JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1621 of 2199

NOTE: The reaction plate is thinner than the pres-
sure plate in a 42RE transmission.
(5) Install first clutch disc followed by first clutch
plate. Then install remaining clutch discs and plates
in same order.
(6) Install clutch pack pressure plate.
(7) Install clutch pack wire-type retaining ring
(Fig. 182).
INTERMEDIATE SHAFT SPACER SELECTION
(1) Place overdrive unit in vertical position. Mount
it on blocks, or in workbench with appropriate size
mounting hole cut into it. Be sure unit is facing
upward for access to direct clutch hub. Also be sure
output shaft is not loaded and internal components
are moved rearward for accurate measurement.
(2) Determine correct thickness intermediate shaft
spacer as follows:
(a) Insert Special Tool 6312 through sun gear,
planetary gear and into pilot bushing in output
shaft. Be sure tool bottoms against planetary
shoulder.
(b) Position Gauge Tool 6311 across face of over-
drive case (Fig. 183). Then position Dial Caliper
C-4962 over gauge tool.
(c) Extend sliding scale of dial caliper downward
through gauge tool slot until scale contacts end of
Gauge Alignment Tool 6312. Lock scale in place.
Remove dial caliper tool and note distance mea-
sured (Fig. 183).
(d) Select proper thickness end play spacer from
spacer chart based on distance measured (Fig.
184).
(e) Remove Gauge Alignment Tool 6312.
Fig. 177 Seating Locating Ring In Rear Bearing
1 - EXPAND BEARING LOCATING RING WITH SNAP-RING
PLIERS
2 - ACCESS HOLE
Fig. 178 Locating Ring Access Cover And Gasket
Installation
1 - TORX SCREWDRIVER (T25)
2 - ACCESS COVER SCREWS
Fig. 179 Overdrive Clutch Reaction Ring Installation
1 - REACTION RING
2 - CLUTCH HUB
Fig. 180 Overdrive Clutch Wave Spring Installation
1 - WAVE SPRING
21 - 102 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1622 of 2199

OD THRUST PLATE SELECTION
(1) Place overdrive unit in vertical position. Mount
it on blocks, or in workbench with appropriate size
mounting hole cut into it. Be sure unit is facing
upward for access to direct clutch hub. Also be sure
output shaft is not loaded and internal components
are moved rearward for accurate measurement.
(2) Determine correct thickness overdrive piston
thrust plate as follows:(a) Position Gauge Tool 6311 across face of over-
drive case. Then position Dial Caliper C-4962 over
gauge tool (Fig. 185).
(b) Measure distance to clutch hub thrust bear-
ing seat at four points 90É apart. Then average
measurements by adding them and dividing by 4.
(c) Select and install required thrust plate from
information in thrust plate chart (Fig. 186).
Fig. 181 42RE Overdrive Clutch Components
1 - REACTION PLATE 2 - PRESSURE PLATE
Fig. 182 Overdrive Clutch Pack Retaining Ring
Installation
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH PACK RETAINING RING
Fig. 183 Shaft End Play Measurement
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6312
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6311
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4962
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 103
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1623 of 2199

(3) Leave Alignment Tool 6227-2 in place. Tool will
keep planetary and clutch hub splines in alignment
until overdrive unit is ready for installation on trans-
mission.
(4) Transmission speed sensor can be installed at
this time if desired. However, it is recommended that
sensor not be installed until after overdrive unit is
secured to transmission.
OVERDRIVE PISTON
(1) Install new seals on over drive piston.
(2) Stand transmission case upright on bellhous-
ing.
(3) Position Guide Ring 8114-1 on outer edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(4) Position Seal Guide 8114-2 on inner edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(5) Install overdrive piston in overdrive piston
retainer by: aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston
to the two mating holes in retainer.
(a) Aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston to
the two mating holes in retainer.(b) Lubricate overdrive piston seals with Mopart
Door Ease, or equivalent.
