spark plugs replace JEEP CJ 1953 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1953, Model line: CJ, Model: JEEP CJ 1953Pages: 376, PDF Size: 19.96 MB
Page 12 of 376
B
LUBRICATION B-3.
SERVICE
MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULE
Perform
the following operations at the mileage shown. Two thousand miles equals
3,200
km.
SERVICE
MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULE
OPERATION
VEHICLE
^ n>
MILEAGE
IN
THOUSANDS
6 8 10 12 24 30
Check Wheel Nut Torque*
Check
Fluid
Level
in Battery X Check
Fluid
Level
in Brake Master Cylinder0. X
Service
Cooling
System X Service Tires X
Lubricate
Distributor
Cam Lubricator (F4-134) X
Lubricate
Steering Linkage X
Lubricate
Propeller Shaft Universal Joints X
Lubricate
Propeller Shaft
Slip
Joints ; X
Lubricate
Tie Rod and Drag
Link
Sockets................................... X Change Engine
Oil
and
Filter,
and Service Air Cleaner (F4 134 Engine)** X
Change Engine Oil and
Filter,
and Service Air Cleaner (V6-225 Engine)**....
Check Brake Operation and Pedal
Free
Play X Check
Clutch
Pedal
Free
Play. .... X
Check all
V-Belt
Tensions X
Check Exhaust Emission System
(If
so equipped)*** \ X
Service Positive
Crankcase
Vent
Valve
and Breather . .' X
Road Test
Including
a Check of all Instrument
Lights
and Controls X Tune-up Engine
Check Operation of
Manifold
Heat
Control
Valve
Clean
Exterior of Radiator
Align
Headlights • Check Brake
Linings
,
Check Exhaust System for Leaks Replace Canister Air
Filter
(F. E. E. C. System)
Check
Axle
U-Bolt
Torque. Check Lubricaunt
Level
of Front
Axle
Universal Joints
Check Shock Absorber Mountings and Bushings Check Front and
Rear
Spring Bushings
Lubricate
Distributor
(V6-225).
Replace Spark, Plugs
Check Charging and Starting Circuits
Lubricate
Tailgate Latch, Supports and Hinges.
Lubricate
Door and
Hood
Hinge Pivots ;
Lubricate
Glove Compartment Door Latch
Lubricate
Heater Controls •
Lubricate
Windshield
Wiper and Washer Controls
Clean,
Repack and
Adjust
Wheel Bearings
Change Transmission and Transfer Lubricant. .
Replace
Dry-Type
Air Cleaner • Check Lubricant
Level
of
Differential
Lubricate
Transfer
Case
Shift
LeArer
Control
C«se.
. , . . . . . . . .
Continuing
each
2,000 miles
Continuing
each
6,000 miles
Continuing
each
24,000 miles
X
Continuing
each
30,000 miles
•Check after the
first
200 miles [320
km.
J
of operation.
If
wheel or wheels are changed for any
reason,
have
wheel nut torque rechecked after an additional two hundred miles of operation
••Service mileage shown or every 60 days, whichever occurs
first.
•••Maintenance check on emission system must be performed per
information
in this manual. "See text for brakes.
"Nj
^Miles
2,000
6,000
12,000
18,000
24,000
30,000
Kilometers
3,200
9,600
19,200
28,800
38,400 48,000
B-9.
Engine Oil
For
maximum
engine
protection under all driving conditions encountered during the recommended
oil
change intervals, it is necessary to use only
"MS"
certified
sequence-tested
oils. The term
"MS"
must appear on the oil container singly or
in
conjunction with other designations. "MS" des
ignated oils are heavy-duty detergent oils that are
formulated to withstand all service conditions in
modern powerplants. Engine oils designated only
as
"ML"
and/or
"MM"
are not recommended and should not be used except in an emergency when
"MS"
oil is not available. Certified
sequence-tested
engine
oils are described on their containers by
such
phrases as:
meets,
exceeds,
excels, or has
proven superior in the
test
requirements,
test
sequences, MS Service
tests,
standards, and service
requirements,
of automotive manufacturers, auto
makers,
or car manufacturers for MS service or
Service
MS.
It
may be necessary to change
engine
oil more
frequently than normally recommended, depending upon the type and quality of oil used, the severity
of operation conditions, if the
engine
is used for
short
periods in cold weather, or if the
engine
is allowed to idle for excessive periods.
Always
drain
the crankcase while the
engine
is hot since
dirt
and contaminants are then more
likely
to be held in suspension and therefore
will
drain
out more completely.
Drain
the crankcase as follows:
a.
Position the
drain
receptacle under the
drain
plug.
b.
Remove the
drain
plug using the correct size
wrench.
Be careful of hot oil.
c.
Carefully
clean the
drain
plug. Inspect and
replace
the gasket, if deteriorated.
d.
When the oil has drained, replace and tighten
the crankcase
drain
plug. 12
Page 13 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
B
e.
Check
for the presence of
excess
water in the
oil
that might indicate an internal leak from the
cooling system.
f.
Pour oil into the oil filler tube. Replace the oil
filler
cap.
B-10.
Engine Oil
Filter
Service —
Hurricane
F4 Engine
The
engine
oil filter assembly should be replaced at each
2000
miles
[3.200
km.] of normal
engine
use. To remove the filter, use oil filter wrench
C-4065.
To install a new filter, wipe the gasket —
contact surface with
engine
oil, screw on the unit
until
gasket contacts the sealing surface, and then tighten at least one
half
turn
more. DO NOT USE
TOOLS.
Turn
by hand only. When refilling the
engine
crankcase after filter has been changed be
sure
to add one extra quart [1 ltr.] of oil to
fill
filter
and oil passages. Run
engine
to make sure there is no leak at oil filter.
B-l 1.
Engine Oil
Filter
Service — Dauntless V-6 Engine
To
replace the oil filter, use oil filter wrench, Tool
C-4065,
to remove the filter. After the filter has
been removed from the oil pump housing located
on the right front side of the engine, wipe the
housing surface clean and oil the gasket on the base of the new filter to make a
good
seal. Screw
the new filter in position until its gasket contacts
the pump housing surface, then tighten at least
one-half
turn
until filter fits snug.
Note:
Tighten by hand only, do not use a tool to
tighten.
Replace
oil filter each
6000
miles
[9.600
km.] at
engine
oil change.
B-12.
Exhaust
Manifold
Heat
Control
Valve
— Dauntless V-6 Engine
A
thermally-actuated heat control valve is located at
rear
of the right exhaust manifold of the Daunt
less
V-6 engine.
This
valve has a bimetal thermo
static spring which holds the valve closed when
the
engine
is cold.
