cylinder block drain plug JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1261 of 2199
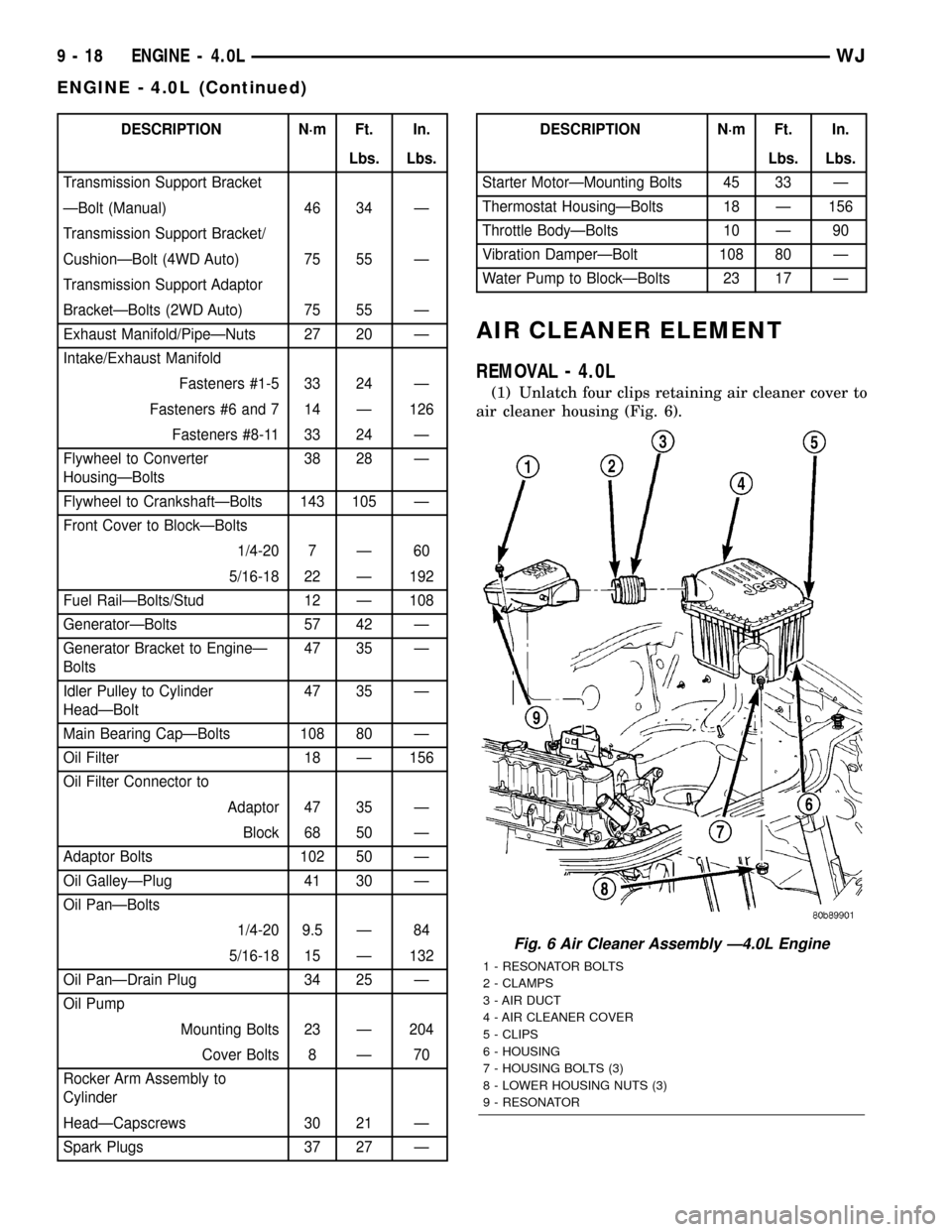
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Transmission Support Bracket
ÐBolt (Manual) 46 34 Ð
Transmission Support Bracket/
CushionÐBolt (4WD Auto) 75 55 Ð
Transmission Support Adaptor
BracketÐBolts (2WD Auto) 75 55 Ð
Exhaust Manifold/PipeÐNuts 27 20 Ð
Intake/Exhaust Manifold
Fasteners #1-5 33 24 Ð
Fasteners #6 and 7 14 Ð 126
Fasteners #8-11 33 24 Ð
Flywheel to Converter
HousingÐBolts38 28 Ð
Flywheel to CrankshaftÐBolts 143 105 Ð
Front Cover to BlockÐBolts
1/4-20 7 Ð 60
5/16-18 22 Ð 192
Fuel RailÐBolts/Stud 12 Ð 108
GeneratorÐBolts 57 42 Ð
Generator Bracket to EngineÐ
Bolts47 35 Ð
Idler Pulley to Cylinder
HeadÐBolt47 35 Ð
Main Bearing CapÐBolts 108 80 Ð
Oil Filter 18 Ð 156
Oil Filter Connector to
Adaptor 47 35 Ð
Block 68 50 Ð
Adaptor Bolts 102 50 Ð
Oil GalleyÐPlug 41 30 Ð
Oil PanÐBolts