(c) Install piston over Seal Guide 8114-2 and
inside Guide Ring 8114-1.
(d) Push overdrive piston into position in
retainer.
(e) Verify that the locating lugs entered the lug
bores in the retainer.
(6) Install intermediate shaft spacer on intermedi-
ate shaft.
(7) Install overdrive piston thrust plate on over-
drive piston.
(8) Install overdrive piston thrust bearing on over-
drive piston.
(9) Install transmission speed sensor and O-ring
seal in overdrive case (Fig. 127).
INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure overdrive unit Alignment Tool 6227-2
is fully seated before moving unit. If tool is not
seated and gear splines rotate out of alignment, over-
drive unit will have to be disassembled in order to
realign splines.
(2) If overdrive piston retainer was not removed
during service and original case gasket is no longer
reusable, prepare new gasket by trimming it.
(3) Cut out old case gasket around piston retainer
with razor knife (Fig. 187).
(4) Use old gasket as template and trim new gas-
ket to fit.
(5) Position new gasket over piston retainer and
on transmission case. Use petroleum jelly to hold
gasket in place if necessary. Do not use any type of
sealer to secure gasket. Use petroleum jelly only.
(6) Install selective spacer on intermediate shaft, if
removed. Spacer goes in groove just rearward of
shaft rear splines (Fig. 188).
(7) Install thrust bearing in overdrive unit sliding
hub. Use petroleum jelly to hold bearing in position.
Fig. 184 Intermediate Shaft End Play Spacer
Selection
Fig. 185 Overdrive Piston Thrust Plate Measurement
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6311
2 - DIRECT CLUTCH HUB THRUST BEARING SEAT
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4962
Fig. 186 Overdrive Piston Thrust Plate Selection
21 - 104 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1624 of 2199

CAUTION: Be sure the shoulder on the inside diam-
eter of the bearing is facing forward.
(8) Verify that splines in overdrive planetary gear
and overrunning clutch hub are aligned with Align-
ment Tool 6227-2. Overdrive unit cannot be installed
if splines are not aligned. If splines have rotated out
of alignment, unit will have to be disassembled to
realign splines.
(9) Carefully slide Alignment Tool 6227-2 out of
overdrive planetary gear and overrunning clutch
splines.
(10) Raise overdrive unit and carefully slide it
straight onto intermediate shaft. Insert park rod into
park lock reaction plug at same time. Avoid tilting
overdrive during installation as this could cause
planetary gear and overrunning clutch splines to
rotate out of alignment. If this occurs, it will be nec-essary to remove and disassemble overdrive unit to
realign splines.
(11) Work overdrive unit forward on intermediate
shaft until seated against transmission case.
(12) Install bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission unit. Tighten bolts in diagonal pattern to 34
N´m (25 ft-lbs).
(13) Connect the transmission speed sensor and
overdrive wiring connectors.
(14) Install the transfer case, if equipped.
(15) Align and install rear propeller shaft, if nec-
essary. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/
PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
INSTALLATION)
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON
RETAINER
DESCRIPTION
The overrunning clutch (Fig. 189) consists of an
inner race, an outer race (or cam), rollers and
springs, and the spring retainer. The number of roll-
ers and springs depends on what transmission and
which overrunning clutch is being dealt with.
OPERATION
As the inner race is rotated in a clockwise direction
(as viewed from the front of the transmission), the
race causes the rollers to roll toward the springs,
causing them to compress against their retainer. The
compression of the springs increases the clearance
Fig. 187 Trimming Overdrive Case Gasket
1 - GASKET
2 - SHARP KNIFE
Fig. 188 Intermediate Shaft Selective Spacer
Location
1 - SELECTIVE SPACER
2 - SPACER GROOVE
3 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
Fig. 189 Overrunning Clutch
1 - OUTER RACE (CAM)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - SPRING RETAINER
5 - INNER RACE (HUB)
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 105
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1625 of 2199

between the rollers and cam. This increased clear-
ance between the rollers and cam results in a free-
wheeling condition. When the inner race attempts to
rotate counterclockwise, the action causes the rollers
to roll in the same direction as the race, aided by the
pushing of the springs. As the rollers try to move in
the same direction as the inner race, they are
wedged between the inner and outer races due to the
design of the cam. In this condition, the clutch is
locked and acts as one unit.