Each
time the vehicle is lubricated place a few drops of penetrating oil on the valve shaft bushings
and
then work the valve by hand making sure that
the lubricant is worked into the bushings.
Note:
If the valve shaft
does
not operate freely
penetrating oil should be used to free the shaft.
B-l 3.
Positive
Crankcase
Ventilation
System
Service
the ventilation system of the
engine
each
multiple of
6000
miles
[9.600
km.] on the odometer
after
initial
2000
miles
[3.200
km.] service. Re
place the ventilation valve each
12,000
miles
[19.200
km.].
For
information on servicing the positive crankcase
ventilation system on the
Hurricane
F4
engine
and
the Dauntless V-6 engine, refer to the Tune-up Section.
B-l4.
Distributor
— Hurricane F4 Engine
The
distributor shaft is lubricated through an oiler mounted on the side of the housing. Place three or four drops of light
engine
oil in the oiler each
2,000
miles
[3.200
km.]. Also place one drop of light
engine
oil on the wick located on the top of the
shaft, which is made accessible by removing the
rotor
arm. Sparingly apply cam lubricant to the
breaker
arm cam and place a drop of oil on the
breaker
arm pivot.
B-l
5.
Distributor
— Dauntless V-6 Engine
The
distributor has a lubricant reservoir that
car
ries
sufficient
lubricant
for the life of the distributor.
When
servicing breaker points, place one drop of
light
engine
oil on the wick located on the top of the shaft Also, apply cam lubricant sparingly to
the breaker arm cam, and place a drop of oil on the
breaker
arm pivot.
B-l6.
Generator
On
early production vehicles oilers are provided
at each end of the generator, for lubrication
pur
pose.
On late production vehicles one oiler is pro
vided at the
rear
(bushing end) of the generator for lubrication purpose. Place two to four drops of
light
engine
oil in each oiler every
2,000
miles
[3.200
km.].
B-l
7. Spark Plugs
Replace
spark
plugs. Refer to Section C.
B-18.
Starting
Circuit
Check
the starting
circuit.
Refer to Section H.
B-l
9. Charging
Circuit
Check
the charging
circuit.
Refer to Section H.
B-20.
Engine Tune-Up
Refer
to Section C of this manual.
B-21.
Adjust
Fan
Belt
Refer
to Section C.
B-22.
Exhaust Emission
Control
System or
Controlled
Combustion System
•
Refer to the appropriate section in this manual.
B-23.
Exhaust System
Check
the exhaust system for leaks. Refer to Section F.
B-24.
Fuel Evaporative Emission
Control
Canister Air
Filter
The
only service required for the
F.E.E.C.
system
is cleaning the air cleaner filter mounted at the
bottom
of the canister. The filter requires replace
ment at
12,000
mile intervals. Refer to Section
E,
Par. E-9 for service procedure.
B-25.
Oil Bath Air Cleaner
Some 'Jeep' Universal vehicles are equipped with
an
oil bath type air cleaner.
This
type air cleaner
thoroughly removes all dust from the air before it enters the carburetor, if it is properly serviced.
When
the vehicle is operated under normal condi
tions the air cleaner must be serviced at regular
intervals
as care of the air cleaner is extremely 13
Page 19 of 376

Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
c
TUNE-UP
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
GENERAL
C-l
TUNE-UP
.C-2
Air
Cleaner
C-21
Battery
. C-3
Carburetor
Adjustments
C-2 5
Coil
C-20
Crankcase
Ventilation C-6
Cylinder
Compression C-9
Cylinder
Head(s) .C-5
Dash
Pot Adjustments .C-26
Distributor
Service C-10
thru
C-13
Distributor
Resistance Test C-l6
Fan
Belt
C-2 7
Fuel
Lines
and Screens
C-2
2
C-l.
GENERAL
An
engine tune-up should be performed for all
Jeep Vehicles each 6000 miles [9.600 km.] or at the end of each 250 hours off-the-road operation,
to ensure best possible performance at all times.
The
tune-up should follow the sequence given in
this section.
Because of federal laws limiting exhaust emissions,
it
is even more important that the engine tune-up is
done
accurately, using the specifications listed
on the tune-up sticker found in each engine com
partment.
Note;
To ensure proper operation and effectiveness
of the exhaust emission control system, and to
comply with
Federal
and State requirements, a
recheck
of ignition timing, idle speed and idle mix
ture
and necessary adjustments must be performed
after the first
2,000
miles [3.200 km.] of vehicle
operation.
A
minor engine tune-up should be performed every
6,000
miles [9.600 km.] or at the end of 250 hours
of off-the-road use.
Major
engine tune-up should
be performed every 12,000 miles [19.300 km.].
The
parts of units which affect power and perform
ance may be divided into three groups:
(1) Units affecting compression
(2) Units affecting ignition
(3) Units affecting carburetion
The
tune-up procedure should cover
these
groups
in
the order given. While the items affecting com
pression and ignition may be handled according
to personal preference, correction of items in the
carburetion
group should not be attempted until
all
items affecting compression and ignition have
been satisfactorily corrected.
Note:
To make sure hydro-carbon and carbon
monoxide emissions
will
be within limits, it is very
impotrant
that the adjustments be followed exactly
as listed on the sticker found in each engine compartment.
SUBJECT
PAR.
Fuel
Pump . . C-23
Heat
Control
Valve C-7
Ignition
Cables C-19
Ignition
Timing
. C-14
Ignition
Wires C-l8
Manifold
C-5
Manifold
Vacuum C-24
Point
Dwell C-17
Primary
Circuit
Tests
.................
C-15
Spark
Plugs C-4
Tappets
C-8
ROAD TEST C-2
8
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
. : C-29
TUNE-UP SPECIFICATIONS..
C-30
Minor
engine tune-up consists of the following.
Inspect
and correct as required:
Battery
cables and connections.
Alternator
and regulator wiring.
Primary
— Secondary wiring, distributor cap.
Cylinder
head torque.
Contact
point dwell.
Vacuum
and centrifugal advance.
Ignition
timing.
Spark
plugs for correct air gap.
Adjust
idle speed and idle air mixture.
Adjust
all drive belt tensions.
Clean
carburetor air cleaner.
Lubricate
exhaust manifold damper.
Major
engine tune-up includes the following.
Inspect
and correct as required:
Battery
condition and charging
circuit.
Clean,
lubricate
and tighten battery cable connec
tions.
Ingition
system.
Spark
plugs; replace if necessary or clean and gap.
Compression
check.
Primary—Secondary
wiring, distributor cap.
Replace
contact points and condenser.
Lubricate
distributor cam with cam grease.
Adjust
contact points.
Check
vacuum and centrifugal advance. Set ignition timing.
