wheel JEEP DJ 1953 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1953, Model line: DJ, Model: JEEP DJ 1953Pages: 376, PDF Size: 19.96 MB
Page 208 of 376

H
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
sibility
of the cable shorting at the
engine
or frame.
Remove nut and lock washer securing the ignition
wire
to the solenoid
post
and remove the two screws and lock washers securing the solenoid to
the starter frame. Remove the switch,
b.
To install the solenoid switch reverse the re
moval
procedure given above.
H-10S.
STARTING MOTOR
—
DELCO
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
Refer
to Fig. H-45.
The
starting motor used on the Dauntless V-6 en
gine
has an integral solenoid switch and enclosed
shift lever which first shifts the overrunning clutch
pinion into
engagement
with the ring gear on the
flywheel of the
engine
and then
closes
the electrical
circuit
to cause
engine
cranking. When the
engine
starts,
the overrunning clutch
disengages
to pre vent transfer of
engine
speed to the starting motor.
Note:
Should a service replacement starter motor
be required the factory recommends replacement
with
original equipment parts; however, should the need arise an existing starter motor (Delco or
Prestolite) could be replaced with the current
Delco-Remy
starter, model 1108375, with the
following modifications to the wiring harness. If
the existing starter motor wiring harness
does
not
provide a 12 ga. purple conduit wire, (connects the ignition switch to the starter motor) then a 12 ga.
purple
conduit wire 70 inches long, must be in
stalled.
Should the existing starter motor wiring
harness
contain a 16 ga. light blue conduit wire, (connects the ignition switch and starter motor)
bend this wire back and tape out of the way.
H-109.
Starting Motor Disassembly
a.
Before removing the starting motor from the
engine, disconnect leads and cover battery lead
terminal
with piece of
hose
or tape to prevent
short circuiting.
Note
locations of wiring connec
tions to assure proper reconnection. Remove the cap screw that secures the starting motor to the
angle bracket on the side of the engine. Remove
the two cap screws that secure the drive end of
the starting motor to the cylinder block; remove
the starting motor.
b.
Remove terminal nut and disconnect field lead,
which
passes through grommet at top of motor,
from
motor terminal of solenoid. Remove two
thru
bolts
from motor. Remove commutator end frame
and
field frame assembly from solenoid and drive assembly.
e.
Pull
out pivot pins of brush holders and remove each of two brush holder and spring assemblies
from
field housing. Remove screws which attach
brushes and leads to holders.
d.
Remove armature and drive assembly from
drive
housing. Remove thrust collar from pinion
end of armature shaft. Remove leather thrust
washer
from
opposite
end of shaft.
e. To separate drive assembly from
armature,
place
a
metal cylinder of proper size (J^" [12,7 mm.]
pipe coupling is satisfactory) over end of armature
shaft to bear against the pinion
stop
retainer. Tap
retainer
toward armature to
expose
snap ring as
shown in
Fig.
H-47. Remove snap ring from
groove
in
shaft; slide retainer and pinion drive assembly
from
shaft. Remove assist spring from shaft,
f.
Remove two screws holding solenoid switch to
drive
housing remove switch. Remove small nut
and
insulating washer from the solenoid S terminal.
Remove nut and insulating washer from the
sole
noid battery (large) terminal. Remove two screws that attach switch cover to solenoid and remove cover for inspection of switch parts. Remove shift
lever fulcrum bolt and remove shift lever, plunger,
and
return spring.
12765
FIG.
H-47—REMOVING PINION
DRIVE
ASSEMBLY
FROM
ARMATURE SHAFT
1— XA ' Pipe Coupling
2—
Snap
Ring
and Retainer
3—
Armature
Shaft
4—
Drive
Assembly
H-110.
Starting
Motor
Cleaning and
Inspection
a.
Wipe all parts clean with clean cloths. The
arma
ture,
field coils, and drive assembly must not be
cleaned by any degreasing or high temperature
method.
This
might damage insulation so that a
short
circuit
or ground would subsequently develop.
It
would also remove lubricant originally packed
in
the overrunning clutch so that clutch would
soon
be ruined.
b.
Carefully
inspect all parts visually for wear or
damage. Make necessary repairs or replace unserv
iceable parts. Any soldering must be
done
with
rosin
flux.
