transmission JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1533 of 3039
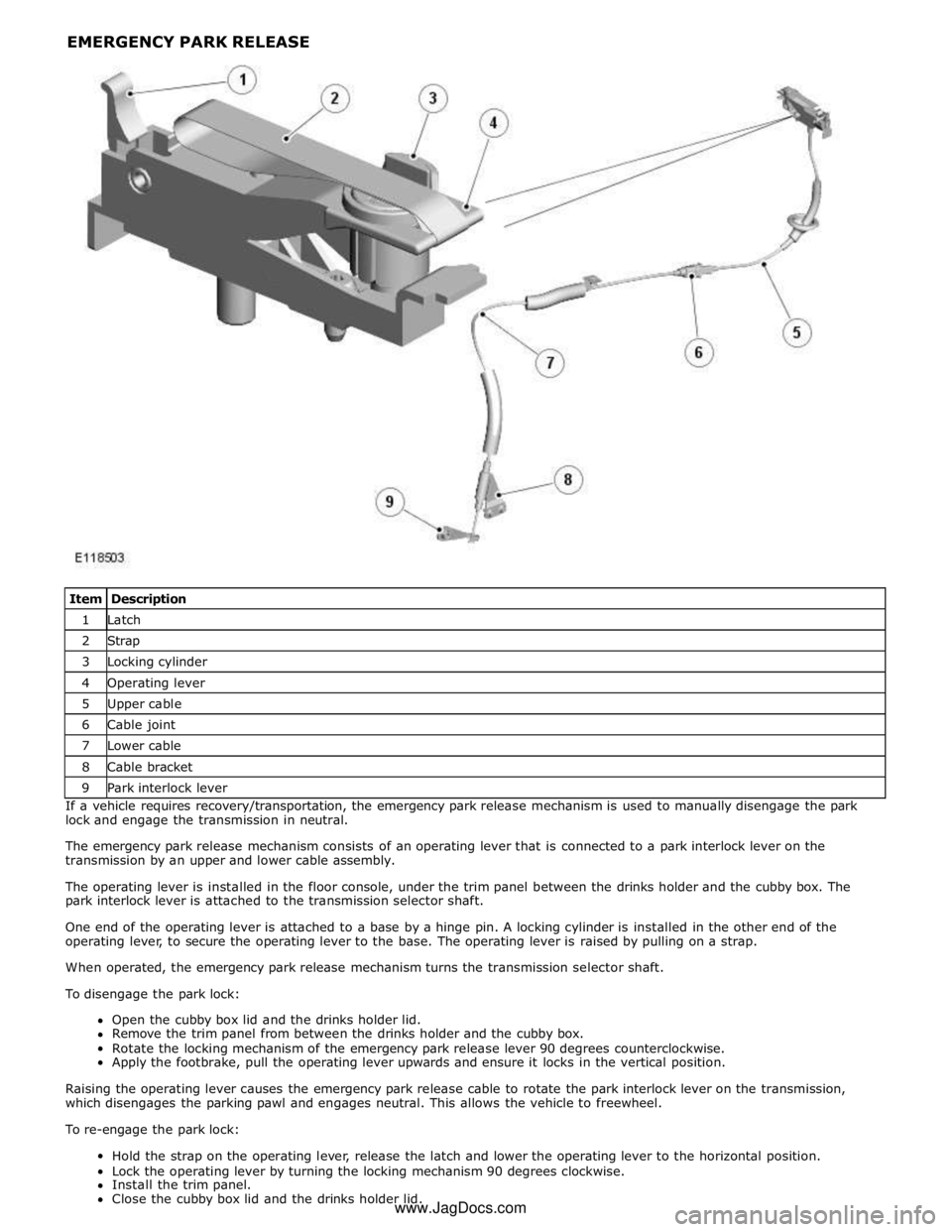
1 Latch 2 Strap 3 Locking cylinder 4 Operating lever 5 Upper cable 6 Cable joint 7 Lower cable 8 Cable bracket 9 Park interlock lever If a vehicle requires recovery/transportation, the emergency park release mechanism is used to manually disengage the park
lock and engage the transmission in neutral.
The emergency park release mechanism consists of an operating lever that is connected to a park interlock lever on the
transmission by an upper and lower cable assembly.
The operating lever is installed in the floor console, under the trim panel between the drinks holder and the cubby box. The
park interlock lever is attached to the transmission selector shaft.