Torque
cylinder head.
Adjust
idle speed and idle air mixture.
Replace
fuel filter element (every 12,000 miles [19.300
km.]).
Adjust
all drive belt tensions.
IMPORTANT: SPECIFICATIONS
FOR EN-
GINE
RPM.
DISTRIBUTOR POINT DWELL,
AND IGNITION TIMING GIVEN
IN
TUNE- UP SECTION
C
REFER
TO
VEHICLES
WITH
AND WITHOUT EXHAUST EMISSION CON
TROL
SYSTEMS.
FOR
VEHICLES
EQUIPPED WITH EXHAUST
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS ALSO
REFER
TO
SECTION
Fl (F4-134
ENGINE)
AND
F2 (V6-225
ENGINE).
19
Page 20 of 376

c
TUNE-UP
C-2.
TUNE-UP SEQUENCE
The
following
Pars.
C-3 through
C-2
7
give the
sequence and describe the services to be performed
when tuning the engine.
C-3.
Clean
and
Check
Battery
Inspect
battery and cables. If the battery is not
satisfactory, install a fully-charged battery to allow
completion of the tune-up.
Note: If the battery fails any of the following tests,
remember that the cause may be other electrical
trouble, and not necessarily only a defective battery.
Refer
to Section H for electrical troubleshooting
and
tests.
a.
Check
the specific gravity of the eletrolyte in
each cell of the battery. A hydrometer reading of 1.260 indicates that the battery is fully charged.
If
the reading is 1.225 or below, the battery
needs
recharging.
If one or more cells is 25 "points" (.025)
or
more lower than the other cells, this indicates
that the cell is shorted, the cell is about to
fail,
or
there is a
crack
in the battery partition in the case.
Unless the battery is repaired or replaced, battery trouble
will
soon be experienced.
b.
Check
the electrolyte level in each cell, add
distilled
water to maintain the solution %" [9.5
mm.] above the plates. Avoid overfilling. Replace
the filler caps and tighten securely. It is important
to keep the electrolyte level above the plates at
all
times because plates that are exposed for any
length of time
will
be seriously damaged.
c.
Check
the wing nuts on the hold-down frame
for tightness. Tighten them only with finger pres
sure,
never with pliers or a wrench. Excessive pres
sure
could damage the battery case.
d.
Clean
the battery terminals and cable connec-
FIG.
C-l—FRAME
GROUND
STRAP
—
HURRICANE
F4
1—
Right
Front
Engine Mount
2—
Frame
Ground
Strap
DAUNTLESS
V-6
tors.
Prepare a strong solution of baking soda and
water
and brush it around the terminals to remove
any
corrosion that is present. The cell caps must
be tight and their vents sealed to prevent cleaning
solution entering the cells. After cleaning install
cable connectors on terminals and coat the ter
minals
and connectors with heavy grease.
e. Inspect the battery cables and replace if badly
corroded
or frayed.
Check
tightness of terminal
screws to ensure
good
electrical connections.
Check
the tightness of the negative ground cable connec tion at the engine to ensure a
good
ground con nection.
f.
Load
test
the battery. Connect a voltmeter across the battery. Run the starting motor for 15 seconds.
If
the voltage
does
not drop below 10 volts on a 12 volt battery the battery is satisfactory. If the
voltage falls below
these
values, yet the specific
gravity
is above
1.225,
the condition of the battery
is questionable.
g.
Make sure the engine to frame ground strap or
cable connections are tight. If
these
connections
are
loose,
corroded or dirty,
hard
starting or failure
of the vehicle electrical system may result. Refer
to
Fig.
C-l
for location of the
Hurricane
F4 engine
to frame ground strap and its connections. Refer to Fig. C-2 for location of the Dauntless V-6 en gine to frame ground cable.
C-4.
Clean and
Adjust
Spark Plugs
Clean,
inspect, and gap
spark
plugs. Do not install
spark
plugs until completion of compression tests.
a.
Use a
Spark
Cable
and Installing
Plier
Tool,
W-2
74,
to remove the leads from the
spark
plugs.
Caution:
Pulling on the cables to remove them
from
the
spark
plugs can cause internal breaks in
the leads that
will
cause ignition failure.
b.
Using a
spark
plug wrench, loosen each
spark
plug one or two turns to break
loose
any carbon
deposits on the plug base. 20
Page 21 of 376
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
FIG.
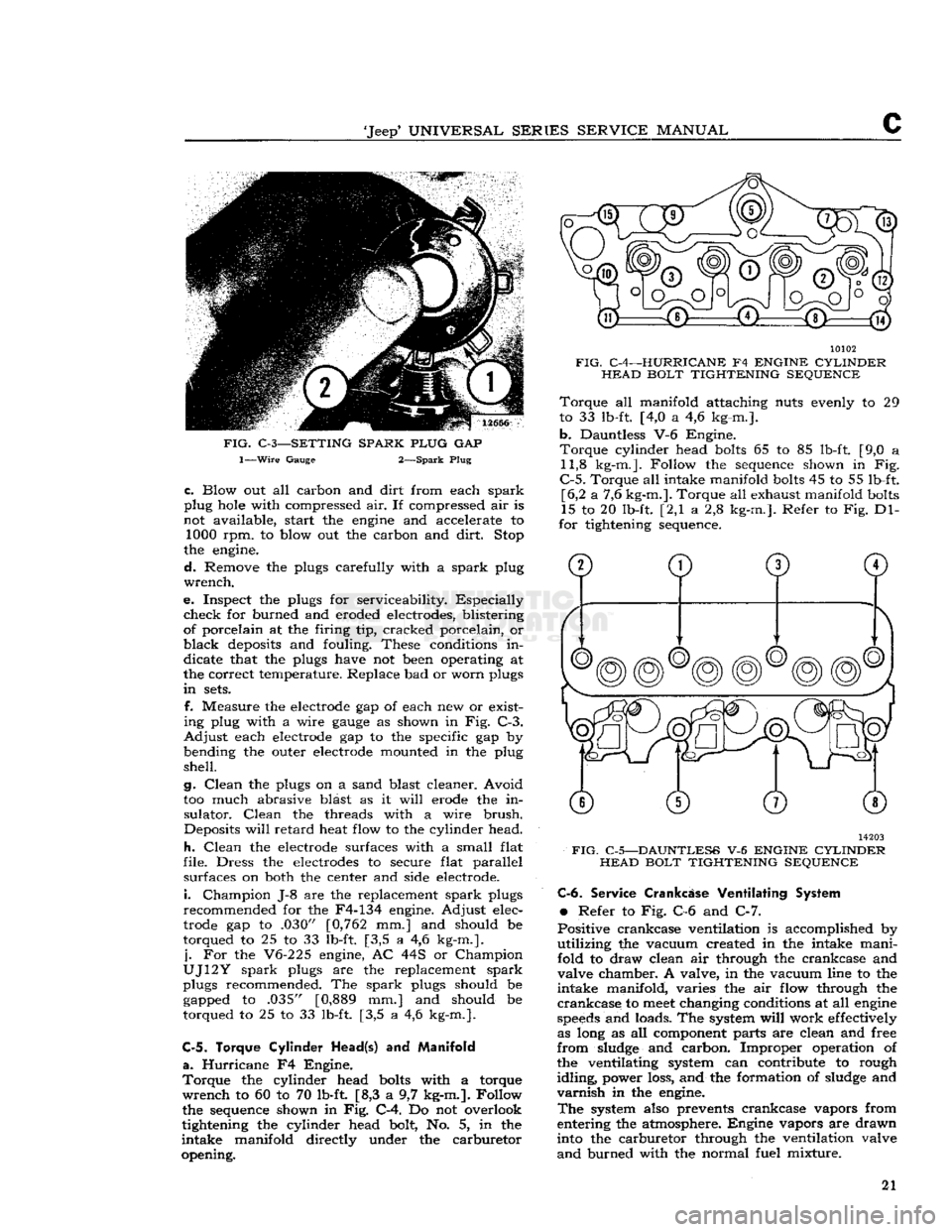
C-3—SETTING SPARK PLUG
GAP
1—Wire
Gauge 2—Spark Plug
c.
