ECO mode JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 198 of 2198

secondary brakeshoes move the shoes directly into
contact with the drum braking surface. The actuating
levers are interconnected by a system of cables and a
tensioner mechanism. The tensioner mechanism con-
trols parking brake adjustment.
A parking brake switch is used on all models. It is
mounted on the parking brake lever or foot pedal and
is actuated by movement of the lever/pedal. The
switch, which is in circuit with the red warning light
in the dash, will illuminate the warning light when-
ever the parking brakes are applied.
On XJ models, the cable tensioner is part of the lever
assembly. On YJ models, the tensioner and equalizer
are mounted in a bracket attached to the underbody.
On YJ models, the parking brake front cable is at-
tached to the foot pedal and cable tensioner. The ten-
sioner and rear cables are connected to the equalizer
(Fig. 1).
On XJ models, the cable tensioner is connected di-
rectly to the hand lever (a front cable is not used).
The tensioner rod is attached to the equalizer which
is the connecting point for the rear cables (Fig. 2).
The rear cables are connected to the actuating le-
ver on each secondary brakeshoe. The levers are at-
tached to the brakeshoes by a pin either pressed into,
or welded to the lever. A clip is used to secure the pin
in the brakeshoe. The pin allows each lever to pivot
independently of the brakeshoe.
Struts installed between each brakeshoe, are used to
maintain shoe alignment and equal motion when the
parking brakes are applied. Each strut is equipped with
a combination tension and anti-rattle spring.
Parking Brake Application
To apply the parking brakes, the foot pedal is
pressed downward, or the hand lever is pulled up-
ward, to an engaged position. This pulls the rear
brakeshoe actuating levers forward, by means of the
interconnected tensioner and cables.
As the actuating lever is pulled forward, the park-
ing brake strut (which is connected to both shoes),
exerts a linear force against the primary brakeshoe.
This action presses the primary shoe into contact
with the drum.
Once the primary shoe contacts the drum, force ex-
