tow JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1651 of 2199

OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 251) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 252).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the overrun-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
Fig. 251 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
21 - 132 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1663 of 2199
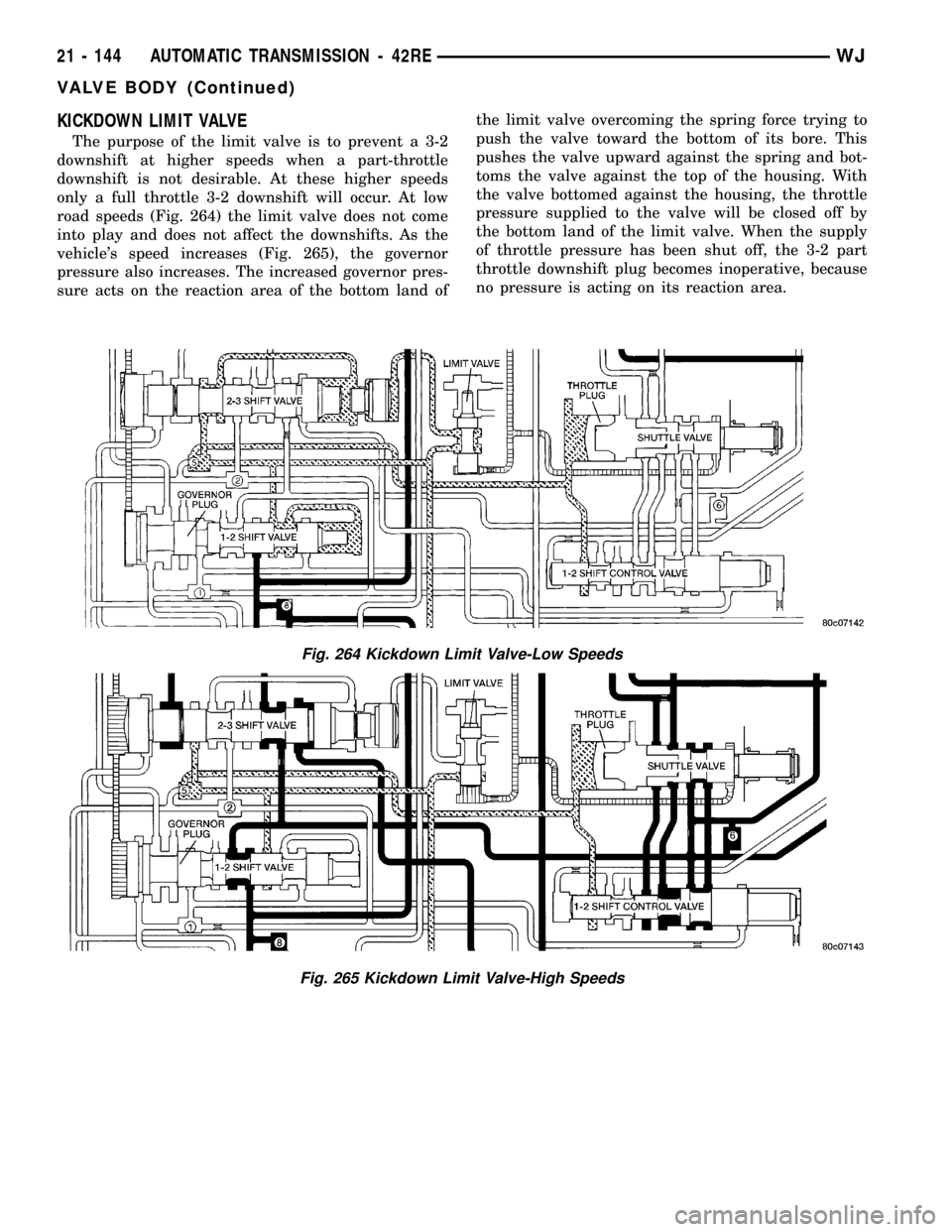
KICKDOWN LIMIT VALVE
The purpose of the limit valve is to prevent a 3-2
downshift at higher speeds when a part-throttle
downshift is not desirable. At these higher speeds
only a full throttle 3-2 downshift will occur. At low
road speeds (Fig. 264) the limit valve does not come
into play and does not affect the downshifts. As the
vehicle's speed increases (Fig. 265), the governor
pressure also increases. The increased governor pres-
sure acts on the reaction area of the bottom land ofthe limit valve overcoming the spring force trying to
push the valve toward the bottom of its bore. This
pushes the valve upward against the spring and bot-
toms the valve against the top of the housing. With
the valve bottomed against the housing, the throttle
pressure supplied to the valve will be closed off by
the bottom land of the limit valve. When the supply
of throttle pressure has been shut off, the 3-2 part
throttle downshift plug becomes inoperative, because
no pressure is acting on its reaction area.
