Oil sensor JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 2112 of 2199

controlled vehicle accessories during periods of low
engine vacuum such as when the vehicle is climbing
a steep grade, or under other high engine load oper-
ating conditions.
The vacuum reservoir cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the right side headlamp mounting
module and headlamp assembly. Refer to Lamps/
Lighting for the procedures.
(2) Remove the two screws that secure the vacuum
reservoir to the base of the radiator closure panel.
(3) Remove the vacuum reservoir.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the vacuum reservoir in the vehicle and
tighten the two screws to 3.4 N´m (30 in. lbs.).
(2) Install the right side headlamp mounting mod-
ule and headlamp assembly. Refer to Lamps/Lighting
for the procedures.
EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The evaporator probe is a 2 wire temperature sens-
ing element located at the coldest point on the face of
the evaporator. The switch is attached to the evapo-
rator coil fins. The evaporator temperature probe
prevents condensate water on the evaporator coil
from freezing and obstructing A/C system air flow.
OPERATION
The probe is used to switch the clutch OFF before
evaporator freeze-up occurs. Output from the probe is
sampled by the Body Control Module (BCM). The
clutch is switched OFF when the probe temperature
reaches 1.1É C (34É F). It is allowed to switch ON
when the probe temperature reaches 2.2É C (36É F).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehi-
cle(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(3) Disassemble the HVAC housing(Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - DISASSEMBLY).
(4) Carefully pull the probe out of the evaporator
core.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the new probe into the evaporator.
NOTE: The new probe must not go into the same
hole (in the evaporator core) that the old probe was
removed from.
(2) Reassemble the HVAC housing(Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - ASSEMBLY).
(3) Reinstall the HVAC assembly in the vehicle(Re-
fer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DIS-
TRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
Fig. 22 VACUUM RESERVOIR
1 - FAN RELAY
2 - SPEED CONTROL SERVO
3 - VACUUM RESERVOIR
WJCONTROLS 24 - 35
VACUUM RESERVOIR (Continued)
Page 2142 of 2199

ING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C
PRESSURE TRANSDUCER - INSTALLATION).
(9) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(10) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
(11) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) Remove the tape or plugs from the discharge
line block fitting and the manifold on the compressor.
Install the discharge line block fitting to the manifold
on the compressor. Tighten the mounting bolt to 25.4
N´m (225 in. lbs.).
(2) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the condenser inlet and the discharge
line. Connect the discharge line to the condenser
inlet. Tighten the retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in.
lbs.).
(3) Install the a/c high pressure transducer(Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CON-
TROLS/A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER - INSTAL-
LATION).
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
(5) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)(6) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
A/C EXPANSION VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The ªHº valve type thermal expansion valve (TXV)
is located at the front of the heater-A/C housing
between the liquid and suction lines and the evapo-
rator coil.
The expansion valve is a factory calibrated unit
and cannot be adjusted or repaired. If faulty or dam-
aged, the expansion valve must be replaced.
OPERATION
High-pressure, high temperature liquid refrigerant
from the liquid line passes through the expansion
valve orifice, converting it inot a low-pressure, low-
temperature mixture of liquid and gas before it
enters the evaporator coil. A temperature sensor in
the expansion valve control head monitors the tem-
perature of the refrigerant leaving the evaporator coil
throught the suction line, and adjusts the orifice size
at the liquid line to let the proper amoount of refrig-
erant into the evaporator coil to meet the vehicle
cooling requirements. Controlling the refrigerant flow
through the evaporator ensures that none of the
refrigerant leaving the evaporator is still in a liquid
state, which could damage the compressor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C EXPANSION
VALVE
The expansion valve is located on the engine side
of the dash panel near the shock tower.
The expansion valve can fail in three different
positions (open, closed or restricted).
In an Open Position: this will result in a noisy
compressor or no cooling. The cause can be broken
spring, broken ball or excessive moisture in the A/C
system. If the spring or ball are found to be defective,
replace the expansion valve. If excessive moisture is
found in the A/C system, recycle the refrigerant.
In a Closed Position: There will be low suction
pressure and no cooling. This may be caused by a
failed power dome or excessive moisture in the A/C
system. If the power dome on the expansion valve is
found to be defective replace the expansion valve. If
excessive moisture is found recycle the refrigerant.
A Restricted Orifice: There will be low suction
pressure and no cooling. This may be caused by
debris in the refrigerant system. If debris is believed
to be the cause, recycle the refrigerant and replace
the expansion valve and the receiver/drier.
WJPLUMBING 24 - 65
A/C DISCHARGE LINE (Continued)
Page 2147 of 2199

INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) Install the evaporator coil in the bottom half of
the HVAC housing. Be certain that the evaporator
foam insulator wrap is reinstalled.