Note:
Never use acid flux when solding any elec
trical
connections and never use emery cloth to
clean
armature
commutator or other
electrical
units. 208
Page 216 of 376
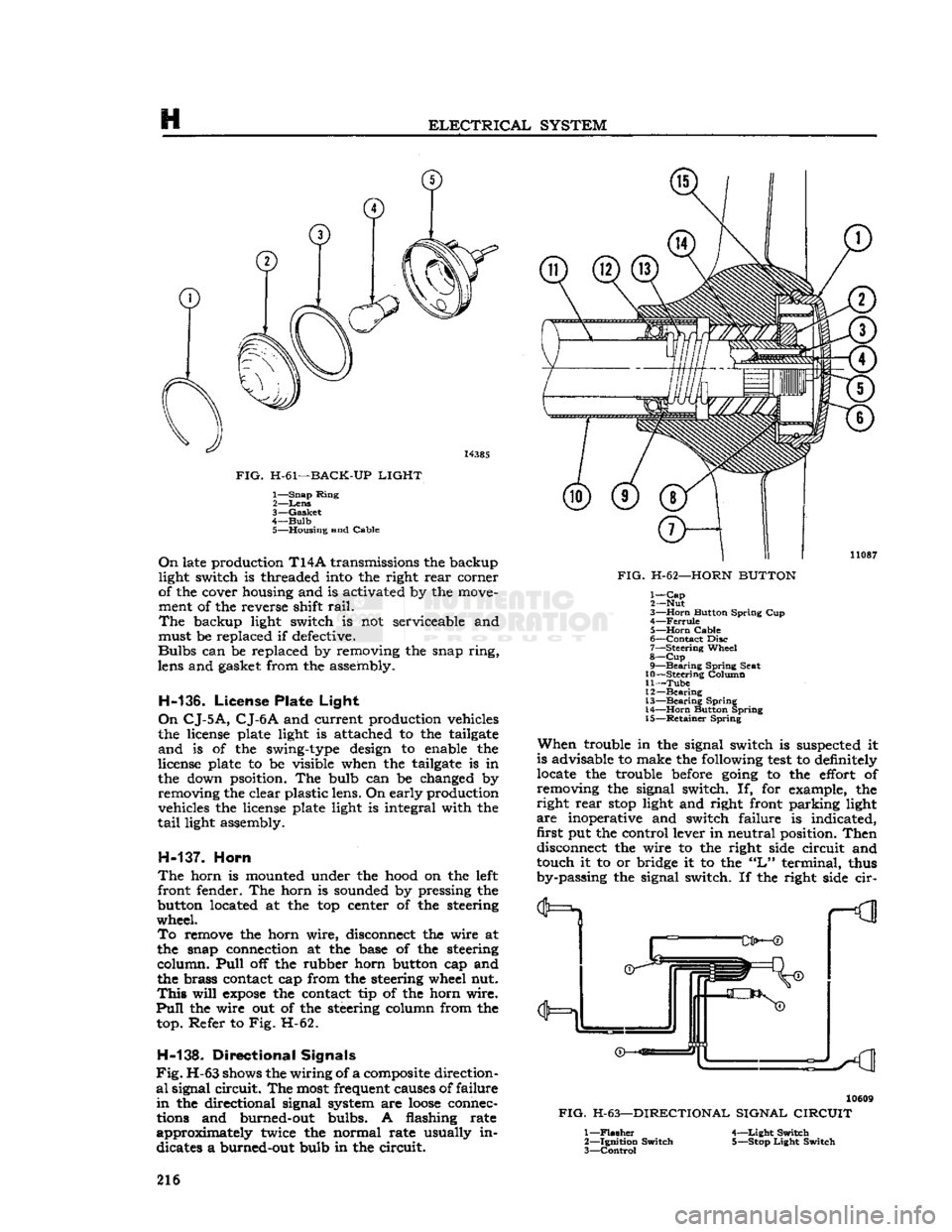
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
14385
FIG.
H-61—BACK-UP
LIGHT
1—
Snap
Ring
2—
Lens
3—
Gasket
4—
Bulb
5—
Housing
and
Cable
On
late production
T14A
transmissions the backup
light switch is threaded into the right
rear
corner
of the cover housing and is activated by the move
ment of the reverse shift
rail.
The
backup light switch is not serviceable and
must be replaced if defective.
Bulbs
can be replaced by removing the snap
ring,
lens and gasket from the assembly.
H-136.
License Plate
Light
On
CJ-5A,
CJ-6A
and current production vehicles
the license plate light is attached to the tailgate
and
is of the swing-type design to enable the
license plate to be visible when the tailgate is in
the down psoition. The bulb can be changed by
removing
the clear plastic lens. On early production
vehicles the license plate light is integral with the
tail
light assembly.
H-137.
Horn
The
horn is mounted under the hood on the
left
front
fender. The horn is sounded by pressing the
button located at the top center of the steering
wheel.
To
remove the horn wire, disconnect the wire at
the snap connection at the base of the steering
column.
Pull
off the rubber horn button cap and
the brass contact cap from the steering wheel nut.
This
will
expose
the contact tip of the horn wire.
Pull
the wire out of the steering column from the top. Refer to Fig. H-62.
H-13S.
Directional
Signals
Fig.
H-63 shows the
wiring
of a
composite
direction
al
signal
circuit.
The most frequent causes of
failure
in
the directional signal system are
loose
connec
tions and burned-out bulbs. A flashing rate
approximately
twice the normal rate usually in
dicates a burned-out bulb in the
circuit.
11087
FIG.
H-62—HORN
BUTTON 1—
Cap
2— Nut
3—
Horn
Button
Spring
Cup 4—
Ferrule
5—
Horn
Cable
6—
Contact
Disc
7—
Steering
Wheel
8—
Cup
9—
Bearing
Spring
Seat
10—
Steering
Column
11—
Tube
12—
Bearing
13—
Bearing
Spring
14—
Horn
Button
Spring
15—
Retainer
Spring
When
trouble in the signal switch is suspected it
is advisable to make the following
test
to definitely
locate the trouble before
going
to the effort of
removing
the signal switch. If, for example, the
right
rear
stop
light and right front parking light
are
inoperative and switch failure is indicated, first put the control lever in neutral position.
Then
disconnect the wire to the right side
circuit
and
touch it to or bridge it to the
"L"
terminal, thus
by-passing the signal switch. If the right side cir- 10609
FIG.
H-63—DIRECTIONAL SIGNAL
CIRCUIT
1—
Flasher
2—
Ignition
Switch
3—
Control
4—
Light
Switch
5— Stop
Light
Switch
216
Page 217 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
H
cuit
lights,
the
signal switch
is
inoperative
and
must
be
replaced.