erted through the strut does not stop. Instead, fur-
ther lever movement exerts continuing force against
the strut. This force is transferred through the strut
to the secondary brakeshoe causing it to pivot into
the drum as well.
The brakeshoes remain engaged with the drum until
the levers and cables are released. A gear type ratchet-
ing mechanism is used to hold the pedal or lever in an
applied position. Parking brake release is accomplished
by means of the release handle on YJ models. Or by the
hand lever release button on XJ models.
Fig. 2 Parking Brake Components (XJ)
JPARKING BRAKES 5 - 61
Page 205 of 2198
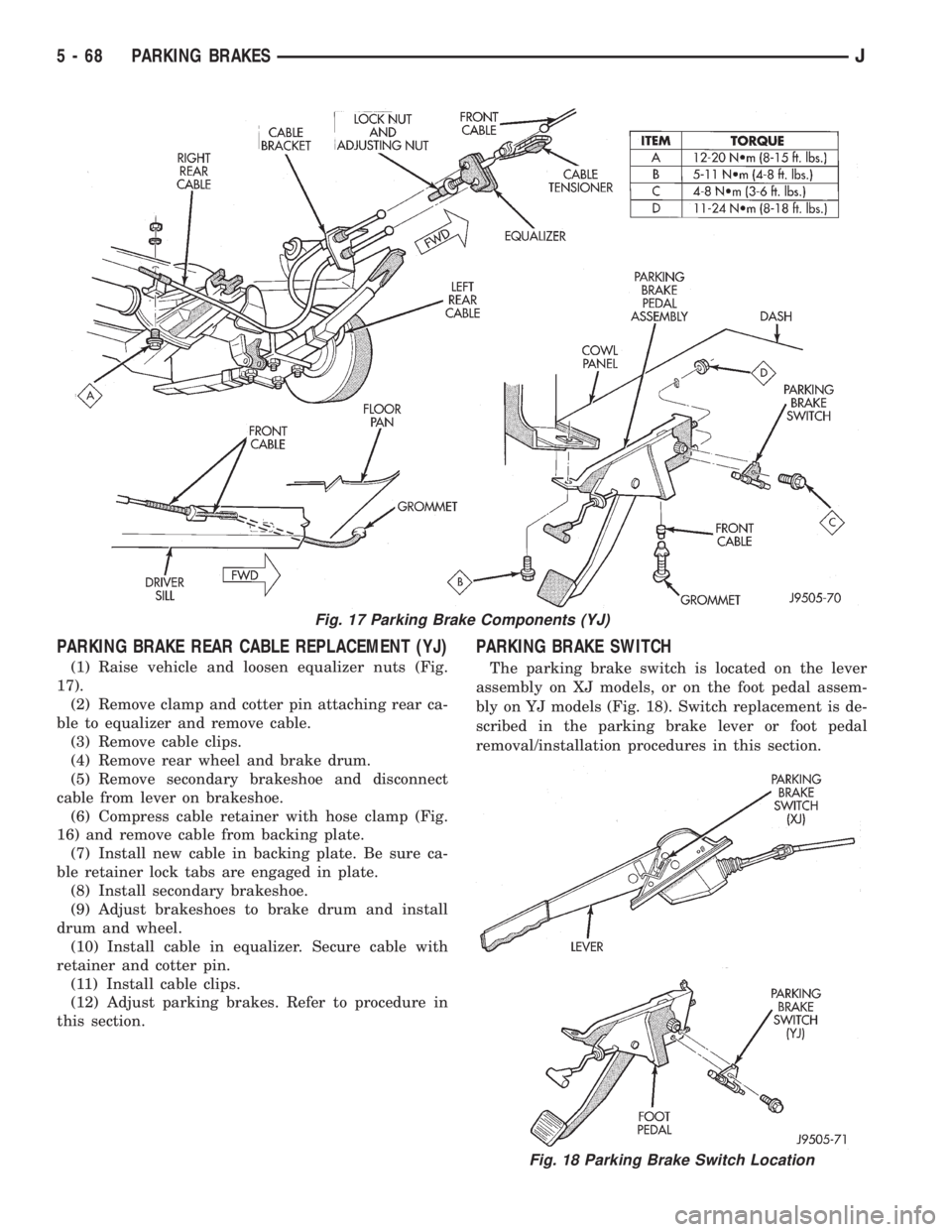
PARKING BRAKE REAR CABLE REPLACEMENT (YJ)
(1) Raise vehicle and loosen equalizer nuts (Fig.
17).
(2) Remove clamp and cotter pin attaching rear ca-
ble to equalizer and remove cable.
(3) Remove cable clips.
(4) Remove rear wheel and brake drum.
(5) Remove secondary brakeshoe and disconnect
cable from lever on brakeshoe.
(6) Compress cable retainer with hose clamp (Fig.
16) and remove cable from backing plate.
(7) Install new cable in backing plate. Be sure ca-
ble retainer lock tabs are engaged in plate.
(8) Install secondary brakeshoe.
(9) Adjust brakeshoes to brake drum and install
drum and wheel.
(10) Install cable in equalizer. Secure cable with
retainer and cotter pin.
(11) Install cable clips.
(12) Adjust parking brakes. Refer to procedure in
this section.
PARKING BRAKE SWITCH
The parking brake switch is located on the lever
assembly on XJ models, or on the foot pedal assem-
bly on YJ models (Fig. 18). Switch replacement is de-
scribed in the parking brake lever or foot pedal
removal/installation procedures in this section.
Fig. 17 Parking Brake Components (YJ)
Fig. 18 Parking Brake Switch Location
5 - 68 PARKING BRAKESJ
Page 220 of 2198

(8) Install transmission. Refer to Group 21 for pro-
cedure.
CLUTCH HOUSING REPLACEMENT
The clutch housing is removable and can be re-
placed when the transmission is out of the vehicle.
The bolts attaching the housing to the transmission
case are located inside the housing (Fig. 8). Recom-
mended tightening torque for the clutch housing-to-
transmission bolts is 38 Nzm (28 ft. lbs.).