Fig. 264 Kickdown Limit Valve-Low Speeds
Fig. 265 Kickdown Limit Valve-High Speeds
21 - 144 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1669 of 2199
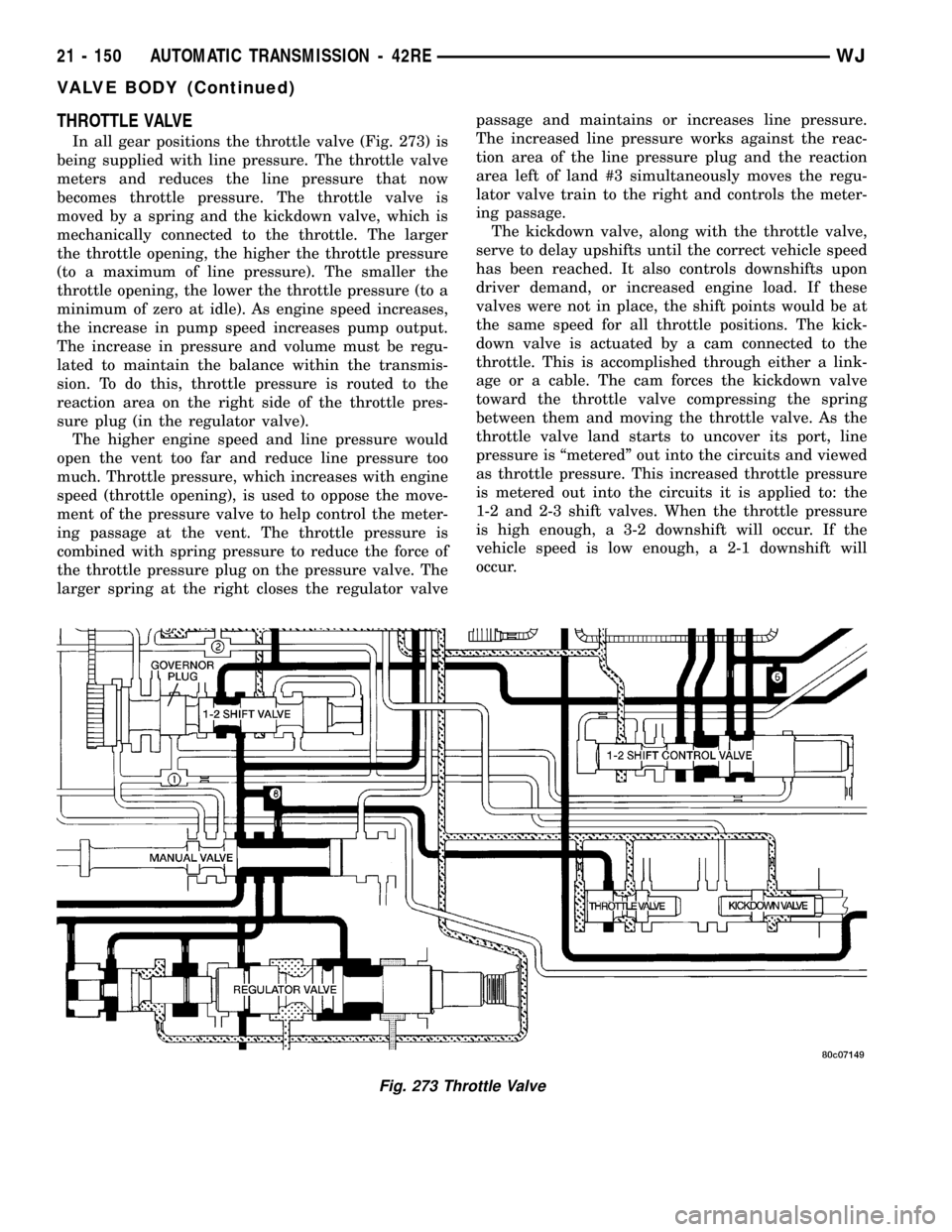
THROTTLE VALVE
In all gear positions the throttle valve (Fig. 273) is
being supplied with line pressure. The throttle valve
meters and reduces the line pressure that now
becomes throttle pressure. The throttle valve is
moved by a spring and the kickdown valve, which is
mechanically connected to the throttle. The larger
the throttle opening, the higher the throttle pressure
(to a maximum of line pressure). The smaller the
throttle opening, the lower the throttle pressure (to a
minimum of zero at idle). As engine speed increases,
the increase in pump speed increases pump output.
