Control JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 236 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING COOLING
SYSTEM - 4.0L ENGINE
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
(1) DO NOT remove radiator cap first. With engine
cold, raise vehicle on a hoist and locate radiator
draincock.
NOTE: Radiator draincock is located on the right/
lower side of radiator facing to rear of vehicle.
(2) Attach one end of a hose to the draincock. Put
the other end into a clean container. Open draincock
and drain coolant from radiator. This will empty the
coolant reserve/overflow tank. The coolant does not
have to be removed from the tank unless the system
is being refilled with a fresh mixture. When tank is
empty, remove radiator cap and continue draining
cooling system.
To drain the engine of coolant, remove the cylinder
block drain plug located on the side of cylinder block
(Fig. 9).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM - 4.0L ENGINE
(1) Tighten the radiator draincock and the cylinder
block drain plug(s) (if removed).
(2) Fill system using a 50/50 mixture of ethylene-
glycol antifreeze and low mineral content water. Fill
radiator to top and install radiator cap. Add suffi-
cient coolant to the reserve/overflow tank to raise
level to FULL mark.
(3) With heater control unit in the HEAT position,
operate engine with radiator cap in place.
(4) After engine has reached normal operating
temperature, shut engine off and allow it to cool.
When engine is cooling down, coolant will be drawn
into the radiator from the reserve/overflow tank.
(5) Add coolant to reserve/overflow tank as neces-
sary.Only add coolant to the reserve/overflow
tank when the engine is cold. Coolant level in a
warm engine will be higher due to thermal
expansion.To purge the cooling system of all air,
this heat up/cool down cycle (adding coolant to cold
engine) must be performed three times. Add neces-
sary coolant to raise tank level to the FULL mark
after each cool down period.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT
The use of aluminum cylinder blocks, cylinder
heads and water pumps requires special corrosion
protection. Only MopartAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (glycol base coolant with
Fig. 8 Cooling System Bleed Plug - 4.7L
1 - COOLING SYSTEM BLEED PLUG
Fig. 9 Drain PlugÐ4.0L Engine
1 - COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - BLOCK DRAIN PLUG
WJCOOLING 7 - 13
COOLING (Continued)
Page 237 of 2199
corrosion inhibitors called HOAT, for Hybrid Organic
Additive Technology) is recommended. This coolant
offers the best engine cooling without corrosion when
mixed with 50% distilled water to obtain to obtain a
freeze point of -37ÉC (-35ÉF). If it loses color or
becomes contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with
fresh properly mixed coolant solution.
CAUTION: Do not use coolant additives that are
claimed to improve engine cooling.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING SYSTEM -
REVERSE FLUSHING
CAUTION: The cooling system normally operates at
97-to-124 kPa (14-to -18 psi) pressure. Exceeding
this pressure may damage the radiator or hoses.
Reverse flushing of the cooling system is the forc-
ing of water through the cooling system. This is done
using air pressure in the opposite direction of normal
coolant flow. It is usually only necessary with very
dirty systems with evidence of partial plugging.
CHEMICAL CLEANING
If visual inspection indicates the formation of
sludge or scaly deposits, use a radiator cleaner
(Mopar Radiator Kleen or equivalent) before flushing.
This will soften scale and other deposits and aid the
flushing operation.
CAUTION: Be sure instructions on the container are
followed.
REVERSE FLUSHING RADIATOR
Disconnect the radiator hoses from the radiator fit-
tings. Attach a section of radiator hose to the radia-
tor bottom outlet fitting and insert the flushing gun.
Connect a water supply hose and air supply hose to
the flushing gun.
CAUTION: The cooling system normally operates at
97-to-124 kPa (14- to-18 psi) pressure. Exceeding
this pressure may damage the radiator or hoses.
Allow the radiator to fill with water. When radiator
is filled, apply air in short blasts allowing radiator to
refill between blasts. Continue this reverse flushing
until clean water flows out through rear of radiator
cooling tube passages. For more information, refer to
operating instructions supplied with flushing equip-
ment. Have radiator cleaned more extensively by a
radiator repair shop.
REVERSE FLUSHING ENGINE
Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE). Remove the thermostat
housing and thermostat. Install the thermostat hous-
ing. Disconnect the radiator upper hose from the
radiator and attach the flushing gun to the hose. Dis-
connect the radiator lower hose from the water
pump. Attach a lead away hose to the water pump
inlet fitting.