H-139.
Hazard
Warning Lights
All
current production vehicles
are
equipped with
a
four-way flasher warning system.
The
control switch
is
located
on the
instrument panel left
of
the steering column.
With
the
switch pulled
out,
the
two
front and
two
rear
turn
signal lights flash
on and
off
simultaneously,
as do
both
turn
signal
indicator
lights
on the
instrument clusters.
H-140.
Marker
Lights and Reflector Assembly
The
marker
lights
and
reflector assemblies
on
current
production vehicles
are
mounted
on the
side
of
the front fender and
on the
side
of
the
rear
quarter
panel.
The
spare wheel also mounts
a
marker
light. Some earlier production vehicles have
reflex reflectors mounted on the side of the hood and
on
the
side
of
the
rear
quarter panel. determine
if
dash wiper switch or wiring
is at
fault,
disconnect wiring harness from wiper motor
and
try
operating wiper independently
of
dash switch.
If
still
inoperative
see
procedure under
Par.
H-145.
b. Wiper
will
not
shut
off
— Determine
if
wiper
has both
low
and high speeds, slow speed only,
or
high speed only.
It is
important that
the
wiper
operates
at low
speed during parking cycle.
Dis
connect wiring harness from wiper motor
and try
operating wiper independently
of
dash switch.
If
wiper
shuts
off
correctly with
crank
arm
in
park
position and wiper has both speeds, check
the
lead
between
terminal
and
dash switch ground
and
check
for
defective dash switch.
If
wiper shuts
off
correctly,
but has
high speed only, check lead
be
tween wiper terminal and dash switch
for an
open
circuit
and check
for
defective dash switch.
If
still
inoperative,
see
Par. H-145.
c. Wiper
has
only fast speed.
Check
for
defective dash switch
or
open lead
between
terminal
and
dash switch.
H-141.
Windshield Wiper System
Early
production vehicles equipped with
the
Dauntless V-6
engine
have
two
single speed wind
shield wiper motors mounted above
the
windshield inside
the
vehicle. The wiper motors
are
operated
and
controlled
by a
switch located
on the
instru
ment panel.
Current
production vehicles with stationary wind
shield have
a
two-speed
electric windshield wiper motor mounted below
the
windshield outside
the
vehicle on the driver's side. The wiper motor switch is located
on the
instrument panel
to the
left
of
the steering column.
H-142.
Two-Speed Wiper Motor
The
two-speed
electric wiper motor
is
operated and
controlled
by a
turn
type, three poled, dash switch,
containing
a 6
amp. circuit breaker.
Current
flow
is directed from
the
battery through
the
ignition
switch
to the
wiper dash switch assembly
to the
two-speed
wiper motor, which passes current from the designated motor brush (high,
low or
park)
to
the armature circuit
to
ground.
H-143.
Troubleshooting Procedure
Troubleshooting procedures
are
divided into
two
categories: wiper troubleshooting
in
vehicle; wiper
troubleshooting
on
bench.
Fig. H-65 and H-66
illustrates connecting leads
of the
two-speed
wiper for either bench operation
or to run
wiper inde
pendently
of
dash switch and vehicle wiring when
installed
in the
vehicle.
H-144. Wiper Troubleshooting
in
Vehicle
Typical
wiper troubles and remedies are
as
follows
:
a.
Wiper
is
inoperative
—
Check
wiper switch
cir
cuit
breaker; wiring harness connection
at
wiper
motor
and
wiper switch; wiper motor
feed
wire
from
ignition starter switch
to
wiper switch;
and
check wiper
on
switch
to be
securely mounted.
With
ignition switch
on,
check
for 12
volts
at
har
ness
terminal that connects
to
wiper terminal.
To
BLACK
PARK
GREEN *-
RED m~
LOW
PARKING
<^^>
SWITCH
V^-O*'
HIGH
FIG.
H-64—WIRING
DIAGRAM
FIG.
H-65—WINDSHIELD
WIPER
SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
(EARLY)
1.
Park
(black)
2. Low (green)
3.
High (red)
d.
Wiper
has
only slow speed
and
shuts
off
with
dash switch in high speed position. Reverse harness
leads that connect
to
wiper terminals.
e. If
blades
do not
return
to
park
position when
wiper
is
turned
off,
check wiper ground connection
to vehicle body. Remove wiper from vehicle
and
check
for
dirty, bent,
or
broken
park
switch con
tacts.
f.
If
wiper speed
is
normal
in
slow,
but too ex
cessive
in
fast speed, check for an open terminal. 217
Page 226 of 376
![JEEP DJ 1953 Workshop Manual
I
CLUTCH 1-1.
GENERAL
The
clutch on current Jeep vehicles is either
Auburn
or Borg and Beck manufactured. Vehicles
equipped with F4-134
engines
have an
Auburn
9.25" [23,4 cm.] single JEEP DJ 1953 Workshop Manual
I
CLUTCH 1-1.
GENERAL
The
clutch on current Jeep vehicles is either
Auburn
or Borg and Beck manufactured. Vehicles
equipped with F4-134
engines
have an
Auburn
9.25" [23,4 cm.] single](/img/16/57041/w960_57041-225.png)
I
CLUTCH 1-1.