The increase in pressure and volume must be regu-
lated to maintain the balance within the transmis-
sion. To do this, throttle pressure is routed to the
reaction area on the right side of the throttle pres-
sure plug (in the regulator valve).
The higher engine speed and line pressure would
open the vent too far and reduce line pressure too
much. Throttle pressure, which increases with engine
speed (throttle opening), is used to oppose the move-
ment of the pressure valve to help control the meter-
ing passage at the vent. The throttle pressure is
combined with spring pressure to reduce the force of
the throttle pressure plug on the pressure valve. The
larger spring at the right closes the regulator valvepassage and maintains or increases line pressure.
The increased line pressure works against the reac-
tion area of the line pressure plug and the reaction
area left of land #3 simultaneously moves the regu-
lator valve train to the right and controls the meter-
ing passage.
The kickdown valve, along with the throttle valve,
serve to delay upshifts until the correct vehicle speed
has been reached. It also controls downshifts upon
driver demand, or increased engine load. If these
valves were not in place, the shift points would be at
the same speed for all throttle positions. The kick-
down valve is actuated by a cam connected to the
throttle. This is accomplished through either a link-
age or a cable. The cam forces the kickdown valve
toward the throttle valve compressing the spring
between them and moving the throttle valve. As the
throttle valve land starts to uncover its port, line
pressure is ªmeteredº out into the circuits and viewed
as throttle pressure. This increased throttle pressure
is metered out into the circuits it is applied to: the
1-2 and 2-3 shift valves. When the throttle pressure
is high enough, a 3-2 downshift will occur. If the
vehicle speed is low enough, a 2-1 downshift will
occur.
Fig. 273 Throttle Valve
21 - 150 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1684 of 2199
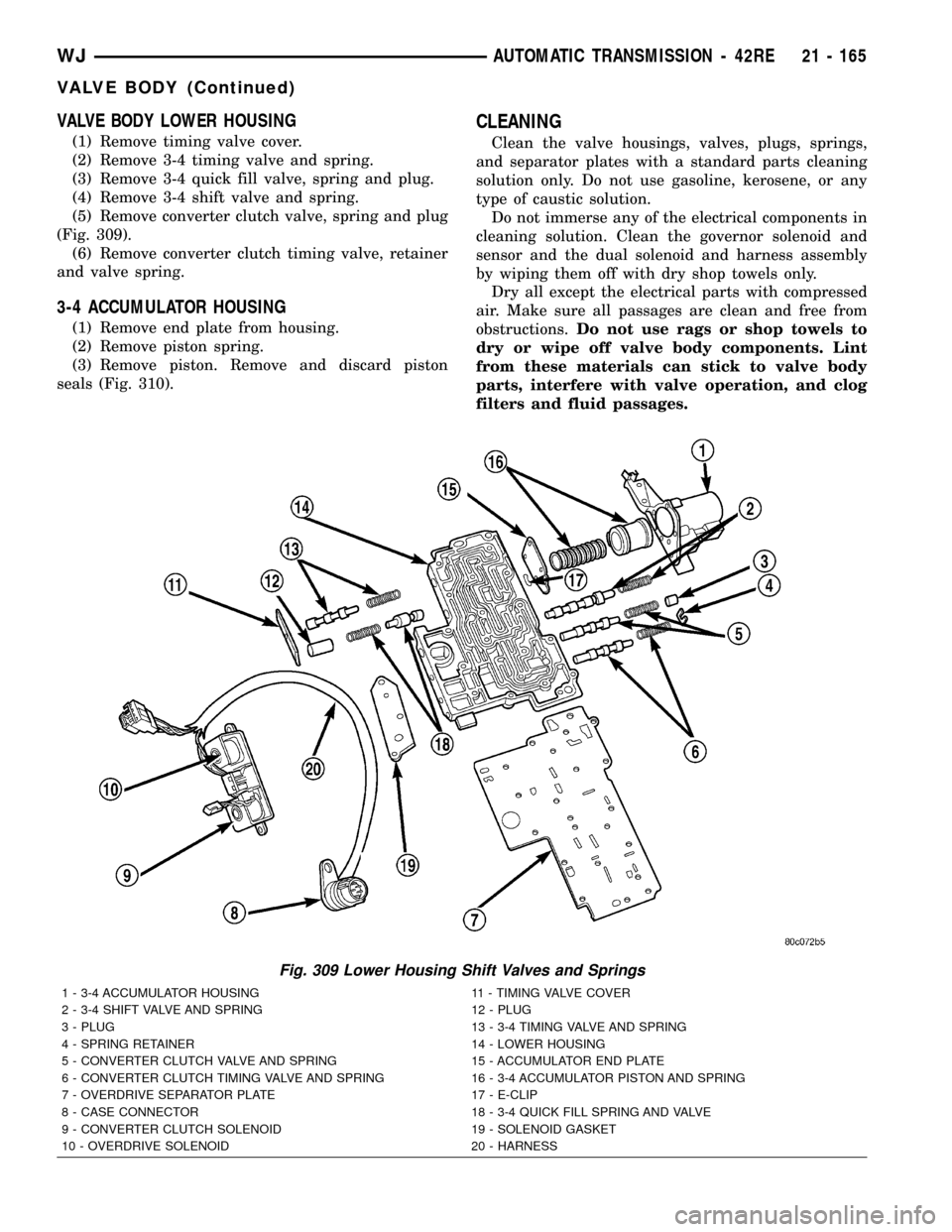
VALVE BODY LOWER HOUSING
(1) Remove timing valve cover.
(2) Remove 3-4 timing valve and spring.
