Map sensor JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1295 of 3039
13 Bypass valve 14 SC 15 Gasket 16 RH intake manifold 17 M08 x 30 mm crew (3 off) 18 M08 x 50 mm screw 19 N.H. pad 20 M6 x 15 mm screw (4 off) 21 M08 x 45 mm screw (4 off) 22 RH charge air cooler 23 M08 x 150 mm screw Supercharger
The SC is a Roots blower with high angle helix rotors driven at 2.1 x engine speed by the secondary belt of the accessory drive.
The two rotors of the SC are contained in a housing. The ends of the rotors are supported in bearings in the front cover and the bearing plate. A rear cover seals the bearing plate and incorporates a filler/level plug for lubricant. A pulley transfers power
from the accessory drive to the shaft of one of the rotors.
A pneumatic actuator on the front cover is attached to a by-pass valve in the housing. The bypass valve regulates a flow of air
from the outlet of the SC back to the inlet side of the rotors, to control the outlet pressure of the SC. Hoses connect the pneumatic actuator to the throttle T-piece of the air ducts, upstream of the electric throttle, and to the front cover, downstream
of the electric throttle. A lever connects the actuating rod of the pneumatic actuator to the shaft of the bypass
valve. A screw in the front cover limits movement of the lever in the closed direction to allow calibration of the SC output. The front cover also incorporates:
The SC air inlet and mounting face for the electric throttle. A connector stub for the part load breather.
A MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor.
A connector stub for a hose from the EVAP (evaporative emission) canister purge valve.
Intake Manifolds
Each intake manifold is attached to the SC with three screws and a bolt. Two dowels ensure correct alignment of each intake manifold. The RHD (right-hand drive) intake manifold incorporates a connection port for the noise feedback system. The LH intake manifold incorporates:
A connector stub for the brake vacuum system.
A MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor.
Page 1299 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Intake Air
Distribution and Filtering
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the intake air distribution and filtering system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and
Operation section of the workshop manual. REFER to: (303-12D Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering (Description and Operation), Intake Air Distribution and Filtering (Description and Operation), Intake Air Distribution and Filtering (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Hoses and ducts (damage/connections)
Air cleaner element (contaminated/blocked)
Restricted air intake
Supercharger
Supercharger (cooling fan) drive belt
Supercharger seals and gaskets
Charge air coolers (damage/connection)
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor
Manifold Absolute Pressure/Temperature (MAPT) sensor
Throttle body
Harness (security/damage)
Connections (security/damage)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Vehicle does not
start/hard
starting/poor
performance
Restricted/Blocked air intake
Restricted/Blocked air
cleaner element Clear the restriction. Replace the air cleaner element as necessary.
Refer to the relevant workshop manual section. Excessive intake
noise
Intake pipe
disconnected/damaged after
the air cleaner
Air cleaner assembly
incorrectly
assembled/damaged Check the intake system and hoses for correct installation/damage.
Refer to the relevant workshop manual section. Lack of boost
Supercharger drive belt
broken/slipping
Supercharger fault
Supercharger air intake fault
Major air leakage (after the
supercharger) Check the supercharger and drive belt. Check the charge air coolers.
Refer to the relevant workshop manual section. Noise
Supercharger drive belt
slipping
Supercharger fault
Major air leakage (after the
supercharger) Check the supercharger and drive belt. Remove the supercharger drive
belt and recheck for noise. Turn the supercharger by hand and check
for excessive resistance. Check for excessive play at the supercharger
pulley. Check the charge air coolers. Refer to the relevant workshop
manual section.
Page 1319 of 3039

Published: 30-Jan-2014
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Supercharger
Removal and Installation
Special Tool(s)
303-1449-01
Supercharger Installation Guide Pins - Threaded
303-1449-02
Supercharger Installation Guide Pins - Unthreaded Removal
CAUTION: If a new cylinder head has been installed, then new taptite bolts must be used to install the supercharger.
