light JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 60 of 2198

(17) Tighten the track bar nut at the axle bracket
to 100 Nzm (74 ft. lbs.) torque.
(18) Check the front wheel alignment.
PINION SEAL REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Mark the propeller shaft yoke and pinion yoke
for installation alignment reference.
(4) Remove the propeller shaft from the yoke.
(5) Remove the pinion yoke nut and washer. Use
Remover C-452 and Wrench C-3281 to remove the
pinion yoke (Fig. 2).
(6) Mark the positions of the yoke and pinion gear
for installation alignment reference.
(7) Use Remover 7794A and slide hammer to re-
move the pinion gear seal (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal. Install seal with Installer D-163
and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 4).
(2) Align the reference marks and install yoke on
the pinion gear with Installer W-162-D.
(3) Install a new pinion nut on pinion shaft.Tighten
the nut to 217-352 Nzm (160-260 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 5).
(4) Align the installation reference marks and at-
tach the propeller shaft to the yoke.
(5) Add API grade GL 5 hypoid gear lubricant to
the differential housing, if necessary.
(6) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(7) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
HUB BEARING AND AXLE SHAFT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the brake components from the axle,
refer to Group 5, Brakes.
(4) Remove the cotter pin, nut retainer and axle
hub nut (Fig. 6).
(5) Remove the hub to knuckle bolts (Fig. 6). Remove
the hub from the steering knuckle and axle shaft.
(6) Remove the disc brake rotor shield from the
bearing carrier (Fig. 6).
(7) On disconnect axles, remove vacuum shift mo-
tor housing. Refer to Vacuum Disconnect Axle in this
section.
(8) Remove the axle shaft from the housing.Avoid
damaging the axle shaft oil seals in the differen-
tial.
Fig. 2 Pinion Yoke Removal
Fig. 3 Seal Removal
Fig. 4 Pinion Seal Installation
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 25
Page 66 of 2198
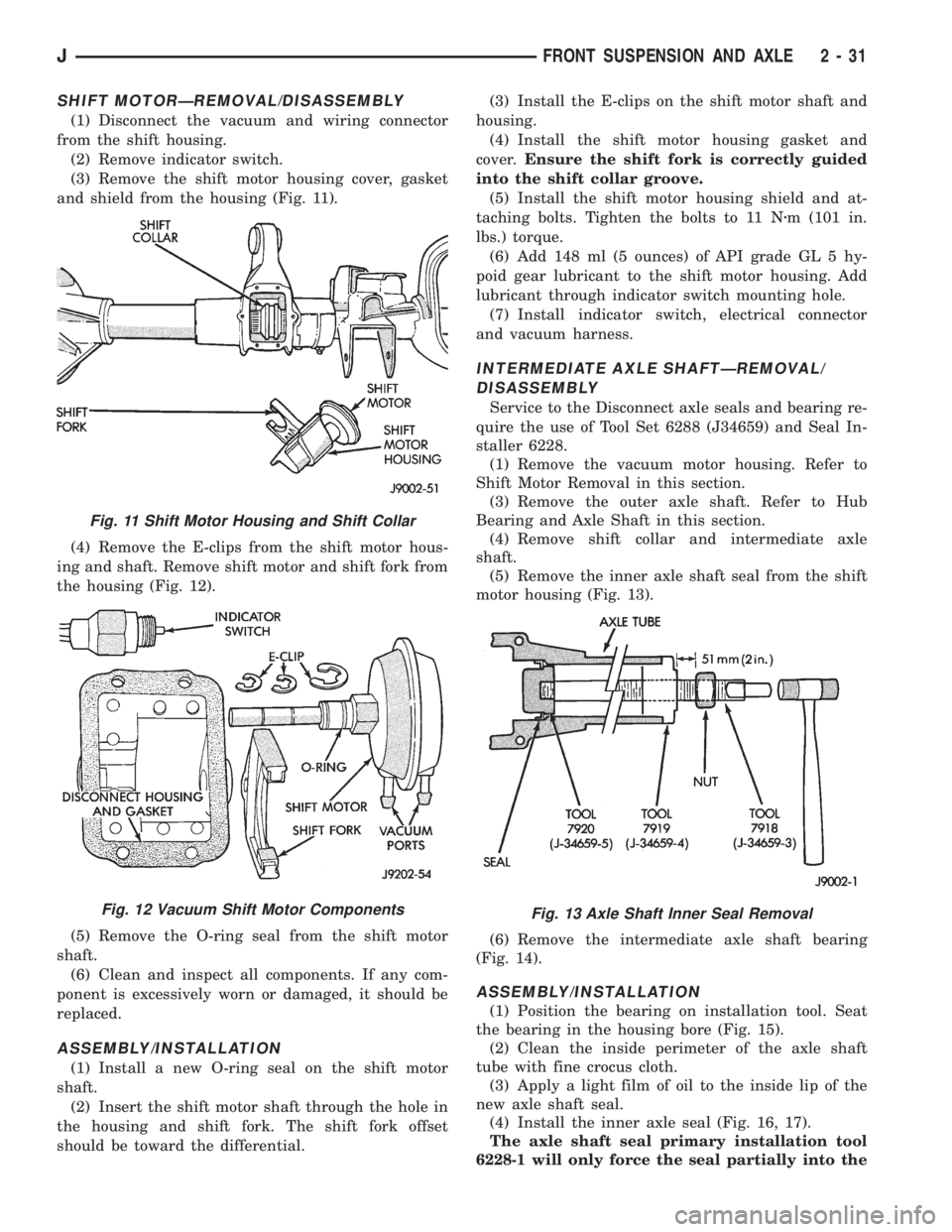
