power steering JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 303 of 3039
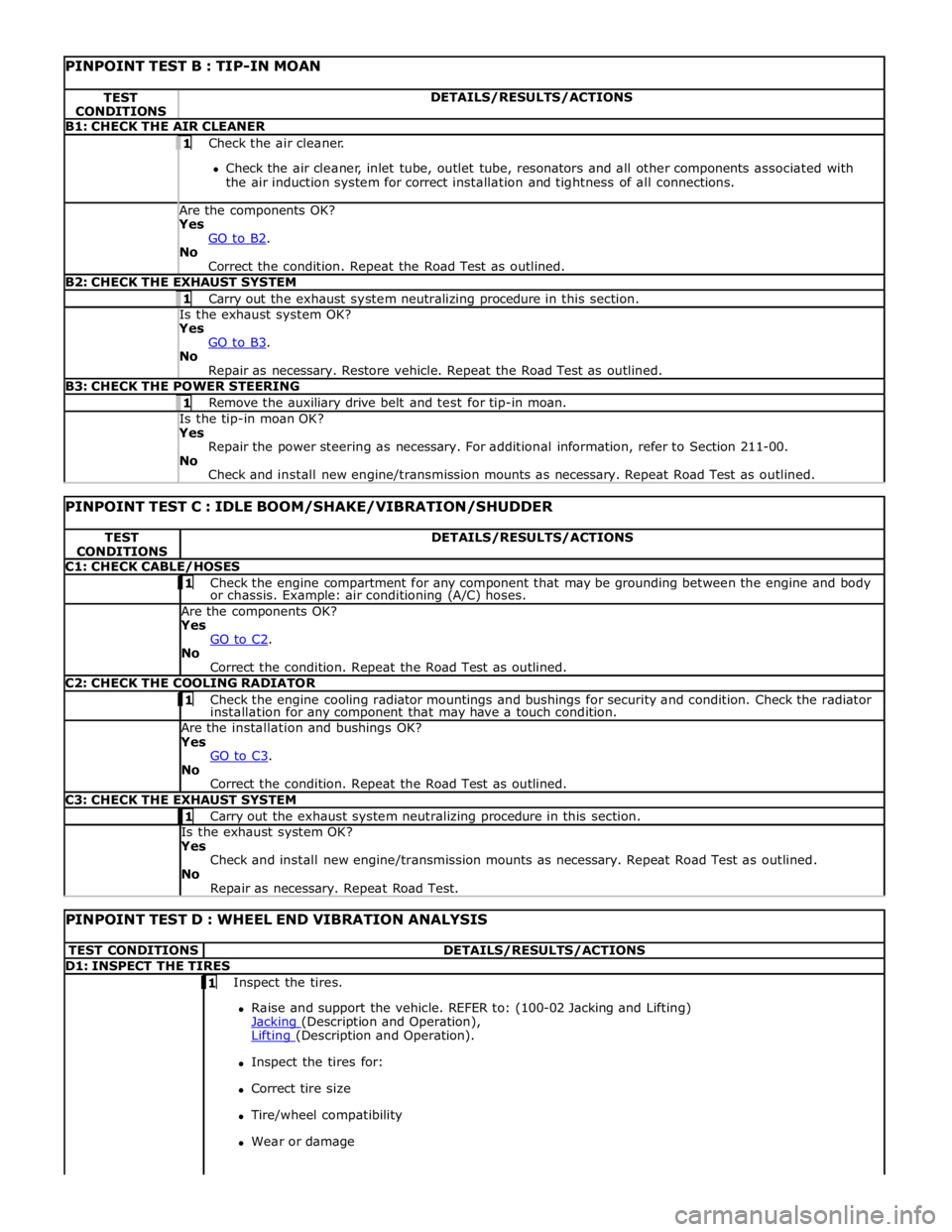
PINPOINT TEST B : TIP-IN MOAN TEST
CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS B1: CHECK THE AIR CLEANER 1 Check the air cleaner.
Check the air cleaner, inlet tube, outlet tube, resonators and all other components associated with
the air induction system for correct installation and tightness of all connections. Are the components OK? Yes
GO to B2. No
Correct the condition. Repeat the Road Test as outlined. B2: CHECK THE EXHAUST SYSTEM 1 Carry out the exhaust system neutralizing procedure in this section. Is the exhaust system OK? Yes
GO to B3. No
Repair as necessary. Restore vehicle. Repeat the Road Test as outlined. B3: CHECK THE POWER STEERING 1 Remove the auxiliary drive belt and test for tip-in moan. Is the tip-in moan OK? Yes
Repair the power steering as necessary. For additional information, refer to Section 211-00.
No
Check and install new engine/transmission mounts as necessary. Repeat Road Test as outlined.