1/4-20 9.5 Ð 84
5/16-18 15 Ð 132
Oil PanÐDrain Plug 34 25 Ð
Oil Pump
Mounting Bolts 23 Ð 204
Cover Bolts 8 Ð 70
Rocker Arm Assembly to
Cylinder
HeadÐCapscrews 30 21 Ð
Spark Plugs 37 27 ÐDESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Starter MotorÐMounting Bolts 45 33 Ð
Thermostat HousingÐBolts 18 Ð 156
Throttle BodyÐBolts 10 Ð 90
Vibration DamperÐBolt 108 80 Ð
Water Pump to BlockÐBolts 23 17 Ð
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 4.0L
(1) Unlatch four clips retaining air cleaner cover to
air cleaner housing (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6 Air Cleaner Assembly Ð4.0L Engine
1 - RESONATOR BOLTS
2 - CLAMPS
3 - AIR DUCT
4 - AIR CLEANER COVER
5 - CLIPS
6 - HOUSING
7 - HOUSING BOLTS (3)
8 - LOWER HOUSING NUTS (3)
9 - RESONATOR
9 - 18 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1262 of 2199
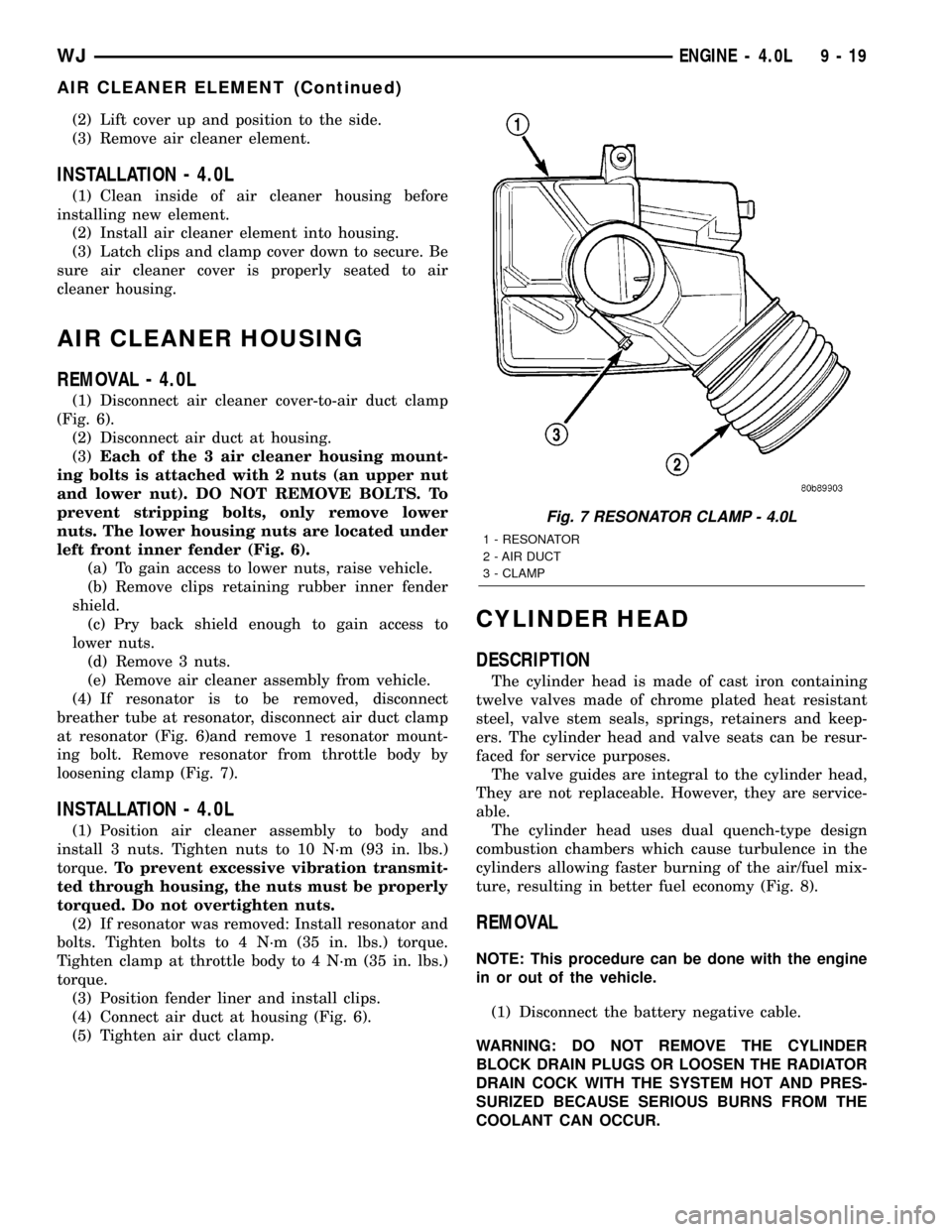

(2) Lift cover up and position to the side.
