ABS JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 764 of 3039
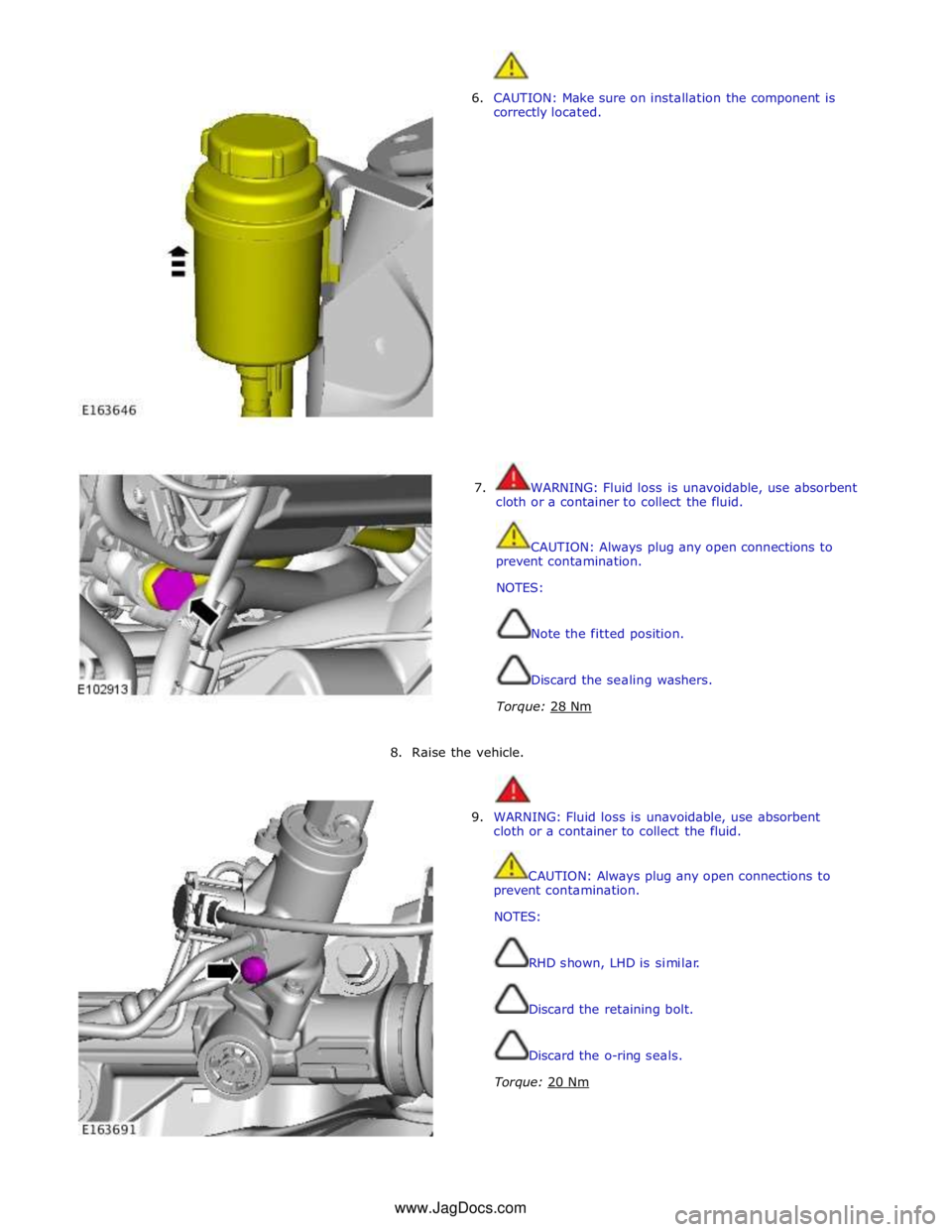
6. CAUTION: Make sure on installation the component is
correctly located.
7. WARNING: Fluid loss is unavoidable, use absorbent
cloth or a container to collect the fluid.
CAUTION: Always plug any open connections to
prevent contamination.
NOTES:
Note the fitted position.
Discard the sealing washers.
Torque: 28 Nm
8. Raise the vehicle.
9. WARNING: Fluid loss is unavoidable, use absorbent
cloth or a container to collect the fluid.
CAUTION: Always plug any open connections to
prevent contamination.
NOTES:
RHD shown, LHD is similar.
Discard the retaining bolt.
Discard the o-ring seals.