Blow out all carbon and
dirt
from each
spark
plug hole with compressed air. If compressed air is
not available, start the engine and accelerate to 1000 rpm. to blow out the carbon and
dirt.
Stop
the engine.
d.
Remove the plugs carefully with a
spark
plug
wrench.
e. Inspect the plugs for serviceability. Especially
check
for burned and eroded electrodes, blistering
of porcelain at the firing tip, cracked porcelain, or
black
deposits and fouling. These conditions in
dicate that the plugs have not been operating at
the correct temperature. Replace bad or worn plugs
in
sets.
f. Measure the electrode gap of each new or exist
ing plug with a wire
gauge
as shown in Fig. C-3.
Adjust
each electrode gap to the specific gap by
bending the outer electrode mounted in the plug
shell.
g.
Clean
the plugs on a sand blast cleaner. Avoid
too much abrasive blast as it
will
erode the in
sulator.
Clean
the threads with a wire
brush.
Deposits
will
retard
heat flow to the cylinder head.
h.
Clean
the electrode surfaces with a small flat
file. Dress the electrodes to secure flat parallel surfaces on both the center and side electrode.
i.
Champion J-8 are the replacement
spark
plugs
recommended for the F4-134 engine. Adjust elec
trode gap to .030" [0,762 mm.] and should be
torqued to 25 to 33 lb-ft. [3,5 a 4,6 kg-m.].
j.
For the V6-225 engine, AC 44S or Champion
UJ12Y
spark
plugs are the replacement
spark
plugs recommended. The
spark
plugs should be gapped to .035" [0,889 mm.] and should be
torqued to 25 to 33 lb-ft. [3,5 a 4,6 kg-m.].
C-5. Torque Cylinder
Head(s)
and
Manifold
a.
Hurricane
F4 Engine.
Torque
the cylinder head bolts with a torque
wrench
to 60 to 70 lb-ft [8,3 a 9,7 kg-m.]. Follow
the sequence shown in Fig. C-4. Do not overlook
tightening the cylinder head bolt, No. 5, in the
intake
manifold directly under the carburetor
opening. 10102
FIG.
C-4—HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE CYLINDER HEAD BOLT TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
Torque
all manifold attaching nuts evenly to 29
to 33 lb-ft. [4,0 a 4,6 kg-m.].
b.
Dauntless V-6 Engine.
Torque
cylinder head bolts 65 to 85 lb-ft. [9,0 a 11,8 kg-m.]. Follow the sequence shown in Fig.
C-5.
Torque all intake manifold bolts 45 to 55 lb-ft. [6,2 a 7,6 kg-m.]. Torque all exhaust manifold bolts
15 to 20 lb-ft. [2,1 a 2,8 kg-m.]. Refer to Fig. Dl-
for tightening sequence. 14203
FIG.
C-5—DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE CYLINDER HEAD BOLT TIGHTENING SEQUENCE C-6.
Service
Crankcase
Ventilating System
•
Refer to Fig. C-6 and C-7.
Positive crankcase ventilation is accomplished by
utilizing
the vacuum created in the intake mani
fold to draw clean air through the crankcase and
valve chamber. A valve, in the vacuum line to the
intake
manifold, varies the air flow through the
crankcase
to
meet
changing conditions at all engine
speeds
and loads. The system
will
work effectively as long as all component parts are clean and free
from
sludge and carbon. Improper operation of the ventilating system can contribute to rough
idling,
power loss, and the formation of sludge and
varnish
in the engine.
The
system also prevents crankcase vapors from
entering the atmosphere. Engine vapors are drawn
into the carburetor through the ventilation valve
and
burned with the normal fuel mixture. 21
Page 30 of 376

c
TUNE-UP
meter during this
test
Connect the red lead
tc*
dis
tributor
primary
lead at the coil as shown in Fig.
C-21.
Connect black lead to the ground.
Turn
ignition switch on; with
engine
stopped, observe
dwell
meter. If the meter reads zero,
crank
the
engine
a fraction of a revolution to
close
the
breaker
points.
Distributor
resistance is normal, if dwell meter
pointer is within range of
black
bar. Distributor resistance is high, if
dwell
meter pointer is not
within
the black bar.
Remove test lead from
distri
butor terminal of coil and
connect
to
each
of the
following points to determine
where
the excessive resistance is:
Distributor
primary
terminal
Distributor
primary
terminal in the distributor
Breaker
point bracket
Ground
side of points
Distributor
housing
Where
a noticeable change occurs in the meter
reading
in
these
steps, make the necessary correc
tion and repeat the
test.
C-l 7. Distributor
Point
Dwell
Using
a dwell tester, connect red
lead
to the
distri
butor terminal at coil. Connect black lead to
ground.
Set selector switch to the number of
cylin
ders in the
engine
being tested. Operate
engine
speed at specified rpm. and
note
readings. Cam
dwell
angle must be 30° for the Dauntless V-6
Delco equipped engine, 29° ±: 3° Prestolite equipped
engine
and 42° for the
Hurricane
F4 engine. If the dwell reading is not to specifications,
trouble could be improper point spacing, point
rubbing,
defective block or breaker arm, or mis
aligned and worn distributor cam.