(3) Remove air cleaner element.
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
(1) Clean inside of air cleaner housing before
installing new element.
(2) Install air cleaner element into housing.
(3) Latch clips and clamp cover down to secure. Be
sure air cleaner cover is properly seated to air
cleaner housing.
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL - 4.0L
(1) Disconnect air cleaner cover-to-air duct clamp
(Fig. 6).
(2) Disconnect air duct at housing.
(3)Each of the 3 air cleaner housing mount-
ing bolts is attached with 2 nuts (an upper nut
and lower nut). DO NOT REMOVE BOLTS. To
prevent stripping bolts, only remove lower
nuts. The lower housing nuts are located under
left front inner fender (Fig. 6).
(a) To gain access to lower nuts, raise vehicle.
(b) Remove clips retaining rubber inner fender
shield.
(c) Pry back shield enough to gain access to
lower nuts.
(d) Remove 3 nuts.
(e) Remove air cleaner assembly from vehicle.
(4) If resonator is to be removed, disconnect
breather tube at resonator, disconnect air duct clamp
at resonator (Fig. 6)and remove 1 resonator mount-
ing bolt. Remove resonator from throttle body by
loosening clamp (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
(1) Position air cleaner assembly to body and
install 3 nuts. Tighten nuts to 10 N´m (93 in. lbs.)
torque.To prevent excessive vibration transmit-
ted through housing, the nuts must be properly
torqued. Do not overtighten nuts.
(2) If resonator was removed: Install resonator and
bolts. Tighten bolts to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
Tighten clamp at throttle body to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Position fender liner and install clips.
(4) Connect air duct at housing (Fig. 6).
(5) Tighten air duct clamp.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head is made of cast iron containing
twelve valves made of chrome plated heat resistant
steel, valve stem seals, springs, retainers and keep-
ers. The cylinder head and valve seats can be resur-
faced for service purposes.
The valve guides are integral to the cylinder head,
They are not replaceable. However, they are service-
able.
The cylinder head uses dual quench-type design
combustion chambers which cause turbulence in the
cylinders allowing faster burning of the air/fuel mix-
ture, resulting in better fuel economy (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure can be done with the engine
in or out of the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAIN COCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE
COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
Fig. 7 RESONATOR CLAMP - 4.0L
1 - RESONATOR
2 - AIR DUCT
3 - CLAMP
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 19
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT (Continued)
Page 1274 of 2199

REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CAMSHAFT BEARINGS
The camshaft rotates within four steel-shelled,
babbitt-lined bearings that are pressed into the cyl-
inder block and then line reamed. The camshaft
bearing bores and bearing diameters are not the
same size. They are stepped down in 0.254 mm
(0.010 inch) increments from the front bearing (larg-
est) to the rear bearing (smallest). This permits eas-
ier removal and installation of the camshaft. The
camshaft bearings are pressure lubricated. Camshaft
end play is maintained by the thrust plate.
(1) Remove the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: It is not advisable to attempt to replace cam-
shaft bearings unless special removal and installa-
tion tools are available, such as recommended tool
8544 Camshaft Bushing Remover Installer.
(2) Using Special tool 8544 Camshaft Bushing
Remover Installer, remove the camshaft bearings.
REMOVAL - CAMSHAFT
WARNING: THE COOLANT IN A RECENTLY OPER-
ATED ENGINE IS HOT AND PRESSURIZED.RELEASE THE PRESSURE BEFORE REMOVING
THE DRAIN COCK, CAP AND DRAIN PLUGS.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL) and condenser
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/A/C CONDENSER - REMOVAL), if
equipped with A/C.