Torque: 20 Nm www.JagDocs.com
Page 782 of 3039
16 Ball (12 off) 17 Distance keeper 18 Crash tube The column comprises a cast magnesium mounting bracket which provides the attachment to the cross-beam. Attached to the
mounting bracket is a rake lever which is attached to the mounting bracket at the lower end with two pivot bearings. The
bearings allow the rake lever to rotate upwards or downward to adjust the column rake.
The rake lever also provides for the attachment of the rake housing which can slide within the lever to provide the reach
adjustment. Within the rake housing is the axial housing which is supported on each side with 6 ball bearings which allow the
rake housing to move forward or backwards. The bearings on each side are arranged in groups of 3 bearings and are separated
by a distance keeper which allows the housing to supported on bearings along its length. Within the axial housing is a tube
which is supported at the upper end of the column on the upper bearing. The tube has a central splined hole which provides for
the fitment of the splined shaft. The splined shaft can slide within the tube on the splines when the column reach is adjusted
or the column collapses in a crash condition. The splined shaft also passes rotary motion from the steering wheel through the
length of the column to the outer clamping yoke which is supported on the lower bearing.
The electric steering column lock is attached to the top of the rake lever. A lock bolt within the steering column lock engages in
one of 8 slots in the locking sleeve located at the lower end of the column preventing rotation of the steering wheel. The
locking sleeve is retained by a tolerance ring which in turn is located on the outer diameter of the tube yoke. The tolerance
ring allows a specified amount of torque to be applied to the splined shaft before it slips, preventing damage to the column
lock due to excessive force being applied to the steering wheel when the lock is engaged. The tolerance ring is designed to
slip on the splined shaft when the applied torque exceeds the fitted slip load of 200 Nm minimum. Repeated rotation of the
lock collar will reduce its slipping torque to 100 Nm minimum. The lock is controlled by the CJB.
A steering angle sensor is located at the upper end of the steering column and is attached to the crash adaptor. The sensor
measures steering rotation via a toothed wheel located on the splined tube at the upper end of the column. The sensor
receives a power supply from the CJB and supplies 2 signals (A and B) relating to the steering rotation to the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module. The module transmits this data on the high speed CAN bus for use by other vehicle systems. Refer to: Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist (206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist, Description and Operation).
The steering column is adjustable electrically, for reach and rake. The adjustment mechanism comprises an electric adjustment
motor, a lead screw, a rake solenoid, a reach solenoid, a reach clutch and a rake clutch. The column adjustment is controlled
manually using a joystick switch located on the LH (left-hand) side of the column lower cowl. The joystick can be moved
forward and backward to adjust the column reach in and out and moved up and down to adjust the rake. The switch selection
energizes the adjustment motor in the applicable direction and also engages the applicable solenoid and clutch.
When the joystick switch is rotated to the 'auto' position, the steering column will adjust to the uppermost rake position when
the ignition is switched off. It will re-adjust to the position corresponding to the memory position for the remote handset when
the ignition is switched on.
The memory function of the electric column is linked to and controlled by the driver's seat module. The module provides for the
storage of three separate memory positions which are stored against 3 individual remote handsets.
Refer to: Seats (501-10 Seating, Description and Operation).
The steering wheel locates on a splined shaft in the upper column assembly and is secured with a bolt. The steering wheel
houses the driver's airbag and switches for the audio system, gear change and speed control. A clockspring is used to connect
the steering wheel electrical components to the vehicle harness.
Two plastic shrouds are fitted to the upper column assembly. The lower shroud is fitted with an energy absorbing foam pad to
minimize leg injury in the event of an accident.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 845 of 3039

Item Specification Camshaft journal maximum run out limit (mm) Camshaft journals to end journals 0.03 Camshaft journals to adjacent journals 0.015 Camshaft journal maximum out of round (mm) - all journals 0.005 Torque Specification
NOTE: A = Refer to procedure for correct torque sequence.
