Knock JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 23 of 2199
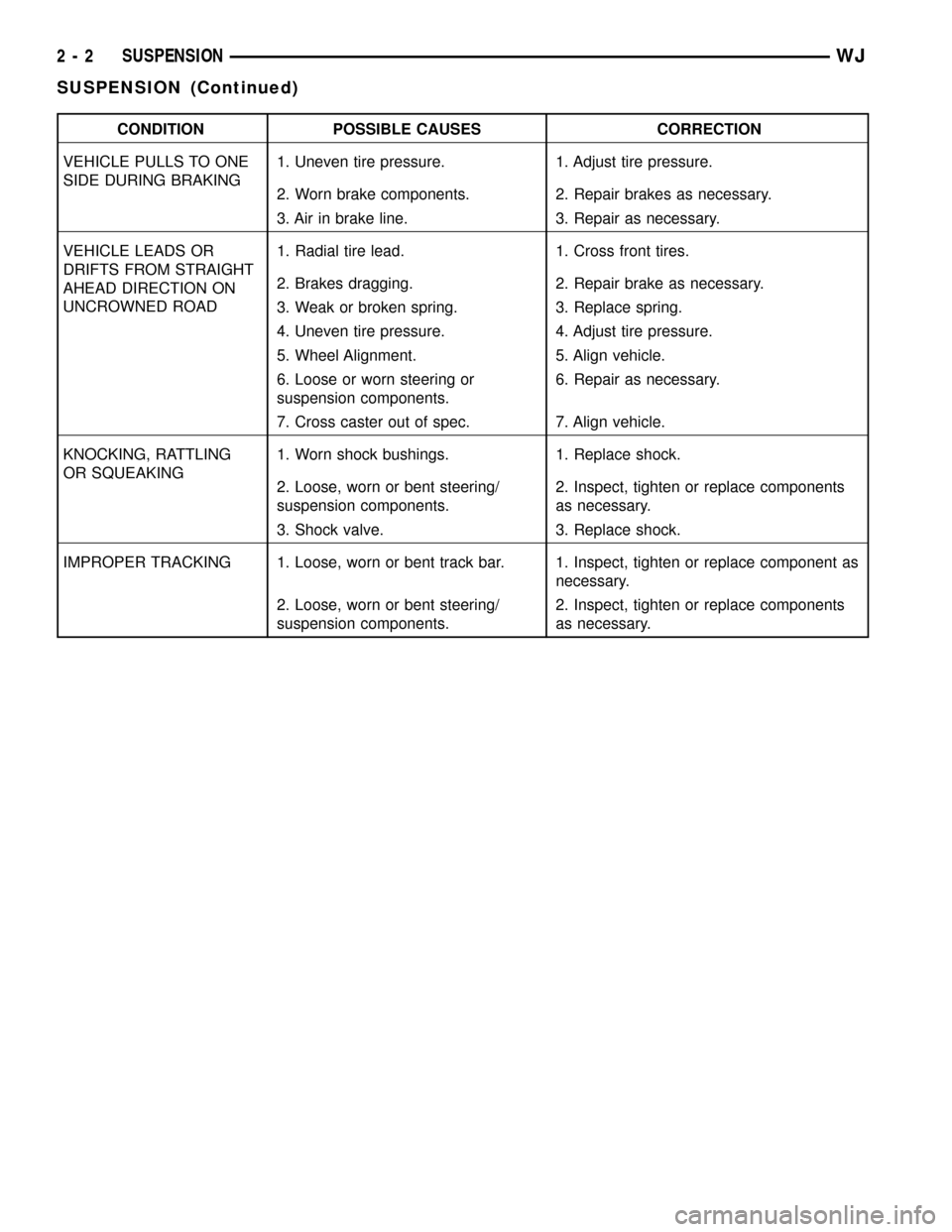
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
VEHICLE PULLS TO ONE
SIDE DURING BRAKING1. Uneven tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Worn brake components. 2. Repair brakes as necessary.
3. Air in brake line. 3. Repair as necessary.
VEHICLE LEADS OR
DRIFTS FROM STRAIGHT
AHEAD DIRECTION ON
UNCROWNED ROAD1. Radial tire lead. 1. Cross front tires.
2. Brakes dragging. 2. Repair brake as necessary.
3. Weak or broken spring. 3. Replace spring.
4. Uneven tire pressure. 4. Adjust tire pressure.
5. Wheel Alignment. 5. Align vehicle.
6. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.6. Repair as necessary.