CAUTION: Be sure that the heater control valve is
closed (heat off). This is done to prevent coolant
flow with scale and other deposits from entering
the heater core.
Connect the water supply hose and air supply hose
to the flushing gun. Allow the engine to fill with
water. When the engine is filled, apply air in short
blasts, allowing the system to fill between air blasts.
Continue until clean water flows through the lead
away hose. For more information, refer to operating
instructions supplied with flushing equipment.
Remove the lead away hose, flushing gun, water
supply hose and air supply hose. Remove the thermo-
stat housing (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/EN-
GINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - REMOVAL).
Install the thermostat and housing with a replace-
ment gasket (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/EN-
GINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT -
INSTALLATION). Connect the radiator hoses. Refill
the cooling system with the correct antifreeze/water
mixture (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Automatic Belt Tensioner to
Mounting
BracketÐBolt
4.0L 28 Ð 250
4.7L 41 30 Ð
Automatic Belt Tensioner
PulleyÐ
Bolt
(4.7L) 61 45 Ð
Block HeaterÐBolt
7 - 14 COOLINGWJ
COOLING (Continued)
Page 247 of 2199

ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLANT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLANT.......25
DESCRIPTION - HOAT COOLANT.........25
OPERATION...........................26
COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION.........................27
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................28
REMOVAL.............................29
CLEANING............................30
INSTALLATION.........................30
RADIATOR FAN - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................31
REMOVAL.............................31
CLEANING............................32
INSPECTION..........................32
INSTALLATION.........................32
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.7L ENGINE............32
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.0L ENGINE............32
OPERATION...........................33
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE BLOCK
HEATER ............................33
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐ4.7L ENGINE...............33
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE...............34
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATIONÐ4.7L ENGINE...........34
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE...........34
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE...............35
REMOVALÐ4.7L ENGINE...............36
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE...........36
INSTALLATIONÐ4.7L ENGINE...........36
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.7L ENGINE............36
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.0L ENGINE............37
OPERATION...........................37DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐTHERMOSTAT . . . 37
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE...............38
REMOVALÐ4.7L ENGINE...............38
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE...........38
INSTALLATIONÐ4.7L ENGINE...........39
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................40
OPERATION...........................40
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐVISCOUS FAN
DRIVE..............................40
PWM FAN CONTROL MODULE - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................41
REMOVAL.............................41
INSTALLATION.........................42
RADIATOR - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION.........................42
REMOVAL.............................42
CLEANING............................43
INSPECTION..........................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
RADIATOR - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................44
REMOVAL.............................44
CLEANING............................46
INSPECTION..........................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
RADIATOR FAN MOTOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐELECTRIC
COOLING FAN........................47
WATER PUMP - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONÐWATER PUMP...........47
DESCRIPTIONÐWATER PUMP BYPASS....47
OPERATION
OPERATIONÐWATER PUMP............47
OPERATIONÐWATER PUMP BYPASS.....48
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐWATER PUMP . . . 48
REMOVAL.............................49
CLEANING............................49
INSPECTION..........................49
INSTALLATION.........................49
WATER PUMP - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................50
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐWATER PUMP . . . 50
REMOVAL.............................51
CLEANING............................52
7 - 24 ENGINEWJ
Page 250 of 2199

(1) Position sensor into the coolant recovery pres-
sure container (Fig. 1).
(2) Connect the coolant level sensor electrical con-
nector (Fig. 2).
(3) Close hood.
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS
CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION
This system works along with the radiator pres-
sure cap. This is done by using thermal expansion
and contraction of the coolant to keep the coolant
free of trapped air. It provides:
²A volume for coolant expansion and contraction.
²A convenient and safe method for checking/ad-
justing coolant level at atmospheric pressure. This is
done without removing the radiator pressure cap.
²Some reserve coolant to the radiator to cover
minor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
As the engine cools, a vacuum is formed in the
cooling system of both the radiator and engine. Cool-
ant will then be drawn from the coolant tank and
returned to a proper level in the radiator.
The coolant reservoir/overflow system has a radia-
tor mounted pressurized cap, an overflow tube and a
plastic coolant reservoir/overflow tank (Fig. 3)
mounted to the right inner fender.
