JEEP COMPASS 2018 Owner handbook (in English)
Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2018, Model line: COMPASS, Model: JEEP COMPASS 2018Pages: 348, PDF Size: 6.03 MB
Page 121 of 348
Customer Action Customer Will See
NOTE:
Each step MUST BE held for at least two
seconds
12. Turn ignition
MAR/ACC/ON/RUN.
(Entire sequence
needs to be com-
pleted within one
minute or sequence
will need to be re-
peated).System is now reset
and the engine may
be started.
Turn hazard flashers
OFF (Manually).
If a reset procedure step is not completed
within 60 seconds, then the turn signal lights
will blink and the reset procedure must be
performed again in order to be successful.
Maintaining Your Air Bag System
WARNING!
• Modifications to any part of the air bag
system could cause it to fail when you
need it. You could be injured if the air
bag system is not there to protect you.
WARNING!
Do not modify the components or wiring,
including adding any kind of badges or
stickers to the steering wheel hub trim
cover or the upper right side of the in-
strument panel. Do not modify the front
bumper, vehicle body structure, or add
aftermarket side steps or running
boards.
• It is dangerous to try to repair any part of
the air bag system yourself. Be sure to
tell anyone who works on your vehicle
that it has an air bag system.
• Do not attempt to modify any part of your
air bag system. The air bag may inflate
accidentally or may not function prop-
erly if modifications are made. Take your
vehicle to an authorized dealer for any
air bag system service. If your seat, in-
cluding your trim cover and cushion,
needs to be serviced in any way (includ-
ing removal or loosening/tightening of
seat attachment bolts), take the vehicle
to your authorized dealer. Only manufac-
turer approved seat accessories may be
used. If it is necessary to modify the air
WARNING!
bag system for persons with disabilities,
contact your authorized dealer.
Event Data Recorder (EDR)
This vehicle is equipped with an event data
recorder (EDR). The main purpose of an EDR
is to record, in certain crash or near crash-like
situations, such as an air bag deployment or
hitting a road obstacle, data that will assist in
understanding how a vehicle’s systems per-
formed. The EDR is designed to record data
related to vehicle dynamics and safety sys-
tems for a short period of time, typically
30 seconds or less. The EDR in this vehicle is
designed to record such data as:
• How various systems in your vehicle were
operating;
• Whether or not the driver and passenger
safety belts were buckled/fastened;
• How far (if at all) the driver was depressing
the accelerator and/or brake pedal; and,
• How fast the vehicle was traveling.
119
Page 122 of 348

These data can help provide a better under-
standing of the circumstances in which
crashes and injuries occur.
NOTE:
EDR data are recorded by your vehicle only if
a non-trivial crash situation occurs; no data
are recorded by the EDR under normal driving
conditions and no personal data (e.g., name,
gender, age, and crash location) are re-
corded. However, other parties, such as law
enforcement, could combine the EDR data
with the type of personally identifying data
routinely acquired during a crash investiga-
tion.
To read data recorded by an EDR, special
equipment is required, and access to the
vehicle or the EDR is needed. In addition to
the vehicle manufacturer, other parties, such
as law enforcement, that have the special
equipment, can read the information if they
have access to the vehicle or the EDR.Child Restraints — Carrying Children
Safely
Everyone in your vehicle needs to be buckled
up at all times, including babies and chil-
dren. EC directive 2003/20/EC requires
proper use of restraints in all EC countries.
Children less than 1.5 meters tall and
12 years or younger should ride properly
buckled up in a rear seat, if available. Ac-cording to crash statistics, children are safer
when properly restrained in the rear seats
rather than in the front.
WARNING!
• NEVER use a rearward facing child re-
straint on a seat protected by an ACTIVE
AIRBAG in front of it, DEATH or SERI-
OUS INJURY to the CHILD can occur.
• Only use a rear-facing child restraint in a
vehicle with a rear seat.
• A deploying passenger front airbag can
cause death or serious injury to a child
12 years or younger, including a child in
a rear-facing child restraint.
• In a collision, an unrestrained child can
become a projectile inside the vehicle.
The force required to hold even an infant
on your lap could become so great that
you could not hold the child, no matter
how strong you are. The child and others
could be badly injured or killed. Any
child riding in your vehicle should be in
a proper restraint for the child’s size.
