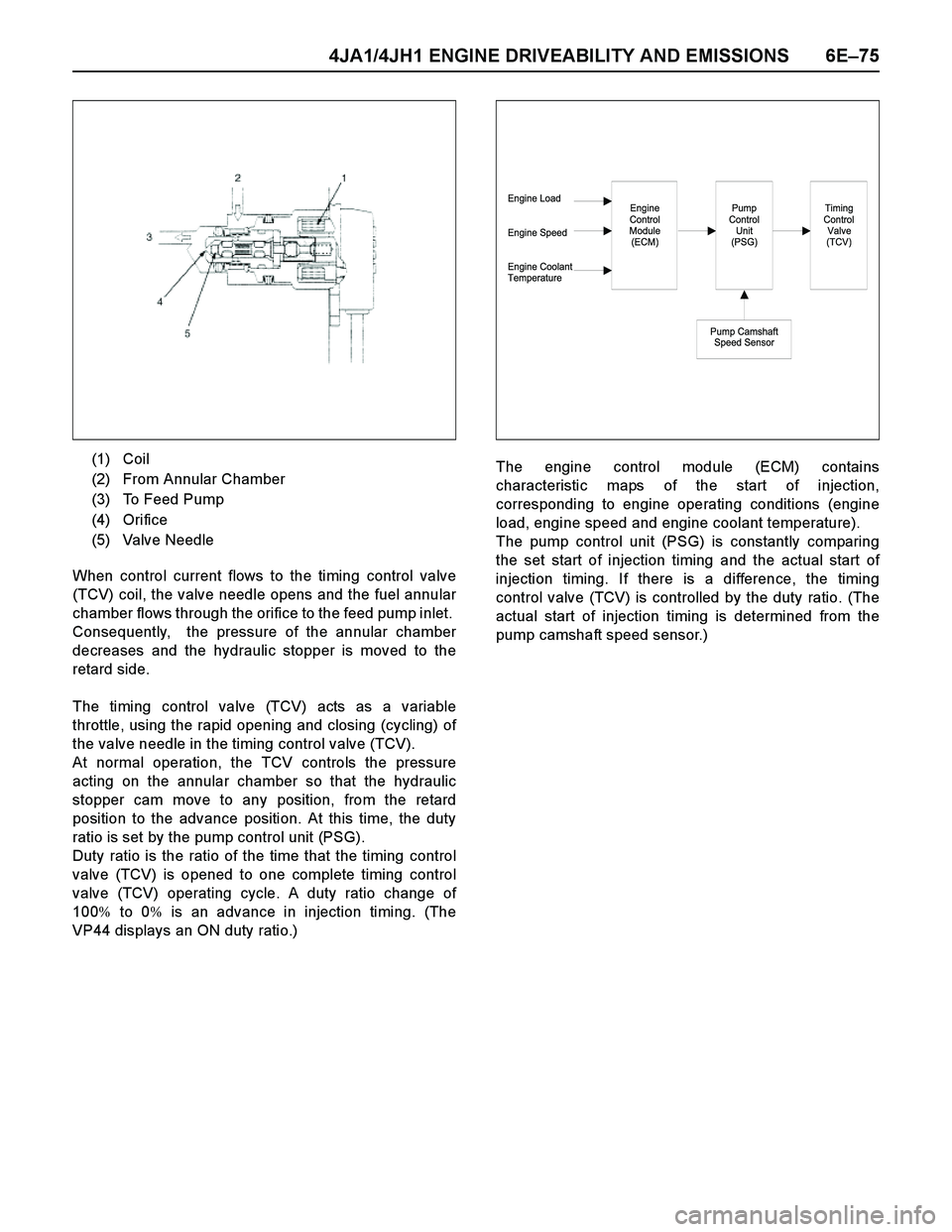
(to the spring side) advances injection timing. (1) Valve Needle
(2) Coil
(1) Cam Ring
(2) Servo Valve
(3) Timer Piston
(4) Outlet
(5) Feed Pump
(6) Inlet
(7) Fuel Suction
(8) Ball Pin
(9) Annular Chamber
(10) Hydraulic Stopper
(11) Return Passage
(12) Timing Control Valve (TCV)
Page 1447 of 4264
4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–75
When control current flows to the timing control valve
(TCV) coil, the valve needle opens and the fuel annular
chamber flows through the orifice to the feed pump inlet.