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION
The hydraulic fan (Fig. 4) used on vehicles
equipped the 4.7L engine, replaces both the electric
fan and the engine driven mechanical fan. The
hydraulic cooling fan is integral to the fan shroud
and is located between the radiator and the engine.
The power steering pump supplies the hydraulic
fluid and pressure to rotate the cooling fan blade,
while the electrical part of the fan is controlled by
the JTEC.
The hydraulic fan drive (motor) consists of the
three major following components:
²Steering flow control valve
Fig. 1 COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR ELECTRICAL
CONNECTOR
Fig. 2 COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION
Fig. 3 Coolant Reservoir / Overflow Tank
1 - COOLANT OVERFLOW HOSE
2 - COOLANT RESERVOIR/OVERFLOW TANK
3 - COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR
4 - BOLT
WJENGINE 7 - 27
COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR (Continued)
Page 251 of 2199

²Fan control valve
²Two stage G-rotor hydraulic drive
The hydraulic fan and drive is not serviceable.
Therefore any failure of the fan blade, hydraulic fan
drive or fan shroud requires replacement of the fan
module because the fan blade and hydraulic fan drive
are matched and balanced as a system and servicing
either separately would disrupt this balance.
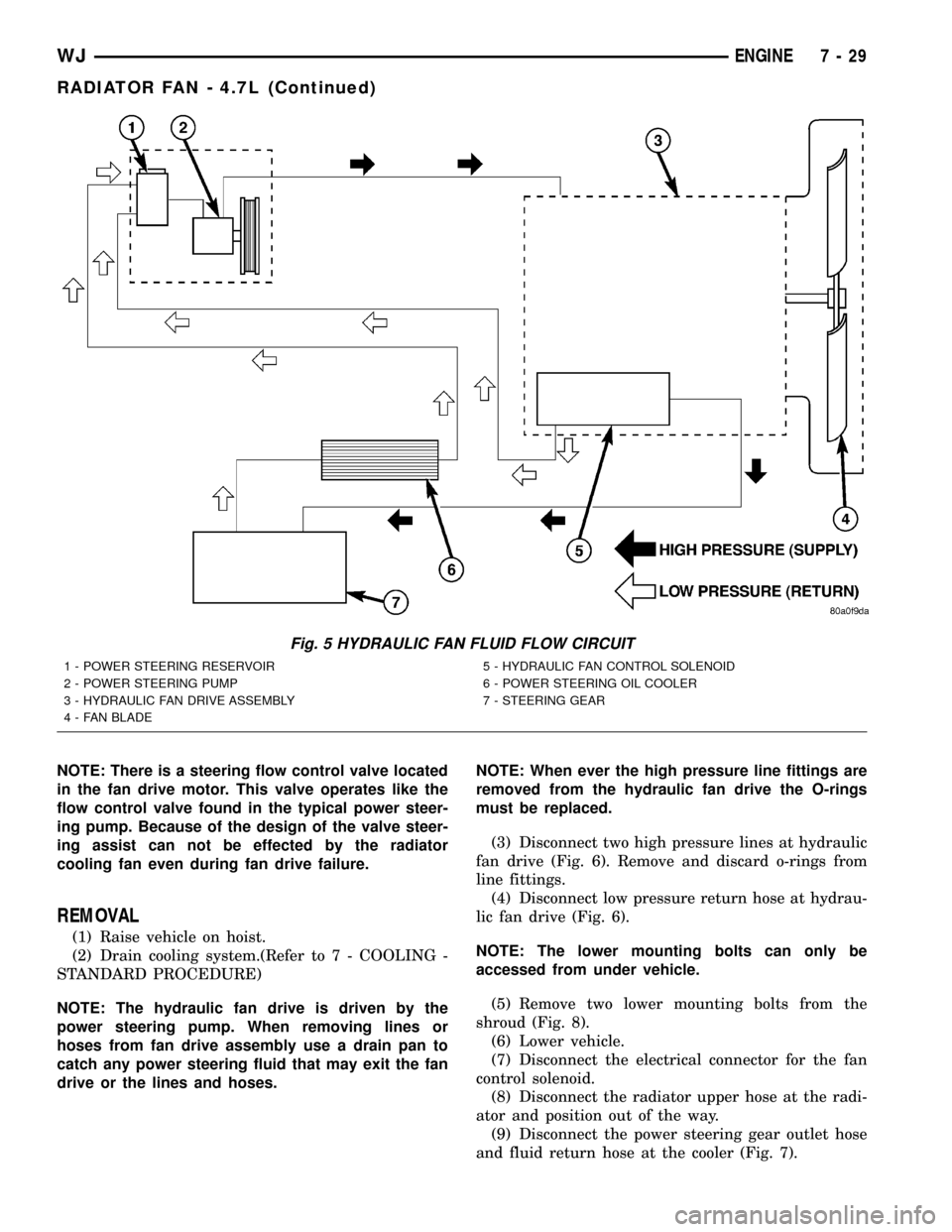
For hydraulic fluid routing information refer to
(Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not attempt to service the hydraulic
cooling fan or fan drive separately replace the cooling
module as an assembly. Failure to do so may cause
severe damage to the hydraulic cooling fan assembly.