SHIFT MOTORÐREMOVAL/DISASSEMBLY
(1) Disconnect the vacuum and wiring connector
from the shift housing.
(2) Remove indicator switch.
(3) Remove the shift motor housing cover, gasket
and shield from the housing (Fig. 11).
(4) Remove the E-clips from the shift motor hous-
ing and shaft. Remove shift motor and shift fork from
the housing (Fig. 12).
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the shift motor
shaft.
(6) Clean and inspect all components. If any com-
ponent is excessively worn or damaged, it should be
replaced.
ASSEMBLY/INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new O-ring seal on the shift motor
shaft.
(2) Insert the shift motor shaft through the hole in
the housing and shift fork. The shift fork offset
should be toward the differential.(3) Install the E-clips on the shift motor shaft and
housing.
(4) Install the shift motor housing gasket and
cover.Ensure the shift fork is correctly guided
into the shift collar groove.
(5) Install the shift motor housing shield and at-
taching bolts. Tighten the bolts to 11 Nzm (101 in.
lbs.) torque.
(6) Add 148 ml (5 ounces) of API grade GL 5 hy-
poid gear lubricant to the shift motor housing. Add
lubricant through indicator switch mounting hole.
(7) Install indicator switch, electrical connector
and vacuum harness.
INTERMEDIATE AXLE SHAFTÐREMOVAL/
DISASSEMBLY
Service to the Disconnect axle seals and bearing re-
quire the use of Tool Set 6288 (J34659) and Seal In-
staller 6228.
(1) Remove the vacuum motor housing. Refer to
Shift Motor Removal in this section.
(3) Remove the outer axle shaft. Refer to Hub
Bearing and Axle Shaft in this section.
(4) Remove shift collar and intermediate axle
shaft.
(5) Remove the inner axle shaft seal from the shift
motor housing (Fig. 13).
(6) Remove the intermediate axle shaft bearing
(Fig. 14).
ASSEMBLY/INSTALLATION
(1) Position the bearing on installation tool. Seat
the bearing in the housing bore (Fig. 15).
(2) Clean the inside perimeter of the axle shaft
tube with fine crocus cloth.
(3) Apply a light film of oil to the inside lip of the
new axle shaft seal.
(4) Install the inner axle seal (Fig. 16, 17).