PINPOINT TEST C : IDLE BOOM/SHAKE/VIBRATION/SHUDDER TEST
CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS C1: CHECK CABLE/HOSES 1 Check the engine compartment for any component that may be grounding between the engine and body or chassis. Example: air conditioning (A/C) hoses. Are the components OK? Yes
GO to C2. No
Correct the condition. Repeat the Road Test as outlined. C2: CHECK THE COOLING RADIATOR 1 Check the engine cooling radiator mountings and bushings for security and condition. Check the radiator installation for any component that may have a touch condition. Are the installation and bushings OK? Yes
GO to C3. No
Correct the condition. Repeat the Road Test as outlined. C3: CHECK THE EXHAUST SYSTEM 1 Carry out the exhaust system neutralizing procedure in this section. Is the exhaust system OK? Yes
Check and install new engine/transmission mounts as necessary. Repeat Road Test as outlined.
No
Repair as necessary. Repeat Road Test.
PINPOINT TEST D : WHEEL END VIBRATION ANALYSIS TEST CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS D1: INSPECT THE TIRES 1 Inspect the tires.
Raise and support the vehicle. REFER to: (100-02 Jacking and Lifting)
Jacking (Description and Operation), Lifting (Description and Operation).
Inspect the tires for:
Correct tire size
Tire/wheel compatibility
Wear or damage
Page 483 of 3039
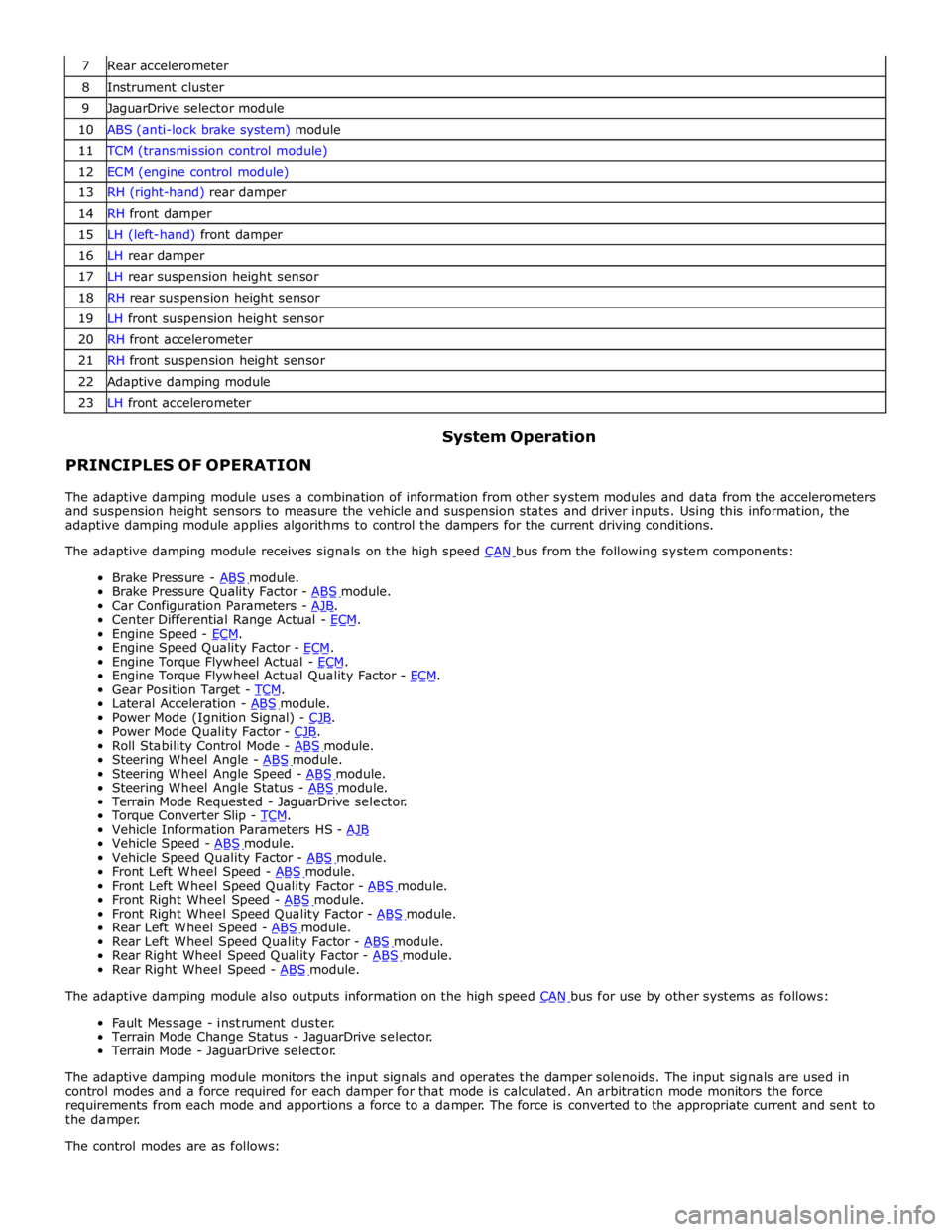
7 Rear accelerometer 8 Instrument cluster 9 JaguarDrive selector module 10 ABS (anti-lock brake system) module 11 TCM (transmission control module) 12 ECM (engine control module) 13 RH (right-hand) rear damper 14 RH front damper 15 LH (left-hand) front damper 16 LH rear damper 17 LH rear suspension height sensor 18 RH rear suspension height sensor 19 LH front suspension height sensor 20 RH front accelerometer 21 RH front suspension height sensor 22 Adaptive damping module 23 LH front accelerometer
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION System Operation
The adaptive damping module uses a combination of information from other system modules and data from the accelerometers
and suspension height sensors to measure the vehicle and suspension states and driver inputs. Using this information, the
adaptive damping module applies algorithms to control the dampers for the current driving conditions.