NOTES:
New taptite bolts when used cut their own threads on the first application.
Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
2. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Charge Air Cooler (303-12D Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
4. Refer to: Throttle Body (303-04E Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
5. Refer to: Supercharger Belt (303-05 Accessory Drive - 5.0L, Removal and
Installation).
6. Refer to: Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
Page 1353 of 3039
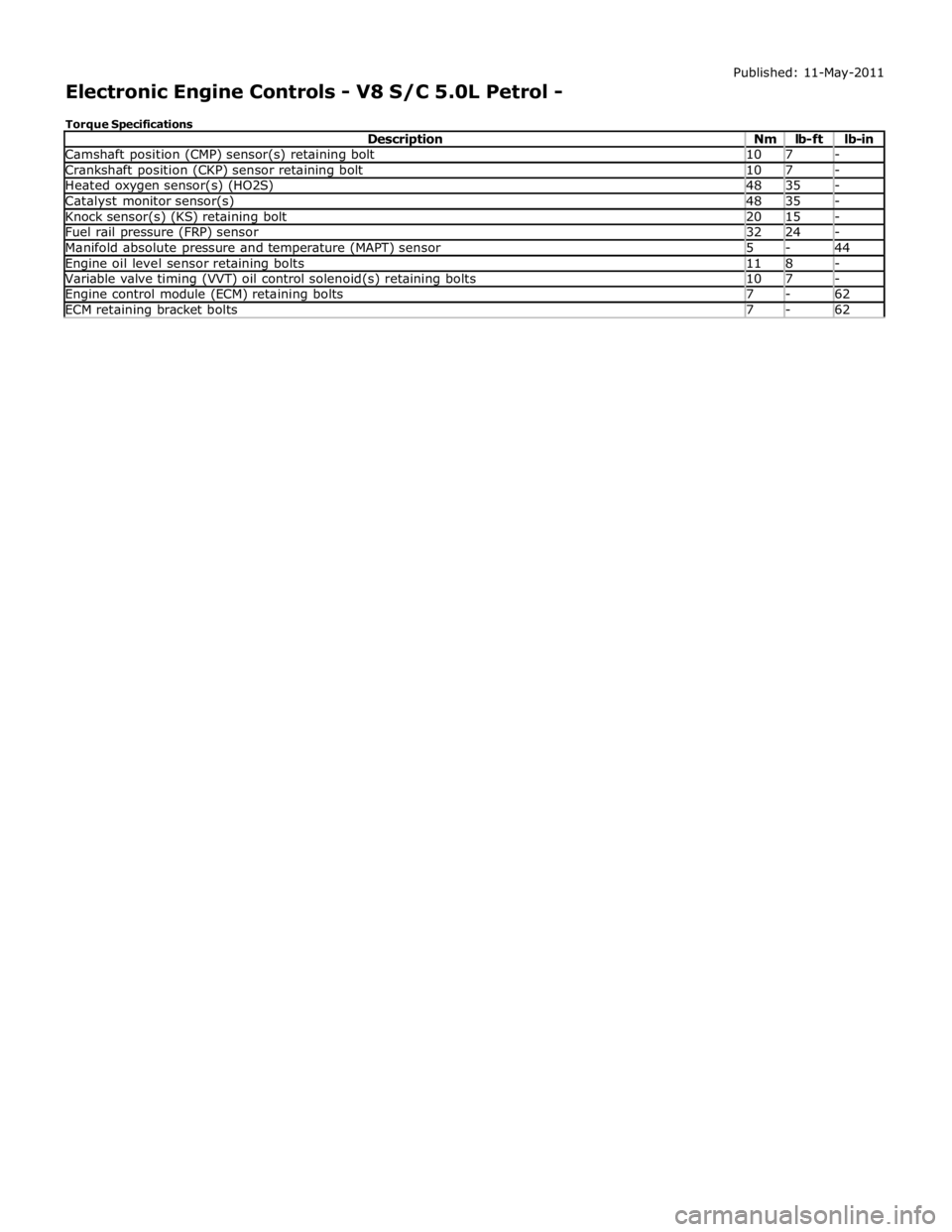
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor(s) retaining bolt 10 7 - Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor retaining bolt 10 7 - Heated oxygen sensor(s) (HO2S) 48 35 - Catalyst monitor sensor(s) 48 35 - Knock sensor(s) (KS) retaining bolt 20 15 - Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor 32 24 - Manifold absolute pressure and temperature (MAPT) sensor 5 - 44 Engine oil level sensor retaining bolts 11 8 - Variable valve timing (VVT) oil control solenoid(s) retaining bolts 10 7 - Engine control module (ECM) retaining bolts 7 - 62 ECM retaining bracket bolts 7 - 62
Page 1354 of 3039
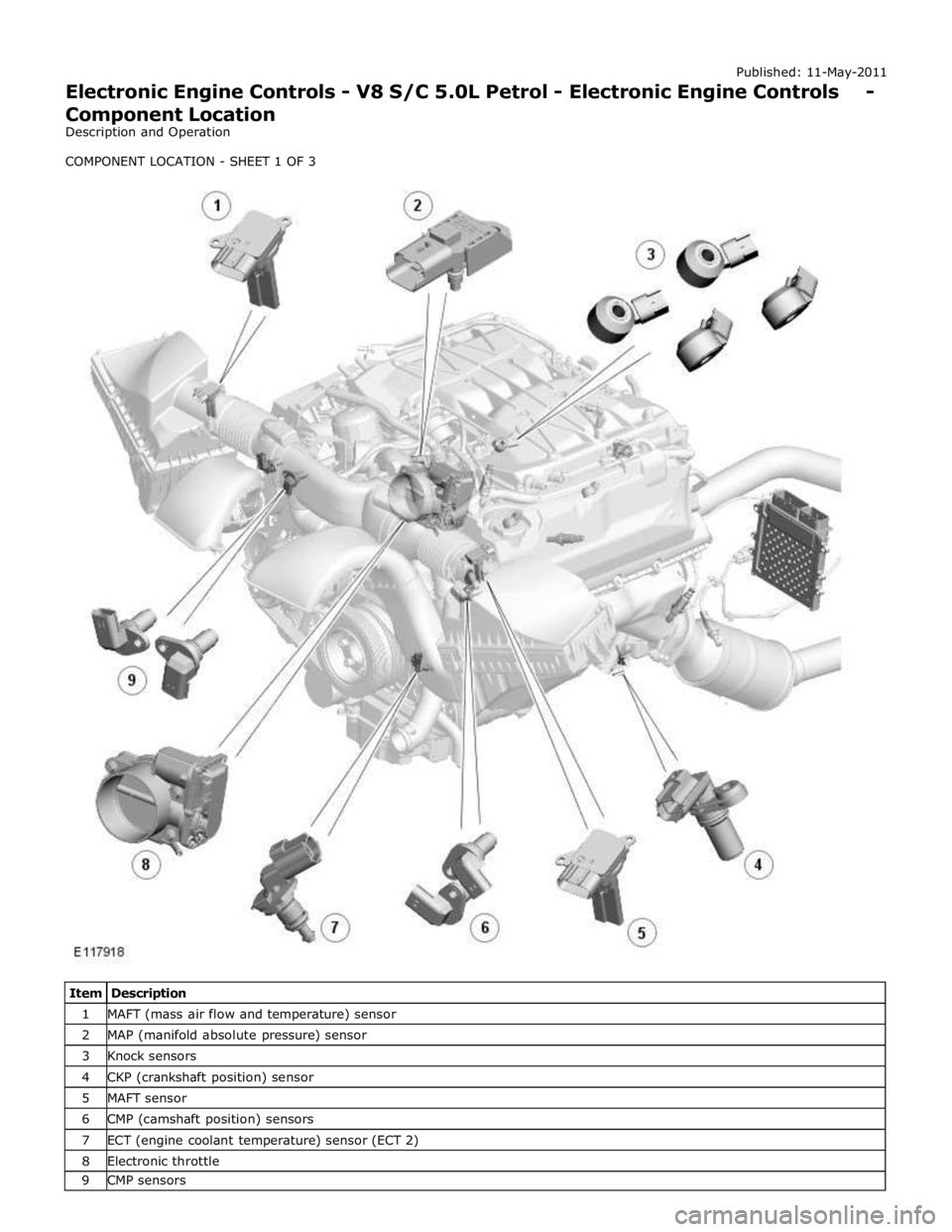