(3) Remove 3-4 quick fill valve, spring and plug.
(4) Remove 3-4 shift valve and spring.
(5) Remove converter clutch valve, spring and plug
(Fig. 309).
(6) Remove converter clutch timing valve, retainer
and valve spring.
3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
(1) Remove end plate from housing.
(2) Remove piston spring.
(3) Remove piston. Remove and discard piston
seals (Fig. 310).
CLEANING
Clean the valve housings, valves, plugs, springs,
and separator plates with a standard parts cleaning
solution only. Do not use gasoline, kerosene, or any
type of caustic solution.
Do not immerse any of the electrical components in
cleaning solution. Clean the governor solenoid and
sensor and the dual solenoid and harness assembly
by wiping them off with dry shop towels only.
Dry all except the electrical parts with compressed
air. Make sure all passages are clean and free from
obstructions.Do not use rags or shop towels to
dry or wipe off valve body components. Lint
from these materials can stick to valve body
parts, interfere with valve operation, and clog
filters and fluid passages.
Fig. 309 Lower Housing Shift Valves and Springs
1 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING 11 - TIMING VALVE COVER
2 - 3-4 SHIFT VALVE AND SPRING 12 - PLUG
3 - PLUG 13 - 3-4 TIMING VALVE AND SPRING
4 - SPRING RETAINER 14 - LOWER HOUSING
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH VALVE AND SPRING 15 - ACCUMULATOR END PLATE
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH TIMING VALVE AND SPRING 16 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR PISTON AND SPRING
7 - OVERDRIVE SEPARATOR PLATE 17 - E-CLIP
8 - CASE CONNECTOR 18 - 3-4 QUICK FILL SPRING AND VALVE
9 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID 19 - SOLENOID GASKET
10 - OVERDRIVE SOLENOID 20 - HARNESS
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 165
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1685 of 2199

Wipe the governor pressure sensor and solenoid
valve with dry, lint free shop towels only. The O-rings
on the sensor and solenoid valve are the only service-
able components. Be sure the vent ports in the sole-
noid valve are open and not blocked by dirt or debris.