GENERAL
The
clutch on current 'Jeep' vehicles is either
Auburn
or Borg and Beck manufactured. Vehicles
equipped with F4-134
engines
have an
Auburn
9.25" [23,4 cm.] single plate dry-disc clutch. The
pressure plate has three coil pressure springs and
three levers or fingers.
The
V6-225
engine
is equipped with a 10.4" [26,4
cm.] Borg and Beck single plate dry-disc clutch.
The
pressure plate utilizes either a finger-type
diaphragm spring, or a coil
type
spring pressure plate for clutch release.
The
driven plates of all
models
are built with
vibra
tion damper springs and have two flexible facings
which
provide
smooth
engagement
of the
engine
power.
Early
'Jeep' vehicles equipped with a Dauntless
V-6
engine
use a 10.4" [26,4 cm.] single plate, dry-
disc clutch, incorporating a diaphram-type spring assembly.
The
clutch is of the centrifugal single dry disc
type
and
consists of the clutch disc, pressure plate and
the clutch release bearing.
The
clutch is actuated by a clutch pedal and a
series of mechanical linkage.
When
the clutch pedal is in the
engaged
position,
the clutch disc facings are clamped
between
the
friction surface of the
engine
flywheel and the face of the clutch pressure plate, thereby connect
ing
engine
power to the transmission. Depressing
the clutch pedal actuates the clutch release shaft
fork
which
moves
the clutch release bearing against
the clutch fingers.
This,
in
turn,
moves
the pressure
plate away from the clutch disc. Since the disc is splined to the transmission input shaft, the clutch
disc and transmission input shaft
will
stop
when
the clutch is disengaged, thereby disconnecting
engine
power from the transmission.
1-2.
Clutch
Maintenance
To
obtain normal life and satisfactory performance
from any clutch it must be correctly operated and
properly maintained. Two conditions which shorten
clutch life are continuous operation of the clutch
release bearing and clutch slippage.
The
clutch release bearing is
designed
for inter
mittent use. If run continuously the bearing
lubri
cant
will
become
exhausted causing the bearing to
become
dry, noisy, or
will
seize, resulting in clutch
finger or diaphragm wear. The clutch must be properly adjusted so that the release bearing is
free of the clutch fingers or diaphragm at all times,
except
when the clutch pedal is depressed.
Excessive
clutch slippage
often
occurs when the
vehicle is overloaded, the vehicle load is applied
too quickly, or when the pressure of the clutch fingers or diaphragm is only partially applied to the clutch plate.
Friction
between
the clutch facing
and
flywheel produces
excessive
heat causing
burned,
glazed and worn linings, resulting in shortened clutch life. Avoid clutch slippage under
heavy loads by using a lower gear or reducing the load.
1-3.
Clutch
Pedal
Linkage
and Adjustment
Adjust
the clutch pedal free travel whenever the clutch
does
not
disengage
properly, or when new
clutch parts are installed. Improper adjustment of
the clutch pedal free travel is one of the
most
fre
quent causes of clutch failure and can be a con tributing factor in
some
transmission failures.
As
the clutch facings wear the free travel of the clutch pedal diminishes. When sufficient wear oc
curs
the pedal clearance must be adjusted.
Two
types
of clutch linkage have
been
used on Jeep vehicles, a cross shaft
tube
and lever
type
shown in Fig. 1-1, and a clutch control cable
type
shown in Fig. 1-2. The clutch pedal adjustment
procedures for both
type
linkages are as follows.
•
Cross
Shaft
Lever
and Tube Type
Refer
to Fig. 1-1.
Note:
Two different
Clutch
Control
Lever
and
Tube
Assemblies have
been
installed on 'Jeep*
Universal
vehicles equipped with a V-6
engine
and
T14A
transmission.
Should difficulty in shifting the transmission be
noted, check the length of the clutch release pedal
rod,
item (16) in Fig. 1-1. Measure the distance
between
the centerlines of the cotter key holes.
FIG.
1-2—CLUTCH
LINKAGE AND
ADJUSTMENT,
CONTROL
CABLE TYPE
A—Top
View,
Cable
to
Clutch
Fork
1—
Retracting
Spring
(Clutch
Fork)
2—
Clutch
Fork
3—
Ball
Adjusting Nut
4—
Lock
Nut 5—
Clutch
Cable
B—Side
View,
Cable
to
Clutch
Pedal 6—
Clutch
Cable
Support
Bracket
7—
Clutch
Cable
Housing
8—
Anchor
Bracket-to-Frame Side
Rail
9—
Retracting
Spring
(Clutch
Pedal)
10—Clutch
Pedal Assembly
*
© © ©
1437S
226
Page 227 of 376
![JEEP DJ 1953 Workshop Manual
Jeep
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
The
correct distance should be 10%"
[26,04
cm.].
If
the length of the clutch release pedal rod is
other than
10
W
[26,04
cm.], the vheicle is eq JEEP DJ 1953 Workshop Manual
Jeep
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
The
correct distance should be 10%"
[26,04
cm.].
If
the length of the clutch release pedal rod is
other than
10
W
[26,04
cm.], the vheicle is eq](/img/16/57041/w960_57041-226.png)
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
The
correct distance should be 10%"
[26,04
cm.].
If
the length of the clutch release pedal rod is
other than
10
W
[26,04
cm.], the vheicle is equipped with the early
type
Clutch
Control
Lever
and
Tube Assembly, which should be removed, and^trie latest
designed
parts should be installed.