7. Cross caster out of spec. 7. Align vehicle.
KNOCKING, RATTLING
OR SQUEAKING1. Worn shock bushings. 1. Replace shock.
2. Loose, worn or bent steering/
suspension components.2. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
3. Shock valve. 3. Replace shock.
IMPROPER TRACKING 1. Loose, worn or bent track bar. 1. Inspect, tighten or replace component as
necessary.
2. Loose, worn or bent steering/
suspension components.2. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
2 - 2 SUSPENSIONWJ
SUSPENSION (Continued)
Page 39 of 2199
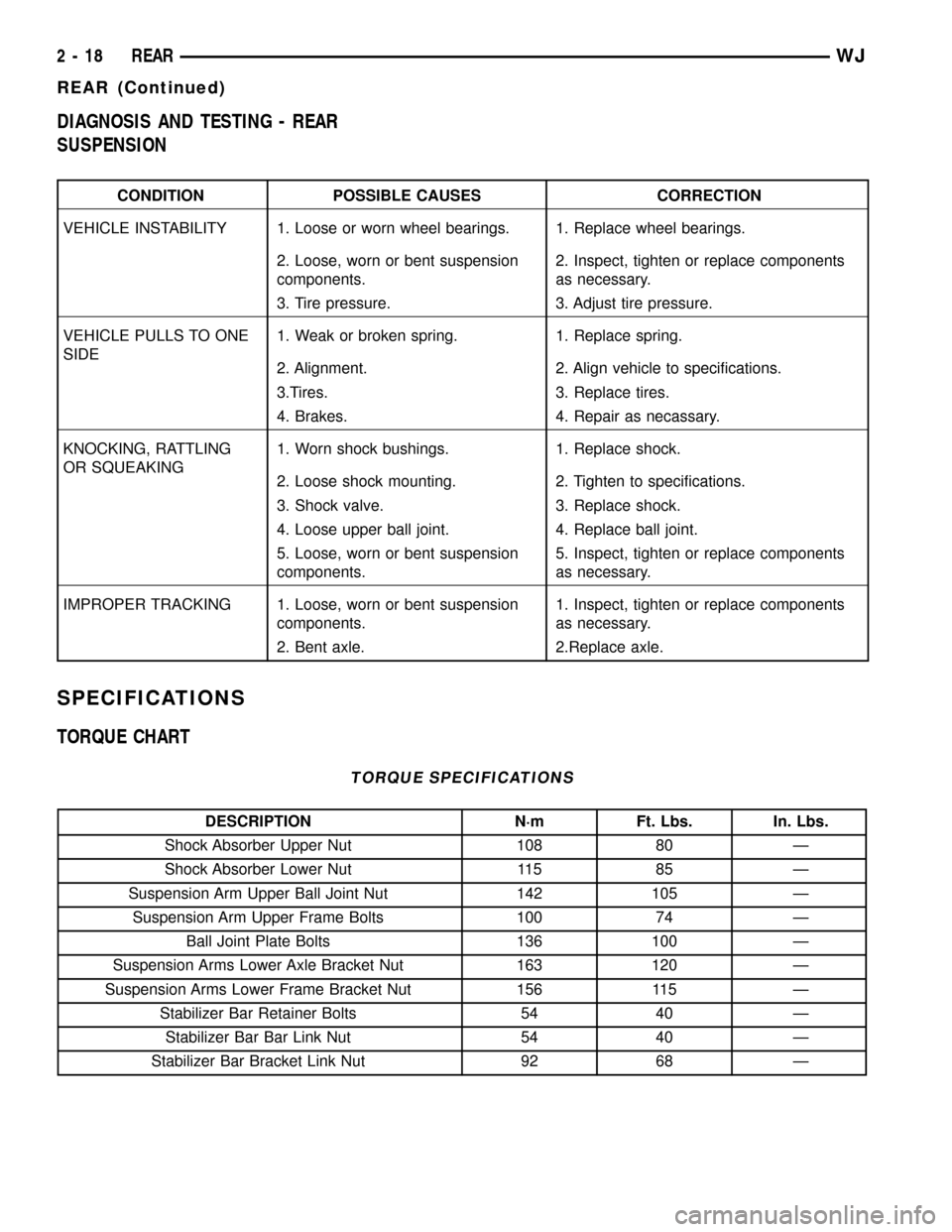
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR
SUSPENSION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
VEHICLE INSTABILITY 1. Loose or worn wheel bearings. 1. Replace wheel bearings.