Warning Label On Front Passenger Sun
Visor
SAFETY
120
Page 123 of 348
There are different sizes and types of re-
straints for children from newborn size to the
child almost large enough for an adult safety
belt. Children should ride rearward facing as
long as possible; this is the most protected
position for a child in the event of a crash.
Always check the child seat Owner’s Manual
to make sure you have the correct seat for
your child. Carefully read and follow all the
instructions and warnings in the child re-
straint Owner’s Manual and on all the labels
attached to the child restraint.
In Europe, children restraint systems are de-
fined by regulation ECE-R44, which divides
them into five weight groups:
Restraint Group Weight Group
Group 0 up to 10 kg
Group 0+ up to 13 kg
Group 1 9-18 kg
Group 2 15-25 kg
Group 3 22-36 kg
Check the label of your child restraint. All
approved child restraints must include type-
approval data and the control mark on itslabel. The label must be permanently se-
cured to the child restraint system. You
should not remove this label from the child
restraint.
WARNING!
Extreme Hazard! Do not place a rear-
facing child restraint in front of an active
air bag. Refer to visor and door shut face
mounted labels for information. Deploy-
ment of the air bag in an accident could
cause fatal injuries to the baby regardless
of the severity of the collision. It is advis-
able to always carry children in a child
restraint system on the rear seat, which is
the most protected position in the event of
a collision.
WARNING!
Should it be necessary to carry a child on
the passenger side front seat in a rear-
facing child restraint system, the passen-
ger side front airbag and side bag (for
versions/markets, where provided) must
be deactivated through the Setup menu.
WARNING!
Deactivation should be verified by check-
ing whether the warning light is switched
on in the instrument panel. The passenger
seat must also be positioned backward as
far as possible to avoid the child restraint
system from coming into contact with the
dashboard.
“Universal” Child Restraint Systems
• The figures in the following sections are
examples of each type of universal child
restraint system. Typical installations are
shown. Always install your child restraint
system according to the child restraint
manufacturer’s instructions, which must be
included with this type of restraint system.
• Child restraint systems with ISOFIX anchor-
ages are available for installing the child
restraint system to the vehicle without us-
ing the vehicle’s seat belts.
121
Page 124 of 348
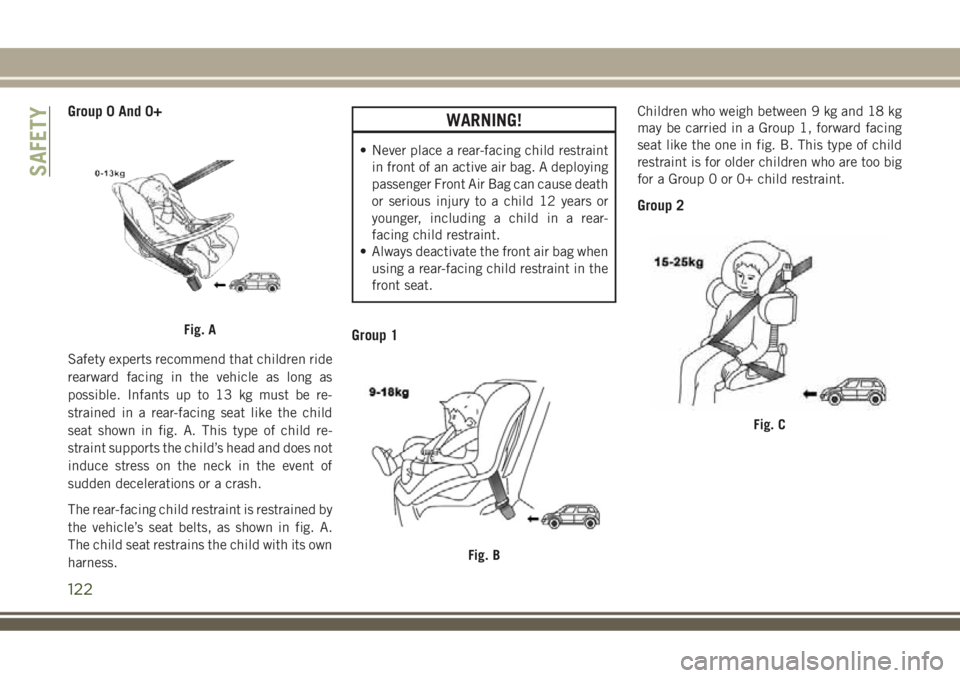
Group 0 And 0+
Safety experts recommend that children ride
rearward facing in the vehicle as long as
possible. Infants up to 13 kg must be re-
strained in a rear-facing seat like the child
seat shown in fig. A. This type of child re-
straint supports the child’s head and does not
induce stress on the neck in the event of
sudden decelerations or a crash.