Be sure the transmission and housing mating
surfaces are clean before installing an original,
or replacement clutch housing. Dirt/foreign ma-
terial trapped between the housing and trans-
mission will cause misalignment. If
misalignment is severe enough, the result will
be clutch drag, incomplete release and hard
shifting.
CLUTCH HYDRAULIC LINKAGE REMOVAL
The clutch master cylinder, slave cylinder
and connecting line are serviced as an assem-
bly only. The linkage components cannot be
overhauled or serviced separately. The cylin-
ders and connecting line are sealed units. Also
note that removal/installation procedures forright and left hand drive models are basically
the same. Only master cylinder location is dif-
ferent.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove fasteners attaching slave cylinder to
clutch housing.
(3) Remove slave cylinder from clutch housing (Fig.
9).
(4) Disengage clutch fluid line from body clips.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Verify that cap on clutch master cylinder reser-
voir is tight. This is necessary to avoid undue spill-
age during removal.
(7) Remove clutch master cylinder attaching nuts.
Note that one nut is accessible from engine compart-
ment and one nut is accessible from under instru-
ment panel (Figs. 10 and 11).
(8) Remove clip securing clutch master cylinder
push rod to pedal and slide push rod off pedal pin.
(9) Disconnect clutch pedal position switch wires.
(10) If pedal pin is equipped with bushing, inspect
condition of bushing and replace it if worn or dam-
aged.
(11) Remove clutch hydraulic linkage through en-
gine compartment.
Fig. 8 Clutch Housing AttachmentFig. 7 Pilot Bearing Installation
JCLUTCH SERVICE 6 - 13
Page 229 of 2198
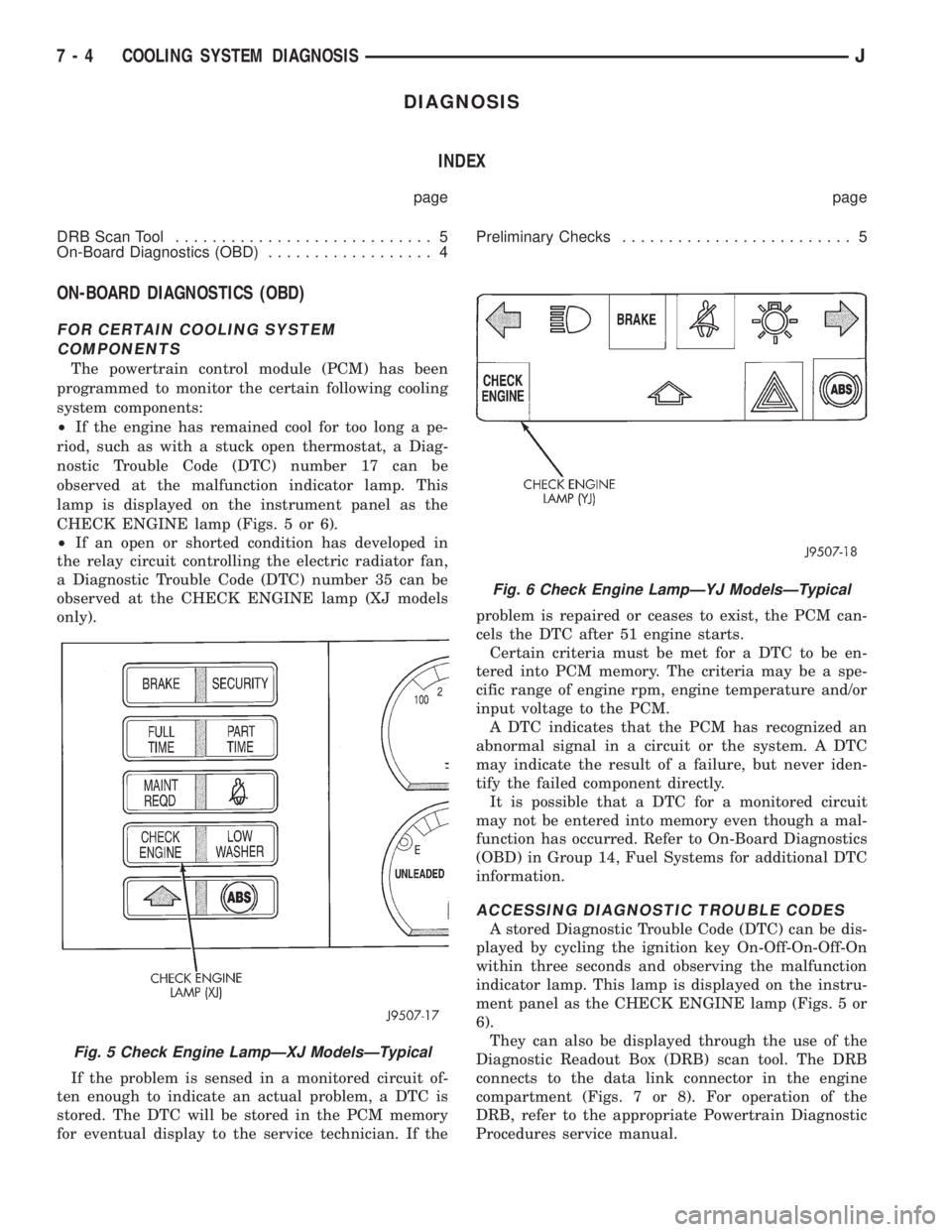
DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
DRB Scan Tool............................ 5
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD).................. 4Preliminary Checks......................... 5
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
FOR CERTAIN COOLING SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
The powertrain control module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor the certain following cooling
system components:
²If the engine has remained cool for too long a pe-
riod, such as with a stuck open thermostat, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) number 17 can be
observed at the malfunction indicator lamp. This
lamp is displayed on the instrument panel as the
CHECK ENGINE lamp (Figs. 5 or 6).
²If an open or shorted condition has developed in