The
free pedal clearance is adjusted by lengthening
or shortening the" clutch fork cable. To make this adjustment,
loosen
the jam nut on the cable clevis
and
lengthen or shorten the cable to obtain %"
[19,05
mm.] free travel at the pedal pad, then
tighten the jam unit.
•
Clutch
Control Cable Type
Refer
to Fig. 1-2.
a.
With the clutch pedal pad against the floor
panel, (pedal up, clutch
engaged)
adjust ball ad
justing nut until slack is removed from the cable
and
the clutch throwout bearing contacts the clutch
pressure plate, release levers or diaphragm plate.
b. Back-off ball adjusting nut 2
V2
turns to obtain
approximately %"
[19,05
mm.] free travel.
Lock
hex nut.
FIG.
1-3—AUBURN
CLUTCH
ASSEMBLY —
HURRICANE F4 ENGINE 1—
Driven
Plate and Hub
2—
Pressure
Plate
3—
Pivot Pin
4—
Bracket
5—
Spring
Cup 6—
Pressure
Spring 7— Release
Lever
8—
Return
Spring
9—
Adjusting
Screw
10—
Jam
Nut 11—
Washer
Note:
Some older 'Jeep' vehicles may
develop
side
movement
of the clutch and brake pedals resulting
from wear of the pedals, shafts, and bushings. One way to
compensate
for this wear is to install a pedal
slack
adjuster kit 1-4.
CLUTCH
—
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
•
Auburn
Vehicles equipped with the Hurricane F4
engine
have a 9.25" [23,4 cm.] driven plate. The auburn clutch driving (pressure) plate assembly (Fig. 1-3)
has three pressure springs and three levers or
fingers.
1-5.
Clutch
Removal
When
necessary to remove the clutch,
follow
the procedures outlined in Section J for the removal
of the transmission and transfer case from the vehicle. Then remove the flywheel housing and use
the following procedures for removing the clutch assembly.
Note:
The F4
engine
may be removed from the
vehicle when inspecting or replacing the clutch.
Refer
to Section D for Hurricane F4
engine
removal and then
follow
the instructions given
below
to remove the clutch assembly.
a.
Mark
the clutch pressure plate and
engine
fly
wheel with a center punch so the clutch assembly
may be installed in the same position after adjust
ments
or replacement are completed.
b. Remove the clutch pressure plate bracket
bolts
equally, a little at a time, to prevent distortion and
to relieve the clutch springs evenly.
c. Remove the pressure plate assembly and driven
plate from the flywheel.
1-6.
Clutch
Pressure Plate and Disc Inspection
Inspect the pressure plate face for
cracks,
chips,
and
warpage.
Check
the pressure plate levers for
excessive
wear and the springs for breaks. If any of the
above
conditions exist, the
complete
pressure
plate must be replaced.
Check
the clutch disc for
excessive
wear,
loose
or damaged facings, broken
vibration damper springs and evidence of grease
or oil. If any of the
above
conditions exist, replace
the clutch disc.
1-7.
Clutch
Pressure Plate Adjustment —
Auburn
The
clutch pressure plate must be checked
before
installing a new or reconditioned clutch. The proper 11339
FIG.
1-4—CHECKING
AUBURN
CLUTCH
LEVER
ADJUSTMENT
1— Adjustment Gauge
2—
Fixture
Mounting Bolt
3—
Clutch
Fixture
227
Page 228 of 376

CLUTCH
©—*
11378
FIG.
1-5—ADJUSTING
AUBURN
CLUTCH
LEVERS
1—
Gauge
5—Mounting Bolt
2—
Clutch
Lever
6—Clutch
Pressure
Plate
3—
Adjusting
Screw
7—Thickness
Spacer
4—
Locknut
8—Clutch
Adjusting
Fixture
spacer thickness and
gauge
length is listed in
Par.
1-30. Use
Clutch
Adjusting Fixture W-296
and
proceed as follows:
a.
Place the thickness spacers
between
the pressure
plate face and clutch adjusting fixture. Locate the spacers under the pressure plate levers and at the
center of the pressure plate face, see Fig. 1-5.
b. With the spacers properly installed, bolt the
pressure plate to the adjusting fixture.
Draw
the
bolts
down evenly a little at a time until they are
tight.
c. Using the proper
gauge
length check the lever adjustment as shown in Fig. 1-4.
d.
Lever
adjustment can be altered by removing
the lever clips, loosening the locknut and turning
the adjusting screw (Fig. 1-5) in or out as required.
FIG.
1-6—REMOVING
PILOT
BUSHING
1—
Flywheel
2—
Pilot
Bushing
3—
Pilot
Bushing Remover 1-8. Pilot Bushing Inspection and Replacement
•
F4 and V-6 Engine.
Inspect the transmission main shaft pilot bushing
which
is pressed into the center of the flywheel on
the Hurricane F4
engine
and in the center of the
crankshaft
on the Dauntless V-6 engine. If the bushing is worn or damaged, it should be removed,
using a pilot bushing remover. Screw the tapered end of the tool into the damaged bushing, allowing
the tool to cut its own threads until a solid grip is obtained. Insert the puller screw and rotate it
until
bushing is forced out of flywheel, Fig. 1-6 or
crankshaft.
To
install a new bushing, slide the bushing
onto
the end of a pilot bushing installing and burnishing tool and insert the bushing into flywheel or
crank
shaft. A
soft
hammer can be used against the tool
to help drive the bushing in place. When the tool
is removed (by tightening the cap and pressure
nut as shown in Fig. 1-7), the bushing
will
be
burnished
to correct size. Apply a small amount of
lubricant
to the bushing bore.