Adjust
dwell
as shown in Fig. C-14 for the Delco equipped
Dauntless V-6 engine. For cam dwell adjustment
of the Prestolite equipped V6 and
Hurricane
F4 engine, refer to Par. C-10,
step
a.
Dwell
variation is determined by noting any
dwell
change as the
engine
is operated at different
speeds.
Excessive
variation indicates a change in point opening that can result from shaft or bushing wear,
or
from the distributor plate shifting because of
wear
or
looseness.
Measure
dwell variation at idle speed, using same
test
hookup for checking dwell. Increase speed to 1750 rpm.;
note
dwell reading.
Then
slowly reduce
speed to idle while observing dwell meter. Dwell
variation
should not exceed 3°. If dwell variation
exceeds
3°
between
idle speed and 1750 rpm.,
probable wear in the distributor shaft, bushings, or
breaker
plate is indicated. Distributor should then be checked more thoroughly.
C-l8. Check Ignition Wires
and
Connections
Examine
and clean the insulation on all ignition
wires
and check all connections. Wires should be
firm,
flexible, and free from roughness and minute
cracks.
Bend wires to check for brittle,
cracked,
or
loose
insulation. Since defective insulation
will
per
mit
crossfiring or missing of the engine, defective
wires
should be replaced.
C-l9. Test Ignition
Cables
To
remove cables from
spark
plugs, use
Spark
Plug
Cable
Remover
Tool
W-274.
Twist
the
boot
slightly to break the seal and, grasping the rubber
protector
boot,
lift straight up with a steady even
pull.
Do not grasp the cable and
jerk
the cable off; this
will
damage the cables. Do not use a probe
on
these
wires; puncturing them may cause a
separation in the conductor. To remove ignition cables from the distributor cap or coil tower,
loosen
the nipple first, then grasp the upper part of the nipple and the cable and gently
pull
straight up.
Test
the cable with an ohmmeter. Resistance value
per
foot
is
3000-7000
ohms. The ignition cables
can
be checked for
circuit
continuity by removing
the cable from the
spark
plug and holding the cable
end Vi" [6,35 mm.] from the engine. A strong
spark
indicates
good
conductor continuity.
When
connecting the cable to the
spark
plug, be
certain
a
good
connection is made and that the
protector
boot
fits tight on the
spark
plug. A
partially
seated cable creates an additional gap in
the
circuit
and the resulting
spark
jump
will
cause
terminal
corrosion and cable damage.
C-20. Coil
When
an ignition coil is suspected of being defec tive, it should be checked on the car. A coil may
break
down after it has reached operating tempera
ture.
It is important that the coil be at operating
temperature when
tests
are made.
Note:
The ignition coil and ballast resistor for the
V-6
engine
must be of the same manufacturer.
Ballast
resistors and ignition coils of one manufac
turer
are interchangeable with both units of the
other.
C-21.
Service Air
Cleaner
Refer
to Par.
B-2 2
for the correct service of the
air
cleaner.
C-22.
Check Fuel Lines and
Screens
Check
all fuel line connections to guard against
leakage.
Check
fuel pump filter F4
engine
and
fuel
line filter V-6 engine. Replace fuel filter if
necessary.
C-23. Check Fuel Pump a.
Fuel
pump pressure is important, for low pres
sure
will
seriously affect
engine
operation and high
pressure
will
cause excessive fuel consumption and
possibly flood the carburetor. Should there be any doubt of normal operation, check the pressure with
a
gauge
as shown in Fig.
C-2 2.
The minimum and
maximum
allowable pressures are 2% to 3% lbs. [0,176 a
0,264
kg-cm2], for the
Hurricane
F4 en
gine.
Fuel
pump pressure at carburetor (inlet) on
the Dauntless V6-225
engine
should be 3% lbs.
[0,264
kg-cm2] minimum at specified
R.P.M.
idle
with
the vapor
return
hose
squeezed off.
With
the
vapor
return
hose
open pump pressure should be
2
V2
lbs. [0,176 kg-cm2] minimum.
b.
Test for volume, as a pump may build up suffi
cient pressure but
fail
to produce sufficient volume.
Turn
down the carburetor fuel line fitting on the
pump and with the tank line connected, pump out
30
Page 37 of 376

'Jeep9
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
GENERAL...
D-l Description D-2
Engine
Ground Strap D-4
Engine
Mountings D-3
ENGINE REMOVAL
D-5
ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
D-6
Camshaft
.......
D-28
Clutch
D-24
Crankshaft.
D-26
Crankshaft
Pulley. D-l2
Cylinder
Head. .D-17
Distributor.
.D-13
Exhaust
Manifold D-8
Exhaust
Valves and Springs D-2
7
Flywheel.
. D-25
Front
End Plate D-23
Oil
Filler
Tube D-9
Oil
Gallery Plugs D-30
Oil
Pan. . ...D-19
Oil
Pump D-l4
Piston and Connecting Rods. . . D-20
Ream
Cylinder Bore Ridges. D-l8
Rocker
Arm Assemblies D-l6 Thermostat D-ll
Timing
Gear
Cover . . D-21
Timing
Gears D-22
Valve
Tappets D-29
Ventilation Valve D-l5
Water
Outlet Fitting D-10
Water
Pump D-7
ENGINE INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR.
.D-31
Camshaft
and Bearings. D-51
Camshaft
End-Play
. . .D-53
Camshaft
Front Bearing Replacement..... D-52
Checking
Connecting Rod
Crank
Pins D-42
Checking
Crankshaft Alignment .
.
D-40
Checking
Main Bearing Journals. D-41
Cleaning.
. D-33 Connecting Rod Bearing Inspection D-48
Connecting Rod Bearings D-47 Connecting Rod Side Play D-50
Core
Hole Expansion Plug D-72
Crankshaft
.
.
D-38, 39
Crankshaft
Main Bearing Inspection D-44
Crankshaft
Main Bearings D-43
Crankshaft
Rear
Bearing Seal D-63
Cylinder
Block D-32
Cylinder
Bores D-35
Cylinder
Head. . . D-73
Exhaust
Valve Seat Insert Replacement. .
.
D-60
Fitting
Crankshaft Main Bearings
Using
Plastigage
D-45
Fitting
Crankshaft Main Bearings
Using
Shim Stock D-46
Floating
Oil Intake D-64
Flywheel.
. . .D-67
Flywheel
Housing D-71
SUBJECT
FAR.
Flywheel
Inspection. D-6 8
Flywheel
Pilot Bushing D-70 Inspection D-3 4
Inspection of Valves, Springs and Guides. .D-57
Installing
Connecting Rod Bearings....... D-49
Oil
Pan D-66
Oil
Pump D-65
Piston Ring Application
Chart
D-3 7
Pistons, Rings, and Connecting Rods..... D-36
Refacing
Valves
.