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: To service the overrunning clutch cam and
the overdrive piston retainer, the transmission
geartrain and the overdrive unit must be removed
from the transmission.
(1) Remove the overdrive piston (Fig. 190).
(2) Remove the overdrive piston retainer bolts.
(3) Remove overdrive piston retainer.
(4) Remove case gasket.
(5) Mark the position of the overrunning clutch
cam in the case (Fig. 191).
(6) Remove the overrunning clutch cam bolts.
(7) Remove the overrunning clutch cam.
CLEANING
Clean the overrunning clutch assembly, clutch cam,
low-reverse drum, and overdrive piston retainer in
solvent. Dry them with compressed air after clean-
ing.
INSPECTION
Inspect condition of each clutch part after cleaning.
Replace the overrunning clutch roller and spring
assembly if any rollers or springs are worn or dam-
aged, or if the roller cage is distorted, or damaged.
Replace the cam if worn, cracked or damaged.
Replace the low-reverse drum if the clutch race,
roller surface or inside diameter is scored, worn or
damaged.Do not remove the clutch race from
the low-reverse drum under any circumstances.
Replace the drum and race as an assembly if
either component is damaged.
Examine the overdrive piston retainer carefully for
wear, cracks, scoring or other damage. Be sure the
retainer hub is a snug fit in the case and drum.
Replace the retainer if worn or damaged.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Examine bolt holes in overrunning clutch cam.
Note that one hole isnot threaded(Fig. 192). This
hole must align with blank area in clutch cam bolt
circle (Fig. 193). Mark hole location on clutch cam
and blank area in case with grease pencil, paint
stripe, or scribe mark for assembly reference.
(2) Mark location of non-threaded hole in clutch
cam and blank area in bolt circle with grease pencil.
(3) Align and install overrunning clutch and cam
in case (Fig. 194). Be sure cam is correctly installed.
Bolt holes in cam are slightly countersunk on one
side. Be sure this side of cam faces rearward (toward
piston retainer).
(4) Verify that non-threaded hole in clutch cam is
properly aligned. Check alignment by threading a
bolt into each bolt hole. Adjust clutch cam position if
necessary.
Fig. 190 Overdrive Piston Removal
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH PISTON
2 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
3 - SELECTIVE SPACER
4 - PISTON RETAINER
Fig. 191 Overrunning Clutch Cam Removal
1 - ALIGN MARKS IDENTIFYING NON-THREADED HOLE IN
CAM AND CASE
2 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
21 - 106 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1626 of 2199

(5) Install and tighten overrunning clutch cam
bolts to 17 N´m (13 ft. lbs.) torque. Note that clutch
cam bolts are shorter than piston retainer bolts.
(6) Install new gasket at rear of transmission case.
Use petroleum jelly to hold gasket in place. Be sure
to align governor feed holes in gasket with feed pas-
sages in case (Fig. 195). Also install gasket before
overdrive piston retainer. Center hole in gasket is
smaller than retainer and cannot be installed over
retainer.(7) Position overdrive piston retainer on transmis-
sion case and align bolt holes in retainer, gasket and
case (Fig. 196). Then install and tighten retainer
bolts to 17 N´m (13 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 192 Location Of Non-Threaded Hole In Clutch
Cam
1 - NON-THREADED HOLE
2 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM
Fig. 193 Location Of Blank Area In Clutch Cam Bolt
Circle
1 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM SEAT IN CASE
2 - NON-THREADED HOLE IN CLUTCH CAM ALIGNS HERE
(BLANK AREA) OF SEAT
Fig. 194 Overrunning Clutch Installation
1 - ALIGN MARKS IDENTIFYING NON-THREADED HOLE IN
CAM AND CASE
2 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 195 Installing/Aligning Case Gasket
1 - CASE GASKET
2 - BE SURE GOVERNOR TUBE FEED HOLES IN CASE AND
GASKET ARE ALIGNED
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 107
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1627 of 2199

(8) Install new seals on over drive piston.