(2) Reassemble the HVAC housing and install in
the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
ASSEMBLY) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
INSTALLATION)
NOTE: If the evaporator is replaced, add 60 millili-
ters (2 fluid ounces) of refrigerant oil to the refrig-
erant system.
Fig. 11 HVAC HOUSING- CASE SEPARATED
1 - ELECTRICIAL CONNECTORS
2 - VACUUM ACTUATOR
3 - RECIRCULATION DOOR
4 - THERMAL EXPANSION VALVE
5 - BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR/CONTROLLER
6 - BLOWER WHEEL
7 - EVAPORATOR AND TUBES
8 - FIN SENSOR PROBE9 - BLEND DOOR
10 - PIVOT SHAFT (MOTOR REMOVED)
11 - PANEL/OUTLET DOOR
12 - LOWER HOUSING
13 - VACUUM ACTUATORS
14 - UPPER HOUSING
15 - VACUUM HARNESS
24 - 70 PLUMBINGWJ
A/C EVAPORATOR (Continued)
Page 2162 of 2199
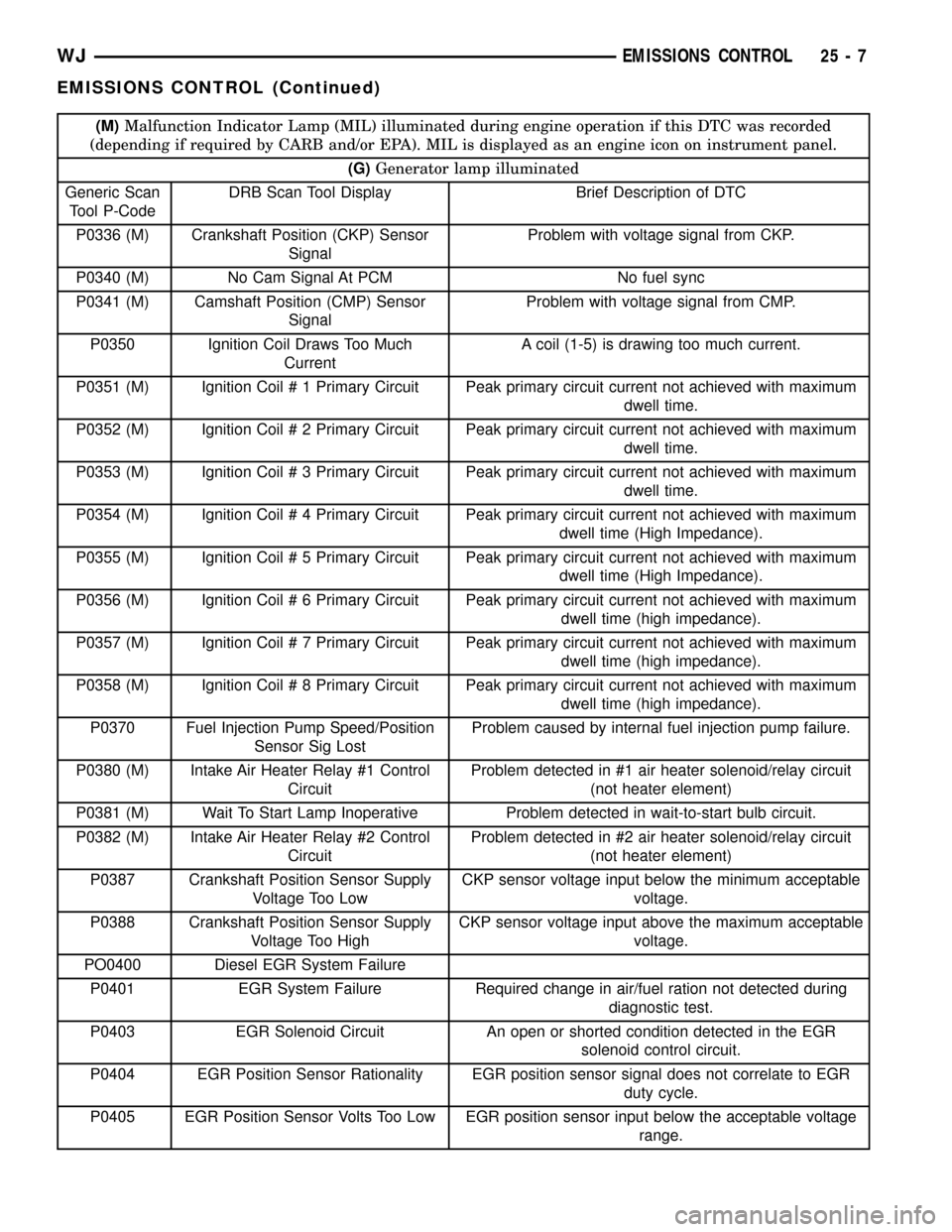
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0336 (M) Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
SignalProblem with voltage signal from CKP.