The adaptive damping module receives signals on the high speed CAN bus from the following system components: Brake Pressure - ABS module. Brake Pressure Quality Factor - ABS module. Car Configuration Parameters - AJB. Center Differential Range Actual - ECM. Engine Speed - ECM. Engine Speed Quality Factor - ECM. Engine Torque Flywheel Actual - ECM. Engine Torque Flywheel Actual Quality Factor - ECM. Gear Position Target - TCM. Lateral Acceleration - ABS module. Power Mode (Ignition Signal) - CJB. Power Mode Quality Factor - CJB. Roll Stability Control Mode - ABS module. Steering Wheel Angle - ABS module. Steering Wheel Angle Speed - ABS module. Steering Wheel Angle Status - ABS module. Terrain Mode Requested - JaguarDrive selector.
Torque Converter Slip - TCM. Vehicle Information Parameters HS - AJB Vehicle Speed - ABS module. Vehicle Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Front Left Wheel Speed - ABS module. Front Left Wheel Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Front Right Wheel Speed - ABS module. Front Right Wheel Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Rear Left Wheel Speed - ABS module. Rear Left Wheel Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Rear Right Wheel Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Rear Right Wheel Speed - ABS module. The adaptive damping module also outputs information on the high speed CAN bus for use by other systems as follows: Fault Message - instrument cluster.
Terrain Mode Change Status - JaguarDrive selector.
Terrain Mode - JaguarDrive selector.
The adaptive damping module monitors the input signals and operates the damper solenoids. The input signals are used in
control modes and a force required for each damper for that mode is calculated. An arbitration mode monitors the force
requirements from each mode and apportions a force to a damper. The force is converted to the appropriate current and sent to
the damper.
The control modes are as follows:
Page 484 of 3039
each damper to the appropriate level to maintain a flat and level body.
Roll Rate Control – Uses CAN inputs. Predicts vehicle roll rate due to driver steering inputs 100 times a second and increases damping to reduce roll rate.
Pitch Rate Control – Uses CAN inputs. Predicts vehicle pitch rate due to driver throttle and braking inputs 100 times a second and increases damping to reduce pitch rate.
Bump Rebound Control – Uses suspension height sensor and CAN inputs. Monitors the position of the wheel 500 times a second and increases the damping rate as the damper approaches the end of its travel.
Wheel Hop Control – Uses suspension height sensor and CAN inputs. Monitors the position of the wheel 500 times a second and detects when the wheel is at its natural frequency and increases the dampingto reduce vertical wheel
motion.
Under normal road conditions when the vehicle is stationary with the engine running, the dampers are set to the firm condition
to reduce power consumption.
The adaptive damping module receives its power supply via a relay and fuse in the CJB. The relay remains energized for a period of time after the ignition is off. This allows the adaptive damping module to record and store any DTC (diagnostic
trouble code) relating to adaptive dynamics system faults.
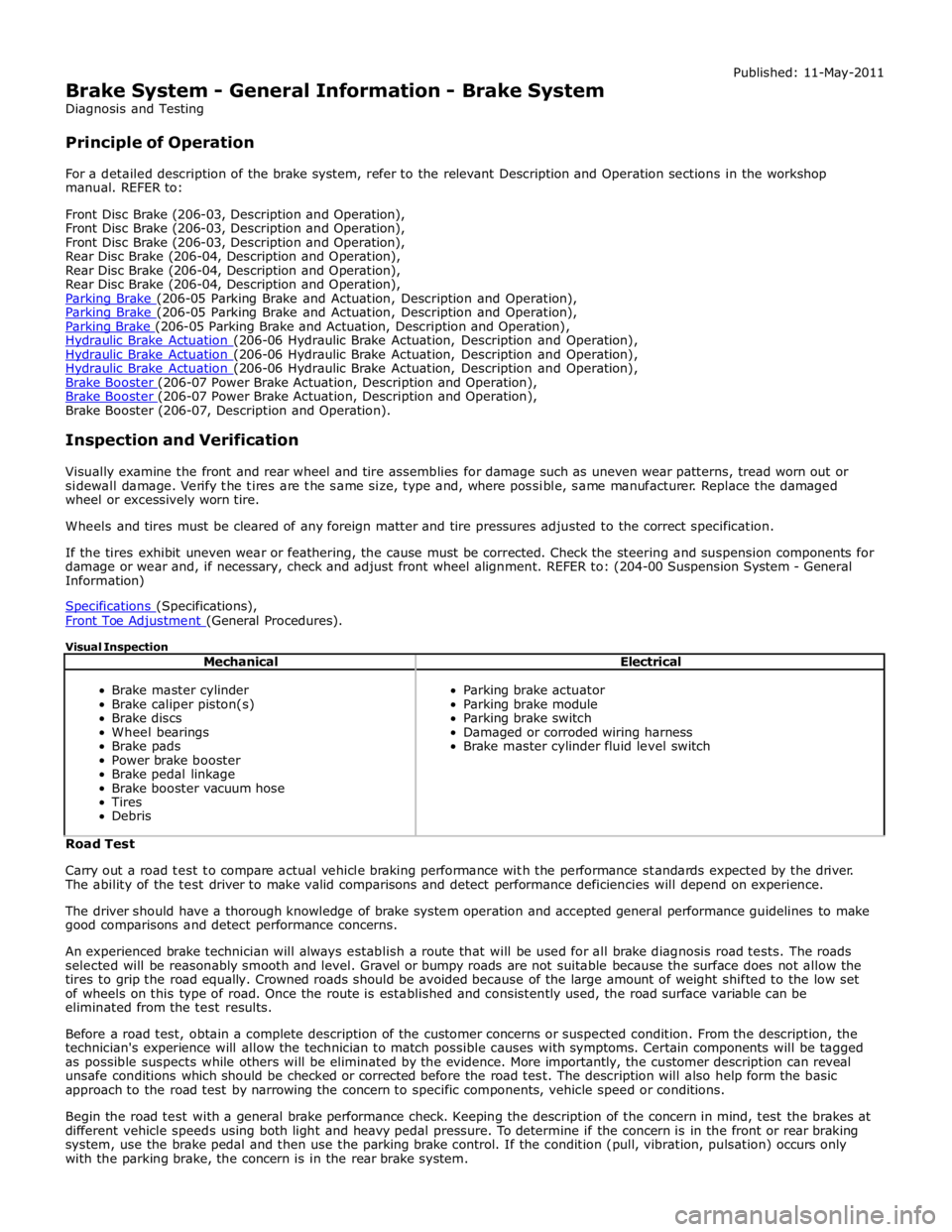
DAMPERS Component Description
Item Description A Front spring and damper assembly B Rear spring and damper assembly The 'Adaptive Dynamics' dampers are monotube, nitrogen gas and oil filled units, manufactured by Bilstein. The dampers are
continuously variable, which allows the damping force to be electrically adjusted when the vehicle is being driven. The variable