(9) Stand transmission case upright on bellhous-
ing.
(10) Position Guide Ring 8114-1 on outer edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(11) Position Seal Guide 8114-2 on inner edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(12) Install overdrive piston in overdrive piston
retainer by: aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston
to the two mating holes in retainer.
(a) Aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston to
the two mating holes in retainer.
(b) Lubricate overdrive piston seals with Mopart
Door Ease, or equivalent.
(c) Install piston over Seal Guide 8114-2 and
inside Guide Ring 8114-1.
(d) Push overdrive piston into position in
retainer.
(e) Verify that the locating lugs entered the lug
bores in the retainer.
NOTE: Install the remaining transmission compo-
nents and the overdrive unit.
PARK LOCK CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Place the shifter in the PARK position.
(2) Lower the steering column cover.
(3) With the ignition switch in the ªRUNº position
depress the park lock cable locking tab, located on
top of the cable connector at the steering column and
pull the park lock cable straight out.
(4) Remove the park lock cable from steering col-
umn (Fig. 197).
(5) Remove the floor console and related trim.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE -
REMOVAL)
(6) Disconnect the park lock cable from the shift
BTSI lever and remove the cable from the shifter
assembly bracket.
(7) Release the park lock cable from any remaining
clips.
(8) Remove park lock cable from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The gearshift cable must be secured into
position and properly adjusted before the installa-
tion of the Park Lock Cable.
(1) Verify that the shifter is in the PARK position.
(2) Push the park lock cable straight into the
square mounting hole in the steering column until
cable snaps in place.
(3) Route park lock cable to the shifter mecha-
nism.
(4) Install the park lock cable end fitting into
shifter BTSI lever.
(5) Pull rearward on the cable housing to snap
park lock cable adjuster ears into floor shifter
bracket.
(6) Place the ignition key cylinder in the ACCES-
SORY position.
(7) Push the cable adjuster lock clamp downward
to lock it.
(8) Test the park lock cable operation.
(9) Install the floor console and related trim.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE -
INSTALLATION)
Fig. 196 Aligning Overdrive Piston Retainer
1 - PISTON RETAINER
2 - GASKET
3 - RETAINER BOLTS
21 - 108 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1628 of 2199

PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION
SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PARK/NEUTRAL
POSITION SWITCH
The center terminal of the park/neutral position
switch is the starter-circuit terminal. It provides the
ground for the starter solenoid circuit through the
selector lever in PARK and NEUTRAL positions only.
The outer terminals on the switch are for the backup
lamp circuit.
SWITCH TEST
To test the switch, remove the wiring connector.
Test for continuity between the center terminal and
the transmission case. Continuity should exist only
when the transmission is in PARK or NEUTRAL.Shift the transmission into REVERSE and test
continuity at the switch outer terminals. Continuity
should exist only when the transmission is in
REVERSE. Continuity should not exist between the
outer terminals and the case.
Check gearshift linkage adjustment before replac-
ing a switch that tests faulty.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and position drain pan under
switch.
(2) Disconnect switch wires.
(3) Remove switch from case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Move shift lever to PARK and NEUTRAL posi-
tions. Verify that switch operating lever fingers are
centered in switch opening in case (Fig. 198).
Fig. 197 Brake Transmission Shift Interlock
1 - SHIFT MECHANISM 4 - STEERING COLUMN ASSEMBLY
2 - SHIFTER BTSI LEVER 5 - INTERLOCK CABLE
3 - ADJUSTMENT CLIP
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 109
PARK LOCK CABLE (Continued)
Page 1629 of 2199

(2) Install new seal on switch and install switch in
case. Tighten switch to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Test continuity of new switch with 12V test
lamp.