2. Loose, worn or bent suspension
components.2. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
3. Tire pressure. 3. Adjust tire pressure.
VEHICLE PULLS TO ONE
SIDE1. Weak or broken spring. 1. Replace spring.
2. Alignment. 2. Align vehicle to specifications.
3.Tires. 3. Replace tires.
4. Brakes. 4. Repair as necassary.
KNOCKING, RATTLING
OR SQUEAKING1. Worn shock bushings. 1. Replace shock.
2. Loose shock mounting. 2. Tighten to specifications.
3. Shock valve. 3. Replace shock.
4. Loose upper ball joint. 4. Replace ball joint.
5. Loose, worn or bent suspension
components.5. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
IMPROPER TRACKING 1. Loose, worn or bent suspension
components.1. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
2. Bent axle. 2.Replace axle.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Shock Absorber Upper Nut 108 80 Ð
Shock Absorber Lower Nut 115 85 Ð
Suspension Arm Upper Ball Joint Nut 142 105 Ð
Suspension Arm Upper Frame Bolts 100 74 Ð
Ball Joint Plate Bolts 136 100 Ð
Suspension Arms Lower Axle Bracket Nut 163 120 Ð
Suspension Arms Lower Frame Bracket Nut 156 115 Ð
Stabilizer Bar Retainer Bolts 54 40 Ð
Stabilizer Bar Bar Link Nut 54 40 Ð
Stabilizer Bar Bracket Link Nut 92 68 Ð
2 - 18 REARWJ
REAR (Continued)
Page 61 of 2199

VARI-LOKTDIFFERENTIAL
In a standard differential if one wheel spins, the
opposite wheel will generate only as much torque as
the spinning wheel.
A gerotor pump and clutch pack are used to pro-
vide the torque transfer capability. One axle shaft is
splined to the gerotor pump and one of the differen-
tial side gears, which provides the input to the pump.
As a wheel begins to lose traction, the speed differ-
ential is transmitted from one side of the differential
to the other through the side gears. The motion of
one side gear relative to the other turns the inner
rotor of the pump. Since the outer rotor of the pump
is grounded to the differential case, the inner and
outer rotors are now moving relative to each other
and therefore creates pressure in the pump. The tun-ing of the front and rear axle orifices and valves
inside the gerotor pump is unique and each system
includes a torque-limiting pressure relief valve to
protect the clutch pack, which also facilitates vehicle
control under extreme side-to-side traction varia-
tions. The resulting pressure is applied to the clutch
pack and the transfer of torque is completed.
Under conditions in which opposite wheels are on
surfaces with widely different friction characteristics,
Vari-loktdelivers far more torque to the wheel on
the higher traction surface than do conventional
Trac-loktsystems. Because conventional Trac-lokt
differentials are initially pre-loaded to assure torque
transfer, normal driving (where inner and outer
wheel speeds differ during cornering, etc.) produces
torque transfer during even slight side-to-side speed
variations. Since these devices rely on friction from
this preload to transfer torque, normal use tends to
cause wear that reduces the ability of the differential
to transfer torque over time. By design, the Vari-lokt
system is less subject to wear, remaining more con-
sistent over time in its ability to transfer torque. The
coupling assembly is serviced as a unit. From a ser-
vice standpoint the coupling also benefits from using
the same lubricant supply as the ring and pinion
gears.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
Fig. 1 DIFFERENTIAL-STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING
1 - IN STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING EACH WHEEL ROTATES AT
100% OF CASE SPEED
2 - PINION GEAR
3 - SIDE GEAR
4 - PINION GEARS ROTATE WITH CASE
Fig. 2 DIFFERENTIAL-ON TURNS
1 - PINION GEARS ROTATE ON PINION SHAFT
3 - 16 FRONT AXLE - 186FBIWJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 62 of 2199

BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front±end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear-end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
WJFRONT AXLE - 186FBI 3 - 17
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 97 of 2199

peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
3 - 52 REAR AXLE - 198RBIWJ
REAR AXLE - 198RBI (Continued)
Page 137 of 2199

and therefore creates pressure in the pump. The tun-
ing of the front and rear axle orifices and valves
inside the gerotor pump is unique and each system
includes a torque-limiting pressure relief valve to
protect the clutch pack, which also facilitates vehicle
control under extreme side-to-side traction varia-
tions. The resulting pressure is applied to the clutch
pack and the transfer of torque is completed.
