JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 1211 of 2198
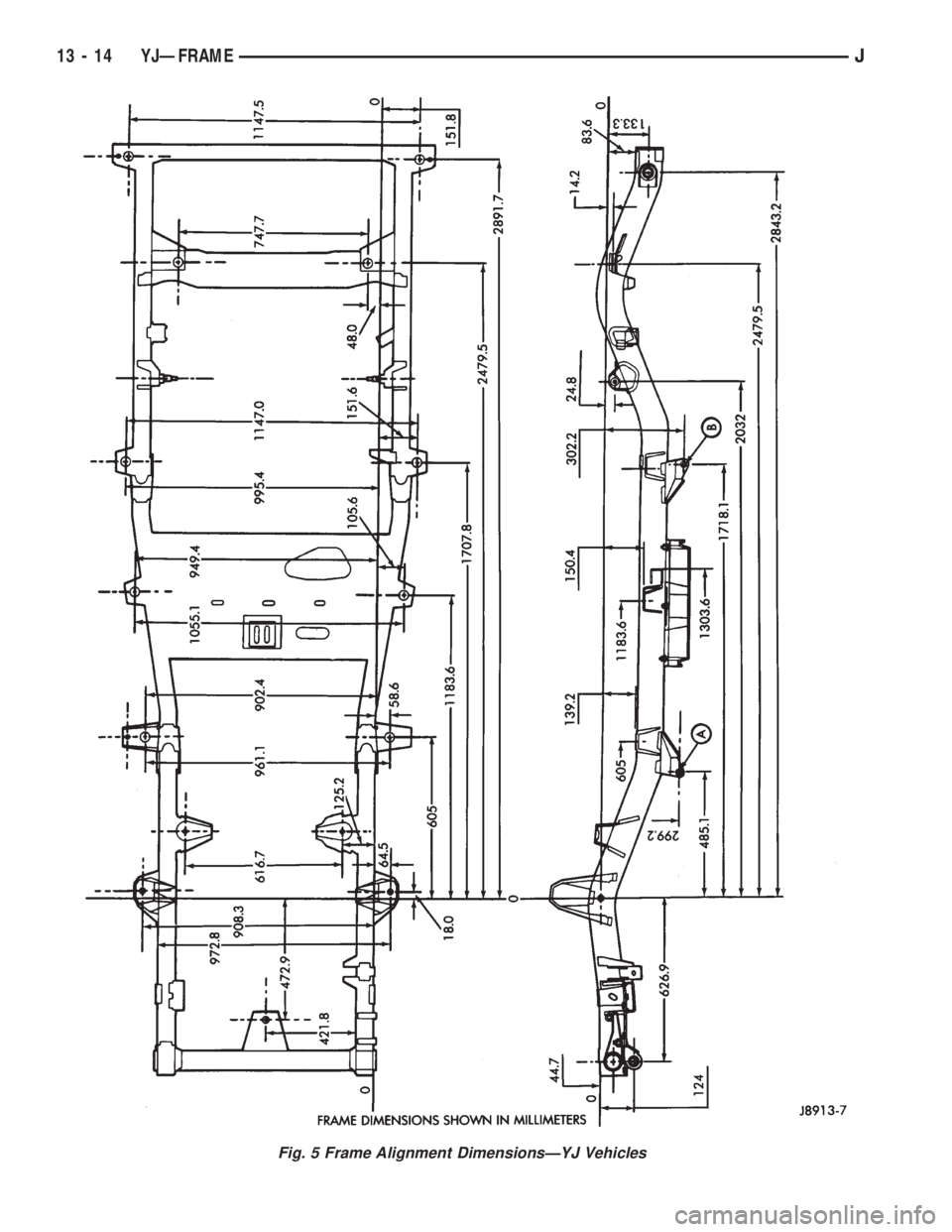
Fig. 5 Frame Alignment DimensionsÐYJ Vehicles
13 - 14 YJÐFRAMEJ
Page 1212 of 2198
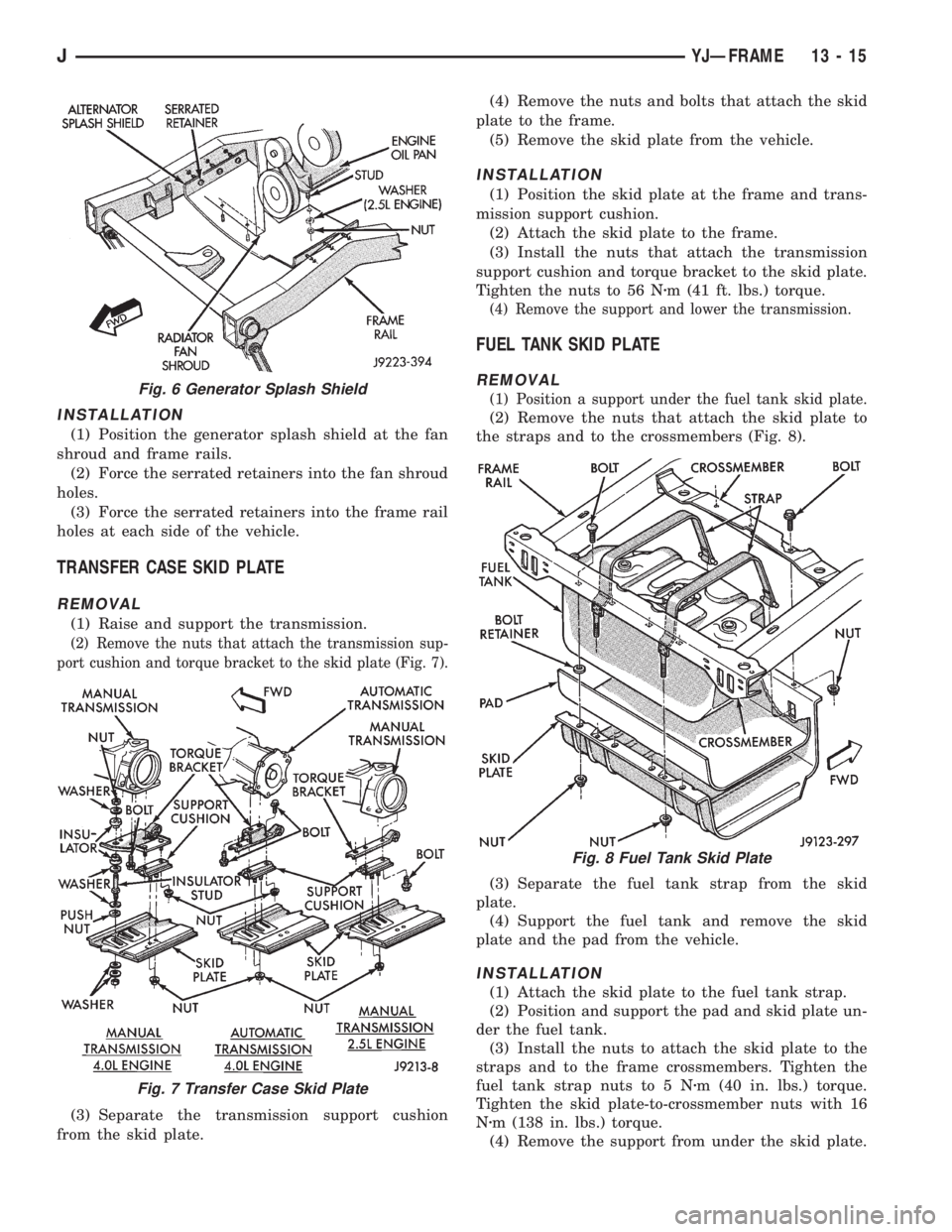
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the generator splash shield at the fan
shroud and frame rails.
(2) Force the serrated retainers into the fan shroud
holes.
(3) Force the serrated retainers into the frame rail
holes at each side of the vehicle.
TRANSFER CASE SKID PLATE
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the transmission.
(2) Remove the nuts that attach the transmission sup-
port cushion and torque bracket to the skid plate (Fig. 7).
(3) Separate the transmission support cushion
from the skid plate.(4) Remove the nuts and bolts that attach the skid
plate to the frame.
(5) Remove the skid plate from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the skid plate at the frame and trans-
mission support cushion.
(2) Attach the skid plate to the frame.
(3) Install the nuts that attach the transmission
support cushion and torque bracket to the skid plate.
Tighten the nuts to 56 Nzm (41 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Remove the support and lower the transmission.
FUEL TANK SKID PLATE
REMOVAL
(1) Position a support under the fuel tank skid plate.
(2) Remove the nuts that attach the skid plate to
the straps and to the crossmembers (Fig. 8).
(3) Separate the fuel tank strap from the skid
plate.
(4) Support the fuel tank and remove the skid
plate and the pad from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Attach the skid plate to the fuel tank strap.
(2) Position and support the pad and skid plate un-
der the fuel tank.
(3) Install the nuts to attach the skid plate to the
straps and to the frame crossmembers. Tighten the
fuel tank strap nuts to 5 Nzm (40 in. lbs.) torque.
Tighten the skid plate-to-crossmember nuts with 16
Nzm (138 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Remove the support from under the skid plate.
Fig. 6 Generator Splash Shield
Fig. 7 Transfer Case Skid Plate
Fig. 8 Fuel Tank Skid Plate
JYJÐFRAME 13 - 15
Page 1213 of 2198
BUMPERS
INDEX
page page
Frame Crossmember Cover................. 16
Front Bumper............................ 16Rear Bumper............................ 16
Service Information........................ 16
SERVICE INFORMATION
In some cases, components in the following proce-
dures either support, or are hidden by other compo-
nents.