(4) Connect switch wires and lower vehicle.
(5) Top off transmission fluid level.
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION
There are several sizes and types of pistons used in
an automatic transmission. Some pistons are used to
apply clutches. They all have in common the fact
that they are round or circular in shape, located
within a smooth walled cylinder, which is closed at
one end and converts fluid pressure into mechanical
movement. The fluid pressure exerted on the piston
is contained within the system through the use of
piston rings or seals.
OPERATION
The principal which makes this operation possible
is known as Pascal's Law. Pascal's Law can be stated
as: ªPressure on a confined fluid is transmitted
equally in all directions and acts with equal force on
equal areas.º
PRESSURE
Pressure (Fig. 199) is nothing more than force
(lbs.) divided by area (in or ft.), or force per unit
area. Given a 100 lb. block and an area of 100 sq. in.
on the floor, the pressure exerted by the block is: 100lbs. 100 in or 1 pound per square inch, or PSI as it is
commonly referred to.
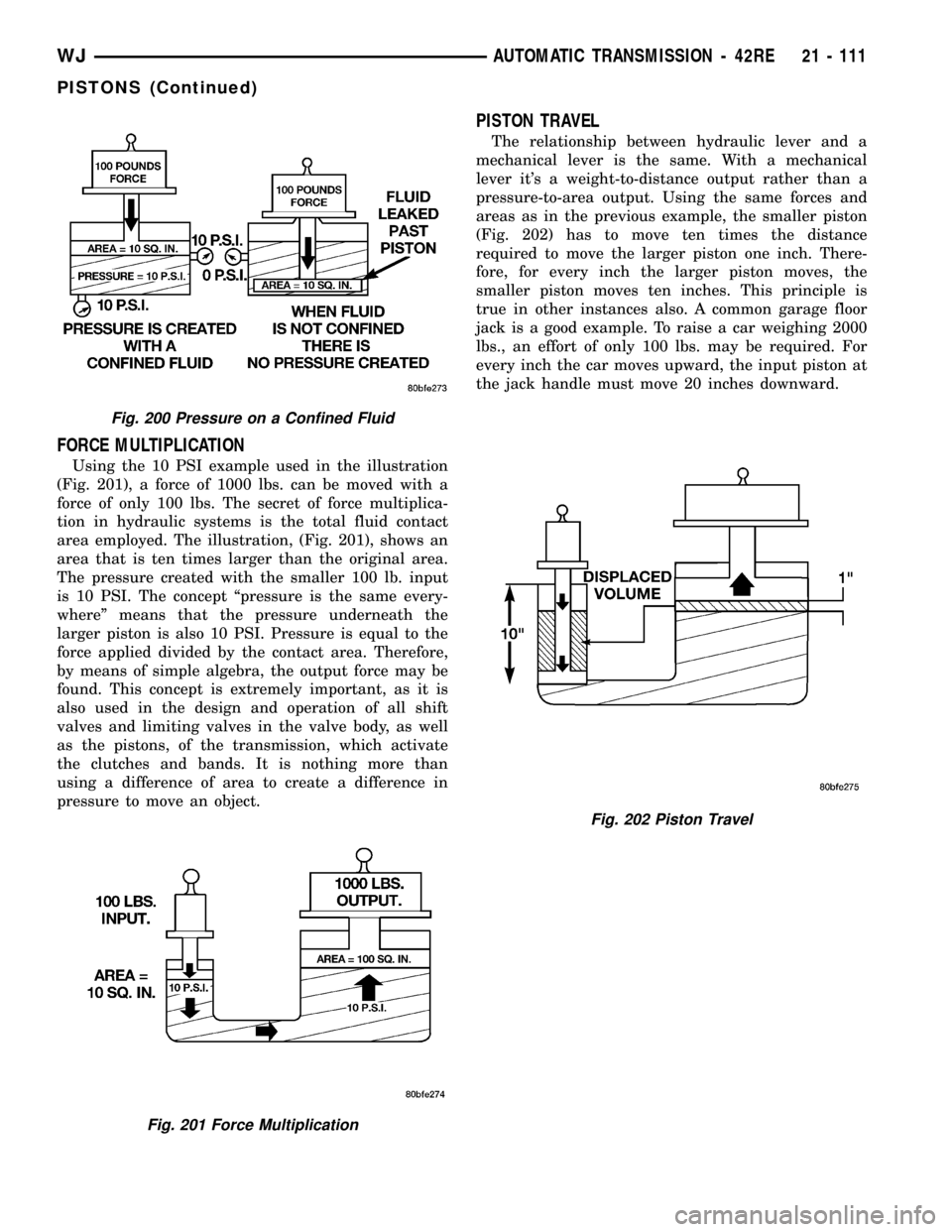
PRESSURE ON A CONFINED FLUID
Pressure is exerted on a confined fluid (Fig. 200)
by applying a force to some given area in contact
with the fluid. A good example of this is a cylinder
filled with fluid and equipped with a piston that is
closely fitted to the cylinder wall. If a force is applied
to the piston, pressure will be developed in the fluid.