FIG.
1-7—INSTALLING
PILOT
BUSHING
1—
Pilot
Bushing
Installing
and
Burnishing
Tool
2—
Flywheel
1-9.
Clutch
Installation
a.
Inspect
Clutch
Disc
Before the clutch disc is installed, it should be
carefully
inspected for warpage. If grease or oil is evident on the friction facings, the facings should
be replaced and the cause of oil accumulation cor rected. Excessively worn facings should also be
replaced with factory recommended parts.
b. Inspect
Clutch
Release Bearing and Sleeve
The
clutch release bearing and
sleeve
are attached to the front facing of the transmission case by a
spring.
Check
the bearing and
sleeve
for evidence
of grease leaks from within the bearing or for wear
and
looseness.
Replace parts as necessary. 228
Page 229 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
I
Note:
The clutch release bearing is lubricated at
time of assembly and no attempt should be made
to lubricate it Refer to Fig. 1-23 when lubricating
the clutch throwout bearing collar. c. Reassembly
To
assemble the clutch to the flywheel, first put
a
small amount of light cup grease in the flywheel
pilot bushing, install the driven plate, with short
end of hub toward the flywheel, then place the pressure plate assembly in position.
With
a clutch
plate aligning arbor or a spare transmission main
shaft, align the driven plate splines leaving the
arbor
in position while tightening the pressure plate
screws evenly.
Next, assemble the flywheel housing to the
engine
and
reinstall the transmission and transfer case or
install
the
engine
in the vehicle, depending on the
procedure of removal. Make sure that the clutch
release bearing
carrier
return spring is hooked in place. For the remainder of the assembly reverse
the operations that were used in removing the
transmission and transfer case or the
engine
referring
to the instructions given in Section J for the transmission and Section D and Dl for the
engine.
d.
Adjust the clutch control cable so there is 3A" [19,05 mm.] free pedal travel. (Refer to Par. 1-3)
1-10.
CLUTCH
—
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
•
Diaphragm Spring Type
(Early
Models)
*
Jeep' vehicles equipped with a Dauntless V-6 en
gine
use a 10.4" [26,4 cm.] single-plate, dry-disc
clutch,
incorporating a diaphragm-type spring as
sembly.
When
the clutch pedal is depressed, it
moves
the
clutch
fork in the direction shown in Fig. 1-8. The
clutch
fork, pivoting on a
ball
stud, acts upon the
throwout bearing. The bearing then forces the
prongs of the diaphragm spring in the direction shown in
Fig.
1-8. The diaphragm spring is mounted
so that it pivots on its retaining rings.
This
reverses
the direction of force.
Force
is applied directly to
the three retracting springs which then
move
the
pressure plate
rearward,
away from the driven plate.
The
clutch driven plate assembly slides freely on
the transmission main drive gear splined shaft. It is keyed to the gear shaft by ten splines. The
front end of the main drive gear shaft is piloted by a bushing pressed into a recess in the
rear
end
of the
engine
crankshaft. See Fig. 1-8.
The
outer area of the driven plate is divided into
segments
formed in low waves to provide springs
between
the plate facings and cushion
engagement
of the clutch. A molded facing is riveted to each
side of every
segment.
When the clutch is fully
released, the waved
segments
cause the facings to
spread
approximately .045" [1,14 mm.]. Pressure
plate movement provides an additional clearance
of approximately .030" [0.76 mm.] to assure
full
release of the driven plate. See Fig. 1-8.
The
driven plate assembly is designed to prevent
torsional fluctuation of the
engine
from being
transmitted to the transmission gears. Its hub is
FIG.
1-8—CLUTCH
RELEASE
ACTION
1—
Pressure
Plate 5—Engine
Crankshaft
2—
Throwout
Bearing
6—Pilot
Bearing
3—
Pivot
Point
7—Flywheel
4—
Clutch
Fork
8—Driven
Plate
driven
through torsional coil springs; additional
frictional
dampening is supplied by molded
fric-
tional washers.
1-11.
Clutch
Removal
a.
Remove transmission as described in Section J. b. Remove clutch throwout bearing and pedal re
turn
spring from clutch fork.
c. Remove flvwheel housing from engine.
d.
Disconnect clutch fork from
ball
stud by forc
ing it toward the center of the vehicle.
e.
Mark
clutch cover and flywheel with a center
punch
so that cover can later be installed in the same position on the flywheel.
This
is necessary to
maintain
engine
balance.
f. Loosen the clutch attaching
bolts
alternately,
one
turn
at a time, to avoid distorting the clutch
cover flange, until diaphragm spring is released.
g. Support the pressure plate and cover assembly
while removing last bolts; remove pressure plate
and
driven plate from flywheel.
Caution:
Use extreme care to keep clutch driven plate clean.
h.
If it is necessary to disassemble pressure plate,
remove three drive strap-to-pressure plate
bolts
and
retracting springs. Remove pressure plate from
clutch
cover.
Note:
When disassembling,
note
position of
grooves
on
edge
of pressure plate and cover. These marks must be aligned in assembly to maintain balance.
i.
The clutch diaphragm spring and two pivot rings
are
riveted to the clutch cover. Inspect spring, rings
and
cover for excessive wear or damage. If there
is a
defect,
replace the complete cover assembly.
1-12.