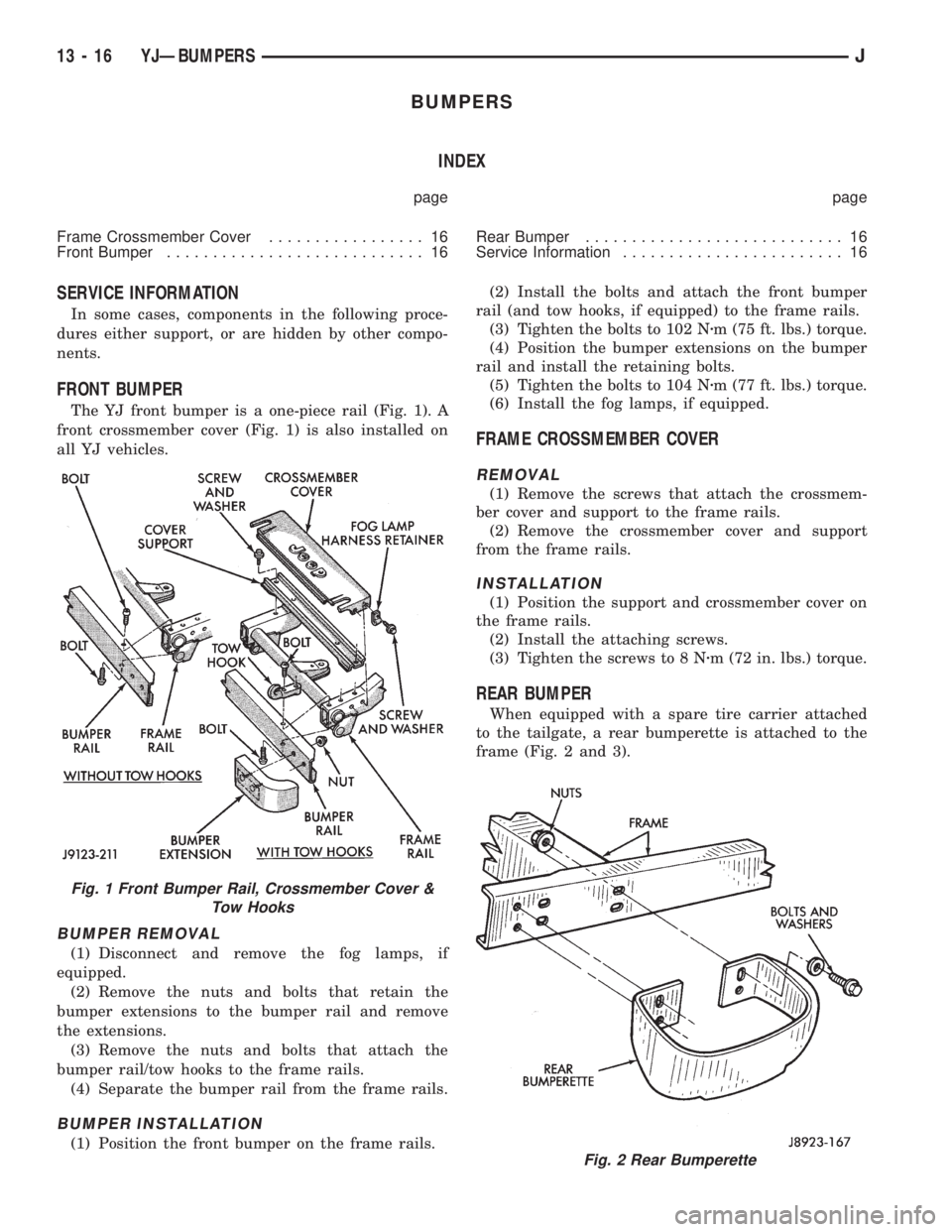
FRONT BUMPER
The YJ front bumper is a one-piece rail (Fig. 1). A
front crossmember cover (Fig. 1) is also installed on
all YJ vehicles.
BUMPER REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and remove the fog lamps, if
equipped.
(2) Remove the nuts and bolts that retain the
bumper extensions to the bumper rail and remove
the extensions.
(3) Remove the nuts and bolts that attach the
bumper rail/tow hooks to the frame rails.
(4) Separate the bumper rail from the frame rails.
BUMPER INSTALLATION
(1) Position the front bumper on the frame rails.(2) Install the bolts and attach the front bumper
rail (and tow hooks, if equipped) to the frame rails.
(3) Tighten the bolts to 102 Nzm (75 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Position the bumper extensions on the bumper
rail and install the retaining bolts.
(5) Tighten the bolts to 104 Nzm (77 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install the fog lamps, if equipped.
FRAME CROSSMEMBER COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the screws that attach the crossmem-
ber cover and support to the frame rails.
(2) Remove the crossmember cover and support
from the frame rails.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the support and crossmember cover on
the frame rails.
(2) Install the attaching screws.