dampers provide the optimum compromise between vehicle control and ride comfort.
The dampers have an electrical connector on the end of the piston rod, in the center of the top mount (the dampers look
identical to those on the Computer Active Technology Suspension (CATS) system of 4.2L supercharged vehicles, but have a
different part number).
In each damper, the continuous damping adjustment is achieved by a solenoid operated variable orifice, which opens up an
alternative path for oil flow within the damper. When de-energized the bypass is closed and all the oil flows through the main
(firm) piston. When energized, the solenoid moves an armature and control blade, which work against a spring. The control
blade incorporates an orifice which slides inside a sintered housing to open up the bypass as required. In compression, oil
flows from the lower portion of the damper through a hollow piston rod, a separate soft (comfort) valve, the slider housing and
orifice and into the upper portion of the damper, thereby bypassing the main (firm) valve. In rebound the oil flows in the www.JagDocs.com
Page 582 of 3039
Brake System - General Information - Brake System
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation Published: 11-May-2011
For a detailed description of the brake system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the workshop
manual. REFER to:
Front Disc Brake (206-03, Description and Operation),
Front Disc Brake (206-03, Description and Operation),
Front Disc Brake (206-03, Description and Operation),
Rear Disc Brake (206-04, Description and Operation),
Rear Disc Brake (206-04, Description and Operation),
Rear Disc Brake (206-04, Description and Operation),
Parking Brake (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, Description and Operation), Parking Brake (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, Description and Operation), Parking Brake (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, Description and Operation), Hydraulic Brake Actuation (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Hydraulic Brake Actuation (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Hydraulic Brake Actuation (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Brake Booster (206-07 Power Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Brake Booster (206-07 Power Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Brake Booster (206-07, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
Visually examine the front and rear wheel and tire assemblies for damage such as uneven wear patterns, tread worn out or
sidewall damage. Verify the tires are the same size, type and, where possible, same manufacturer. Replace the damaged
wheel or excessively worn tire.
Wheels and tires must be cleared of any foreign matter and tire pressures adjusted to the correct specification.
If the tires exhibit uneven wear or feathering, the cause must be corrected. Check the steering and suspension components for
damage or wear and, if necessary, check and adjust front wheel alignment. REFER to: (204-00 Suspension System - General
Information)
Specifications (Specifications), Front Toe Adjustment (General Procedures).
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Brake master cylinder
Brake caliper piston(s)
Brake discs
Wheel bearings
Brake pads
Power brake booster
Brake pedal linkage
Brake booster vacuum hose
Tires
Debris
Parking brake actuator
Parking brake module
Parking brake switch
Damaged or corroded wiring harness
Brake master cylinder fluid level switch Road Test
Carry out a road test to compare actual vehicle braking performance with the performance standards expected by the driver.