the relay circuit controlling the electric radiator fan,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) number 35 can be
observed at the CHECK ENGINE lamp (XJ models
only).
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit of-
ten enough to indicate an actual problem, a DTC is
stored. The DTC will be stored in the PCM memory
for eventual display to the service technician. If theproblem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM can-
cels the DTC after 51 engine starts.
Certain criteria must be met for a DTC to be en-
tered into PCM memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine rpm, engine temperature and/or
input voltage to the PCM.
A DTC indicates that the PCM has recognized an
abnormal signal in a circuit or the system. A DTC
may indicate the result of a failure, but never iden-
tify the failed component directly.
It is possible that a DTC for a monitored circuit
may not be entered into memory even though a mal-
function has occurred. Refer to On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) in Group 14, Fuel Systems for additional DTC
information.
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A stored Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be dis-
played by cycling the ignition key On-Off-On-Off-On
within three seconds and observing the malfunction
indicator lamp. This lamp is displayed on the instru-
ment panel as the CHECK ENGINE lamp (Figs. 5 or
6).
They can also be displayed through the use of the
Diagnostic Readout Box (DRB) scan tool. The DRB
connects to the data link connector in the engine
compartment (Figs. 7 or 8). For operation of the
DRB, refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures service manual.
Fig. 5 Check Engine LampÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
Fig. 6 Check Engine LampÐYJ ModelsÐTypical
7 - 4 COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSISJ
Page 230 of 2198

EXAMPLES:
²If the lamp (Figs. 5 or 6) flashes 1 time, pauses
and flashes 2 more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC) number 12 is indicated. If this code is
observed, it is indicating that the battery has been
disconnected within the last 50 key-on cycles. It
could also indicate that battery voltage has been dis-
connected to the PCM. In either case, other DTC's
may have been erased.
²If the lamp flashes 1 time, pauses and flashes 7
more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) number 17 is indicated.
²If the lamp flashes 3 times, pauses and flashes 5
more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) number 35 is indicated.