One end of the operating lever is attached to a base by a hinge pin. A locking cylinder is installed in the other end of the
operating lever, to secure the operating lever to the base. The operating lever is raised by pulling on a strap.
When operated, the emergency park release mechanism turns the transmission selector shaft.
To disengage the park lock:
Open the cubby box lid and the drinks holder lid.
Remove the trim panel from between the drinks holder and the cubby box.
Rotate the locking mechanism of the emergency park release lever 90 degrees counterclockwise.
Apply the footbrake, pull the operating lever upwards and ensure it locks in the vertical position.
Raising the operating lever causes the emergency park release cable to rotate the park interlock lever on the transmission,
which disengages the parking pawl and engages neutral. This allows the vehicle to freewheel.
To re-engage the park lock:
Hold the strap on the operating lever, release the latch and lower the operating lever to the horizontal position.
Lock the operating lever by turning the locking mechanism 90 degrees clockwise.
Install the trim panel.
Close the cubby box lid and the drinks holder lid. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1534 of 3039

Published: 19-Jun-2013
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle External Controls - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - External Controls
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the transmission external controls, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the
workshop manual. REFER to: (307-05)
External Controls (Description and Operation),
External Controls (Description and Operation),
External Controls (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Check for stuck/jammed switches and buttons
Visibly damaged or worn components
Loose or missing fasteners
Fuse(s)
Loose or corroded electrical connector(s)
Transmission control module
Transmission control switch
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
DTC Index
For a list of DTCs that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.
REFER to: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Transmission Control Module (TCM) (100-00, Description and Operation)
/
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Transmission Control Switch (TCS) (100-00, Description and Operation).
Page 1535 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle External Controls - V6 3.0L Petrol -
Transmission Control Switch (TCS)
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain inst allation details.
Refer to: Batt ery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and
Cables, General Procedures). 1.
Refer to: Audio and Climate Control Assembly (415-01A Informat ion and
Entert ainment Syst em, Removal and Installat ion). 2.3.4.
Page 1538 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle External Controls - V6 3.0L Petrol -
Transmission Control Switch (TCS) Knob
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain inst allation details.
Start the engine and make sure that 'P' is selected.1.T orque: 2 Nm 2.
Installation
To inst all, reverse t he removal procedure. 1.www.JagDocs.com
Page 1539 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle External Controls - V6 3.0L Petrol -
Emergency Park Position Release Lever
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain inst allation details.
Refer to: Batt ery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and
Cables, General Procedures). 1.
Refer to: Air Deflector (501-02, Removal and Installation). 2.
Refer to: Engine Rear Undershield (501-02 Front End Body Panels,
Removal and Installation). 3.
Refer to: Floor Console Side Trim Panel (501-12 Inst rument Panel and
Console, Removal and Installation). 4.WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle
stands.
T orque: 11 Nm 5.
Page 1542 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle External Controls - V6 3.0L Petrol - Upshift
Paddle Switch
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain inst allation details.T orque: 3 Nm 1.2.
Installation
NOTE: Make sure the wiring harness is routed correct ly. 1.To inst all, reverse t he removal procedure.
Page 1543 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle External Controls - V6 3.0L Petrol -
Downshift Paddle Switch
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain inst allation details.T orque: 3 Nm 1.2.