OPERATION
The hydraulic radiator cooling fan used on the
Grand Cherokee with the 4.7L engine replaces both
the electric fan and the engine driven mechanical
fan. The use of this hydraulic fan provides the 4.7L
equipped Grand Cherokee with heavy trailer tow
capability while at the same time reducing unneces-
sary power drain on both the engine and the vehicles
electrical system.
HYDRAULIC FAN STRATEGY
The hydraulic radiator cooling fan is controlled by
the JTEC. A PWM (Pulse With Modulated) signal
from the JTEC controls the fan from 0 to 100% of the
available fan speed. There are four inputs to the
JTEC that determine what speed percentage of fan is
required by the vehicle. These inputs are:
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Transmission Oil Temperature
²Battery Temperature
²A/C System Pressure
By monitoring these four parameters, the JTEC
can determine if cooling airflow is required. If airflow
is required, the JTEC will slowly ramp up (speed up)
the fan speed until the parameter(s) are under con-
trol. Once the temperature or pressure is reduced to
within operating parameters the fan will ramp up,
ramp down, or hold its speed to maintain the temper-
ature / pressure requirements.
NOTE: Even if the JTEC is not requesting fan on
operation the fan blade will usually spin between
100 and 500 RPM when the vehicle is at idle. This is
due to a controlled minimum oil flow requirement
through the fan drive motor.
ACTIVATING THE HYDRAULIC FAN WITH THE DRB
Under the Engine Systems test heading, there is a
subheading. ªHydraulic fan solenoid testº, that has
the selections, on /off. Activating the fan with the
DRB will run the fan at 100% duty cycle, which will
help troubleshoot any system problems, and also help
with the deaeration procedure.
NOTE: Engine must be running to activate the fan
with the DRB.
RADIATOR COOLING FAN HYDRAULIC FLUID PATH
Hydraulic fluid is pumped through the power
steering pump, from the pump the fluid travels
though a high pressure delivery line to the fan drive
motor. As fluid is diverted through the G-rotors, rota-
tional motion is created as fluid moves from the high-
pressure (inlet) side of the motor to the low-pressure
(outlet) side. Fluid exiting the drive motor is divided
into two paths. Path one continues through a high
pressure delivery line to the vehicles steering gear to
provide steering assist. and path two sends fluid
back to the power steering pump through a low pres-
sure line. Fluid exits the steering gear under low
pressure and travels through a low pressure line to
the power steering fluid cooler to be cooled before
being returned back the the power steering fluid res-
ervoir (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 HYDRAULIC RADIATOR COOLING FAN AND
FAN DRIVE
1 - POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
2 - RADIATOR
3 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE FROM STEERING GEAR PUMP TO
HYDRAULIC FAN MOTOR
4 - HYDRAULIC FAN MOTOR
5 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE FROM HYDRAULIC FAN MOTOR TO
STEERING GEAR
6 - FAN SHROUD
7 - 28 ENGINEWJ
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 252 of 2199

NOTE: There is a steering flow control valve located
in the fan drive motor. This valve operates like the
flow control valve found in the typical power steer-
ing pump. Because of the design of the valve steer-
ing assist can not be effected by the radiator
cooling fan even during fan drive failure.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Drain cooling system.(Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
NOTE: The hydraulic fan drive is driven by the
power steering pump. When removing lines or
hoses from fan drive assembly use a drain pan to
catch any power steering fluid that may exit the fan
drive or the lines and hoses.NOTE: When ever the high pressure line fittings are
removed from the hydraulic fan drive the O-rings
must be replaced.