Consequently, the pressure of the annular chamber
decreases and the hydraulic stopper is moved to the
retard side.
The timing control valve (TCV) acts as a variable
throttle, using the rapid opening and closing (cycling) of
the valve needle in the timing control valve (TCV).
At normal operation, the TCV controls the pressure
acting on the annular chamber so that the hydraulic
stopper cam move to any position, from the retard
position to the advance position. At this time, the duty
ratio is set by the pump control unit (PSG).
Duty ratio is the ratio of the time that the timing control
valve (TCV) is opened to one complete timing control
valve (TCV) operating cycle. A duty ratio change of
100% to 0% is an advance in injection timing. (The
VP44 displays an ON duty ratio.)The engine control module (ECM) contains
characteristic maps of the start of injection,
corresponding to engine operating conditions (engine
load, engine speed and engine coolant temperature).
The pump control unit (PSG) is constantly comparing
the set start of injection timing and the actual start of
injection timing. If there is a difference, the timing
control valve (TCV) is controlled by the duty ratio. (The
actual start of injection timing is determined from the
pump camshaft speed sensor.) (1) Coil
(2) From Annular Chamber
(3) To Feed Pump
(4) Orifice
(5) Valve Needle
Engine Load
Engine Speed
Engine Coolant
TemperatureEngine
Control
Module
(ECM)Pump
Control
Unit
(PSG)
Pump Camshaft
Speed Sensor
Timing
Control
Valve
(TCV)
Page 1460 of 4264
6E–88 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
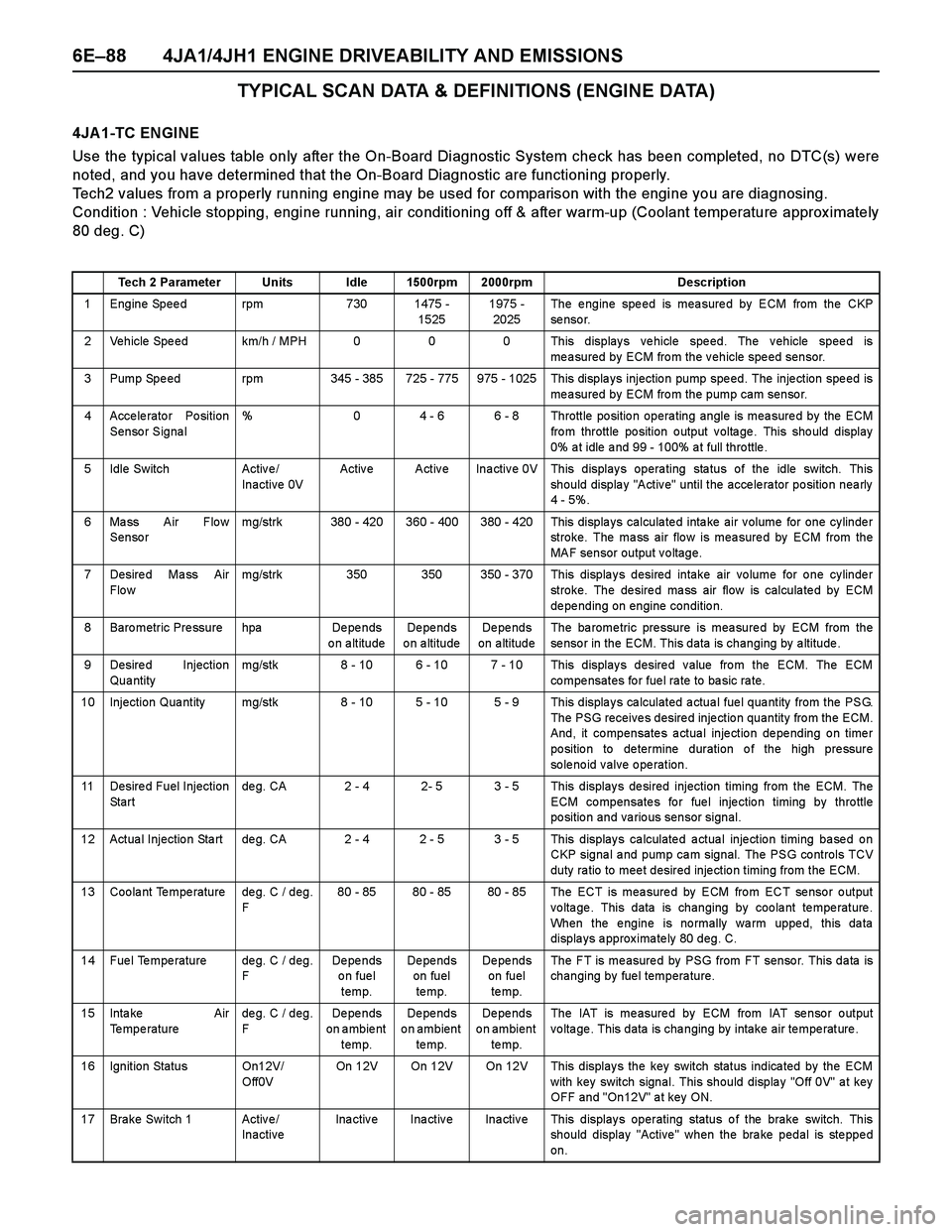
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS (ENGINE DATA)
4JA 1-TC ENGINE
Use the typical values table only after the On-Board Diagnostic System check has been completed, no DTC(s) were
noted, and you have determined that the On-Board Diagnostic are functioning properly.
Tech2 values from a properly running engine may be used for comparison with the engine you are diagnosing.
Condition : Vehicle stopping, engine running, air conditioning off & after warm-up (Coolant temperature approx imately