After any stored DTC information has been ob-
served, the display will end with a flashing DTC
number 55. This will indicate the end of all stored in-
formation.
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, the DRB scan
tool must be used to erase a DTC. Refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual for operation of the DRB scan tool.
DRB SCAN TOOL
For operation of the DRB scan tool, refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual.
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM OVERHEATING
Establish what driving conditions caused the com-
plaint. Abnormal loads on the cooling system such as
the following may be the cause.
1. PROLONGED IDLE, VERY HIGH AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE, SLIGHT TAIL WIND AT IDLE,
SLOW TRAFFIC, TRAFFIC JAMS, HIGH
SPEED, OR STEEP GRADES:
Driving techniques that avoid overheating are:
²Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range.
²Increasing engine speed for more air flow is recom-
mended.
2. TRAILER TOWING:
Consult Trailer Towing section of owners manual.
Do not exceed limits.
3. AIR CONDITIONING; ADD-ON OR AFTER
MARKET:
A maximum cooling package should have been or-
dered with vehicle if add-on or after market A/C is
installed. If not, maximum cooling system compo-
nents should be installed for model involved per
manufacturer's specifications.
4. RECENT SERVICE OR ACCIDENT REPAIR:
Determine if any recent service has been performed
on vehicle that may effect cooling system. This may
be:
²Engine adjustments (incorrect timing)
²Slipping engine accessory drive belt(s)
²Brakes (possibly dragging)
²Changed parts (incorrect water pump rotating in
wrong direction)
²Reconditioned radiator or cooling system refilling
(possibly under-filled or air trapped in system).
If investigation reveals none of the previous
items as a cause for an engine overheating com-
plaint, refer to following Cooling System Diag-
nosis charts.
These charts are to be used as a quick-reference
only. Refer to the group text for information.
Fig. 7 Data Link ConnectorÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
Fig. 8 Data Link ConnectorÐYJ ModelsÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 7 - 5
Page 243 of 2198

temperature, coolant is allowed to flow to the radia-
tor. This provides quick engine warmup and overall
temperature control.
An arrow plus the wordUPis stamped on the
front flange next to the air bleed. The wordsTO
RADare stamped on one arm of the thermostat.
They indicate the proper installed position.
The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-
out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes other prob-
lems. These are: longer engine warmup time, unreli-
able warmup performance, increased exhaust
emissions and crankcase condensation. This conden-
sation can result in sludge formation.
CAUTION: Do not operate an engine without a ther-
mostat, except for servicing or testing.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
XJ and YJ models are equipped with On-Board Di-
agnostics for certain cooling system components. Re-
fer to On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) in the Diagnosis
section of this group for additional information. If the
powertrain control module (PCM) detects low engine
coolant temperature, it will record a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC) in the PCM memory. The DTC num-
ber for low coolant temperature is 17. Do not change
a thermostat for lack of heat as indicated by the in-
strument panel gauge or heater performance unless a
DTC number 17 is present. Refer to the Diagnosis
section of this group for other probable causes. For
other DTC numbers, refer to On-Board Diagnostics
in the General Diagnosis section of Group 14, Fuel
Systems.
The DTC can also be accessed through the DRB
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
nostic Procedures manual for diagnostic information
and operation of the DRB scan tool.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
(1) Drain the coolant from the radiator until the
level is below the thermostat housing.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094) (FIG. 15). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. AL-
WAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING
CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps (Fig. 16). If re-
placement is necessary, use only an original equip-
ment clamp with matching number or letter.
(2) Remove radiator upper hose and heater hose at
thermostat housing.
(3) Disconnect wiring connector at engine coolant
temperature sensor.
(4) Remove thermostat housing mounting bolts,
thermostat housing, gasket and thermostat (Fig. 17).
Discard old gasket.
(5) Clean the gasket mating surfaces.
Fig. 13 XJ Models with 4.0L 6-Cylinder EngineÐ
Without A/C
Fig. 14 XJ Models With 4.0L 6-Cylinder EngineÐ
With A/C
7 - 18 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 251 of 2198

(4) When checking for vacuum leaks.
