fan operation JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 224 of 2199

COOLING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L
ENGINE..............................1
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
ROUTING 4.7L ENGINE..................1
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM 4.0L
ENGINE..............................1
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM
ROUTING 4.0L ENGINE..................1
DESCRIPTIONÐHOSE CLAMPS...........1
OPERATION
OPERATIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM.........2
OPERATIONÐHOSE CLAMPS............2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)...................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐPRELIMINARY
CHECKS.............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART.............5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM LEAKS......................10DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM DEAERATION.................12
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐDRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L ENGINE.........12
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L ENGINE.........12
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM - 4.0L ENGINE........13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM - 4.0L ENGINE........13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT.................13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM - REVERSE FLUSHING..........14
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................14
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING...........................15
ACCESSORY DRIVE......................16
ENGINE...............................24
TRANSMISSION.........................55
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L
ENGINE
The cooling system consists of the following items:
²Hydraulic cooling fan and fan drive assembly
²Radiator
²Power steering oil cooler
²Radiator pressure cap
²Thermostat
²Coolant reserve/overflow system
²Transmission oil cooler (if equipped with an
automatic transmission)
²Coolant
²Water pump
²Hoses and hose clamps
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM ROUTING
4.7L ENGINE
For cooling system routing refer to (Fig. 1).
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM 4.0L
ENGINE
The cooling system consists of:
²A radiator
²Mechanical Cooling Fan
²Thermal viscous fan drive-Low disengaged
²Fan shroud (Fig. 2)
²Radiator pressure cap
²Thermostat
²Coolant reserve/overflow system
²Transmission oil cooler (if equipped with an
automatic transmission)
²Coolant
²Water pump
²Hoses and hose clamps
²Accessory drive belt
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM ROUTING
4.0L ENGINE
For cooling system routing refer to (Fig. 3).
DESCRIPTIONÐHOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system utilizes both worm drive and
spring type hose clamps. If a spring type clamp
WJCOOLING 7 - 1
Page 226 of 2199

The spring type hose clamp applies constant ten-
sion on a hose connection. To remove a spring type
hose clamp, only use constant tension clamp pliers
designed to compress the hose clamp.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
COOLING SYSTEM RELATED DIAGNOSTICS
The powertrain control module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor certain cooling system com-
ponents:
²If the engine has remained cool for too long a
period, such as with a stuck open thermostat, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
²If an open or shorted condition has developed in
the relay circuit controlling the electric radiator fan