Of course, no pressure will be created if the fluid is
not confined. It will simply ªleakº past the piston.
There must be a resistance to flow in order to create
pressure. Piston sealing is extremely important in
hydraulic operation. Several kinds of seals are used
to accomplish this within a transmission. These
include but are not limited to O-rings, D-rings, lip
seals, sealing rings, or extremely close tolerances
between the piston and the cylinder wall. The force
exerted is downward (gravity), however, the principle
remains the same no matter which direction is taken.
The pressure created in the fluid is equal to the force
applied, divided by the piston area. If the force is 100
lbs., and the piston area is 10 sq. in., then the pres-
sure created equals 10 PSI. Another interpretation of
Pascal's Law is that regardless of container shape or
size, the pressure will be maintained throughout, as
long as the fluid is confined. In other words, the
pressure in the fluid is the same everywhere within
the container.
Fig. 198 Park/Neutral Position Switch
1 - NEUTRAL CONTACT
2 - MANUAL LEVER AND SWITCH PLUNGER IN REVERSE
POSITION
3 - PARK CONTACT
4 - SWITCH
Fig. 199 Force and Pressure Relationship
21 - 110 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1630 of 2199
FORCE MULTIPLICATION
Using the 10 PSI example used in the illustration
(Fig. 201), a force of 1000 lbs. can be moved with a
force of only 100 lbs. The secret of force multiplica-
tion in hydraulic systems is the total fluid contact
area employed. The illustration, (Fig. 201), shows an
area that is ten times larger than the original area.
The pressure created with the smaller 100 lb. input
is 10 PSI. The concept ªpressure is the same every-
whereº means that the pressure underneath the
larger piston is also 10 PSI. Pressure is equal to the
force applied divided by the contact area. Therefore,
by means of simple algebra, the output force may be
found. This concept is extremely important, as it is
also used in the design and operation of all shift
valves and limiting valves in the valve body, as well
as the pistons, of the transmission, which activate
the clutches and bands. It is nothing more than
using a difference of area to create a difference in
pressure to move an object.
PISTON TRAVEL
The relationship between hydraulic lever and a
mechanical lever is the same. With a mechanical
lever it's a weight-to-distance output rather than a
pressure-to-area output. Using the same forces and
areas as in the previous example, the smaller piston
(Fig. 202) has to move ten times the distance
required to move the larger piston one inch. There-
fore, for every inch the larger piston moves, the
smaller piston moves ten inches. This principle is
true in other instances also. A common garage floor
jack is a good example. To raise a car weighing 2000
lbs., an effort of only 100 lbs. may be required. For
every inch the car moves upward, the input piston at
the jack handle must move 20 inches downward.
Fig. 200 Pressure on a Confined Fluid
Fig. 201 Force Multiplication
Fig. 202 Piston Travel
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 111
PISTONS (Continued)