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN RECENTLY,
WAIT AT LEAST 15 MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING
RADIATOR CAP. WITH A RAG, SQUEEZE RADIATOR
UPPER HOSE TO CHECK IF SYSTEM IS UNDER
PRESSURE. PLACE A RAG OVER THE CAP AND
WITHOUT PUSHING DOWN, ROTATE CAP
COUNTER-CLOCKWISE TO THE FIRST STOP. AL-
LOW FLUID TO ESCAPE THROUGH OVERFLOW
HOSE INTO COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW
TANK. SQUEEZE RADIATOR UPPER HOSE TO DE-
TERMINE WHEN PRESSURE HAS BEEN RE-
LEASED. WHEN COOLANT AND STEAM STOP
BEING PUSHED INTO TANK AND SYSTEM PRES-
SURE DROPS, REMOVE RADIATOR CAP COM-
PLETELY.
PRESSURE TESTING RADIATOR CAPS
Remove cap from radiator. Be sure that sealing
surfaces are clean. Moisten rubber gasket with water
and install the cap on pressure tester (tool 7700 or
an equivalent) (Fig. 26).
Operate the tester pump and observe the gauge
pointer at its highest point. The cap release pressure
should be 83-to-110 kPa (12-to-16 psi). The cap is sat-
isfactory when the pressure holds steady. It is also
good if it holds pressure within the 83-to-110 kPa
(12-to-16 psi) range for 30 seconds or more. If the
pointer drops quickly, replace the cap.
CAUTION: Radiator pressure testing tools are very
sensitive to small air leaks, which will not causecooling system problems. A pressure cap that does
not have a history of coolant loss should not be re-
placed just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to tool. Turn tool upside
down and recheck pressure cap to confirm that cap
needs replacement.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the pressure valve gasket on the
cap. Replace cap if the gasket is swollen, torn or
worn. Inspect the area around radiator filler neck for
white deposits that indicate a leaking cap.
RADIATORS
GENERAL INFORMATION
All radiators are down flow types except XJ models
equipped with 4.0L 6-cylinder engines. Radiators in
XJ models equipped with the 4.0L 6-cylinder engine
are the cross flow type. Plastic tanks are used on all
radiators.
CAUTION: Plastic tanks, while stronger than brass,
are subject to damage by impact, such as
wrenches.
If the plastic tank has been damaged, the plastic
tank and/or o-rings are available for service repair.
Tank replacement should be done by qualified per-
sonal with proper equipment.
RADIATOR COOLANT FLOW CHECK
The following procedure will determine if coolant is
flowing through the cooling system.
If engine is cold, idle engine until normal operating
temperature is reached. Then feel the upper radiator
hose. If hose is hot, the thermostat is open and water
is circulating through cooling system.
RADIATOR CLEANING
The radiator and air conditioning fins should be
cleaned when an accumulation of bugs, leaves etc.
has occurred. Clean radiator fins are necessary for
good heat transfer. With the engine cold, apply cold
water and compressed air to the back (engine side) of
the radiator to flush the radiator and/or A/C con-
denser of debris.
RADIATOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS, RADIATOR CAP, OR
LOOSEN THE RADIATOR DRAINCOCK WITH THE
SYSTEM HOT AND PRESSURIZED. SERIOUS
BURNS FROM THE COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
Fig. 26 Pressure Testing Radiator Pressure
CapÐTypical
7 - 26 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 261 of 2198

nostic Procedures manual for diagnostic information
and operation of the DRB scan tool.
To test operation of the fan relay only, refer to Re-
laysÐOperation/Testing. This can be found in Group
14, Fuel Systems.
REMOVAL
The auxiliary cooling fan is attached to the radia-
tor upper crossmember behind the radiator.
(1) Remove the two fan mounting bolts from radi-
ator upper crossmember (Fig. 43).
(2) Disconnect the electric fan connector.
(3) Lift fan straight up and out of vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Align lower retaining tabs of fan shroud with
slots in bracket at bottom of radiator. Push fan down
into position.