The ability of the test driver to make valid comparisons and detect performance deficiencies will depend on experience.
The driver should have a thorough knowledge of brake system operation and accepted general performance guidelines to make
good comparisons and detect performance concerns.
An experienced brake technician will always establish a route that will be used for all brake diagnosis road tests. The roads
selected will be reasonably smooth and level. Gravel or bumpy roads are not suitable because the surface does not allow the
tires to grip the road equally. Crowned roads should be avoided because of the large amount of weight shifted to the low set
of wheels on this type of road. Once the route is established and consistently used, the road surface variable can be
eliminated from the test results.
Before a road test, obtain a complete description of the customer concerns or suspected condition. From the description, the
technician's experience will allow the technician to match possible causes with symptoms. Certain components will be tagged
as possible suspects while others will be eliminated by the evidence. More importantly, the customer description can reveal
unsafe conditions which should be checked or corrected before the road test. The description will also help form the basic
approach to the road test by narrowing the concern to specific components, vehicle speed or conditions.
Begin the road test with a general brake performance check. Keeping the description of the concern in mind, test the brakes at
different vehicle speeds using both light and heavy pedal pressure. To determine if the concern is in the front or rear braking
system, use the brake pedal and then use the parking brake control. If the condition (pull, vibration, pulsation) occurs only
with the parking brake, the concern is in the rear brake system.
Page 692 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist - Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist - Overview
Description and Operation
Overview
The ABS (anti-lock brake system) and DSC (dynamic stability control) system features a Bosch modulator, which is an
integrated four-channel HCU (hydraulic control unit) and ABS module. The unit is located in the rear of the engine compartment on the passenger side, and is installed in the brake hydraulic circuit between the brake master cylinder and the four brake
calipers.
The ABS module is connected to the high speed CAN (controller area network) bus, and actively interacts with other vehicle system control modules and associated sensors to receive and transmit current vehicle operating information.
When required, the ABS module will actively intervene and operate the HCU during braking or vehicle maneuvers to correct the vehicle attitude, stability, traction or speed. During incidents of vehicle correction, the ABS module may also request the ECM (engine control module) to control engine power in order to further stabilize and correct the vehicle.
To provide full system functionality, the ABS and DSC system comprise the following components: DSC switch.
Four wheel speed sensors.
Steering angle sensor.
Yaw rate and lateral acceleration sensor.
Stoplamp switch.
Instrument cluster indicator lamps.
Integrated ABS module and HCU. Brake booster vacuum sensor (3.0L vehicles only).
Two variants of ABS module are available, Bosch ESP®8.1 and Bosch ESP®plus8.1. The Bosch ESP®plus8.1 system is fitted to vehicles with ACC (adaptive cruise control) and incorporates a new feature to Jaguar known as 'electronic brake prefill'.
Electronic brake prefill, senses any rapid throttle lift off, activating a small brake hydraulic pressure build-up of approximately 3
to 5 bar (43.5 to 72.5 lbf/in²) in anticipation of the brakes being applied. This application produces a quicker brake pedal
response and consequently slightly shorter stopping distances. When the ECM detects rapid throttle lift off it signals the ABS module which controls the HCU to apply a low brake pressure to assist in a quicker brake application.
NOTE: All vehicles with ACC are supported by the Bosch ESP®plus8.1 system.
The ABS provides the following brake functions that are designed to assist the vehicle or aid the driver: ABS. DSC, including Trac DSC.
CBC (corner brake control).
EBD (electronic brake force distribution).
ETC (electronic traction control).
EBA (emergency brake assist).
EDC (engine drag-torque control).
Understeer control.
Electronic brake prefill (vehicles with ACC only).
Brake vacuum assist (3.0L vehicles only).
All the brake functions listed are automatically active when the ignition is in power mode and the engine is running. The DSC
system can be selected to off using the DSC switch.
WARNING: Although the vehicle is fitted with DSC, it remains the drivers responsibility to drive safely according to the
prevailing conditions.
Page 694 of 3039

7 Brake fluid level switch 8 LH rear wheel speed sensor 9 RH rear wheel speed sensor 10 RJB (rear junction box) 11 High mounted stop lamp 12 LH stop lamp 13 RH stop lamp 14 Diagnostic socket 15 TCM (transmission control module) 16 Electronic parking brake module 17 ECM (engine control module) 18 Instrument cluster 19 ABS (anti-lock brake system) module 20 JaguarDrive selector module 21 Adaptive damping control module 22 Adaptive speed control module 23 Yaw rate and lateral acceleration sensor 24 Roof opening panel motor/module 25 Brake booster vacuum sensor (3.0L vehicles only) 26 Steering angle sensor
Anti-Lock Brake System System Operation
ABS controls the speed of all road wheels to ensure optimum wheel slip when braking at the adhesion limit. The wheels are prevented from locking to retain effective steering control of the vehicle.
The brake pressures are modulated separately for each wheel. Rear brake pressures are controlled to maintain rear stability on
split friction surfaces.
