battery replacement JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 2616 of 3039
and the safety belt buckle sensor. Based on this data, the RCM decides which level of airbag module deployment is required and forwards the information to the second area, the deployment handler.
The deployment handler evaluates the status of the seat track position sensor and safety belt buckle sensors before a decision
is made about which restraints should finally be deployed.
Data from the side crash sensors is used by the RCM in conjunction with acceleration data from the RCM internal accelerometer to make a deployment decision. The RCM processes the acceleration data and subject to an impact being of high enough severity, decides whether the side airbag module should be deployed.
On board testing of the airbag modules, front safety belt pretensioner firing circuits, warning indicator circuits and module
status (the crash and side impact sensors perform basic self-tests) is performed by the RCM together with the storing of fault codes.
The RCM drives the SRS indicator on the instrument pack via a CAN signal. If the warning lamp fails, a fault code is recorded and a warning tone is sounded in place of the lamp if a further fault occurs. It also provides a temporary back-up power supply
to operate the airbag modules in the event that in crash conditions, the battery supply is lost. In the event of a crash, it
records certain data which can be accessed via the diagnostic connector.
A safing sensor in the RCM provides confirmation of an impact to verify if airbag and pretensioner activation is necessary. A roll-over sensor monitors the lateral attitude of the vehicle. Various firing strategies are employed by the RCM to ensure that during an accident only the appropriate airbags and pretensioners are fired. The firing strategy used also depends on the
inputs from the safety belt switches and the occupant monitoring system.
An energy reserve in the RCM ensures there is always a minimum of 150 milliseconds of stored energy available if the power supply from the ignition switch is disrupted during a crash. The stored energy is sufficient to produce firing signals for the
driver airbag, the passenger airbag and the safety belt pretensioners.
When the ignition is switched on, the RCM performs a self-test and then performs cyclical monitoring of the system. If a fault is detected the RCM stores a related fault code and illuminates the airbag warning indicator. The faults can be retrieved by the recommended Jaguar diagnostic tool over the CAN bus. If a fault that could cause a false fire signal is detected, the RCM disables the respective firing circuit, and keeps it disabled during a crash event.
Clock Spring
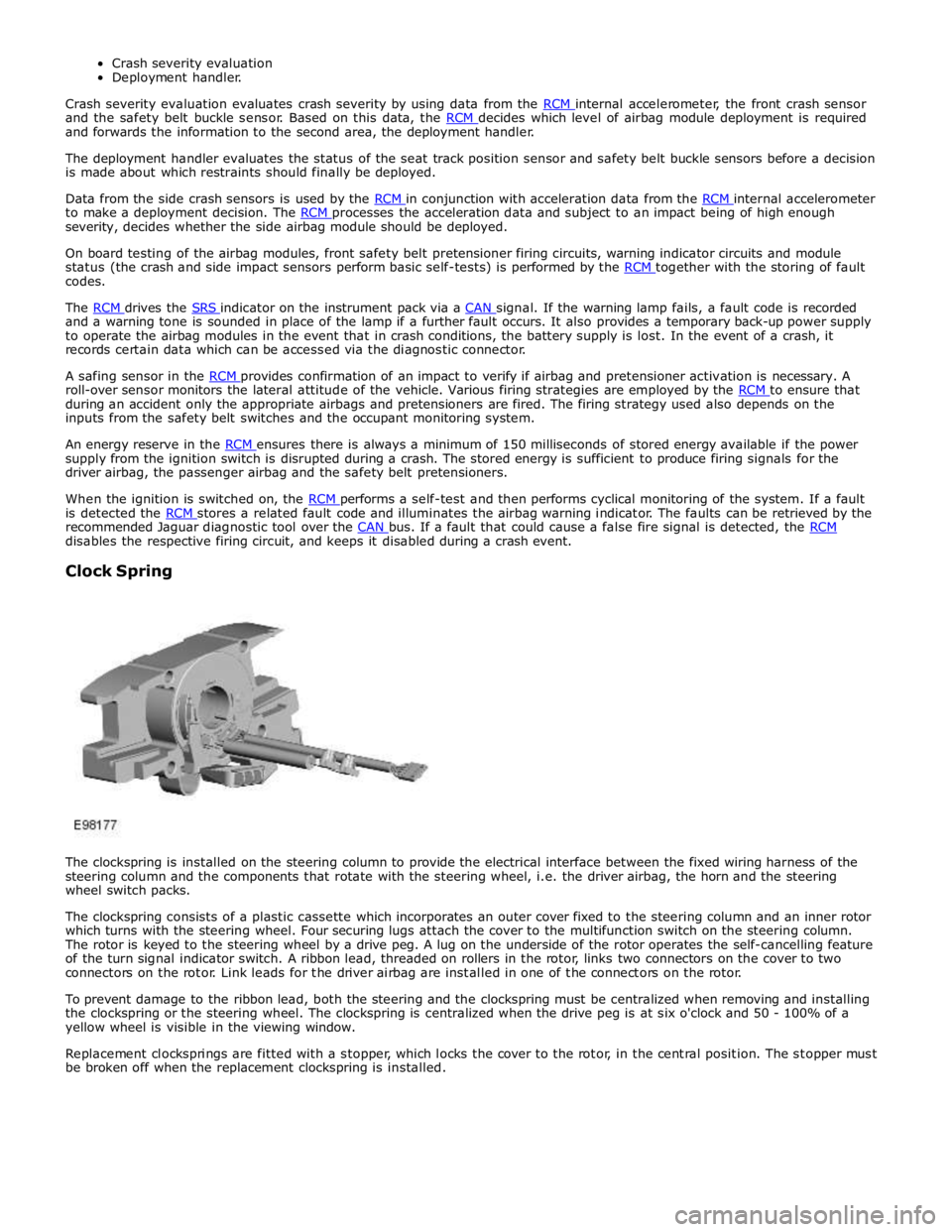
The clockspring is installed on the steering column to provide the electrical interface between the fixed wiring harness of the
steering column and the components that rotate with the steering wheel, i.e. the driver airbag, the horn and the steering
wheel switch packs.