(2) Tighten the mounting bolts to 4 Nzm (31 in.
lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect auxiliary cooling fan electrical connec-
tor.
TRANSMISSION OIL COOLERS
WATER-TO-OIL COOLER
All models equipped with an automatic transmis-
sion are equipped with a transmission oil cooler
mounted internally within the radiator tank. This in-
ternal cooler is supplied as standard equipment on
all models equipped with an automatic transmission.
Transmission oil is cooled when it passes through
this separate cooler. In case of a leak in the internalradiator mounted transmission oil cooler, engine cool-
ant may become mixed with transmission fluid or
transmission fluid may enter engine cooling system.
Both cooling system and transmission should be
drained and inspected if the internal radiator
mounted transmission cooler is leaking.
Also refer to the section on Transmission Air-to-Oil
Coolers. This auxiliary air-to-oil cooler is an option
on most engine packages.
REPLACING WATER-TO-OIL COOLER IN
RADIATOR SIDE TANK
The internal transmission oil cooler located within
the radiator is not serviceable. If it requires service,
the radiator must be replaced.
Once the repaired or replacement radiator has
been installed, fill the cooling system and inspect for
leaks. Refer to the Refilling Cooling System and Test-
ing Cooling System For Leaks sections in this group.
If the transmission operates properly after repairing
the leak, drain the transmission and remove the
transmission oil pan. Inspect for sludge and/or rust.
Inspect for a dirty or plugged inlet filter. If none of
these conditions are found, the transmission and
torque convertor may not require reconditioning. Re-
fer to Group 21 for automatic transmission servicing.
AIR-TO-OIL COOLER
An auxiliary air-to-oil transmission oil cooler is
available with most engine packages.
On XJ and YJ models, the cooler is located in front
of the radiator or A/C condenser (if equipped) and be-
hind the grill (Figs. 44, 45 or 46). It is mounted to
the front frame crossmember.
Fig. 43 Auxiliary Cooling FanÐRemove/InstallÐ
Typical
Fig. 44 Auxiliary Air-To-Oil CoolerÐYJ Models
7 - 36 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 288 of 2198

CHARGING SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The charging system consists of:
²generator
²voltage regulator circuitry (within PCM)
²ignition switch
²battery
²generator warning lamp or voltmeter (depending
on vehicle equipment)
²wiring harness and connections.
Following is a general description of the major
charging system components. Refer to Group 8W -
Wiring Diagrams for complete circuit descriptions
and diagrams.
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. When the ignition switch is turned to
the ON position, battery voltage is applied to the
generator rotor through one of the two field termi-
nals to produce a magnetic field. The generator is
driven by the engine through a serpentine belt and
pulley arrangement.
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the
generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a cur-
rent into the windings of the stator coil. Once the
generator begins producing sufficient current, it also
provides the current needed to energize the rotor.
The wye (Y) type stator winding connections de-
liver the induced AC current to 3 positive and 3 neg-
ative diodes for rectification. From the diodes,
rectified DC current is delivered to the vehicle elec-
trical system through the generator battery and
ground terminals.
The amount of DC current produced by the gener-
ator is controlled by the generator voltage regulator
(field control) circuitry, contained within the Power-
train Control Module (PCM)(Fig. 1). This circuitry is
connected in series with the second rotor field termi-
nal and ground.
Voltage is regulated by cycling the ground path to
control the strength of the rotor magnetic field. The
generator voltage regulator circuitry monitors system
line voltage and ambient temperature. It then com-
pensates and regulates generator current output ac-
cordingly.
The generator is serviced only as a complete as-
sembly. If the generator fails for any reason, the en-
tire assembly must be replaced. The generator
voltage regulator (field control) circuitry can be ser-
viced only by replacing the entire PCM.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including the
generator voltage regulator (field control) circuitry,
are monitored by the PCM. Each monitored circuit is
assigned a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM
will store a DTC in electronic memory for any failureit detects. See Using On-Board Diagnostic System in
this group for more information.