1 MAFT (mass air flow and temperature) sensor 2 MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor 3 Knock sensors 4 CKP (crankshaft position) sensor 5 MAFT sensor 6 CMP (camshaft position) sensors 7 ECT (engine coolant temperature) sensor (ECT 2) 8 Electronic throttle 9 CMP sensors
Page 1355 of 3039
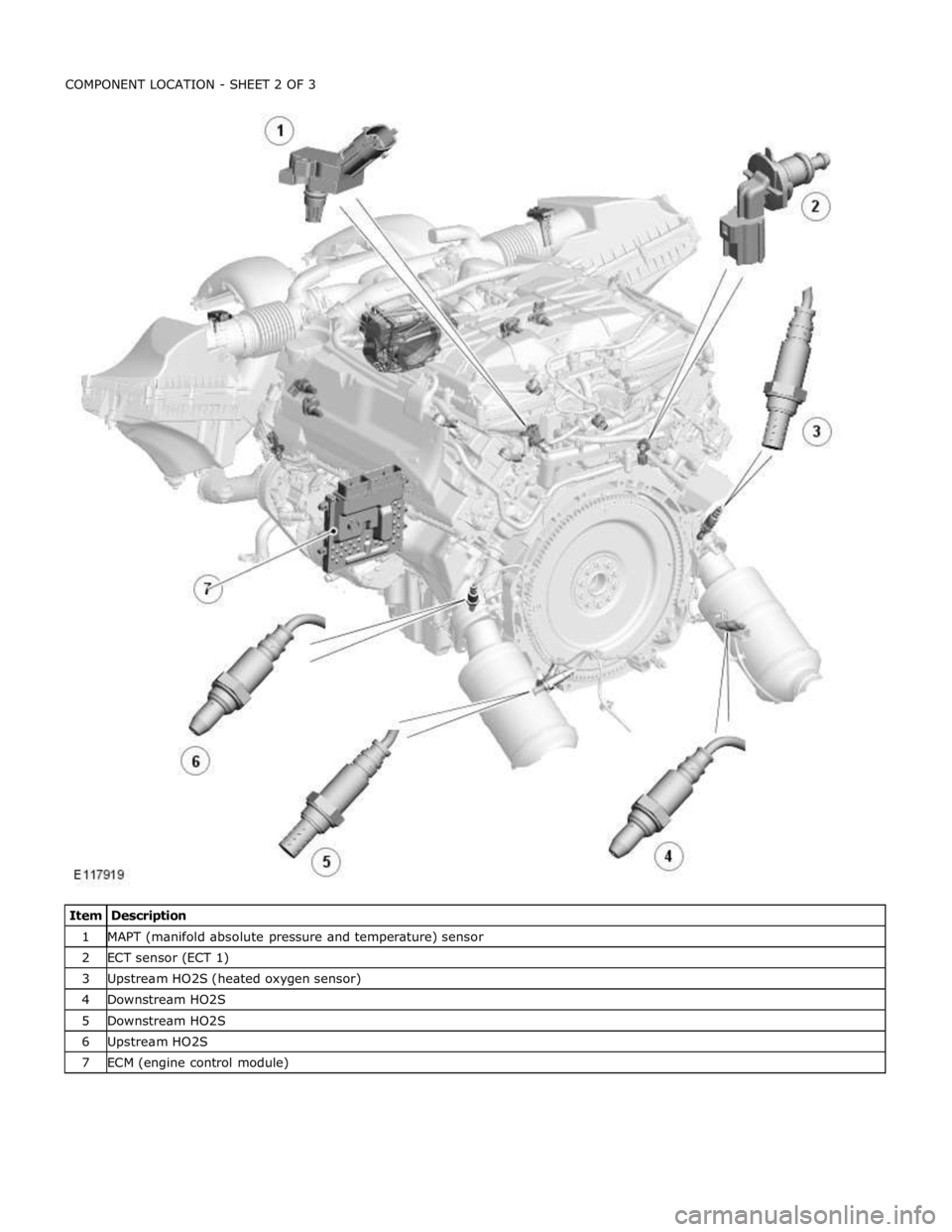
1 MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor 2 ECT sensor (ECT 1) 3 Upstream HO2S (heated oxygen sensor) 4 Downstream HO2S 5 Downstream HO2S 6 Upstream HO2S 7 ECM (engine control module)
Page 1359 of 3039

6 LH exhaust CMP sensor 7 LH MAFT sensor 8 LH front knock sensor 9 LH rear knock sensor 10 RH (right hand) rear knock sensor 11 RH front knock sensor 12 RH intake CMP sensor 13 RH exhaust CMP sensor 14 RH MAFT sensor CONTROL DIAGRAM SHEET 2 OF 2
Item Description 1 MAP sensor 2 ECT sensor (ECT 2)
Page 1360 of 3039

4 Diagnostic socket 5 To other system control modules 6 ECM 7 Electronic throttle 8 APP sensor 9 AAT sensor 10 ECT sensor (ECT 1) 11 LH upstream HO2S 12 LH downstream HO2S 13 MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor 14 RH downstream HO2S 15 RH upstream HO2S
ECM ADAPTIONS System Operation
The ECM (engine control module) has the ability to adapt the input values it uses to control certain outputs. This capability
maintains engine refinement and ensures the engine emissions remain within the legislated limits. The components which