(3) Tighten the screws to 8 Nzm (72 in. lbs.) torque.
REAR BUMPER
When equipped with a spare tire carrier attached
to the tailgate, a rear bumperette is attached to the
frame (Fig. 2 and 3).
Fig. 2 Rear Bumperette
Fig. 1 Front Bumper Rail, Crossmember Cover &
Tow Hooks
13 - 16 YJÐBUMPERSJ
Page 1214 of 2198
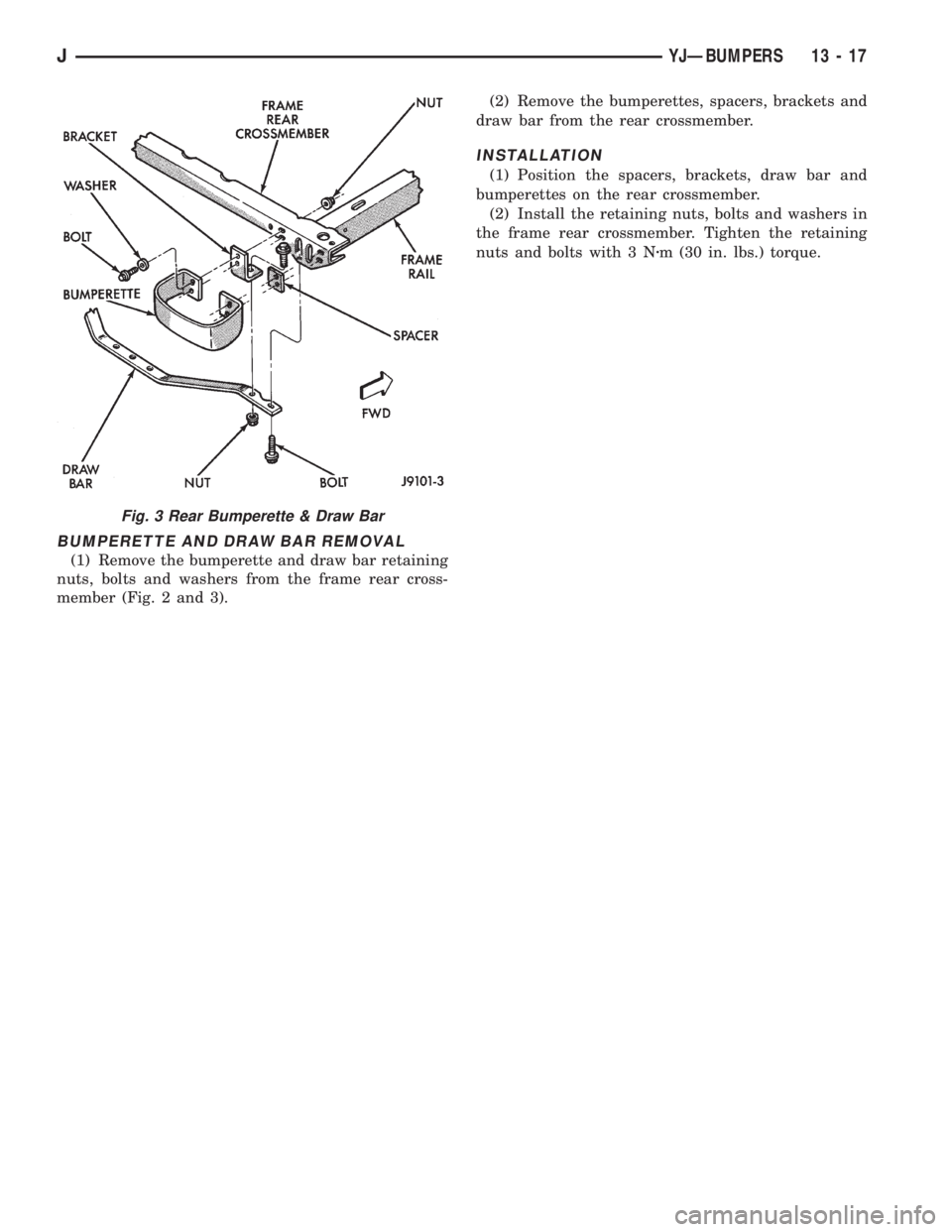
BUMPERETTE AND DRAW BAR REMOVAL
(1) Remove the bumperette and draw bar retaining
nuts, bolts and washers from the frame rear cross-
member (Fig. 2 and 3).(2) Remove the bumperettes, spacers, brackets and
draw bar from the rear crossmember.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the spacers, brackets, draw bar and
bumperettes on the rear crossmember.