Dynamic Stability Control
DSC (dynamic stability control) uses brakes and powertrain torque control to assist in maintaining the yaw stability of the
vehicle. While the ignition is energized the DSC function is permanently enabled, unless selected off using the DSC switch.
DSC enhances driving safety in abrupt maneuvers and in under-steer or over-steer situations that may occur in a bend. The
ABS module monitors the yaw rate and lateral acceleration of the vehicle, steering input and individual wheel speeds, then selectively applies individual brakes and signals for powertrain torque adjustments to reduce under-steer or over-steer
conditions.
In general:
In an under-steer situation the inner wheels are braked to counteract the yaw movement towards the outer edge of the
bend.
In an over-steer situation the outer wheels are braked to prevent the rear end of the vehicle from pushing towards the
outer edge of the bend.
The ABS module monitors the tracking stability of the vehicle using inputs from the wheel speed sensors, the steering angle sensor, and the yaw rate and lateral acceleration sensor. The tracking stability is compared with stored target data. Whenever
the tracking stability deviates from the target data, the ABS module intervenes by applying the appropriate control strategy. The following interactions occur in an intervention situation:
High speed CAN signal to the ECM, to reduce engine torque. Application of braking to the appropriate corner of the vehicle.
Trac DSC
TracDSC is an alternative setting of DSC with reduced system interventions. With TracDSC engaged, traction may be somewhat
increased, although stability may be reduced compared to normal DSC. TracDSC is intended for use only on dry tarmac, by
suitably experienced drivers and should not be selected for other surfaces or by drivers with insufficient skill and training to
operate the vehicle safely with the TracDSC function engaged.
The less restrictive TracDSC setting may be preferred, for example, by expert drivers engaged in high performance driving on
dry Tarmac surfaces such as tracks and circuits.
Switching between DSC and Trac DSC:
Page 699 of 3039
beams change state. The LEDs and detectors are mounted in such a way that only one beam will change state, either to broken or restored, at any one time.
The center (straight ahead) position of the steering wheel has to be learned by the ABS module every time the ignition is switched ON. The steering angle sensor is unable to determine the center position so inputs from the yaw rate and lateral
acceleration sensor and wheel speed signals are also used by the ABS module to help it perform this process. If extreme weather conditions are present, for example ice causing extreme wheel spin or understeer/oversteer, the ABS module may not be able to determine the center position of the steering wheel. In this situation 'DSC NOT AVAILABLE' will be displayed in the
instrument cluster message center and the amber warning indicator will illuminate.
Refer to: Information and Message Center (413-08 Information and Message Center, Description and Operation).
'DSC NOT AVAILABLE' will also be displayed if the ABS module detects a steering angle sensor fault. The amber warning indicator will illuminate until the fault is rectified.
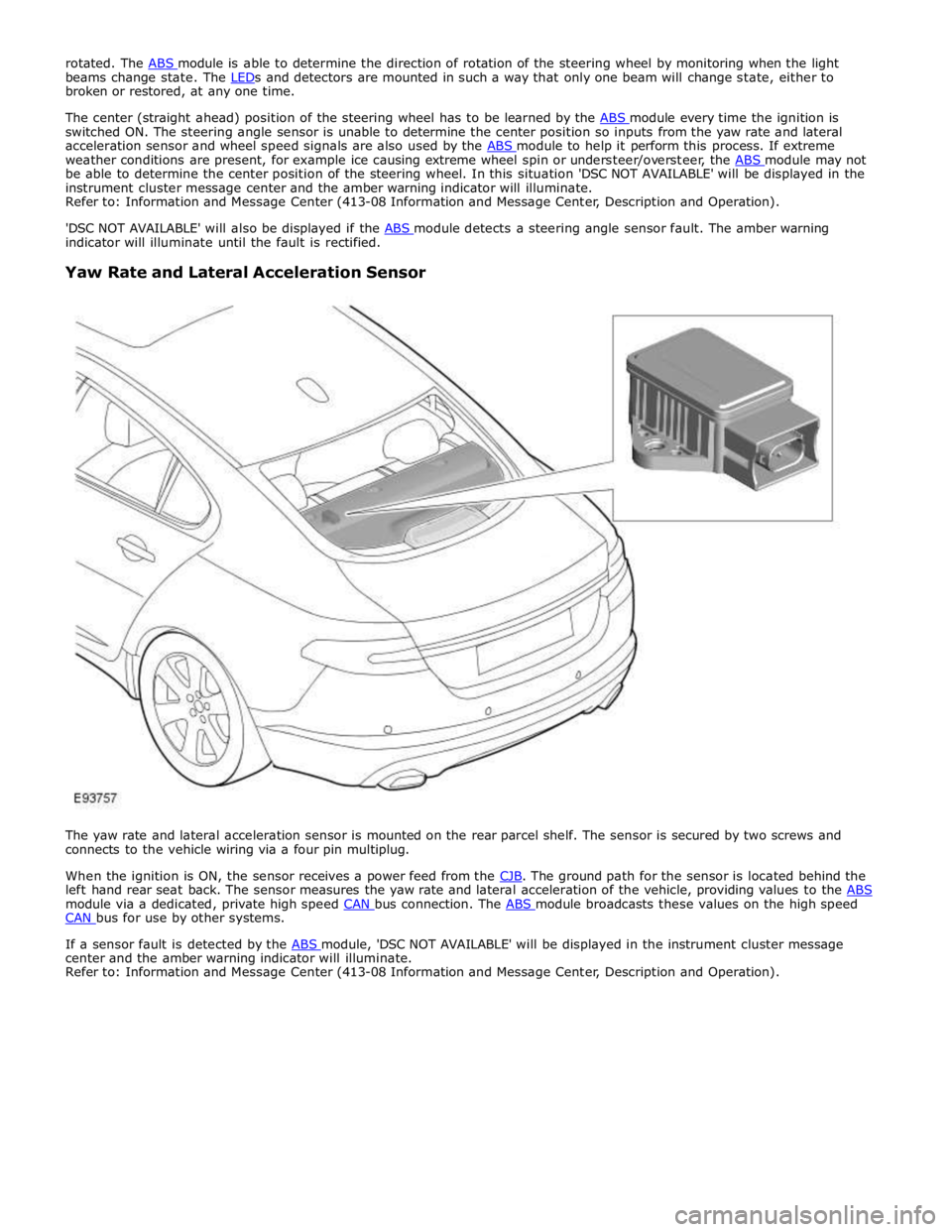
Yaw Rate and Lateral Acceleration Sensor
The yaw rate and lateral acceleration sensor is mounted on the rear parcel shelf. The sensor is secured by two screws and
connects to the vehicle wiring via a four pin multiplug.