Description Nm lb-ft lb-in Engine cover mounting bolts 10 7 - Accessory drive belt tensioner retaining bolt 40 30 - Supercharger belt idler/tensioner bracket retaining bolts 25 18 - Secondary drive belt idler retaining bolts 40 30 - Power steering pump pulley retaining bolts 25 18 - Power steering pump retaining bolts 25 18 - Power steering pump bracket to engine retaining bolts 25 18 - Generator retaining bolts 48 35 - Starter motor retaining bolts 48 35 - Air conditioning compressor retaining bolts 25 18 - Engine mounting to engine mounting bracket retaining nuts 48 35 - Engine mounting to subframe retaining nuts 63 46 - Engine mounting bracket to engine retaining bolts 48 35 - Crankshaft damper pulley retaining LH threaded bolt 200 + 270° 148 + 180° - Flexplate retaining bolts 45 + 90° 33 + 90° - Exhaust manifold heat shield retaining bolts A - - Exhaust manifold retaining bolts A - - Engine wiring harness bracket retaining bolts 10 7 - Coolant outlet pipe 10 7 - Intercooler retaining bolts 25 18 - Intake manifold retaining bolts 25 18 - Oil Cooler retaining bolts 13 10 - Knock sensor (KS) retaining bolt 20 14 - Ignition coil retaining bolts 8 - 71 Spark plugs 20 15 - Fuel rail retaining bolts A - - High pressure fuel pipe retaining bolts A - - High pressure fuel pump retaining bolts 12 9 - Oil filter housing assembly retaining bolts 12 9 - Oil filter cap 28 21 - Lifting eye bolts 25 + 90° 18 + 90° - Manifold absolute pressure and temperature (MAPT) sensor sensor retaining bolts 5 - 44 Coolant pump retaining bolts 12 9 - Variable valve timing (VVT) oil control solenoid retaining bolts 10 7 - Camshaft position (CMP) sensor retaining bolts 10 7 - Camshaft cover retaining