have adaptions associated with them are:
The APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor
The heated oxygen sensors
The MAFT (mass air flow and temperature) sensors
The CKP (crankshaft position) sensor
Electronic throttle.
OXYGEN AND MAFT SENSORS
There are several adaptive maps associated with the fueling strategy. Within the fueling strategy the ECM calculates short-term adaptions and long term adaptions. The ECM will monitor the deterioration of the heated oxygen sensors over a period of time. It will also monitor the current correction associated with the sensors.
The ECM will store a fault code in circumstances where an adaption is forced to exceed its operating parameters. At the same time, the ECM will record the engine speed, engine load and intake air temperature.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The characteristics of the signal supplied by the CKP sensor are learned by the ECM. This enables the ECM to set an adaption and support the engine misfire detection function. Due to the small variation between different drive plates and different CKP sensors, the adaption must be reset if either component is renewed, or removed and refitted. It is also necessary to reset the
drive plate adaption if the ECM is renewed or replaced. The ECM supports four drive plate adaptions for the CKP sensor. Each adaption relates to a specific engine speed range. The engine speed ranges are detailed in the table below:
Adaption Engine Speed, rev/min 1 1800 - 3000 2 3001 - 3800 3 3801 - 4600 4 4601 - 5400 MISFIRE DETECTION
Legislation requires that the ECM must be able to detect the presence of an engine misfire. It must be able to detect misfires at two separate levels. The first level is a misfire that could lead to the legislated emissions limit being exceeded by a given
amount. The second level is a misfire that may cause catalytic converter damage.
The ECM monitors the number of misfire occurrences within two engine speed ranges. If the ECM detects more than a predetermined number of misfire occurrences within either of these two ranges, over two consecutive journeys, it will record a
fault code and details of the engine speed, engine load and engine coolant temperature. In addition, the ECM monitors the number of misfire occurrences that happen in a 'window' of 200 engine revolutions. The misfire occurrences are assigned a
weighting according to their likely impact on the catalytic converters. If the number of misfires exceeds a given value, the ECM stores catalytic converter damage fault codes, along with the engine speed, engine load and engine coolant temperature.