When the ignition is ON, the sensor receives a power feed from the CJB. The ground path for the sensor is located behind the left hand rear seat back. The sensor measures the yaw rate and lateral acceleration of the vehicle, providing values to the ABS module via a dedicated, private high speed CAN bus connection. The ABS module broadcasts these values on the high speed CAN bus for use by other systems.
If a sensor fault is detected by the ABS module, 'DSC NOT AVAILABLE' will be displayed in the instrument cluster message center and the amber warning indicator will illuminate.
Refer to: Information and Message Center (413-08 Information and Message Center, Description and Operation).
Page 717 of 3039

Free play (measured at the steering wheel rim) 0-6 0-0.24 Power Steering Pump Specifications
Item Specification Power steering pump relief pressure 106-114 bar Lubricants, Fluids, Sealers and Adhesives
Item Specification Power steering fluid Dexron 3
Page 718 of 3039

Steering System - General Information - Steering System
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation Published: 11-May-2011
For a detailed description of the steering system operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections of the
workshop manual. REFER to:
Power Steering (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation), Power Steering (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation), Power Steering (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation), Steering Linkage (211-03 Steering Linkage, Description and Operation), Steering Linkage (211-03 Steering Linkage, Description and Operation), Steering Linkage (211-03 Steering Linkage, Description and Operation), Steering Column (211-04 Steering Column, Description and Operation), Steering Column (211-04 Steering Column, Description and Operation), Steering Column (211-04 Steering Column, Description and Operation), Steering Column Switches (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Description and Operation), Steering Column Switches (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Description and Operation), Steering Column Switches (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Tire condition/pressure
Fluid level
Leaks
Security, condition and correct installation of suspension components
Security, condition and correct installation of steering system components
Fuses
Harnesses for damage/corrosion
Electrical connector(s)
Damaged/corroded pins
CAUTION: If a steering gear assembly is returned under warranty with leaking output shaft seals, but there is also
damage to the steering gear boot/boots the steering gear warranty will be invalid. This is due to the steering gear output
shaft seals being damaged due to foreign materials entering the steering gear boot and damaging the steering gear output
shaft seals thereafter.
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the concern is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the symptom chart.
Symptom Charts
WARNING: It is not possible to CHECK the torque of a patchlock bolt, if the torque is suspected to be low, the bolt must
be REMOVED/DISCARDED and a new bolt MUST be INSTALLED and torque to the correct value.
NOTE: If the module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
Warranty Policy and Procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component.
Fluid Leakage
NOTE: Confirm the location of the fluid leak. CLEAN the area of the leak, inspect the area and confirm the exact position.
Ensure the fluid is not from another system on the vehicle.