Installation
NOTE: Make sure the wiring harness is routed correct ly. 1.To inst all, reverse t he removal procedure.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1597 of 3039
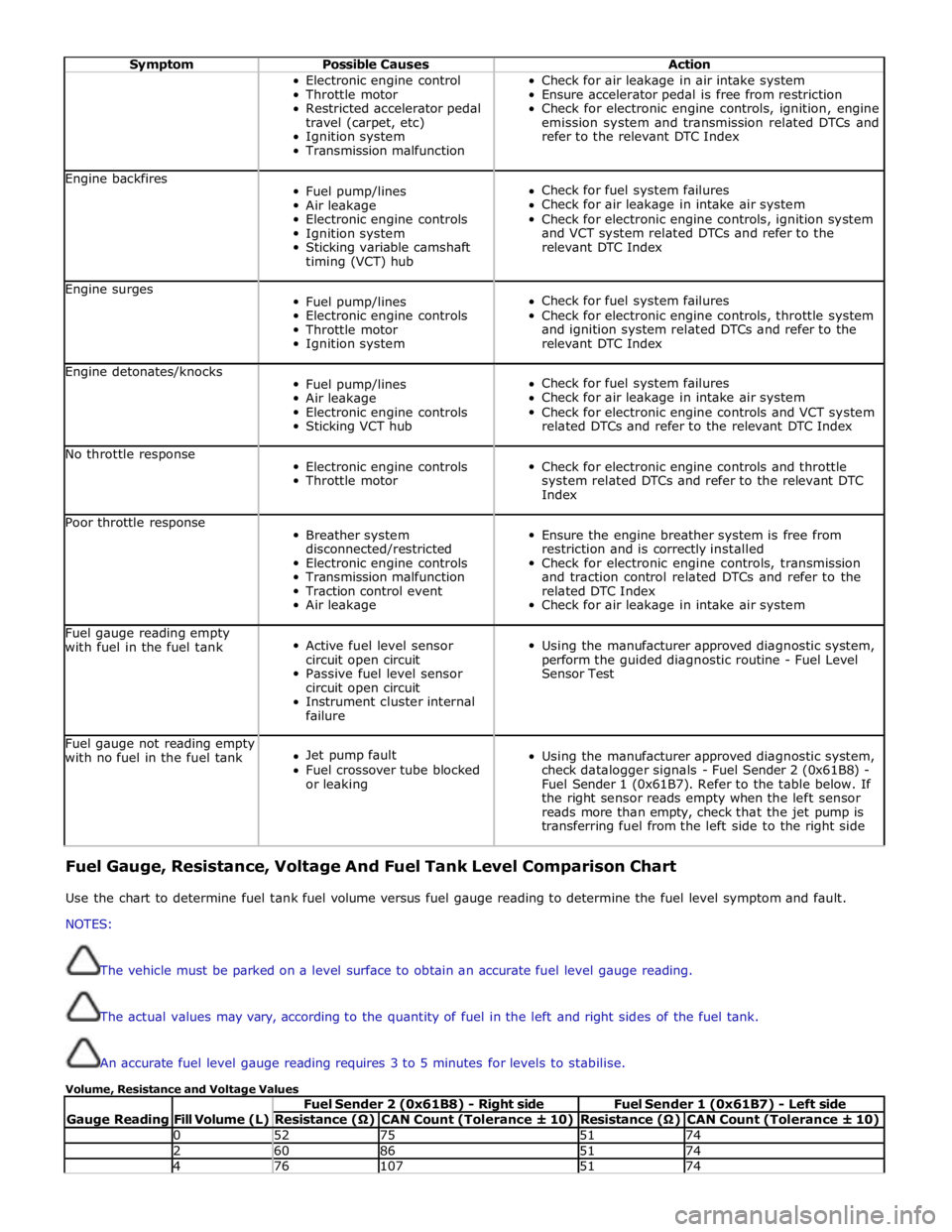
Symptom Possible Causes Action Electronic engine control
Throttle motor
Restricted accelerator pedal
travel (carpet, etc)
Ignition system
Transmission malfunction Check for air leakage in air intake system
Ensure accelerator pedal is free from restriction
Check for electronic engine controls, ignition, engine
emission system and transmission related DTCs and
refer to the relevant DTC Index Engine backfires
Fuel pump/lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
Sticking variable camshaft
timing (VCT) hub
Check for fuel system failures
Check for air leakage in intake air system
Check for electronic engine controls, ignition system
and VCT system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine surges
Fuel pump/lines
Electronic engine controls
Throttle motor
Ignition system
Check for fuel system failures
Check for electronic engine controls, throttle system
and ignition system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine detonates/knocks
Fuel pump/lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Sticking VCT hub
Check for fuel system failures
Check for air leakage in intake air system
Check for electronic engine controls and VCT system
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC Index No throttle response
Electronic engine controls
Throttle motor
Check for electronic engine controls and throttle
system related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC
Index Poor throttle response
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
Electronic engine controls
Transmission malfunction
Traction control event
Air leakage
Ensure the engine breather system is free from
restriction and is correctly installed
Check for electronic engine controls, transmission
and traction control related DTCs and refer to the
related DTC Index
Check for air leakage in intake air system Fuel gauge reading empty
with fuel in the fuel tank
Active fuel level sensor
circuit open circuit
Passive fuel level sensor
circuit open circuit
Instrument cluster internal
failure
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system,
perform the guided diagnostic routine - Fuel Level
Sensor Test Fuel gauge not reading empty
with no fuel in the fuel tank
Jet pump fault
Fuel crossover tube blocked
or leaking
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system,
check datalogger signals - Fuel Sender 2 (0x61B8) -
Fuel Sender 1 (0x61B7). Refer to the table below. If
the right sensor reads empty when the left sensor
reads more than empty, check that the jet pump is
transferring fuel from the left side to the right side Fuel Gauge, Resistance, Voltage And Fuel Tank Level Comparison Chart
Use the chart to determine fuel tank fuel volume versus fuel gauge reading to determine the fuel level symptom and fault.
