heating JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 226 of 2198

COOLING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
DIAGNOSIS............................. 4
ENGINE ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS......... 38
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER.................. 44GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
SERVICE PROCEDURES.................. 13
SPECIFICATIONS........................ 45
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references are made to par-
ticular vehicle models by alphabetical designation
(XJ or YJ) or by the particular vehicle nameplate. A
chart showing a breakdown of alphabetical designa-
tions is included in the Introduction section at the
beginning of this manual.
COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system regulates engine operating tem-
perature. It allows the engine to reach normal oper-
ating temperature as quickly as possible, maintains
normal operating temperature and prevents over-
heating.
The cooling system also provides a means of heat-
ing the passenger compartment and cooling the auto-
matic transmission fluid (if equipped). The cooling
system is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water
pump to circulate coolant throughout the system.
An optional factory installed heavy duty cooling
package is available on most models. The package
consists of a radiator that has an increased number
of cooling fins. XJ models equipped with a 4.0L 6-cyl-inder engine and heavy duty cooling and/or air con-
ditioning also have an auxiliary electric cooling fan.
COOLING SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The cooling system consists of:
²A radiator
²Cooling fan (mechanical and/or electrical)
²Thermal viscous fan drive
²Fan shroud
²Radiator pressure cap
²Thermostat
²Coolant reserve/overflow system
²Transmission oil cooler (if equipped with an auto-
matic transmission)
²Coolant
²Water pump
²Hoses and hose clamps
SYSTEM COOLANT ROUTING
For cooling system flow routings, refer to Figs. 1, 2,
3or4.
JCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 1
Page 230 of 2198

EXAMPLES:
²If the lamp (Figs. 5 or 6) flashes 1 time, pauses
and flashes 2 more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC) number 12 is indicated. If this code is
observed, it is indicating that the battery has been
disconnected within the last 50 key-on cycles. It
could also indicate that battery voltage has been dis-
connected to the PCM. In either case, other DTC's
may have been erased.
²If the lamp flashes 1 time, pauses and flashes 7
more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) number 17 is indicated.
²If the lamp flashes 3 times, pauses and flashes 5
more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) number 35 is indicated.
After any stored DTC information has been ob-
served, the display will end with a flashing DTC
number 55. This will indicate the end of all stored in-
formation.
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, the DRB scan
tool must be used to erase a DTC. Refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual for operation of the DRB scan tool.
DRB SCAN TOOL
For operation of the DRB scan tool, refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual.
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM OVERHEATING
Establish what driving conditions caused the com-
plaint. Abnormal loads on the cooling system such as
the following may be the cause.
1. PROLONGED IDLE, VERY HIGH AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE, SLIGHT TAIL WIND AT IDLE,
SLOW TRAFFIC, TRAFFIC JAMS, HIGH
SPEED, OR STEEP GRADES:
Driving techniques that avoid overheating are:
²Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range.
²Increasing engine speed for more air flow is recom-
mended.
2. TRAILER TOWING:
Consult Trailer Towing section of owners manual.
Do not exceed limits.
3. AIR CONDITIONING; ADD-ON OR AFTER
MARKET:
A maximum cooling package should have been or-
dered with vehicle if add-on or after market A/C is
installed. If not, maximum cooling system compo-
nents should be installed for model involved per
manufacturer's specifications.
4. RECENT SERVICE OR ACCIDENT REPAIR:
Determine if any recent service has been performed
on vehicle that may effect cooling system. This may
be:
²Engine adjustments (incorrect timing)
²Slipping engine accessory drive belt(s)
²Brakes (possibly dragging)
²Changed parts (incorrect water pump rotating in
wrong direction)
²Reconditioned radiator or cooling system refilling
(possibly under-filled or air trapped in system).
If investigation reveals none of the previous
items as a cause for an engine overheating com-
plaint, refer to following Cooling System Diag-
nosis charts.
These charts are to be used as a quick-reference
only. Refer to the group text for information.