Replace the valve and/or sensor only when DRB scan
tool diagnosis indicates this is necessary. Or, if either
part has sustained physical damage (dented,
deformed, broken, etc.).
CAUTION: Do not turn the small screw at the end of
the solenoid valve for any reason. Turning the
screw in either direction will ruin solenoid calibra-
tion and result in solenoid failure. In addition, the
filter on the solenoid valve is NOT serviceable. Do
not try to remove the filter as this will damage the
valve housing.
INSPECTION
Inspect the throttle and manual valve levers and
shafts. Do not attempt to straighten a bent shaft or
correct a loose lever. Replace these components if
worn, bent, loose or damaged in any way.
Inspect all of the valve body mating surfaces for
scratches, nicks, burrs, or distortion. Use a straight-
edge to check surface flatness. Minor scratches may
be removed with crocus cloth using only very light
pressure.Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with a
sheet of crocus cloth. Position the crocus cloth on a
surface plate, sheet of plate glass or equally flat sur-
face. If distortion is severe or any surfaces are
heavily scored, the valve body will have to be
replaced.
CAUTION: Many of the valves and plugs, such as
the throttle valve, shuttle valve plug, 1-2 shift valve
and 1-2 governor plug, are made of coated alumi-
num. Aluminum components are identified by the
dark color of the special coating applied to the sur-
face (or by testing with a magnet). Do not sand alu-
minum valves or plugs under any circumstances.
This practice could damage the special coating
causing the valves/plugs to stick and bind.
Inspect the valves and plugs for scratches, burrs,
nicks, or scores. Minor surface scratches on steel
valves and plugs can be removed with crocus cloth
butdo not round off the edges of the valve or
plug lands.Maintaining sharpness of these edges is
vitally important. The edges prevent foreign matter
from lodging between the valves and plugs and the
bore.
Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the valve
body. Use a penlight to view the bore interiors.
Replace the valve body if any bores are distorted or
scored. Inspect all of the valve body springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Check the two separator plates for distortion or
damage of any kind. Inspect the upper housing,
lower housing, 3-4 accumulator housing, and transfer
plate carefully. Be sure all fluid passages are clean
and clear. Check condition of the upper housing and
transfer plate check balls as well. The check balls
and ball seats must not be worn or damaged.
Trial fit each valve and plug in its bore to check
freedom of operation. When clean and dry, the valves
and plugs should drop freely into the bores.
Valve body bores do not change dimensionally with
use. If the valve body functioned correctly when new,
it will continue to operate properly after cleaning and
inspection. It should not be necessary to replace a
valve body assembly unless it is damaged in han-
dling.
The only serviceable valve body components are
listed below. The remaining valve body components
are serviced only as part of a complete valve body
assembly. Serviceable parts are:
²dual solenoid and harness assembly
²solenoid gasket
²solenoid case connector O-rings and shoulder
bolt
²switch valve and spring
Fig. 310 Accumulator Housing Components
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
3 - TEFLON SEALS
4 - PISTON SPRING
5 - COVER PLATE AND SCREWS
21 - 166 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1709 of 2199

(48) Remove the manual selector shaft seal.
(49) Remove the dipstick tube seal.
CLEANING
The use of crocus cloth is permissible where neces-
sary, providing it is used carefully. When used on
shafts, or valves, use extreme care to avoid rounding
off sharp edges. Sharp edges are vital as they pre-
vent foreign matter from getting between the valve
and valve bore.
Do not reuse oil seals, gaskets, seal rings, or
O-rings during overhaul. Replace these parts as a
matter of course. Also do not reuse snap rings or
E-clips that are bent or distorted. Replace these parts
as well.