The rear-facing child restraint is restrained by
the vehicle’s seat belts, as shown in fig. A.
The child seat restrains the child with its own
harness.
WARNING!
• Never place a rear-facing child restraint
in front of an active air bag. A deploying
passenger Front Air Bag can cause death
or serious injury to a child 12 years or
younger, including a child in a rear-
facing child restraint.
• Always deactivate the front air bag when
using a rear-facing child restraint in the
front seat.
Group 1
Children who weigh between 9 kg and 18 kg
may be carried in a Group 1, forward facing
seat like the one in fig. B. This type of child
restraint is for older children who are too big
for a Group 0 or 0+ child restraint.
Group 2
Fig. A
Fig. B
Fig. C
SAFETY
122
Page 125 of 348

Children who weigh between 15 kg and 25 kg
and who are too big for the Group 1 child
restraint may use a Group 2 child restraint
system.
As shown in fig. C, the Group 2 child restraint
system positions the child correctly with re-
spect to the seat belt so that the shoulder belt
crosses the child’s chest and not the neck,
and the lap belt is snug on the pelvis and not
the abdomen.
Group 3
Children who weigh between 22 kg and 36 kg
and who are tall enough to use the adult
shoulder belt may use a Group 3 child re-
straint. Group 3 child restraints position the
lap belt on the child’s pelvis. The child must
be tall enough that the shoulder belt crosses
the child’s chest and not their neck.
Fig. D shows an example of a Group 3 child
restraint system correctly positioning the
child on the rear seat.
WARNING!
• Improper installation can lead to failure
of an infant or child restraint. It could
come loose in a collision. The child
could be badly injured or killed. Follow
the child restraint manufacturer’s direc-
tions exactly when installing an infant or
child restraint.
• After a child restraint is installed in the
vehicle, do not move the vehicle seat
forward or rearward because it can
WARNING!
loosen the child restraint attachments.
Remove the child restraint before ad-
justing the vehicle seat position. When
the vehicle seat has been adjusted, re-
install the child restraint.
• When your child restraint is not in use,
secure it in the vehicle with the seat belt
or ISOFIX anchorages, or remove it from
the vehicle. Do not leave it loose in the
vehicle. In a sudden stop or accident, it
could strike the occupants or seatbacks
and cause serious personal injury.
Fig. D
123
Page 126 of 348
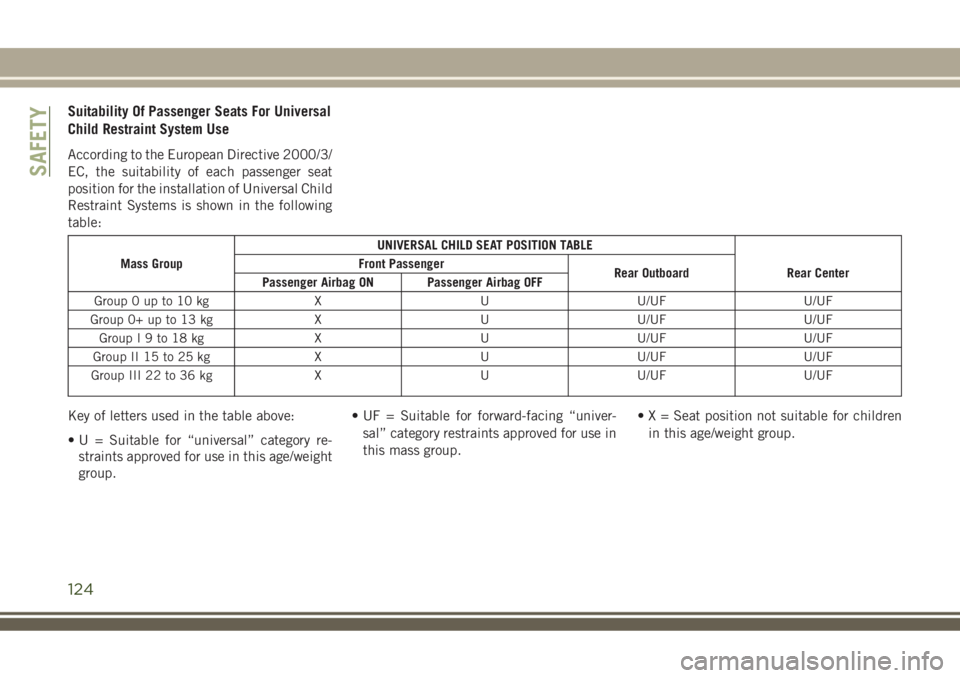
Suitability Of Passenger Seats For Universal
Child Restraint System Use
According to the European Directive 2000/3/
EC, the suitability of each passenger seat
position for the installation of Universal Child
Restraint Systems is shown in the following
table:
Mass GroupUNIVERSAL CHILD SEAT POSITION TABLE
Front Passenger
Rear Outboard Rear Center
Passenger Airbag ON Passenger Airbag OFF
Group 0 up to 10 kg X U U/UF U/UF
Group 0+ up to 13 kg X U U/UF U/UF