Fig. 7 Data Link ConnectorÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
Fig. 8 Data Link ConnectorÐYJ ModelsÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 7 - 5
Page 238 of 2198

SERVICE PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Auxiliary Electric Cooling FanÐXJ Models with 4.0L
6-Cylinder Engine....................... 35
Coolant................................. 20
Coolant Reserve/Overflow System............. 24
Cooling System Cleaning/Reverse Flushing...... 22
Cooling System Fans...................... 32
Cooling System Hoses..................... 32
Draining Cooling System.................... 21
Radiator Pressure Cap..................... 25
Radiators............................... 26Refilling Cooling System.................... 21
Testing Cooling System for Leaks............. 22
Thermostat.............................. 17
Transmission Oil Coolers.................... 36
Viscous Fan Drive......................... 34
Water Pump Tests......................... 13
Water PumpsÐGeneral Information............ 13
Water PumpsÐRemoval/Installation........... 14
WATER PUMPSÐGENERAL INFORMATION
A centrifugal water pump circulates coolant
through the water jackets, passages, intake manifold,
radiator core, cooling system hoses and heater core.
The pump is driven from the engine crankshaft by a
drive belt on all engines.
The water pump impeller is pressed onto the rear
of a shaft that rotates in bearings pressed into the
housing. The housing has a small hole to allow seep-
age to escape. The water pump seals are lubricated
by the antifreeze in the coolant mixture. No addi-
tional lubrication is necessary.
CAUTION: All engines are equipped with a reverse
(counter-clockwise) rotating water pump and vis-
cous fan drive assembly. REVERSE is stamped or
imprinted on the cover of the viscous fan drive and
inner side of the fan. The letter R is stamped into
the back of the water pump impeller (Fig. 1).
Engines from previous model years, depending
upon application, may have been equipped with a for-
ward (clockwise) rotating water pump. Installation of
the wrong water pump will cause engine overheating.
A quick test to determine if the pump is working is
to check if the heater warms properly. A defective wa-
ter pump will not be able to circulate heated coolant
through the long heater hose to the heater core.
WATER PUMP TESTS
LOOSE IMPELLER
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.(1) Drain the cooling system.
(2) Loosen the fan belt(s).
(3) Disconnect the lower radiator hose from the
water pump.
(4) Bend a stiff clothes hanger or welding rod as
shown in (Fig. 2).
(5) Position the rod in the water pump inlet and
attempt to hold the impeller while turning the fan
blades. If equipped with a viscous fan drive, turn the
water pump shaft with a breaker bar and socket at-
tached to a mounting flange nut. If the impeller is
loose and can be held with the rod while the fan
blades are turning, the pump is defective. If the im-
peller turns, the pump is OK.
Connect the hose and install the coolant, or proceed
with repairs.
Fig. 1 Reverse Rotating Water PumpÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES 7 - 13
Page 239 of 2198

INSPECTING FOR INLET RESTRICTIONS
Inadequate heater performance may be caused by a
metal casting restriction in the water pump heater
hose inlet.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.
(1) Drain sufficient coolant from the radiator to de-
crease the level below the water pump heater hose
inlet.
(2) Remove the heater hose.
(3) Inspect the inlet for metal casting flash or
other restrictions.
Remove the pump from engine before remov-
ing restriction to prevent contamination of the
coolant with debris. Refer to Water Pump Re-
moval.
WATER PUMPSÐREMOVAL/INSTALLATION
REMOVALÐALL MODELS
CAUTION: If the water pump is replaced because of
mechanical damage, the fan blades and viscous fan
drive should also be inspected. These components
could have been damaged due to excessive vibra-
tion.The water pump on all models can be removed
without discharging the air conditioning system (if
equipped).
CAUTION: All engines have a reverse (counter-
clockwise) rotating water pump. The letter R is
stamped into the back of the water pump impeller
(Fig. 1) to identify. Engines from previous model
years, depending upon application, may be
equipped with a forward (clockwise) rotating water
pump. Installation of the wrong water pump will
cause engine over heating.
The water pump impeller is pressed on the rear of
the pump shaft and bearing assembly. The water
pump is serviced only as a complete assembly.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE BLOCK DRAIN
PLUG(S) OR LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain coolant into a clean container for re-
use.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Drain the cooling system. Refer to Draining
Cooling System in this group.
(3)XJ models with 4.0L 6-cylinder engine
equipped with A/C or heavy duty cooling sys-
tem:
Loosen (but do not remove at this time) the four
water pump pulley-to-water pump hub mounting
bolts (Fig. 3).