(2) Install the retaining nuts, bolts and washers in
the frame rear crossmember. Tighten the retaining
nuts and bolts with 3 Nzm (30 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 3 Rear Bumperette & Draw Bar
JYJÐBUMPERS 13 - 17
Page 1215 of 2198

Page 1216 of 2198

FUEL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
ACCELERATOR PEDAL AND THROTTLE CABLE.17
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM.................. 3
FUEL TANKS........................... 13
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)Ð
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEMOPERATION.......................... 19
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)Ð
COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.... 58
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)Ð
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS.................. 35
SPECIFICATIONS........................ 67
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references are made to par-
ticular vehicle models by alphabetical designation
(XJ or YJ) or by the particular vehicle nameplate. A
chart showing a breakdown of the alphabetical desig-
nations is included in the Introduction section at the
beginning of this manual.
TheFuel Systemconsists of: the fuel tank, an
electric (fuel tank mounted) fuel pump and a fuel fil-
ter. It also consists of fuel tubes/lines/hoses, vacuum
hoses, throttle body and fuel injectors.
TheFuel Delivery Systemconsists of: the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel tubes/lines/hoses, fuel rail,
fuel injectors and fuel pressure regulator.
AFuel Return Systemis used on all vehicles.
The system consists of: the fuel tubes/lines/hoses that
route fuel back to the fuel tank.
TheFuel Tank Assemblyconsists of: the fuel
tank, filler tube, fuel fill and vent hoses, fuel gauge
sending unit/electric fuel pump module, a pressure
relief/rollover valve and a pressure-vacuum filler cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
Evaporation Control System.This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in Group 25, Emission
Control Systems.
FUEL USAGE STATEMENT
Your vehicle was designed to meet all emission reg-
ulations and provide excellent fuel economy using
high quality unleaded gasoline. Only use unleaded
gasolines having a minimum posted octane of 87.
If your vehicle develops occasional light spark
knock (ping) at low engine speeds, this is not harm-
ful. However,continued heavy knock at high
speeds can cause damage and should be re-
ported to your dealer immediately.Engine dam-
age as a result of heavy knock operation may not becovered by the new vehicle warranty.
In addition to using unleaded gasoline with the
proper octane rating,those that contain deter-
gents, corrosion and stability additives are rec-
ommended.Using gasolines that have these
additives will help improve fuel economy, reduce
emissions and maintain vehicle performance.
Poor quality gasolinecan cause problems such
as hard starting, stalling and stumble. If you experi-
ence these problems, use another brand of gasoline
before considering service for the vehicle.
GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS
Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with
materials that contain oxygen such as alcohol, MTBE
and ETBE. The type and amount of oxygenate used
in the blend is important. The following are generally
used in gasoline blends:
ETHANOL
Ethanol (Ethyl or Grain Alcohol) properly blended,
is used as a mixture of 10 percent ethanol and 90
percent gasoline.Gasoline with ethanol may be
used in your vehicle.
METHANOL
CAUTION: DO NOT USE GASOLINES CONTAINING
METHANOL.Use of methanol/gasoline blends may re-
sult in starting and driveability problems. In addition,
damage may be done to critical fuel system compo-
nents.
Methanol (Methyl or Wood Alcohol) is used in a va-
riety of concentrations blended with unleaded gaso-
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 1217 of 2198

line. You may encounter fuels containing 3 percent or
more methanol along with other alcohols called cosol-
vents.
Problems that are the result of using methanol/gas-
oline blends are not the responsibility of Chrysler
Corporation. They may not be covered by the vehicle
warranty.
MTBE/ETBE
Gasoline and MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether)
blends are a mixture of unleaded gasoline and up to
15 percent MTBE. Gasoline and ETBE (Ethyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether) are blends of gasoline and up to
17 percent ETBE. Gasoline blended with MTBE or
ETBE may be used in your vehicle.CLEAN AIR GASOLINE
Many gasolines are now being blended that con-
tribute to cleaner air, especially in those areas of the
country where air pollution levels are high. These
new blends provide a cleaner burning fuel and some
are referred to asReformulated Gasoline.
In areas of the country where carbon monoxide lev-
els are high, gasolines are being treated with oxygen-
ated materials such as MTBE, ETBE and ethanol.
Chrysler Corporation supports these efforts toward
cleaner air and recommends that you use these gaso-
lines as they become available.
14 - 2 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 1218 of 2198

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
INDEX
page page
Fuel Filter................................ 9
Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test................ 8
Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.............. 6
Fuel Pump Capacity Test.................... 7
Fuel Pump Electrical Control.................. 5Fuel Pump Module......................... 3
Fuel System Pressure Test................... 6
Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps............ 9
Quick-Connect Fittings..................... 10
FUEL PUMP MODULE
The fuel pump module is installed in the top of the
fuel tank. The fuel pump module contains the follow-
ing components:
²Electric fuel pump
²Fuel pump reservoir
²In-tank fuel filter
²Fuel gauge sending unit
²Fuel supply and return tube connections
The fuel pump used on all vehicles is a turbine
type pump. It is driven by a permanent magnet 12
volt electric motor that is immersed in the fuel tank.