(4) Remove the engine cylinder head cover (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the rocker arms, bridges and pivots
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER
ARM / ADJUSTER ASSY - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove the push rods.
(7) Remove the engine cylinder head and gasket
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOV-
AL).
(8) Remove the hydraulic valve tappets from the
engine cylinder block (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE
BLOCK/HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN BLOCK) -
REMOVAL).
(9) Remove the vibration damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(10) Remove the timing case cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(11) Rotate the crankshaft until the crankshaft
sprocket timing mark is aligned on centerline with
the camshaft sprocket timing mark (Fig. 32).
(12) Remove the timing chain and sprockets (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/
CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove the front bumper and/or grille, as
required.
(14) Remove the two thrust plate retaining screws,
thrust plate and camshaft (Fig. 31).
INSPECTION
INSPECTION - CAMSHAFT BEARINGS
(1) Inspect the bearing journals for uneven wear
pattern or finish.
(2) Inspect the bearings for wear.
INSPECTION - CAMSHAFT
(1) Inspect the cam lobes for wear.
(2) Inspect the camshaft position sensor drive gear
for wear.
(3) If the camshaft appears to have been rubbing
against the thrust washer, examine the oil pressure
Fig. 30 CamshaftÐTypical
1 - CAMSHAFT
2 - LOBES
3 - BEARING JOURNAL
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 31
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1284 of 2199

(e) If end play is not within specification, inspect
crankshaft thrust faces for wear. If no wear is
apparent, replace the thrust bearing and measure
end play. If end play is still not within specifica-
tion, replace the crankshaft.
(11) If the crankshaft was removed, install the
crankshaft into the cylinder block.
(12) Install main bearing cap brace tighten nuts to
47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install oil pump assy. and tighten attaching
bolts to 23 N´m (17 ft. lbs.)
(14) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(15) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(16) Lower the vehicle.
(17) Install the spark plugs. Tighten the plugs to
37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(18) Fill the oil pan with engine oil to the full
mark on the dipstick level.
(19) Connect negative cable to battery.
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL -
FRONT
REMOVAL
This procedure is done with the timing case cover
installed.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).(3) Remove the vibration damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the radiator shroud.
(5) Carefully remove the oil seal. Make sure seal
bore is clean.
INSTALLATION
This procedure is done with the timing case cover
installed.
(1) Position the replacement oil seal on Timing
Case Cover Alignment and Seal Installation Tool
6139 with seal open end facing inward. Apply a light
film of Perfect Seal, or equivalent, on the outside
diameter of the seal. Lightly coat the crankshaft with
engine oil.
(2) Position the tool and seal over the end of the
crankshaft and insert a draw screw tool into Seal
Installation Tool 6139 (Fig. 50). Tighten the nut
against the tool until it contacts the cover.
(3) Remove the tools. Apply a light film of engine
oil on the vibration damper hub contact surface of
the seal.
(4) Apply MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant to the keyway in the crankshaft and insert the
key. With the key inserted in the keyway in the
crankshaft, install the vibration damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the serpentine belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
(6) Install the radiator shroud.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
Fig. 49 Crankshaft End Play Measurement
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - CRANKSHAFT
Fig. 50 Timing Case Cover Oil Seal Installation
1 - SEAL INSTALLATION TOOL
2 - DRAW SCREW TOOL
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 41
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1294 of 2199

crankshaft is drilled internally to pass oil from the
main bearing journals (except number 4 main bear-
ing journal) to the connecting rod journals. Each con-
necting rod bearing cap has a small squirt hole, oil
passes through the squirt hole and is thrown off as
the rod rotates. This oil throwoff lubricates the cam-
shaft lobes, distributor drive gear, cylinder walls, and
piston pins.
The hydraulic valve tappets receive oil directly
from the main oil gallery. Oil is provided to the cam-
shaft bearing through galleries. The front camshaft
bearing journal passes oil through the camshaft
sprocket to the timing chain. Oil drains back to the
oil pan under the number one main bearing cap.
The oil supply for the rocker arms and bridged
pivot assemblies is provided by the hydraulic valve
tappets which pass oil through hollow push rods to a
hole in the corresponding rocker arm. Oil from the
rocker arm lubricates the valve train components,
then passes down through the push rod guide holes
in the cylinder head past the valve tappet area, and
returns to the oil pan (Fig. 73).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Disconnect connector and remove oil pressure
sending unit.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292 or equivalent. Start engine and record pres-
sure. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for
the correct pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.If the oil leak source is not pos-itively identified at this time, proceed with the air
leak detection test method.