80 deg. C)
Tech 2 Parameter Units Idle 1500rpm 2000rpm Description
1 Engine Speed rpm 730 1475 -
15251975 -
2025The engine speed is measured by ECM from the CKP
se nso r.
2 Vehicle Speed km/h / MPH 0 0 0 This displays vehicle speed. The vehicle speed is
measured by ECM from the vehicle speed sensor.
3 Pump Spe ed rpm 345 - 385 725 - 775 975 - 1025 This displa ys injectio n pump spe ed. The inje ction spe ed is
measured by ECM from the pump cam sensor.
4 Accelerator Position
Sensor Signal% 0 4 - 6 6 - 8 Throttle position operating angle is measured by the ECM
fro m throttle po sition o utput v olta ge . This sho uld display
0% a t idle a nd 99 - 100% a t full thro ttle .
5 Idle Switch Activ e /
Inactive 0VActive Active Inactive 0V This displays operating status of the idle switch. This
should display "Active" until the accelerator position nearly
4 - 5%.
6 Mass Air Flow
Sensormg/strk 380 - 420 360 - 400 380 - 420 This displays calculated intake air volume for one cylinder
stroke. The mass air flow is measured by ECM from the
MAF sensor output voltage.
7 Desire d Ma ss Air
Flo wmg/strk 350 350 350 - 370 This displays desired intake air volume for one cylinder
stroke. The desired mass air flow is calculated by ECM
de pe nding on engine conditio n.
8 Baro metric Pre ssure hpa De pe nds
on altitudeDe pe nds
o n a ltitudeDe pe nds
on altitudeThe ba rome tric pre ssure is mea sure d by ECM from the
sensor in the ECM. This data is changing by altitude.
9 Desired Injection
Qua ntitymg/stk 8 - 10 6 - 10 7 - 10 This displays desired value from the ECM. The ECM
co mpe nsates fo r fue l ra te to ba sic ra te.
10 Injection Qua ntity mg/stk 8 - 10 5 - 10 5 - 9 This displa y s ca lculated a ctua l fue l qua ntity from the PSG.
The PSG receives desired injection quantity from the ECM.
And, it compensates actual injection depending on timer
po sitio n to de termine duration o f the high pre ssure
solenoid valve operation.
11 Desire d Fuel Injection
St a r tde g. CA 2 - 4 2- 5 3 - 5 This display s de sired injection timing from the ECM. The
ECM compensates for fuel injection timing by throttle
position and various sensor signal.