P0340 (M) No Cam Signal At PCM No fuel sync
P0341 (M) Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
SignalProblem with voltage signal from CMP.
P0350 Ignition Coil Draws Too Much
CurrentA coil (1-5) is drawing too much current.
P0351 (M) Ignition Coil # 1 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0352 (M) Ignition Coil # 2 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0353 (M) Ignition Coil # 3 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0354 (M) Ignition Coil # 4 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0355 (M) Ignition Coil # 5 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0356 (M) Ignition Coil # 6 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0357 (M) Ignition Coil # 7 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0358 (M) Ignition Coil # 8 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0370 Fuel Injection Pump Speed/Position
Sensor Sig LostProblem caused by internal fuel injection pump failure.
P0380 (M) Intake Air Heater Relay #1 Control
CircuitProblem detected in #1 air heater solenoid/relay circuit
(not heater element)
P0381 (M) Wait To Start Lamp Inoperative Problem detected in wait-to-start bulb circuit.
P0382 (M) Intake Air Heater Relay #2 Control
CircuitProblem detected in #2 air heater solenoid/relay circuit
(not heater element)
P0387 Crankshaft Position Sensor Supply
Voltage Too LowCKP sensor voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0388 Crankshaft Position Sensor Supply
Voltage Too HighCKP sensor voltage input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
PO0400 Diesel EGR System Failure
P0401 EGR System Failure Required change in air/fuel ration not detected during
diagnostic test.
P0403 EGR Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EGR
solenoid control circuit.
P0404 EGR Position Sensor Rationality EGR position sensor signal does not correlate to EGR
duty cycle.
P0405 EGR Position Sensor Volts Too Low EGR position sensor input below the acceptable voltage
range.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 7
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2163 of 2199
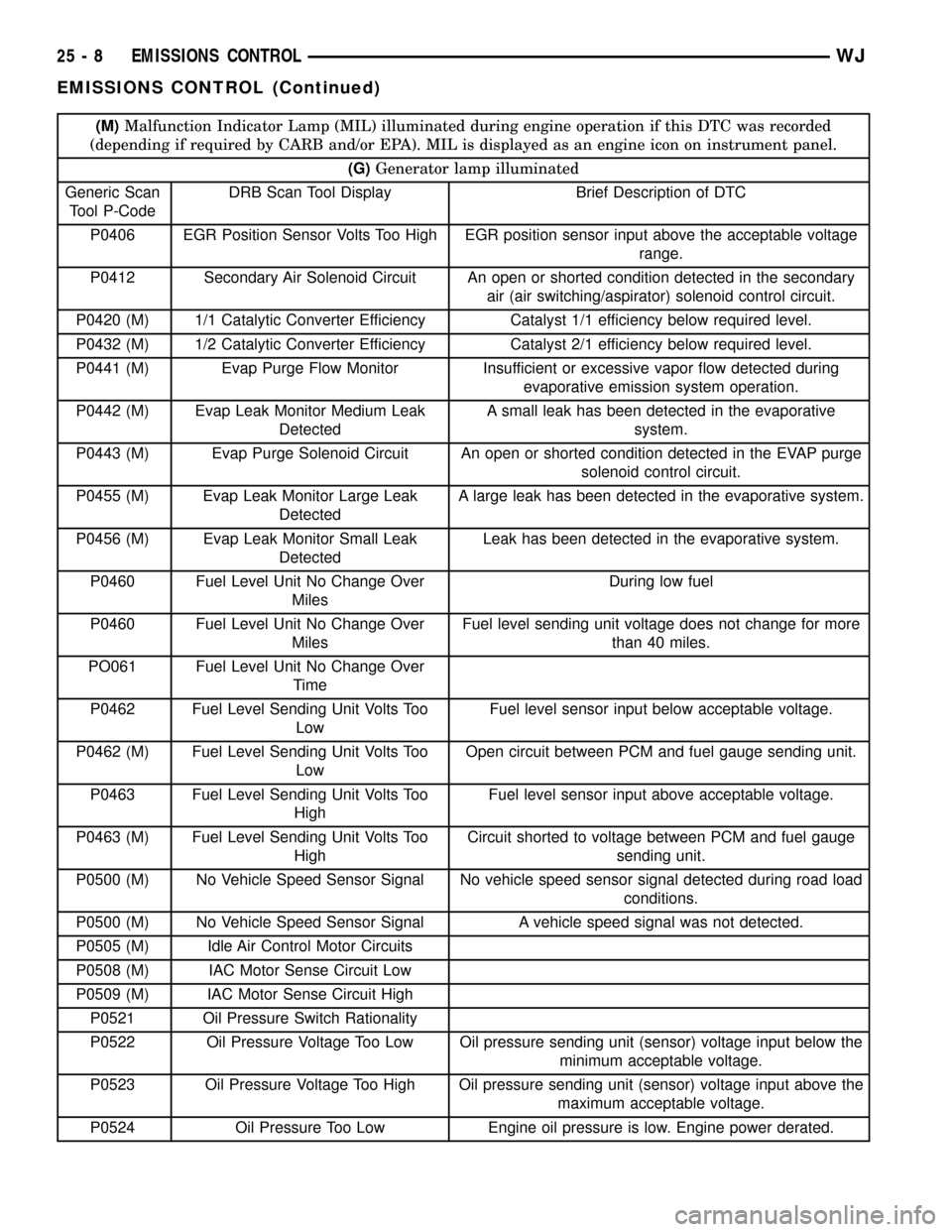
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0406 EGR Position Sensor Volts Too High EGR position sensor input above the acceptable voltage
range.