bolts 13 10 - Front upper timing cover retaining bolts 12 9 - Front lower timing cover retaining bolts A - - Engine rear cover retaining bolts A - - VVT to camshaft retaining bolts 32 24 - Camshaft bearing caps retaining bolts 11 8 - Primary timing chain fixed guide retaining bolts 12 9 - Primary timing chain tensioner retaining bolts 12 9 - Primary timing chain tensioner guide blade retaining bolts 25 18 - Auxiliary chain tensioner guide retaining bolts 21 15 - Auxiliary chain fixed guide retaining bolt 12 9 - Oil pump sprocket retaining bolt 21 15 - Cylinder head retaining bolts A - - Engine oil level (EOL) sensor retaining bolt 12 9 - Oil pan to oil sump body retaining bolts 12 9 - Oil sump body to engine retaining bolts 25 18 - Oil pan drain plug 23 17 - Oil transfer tube to Oil pan body retaining bolts 11 8 - Oil pump to engine block retaining bolts 25 18 - Pick-up pipe to oil pump retaining bolts 12 9 - Windage tray retaining bolts 25 18 - Piston cooling jet retaining bolts 12 9 - Engine block coolant draining plug 50 37 - Connecting Rod bolts Stage 1 10 7 - Stage 2 50 37 -
Page 1155 of 3039
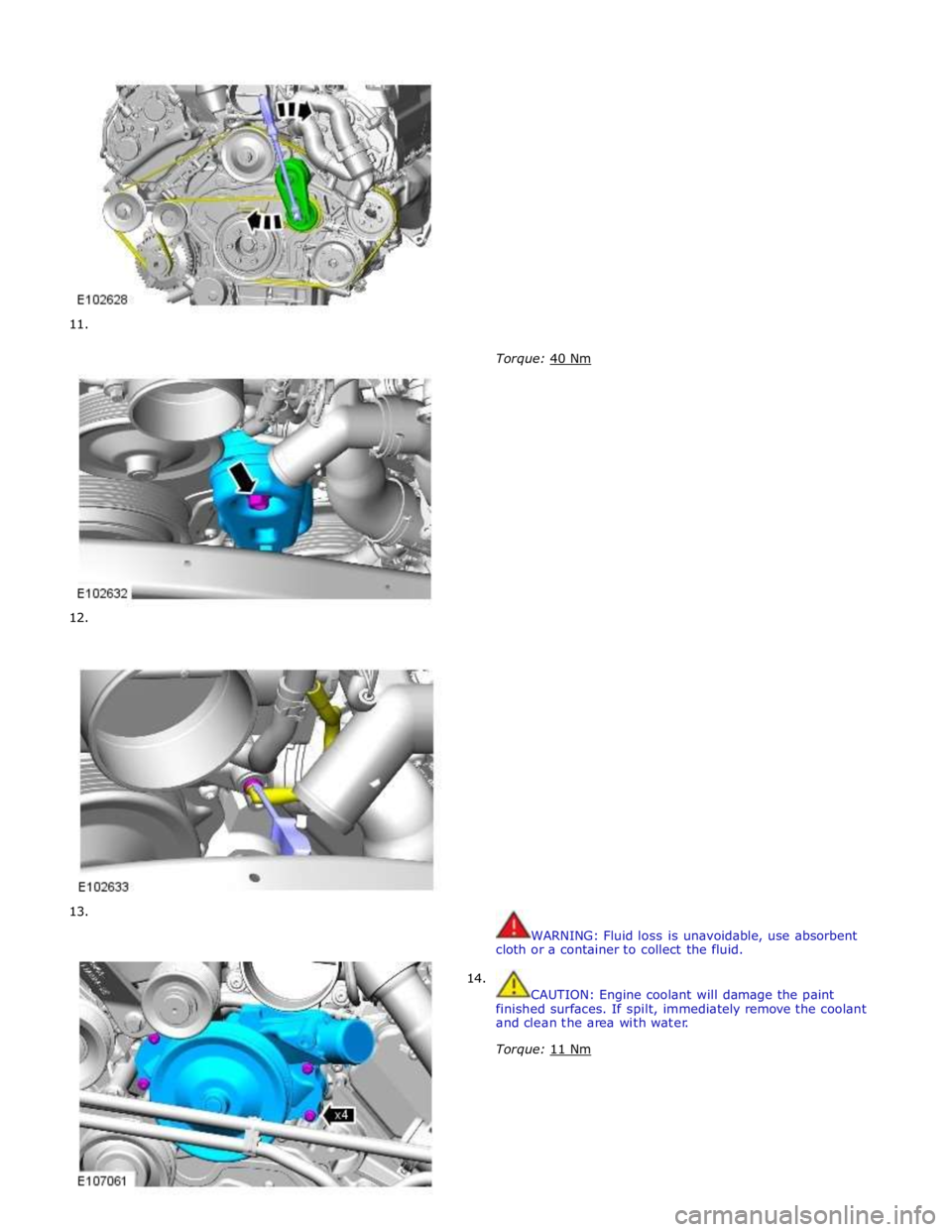
11.
12.
13.
14.
Torque: 40 Nm
WARNING: Fluid loss is unavoidable, use absorbent
cloth or a container to collect the fluid.
CAUTION: Engine coolant will damage the paint
finished surfaces. If spilt, immediately remove the coolant
and clean the area with water.
Torque: 11 Nm
Page 1183 of 3039
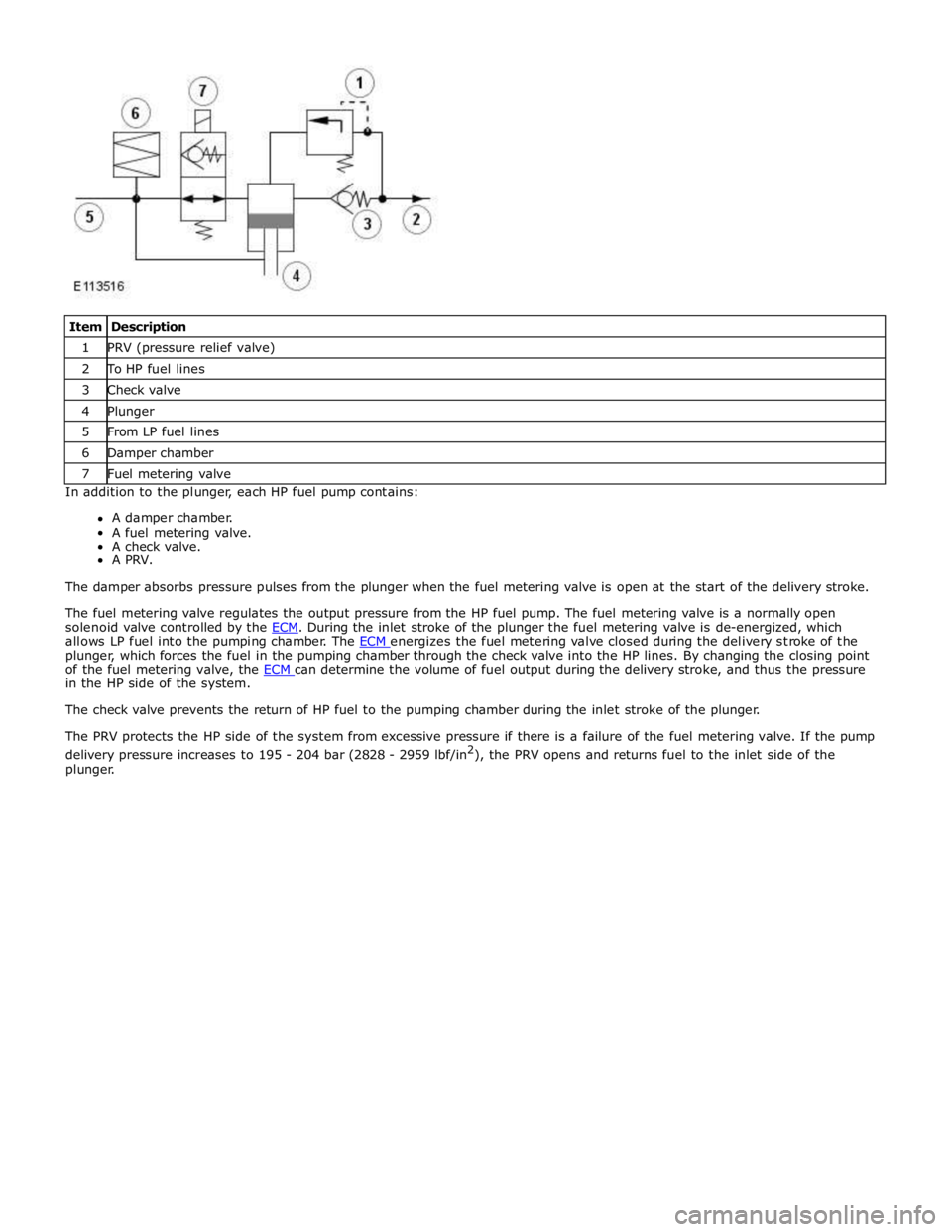
1 PRV (pressure relief valve) 2 To HP fuel lines 3 Check valve 4 Plunger 5 From LP fuel lines 6 Damper chamber 7 Fuel metering valve In addition to the plunger, each HP fuel pump contains:
A damper chamber.