(3) Disconnect two high pressure lines at hydraulic
fan drive (Fig. 6). Remove and discard o-rings from
line fittings.
(4) Disconnect low pressure return hose at hydrau-
lic fan drive (Fig. 6).
NOTE: The lower mounting bolts can only be
accessed from under vehicle.
(5) Remove two lower mounting bolts from the
shroud (Fig. 8).
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Disconnect the electrical connector for the fan
control solenoid.
(8) Disconnect the radiator upper hose at the radi-
ator and position out of the way.
(9) Disconnect the power steering gear outlet hose
and fluid return hose at the cooler (Fig. 7).
Fig. 5 HYDRAULIC FAN FLUID FLOW CIRCUIT
1 - POWER STEERING RESERVOIR
2 - POWER STEERING PUMP
3 - HYDRAULIC FAN DRIVE ASSEMBLY
4 - FAN BLADE5 - HYDRAULIC FAN CONTROL SOLENOID
6 - POWER STEERING OIL COOLER
7 - STEERING GEAR
WJENGINE 7 - 29
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 254 of 2199

NOTE: When ever the high pressure line fittings are
removed from the hydraulic fan drive the o-rings
located on the fittings must be replaced.
(7) Lubricate the o-rings on the fittings with power
steering fluid then connect inlet and outlet high pres-
sure lines to fan drive (Fig. 9). Tighten inlet line to
49 N´m (36 ft. lbs.) tighten outlet line to 29 N´m (21.5
ft. lbs.).
(8) Connect low pressure return hose to fan drive
(Fig. 9).
(9) Lower vehicle.
(10) Install radiator upper hose.
(11) Connect electrical connector for hydraulic fan
control solenoid.
(12) Tighten fan shroud upper mounting bolts to 6
N´m (50 in. lbs.).
(13) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
CAUTION: Do not run engine with power steering
fluid below the full mark in the reservoir. Sever
damage to the hydraulic cooling fan or the engine
can occur.(14) Refill power steering fluid reservoir and bleed
air from steering system (Refer to 19 - STEERING/
PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(15) Run engine and check for leaks.
RADIATOR FAN - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION
The radiator cooling fan used on the 4.0L engine is
an hybrid fan design. The hybrid fan system consist
of a low speed viscous driven mechanical fan and a
electrical fan (Fig. 10).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) The thermal viscous fan drive/fan blade assem-
bly is attached (threaded) to water pump hub shaft.
Remove fan blade/viscous fan drive assembly from
water pump by turning mounting nut counterclock-
wise as viewed from front (Fig. 11). Threads on vis-
cous fan drive areRIGHT HAND.
(3) Do not attempt to remove fan/viscous fan drive
assembly from vehicle at this time.
(4) Do not unbolt fan blade assembly from viscous
fan drive at this time.
(5) Remove fan shroud-to-upper crossmember nuts.
(6) Remove fan shroud and fan blade/viscous fan
drive assembly as a complete unit from vehicle.
Fig. 9 HYDRAULIC LINES/HOSES AND ELECTRICAL
CONNECTOR
1 - LOW PRESSURE RETURN HOSE
2 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE (OUTLET)
3 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE (INLET)
4 - HYDRAULIC FAN DRIVEFig. 10 Radiator Cooling Fan
1 - RADIATOR
2 - ELECTRIC COOLING FAN CONNECTOR
3 - FAN SHROUD
4 - ELECTRIC COOLING FAN
WJENGINE 7 - 31
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 258 of 2199

(2) Insert block heater assembly with element loop
pointing at twelve o'clock (Fig. 19).
(3) With block heater fully seated, tighten center
screw to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is
used to sense engine coolant temperature. The sensor
protrudes into an engine water jacket.
The ECT sensor is a two-wire Negative Thermal
Coefficient (NTC) sensor. Meaning, as engine coolant
temperature increases, resistance (voltage) in the
sensor decreases. As temperature decreases, resis-
tance (voltage) in the sensor increases.
OPERATION
At key-on, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
sends out a regulated 5 volt signal to the ECT sensor.
The PCM then monitors the signal as it passes
through the ECT sensor to the sensor ground (sensor
return).