P0412 Secondary Air Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the secondary
air (air switching/aspirator) solenoid control circuit.
P0420 (M) 1/1 Catalytic Converter Efficiency Catalyst 1/1 efficiency below required level.
P0432 (M) 1/2 Catalytic Converter Efficiency Catalyst 2/1 efficiency below required level.
P0441 (M) Evap Purge Flow Monitor Insufficient or excessive vapor flow detected during
evaporative emission system operation.
P0442 (M) Evap Leak Monitor Medium Leak
DetectedA small leak has been detected in the evaporative
system.
P0443 (M) Evap Purge Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EVAP purge
solenoid control circuit.
P0455 (M) Evap Leak Monitor Large Leak
DetectedA large leak has been detected in the evaporative system.
P0456 (M) Evap Leak Monitor Small Leak
DetectedLeak has been detected in the evaporative system.
P0460 Fuel Level Unit No Change Over
MilesDuring low fuel
P0460 Fuel Level Unit No Change Over
MilesFuel level sending unit voltage does not change for more
than 40 miles.
PO061 Fuel Level Unit No Change Over
Time
P0462 Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
LowFuel level sensor input below acceptable voltage.
P0462 (M) Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
LowOpen circuit between PCM and fuel gauge sending unit.
P0463 Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
HighFuel level sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P0463 (M) Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
HighCircuit shorted to voltage between PCM and fuel gauge
sending unit.
P0500 (M) No Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal No vehicle speed sensor signal detected during road load
conditions.
P0500 (M) No Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal A vehicle speed signal was not detected.
P0505 (M) Idle Air Control Motor Circuits
P0508 (M) IAC Motor Sense Circuit Low
P0509 (M) IAC Motor Sense Circuit High
P0521 Oil Pressure Switch Rationality
P0522 Oil Pressure Voltage Too Low Oil pressure sending unit (sensor) voltage input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0523 Oil Pressure Voltage Too High Oil pressure sending unit (sensor) voltage input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0524 Oil Pressure Too Low Engine oil pressure is low. Engine power derated.
25 - 8 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2175 of 2199

an associated limp in will take two trips to illumi-
nate the MIL.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
causing driveability problems. The PCM might not
store diagnostic trouble codes for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause the
PCM to store diagnostic trouble codes for other sys-
tems or components. For example, a fuel pressure
problem will not register a fault directly, but could
cause a rich/lean condition or misfire. This could
cause the PCM to store an oxygen sensor or misfire
diagnostic trouble code
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system, although it may set a fuel
system fault.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injectoris installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Although the PCM monitors engine exhaust oxygen
content when the system is in closed loop, it cannot
determine excessive oil consumption.
THROTTLE BODY AIRFLOW
The PCM cannot detect a clogged or restricted air
cleaner inlet or filter element.
VACUUM ASSIST
The PCM cannot detect leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices. However, these could cause the PCM
to store a MAP sensor diagnostic trouble code and
cause a high idle condition.
PCM SYSTEM GROUND
The PCM cannot determine a poor system ground.
However, one or more diagnostic trouble codes may
be generated as a result of this condition. The mod-
ule should be mounted to the body at all times, also
during diagnostic.
PCM CONNECTOR ENGAGEMENT
The PCM may not be able to determine spread or
damaged connector pins. However, it might store
diagnostic trouble codes as a result of spread connec-
tor pins.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device with established high and low limits for
the device. If the input voltage is not within limits
and other criteria are met, the PCM stores a diagnos-
tic trouble code in memory. Other diagnostic trouble
code criteria might include engine RPM limits or
input voltages from other sensors or switches that
must be present before verifying a diagnostic trouble
code condition.
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE
ENGINE IDLE/NEUTRAL 2500 RPM/NEUTRAL
All Engines 2% to 8% of Maximum Load 9% to 17% of Maximum Load
25 - 20 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)