XJ models with 4.0L 6-cylinder engine with-
out A/C or heavy duty cooling system; or any
2.5L 4-cylinder engines; or any YJ models:
Loosen (but do not remove at this time) the four
fan hub-to-water pump pulley mounting nuts (Fig. 4).
Fig. 2 Impeller TestÐTypical
Fig. 3 Water Pump Pulley Bolts
7 - 14 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 249 of 2198

CAUTION: Do not operate the engine with a spark
plug shorted for more than a minute. The catalytic
converter may be damaged.
Isolate the compression leak by shorting each
spark plug to the cylinder block. The gauge pointer
should stop or decrease vibration when spark plug
for leaking cylinder is shorted. This happens because
of the absence of combustion pressure.
COMBUSTION LEAKAGE TEST (WITHOUT
PRESSURE TESTER)
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Drain sufficient coolant to allow for thermostat re-
moval. Refer to Thermostat Replacement. Disconnect
the water pump drive belt.
Disconnect the upper radiator hose from the ther-
mostat housing. Remove the housing and thermostat.
Install the thermostat housing.
Add coolant to the radiator to bring the level to
within 6.3 mm (1/4 in) of the top of the thermostat
housing.
CAUTION: Avoid overheating. Do not operate the
engine for an excessive period of time. Open the
draincock immediately after the test to eliminate
boil over of coolant.
Start the engine and accelerate rapidly three times
(to approximately 3000 rpm) while observing the
coolant. If internal engine combustion gases are leak-
ing into the cooling system, bubbles will appear in
the coolant. If bubbles do not appear, there is no in-
ternal combustion gas leakage.
COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW SYSTEM
The system works along with the radiator pressure
cap. This is done by using thermal expansion and
contraction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. It provides:
²A volume for coolant expansion and contraction.
²A convenient and safe method for checking/adjust-
ing coolant level at atmospheric pressure. This is
done without removing the radiator pressure cap.
²Some reserve coolant to the radiator to cover mi-
nor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
As the engine cools, a vacuum is formed in the
cooling system of both the radiator and engine. Cool-ant will then be drawn from the coolant tank and re-
turned to a proper level in the radiator.
The coolant reserve/overflow system consists of a
radiator mounted pressurized cap, a plastic reserve/
overflow tank (Figs. 22, 23 or 24), a tube (hose) con-
necting the radiator and tank, and an overflow tube
on the side of the tank.
Fig. 22 Reserve/Overflow TankÐYJ Models
Fig. 23 Reserve/Overflow TankÐXJ ModelsÐExcept
Right Hand Drive
7 - 24 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 252 of 2198

WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094) (FIG. 27). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. AL-
WAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING
CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps (Fig. 28). If re-
placement is necessary, use only an original equip-
ment clamp with matching number or letter.XJ MODELS WITH 2.5L 4-CYLINDER ENGINE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Observe the previousWARNINGS.Remove ra-
diator cap.
(3) Position drain pan under draincock. Open radi-
ator draincock. Drain radiator.
(4) Remove radiator upper and lower hose clamps
(Figs. 27 and 28). Remove hoses.
(5) Remove E-clip from alignment dowel at radia-
tor lower mounting bracket (Fig. 29).
(6) Disconnect coolant reserve/overflow tank hose
from radiator.
(7) Remove four radiator fan shroud mounting
bolts (Fig. 29). Push shroud back against front of en-
gine.
(8) If equipped, disconnect and plug automatic
transmission fluid cooler lines. Refer to Group 21,
Transmission for procedures.
(9) Remove two radiator top mounting bolts (Fig.
29).
(10) (a) If equipped with air conditioning, remove
the radiator grille mounting screws and remove grill.
Refer to Group 23, Body for procedures.
(b) If equipped, remove the air conditioning con-
denser-to-radiator mounting bolt. Use an open end
wrench to remove bottom bolts (Fig. 30).
(11) Lift radiator straight up and out of vehicle.