The signal from the CKP sensor indicates how fast the poles on the drive plate are passing the sensor tip. A sine wave is generated each time a pole passes the sensor tip. The ECM can detect variations in drive plate speed by monitoring the sine wave signal supplied by the crankshaft position sensor. By assessing this signal, the ECM can detect the presence of an engine misfire. At this time, the ECM will assess the amount of variation in the signal received from the CKP sensor and assign a roughness value to it. This roughness value can be viewed within the real time monitoring feature using Jaguar approved
diagnostic equipment. TheECM will evaluate the signal against a number of factors and will decide whether to record the occurrence or ignore it. The ECM can assign a roughness and misfire signal for each cylinder.
Page 1361 of 3039

DIAGNOSTICS
The ECM stores each fault as a DTC (diagnostic trouble code). The DTC and associated environmental and freeze frame data can be read using Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment, which can also read real time data from each sensor, the adaption
values currently being employed and the current fueling, ignition and idle speed settings.
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE Component Description
The ECM is installed in the front passenger side of the engine compartment, on a bracket attached to the engine bulkhead. The ECM has the capability of adapting its fuel and ignition control outputs in response to several sensor inputs. The ECM receives inputs from the following:
CKP sensor. CMP (camshaft position) sensors (4 off).
ECT (engine coolant temperature) sensor.
Knock sensors (4 off).
MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor.
MAFT sensors (2 off). MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor.
Throttle position sensor.
Heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
APP sensor. Ambient air temperature sensor.
FRP (fuel rail pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls.
Engine cooling fan. For additional information, refer to 303-03D Engine Cooling.
Stoplamp switch. For additional information, refer to 206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist.
Speed control cancel/suspend switch. For additional information, refer to 310-03D Speed Control.
Oil level and temperature sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-01F Engine.
Fuel LP (low pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
Fuel pump driver module. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