12 Actua l Injectio n Sta rt de g. CA 2 - 4 2 - 5 3 - 5 This display s ca lculate d a ctua l inje ctio n timing ba se d o n
CKP signa l a nd pump ca m signal. The PSG controls TCV
duty ra tio to mee t desired inje ctio n timing from the ECM.
13 Coolant Temperature deg. C / deg.
F80 - 85 80 - 85 80 - 85 The ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor output
voltage. This data is changing by coolant temperature.
When the engine is normally warm upped, this data
displays approximately 80 deg. C.
14 Fuel Temperature deg. C / deg.
FDe pe nds
on fuel
temp.De pe nds
on fuel
te mp.De pe nds
on fuel
te mp.The FT is measured by PSG from FT sensor. This data is
changing by fuel temperature.
15 Inta ke Air
Temperaturedeg. C / deg.
FDe pe nds
on ambient
temp.De pe nds
on ambient
te mp.De pe nds
on ambient
te mp.The IAT is measured by ECM from IAT sensor output
voltage. This data is changing by intake air temperature.
16 Ignition Status On12V/
Off0VOn 12V On 12V On 12V This displays the key switch status indicated by the ECM
with key switch signal. This should display "Off 0V" at key
OFF and "On12V" at key ON.
17 Brake Switch 1 Active/
InactiveInactive Inactive Inactive This displays operating status of the brake switch. This
should display "Active" when the brake pedal is stepped
on.
Page 1462 of 4264
6E–90 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
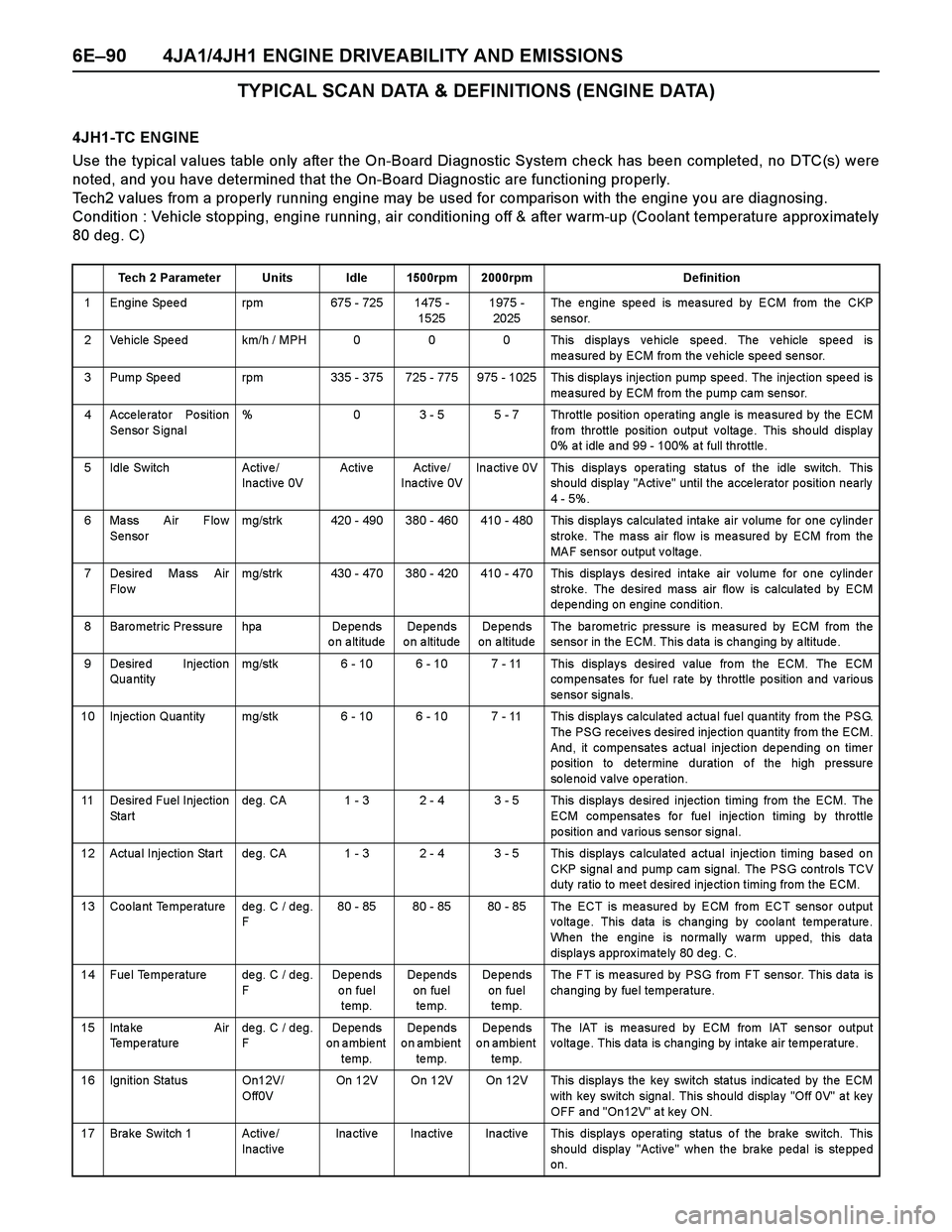
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS (ENGINE DATA)
4JH1-TC ENGINE
Use the typical values table only after the On-Board Diagnostic System check has been completed, no DTC(s) were
noted, and you have determined that the On-Board Diagnostic are functioning properly.
Tech2 values from a properly running engine may be used for comparison with the engine you are diagnosing.
Condition : Vehicle stopping, engine running, air conditioning off & after warm-up (Coolant temperature approx imately
80 deg. C)
Tech 2 Parameter Units Idle 1500rpm 2000rpm Definition
1 Engine Speed rpm 675 - 725 1475 -
15251975 -
2025The engine speed is measured by ECM from the CKP