Take care not to damage radiator fins. When remov-
ing radiator, note position of the rubber seals located
on the top, bottom and sides of radiator (Fig. 29). To
prevent possible overheating, these seals must be in-
stalled to their original positions.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install radiator behind air conditioning con-
denser with bottom alignment dowel inserted into ra-
diator lower mounting bracket (Fig. 29).
(2) Install E-clip to radiator alignment dowel (Fig.
29).
(3) Tighten the four condenser-to-radiator mount-
ing bolts to 6.2 Nzm (55 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) If removed, install radiator grille.
(5) Tighten radiator top mounting bolts to 6 Nzm
(55 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) If equipped, connect automatic transmission
fluid cooler lines to radiator. Refer to Group 21,
Transmission for procedures.
(7) Install the radiator fan shroud.
(8) Connect the coolant reserve/overflow tank hose.
(9) Connect radiator hoses and install hose clamps.
(10) Connect negative battery cable.
(11) Close the draincock.
(12) Fill cooling system with correct coolant.
(13) Install radiator cap.
(14) Check and adjust automatic transmission
fluid level (if equipped).
Fig. 27 Hose Clamp ToolÐTypical
Fig. 28 Clamp Number/Letter Location
JCOOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES 7 - 27
Page 256 of 2198

WAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING
CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps (Fig. 28). If re-
placement is necessary, use only an original equip-
ment clamp with matching number or letter.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Observe the previousWARNINGS.Remove the
radiator cap.
(3) Position drain pan under draincock. Open radi-
ator draincock and drain radiator.
(4) Remove radiator upper and lower hose clamps
(Figs 27 and 28). Remove radiator hoses.
(5) Disconnect coolant reserve/overflow tank hose
from radiator.
(6) Remove the four fan shroud mounting bolts
(Fig. 35). On some models the power steering fluid
reservoir tank is attached to the side of the fan
shroud. Tie the reservoir back to prevent spillage. Po-
sition the fan shroud back over the fan blades.
(7) If equipped, disconnect and plug automatic
transmission fluid cooler lines.(8) Remove six radiator mounting bolts. Position
the front axle vent hose (Fig. 35) to the side.
(9) Lift radiator straight up and out of vehicle tak-
ing care not to damage radiator fins.
When removing radiator, note position of the rub-
ber seals located on the top and bottom of radiator
(figure 35 on certain models only). To prevent possi-
ble overheating, these seals must be installed to their
original positions.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the radiator. Install and tighten the
six mounting bolts (Fig. 35) to 8 Nzm (72 in. lbs.)
torque.
(2) Close radiator draincock.
(3) Position fan shroud and power steering reser-
voir tank (if equipped). Install and tighten four
mounting bolts to 8 Nzm (72 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) If equipped, remove plugs and connect auto-
matic transmission fluid cooler lines.
(5) Connect radiator hoses and install hose clamps.
(6) Connect negative battery cable.
(7) Fill cooling system with correct coolant. Refer
to the Coolant section of this group.
(8) Connect reserve/overflow tank hose.
(9) Install radiator cap.
Fig. 35 RadiatorÐRemove/InstallÐYJ Models
JCOOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES 7 - 31
Page 257 of 2198
(10) Check and adjust automatic transmission
fluid level (if equipped).