A fuel metering valve.
A check valve.
A PRV.
The damper absorbs pressure pulses from the plunger when the fuel metering valve is open at the start of the delivery stroke.
The fuel metering valve regulates the output pressure from the HP fuel pump. The fuel metering valve is a normally open
solenoid valve controlled by the ECM. During the inlet stroke of the plunger the fuel metering valve is de-energized, which allows LP fuel into the pumping chamber. The ECM energizes the fuel metering valve closed during the delivery stroke of the plunger, which forces the fuel in the pumping chamber through the check valve into the HP lines. By changing the closing point
of the fuel metering valve, the ECM can determine the volume of fuel output during the delivery stroke, and thus the pressure in the HP side of the system.
The check valve prevents the return of HP fuel to the pumping chamber during the inlet stroke of the plunger.
The PRV protects the HP side of the system from excessive pressure if there is a failure of the fuel metering valve. If the pump
delivery pressure increases to 195 - 204 bar (2828 - 2959 lbf/in2
), the PRV opens and returns fuel to the inlet side of the
plunger.
Page 1245 of 3039
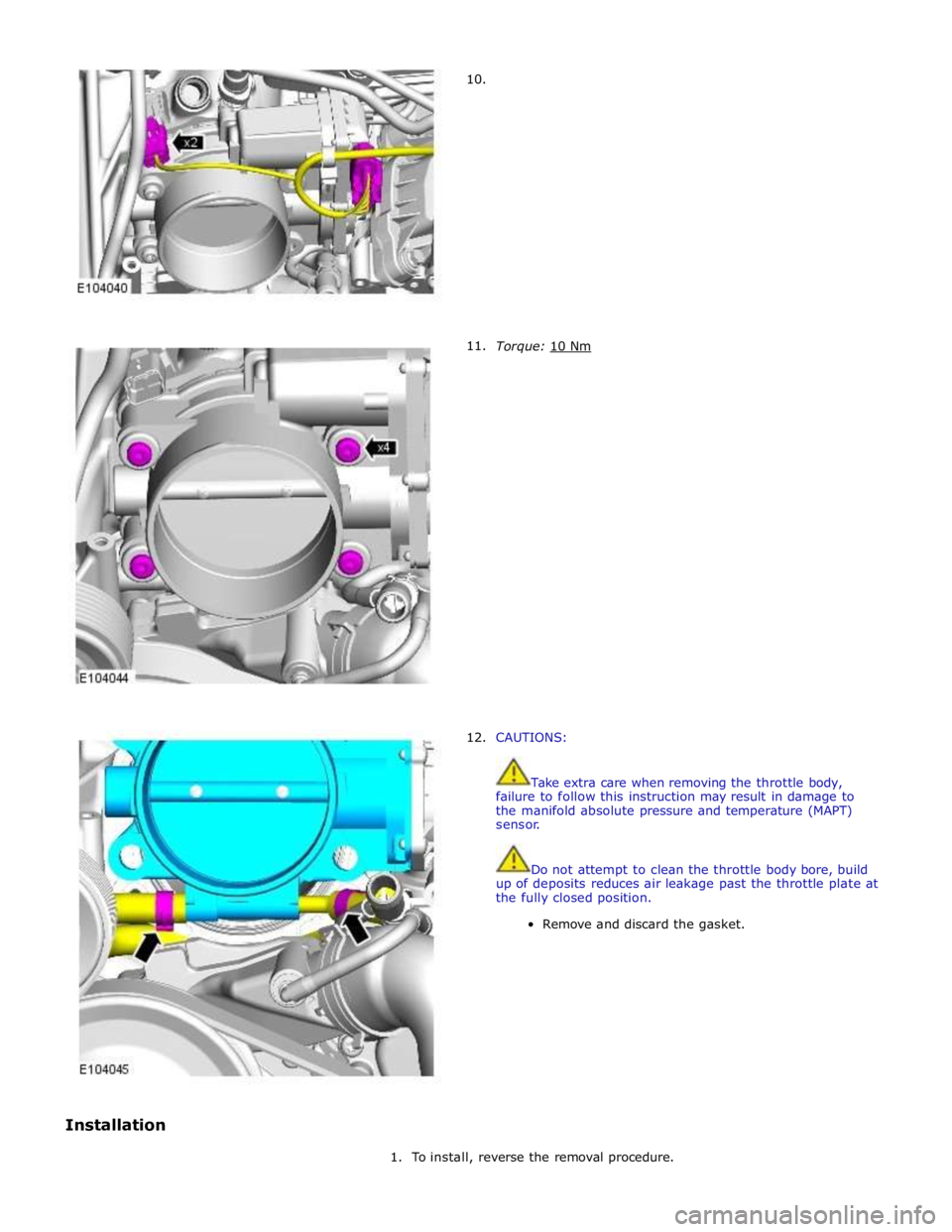
Installation
10.
11.
12.
Torque: 10 Nm
CAUTIONS:
Take extra care when removing the throttle body,
failure to follow this instruction may result in damage to
the manifold absolute pressure and temperature (MAPT)
sensor.
Do not attempt to clean the throttle body bore, build
up of deposits reduces air leakage past the throttle plate at
the fully closed position.
Remove and discard the gasket.
1. To install, reverse the removal procedure.