The electrical pump is integral with the fuel sender
unit. The pump/sender assembly is installed inside
the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a check valve at the outlet end
that consists of a ball held against a seat by force ap-
plied from a spring. When the pump is operating,
fuel pressure overcomes spring pressure and forces
the ball off its seat, allowing fuel to flow. When the
pump is not operating, spring pressure forces the ball
back against the seat preventing fuel backflow
through the pump.
Fuel system pressure is maintained at approxi-
mately 214 kPa (31 psi). This is when the pump is
operating and vacuum is supplied to the fuel pres-
sure regulator. If vacuum is not supplied to the pres-
sure regulator, fuel pressure will be approximately
55-69 kPa (8-10 psi) higher. This may be due to a
broken or clogged vacuum line. When the fuel pump
is not operating, fuel system pressure of 131-269 kPa
(19-39 psi) is maintained for approximately 2 to 6
hours. This is done by the fuel pump outlet check
valve and the vacuum assisted fuel pressure regula-
tor.
REMOVALÐXJ MODELS
The fuel pump/gauge sender unit assembly can be
removed from the fuel tank without removing the
tank from the vehicle.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE,
THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RE-LEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RE-
LEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
WARNING: EXTINGUISH ALL TOBACCO SMOKING
PRODUCTS BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL SYS-
TEM. KEEP OPEN FLAME AWAY FROM FUEL SYS-
TEM COMPONENTS.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap. Perform the Fuel Pres-
sure Release Procedure as outlined in this group.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(3) Using an approved portable gasoline siphon/
storage tank, drain fuel tank until fuel level is below
one quarter (1/4) full.
(4) Raise and support vehicle.
WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND FUEL
HOSES TO ABSORB ANY FUEL SPILLAGE DURING
FUEL TANK REMOVAL.
(5) Disconnect fuel vent supply and return tubes
from fittings on fuel pump module.
(6) Disconnect fuel pump module electrical harness
connector from main harness.
(7) Using a brass punch and hammer, remove fuel
pump module lock ring by carefully tapping it coun-
terclockwise (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Removing Lock RingÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
JFUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM 14 - 3
Page 1219 of 2198
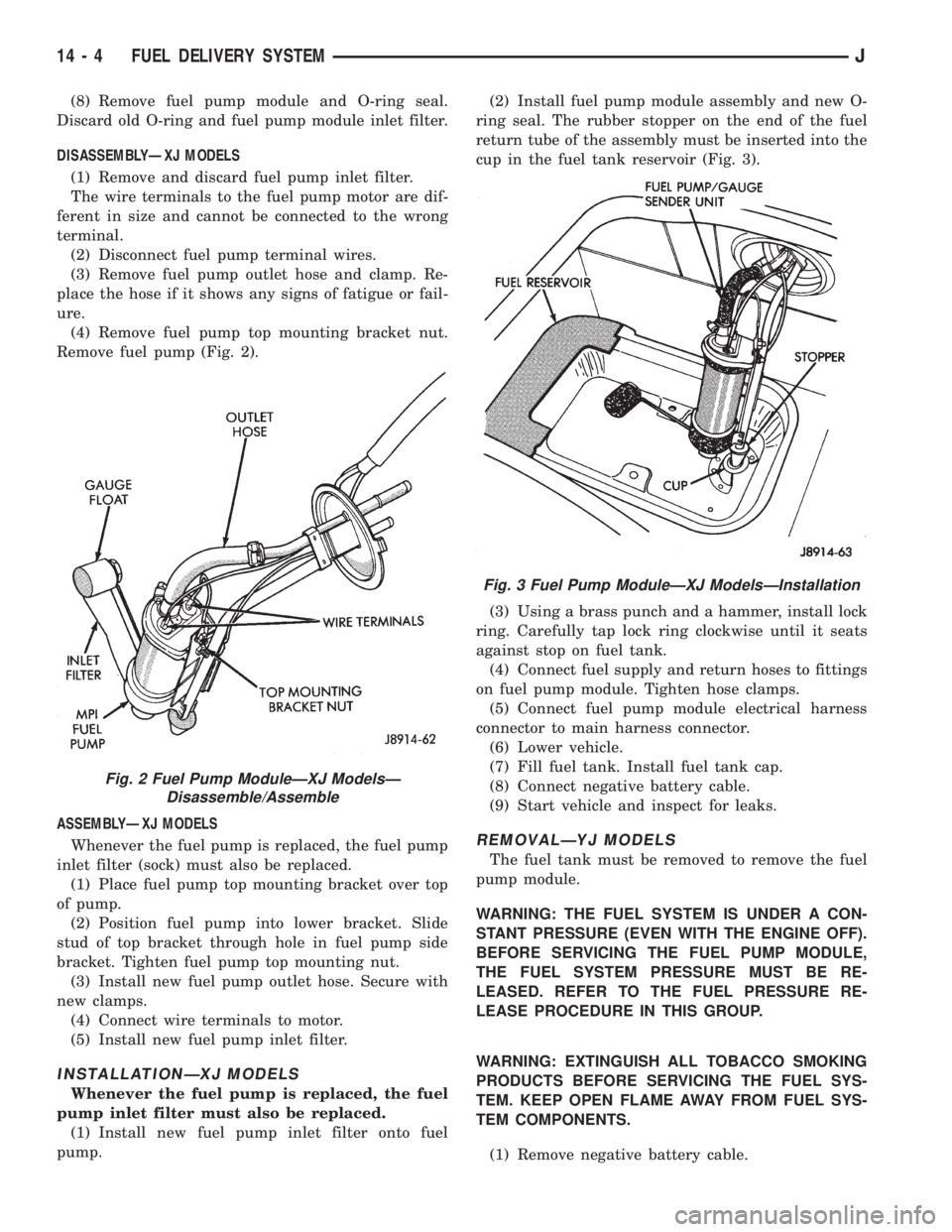
(8) Remove fuel pump module and O-ring seal.