The axle shaft seal primary installation tool
6228-1 will only force the seal partially into the
Fig. 11 Shift Motor Housing and Shift Collar
Fig. 12 Vacuum Shift Motor ComponentsFig. 13 Axle Shaft Inner Seal Removal
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 31
Page 77 of 2198
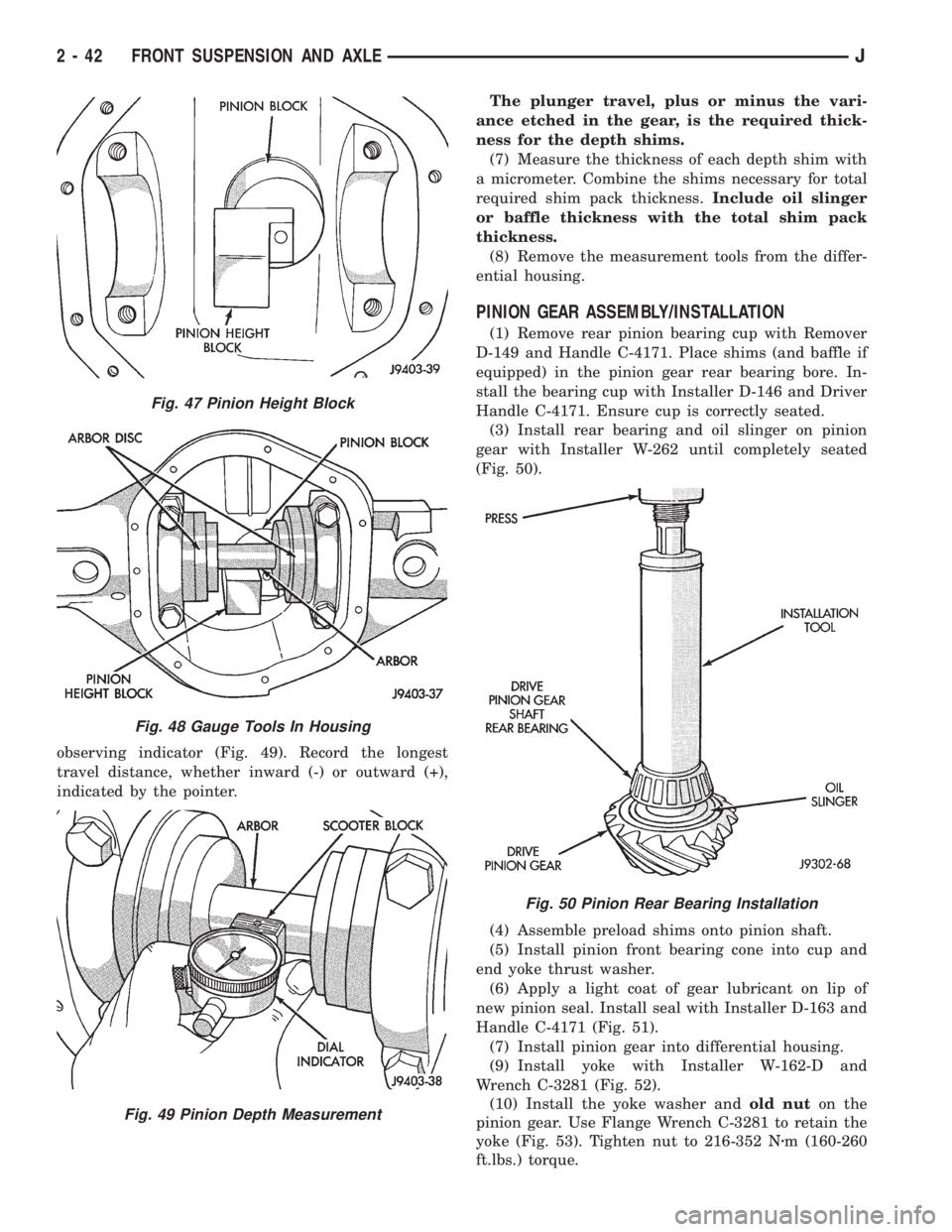
observing indicator (Fig. 49). Record the longest
travel distance, whether inward (-) or outward (+),
indicated by the pointer.The plunger travel, plus or minus the vari-
ance etched in the gear, is the required thick-
ness for the depth shims.
(7) Measure the thickness of each depth shim with
a micrometer. Combine the shims necessary for total
required shim pack thickness.Include oil slinger
or baffle thickness with the total shim pack
thickness.
(8) Remove the measurement tools from the differ-
ential housing.
PINION GEAR ASSEMBLY/INSTALLATION
(1) Remove rear pinion bearing cup with Remover
D-149 and Handle C-4171. Place shims (and baffle if
equipped) in the pinion gear rear bearing bore. In-
stall the bearing cup with Installer D-146 and Driver
Handle C-4171. Ensure cup is correctly seated.