The ECM provides outputs to the following: Electronic throttle.
Main relay.
Heater elements of the heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
Fuel injectors (8 off). For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1363 of 3039
Defaults to base mapping for the ignition timing, with no cylinder correction
Disables the VCT system.
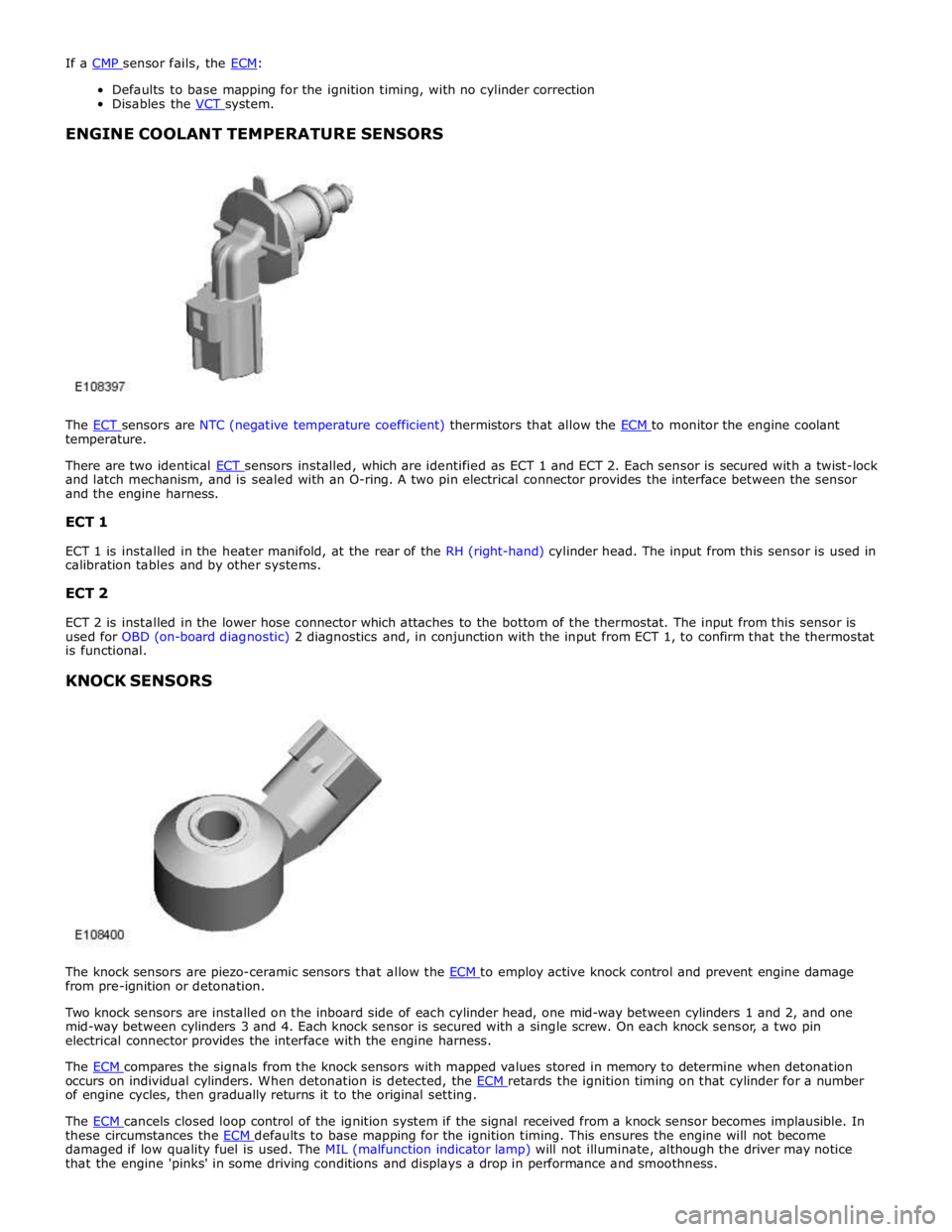
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORS
The ECT sensors are NTC (negative temperature coefficient) thermistors that allow the ECM to monitor the engine coolant temperature.
There are two identical ECT sensors installed, which are identified as ECT 1 and ECT 2. Each sensor is secured with a twist-lock and latch mechanism, and is sealed with an O-ring. A two pin electrical connector provides the interface between the sensor
and the engine harness.
ECT 1
ECT 1 is installed in the heater manifold, at the rear of the RH (right-hand) cylinder head. The input from this sensor is used in
calibration tables and by other systems.
ECT 2
ECT 2 is installed in the lower hose connector which attaches to the bottom of the thermostat. The input from this sensor is
used for OBD (on-board diagnostic) 2 diagnostics and, in conjunction with the input from ECT 1, to confirm that the thermostat
is functional.
KNOCK SENSORS
The knock sensors are piezo-ceramic sensors that allow the ECM to employ active knock control and prevent engine damage from pre-ignition or detonation.
Two knock sensors are installed on the inboard side of each cylinder head, one mid-way between cylinders 1 and 2, and one
mid-way between cylinders 3 and 4. Each knock sensor is secured with a single screw. On each knock sensor, a two pin
electrical connector provides the interface with the engine harness.
The ECM compares the signals from the knock sensors with mapped values stored in memory to determine when detonation occurs on individual cylinders. When detonation is detected, the ECM retards the ignition timing on that cylinder for a number of engine cycles, then gradually returns it to the original setting.
The ECM cancels closed loop control of the ignition system if the signal received from a knock sensor becomes implausible. In these circumstances the ECM defaults to base mapping for the ignition timing. This ensures the engine will not become damaged if low quality fuel is used. The MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) will not illuminate, although the driver may notice
that the engine 'pinks' in some driving conditions and displays a drop in performance and smoothness.