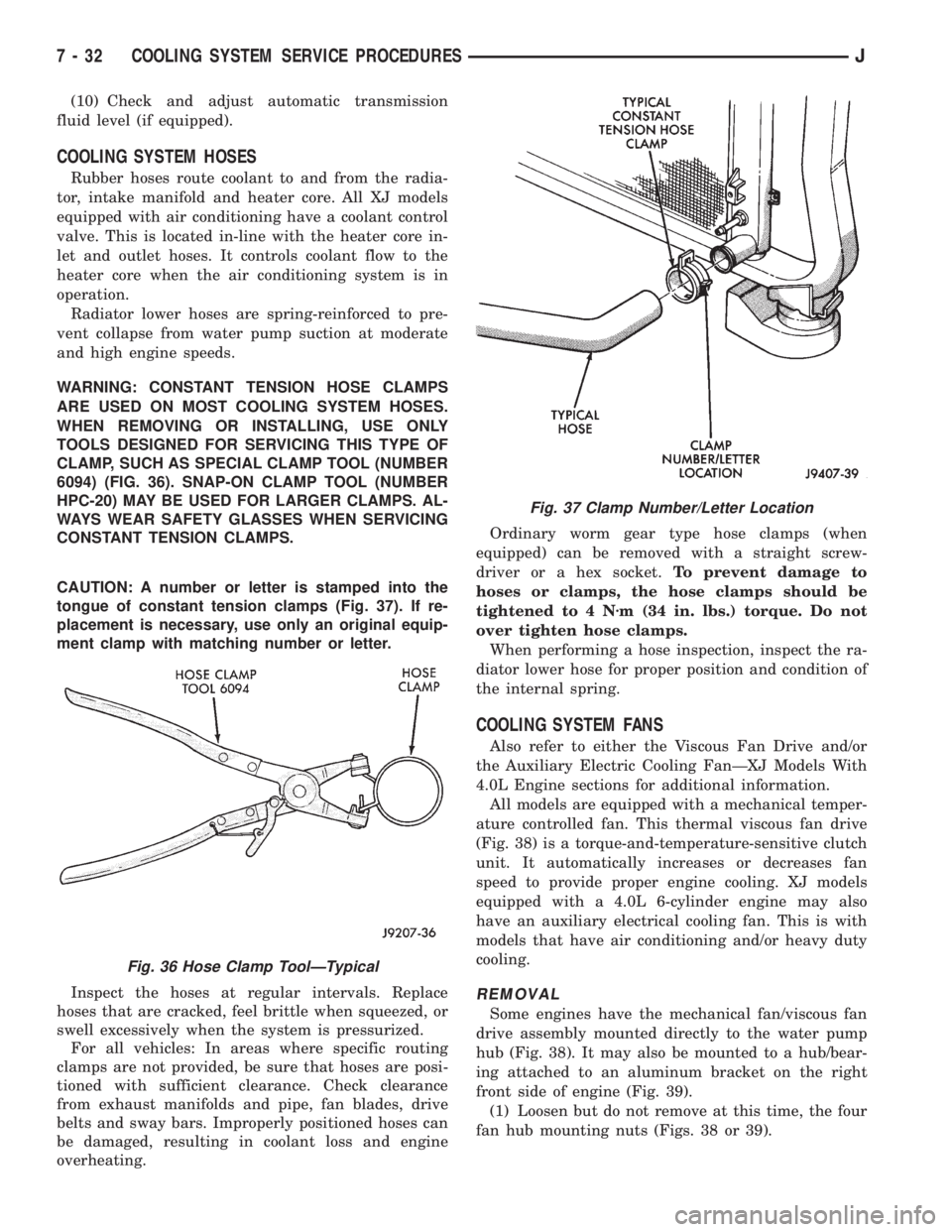
COOLING SYSTEM HOSES
Rubber hoses route coolant to and from the radia-
tor, intake manifold and heater core. All XJ models
equipped with air conditioning have a coolant control
valve. This is located in-line with the heater core in-
let and outlet hoses. It controls coolant flow to the
heater core when the air conditioning system is in
operation.
Radiator lower hoses are spring-reinforced to pre-
vent collapse from water pump suction at moderate
and high engine speeds.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094) (FIG. 36). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. AL-
WAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING
CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps (Fig. 37). If re-
placement is necessary, use only an original equip-
ment clamp with matching number or letter.
Inspect the hoses at regular intervals. Replace
hoses that are cracked, feel brittle when squeezed, or
swell excessively when the system is pressurized.
For all vehicles: In areas where specific routing
clamps are not provided, be sure that hoses are posi-
tioned with sufficient clearance. Check clearance
from exhaust manifolds and pipe, fan blades, drive
belts and sway bars. Improperly positioned hoses can
be damaged, resulting in coolant loss and engine
overheating.Ordinary worm gear type hose clamps (when
equipped) can be removed with a straight screw-
driver or a hex socket.To prevent damage to
hoses or clamps, the hose clamps should be
tightened to 4 Nzm (34 in. lbs.) torque. Do not
over tighten hose clamps.
When performing a hose inspection, inspect the ra-
diator lower hose for proper position and condition of
the internal spring.
COOLING SYSTEM FANS
Also refer to either the Viscous Fan Drive and/or
the Auxiliary Electric Cooling FanÐXJ Models With
4.0L Engine sections for additional information.