(3) Install rear bearing and oil slinger on pinion
gear with Installer W-262 until completely seated
(Fig. 50).
(4) Assemble preload shims onto pinion shaft.
(5) Install pinion front bearing cone into cup and
end yoke thrust washer.
(6) Apply a light coat of gear lubricant on lip of
new pinion seal. Install seal with Installer D-163 and
Handle C-4171 (Fig. 51).
(7) Install pinion gear into differential housing.
(9) Install yoke with Installer W-162-D and
Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 52).
(10) Install the yoke washer andold nuton the
pinion gear. Use Flange Wrench C-3281 to retain the
yoke (Fig. 53). Tighten nut to 216-352 Nzm (160-260
ft.lbs.) torque.
Fig. 47 Pinion Height Block
Fig. 48 Gauge Tools In Housing
Fig. 49 Pinion Depth Measurement
Fig. 50 Pinion Rear Bearing Installation
2 - 42 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 90 of 2198

LEAF SPRING EYE BUSHING REPLACEMENT
(1) Assemble tools shown (Fig. 2). Tighten the nut
located at the socket wrench end of the threaded rod
until the bushing is forced out.
(2) Assemble and align the bushing installation
tools.
(3) Align the bushing with the spring eye. Tighten
the nut located at the socket wrench end of the
threaded rod. Tighten until the bushing is forced into
the spring eye.
The bushing must be centered in the spring
eye. The ends of the bushing must be flush or
slightly recessed within the end surfaces of the
spring eye.
STABILIZER BAR
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Disconnect stabilizer bar links from spring
brackets (Fig. 3).
(3) Disconnect the stabilizer bar brackets from the
frame rails. Remove the stabilizer bar and links.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the stabilizer bar links at the spring
brackets (Fig. 3). Install the attaching bolts and nuts
and tighten to 74 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Attach the stabilizer bar to the frame rail
brackets with the bolts. Tighten to 54 Nzm (40 ft.
lbs.).
(3) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
Fig. 2 Spring Eye Bushing Removal
Fig. 3 Stabilizer BarÐXJ Vehicles
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 5
Page 93 of 2198
The bushing must be centered in the spring
eye. The ends of the bushing must be flush or
slightly recessed within the end surfaces of the
spring eye.
TRACK BAR
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle. Position a hydraulic jack un-
der the axle and raise the axle to relieve the springs
of axle weight.(2) Remove the fasteners that attach the track bar
to the frame bracket and axle bracket (Fig. 3).
(3) Remove the track bar from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the ends of the track bar in the frame
and axle brackets (Fig. 3).
(2) Install and tighten the track bar attaching nuts
to 168 Nzm (125 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
Fig. 2 Spring Eye Bushing Removal
Fig. 3 Track BarÐYJ Vehicles
3 - 8 REAR SUSPENSION AND AXLESJ
Page 95 of 2198

This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion gear shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft
²Missing drive shaft balance weight
²Worn, out-of-balance wheels
²Loose wheel lug nuts
²Worn U-joint
²Loose spring U-bolts
²Loose/broken springs
²Damaged axle shaft bearings
²Loose pinion gear nut
²Excessive pinion yoke run out
²Bent axle shaft
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear-end vi-
bration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined be-
fore starting any repair.
Refer to Group 22, Wheels and Tires for additional
information.
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts
²Worn U-joints
²Loose spring mounts
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke
²Excessive ring gear backlash
²Excessive side gear\ase clearance
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the ve-
hicle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate.
Instruct the helper to shift the transmission into
gear. Listen for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is
helpful in isolating the source of a noise.
REAR AXLE ALIGNMENT
MEASUREMENT
The following procedure can be used to determine
if abnormal rear tire tread wear is the result of a
bent or deformed rear axle shaft.
(1) Raise both rear wheels off the surface with a
frame contact hoist.
(2) Attach a one-inch long piece of masking tape at
the center of each tire tread for use as reference marks.
(3) Rotate the rear wheels until both reference
marks face the front of the vehicle. Measure the dis-
tance between the outside edges of the two pieces of
tape. Record this measurement as the front of tire
(FTR) measurement.