When the engine is cold, the PCM will operate in
Open Loop cycle. It will demand slightly richer air-
fuel mixtures and higher idle speeds. This is done
until normal operating temperatures are reached.
The PCM uses inputs from the ECT sensor for the
following calculations:
²for engine coolant temperature gauge operation
through CCD or PCI (J1850) communications
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance curves
²ASD relay shut-down times
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor key-on steps
²Pulse-width prime-shot during cranking
²O2 sensor closed loop times
²Purge solenoid on/off times
²EGR solenoid on/off times (if equipped)
²Leak Detection Pump operation (if equipped)
²Radiator fan relay on/off times (if equipped)
²Target idle speed
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. COOLING SYSTEM
MUST BE PARTIALLY DRAINED BEFORE REMOV-
ING THE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT)
SENSOR. REFER TO GROUP 7, COOLING.
(1) Partially drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 18 Drain Plug
1 - COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - BLOCK DRAIN PLUG
Fig. 19 Engine Block Heater
1 - ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
WJENGINE 7 - 35
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER (Continued)
Page 259 of 2199

(2) Disconnect electrical connector from ECT sen-
sor (Fig. 20).
(3) Remove sensor from thermostat housing.
REMOVALÐ4.7L ENGINE
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. COOLING SYSTEM
MUST BE PARTIALLY DRAINED BEFORE REMOV-
ING THE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT)
SENSOR. REFER TO GROUP 7, COOLING.
The ECT sensor is located near the front of the
intake manifold (Fig. 21).
(1) Partially drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from ECT sen-
sor.
(3) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE
(1) Install sensor.
(2) Tighten to 11 N´m (8 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(4) Replace any lost engine coolant. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATIONÐ4.7L ENGINE
(1) Install sensor.
(2) Tighten to 11 N´m (8 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(4) Replace any lost engine coolant. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.7L ENGINE
CAUTION: Do not operate an engine without a ther-
mostat, except for servicing or testing.
A pellet-type thermostat controls the operating
temperature of the engine by controlling the amount
of coolant flow to the radiator. On all engines the
thermostat is closed below 195ÉF (90ÉC). Above this
temperature, coolant is allowed to flow to the radia-
tor. This provides quick engine warm up and overall
temperature control. On the 4.7L engine the thermo-
stat is designed to block the flow of the coolant
bypass journal by 50% instead of completely blocking
the flow. This design controls coolant temperature
more accurately (Fig. 22).
Fig. 20 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
1 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
2 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
3 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 21 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
1 - ECT SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (2)
3 - MAP SENSOR
4 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
7 - 36 ENGINEWJ
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR (Continued)
Page 260 of 2199

The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-
out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes other prob-
lems. These are: longer engine warmup time, unreli-
able warmup performance, increased exhaust
emissions and crankcase condensation. This conden-
sation can result in sludge formation.
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.0L ENGINE
CAUTION: Do not operate an engine without a ther-
mostat, except for servicing or testing.
A pellet-type thermostat controls the operating
temperature of the engine by controlling the amount
of coolant flow to the radiator. On all engines the
thermostat is closed below 195ÉF (90ÉC). Above this
temperature, coolant is allowed to flow to the radia-
tor. This provides quick engine warm up and overall
temperature control. (Fig. 23).
The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes other prob-
lems. These are: longer engine warmup time, unreli-
able warmup performance, increased exhaust
emissions and crankcase condensation. This conden-
sation can result in sludge formation.
OPERATION
The wax pellet is located in a sealed container at
the spring end of the thermostat. When heated, the
pellet expands, overcoming closing spring tension
and water pump pressure to force the valve to open.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐTHERMOSTAT
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
All models are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics for certain cooling system components.If the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) detects low engine
coolant temperature, it will record a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). For other DTC numbers, (Refer to 25
- EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIPTION).
The DTC can also be accessed through the DRB
scan tool.
Fig. 22 Thermostat
1 - FROM HEATER
2 - FROM RADIATOR
3 - TO WATER PUMP
4 - ENGINE BYPASS
5 - THERMOSTAT
Fig. 23 Thermostat and Housing
1 - LONG BOLT
2 - GASKET
3 - THERMOSTAT
4 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
5 - SHORT BOLT
WJENGINE 7 - 37
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT (Continued)