The clockspring consists of a plastic cassette which incorporates an outer cover fixed to the steering column and an inner rotor
which turns with the steering wheel. Four securing lugs attach the cover to the multifunction switch on the steering column.
The rotor is keyed to the steering wheel by a drive peg. A lug on the underside of the rotor operates the self-cancelling feature
of the turn signal indicator switch. A ribbon lead, threaded on rollers in the rotor, links two connectors on the cover to two
connectors on the rotor. Link leads for the driver airbag are installed in one of the connectors on the rotor.
To prevent damage to the ribbon lead, both the steering and the clockspring must be centralized when removing and installing
the clockspring or the steering wheel. The clockspring is centralized when the drive peg is at six o'clock and 50 - 100% of a
yellow wheel is visible in the viewing window.
Replacement clocksprings are fitted with a stopper, which locks the cover to the rotor, in the central position. The stopper must
be broken off when the replacement clockspring is installed.
Page 2624 of 3039

Published: 10-Jul-2014
Supplemental Restraint System - Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of the supplemental restraints system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation
section in the workshop manual. REFER to: (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System)
Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (Description and Operation), Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (Description and Operation), Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
WARNING: TO AVOID ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY, THE BACKUP POWER SUPPLY MUST
BE DEPLETED BEFORE REPAIRING OR REPLACING ANY AIR BAG SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS) COMPONENTS. TO
DEPLETE THE BACKUP POWER SUPPLY ENERGY, DISCONNECT THE BATTERY GROUND CABLE AND WAIT ONE MINUTE. FAILURE
TO FOLLOW THIS INSTRUCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Given the legal implications of a restraints system failure, harness repairs to Air Bag module circuits are not
acceptable. Where the text refers to "REPAIR the circuit", this will normally mean the replacement of a harness.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.
REFER to: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation). Electrical
Battery condition, state of charge
Make sure all electrical connector(s) are engaged correctly on the air bag circuits
Wiring harness
Air bag module(s)
Make sure the restraints control module (RCM) is correctly installed
Fuse(s)
Sensor(s)
Pretensioner(s)
Warning lamp bulb(s) Visual Inspection
www.JagDocs.com
Page 2687 of 3039

Pedestrian Protection System - Pedestrian Protection System
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation Published: 09-Dec-2013
For a detailed description of the Pedestrian Protection System, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section in the
workshop manual.
REFER to: Pedestrian Protection System (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Description and Operation) / Pedestrian Protection System (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Description and Operation) / Pedestrian Protection System (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
WARNINGS:
TO AVOID ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY, THE BACKUP POWER SUPPLY MUST BE DEPLETED
BEFORE REPAIRING OR REPLACING ANY PEDESTRIAN PROTECTION SYSTEM COMPONENTS. TO DEPLETE THE BACKUP POWER
SUPPLY ENERGY, DISCONNECT THE BATTERY GROUND CABLE AND WAIT TWO MINUTES. FAILURE TO FOLLOW THIS
INSTRUCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
Do not use a multimeter to probe the pedestrian protection system actuators. It is possible for the power from the
multimeter battery to trigger the activation of the actuator. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
Warranty Policy and Procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component.
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
It is advisable not to use a cellular phone or to have a cellular phone in close proximity when working on the pedestrian
protection system or components
Given the legal implications of a restraints system failure, harness repairs to pedestrian protection system circuits are
not acceptable. Where the text refers to "REPAIR the circuit", this will normally mean the replacement of a harness.