(4) Rotate the rear wheels until both reference
marks face the rear of the vehicle. Measure the dis-
tance between the outside edges of the two pieces of
tape. Record this measurement as the rear of tire
(RTR) measurement.
(5) Subtract the (RTR) measurement from the
(FTR) measurement to obtain the amount of wheel
toe. The acceptable rear wheel toe-in position is 1/16
inch (1.6 mm) to 3/16 inch (4.8 mm) toe-out.
(6) Rotate the rear wheels until the reference
marks are facing downward. Measure the distance
between the outside edges of the two pieces of tape.
Record this measurement as the bottom of tire (BTR)
measurement.
(7) Average the (FTR) and the (RTR) distance mea-
surements. Subtract the (BTR) measurement from
this average distance to obtain the camber. The ac-
ceptable amount of camber is 1/16 inch to 3/32 inch
(1.6 to 2.4 mm).
(FTR + RTR) DIVIDED BY 2 (TWO) MINUS
BTR EQUALS CAMBER
If the (BTR) distance measurement is less
than the average FTR and RTR distance mea-
surement, the camber will be positive(+).If
the (BTR) distance measurement is greater
than the average FTR and RTR distance, the
camber will be negative(-).
If the toe position or camber is not acceptable, a bent
or deformed rear axle shaft is most likely the cause.
LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL
Under normal traction conditions, engine torque is di-
vided evenly. With low-traction surfaces, engine torque
is transferred to the wheel with the most tire traction.
When diagnosing a limited-slip differential the wheel
with the least traction can continue spinning.
The most common problem is a chatter noise when
turning corners. Check for incorrect or contaminated
lubricant. Replace the gear lubricant if necessary.
²With Trac-LokŸ differentials add a container of
MOPAR Trac-Lok Lubricant.
This will correct the condition in most instances. If
the chatter persists, clutch damage could have oc-
curred.
After changing the lubricant, drive the vehicle and
make 10 to 12 slow, figure-eight turns. This maneu-
ver will pump lubricant through the clutches.
3 - 10 REAR SUSPENSION AND AXLESJ
Page 98 of 2198

MODEL 35 AXLE
INDEX
page page
Axle Shaft............................... 16
Axle Shaft Seal and Bearing................. 17
Backlash and Contact Pattern Analysis......... 27
Cleaning/Inspection........................ 20
Differential Assembly....................... 21
Differential Disassembly.................... 18
Differential Measurement and Installation........ 25
Differential Removal....................... 18
Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐXJ Vehicles . . 14Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐYJ Vehicles . . 14
Final Assembly........................... 29
General Information....................... 13
Lubricant Change......................... 13
Lubricant Specifications..................... 13
Pinion Gear Depth Information............... 21
Pinion Measurement and Assembly............ 22
Pinion Removal/Disassembly................. 19
Pinion Shaft Seal Replacement............... 15
GENERAL INFORMATION
The Model 35 housing has an iron center casting
(differential housing) with axle shaft tubes extending
from either side. The tubes are pressed into and
welded to the differential housing to form a one-piece
axle housing.
The integral type housing, hypoid gear design has
the centerline of the pinion set below the centerline
of the ring gear.
The axle has a vent hose to relieve internal pres-
sure caused by lubricant vaporization and internal
expansion.
The axles are equipped with semi-floating axle
shafts, meaning that loads are supported by the axle
shaft and bearings. The axle shafts are retained by
C-clips in the differential side gears.
The cover provides a means for servicing the differ-
ential without removing the axle.
Axles may be equipped with drum or disc brakes.
The axles that are equipped with ABS brake have a
tone ring pressed on the axle shaft. Use care when
removing axle shafts as NOT to damage the tone
wheel or the sensor.
The Model 35 axle has the assembly part number
and gear ratio listed on a tag. The tag is attached to
the housing cover. Build date identification codes are
stamped on the axle shaft tube cover side.
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion mate shaft is retained with a
threaded roll pin. Differential bearing preload and
ring gear backlash is adjusted by the use of spacer
shims. Pinion bearing preload is set and maintained
by the use of a collapsible spacer.
For complete drive axle assembly removal
and installation refer to Drive Axle Assembly
Replacement in this Group.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
Multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant should be
used for Model 35 axle. The lubricant should haveMIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifications.