Page 1285 of 3039

Air cleaner retaining bolts 8 - 71 Supercharger retaining bolts 25 18 - Charge air cooler lower assembly retaining bolts 20 15 - Throttle body retaining studs 10 7 - Charge air cooler top assembly retaining bolts 25 18 - Manifold absolute pressure and temperature (MAPT) sensor 5 - 44 Coolant outlet pipe 11 8 -
Page 1293 of 3039
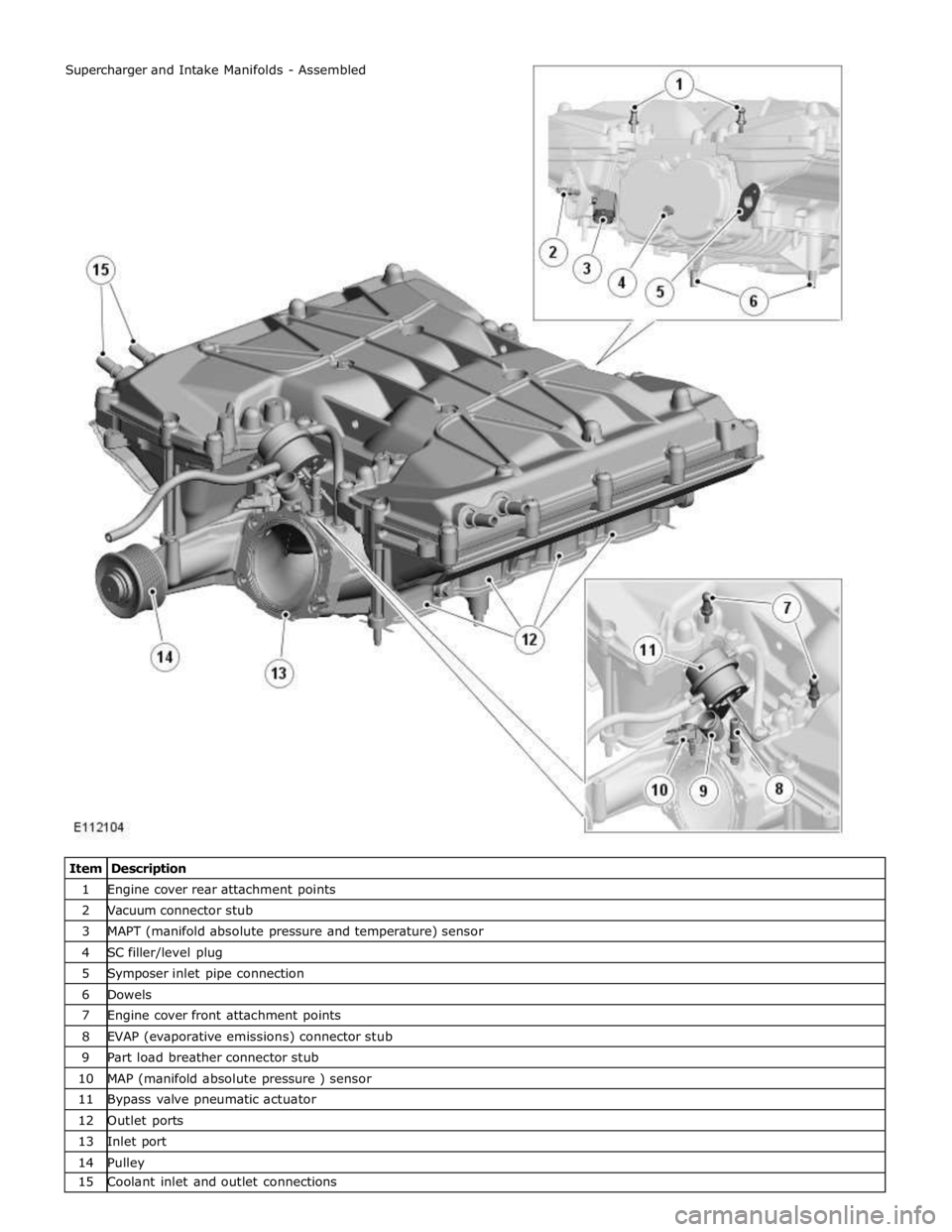
1 Engine cover rear attachment points 2 Vacuum connector stub 3 MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor 4 SC filler/level plug 5 Symposer inlet pipe connection 6 Dowels 7 Engine cover front attachment points 8 EVAP (evaporative emissions) connector stub 9 Part load breather connector stub 10 MAP (manifold absolute pressure ) sensor 11 Bypass valve pneumatic actuator 12 Outlet ports 13 Inlet port 14 Pulley 15 Coolant inlet and outlet connections Supercharger and Intake Manifolds - Assembled
Page 1295 of 3039
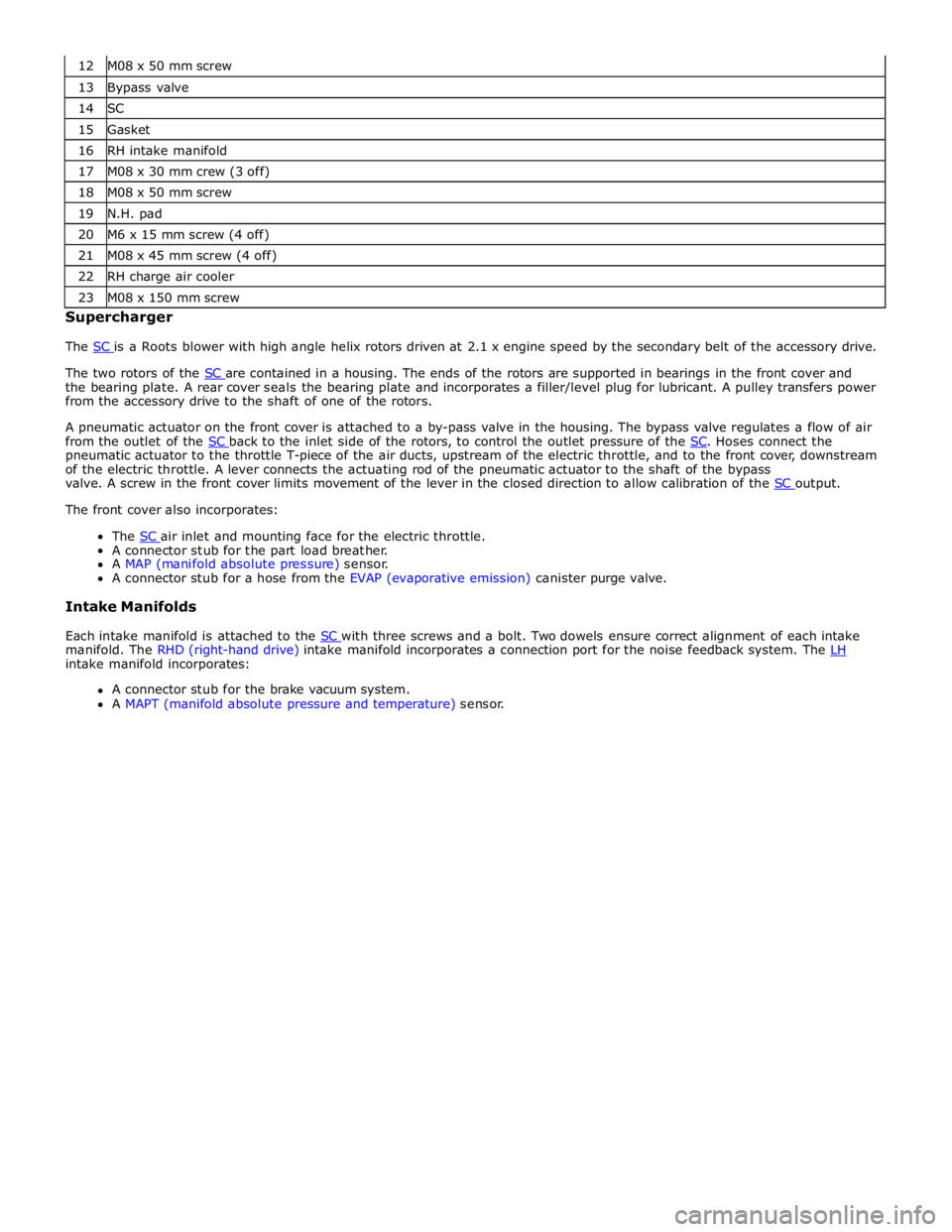
13 Bypass valve 14 SC 15 Gasket 16 RH intake manifold 17 M08 x 30 mm crew (3 off) 18 M08 x 50 mm screw 19 N.H. pad 20 M6 x 15 mm screw (4 off) 21 M08 x 45 mm screw (4 off) 22 RH charge air cooler 23 M08 x 150 mm screw Supercharger
The SC is a Roots blower with high angle helix rotors driven at 2.1 x engine speed by the secondary belt of the accessory drive.
The two rotors of the SC are contained in a housing. The ends of the rotors are supported in bearings in the front cover and the bearing plate. A rear cover seals the bearing plate and incorporates a filler/level plug for lubricant. A pulley transfers power
from the accessory drive to the shaft of one of the rotors.
A pneumatic actuator on the front cover is attached to a by-pass valve in the housing. The bypass valve regulates a flow of air