se nso r.
2 Vehicle Speed km/h / MPH 0 0 0 This displays vehicle speed. The vehicle speed is
measured by ECM from the vehicle speed sensor.
3 Pump Spe ed rpm 335 - 375 725 - 775 975 - 1025 This displa ys injectio n pump spe ed. The inje ction spe ed is
measured by ECM from the pump cam sensor.
4 Accelerator Position
Sensor Signal% 0 3 - 5 5 - 7 Throttle position operating angle is measured by the ECM
fro m throttle po sition o utput v olta ge . This sho uld display
0% a t idle a nd 99 - 100% a t full throttle .
5 Idle Switch Activ e /
Inactive 0VActive Active/
Inactive 0VInactive 0V This displays operating status of the idle switch. This
should display "Active" until the accelerator position nearly
4 - 5%.
6 Mass Air Flow
Sensormg/strk 420 - 490 380 - 460 410 - 480 This displays calculated intake air volume for one cylinder
stroke. The mass air flow is measured by ECM from the
MAF sensor output voltage.
7 Desire d Ma ss Air
Flo wmg/strk 430 - 470 380 - 420 410 - 470 This displays desired intake air volume for one cylinder
stroke. The desired mass air flow is calculated by ECM
de pe nding on engine conditio n.
8 Baro metric Pre ssure hpa De pe nds
on altitudeDe pe nds
o n a ltitudeDe pe nds
on altitudeThe ba rome tric pre ssure is mea sure d by ECM from the
sensor in the ECM. This data is changing by altitude.
9 Desired Injection
Qua ntitymg/stk 6 - 10 6 - 10 7 - 11 This displays desired value from the ECM. The ECM
co mpe nsates for fuel rate by thro ttle po sition a nd va rio us
se nso r signa ls.
10 Injection Qua ntity mg/stk 6 - 10 6 - 10 7 - 11 This displa y s ca lculated a ctua l fue l qua ntity from the PSG.
The PSG receives desired injection quantity from the ECM.
And, it compensates actual injection depending on timer
po sitio n to de termine duration o f the high pre ssure
solenoid valve operation.
11 Desire d Fuel Injection
St a r tde g. CA 1 - 3 2 - 4 3 - 5 This display s de sired injection timing from the ECM. The
ECM compensates for fuel injection timing by throttle
position and various sensor signal.