Air Leak Detection Test Method
(1) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(2) Remove the CCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the CCV valve grommet.
(3) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(4) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service informa-
tion procedures.
(5) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS .
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply
and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the CCV valve and breather cap hose.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks
in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 51
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1297 of 2199

All Jeep engines are equipped with a high quality
full-flow, throw-away type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler
Corporation recommends a Mopartor equivalent oil
filter be used.
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise to remove
it from the cylinder block oil filter boss or filter
adapter housing (Fig. 75).
(4) When filter separates from adapter nipple, tip
gasket end upward to minimize oil spill. Remove fil-
ter from vehicle.
(5) Make sure old gasket comes off with oil filter.
With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing surface
(Fig. 76) of oil and grime.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil or chassis grease.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 76) hand
tighten filter one full turn, do not over tighten.
(3) Add oil, verify crankcase oil level and start
engine. Inspect for oil leaks.
OIL PAN
DESCRIPTION
The oil pan is made of stamped steel. The oil pan
gasket is a one piece steel backbone silicone coated
gasket (Fig. 77).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove the oil pan drain plug and drain the
engine oil.
(4) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the exhaust
manifold.
(5) Disconnect the exhaust hanger at the catalytic
converter and lower the pipe.
(6) Remove the starter motor. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOV-
AL).
(7) Remove the engine flywheel and transmission
torque converter housing access cover.
(8) If equipped with an oil level sensor, disconnect
the sensor.
(9) Position a jack stand directly under the engine
vibration damper.
Fig. 75 Oil FilterÐ4.0L Engine
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - ADAPTER
3 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 76 Oil Filter Sealing SurfaceÐTypical
1 - SEALING SURFACE
2 - RUBBER GASKET
3 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 77 Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - OIL PAN DRAIN PLUG
9 - 54 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
OIL FILTER (Continued)
Page 1298 of 2199

(10) Place a piece of wood (2 x 2) between the jack
stand and the engine vibration damper.
(11) Remove the engine mount through bolts.
(12) Using the jack stand, raise the engine until
adequate clearance is obtained to remove the oil pan.
(13) Remove transmission oil cooling lines (if
equipped) and oxygen sensor wiring supports that
are attached to the oil pan studs.
(14) Remove the oil pan bolts and studs. Carefully
slide the oil pan and gasket to the rear. If equipped
with an oil level sensor, take care not to damage the
sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the block and pan gasket surfaces.
(2) Fabricate 4 alignment dowels from 1 1/2 x 1/4
inch bolts. Cut the head off the bolts and cut a slot
into the top of the dowel. This will allow easier
installation and removal with a screwdriver (Fig. 78).
(3) Install two dowels in the timing case cover.
Install the other two dowels in the cylinder block
(Fig. 79).
(4) Apply MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant on cylinder block to rear main bearing cap cor-
ners and cylinder block to front cover joints (four
places) (Fig. 80).
(5) Slide the one-piece gasket over the dowels and
onto the block and timing case cover.
(6) Position the oil pan over the dowels and onto
the gasket. If equipped with an oil level sensor, take
care not to damage the sensor.
(7) Install the 1/4 inch oil pan bolts. Tighten these
bolts to 9.5 N´m (84 in. lbs.) torque. Install the 5/16
inch oil pan bolts (Fig. 81). Tighten these bolts to 15
N´m (132 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Remove the dowels. Install the remaining 1/4
inch oil pan bolts. Tighten these bolts to 9.5 N´m (84
in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 78 Fabrication of Alignment Dowels
1 - 1/488ý 1 1/288BOLT
2 - DOWEL
3 - SLOT
Fig. 79 Position of Dowels in Cylinder Block
1 - DOWEL HOLES
2 - CYLINDER BLOCK
3 - 5/1688HOLES
4 - 5/1688HOLES
Fig. 80 Oil Pan Sealer Location
1 - SEALER LOCATIONS
Fig. 81 Position of 5/16 inch Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN
2 - OIL PAN DRAIN PLUG
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 55
OIL PAN (Continued)
Page 1299 of 2199
(9) Lower the engine until it is properly located on
the engine mounts.
(10) Install the through bolts and tighten the nuts.
(11) Lower the jack stand and remove the piece of
wood.
(12) Install the engine flywheel and transmission
torque converter housing access cover.