D-58
Ring
Gear
Replacement D-69
Rocker
Arm Shaft Disassembly. D-75, 76
Rocker
Arm Shaft Reassembly.
.
D-77
Rocker
Arms D-74
Tappets and Cover. . D-62
Timing
Gears and Cover D-54, 55
Valve
Guide Replacement D-61
Valve
Seat Inspection and Refacing D-59
Valve,
Springs and Guides D-56
ENGINE REASSEMBLY
D-78
Camshaft
and
Thrust
Plate .D-81
Camshaft
Timing
Gear
D-91
Check
Crankshaft
End-Play.
............D-83
Clutch.
...D-89
Crankshaft
and Bearings................ D-82
Crankshaft
Pulley D-96
Crankshaft
Rear
Bearing Seal.. .
.
D-85
Crankshaft
Timing
Gear
D-84
Cylinder
Head D-98
Distributor
D-l
00
Flywheel
®. . .. D-87
Flywheel
Housing D-88
Front
End Plate D-86
Manifold.......
D-101
Oil
Filler
Tube D-102
Oil
Gallery Plug. D-79
Oil
Pan. D-97
Oil
Pump D-93
Pistons and Connecting Rods D-95
Rocker
Arm Assembly D-99
Spark
Plugs. .D-100
Tappets D-80
Timing
Gear
Cover D-94
Timing
Gear
Oil Jet D-92
Valves
and Springs ... D-90
Water
Outlet Fitting D-104
Water
Pump D-103
ENGINE INSTALLATION.
............D-105
FINAL IN-VEHICLE
ADJUSTMENTS.
.D-106
Check
Valve Timing . . D-109
Crankcase
Ventilation Valve. D-l 10
Oil
Filter
, . .
...D-lll
Valve
Adjustment D-107
Valve
Adjustment Procedure D-l08
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
D-112
SPECIFICATIONS D-l
13 37
Page 38 of 376
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
D-1.
GENERAL
This
section describes service and repair of the
F4
engine. The
engine
code
number shown in Fig.
A-3
is provided to identify the four cylinder engine.
The
meaning of the coded letters and numbers that
are
stamped on the water pump boss, at the front of the cylinder block, is given below.
Letter
to
Designate
Market
M
—
Military
E
—
Export
D
— Domestic
I
—
Industrial
&
Marine
Letter
to
Designate
Engine
Letter
to
Designate
Year
Built
R
— 1969
S
— 1970
T
— 1971
U—
1972
V
— 1973
W
— 1974
Numbers
to Designate
Compression
Ratio
F
— F4-134
Engine
63
67
•
71
-
6.3 to 1
•
6.7 to 1
-
7.1 to 1
Market
-
D
S F
(Domestic)
(1970)
Engine-
EXAMPLE
123 A B S
(F4-134)
Day- "L
Compression
Ratio
(6.7)
-
Service Engine (S)
Short
Block
(R)
-.010*
Oversize Pistons
(123rd)
-.010*
Undersize
Main
and
Rod Bearings
All
disassembly and assembly procedures are
presented in logical order, assuming a complete
engine
overhaul with
engine
removed from the vehicle. However, many of
these
procedures can
also be performed as on-vehicle services if vehicle
or
engine
components are removed to gain access
to parts involved.
Note:
Some
engines
are equipped with an exhaust
emission control system. Service information on
the components of this system is given in Section
F-l.
D-2.
Description
The
Hurricane
F4-134
engine
is an F-head, four-
cyiinder
engine
of combination valve-in-head and valve-in-block construction.
Large
intake valves
mounted in the head allow
rapid,
unobstructed
flow of fuel and air to the combustion chambers through short, water-jacketed intake passages.The
intake valves are operated by push rods through
rocker
arms. The exhaust valves are mounted
in
the block with through water jacketing to provide
effective
cooling. The exhaust valves are
operated by conventional valve tappets.
The
engine
is pressure lubricated. An oil pump
driven
from the camshaft forces the lubricant
through oil channels and drilled passages in the
crankshaft
to efficiently lubricate the main and
connecting rod bearings.
Lubricant
is also force
fed to the camshaft bearings, rocker arms, timing
gears, etc.
Cylinder
walls and piston pins are
lubricated
from spurt
holes
in the "follow" side of
the connecting rods.
Circulation
of the coolant is controlled by a
thermostat in the water
outlet
elbow cast as part
of the cylinder head.
The
cylinder head assembly when installed on the
engine
consists of the inlet valve guides, inlet valves, inlet valve springs, rocker arm and shaft assemblies, spark plugs, temperature indicator
fitting, water
outlet
fitting, and other assembled
parts.
The carburetor and air cleaner assembly
bolt to the top of the cylinder head. The rocker
arm
cover is attached to the top of the head to
enclose
the inlet valve mechanism.
The
engine
is equipped with a fully counterbalanced
crankshaft
supported by three main bearings. To better control balance, the counterweights are in
dependently forged and permanently attached to
the crankshaft with dowels and cap screws that are tack-welded.
Crankshaft
end play is adjusted by
shims placed
between
the crankshaft thrust washer
and
the shoulder on the crankshaft.
The
exhaust manifold is a separate unit. The intake
manifold is cast as an integral part of the cylinder
head and is completely water jacketed.
This
con
struction transfers heat from the cooling system
to the intake passages and assists in vaporizing
the fuel when the
engine
is cold. Therefore, there
is no heat control valve required in the exhaust manifold. Individual exhaust ports in the cylinder
block direct
gasses
into the exhaust manifold for unobstructed flow through the exhaust system.
The
pistons have an extra
groove
directly above
the top ring which acts as a heat dam or insulator.
As
is common practice with manufacturers,
some
engines
are built with oversize cylinder bores or undersize crankshaft journals. These
engines
are
considered standard as replacement parts of the
correct
sizes are supplied. Before ordering parts or
doing any work with a particular engine, it is important to check the
engine
code
number to
determine if oversize or undersize parts are re
quired.
Definite identification is given by a letter
stamped after the
engine
code
number. See Fig.
A-5
for location. The letters used and their mean ings are given here:
A
— .010*
[0,254
mm.] undersize main and
connecting rod bearings.
B
— .010"
[0,254
mm.] oversize pistons.
AB
—
Combination
of A and B.
S
—
Service
engine.
R
—
Short
Block.
Detailed specifications for the
Hurricane
F4
engine
are
at the end of this section.
Torque
specifications
for
engine
service are at the end of this manual in Section U. When adjustments are necessary, refer to
these
specifications so that factory clearances
are
maintained.
D-3.