12 Actua l Injectio n Sta rt de g. CA 1 - 3 2 - 4 3 - 5 This display s ca lculate d a ctua l inje ctio n timing ba se d o n
CKP signa l a nd pump ca m signal. The PSG controls TCV
duty ra tio to mee t desired inje ctio n timing from the ECM.
13 Coolant Temperature deg. C / deg.
F80 - 85 80 - 85 80 - 85 The ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor output
voltage. This data is changing by coolant temperature.
When the engine is normally warm upped, this data
displays approximately 80 deg. C.
14 Fuel Temperature deg. C / deg.
FDe pe nds
on fuel
temp.De pe nds
on fuel
te mp.De pe nds
on fuel
te mp.The FT is measured by PSG from FT sensor. This data is
changing by fuel temperature.
15 Inta ke Air
Temperaturedeg. C / deg.
FDe pe nds
on ambient
temp.De pe nds
on ambient
te mp.De pe nds
on ambient
te mp.The IAT is measured by ECM from IAT sensor output
voltage. This data is changing by intake air temperature.
16 Ignition Status On12V/
Off0VOn 12V On 12V On 12V This displays the key switch status indicated by the ECM
with key switch signal. This should display "Off 0V" at key
OFF and "On12V" at key ON.
17 Brake Switch 1 Active/
InactiveInactive Inactive Inactive This displays operating status of the brake switch. This
should display "Active" when the brake pedal is stepped
on.
Page 1487 of 4264

4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–115
34 P0105 7 ON Vacuum Pressure Sensor
Voltage Supply Circuit High
InputVacuum sensor power
supply voltage is more than
5.2V.1. Fuel injection quantity is
r e d u c e d .
2. ECM use vacuum sensor
output voltage 5.0V
condition as substitute.Vacuum sensor power
supply voltage is below 5.2V.1. Sensor power supply
circuit short to battery
voltage circuit.
2. Vacuum sensor
m a l f u n c t i o n .
3. ECM malfunction.82 — —
9 ON Vacuum Pressure Sensor
Voltage Supply Circuit Low
InputVacuum sensor power
supply voltage is below 4.5V.Vacuum sensor power
supply voltage is more than
4.5V.1. Sensor power supply
circuit short to ground
c i r c u i t .
2. Vacuum sensor
m a l f u n c t i o n .
3. ECM malfunction.82 — —
23 P0110 1 ON Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
Sensor Circuit High InputIAT sensor output voltage is
more than 4.7V.ECM use 0 deg. C conditions
as substitute.IAT sensor output voltage is
below 4.7V.1. Sensor signal circuit
open or short to voltage
c i r c u i t .
2. Sensor ground circuit
open or short to voltage
c i r c u i t .
3. Poor connector
c o n n e c t i o n
4. IAT sensor malfunction.
5. ECM malfunction.8 4 /
92P0100(B)/
P0100(C)
2 ON Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
Sensor Circuit Low InputIAT sensor output voltage is
below 0.3V.IAT sensor output voltage is
more than 0.3V.1. Sensor signal circuit
short to ground circuit.
2. IAT sensor malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction.84 —
14 P0115 1 ON Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) Sensor Circuit High
InputECT sensor output voltage is
more than 4.7V.1. ECM uses fuel
temperature as
s u b s t i t u t e .
2. ECM uses 60 deg. C
condition for injection
t i m i n g c o n t r o l .
3. ECM uses -25 deg. C
condition (4JA1-TC) or -
15 deg. C condition
(4JH1-TC) for glow time
control.ECT sensor output voltage is
below 4.7V.1. Sensor signal circuit
open or short to voltage
c i r c u i t .
2. Sensor ground circuit
open or short to voltage
c i r c u i t .
3. Poor connector
c o n n e c t i o n
4. ECT sensor malfunction.
5. ECM malfunction.8 9 /
93P0105(1)
2 ON Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) Sensor Circuit Low
InputECT sensor output voltage is
below 0.3V.ECT sensor output voltage is
more than 0.3V.1. Sensor signal circuit
short to ground circuit.