Symptom Possible Causes Action
Power steering
fluid leakage
Overfilled system
Correct the fluid level as required
Steering gear
Check and install new steering gear as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of the Symptom
Charts
Page 719 of 3039
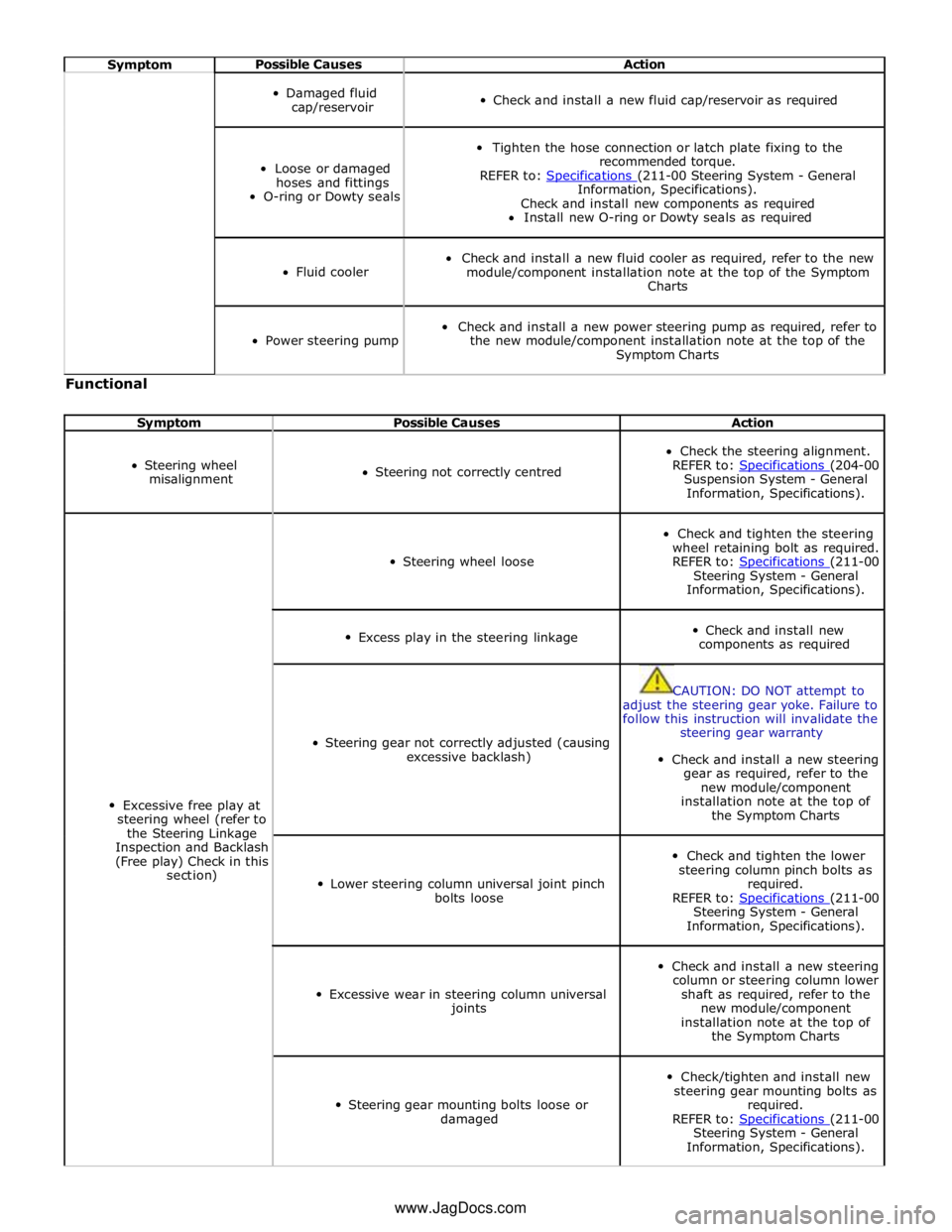
Symptom Possible Causes Action
Damaged fluid
cap/reservoir
Check and install a new fluid cap/reservoir as required
Loose or damaged
hoses and fittings
O-ring or Dowty seals
Tighten the hose connection or latch plate fixing to the
recommended torque.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General Information, Specifications).
Check and install new components as required
Install new O-ring or Dowty seals as required
Fluid cooler
Check and install a new fluid cooler as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of the Symptom
Charts
Power steering pump
Check and install a new power steering pump as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the
Symptom Charts Functional
Symptom Possible Causes Action
Steering wheel
misalignment
Steering not correctly centred
Check the steering alignment.
REFER to: Specifications (204-00 Suspension System - General
Information, Specifications).
Excessive free play at
steering wheel (refer to
the Steering Linkage
Inspection and Backlash
(Free play) Check in this
section)
Steering wheel loose
Check and tighten the steering
wheel retaining bolt as required.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General
Information, Specifications).
Excess play in the steering linkage
Check and install new
components as required
Steering gear not correctly adjusted (causing
excessive backlash)
CAUTION: DO NOT attempt to
adjust the steering gear yoke. Failure to
follow this instruction will invalidate the
steering gear warranty
Check and install a new steering
gear as required, refer to the
new module/component
installation note at the top of
the Symptom Charts
Lower steering column universal joint pinch
bolts loose
Check and tighten the lower
steering column pinch bolts as
required.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General
Information, Specifications).
Excessive wear in steering column universal
joints
Check and install a new steering
column or steering column lower
shaft as required, refer to the
new module/component
installation note at the top of
the Symptom Charts
Steering gear mounting bolts loose or
damaged
Check/tighten and install new
steering gear mounting bolts as
required.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General
Information, Specifications). www.JagDocs.com