Under conditions in which opposite wheels are on
surfaces with widely different friction characteristics,
Vari-loktdelivers far more torque to the wheel on
the higher traction surface than do conventional
Trac-loktsystems. Because conventional Trac-lokt
differentials are initially pre-loaded to assure torque
transfer, normal driving (where inner and outer
wheel speeds differ during cornering, etc.) produces
torque transfer during even slight side-to-side speed
variations. Since these devices rely on friction from
this preload to transfer torque, normal use tends to
cause wear that reduces the ability of the differential
to transfer torque over time. By design, the Vari-lokt
system is less subject to wear, remaining more con-
sistent over time in its ability to transfer torque. The
coupling assembly is serviced as a unit. From a ser-
vice standpoint the coupling also benefits from using
the same lubricant supply as the ring and pinion
gears.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears, or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
3 - 92 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 398 of 2199

IGNITION CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
IGNITION CONTROL
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE FIRING ORDER - 4.0L 6-CYLINDER
ENGINE..............................2
ENGINE FIRING ORDERÐ4.7L V-8 ENGINE . . 2
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 4.0L ENGINE . 2
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCEÐ4.7L V-8
ENGINE..............................2
IGNITION TIMING......................2
SPARK PLUGS........................3
TORQUE - IGNITION SYSTEM............3
AUTO SHUT DOWN RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT.............3
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT.............3
OPERATION - ASD SENSE - PCM INPUT....4
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 4.0L....................4
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L....................5
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L.....................5
OPERATION - 4.7L.....................5
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L.......................6
REMOVAL - 4.7L.......................7INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L...................8
INSTALLATION - 4.7L...................9
COIL RAIL
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION...........................10
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................11
IGNITION COIL
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................12
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................15
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION.........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CONDITIONS.........................15
REMOVAL.............................18
CLEANING............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18
IGNITION CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
Two different ignition systems are used. One type
of system is for the 4.0L 6±cylinder engine. The other
is for the 4.7L V-8 engine.
OPERATION
The 4.0L 6±cylinder engine uses a one-piece coil
rail containing three independent coils. Although cyl-
inder firing order is the same as 4.0L engines of pre-
vious years, spark plug firing is not. The 3 coils dual-
fire the spark plugs on cylinders 1±6, 2±5 and/or 3±4.
When one cylinder is being fired (on compressionstroke), the spark to the opposite cylinder is being
wasted (on exhaust stroke). The one-piece coil bolts
directly to the cylinder head. Rubber boots seal the
secondary terminal ends of the coils to the top of all
6 spark plugs. One electrical connector (located at
the rear end of the coil rail) is used for all three coils.
The 4.7L V-8 engine uses 8 dedicated and individ-
ually fired coil for each spark plug. Each coil is
mounted directly to the top of each spark plug. A sep-
arate electrical connector is used for each coil.
Because of coil design, spark plug cables (second-
ary cables) are not used on either engine. Adistrib-
utor is not usedwith either the 4.0L or 4.7L
engines.
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 1
Page 400 of 2199

SPARK PLUGS
ENGINE PLUG TYPE ELECTRODE GAP
4.0L 6-CYL. RC12ECC 0.89 mm (.035 in.)
4.7L V-8 (Exc. HO) RC12MCC4 1.01 mm (.040 in.)
4.7L V-8 High
Output (HO)RC7PYCB4 1.01 mm (.040 in.)
TORQUE - IGNITION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Bolts - 4.0L Engine7- 60
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Bolt - 4.7L V-8 Engine28 21 -
Camshaft Position
Sensor±to±base bolts - 4.0L
Engine2- 15
Camshaft Position Sensor
Bolt - 4.7L V-8 Engine12 - 106
Oil Pump Drive Hold-down
Bolt - 4.0L Engine23 17 -
Ignition Coil Rail Mounting
Bolts - 4.0L Engine29 - 250
Ignition Coil Mounting Nut -
4.7L V-8 Engine8- 70
* Knock Sensor Bolt - 4.7L
HO V-8 Engine*20 *15 -
Spark Plugs - 4.0L Engine 35-41 26-30 -
Spark Plugs - 4.7L V-8
Engine24-30 18-22 -
* Do not apply any sealant,
thread-locker or adhesive to
bolts. Poor sensor
performance may result.
Refer to Removal / Installation
for additional information.
AUTO SHUT DOWN RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT
The 5±pin, 12±volt, Automatic Shutdown (ASD)
relay is located in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The ASD relay supplies battery voltage (12+ volts)
to the fuel injectors and ignition coil(s). With certain
emissions packages it also supplies 12±volts to the
oxygen sensor heating elements.