Lubricate transmission parts with MopartATF +4,
Type 9602, transmission fluid during overhaul and
assembly. Use petroleum jelly, MopartDoor Ease, or
Ru-Glyde to prelubricate seals, O-rings, and thrust
washers. Petroleum jelly can also be used to hold
parts in place during reassembly.Clean the case in a solvent tank. Flush the case
bores and fluid passages thoroughly with solvent.
Dry the case and all fluid passages with compressed
air. Be sure all solvent is removed from the case and
that all fluid passages are clear.
NOTE: Do not use shop towels or rags to dry the
case (or any other transmission component) unless
they are made from lint-free materials. Lint will stick
to case surfaces and transmission components and
circulate throughout the transmission after assem-
bly. A sufficient quantity of lint can block fluid pas-
sages and interfere with valve body operation.
INSPECTION
Inspect the case for cracks, porous spots, worn
bores, or damaged threads. Damaged threads can be
repaired with Helicoil thread inserts. However, the
case will have to be replaced if it exhibits any type of
damage or wear.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Replace any
components which show evidence of excessive wear
or scoring.
(2) Install the cooler filter bypass valve.
(3) Torque the bypass valve to specification. The
valve uses a tapered pipe thread and excessive
torque can damage the transmission case. Tighten
the cooler filter bypass valve to 4.5 N´m (40 in.lbs.).
(4) Install a new selector shaft seal using Seal
Installer 8253 (Fig. 31).
Fig. 30 Manual Shaft/Park Lock Components
1 - GUIDE
2 - SNAP-RING
3 - SHAFT
4 - SPRING
5 - PARK PAWL
6 - MANUAL SHAFT/LEVER
7 - PARK ROD
Fig. 31 Install Selector Shaft
1 - SEAL
2 - TOOL 8253
21 - 190 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1710 of 2199

(5) Install the manual selector shaft and retaining
screw. Tighten the manual selector shaft retaining
screw to 28 N´m (250 in.lbs.).
(6) Install the park pawl, spring, and shaft (Fig.
32).
(7) Install the park rod and e-clip (Fig. 32).
(8) Install the park rod guide and snap-ring (Fig.
32).
(9) Install a new dipstick tube seal using Seal
Installer 8254 (Fig. 33).
NOTE: Before final assembly of transmission cen-
terline, the 2C/4C clutch components should be
installed into position and measured as follows:
(10) Install the 2C reaction plate into the trans-
mission case (Fig. 34). The reaction plate is direc-
tional. The plate must be installed with the flat side
toward the front of the transmission.
(11) Install the 2C clutch pack into the transmis-
sion case (Fig. 34).(12) Install the flat 2C clutch snap-ring into the
transmission case (Fig. 34).
(13) Install the 4C retainer/bulkhead into the
transmission case. Make sure that the oil feed holes
are pointing toward the valve body area.
(14) Install the 4C retainer/bulkhead tapered
snap-ring into the transmission case. Make sure that
the open ends of the snap-ring are located in the case
opening toward the valve body area.
Fig. 32 Manual Shaft/Park Lock Components
1 - GUIDE
2 - SNAP-RING
3 - SHAFT
4 - SPRING
5 - PARK PAWL
6 - MANUAL SHAFT/LEVER
7 - PARK ROD
Fig. 33 Install Dipstick Tube Seal Using Tool 8254
1 - TOOL 8254
2 - SEAL
Fig. 34 Install 2C Clutch Pack
1 - SNAP-RING
2 - PLATE
3 - DISC
4 - REACTION PLATE
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 191
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1711 of 2199

(15) Using a feeler gauge through the opening in
the rear of the transmission case, measure the 2C
clutch pack clearance between the 2C reaction plate
and the transmission case at four different points.
The average of these measurements is the 2C clutch
pack clearance. The correct clutch clearance is 0.455-
1.335 mm (0.018-0.053 in.). The reaction plate is not
selective. If the clutch pack clearance is not within
specification, the reaction plate, all the friction discs,
and steels must be replaced.
(16) Remove the 4C retainer/bulkhead and all of
the 2C clutch components from the transmission
case.
(17) Install the low/reverse clutch assembly (Fig.
35). Make sure that the oil feed hole points toward
the valve body area and that the bleed orifice is
aligned with the notch in the rear of the transmis-
sion case.