Discard old O-ring and fuel pump module inlet filter.
DISASSEMBLYÐXJ MODELS
(1) Remove and discard fuel pump inlet filter.
The wire terminals to the fuel pump motor are dif-
ferent in size and cannot be connected to the wrong
terminal.
(2) Disconnect fuel pump terminal wires.
(3) Remove fuel pump outlet hose and clamp. Re-
place the hose if it shows any signs of fatigue or fail-
ure.
(4) Remove fuel pump top mounting bracket nut.
Remove fuel pump (Fig. 2).
ASSEMBLYÐXJ MODELS
Whenever the fuel pump is replaced, the fuel pump
inlet filter (sock) must also be replaced.
(1) Place fuel pump top mounting bracket over top
of pump.
(2) Position fuel pump into lower bracket. Slide
stud of top bracket through hole in fuel pump side
bracket. Tighten fuel pump top mounting nut.
(3) Install new fuel pump outlet hose. Secure with
new clamps.
(4) Connect wire terminals to motor.
(5) Install new fuel pump inlet filter.
INSTALLATIONÐXJ MODELS
Whenever the fuel pump is replaced, the fuel
pump inlet filter must also be replaced.
(1) Install new fuel pump inlet filter onto fuel
pump.(2) Install fuel pump module assembly and new O-
ring seal. The rubber stopper on the end of the fuel
return tube of the assembly must be inserted into the
cup in the fuel tank reservoir (Fig. 3).
(3) Using a brass punch and a hammer, install lock
ring. Carefully tap lock ring clockwise until it seats
against stop on fuel tank.
(4) Connect fuel supply and return hoses to fittings
on fuel pump module. Tighten hose clamps.
(5) Connect fuel pump module electrical harness
connector to main harness connector.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Fill fuel tank. Install fuel tank cap.
(8) Connect negative battery cable.
(9) Start vehicle and inspect for leaks.
REMOVALÐYJ MODELS
The fuel tank must be removed to remove the fuel
pump module.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE,
THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RE-
LEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RE-
LEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
WARNING: EXTINGUISH ALL TOBACCO SMOKING
PRODUCTS BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL SYS-
TEM. KEEP OPEN FLAME AWAY FROM FUEL SYS-
TEM COMPONENTS.
(1) Remove negative battery cable.
Fig. 2 Fuel Pump ModuleÐXJ ModelsÐ
Disassemble/Assemble
Fig. 3 Fuel Pump ModuleÐXJ ModelsÐInstallation