All models are equipped with a mechanical temper-
ature controlled fan. This thermal viscous fan drive
(Fig. 38) is a torque-and-temperature-sensitive clutch
unit. It automatically increases or decreases fan
speed to provide proper engine cooling. XJ models
equipped with a 4.0L 6-cylinder engine may also
have an auxiliary electrical cooling fan. This is with
models that have air conditioning and/or heavy duty
cooling.
REMOVAL
Some engines have the mechanical fan/viscous fan
drive assembly mounted directly to the water pump
hub (Fig. 38). It may also be mounted to a hub/bear-
ing attached to an aluminum bracket on the right
front side of engine (Fig. 39).
(1) Loosen but do not remove at this time, the four
fan hub mounting nuts (Figs. 38 or 39).
Fig. 36 Hose Clamp ToolÐTypical
Fig. 37 Clamp Number/Letter Location
7 - 32 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 269 of 2198

ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
GENERAL INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
An optional engine block heater is available for all
models. The heater is equipped with a power cord.
The cord is attached to an engine compartment com-
ponent with tie-straps. The heater warms the engine
providing easier engine starting and faster warm-up
in low temperatures. The heater is mounted in a core
hole of the engine cylinder block (in place of a freeze
plug) with the heating element immersed in engine
coolant. Connect the power cord to a grounded 110-
120 volt AC electrical outlet with a grounded, three-
wire extension cord.
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE ENGINE UNLESS
BLOCK HEATER CORD HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED
FROM POWER SOURCE AND SECURED IN PLACE.
BLOCK HEATER SPECIFICATIONS
²2.5L 4-Cylinder Engine: 115 Volts 400 Watts
²4.0L 6-Cylinder Engine: 120 Volts 600 Watts
REMOVAL
Refer to correct illustration (Figures 11, 12 or 13)
when servicing block heater.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
(1) Drain coolant from radiator and engine cylinder
block.(2) Unplug power cord from block heater.
(3) Loosen screw in center of block heater (Figs. 11,
12 or 13).
(4) Remove block heater from cylinder block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Thoroughly clean the engine core hole and the
block heater seat.
(2) Insert block heater assembly into core hole
with element loop pointingUp.
(3) Seat block heater flush against block face.