NOTES:
The vehicle must be parked on a level surface to obtain an accurate fuel level gauge reading.
The actual values may vary, according to the quantity of fuel in the left and right sides of the fuel tank.
An accurate fuel level gauge reading requires 3 to 5 minutes for levels to stabilise.
Volume, Resistance and Voltage Values
Gauge Reading
Fill Volume (L) Fuel Sender 2 (0x61B8) - Right side Fuel Sender 1 (0x61B7) - Left side Resistance (Ω) CAN Count (Tolerance ± 10) Resistance (Ω) CAN Count (Tolerance ± 10) 0 52 75 51 74 2 60 86 51 74 4 76 107 51 74
Page 1607 of 3039
11.
12. NOTE: On vehicles with supercharger, detach the lower
electric connector from the retaining bracket as well as the
electrical connector indicated.
13.
jack.
WARNING: Secure the component to the transmission
CAUTION: Use suitable packing material to prevent
damage to the component.
Torque: 35 Nm
14. NOTE: Do not disassemble further if the component is
removed for access only.
Page 1641 of 3039

6 Clockspring 7 APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor 8 Electric throttle actuator 9 Brake lamp/brake test switch 10 Adaptive speed control radar sensor 11 Diagnostic socket 12 Instrument cluster 13 TCM (transmission control module) 14 Adaptive speed control module
SPEED CONTROL System Operation
The speed control system uses inputs from the brake lamp/brake test switch, the APP sensor, the ECM and the ABS module.
Speed control is operated by the driver using only the steering wheel switches. When speed control is active, the ECM regulates the PWM (pulse width modulation) signals to the fuel injectors to adjust the fuel supply as required to maintain the
set speed.
During speed control operation, the ECM controls vehicle speed by adjusting fuel injection duration and timing. When the accelerator pedal is pressed with speed control active, the ECM outputs a calculated throttle angle signal in place of the actual throttle angle signals produced by the APP sensor. The calculated throttle angle is derived from fuel demand.
The minimum set speed for speed control is 18 mph (30 (km/h). Speed control is automatically suspended if the following
conditions apply:
Vehicle speed falls below 18 mph (30 km/h)
The brake pedal is pressed
The cancel button is pressed
Neutral, park or reverse gear is selected
The difference between actual speed and the set speed is too great
If the engine speed becomes near to the red line (maximum engine speed)
If the accelerator pedal is used to accelerate beyond the set speed for too long.
ADAPTIVE SPEED CONTROL
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM
Electric throttle actuator
ABS module and pump Adaptive speed control warning indicator.
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained. The
driver can chose between four gap settings, 1, 1.4, 1.8 and 2.2 seconds.
The system will detect but not react to the following:
Vehicles in the oncoming lane
Stationary vehicles
Pedestrians
Vehicles not in the same lane.
Adaptive speed control is active when the vehicle is moving. Adaptive Speed Control only functions when a set speed is
entered in normal speed control mode. The adaptive speed control system only intervenes with the set speed when it detects
a target vehicle, and then only if the minimum time gap is breached.
It is important to note that the system is intended for use in limited driving situations, does not remove control and
responsibility from the driver, and at all times can be quickly overridden. The adaptive speed control system is not a collision
warning system and will not react to stationary objects. The system does not operate below a minimum speed of
approximately 30 km/h (20 mph) since it is unsuitable for use in cities or congested traffic. The system is best suited to main
roads/ highways with gradual bends.
The ECM, throttle body and throttle control are unchanged from those used for non adaptive speed control variants.
The adaptive speed control system is based on the use of a front mounted radar sensor. The sensor transmits a 1.5° wide
beam forward of the vehicle and detects the returning signals reflected off other vehicles and objects ahead.
The 1.5° wide radar beam is mechanically scanned at a rate of 10 sweeps/second across a total arc of 15° centered on the