(13) Install the engine starter motor. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR -
INSTALLATION).
(14) Connect the exhaust pipe to the hanger and to
the engine exhaust manifold.
(15) Install transmission oil cooling lines (if
equipped) and oxygen sensor wiring supports that
attach to the oil pan studs.
(16) Install the oil pan drain plug (Fig. 81).
Tighten the plug to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(17) Lower the vehicle.
(18) Connect negative cable to battery.
(19) Fill the oil pan with engine oil to the specified
level.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO
NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(20) Start the engine and inspect for leaks.
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The 3±wire, solid-state engine oil pressure sensor
(sending unit) is located in an engine oil pressure
gallery.
OPERATION
The oil pressure sensor uses three circuits. They
are:
²A 5±volt power supply from the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM)
²A sensor ground through the PCM's sensor
return
²A signal to the PCM relating to engine oil pres-
sure
The oil pressure sensor has a 3±wire electrical
function very much like the Manifold Absolute Pres-
sure (MAP) sensor. Meaning different pressures
relate to different output voltages.
A 5±volt supply is sent to the sensor from the PCM
to power up the sensor. The sensor returns a voltage
signal back to the PCM relating to engine oil pres-
sure. This signal is then transferred (bussed) to theinstrument panel on either a CCD or PCI bus circuit
(depending on vehicle line) to operate the oil pressure
gauge and the check gauges lamp. Ground for the
sensor is provided by the PCM through a low-noise
sensor return.
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
A gear-type oil pump is mounted at the underside
of the cylinder block opposite the No.4 main bearing.
(1) Drain the engine oil.
(2) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the pump-to-cylinder block attaching
bolts. Remove the pump assembly with gasket (Fig.
82).
CAUTION: If the oil pump is not to be serviced, DO
NOT disturb position of oil inlet tube and strainer
assembly in pump body. If the tube is moved within
the pump body, a replacement tube and strainer
assembly must be installed to assure an airtight
seal.
Fig. 82 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - OIL FILTER ADAPTOR
2 - BLOCK
3 - GASKET
4 - OIL INLET TUBE
5 - OIL PUMP
6 - STRAINER ASSEMBLY
7 - ATTACHING BOLTS
9 - 56 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
OIL PAN (Continued)
Page 1314 of 2199

²Abrasive pad or paper to clean cylinder block
and head
²High speed power tool with an abrasive pad or a
wire brush (Fig. 2)
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Only use the following for cleaning gasket surfaces:
²Solvent or a commercially available gasket
remover
²Plastic or wood scraper (Fig. 2)
²Drill motor with 3M RolocŸ Bristle Disc (white
or yellow) (Fig. 2)
CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM (beyond
the recommended speed), can damage the sealing
surfaces. The mild (white, 120 grit) bristle disc is
recommended. If necessary, the medium (yellow, 80
grit) bristle disc may be used on cast iron surfaces
with care.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 3).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Remove the front fascia.
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(4) Remove exhaust crossover pipe from exhaust
manifolds.
(5) Disconnect two ground straps from the lower
left hand side and one ground strap from the lower
right hand side of the engine.
(6) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor. (Fig. 4)
(7) Remove structural cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER - REMOV-
AL).
(8) Remove starter. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove rubber splash shield.
(10) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Remove torque converter bolts.
(12) Remove transmission to engine mounting
bolts.
Fig. 2 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 - ABRASIVE PAD
2 - 3M ROLOCŸ BRISTLE DISC
3 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
Fig. 3 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 71
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1341 of 2199

VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negitive cable.
(2) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the right side
exhaust manifold.
(4) Drain the engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove oil fill housing from cylinder head.
(9) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(10) Rotate the crankshaft until the damper tim-
ing mark is aligned with TDC indicator mark (Fig.
9).
(11) Verify the V8 mark on the camshaft sprocket
is at the 12 o'clock position (Fig. 11). Rotate the
crankshaft one turn if necessary.
(12) Remove the crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(13) Remove the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(14) Lock the secondary timing chains to the idler
sprocket using Special Tool 8515 (Fig. 10).
NOTE: Mark the secondary timing chain prior to
removal to aid in installation.
(15) Mark the secondary timing chain, one link on
each side of the V8 mark on the camshaft drive gear
(Fig. 11).
(16) Remove the right side secondary chain ten-
sioner (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIM-
ING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(17) Remove the cylinder head access plug (Fig.
29).
(18) Remove the right side secondary chain guide
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
9 - 98 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT (Continued)