Tighten mounting screw to 3.6 Nzm (32 in. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Fill cooling system with coolant. Pressurize sys-
tem and inspect for leaks.
(5) Plug power cord into block heater. Route cord
away from moving parts, linkages and exhaust sys-
tem components. Secure cord in place with tie-straps.
Fig. 13 Heater and CordÐYJ Models
Fig. 11 Heater and CordÐXJ with 2.5L 4-Cylinder
Engine
Fig. 12 Heater and CordÐXJ with 4.0L 6-Cylinder
Engine
7 - 44 ENGINE BLOCK HEATERJ
Page 324 of 2198
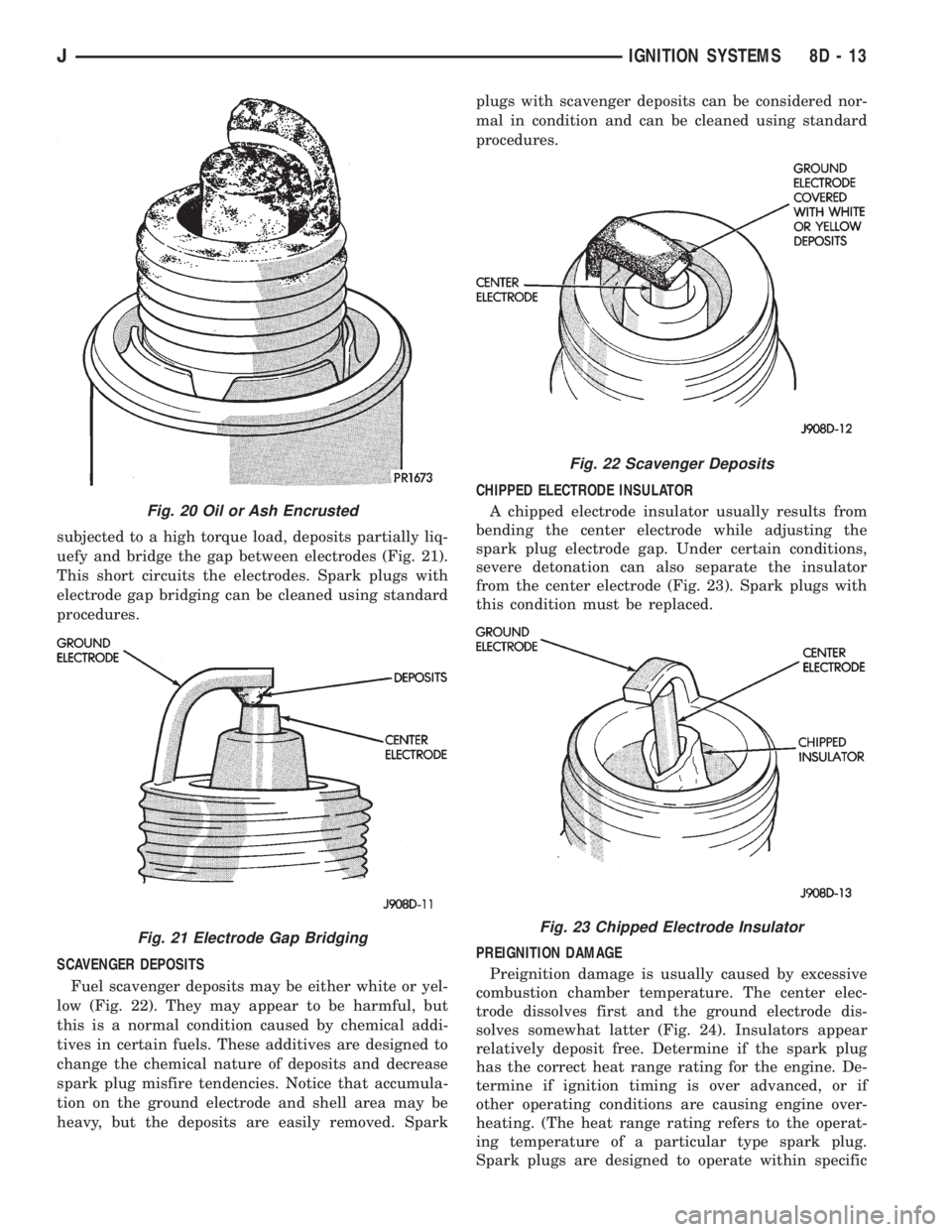
subjected to a high torque load, deposits partially liq-
uefy and bridge the gap between electrodes (Fig. 21).
This short circuits the electrodes. Spark plugs with
electrode gap bridging can be cleaned using standard
procedures.
SCAVENGER DEPOSITS
Fuel scavenger deposits may be either white or yel-
low (Fig. 22). They may appear to be harmful, but
this is a normal condition caused by chemical addi-
tives in certain fuels. These additives are designed to
change the chemical nature of deposits and decrease
spark plug misfire tendencies. Notice that accumula-
tion on the ground electrode and shell area may be
heavy, but the deposits are easily removed. Sparkplugs with scavenger deposits can be considered nor-
mal in condition and can be cleaned using standard
procedures.
CHIPPED ELECTRODE INSULATOR
A chipped electrode insulator usually results from
bending the center electrode while adjusting the
spark plug electrode gap. Under certain conditions,
severe detonation can also separate the insulator
from the center electrode (Fig. 23). Spark plugs with
this condition must be replaced.
PREIGNITION DAMAGE
Preignition damage is usually caused by excessive
combustion chamber temperature. The center elec-
trode dissolves first and the ground electrode dis-
solves somewhat latter (Fig. 24). Insulators appear
relatively deposit free. Determine if the spark plug
has the correct heat range rating for the engine. De-
termine if ignition timing is over advanced, or if
other operating conditions are causing engine over-
heating. (The heat range rating refers to the operat-
ing temperature of a particular type spark plug.
Spark plugs are designed to operate within specific
Fig. 20 Oil or Ash Encrusted
Fig. 21 Electrode Gap Bridging
Fig. 22 Scavenger Deposits
Fig. 23 Chipped Electrode Insulator
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 13