GroupI9to18kg X UU/UF U/UF
Group II 15 to 25 kg X U U/UF U/UF
Group III 22 to 36 kg X U U/UF U/UF
Key of letters used in the table above:
• U = Suitable for “universal” category re-
straints approved for use in this age/weight
group.• UF = Suitable for forward-facing “univer-
sal” category restraints approved for use in
this mass group.• X = Seat position not suitable for children
in this age/weight group.
SAFETY
124
Page 127 of 348

WARNING!
Passenger Air Bag Disable Warning
125
Page 128 of 348

Seat Belts For Older Children
Children over 1.50 m in height can wear seat
belts instead of using child restraints.
Use this simple 5-step test to decide whether
the seat belt properly fits the child or if they
should still use a Group 2 or Group 3 child
restraint to improve the fit of the seat belt:
1. Can the child sit all the way back against
the back of the vehicle seat?
2. Do the child’s knees bend comfortably
over the front of the vehicle seat – while
they are still sitting all the way back?
3. Does the shoulder belt cross the child’s
shoulder between their neck and arm?
4. Is the lap part of the belt as low as
possible, touching the child’s thighs and
not their stomach?
5. Can the child stay seated like this for the
whole trip?If the answer to any of these questions was
“no,” then the child still needs to use a Group
2 or 3 child restraint in this vehicle. If the
child is using the lap/shoulder belt, check
belt fit periodically and make sure the seat
belt buckle is latched. A child’s squirming or
slouching can move the belt out of position.
If the shoulder belt contacts the face or neck,
move the child closer to the center of the
vehicle, or use a booster seat to position the
seat belt on the child correctly.
WARNING!
Never allow a child to put the shoulder belt
under an arm or behind their back. In a
crash, the shoulder belt will not protect a
child properly, which may result in serious
injury or death. A child must always wear
both the lap and shoulder portions of the
seat belt correctly.
ISOFIX Restraint System
Your vehicle is equipped with the child restraint
anchorage system called ISOFIX. This system
allows ISOFIX-equipped child seats to be in-
stalled without using the vehicle’s seat belts.
The ISOFIX system has two lower anchorages
located at the back of the seat cushion where it
meets the seatback and a top tether anchorage
located behind the seating position.
An example of a Universal ISOFIX child re-
straint system for weight group 1 is shown in
fig. E. ISOFIX child restraints are also avail-
able in the other weight groups.
Fig. E
SAFETY
126
Page 129 of 348

Locating The ISOFIX Anchorages
The lower anchorages are round bars that are
found at the rear of the seat cushion where it
meets the seatback, above the anchorage
symbols on the seat cushion. They are just
visible when you lean into the rear seat to
install the child restraint. You will easily feel
them if you run your finger along the gap
between the seatback and seat cushion.