2. ECT sensor malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction.89 —
15 P0180 B ON Fuel Temperature Sensor
Circuit Range/PerformanceFT sensor output is high
temperature (more than 150
deg. C) or low temperature
(below -40 deg. C).The ECM use 75 deg. C
conditions as substitute.FT sensor output is correct
temperature range between
150 deg. C and -40 deg. C.1 . E C M m a l f u n c t i o n .
2. PSG (pump control unit)
malfunction.—— Flash
CodeCodeSymptom
CodeMILDTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up) Recovery Condition Related Failure PartsRelated
ECM Pin
No.Related
Multiple
DTC4JA1-TC
(MT)4JH1-TC
(MT)4JH1-TC
(AT)
Page 1488 of 4264

6E–116 4JA1/4JH1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
52 P0215 A ON Fuel Cutoff Solenoid Valve
Malfunction1. Ignition key switch off.
2. Engine speed is below
1 5 0 0 r p m .
3. Vehicle speed is below
1 . 5 k m / h .
4. PSG (pump control unit)
recognizes MAB (fuel
cutoff solenoid valve)
signal from the ECM, but
the MAB could not
operate. 1. MAB (fuel cutoff solenoid
v a l v e ) i s o p e r a t e d .
2. Desired injection quantity
becomes 0mg/strk.No recovery until condition
match in the next ignition key
cycle.1. PSG (pump control unit)
m a l f u n c t i o n .
2. MAB (fuel cutoff solenoid
valve) malfunction.
——
B ON Fuel Cutoff Solenoid Valve
Circuit High InputECM does not command
MAB (fuel cutoff solenoid
valve) signal to the PSG
(pump control unit), but PSG
detected MAB signal line
circuit is high level.Engine does not start. No recovery. 1. MAB (fuel cutoff solenoid
valve) signal circuit short
t o v o l t a g e c i r c u i t .
2. PSG (pump control unit)
malfunction.105 —
C ON Fuel Cutoff Solenoid Valve
Always Active1. Ignition key switch off.
2. Engine speed is below
1 5 0 0 r p m .
3. Vehicle speed is below
1 . 5 k m / h .
4. PSG (pump control unit)
does not recognize MAB
(fuel cutoff solenoid
valve) signal from the
ECM. 1. MAB (fuel cutoff solenoid
v a l v e ) i s o p e r a t e d .
2. Desired injection quantity
becomes 0mg/strk.No recovery until condition
match in the next ignition key
cycle.1. MAB (fuel cutoff solenoid
valve) signal circuit open
or short to ground circuit.
2. PSG (pump control unit)
malfunction.
105 —
D ON Fuel Cutoff Solenoid Valve
Malfunction1. Ignition key switch off.
2. CAN controller does not
operate Bus-off.N o f a i l - s a f e f u n c t i o n . 1 . E C M m a l f u n c t i o n .
2. PSG (pump control unit)
malfunction.——
54 P0216 A ON Injection Timing Control
Circuit Malfunction1. Engine speed is more
t h a n 7 0 0 r p m .
2. Fuel injection quantity is
more than 4mg/stk.
3. Deviation of actual
injection timing and
desired injection timing is
more than +3 deg. CA or
-6 deg. CA for 8 seconds.Fuel injection quantity is
reduced.Deviation of actual injection
timing and desired injection
timing is more than +3 deg.
CA or -6 deg. CA for 8
seconds.1. Timing control valve
m a l f u n c t i o n .
2 . T i m e r p i s t o n s t i c k i n g .
3. Pump camshaft speed
sensor malfunction.——
B ON Injection Timing Control
Circuit Malfunction 1. Engine speed is more
t h a n 2 0 1 4 r p m .
2. Fluctuation of actual
injection timing is more
than +-5.2 deg. CA.1. Engine speed is more
than 2014rpm.
2. Fluctuation of actual
injection timing is more
than +-5.2 deg. CA.1. Insufficient air bleeding of
f u e l l i n e .
2. Fuel filter clogging.
3. Timing control valve
m a l f u n c t i o n .
4. Pump camshaft speed
sensor malfunction. —— Flash
CodeCodeSymptom
CodeMILDTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up) Recovery Condition Related Failure PartsRelated
ECM Pin
No.Related
Multiple
DTC4JA1-TC
(MT)4JH1-TC
(MT)4JH1-TC
(AT)