After 5 hood deployment events, a new Pedestrian Protection System Control Module (PPSCM) and wiring harness must be
installed.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Hood
Hood hinge
Hood deployment controls
Fuses
Wiring harnesses and connectors
Pedestrian Protection System Control Module (PPSCM)
Impact sensors
Hood deployment controls
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Page 2714 of 3039

- Disadvantage: Scarring and hardening of the surface.
Flattening using a copper electrode.
- Small, sharp dents that face outwards can be worked on with a copper electrode.
Flattening using a flame and body files.
NOTE: When applied correctly, this method can be used with all the attached parts still in place (roof headlining,
wiring harnesses etc.).
- Small, soft dents (only slight stretching): Working at the edges of the dent in an inward spiral pattern, the dent
is heated with an oxyacetylene torch (torch size 1 - 2 mm, excess gas flame) to approx. 250° C.
- Working rapidly with a body file extracts heat from the edge area until the dent is flattened. Preferably alternate
between two files. This increases the amount of heat that can be extracted.
Safety measures
The electronic control modules (ECM) fitted to vehicles make it advisable to follow suitable precautions prior to carrying
out welding repair operations. Harsh conditions of heat and vibration may be generated during these operations which
could cause damage to the modules. In particular, it is essential to follow the appropriate precautions when
disconnecting or removing the airbag RCM.
Do not allow electronic modules or lines to come into contact with the ground connection or the welding electrode.
Seat belt anchorages are a safety critical. When making repairs in these areas, it is essential to follow design
specifications. Note that extra strength low alloy steel may be used for seat belt anchorages. Where possible, the
original production assembly should be used, complete with its seat belt anchorages, or the cut line should be so
arranged that the original seat belt anchorage is not disturbed.
All welds within 250mm (9.842) of seat belt anchorages must be carefully checked for weld quality, including spacing of
spot welds.
Remove the battery before carrying out welding work in its vicinity.
Utmost care must be taken when welding near the fuel tank or other components that contain fuel. If the tank filler
neck or a fuel line must be detached to allow access for welding work, then the fuel tank must be drained and removed.
Never weld, on components of a filled air conditioning system. The same applies if there is a risk of the air conditioning
system heating up.
Connect the ground connection of the electrical welder directly to the part that is to be welded. Make sure that there
are no electrically insulating parts between the ground connection and the welding point.
Adjacent vehicle parts and adjacent vehicles must be shielded against flying sparks and heat.
Pedestrian protection system
The pedestrian protection system is designed to mitigate injuries in a pedestrian collision with the vehicle. It does this by
utilizing a pair of pyrotechnic actuators to lift the hood away from the engine, creating a cushioned impact between the
pedestrian and the vehicle. It is essential that any repair or replacement operations do not affect the safe working of the
system.
For additional information, refer to: Pedestrian Protection System (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Description and Operation).
Resistance spot welding
Where resistance spot welds have been used in production, they must be reproduced with new spot welds in replacement
where possible. All such reproduction spot welds should be spaced 25 to 30mm apart.
Setting up the equipment and co-ordinating the welding parameters.
Equipment:
- Follow the equipment manufacturer's instructions for the equipment settings.
- Select the correct electrode arms (as short as possible).
- Align the electrode arms and tips exactly.
- Electrode tips should be convex (rough shaping with a file, fine shaping with a sanding block).
Body:
- Make sure that the flanges to be joined lie perfectly flat to one another.
- Prepare a bare metal joint surface (inside and outside).
Notes on technique/method:
- Carry out a test weld on a sample piece of the material coated in welding paste.
- If any metal parts are located between the electrode arms then there will be a loss of induction and therefore
power (adjust current setting).
- The power needs to be adjusted for high-strength low alloy steel.
- Repeated welding on old welding points often leads to poor quality welds.
- Keep the electrode tips as near as possible to an angle of 90° to the contact surface.
- Keep the pressure on the electrodes for a short period after finishing the weld.
- The electrodes work best if their shape is convex. Clean the contact surface of the electrodes regularly.
Resistance spot welding panels where the total thickness is 3 mm or more
For all repairs to modern Jaguar vehicles, spot-welding equipment should be suitable for reliable welding of zinc-plated,
high-strength and high-tensile steels in three or more layers, up to 5 mm total thickness. If these requirements are not
fulfilled, plug welding must be used for safety reasons. The electrical specifications (current, resistance, heat) of the
spot-welding equipment have different validity, depending upon the type of equipment. Therefore, it is essential that the
manufacturer's instructions are observed with regard to the actual welding performance.
www.JagDocs.com