DIAGNOSIS
When operating normally, the indicator lamp on
models with the base instrument cluster will light
when the ignition switch is turned to the ON or
START position. After the engine starts, the indicator
lamp goes off. With the engine running, the charge
indicator lamp should light only when there is a
problem in the charging system (base cluster only).
On models with a voltmeter, when the ignition
switch is turned to the ON position, battery potential
will register on the meter. During engine cranking a
lower voltage will appear on the meter. With the en-
gine running, a voltage reading higher than the first
reading (ignition in ON) should register.
The following procedures may be used to diagnose
the charging system if:
²the indicator or voltmeter do not operate properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condition
occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
Fig. 1 Charging System Components (Typical)
JBATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 17
Page 304 of 2198

OVERHEAD CONSOLE
CONTENTS
page page
DIAGNOSIS............................. 2
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1SERVICE PROCEDURES................... 5
GENERAL INFORMATION
An overhead console featuring an electronic com-
pass and thermometer is an available option for XJ
(Cherokee) models. Following are general descrip-
tions of major components used in the overhead con-
sole. Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams for
complete circuit descriptions and diagrams.
COMPASS
The compass will display the direction in which the
vehicle is pointed using the eight major compass
headings (Examples: north is N, northeast is NE). It
does not display the headings in actual degrees. The
display is turned on or off using the COMP/TEMP
button to the left of the display.
The self-calibrating compass unit requires no ad-
justing in normal use. The only calibration that may
prove necessary is to drive the vehicle in 3 complete
circles, on level ground, in not less than 48 seconds.
This will reorient the unit to its vehicle.
The unit also will compensate for magnetism the
body of the vehicle may acquire during normal use.
However, avoid placing anything magnetic directly on
the roof of the vehicle. Magnetic mounts for an an-
tenna, a repair order hat or a funeral procession flag
can exceed the compensating ability of the compass
unit if placed on the roof panel. Magnetic bit drivers
used on the fasteners that hold the assembly to the
roof header can also affect compass operation.
If the vehicle roof should become magnetized, the
demagnetizing and calibration procedures may be re-
quired to restore proper operation.
THERMOMETER
The thermometer displays the outside ambient
temperature. The temperature displayed can be
changed from Fahrenheit to Celsius using the US/
METRIC button. The displayed temperature is not
an instant reading of conditions, but an average tem-
perature. It may take the unit several minutes to re-
act to a major temperature change such as driving
out of a heated garage into winter temperatures.
When the ignition switch is turned OFF, the lastdisplayed temperature reading stays in memory.
When the ignition switch is turned ON again, the
thermometer will display the memory temperature
for one minute; then update the display to the cur-
rent average temperature reading within five min-
utes.
READING AND COURTESY LAMPS
All reading and courtesy lamps in the overhead
console are activated by the door jamb switches.
When all doors and the liftgate are closed, the lamps
can be individually activated by depressing the corre-
sponding lens. When a door and/or the liftgate is
open, depressing the lamp lens switches will not turn
the lamps off. Refer to Group 8L - Lamps, for diag-
nosis and service of these lamps.
KEYLESS ENTRY RECEIVER
The overhead console houses the keyless entry re-
ceiver. Refer to Group 8P - Power Locks, for diagno-
sis and service of this component.
REMOTE GARAGE DOOR OPENER STORAGE
A compartment in the overhead console is designed
to hold most remote garage door opener transmitters.
The transmitter is mounted within the compartment
with an adhesive-backed hook and loop fastener
patch. Then one to three pegs are selected and
mounted on a post on the inside of the storage com-
partment door. The pegs may be stacked, if neces-
sary. The peg(s) selected must be long enough to
activate the button of the transmitter each time the
storage compartment door is depressed.
SUNGLASSES STORAGE
A flocked storage compartment for sunglasses is in-
cluded in the overhead console. This compartment
features a push/push-type latch and a viscous damp-
ening system for a fluid opening motion.
JOVERHEAD CONSOLE 8C - 1