The ground circuit for the coil within the ASD
relay is controlled by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM operates the ASD relay by switch-
ing its ground circuit on and off.
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 3
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)
Page 410 of 2199

IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR
DESCRIPTION
Two coil capacitors are used. One of them is
located near the center of, and on the left side of the
intake manifold (Fig. 20). The other capacitor is
located near the center of, and on the right side of
the intake manifold.
OPERATION
The 2 coil capacitors are used to prevent high-volt-
age spikes from interfering with the operation of cer-
tain powertrain sensors. They are also used to help
prevent radio interference.
REMOVAL
Two coil capacitors are used. One of them is
located near the center of, and on the left side of the
intake manifold (Fig. 21). The other capacitor is
located near the center of, and on the right side of
the intake manifold.
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at coil capacitor
(Fig. 21).
(2) Remove mounting nut.
(3) Remove capacitor from mounting stud.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position capacitor to manifold mounting stud.(2) Install nut and tighten to 8 N´m (70 in. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to capacitor (Fig.
21).
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
4.7L High-Output Engine
The 2 knock sensors are bolted into the cylinder
block under the intake manifold.
OPERATION
4.7L High-Output Engine
Two knock sensors are used on the 4.7L V-8 engine
if equipped with the high-output package; one for
each cylinder bank. When the knock sensor detects a
knock in one of the cylinders on the corresponding
bank, it sends an input signal to the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). In response, the PCM retards
ignition timing for all cylinders by a scheduled
amount.
Knock sensors contain a piezoelectric material
which constantly vibrates and sends an input voltage
(signal) to the PCM while the engine operates. As the
intensity of the crystal's vibration increases, the
knock sensor output voltage also increases.
Fig. 20 Coil Capacitor (Left Side Shown)
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - COIL CAPACITOR
3 - MOUNTING NUT
Fig. 21 Coil Capacitor (Left Side Shown)
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - COIL CAPACITOR
3 - MOUNTING NUT
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 13
Page 411 of 2199

The voltage signal produced by the knock sensor
increases with the amplitude of vibration. The PCM
receives the knock sensor voltage signal as an input.
If the signal rises above a predetermined level, the
PCM will store that value in memory and retard
ignition timing to reduce engine knock. If the knock
sensor voltage exceeds a preset value, the PCM
retards ignition timing for all cylinders. It is not a
selective cylinder retard.
The PCM ignores knock sensor input during engine
idle conditions. Once the engine speed exceeds a
specified value, knock retard is allowed.
Knock retard uses its own short term and long
term memory program.
Long term memory stores previous detonation
information in its battery-backed RAM. The maxi-
mum authority that long term memory has over tim-
ing retard can be calibrated.
Short term memory is allowed to retard timing up
to a preset amount under all operating conditions (as
long as rpm is above the minimum rpm) except at
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). The PCM, using short
term memory, can respond quickly to retard timing
when engine knock is detected. Short term memory
is lost any time the ignition key is turned off.
NOTE: Over or under tightening the sensor mount-
ing bolts will affect knock sensor performance, pos-
sibly causing improper spark control. Always use
the specified torque when installing the knock sen-
sors.
REMOVAL
4.7L High-Output Engine Only
The 2 knock sensors are bolted into the cylinder
block under the intake manifold (Fig. 22).
NOTE: The left sensor is identified by an identifica-
tion tag (LEFT). It is also identified by a larger bolt
head. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) must
have and know the correct sensor left/right posi-
tions. Do not mix the sensor locations.
(1) Disconnect knock sensor dual pigtail harness
connector from engine wiring harness connector. This
connection is made near the right/rear of intake man-
ifold (Fig. 23).
(2) Remove intake manifold. Refer to Engine sec-
tion.
(3) Remove sensor mounting bolts (Fig. 22). Note
foam strip on bolt threads. This foam is used only to
retain the bolts to sensors for plant assembly. It is
not used as a sealant. Do not apply any adhesive,
sealant or thread locking compound to these bolts.
(4) Remove sensors from engine.
Fig. 22 KNOCK SENSOR LOCATION - 4.7L H.O.
1 - KNOCK SENSORS (2)
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - INTAKE MANIFOLD (CUTAWAY)
4 - PIGTAIL CONNECTOR
Fig. 23 KNOCK SENSOR ELEC. CONNECTOR - 4.7L
H.O.
1 - KNOCK SENSOR PIGTAIL HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - ENGINE WIRING HARNESS
8I - 14 IGNITION CONTROLWJ
KNOCK SENSOR (Continued)