MOPAR Hypoid Gear Lubricant conforms to both of
these specifications.
²Lubricant for Model 35 axle is a thermally stable
SAE 80W-90 gear lubricant.
²Lubricant for Model 35 axle with Trailer Tow is
SAE 75W-140 SYNTHETIC gear lubricant.
²Trac-Lok differentials add 4 oz. of friction modifier.
²Lubricant quantity is 1.66 L (3.50 pts.).
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information.
CAUTION: If axle is submerged in water, lubricant
must be replaced immediately to avoid possible
premature axle failure.
LUBRICANT CHANGE
The gear lubricant will drain quicker if the vehicle
has been recently driven.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the dif-
ferential housing cover.
(3) Remove the differential housing cover and
drain the lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove the sealant from the housing and cover
surfaces.
(6) Apply a bead of MOPARtSilicone Rubber Seal-
ant to the housing cover (Fig. 1).Allow the sealant
to cure for a few minutes.
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes af-
ter applying the sealant. If not installed the
sealant must be removed and another bead ap-
plied.
(7) Install the cover and any identification tag.
Tighten the cover bolts to 41 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Refill differential with Mopar Hypoid Gear Lu-
bricant to bottom of the fill plug hole.
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 13
Page 99 of 2198

CAUTION: Overfilling the differential can result in
lubricant foaming and overheating.
Trac-Lok Differentials; A container of Trac-Lok lu-
bricant (friction modifier) should be added after re-
pair service or a lubricant change.
(9) Install the fill hole plug and lower the vehicle.
LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL vehicles should
be road tested by making 10 to 12 slow figure-eight
turns. This maneuver will pump the lubricant
through the clutch discs to eliminate a possible chat-
ter noise complaint.
DRIVE AXLE ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENTÐXJ
VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle and position support stands
under the frame rails slightly in front the springs.
(2) Remove the rear wheels.
(3) Mark the drive shaft yoke and axle pinion yoke
for alignment reference. Disconnect the drive shaft
from the axle.
(4) Disconnect the axle vent hose.
(5) Disconnect the parking brake cables at the
equalizer or backing plate.
(6) Disconnect the shock absorbers from the axle
brackets.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block.Do not disconnect the wheel cylinder tub-
ing fittings.
(8) If equipped, disconnect ABS wiring connections
at the axle.(9) Support the axle with a hydraulic jack under
the differential.
(10) Remove the spring U-bolts from the plate
brackets.
(11) Lower the jack enough to remove the axle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the vehicle at
normal height. It is important to have the springs
supporting the weight of the vehicle when the fas-
teners are torqued. If springs are not at their normal
ride position, vehicle ride comfort could be affected
and premature bushing wear may occur. Rubber
bushings must never be lubricated.
(1) Support the axle on a hydraulic jack under the
differential. Position the axle under the vehicle.
(2) Raise the axle and align the spring center bolts
with the locating holes in the axle pads and plate
brackets.
(3) Install the spring U-bolts through the plate
brackets and tighten to 70 Nzm (52 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install ABS wiring connections (if equipped) at
the axle.
(5) Connect the brake hose at the axle junction
block.
(6) Install the shock absorbers to the axle brackets
and tighten to 62 Nzm (46 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Connect the parking brake cables at the equal-
izer or backing plate.
(8) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting.
(9) Align the reference marks and connect the
drive shaft to the axle yoke. Tighten the U-joint
clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Check differential lubricant and add if neces-
sary.
(11) Install the wheel and tire.
(12) Bleed the brakes.
(13) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
DRIVE AXLE ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENTÐYJ
VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle and position support stands
under the frame rails slightly in front the springs.
(2) Remove the rear wheels.
(3) Mark the drive shaft yoke and axle pinion yoke
for alignment reference. Disconnect the drive shaft
from the axle.
(4) Disconnect the axle vent hose.
(5) Disconnect the parking brake cables at the
equalizer or backing plate.
(6) Disconnect the shock absorbers from the plate
brackets.
Fig. 1 Typical Housing Cover With Sealant
3 - 14 REAR SUSPENSION AND AXLESJ
Page 100 of 2198

(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block.Do not disconnect the wheel cylinder tub-
ing fittings.
(8) Disconnect the track bar at the axle bracket.