Engine Mountings
The
front of the
engine
is supported by two rubber
Text continued on
page
41. 38
Page 55 of 376
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
develop
into surface cracks and cause failure.
Measure
the over all free length of the springs and
replace any that do not measure to standard: 1%" [35,7 mm.] for intake valve springs and 2j^"
[63,5 mm.] for exhaust valve springs. If possible,
check each valve spring in a valve spring testing
fixture C-647 or equivalent as shown in Fig. D-l9.
Test
each spring when compressed to the two
different spring lengths given (representing valve closed and valve open spring length). If any spring
fails to register spring tension equal to or greater
than
the minimum load limit in pounds specified for that spring length, replace the spring.
Length
Minimun
Load
Intake
valve spring. . .
1.660"
[4,216 cm.] 66 lb. [29,9 kg.]
1.400"
[3,556 cm.] 140 lb. [63,5 kg.]
Exhaust
valve spring. 2.109" [5,356 cm.] 47 lb. [21,3 kg.]
1.750"
[4,445 cm.] 110 lb. [49,9 kg.]
Note:
When using a spring checking fixture C-647
or
equivalent as shown in Fig. D-l9, it is necessary
to convert the torque wrench reading which is in pounds-feet to the static pound pressure specified above according to the instructions furnished with
the wrench. For example, should the torque wrench reading be 50 lb-ft. and the wrench is two
feet
long
the static pressure of the spring
will
be 50 x 2 or 100 lbs.
Clean
the valve
guides
with a standard valve guide
cleaner or a wire
brush.
Check
the valve
guides
in the cylinder block. Replace valve
guides
which are
broken
or worn enough to cause excessive valve
stem-to-guide
clearance. See Par. D-61.
Standard
intake valve clearance is .0007" to .0022"
[0,0178
a
0,0559
mm.] and the exhaust valve
clearance is .0025" to .0045" [0,0635 a
0,1143
mm.].
Excessive
clearance
between
the valve
stems
and
guides
will
cause improper seating and burned
valves. When there is a tendency to draw oil vapor
through the guide causing excessive oil consump tion, fouled
spark
plugs, and poor low-speed per
formance. To check the clearance of the valve stem
to the valve guide, take a new valve and place in
each valve guide.
Check
the clearance with a
suitably mounted
dial
indicator or feel the clearance by moving the valve stem back and forth. If this
check shows excessive clearance it
will
be necessary to replace the valve guide.
D-58.
Refacing Valves
Re
face the valves with a valve refacer. The valve
refacer
manufacturer's instructions should be fol
lowed carefully to ensure a valve face concentric
with
the valve stem. Reface both intake and ex
haust valves to an angle of 46°.
Take
off only the
minimum
of metal required to clean up the valve faces.
If
the thickness of the
edge
of the valve head is
reduced to
less
than
J^>"
[0>8 mm.] replace the valve.
Note:
Cocked or deformed valve springs or im
properly
installed or missing locks can be responsible
for valve problems.
D-59.
Valve Seat Inspection
and
Refacing
Inspect the valve
seats
for
cracks,
burns, pitting,
ridges, or improper angle.
During
any general
engine
overhaul it is advisable to reface the valve
seats
in both the cylinder block and head regardless
of their condition. If the valve
guides
are to be re placed, this must be
done
before refacing the valve
seats.
Note
that later
engines
have hardened
exhaust valve seat inserts.
Valve
seat inserts must be concentric with finish
ream
of valve stem
guides
(exhaust) within .002"
[0,051
mm.] total indicator reading.
When
necessary to reface the valve seats, use a
valve seat grinder in accordance with the grinder
manufacturer's
instructions. Any grinding of valve
seats
should be preceded by touching up the
grinding
stone
so that their angles are accurate and
the
stone
is not
clogged.
Grind
each valve seat to
a
true 45° angle. Never grind any more than is necessary to clean up pits, grooves, or to correct
the valve seat runout.
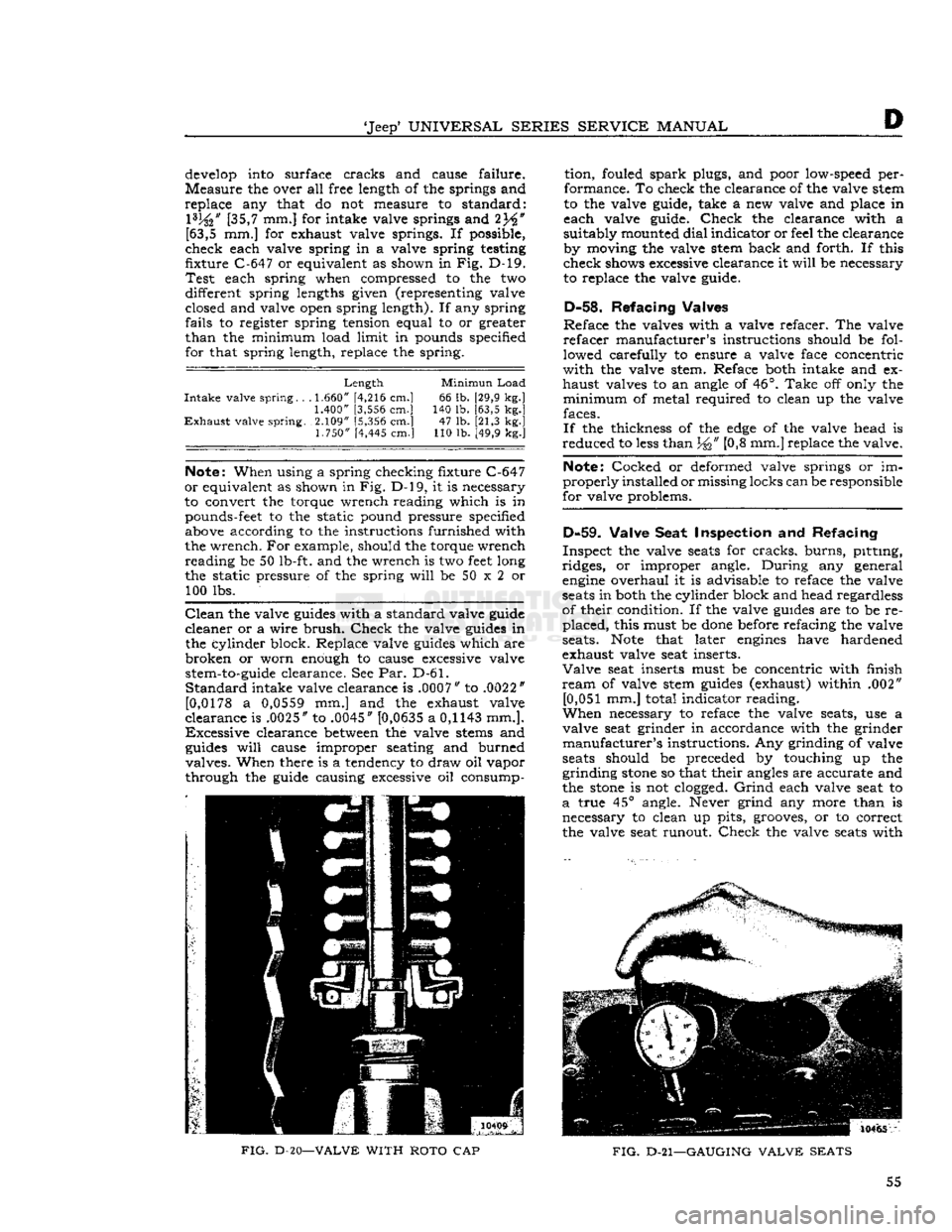
Check
the valve
seats
with
10465
FIG.