Locating Tether Anchorages
There are tether strap anchorages behind
each rear outboard seating position located
on the back of the seat.ISOFIX child restraint systems will be
equipped with a rigid bar on each side. Each
will have a connector to attach to the lower
anchorage and a way to tighten the connec-
tion to the anchorage. Forward-facing child
restraints and some rear-facing child re-
straints may also be equipped with a tether
strap. The tether strap will have a hook at the
end to attach to the top tether anchorage and
a way to tighten the strap after it is attached
to the anchorage.
Center Seat ISOFIX
WARNING!
• This vehicle does not have center ISOFIX
or tether anchorages. This position is not
approved for any type of ISOFIX child
restraint system. Do not install a forward
facing child seat with a tether strap in
the center seating position.
• Use the seat belt to install a child seat in
the center seating position.
• Never use the same lower anchorage to
attach more than one child restraint.
Please refer to “To Install An ISOFIX
Child Restraint” for typical installation
instructions.
Lower Anchorage Location
Tether Anchorage Locations
127
Page 130 of 348
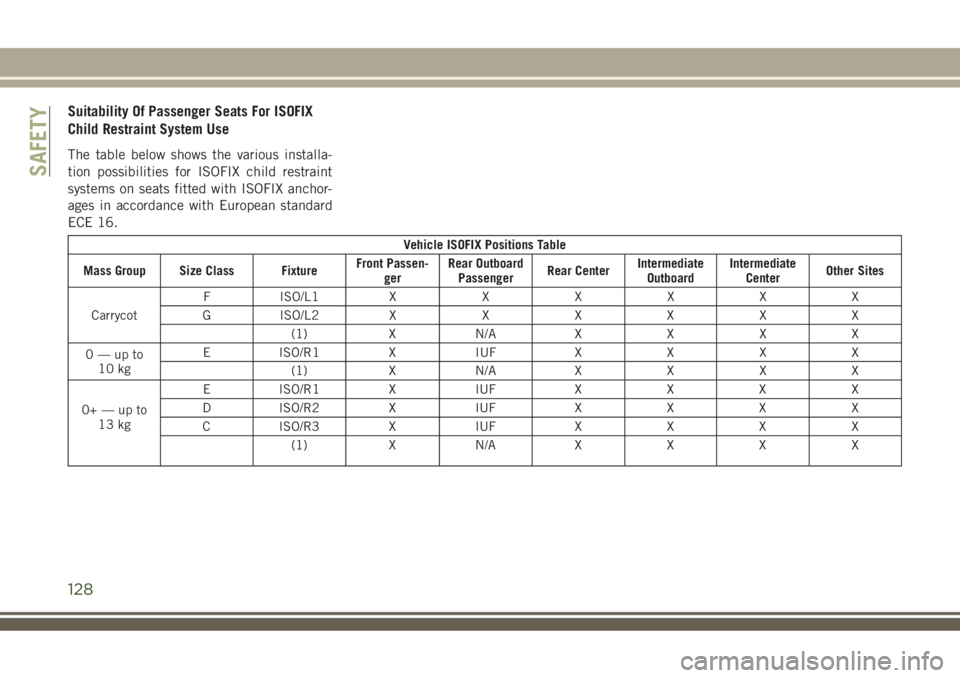
Suitability Of Passenger Seats For ISOFIX
Child Restraint System Use
The table below shows the various installa-
tion possibilities for ISOFIX child restraint
systems on seats fitted with ISOFIX anchor-
ages in accordance with European standard
ECE 16.
Vehicle ISOFIX Positions Table
Mass Group Size Class FixtureFront Passen-
gerRear Outboard
PassengerRear CenterIntermediate
OutboardIntermediate
CenterOther Sites
CarrycotF ISO/L1 X X X X X X
G ISO/L2 X X X X X X
(1)XN/AXXXX
0—upto
10 kgE ISO/R1 X IUF X X X X
(1)XN/AXXXX
0+—upto
13 kgE ISO/R1 X IUF X X X X
D ISO/R2 X IUF X X X X
C ISO/R3 X IUF X X X X
(1)XN/AXXXX
SAFETY
128