(9) Support the axle with a hydraulic jack under
the differential. Raise the axle just enough to relieve
the axle weight from the springs.
(10) Remove the spring U-bolts from the plate
brackets.
(11) Loosen BUT DO NOT REMOVE the bolts that
attach the spring front pivot at the frame rail brack-
ets. This will allow the springs to pivot without bind-
ing on the bushings.
(12) Disconnect shackle from the springs and lower
the springs to the surface.
(13) Lower the jack enough to remove the axle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the vehicle at
normal height. It is important to have the springs
supporting the weight of the vehicle when the fas-
teners are torqued. If springs are not at their normal
ride position, vehicle ride comfort could be affected
and premature bushing wear may occur. Rubber
bushings must never be lubricated.
(1) Support the axle on a hydraulic jack under the
differential. Position the axle under the vehicle.
(2) Raise the springs and install the spring shackle
bolts.Do not tighten at this time.
(3) Lower the axle and align the spring center
bolts with the locating holes in the axle pads and
plate brackets.
(4) Install the spring U-bolts through the plate
brackets and tighten to 122 Nzm (90 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect the track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt. Do not tighten at this time.
It is important that the springs support the
weight of the vehicle when the track bar is con-
nected. If the springs are not at their usual po-
sition, vehicle ride comfort could be affected.
(6) Connect the brake hose at the axle junction
block.
(7) Install the shock absorbers to the axle brackets
and tighten to 61 Nzm (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Connect the parking brake cables at the equal-
izer or backing plate.
(9) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting.
(10) Align the reference marks and connect the
drive shaft to the axle yoke. Tighten the U-joint
clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Check differential lubricant and add if neces-
sary.
(12) Install the wheel and tire.
(13) Bleed the brakes.
(14) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.(15) Tighten the spring front pivot bolt/nut to 142
Nzm (105 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the spring shackle
bolt/nut to 135 Nzm (100 ft. lbs.) torque.
(16) Tighten the track bar bolt at the axle bracket
to 142 Nzm (105 ft. lbs.) torque.
PINION SHAFT SEAL REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Mark the drive shaft yoke and pinion yoke for
installation alignment reference.
(4) Remove the drive shaft from the yoke.
(5) Rotate the pinion gear three or four times.
Make sure brakes are not dragging during this
procedure.
(6) Measure the amount of torque (in Newton-
meters or inch-pounds) necessary to rotate the pinion
gear with a torque wrench. Note the torque for in-
stallation reference.It must be known to properly
adjust the pinion gear bearing preload torque
after seal installation.
(7) Remove the pinion yoke nut and washer. Use
Remover C-452 and Wrench C-3281 to remove the
pinion yoke (Fig. 2).
(8) Mark the positions of the yoke and pinion gear
for installation alignment reference.
(9) Use Remover 7794A and slide hammer to re-
move the pinion gear seal (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal. Install seal with Installer D-163
and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 4).
(2) Align the installation reference marks and in-
stall yoke on the pinion gear with Installer W-162-D.
(3) Install a new nut on the pinion gear.Tighten
the nut only enough to remove the shaft end
play.