from the outlet of the SC back to the inlet side of the rotors, to control the outlet pressure of the SC. Hoses connect the pneumatic actuator to the throttle T-piece of the air ducts, upstream of the electric throttle, and to the front cover, downstream
of the electric throttle. A lever connects the actuating rod of the pneumatic actuator to the shaft of the bypass
valve. A screw in the front cover limits movement of the lever in the closed direction to allow calibration of the SC output. The front cover also incorporates:
The SC air inlet and mounting face for the electric throttle. A connector stub for the part load breather.
A MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor.
A connector stub for a hose from the EVAP (evaporative emission) canister purge valve.
Intake Manifolds
Each intake manifold is attached to the SC with three screws and a bolt. Two dowels ensure correct alignment of each intake manifold. The RHD (right-hand drive) intake manifold incorporates a connection port for the noise feedback system. The LH intake manifold incorporates:
A connector stub for the brake vacuum system.
A MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor.
Page 1299 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Intake Air
Distribution and Filtering
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the intake air distribution and filtering system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and
Operation section of the workshop manual. REFER to: (303-12D Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering (Description and Operation), Intake Air Distribution and Filtering (Description and Operation), Intake Air Distribution and Filtering (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Hoses and ducts (damage/connections)
Air cleaner element (contaminated/blocked)
Restricted air intake
Supercharger
Supercharger (cooling fan) drive belt
Supercharger seals and gaskets
Charge air coolers (damage/connection)
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor
Manifold Absolute Pressure/Temperature (MAPT) sensor
Throttle body
Harness (security/damage)
Connections (security/damage)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Vehicle does not
start/hard
starting/poor
performance
Restricted/Blocked air intake
Restricted/Blocked air
cleaner element Clear the restriction. Replace the air cleaner element as necessary.
Refer to the relevant workshop manual section. Excessive intake
noise
Intake pipe
disconnected/damaged after
the air cleaner
Air cleaner assembly
incorrectly
assembled/damaged Check the intake system and hoses for correct installation/damage.
Refer to the relevant workshop manual section. Lack of boost
Supercharger drive belt
broken/slipping
Supercharger fault
Supercharger air intake fault
Major air leakage (after the
supercharger) Check the supercharger and drive belt. Check the charge air coolers.
Refer to the relevant workshop manual section. Noise
Supercharger drive belt
slipping
Supercharger fault
Major air leakage (after the
supercharger) Check the supercharger and drive belt. Remove the supercharger drive
belt and recheck for noise. Turn the supercharger by hand and check
for excessive resistance. Check for excessive play at the supercharger
pulley. Check the charge air coolers. Refer to the relevant workshop
manual section.