D-20—VALVE
WITH
ROTO
CAP
FIG.
D-21—GAUGING
VALVE
SEATS
55
Page 62 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE d.
Remove the intake valve adjusting screw lock-
nuts from each of the rocker arm valve lash ad
justing
screws. Remove the screws from the rocker
arms.
D-76.
Inspection and
Repair
Run
a round wire brush through the bore of the
rocker
arm shaft and clean out the drilled oil holes.
Clean
out the oil
holes
in the rocker arm shaft
brackets,
and the oil
holes
and
grooves
in the bores
of the rocker arm.
Inspect
the diameter of the shaft at the rocker arm
bearing
areas. Replace the shaft if there are scores
or
abrasion marks along the length of the shaft.
Check
the shaft for alignment by rolling it across
a
smooth level surface. If the shaft
will
not
roll
freely, or if it rolls with a bumping motion, the
shaft is out of alignment and must be replaced.
Inspect
the threads of the adjusting screw
hole
in
the rocker arms and if necessary clean with a
proper
size tap. Replace the adjusting screw lock-
nut or the adjusting screw if either part is damaged
or
deformed.
Inspect
the threads in the tapped
hole
in the top
of the rocker arm shaft brackets and if necessary
clean
with a proper size tap. Replace the bracket
if
either side is worn or scored.
D-77.
Reassembly
a.
Install
two rocker arm shaft plugs, one in each
end of the shaft. Slide two
rocker
arm
shaft brackets
onto
the center of the shaft. Align the tapped
holes
in
the brackets with the drilled
holes
in the top of
the shaft and install the rocker arm shaft lock
screws,
making sure the points of the screws enter
the drilled
holes
in the shaft.
b.
Screw the intake valve adjusting screws into
the rocker arms and install the locknuts.
c.
The rocker arms are paired; that is, two of the
arms
are angled to the right and two are angled to
the left. One of each type is used on each end of
the rocker arm shaft. Slide a rocker arm with the
adjusting
screw end of the rocker arm angling
away
from the bracket
onto
the shaft so that the
adjusting
screw is on the same side of the shaft
as the mounting
hole
in the bracket.
d.
Temporarily
secure the end bracket in place by
installing
a rocker arm cover stud in the tapped
opening in the top of the support.
e. Assemble the parts on the
opposite
end of the
rocker
arm shaft repeating
steps
c and d above.
D-78. ENGINE REASSEMBLY
The
engine
reassembly procedure in the following
paragraphs
is given in the sequence to be followed
when the
engine
is being completely overhauled.
Individual
inspection,
repair,
and fitting operations
previously covered in detail are made throughout
the reassembly procedure. The reassembly pro
cedure
does
not cover accessories. If a new cylinder
block
fitted with pistons is used, many of the
operations
will
not be required.
Mount
the cylinder block in an
engine
repair stand.
If
an
engine
stand is not available, perform the fol
lowing reassembly operation in a manner designed to protect personnel against an accident and the
engine
and its parts against damage.
Note:
During
engine
reassembly, use Perfect Seal
Aerosol
Spray
Sealer
Part
No.
994757
on all
engine
gaskets to ensure against vacuum, oil, gasoline and
water
leaks. Apply to head gaskets, valve covers,
water
pumps, oil pan gaskets, radiator and heater
hose
connections, felt gaskets, gasoline and oil line
connections, stud bolts,
spark
plug threads, and
grease retainer washers. Refer to manufacturer's in
structions on container for proper application pro
cedure.
D-79.
Install
Oil
Gallery
Plug
Coat
plug threads with a suitable sealing compound
and
install the plugs in the front and
rear
ends of
the oil gallery in the cylinder block and the
rear
end of the cylinder head. Torque the plugs 20 to 25 lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,4 kg-m.].
There
is also a pipe plug
(}/g,f
[3,2 mm.] slotted, headless) in the opening in the main oil gallery inside the cylinder block at No. 2 cylinder and another pipe plug
(}/g
"
square-head) in the opening
in
the oil passage directly below the oil pump intake
passage. If
these
two pipe plugs were removed,
make
certain they are reinstalled in the locations
described above or the counterweight of the
crankshaft
might strike the projecting head of the
square-head
plug.
D-80.
Install
Tappets
Turn
the block upside down. Beginning at the
rear
end of the cylinder block, install the intake
and
exhaust valve tappets in the tappet bores in the cylinder block in the following order: one
exhaust, two intake, two exhaust, two intake, and
finally
one exhaust valve tappet.
Check
the tappet to bore fit of each tappet as it
is installed in the block. If the stem-to-block
clearance
tolerance of .0005" to .002" [0,0127 a
0,051 mm.] is
exceeded
install a new tappet fitting
within
this tolerance or ream the bore to accomo date the next oversize tappet which is available
in
.004" oversize.
D-81.
Install
Camshaft and
Thrust
Plate
Lubricate
all camshaft bearings and cam surfaces generously with clean, light
engine
oil.
Carefully,
so not to damage or score the camshaft front bear
ing,
install the camshaft, locating it properly in the bearings. Do not allow the
rear
end of the camshaft to strike sharply against the expansion plug
installed
in the
rear
end of the bore.
Install
the camshaft thrust plate. Slide the thrust
plate spacer
onto
the end of the camshaft with the
beveled inner
edge
of the spacer facing the cam
shaft. If the same camshaft is being reinstalled,
install
any shims previously removed. These shims
are
placed
between
the camshaft shoulder and the
spacer.
Torque the thrust plate attaching
bolts
20
to 26 lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,6 kg-m.].
End
play of the camshaft is determined by running
clearance
between
the
rear
face of the camshaft
gear and the thrust plate. The standard clearance 62