(18) Install the snap-ring to hold the low/reverse
clutch retainer into the transmission case (Fig. 35).
The snap-ring is tapered and must be installed with
the tapered side forward. Once installed, verify that
the snap-ring is fully seated in the snap-ring groove.
(19) Air check the low/reverse clutch and verify
correct overrunning clutch operation.
(20) Install the number 12 bearing over the output
shaft and against the rear planetary gear set. The
flat side of the bearing goes toward the planetary
gearset and the raised tabs on the inner race should
face the rear of the transmission.(21) Install the reverse/input planetary assembly
through the low/reverse clutch assembly (Fig. 36).
(22) Install the park sprag onto the output shaft
(Fig. 37).
(23) Install the snap-ring to hold the park sprag
onto the output shaft (Fig. 38).
Fig. 35 Install Low/Reverse Clutch Retainer
1 - LOW/REVERSE OVERRUNNING CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
2 - SNAP-RING
Fig. 36 Install Input/Reverse Planetary Assembly
1 - INPUT/REVERSE PLANETARY ASSEMBLY
2 - BEARING NUMBER 9
3 - BEARING NUMBER 12
Fig. 37 Install Park Sprag Gear
1 - PARK SPRAG GEAR
21 - 192 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1712 of 2199

(24) Install the 2C reaction plate into the trans-
mission case (Fig. 39). The reaction plate is direc-
tional. The plate must be installed with the flat side
toward the front of the transmission.
(25) Install the 2C clutch pack into the transmis-
sion case (Fig. 39).(26) Install the number 8 bearing inside the reac-
tion carrier with the outer race against the reaction
planetary carrier.
(27) Install the reaction planetary gear set and the
number 9 bearing, with the inner race against the
reaction planetary carrier, into the transmission case
(Fig. 40).
(28) Install the flat 2C clutch snap-ring into the
transmission case (Fig. 39).
(29) Install the reaction sun gear into the reaction
planetary gear set.Make surethe small shoulder is
facing the front of the transmission (Fig. 40).
(30) Install the number 7 bearing onto the reaction
sun gear with the inner race against the sun gear
(Fig. 40).
(31) Install the output shaft selective thrust plate
onto the reaction annulus with the oil grooves facing
the annulus gear and the tabs and notches aligned as
shown in (Fig. 41).
(32) Install the number 6 bearing against the out-
put shaft selective thrust plate with the flat side
against the thrust plate (Fig. 40) and the raised tabs
on the inner race facing the front of the transmis-
sion.
(33) Install the reaction annulus into the reaction
planetary gear set (Fig. 40).
(34) Install the 4C retainer/bulkhead into the
transmission case. Make sure that the oil feed holes
are pointing toward the valve body area. Rotate the
reaction annulus during the installation of the 4C
retainer/bulkhead to ease installation.
(35) Install the 4C retainer/bulkhead tapered
snap-ring into the transmission case (Fig. 42) with
the taper toward the front of the case. Make sure
that the open ends of the snap-ring are located in the
case opening toward the valve body area.
(36) Air check the 2C and 4C clutch operation.
Fig. 38 Install Park Sprag Snap-Ring
1 - SNAP-RING
Fig. 39 Install 2C Clutch Pack
1 - SNAP-RING
2 - PLATE
3 - DISC
4 - REACTION PLATE
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 193
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1747 of 2199

(8) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL gate positions only.
Engine starts must not be possible in any other gate
positions other than PARK or NEUTRAL.
(9) With shifter lever handle push-button not
depressed and lever detent in:
²PARK position- apply forward force on center of
handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²PARK position- apply rearward force on center
of handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²NEUTRAL position- engine start must be possi-
ble.
²NEUTRAL position, engine running and brakes
applied- Apply forward force on center of shift han-
dle. Transmission should not be able to shift into
REVERSE detent.
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
sludge and/or debris. The torque converter should
also be replaced at the same time.
Failure to flush the cooler and lines will result in
recontamination. Flushing applies to auxiliary cool-
ers as well. The torque converter should also be
replaced whenever a failure generates sludge and
debris. This is necessary because normal converter
flushing procedures will not remove all contami-
nants.
21 - 228 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM (Continued)