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEMJ
Page 1220 of 2198
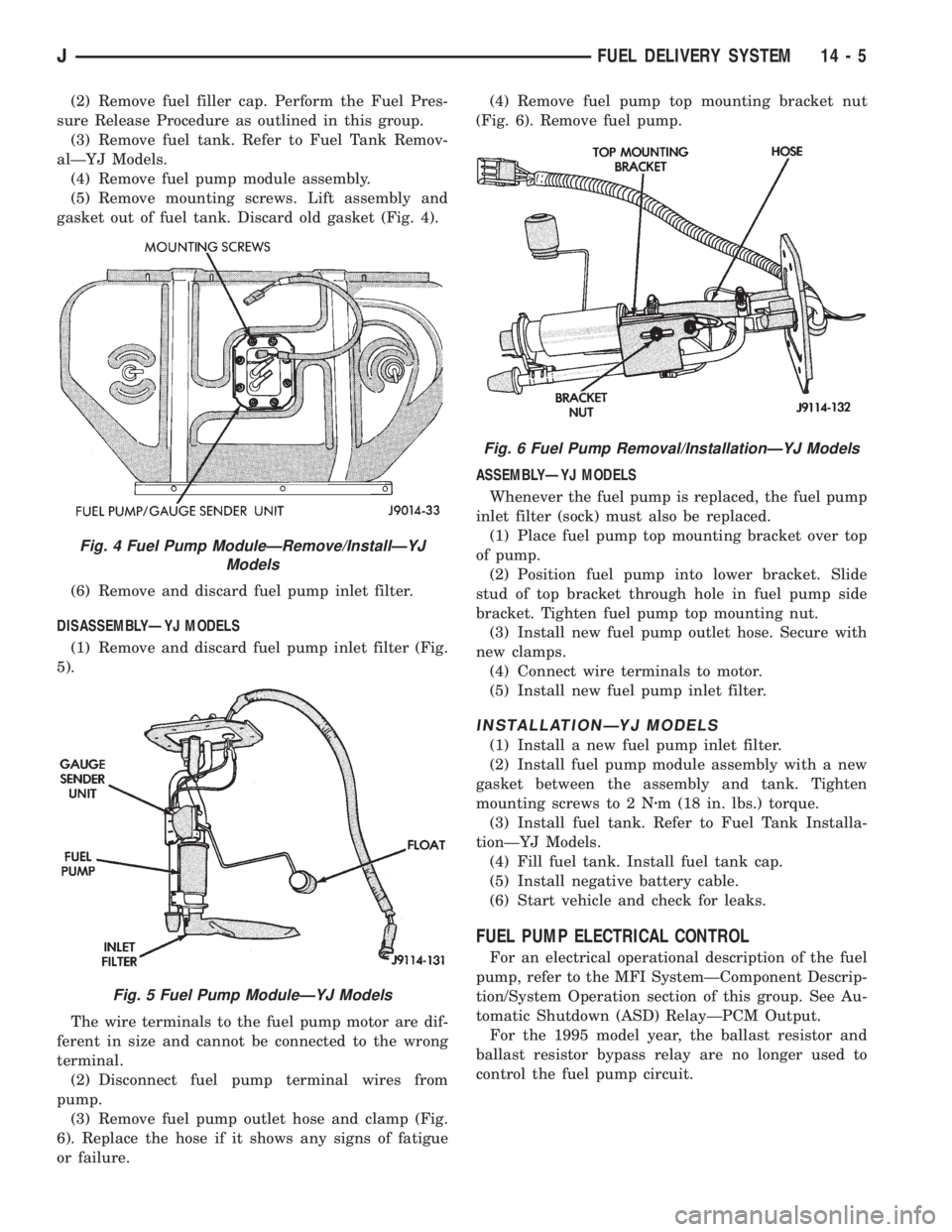
(2) Remove fuel filler cap. Perform the Fuel Pres-
sure Release Procedure as outlined in this group.
(3) Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Remov-
alÐYJ Models.
(4) Remove fuel pump module assembly.
(5) Remove mounting screws. Lift assembly and
gasket out of fuel tank. Discard old gasket (Fig. 4).
(6) Remove and discard fuel pump inlet filter.
DISASSEMBLYÐYJ MODELS
(1) Remove and discard fuel pump inlet filter (Fig.
5).
The wire terminals to the fuel pump motor are dif-
ferent in size and cannot be connected to the wrong
terminal.
(2) Disconnect fuel pump terminal wires from
pump.
(3) Remove fuel pump outlet hose and clamp (Fig.
6). Replace the hose if it shows any signs of fatigue
or failure.(4) Remove fuel pump top mounting bracket nut
(Fig. 6). Remove fuel pump.
ASSEMBLYÐYJ MODELS
Whenever the fuel pump is replaced, the fuel pump
inlet filter (sock) must also be replaced.
(1) Place fuel pump top mounting bracket over top
of pump.
(2) Position fuel pump into lower bracket. Slide
stud of top bracket through hole in fuel pump side
bracket. Tighten fuel pump top mounting nut.
(3) Install new fuel pump outlet hose. Secure with
new clamps.
(4) Connect wire terminals to motor.
(5) Install new fuel pump inlet filter.
INSTALLATIONÐYJ MODELS
(1) Install a new fuel pump inlet filter.
(2) Install fuel pump module assembly with a new
gasket between the assembly and tank. Tighten
mounting screws to 2 Nzm (18 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Installa-
tionÐYJ Models.
(4) Fill fuel tank. Install fuel tank cap.
(5) Install negative battery cable.
(6) Start vehicle and check for leaks.
FUEL PUMP ELECTRICAL CONTROL
For an electrical operational description of the fuel
pump, refer to the MFI SystemÐComponent Descrip-
tion/System Operation section of this group. See Au-
tomatic Shutdown (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output.
For the 1995 model year, the ballast resistor and
ballast resistor bypass relay are no longer used to
control the fuel pump circuit.
Fig. 4 Fuel Pump ModuleÐRemove/InstallÐYJ
Models
Fig. 5 Fuel Pump ModuleÐYJ Models
Fig. 6 Fuel Pump Removal/InstallationÐYJ Models
JFUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM 14 - 5