Clutch
inspection
Wash
all metal parts of clutch, except release bear
ing and driven plate, in suitable cleaning solution to remove
dirt
and grease. If solvent
seeps
into
bearing,
lubricant may be dissolved. Cleaning sol
vent
will
also damage the facings of driven plate,
a.
Inspect friction surfaces of flywheel and pres
sure
plate for scoring or roughness. Slight roughness
may be smoothed with fine emery cloth. If surface 229
Page 230 of 376

CLUTCH
is deeply scored or grooved, the part should be
replaced.
b. Inspect driven plate for wear or damage to fac
ings,
loose
rivets, broken or
loose
torsion springs,
and
flattened cushion springs. If facings are worn
near
rivets or are oily, replace the plate assembly.
A
slight amount of oil on clutch facings
will
cause
clutch
grab and chatter; excessive oil on facings
will
cause slippage. It is not practical to remove
oil
with solvents or by buffing since oil
will
con
tinue to bleed from facing material when hot. If
oil
is found on driven plate facings, examine trans
mission drainback hole, pilot bushing,
engine
rear
main
bearing and other points of possible oil leakage. Test the fit of driven plate hub on trans
mission main drive gear for an easy sliding fit.
c. Inspect clutch release bearing for scoring or ex cessive wear on front contact face. Test for rough
ness
of balls and races by pressing and turning
front race slowly. Inspect main drive gear pilot
bushing in crankshaft. Replace bushing if it is rough or worn. Regardless of whether the old plate
or
a new plate is to be installed, check the plate
for runout. Slide the driven plate, front side first,
over the transmission main drive gear shaft so that
it
is tight on the spline. Index a
dial
indicator to the plate facing as shown in
Fig.
1-9. While holding
firmly
against front end of main drive gear, to take up play in main drive gear bearing, slowly
rotate driven plate and observe the amount of
run
out shown by indicator. If runout of front facing
exceeds
.025" [0,635 mm.], replace the plate. It
is not practical to correct excessive runout by bending. 12769
FIG.
1-9—RUNOUT
CHECK
—
CLUTCH
PLATE
1—
Front
Facing
(Flywheel
Side)
2—
Dial
Indicator
Set
d.
Check
clutch pilot bushing for excessive wear
or
damage. Replace pilot bushing, if necessary, with
special
removal and installation
tools.
(See
Figs.
1-6 and 1-7). 1-13.
SERVICING
CLUTCH
PRESSURE
PLATE
AND
DISC
—
BORG
&
BECK
V6
(Late
Models)
The
Borg & Beck clutch is a single plate, dry disk
type. It provides smooth
engagement
of
engine
power to the wheels. The clutch consists of a pres
sure
plate assembly with pressure springs and
release levers, and driven plate assembly. The
driven
plate assembly
uses
spring center vibration
neutralizes and two flexible facings.
The
clutch driven plate is spring cushioned with a facing riveted to both sides. The coil springs around
the hub absorb the power shocks and cushion the
driving
mechanism. The clutch throw-out bearing is of the
ball
type, packed at time of manufacture,
and
requires no further lubrication.
No adjustment for wear is provided in the clutch itself. An individual adjustment is built into the
clutch
cover to adjust the height of the release
levers.
This
adjusting nut is locked in position
and
should never be disturbed unless the clutch assembly has been disassembled for the replace
ment of worn parts or to correct the height of the release levers.
When
the clutch pedal is depressed (disengaged),
the release bearing is moved toward the flywheel
and
contacts the inner ends of the release levers.
Each
lever is pivoted on a floating pin which re
mains stationary in the lever and rolls across a short flat portion of the enlarged
hole
in the eye-
bolt. The outer ends of the
eyebolts
extend
through
holes
in the stamped cover and are fitted
with
adjusting nuts to secure the levers in the
correct
position. The outer ends of the release levers
engage
the pressure plate lugs by means of ful-
crums,
which provide knife-edge contact
between
the outer ends of the levers and the lugs as shown
in
Fig.
I-10. 12190
FIG.
MO—CLUTCH
LEVER
POSITIONS
A—Clutch
Engaged
B—Clutch
Disengaged 1-14.
Clutch
Pressure Plate Adjustment
The
clutch pressure plate adjustment must be
checked before installing a new or reconditioned
clutch.
The proper spacer thickness and
gage
length for a particular clutch is listed in Par. 1-30.
Use
Clutch
Adjusting
Fixture
W-296. If the W-296
fixture is not available one can be fabricated as
described in Par. 1-26. 230
Page 233 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
b.
Check
the anti-rattle springs in the clutch cover
and
place the cover on top of the pressure plate
assembly. The top of each pressure spring must enter its spring seat in the cover.
Line
up punch
marks
on cover and pressure plate for balance.
c.
Slowly compress the cover making sure that
the
eyebolts
and pressure plate lugs are guided through the proper
holes
in the cover.
d.
Hold the clutch under compression and screw
down the adjusting nuts until they are flush with
the
tops
of the eyebolts. Release the spindle of
the press.
1-24.
Clutch
Lever Adjustment
Important:
Always inspect release lever height
adjustment when installing a new clutch drive
plate.
Place
a clutch
gauge
plate on the flywheel in the
position normally occupied by the driven plate.
FIG.
1-16—CLUTCH WITH GAUGE
PLATE
1—Machined
Land
2—Gauge Plate
FIG.