Fig. 2 Pinion Yoke Removal
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 15
Page 109 of 2198
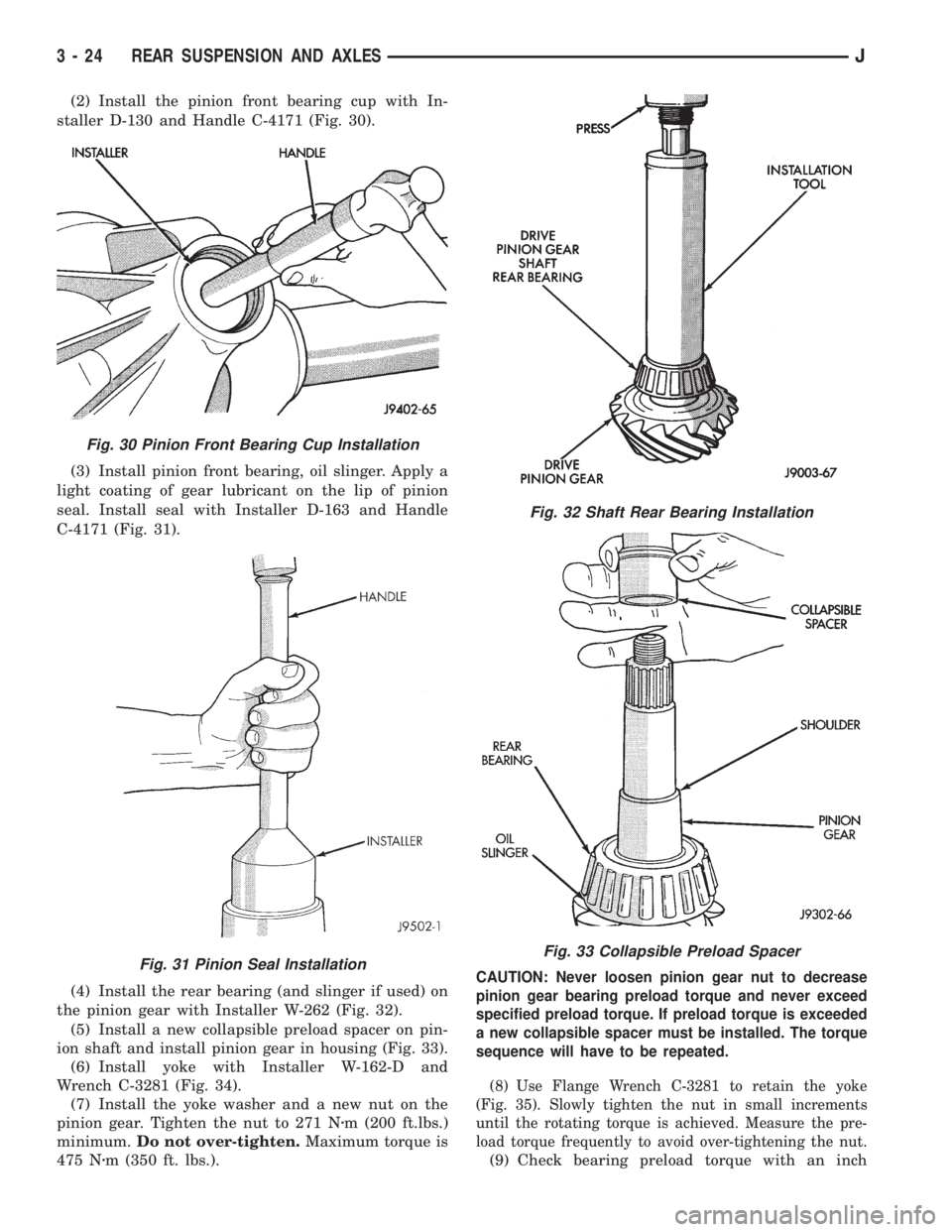
(2) Install the pinion front bearing cup with In-
staller D-130 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 30).
(3) Install pinion front bearing, oil slinger. Apply a
light coating of gear lubricant on the lip of pinion
seal. Install seal with Installer D-163 and Handle
C-4171 (Fig. 31).
(4) Install the rear bearing (and slinger if used) on
the pinion gear with Installer W-262 (Fig. 32).
(5) Install a new collapsible preload spacer on pin-
ion shaft and install pinion gear in housing (Fig. 33).
(6) Install yoke with Installer W-162-D and
Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 34).
(7) Install the yoke washer and a new nut on the
pinion gear. Tighten the nut to 271 Nzm (200 ft.lbs.)
minimum.Do not over-tighten.Maximum torque is
475 Nzm (350 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Never loosen pinion gear nut to decrease
pinion gear bearing preload torque and never exceed
specified preload torque. If preload torque is exceeded
a new collapsible spacer must be installed. The torque
sequence will have to be repeated.
(8) Use Flange Wrench C-3281 to retain the yoke
(Fig. 35). Slowly tighten the nut in small increments
until the rotating torque is achieved. Measure the pre-
load torque frequently to avoid over-tightening the nut.
(9) Check bearing preload torque with an inch
Fig. 30 Pinion Front Bearing Cup Installation
Fig. 31 Pinion Seal Installation
Fig. 32 Shaft Rear Bearing Installation
Fig. 33 Collapsible Preload Spacer
3 - 24 REAR SUSPENSION AND AXLESJ