1-17—CHECKING
LEVERS
FOR
FREE
MOVEMENT
Mount
the cover assembly, center the plate and
line up the three machined lands on the
gauge
plate directly under the levers, as shown in
Fig.
1-16.
Tighten
the cover screws in rotation, one to two
turns
at a time, to avoid distortion of the cover.
FIG.
1-18—CLUTCH HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT
Each
lever should be depressed several times be
fore checking.
This
will
seat the levers in their operating positions, as shown in Fig. 1-17.
Place
the
gauge
on the hub as shown in Fig. 1-18.
To
adjust the levers,
turn
the lever adjustment nut until the levers are
%{'
to %6" [0,93 a 1,59 mm.]
above the hub. Before staking the adjusting nuts
to lock them in place, work the lever up and down
and
recheck lever adjustment again. Stake the nut with a
dull
punch, as shown in Fig. 1-19.
FIG.
1-19—LOCKING ADJUSTING NUTS
1-25.
Clutch Throwout
Release Bearing
The
clutch throwout or release mechanism consists
of a forked lever which pivots on a
ball
pivot threaded into the clutch housing. A throwout lever
return
spring is anchored to a clip under the
ball
pivot and holds the lever in contact with the
ball
pivot. The clutch throwout bearing, which is a
pre-lubricated
unit, is attached to the forked end of the throwout lever.
Never wash the clutch throwout release bearing in
gasoline or any solvent that
will
dissolve the
lubri
cant.
It is neither necessary nor possible to
lubri
cate this bearing at any time. Connect linkage
to the throwout release lever. Adjust free-play as
directed
in Par. 1-3. 233
Page 235 of 376
![JEEP DJ 1953 Workshop Manual
Jeep
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
I thickness: .285"
[0,724
cm.], .305"
[0,775
cm.].
Each
spacer should be hardened and ground to size, and then have the dimensional thickness
sta JEEP DJ 1953 Workshop Manual
Jeep
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
I thickness: .285"
[0,724
cm.], .305"
[0,775
cm.].
Each
spacer should be hardened and ground to size, and then have the dimensional thickness
sta](/img/16/57041/w960_57041-234.png)
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
I thickness: .285"
[0,724
cm.], .305"
[0,775
cm.].
Each
spacer should be hardened and ground to size, and then have the dimensional thickness
stamped thereon.
c.
From
flat bar stock at least Vfe" [3 mm.] thick,
make a
gauge
as shown in Fig. 1-22. Harden, grind
to size, and stamp sizes on the
gauge.
1-27.
Clutch Installation
a.
Very
sparingly, apply wheel bearing lubricant
to inner surface of pilot bushing in crankshaft.
Caution:
If
excessive
lubricant is applied to pilot bushing, it
will
run out on face of flywheel when
hot and
ruin
the driven plate facings.
b. Make sure that splines in the driven plate hub
are
clean; apply a light coat of lubricant to splines
of hub and transmission drive gear shaft. Slide plate over gear shaft several times; remove plate
from shaft and wipe off
excess
lubricant.
Caution:
Driven plate facings must be kept clean
and
dry.
c.
Fill
groove
in throwout bearing collar with wheel bearing lubricant. See Fig. 1-23. Make sure
that front bearing retainer of transmission is clean;
apply a light coat of wheel bearing lubricant. Slide
throwout bearing over bearing retainer several times. Remove bearing from retainer and wipe off
excess
lubricant.
12736
FIG.
1-23—LUBRICATION
POINTS
—
CLUTCH
THROWOUT
BEARING
COLLAR
1—Coat
This
Groove 2—Pack
This
Recess
d.
Clean
and apply wheel bearing lubricant to ball
stud in flywheel housing and to the
seat
in clutch
fork.
e.
If disassembled, install pressure plate in the cover assembly, lining up the
groove
on its
edge
with the
groove
on the
edge
of the cover.
Install
pressure plate retracting springs, and the three
drive
strap-to-pressure plate
bolts
and lock washers.
Torque
bolts
11 lb-ft. [1,51 kg-m.].
Note:
The diaphragm
type
clutch assembly is fac
tory calibrated and requires no adjustment
before
installation. Refer to Par. 1-14 to adjust Borg and
Beck
coil spring
type
clutch assembly.
f.
Install
the pressure plate and driven plate on
flywheel. Support both assemblies with a spare
main
drive gear.
Note:
Be certain that
mark
on clutch cover is
aligned with the
mark
made on the flywheel during
clutch removal.
g.
Install
clutch attaching
bolts
and tighten alter nately so that clutch is drawn squarely
into
position
on flywheel.
Each
bolt
must be
tightened
one turn at a time to avoid bending the clutch cover flange.
Torque
bolts
30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,5 kg-m.].
h.
Lubricate
the ball stud and clutch fork with
wheel bearing lubricant and install clutch fork.
Note:
Be certain that fork retaining spring is
tight
on pivot ball stud.
i.
Install
flywheel housing on
engine
cylinder
block.
Caution:
Be certain that dowel pins are installed
in
cylinder block.
j.
Lubricate
the recess on the inside of the throw-
out bearing collar. Be careful not to use too much
lubricant.
See Fig. 1-23.
Caution:
Make certain that the lips of the spring
retainer (attached to the clutch fork) are in
groove
of the bearing. See Fig. 1-24.
k.
Install
throwout bearing assembly and connect
clutch linkage.
I.
Install
transmission as described in Section J. m. Adjust clutch for %"
[19,05
mm.] free travel,
see
Par.
1-3. 235