or fan control solenoid circuit controling the hydrau-
lic fan, a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit
often enough to indicated an actual problem, a DTC
is stored. The DTC will be stored in the PCM mem-
ory for eventual display to the service technician.
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
To read DTC's and to obtain cooling system data,
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the DRB
scan tool to erase a DTC. Refer to the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service informa-
tion for operation of the DRB scan tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐPRELIMINARY
CHECKS
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM OVERHEATING
Establish what driving conditions caused the com-
plaint. Abnormal loads on the cooling system such as
the following may be the cause:
²PROLONGED IDLE
²VERY HIGH AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
Fig. 2 Cooling Module with Electric Fan
1 - RADIATOR
2 - ELECTRIC COOLING FAN CONNECTOR
3 - FAN SHROUD
4 - ELECTRIC COOLING FAN
Fig. 3 Engine Cooling SystemÐ4.0L EngineÐ
Typical
1 - HEATER CORE
2 - TO COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW TANK
3 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
4 - RADIATOR
5 - WATER PUMP
WJCOOLING 7 - 3
COOLING (Continued)
Page 230 of 2199
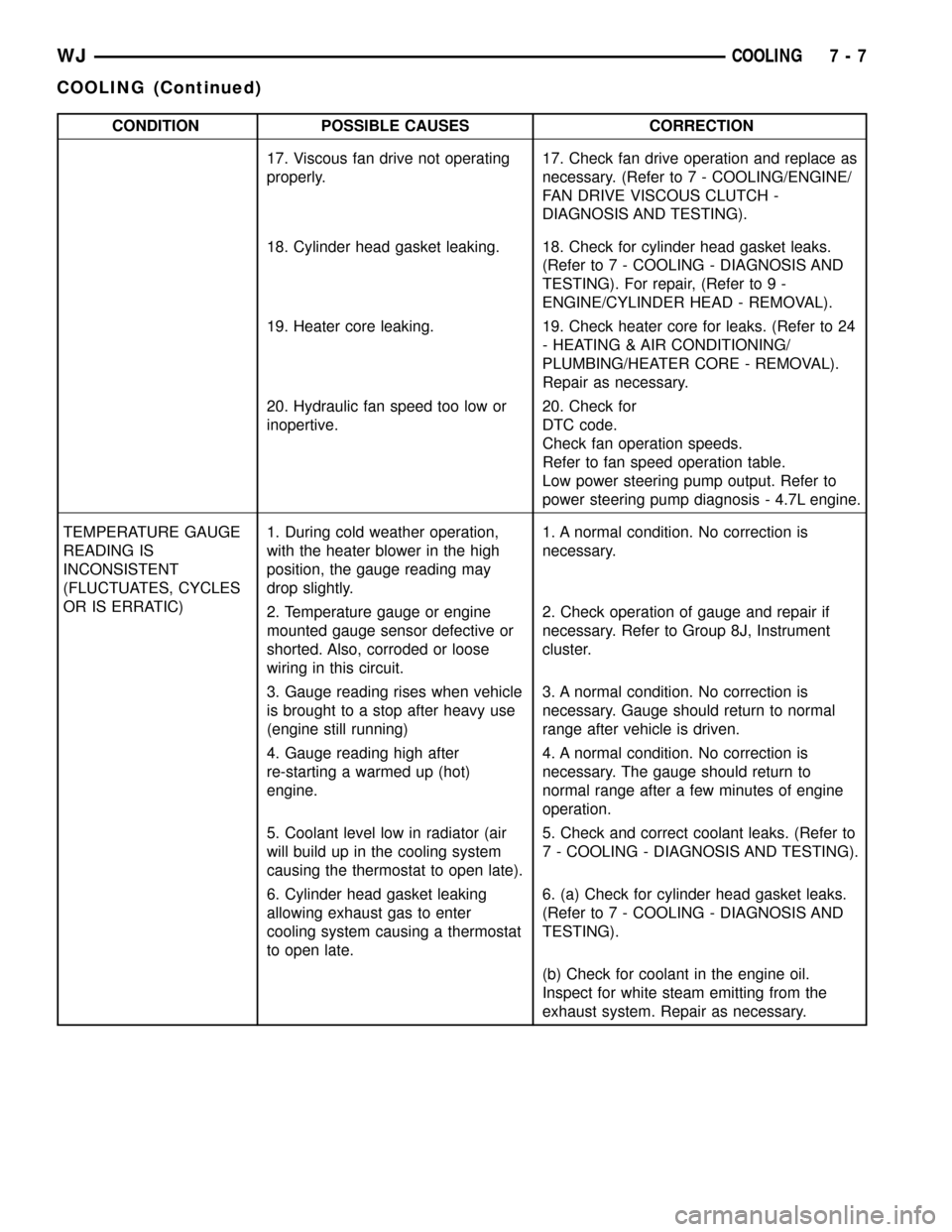
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
17. Viscous fan drive not operating
properly.17. Check fan drive operation and replace as
necessary. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
18. Cylinder head gasket leaking. 18. Check for cylinder head gasket leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). For repair, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
19. Heater core leaking. 19. Check heater core for leaks. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/HEATER CORE - REMOVAL).
Repair as necessary.
20. Hydraulic fan speed too low or
inopertive.20. Check for
DTC code.
Check fan operation speeds.
Refer to fan speed operation table.
Low power steering pump output. Refer to
power steering pump diagnosis - 4.7L engine.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READING IS
INCONSISTENT
(FLUCTUATES, CYCLES
OR IS ERRATIC)1. During cold weather operation,
with the heater blower in the high
position, the gauge reading may
drop slightly.1. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary.
2. Temperature gauge or engine
mounted gauge sensor defective or
shorted. Also, corroded or loose
wiring in this circuit.2. Check operation of gauge and repair if
necessary. Refer to Group 8J, Instrument
cluster.
3. Gauge reading rises when vehicle
is brought to a stop after heavy use
(engine still running)3. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary. Gauge should return to normal
range after vehicle is driven.
4. Gauge reading high after
re-starting a warmed up (hot)
engine.4. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary. The gauge should return to
normal range after a few minutes of engine
operation.
5. Coolant level low in radiator (air
will build up in the cooling system
causing the thermostat to open late).5. Check and correct coolant leaks. (Refer to
7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Cylinder head gasket leaking
allowing exhaust gas to enter
cooling system causing a thermostat
to open late.6. (a) Check for cylinder head gasket leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(b) Check for coolant in the engine oil.
Inspect for white steam emitting from the
exhaust system. Repair as necessary.
WJCOOLING 7 - 7
COOLING (Continued)
Page 232 of 2199
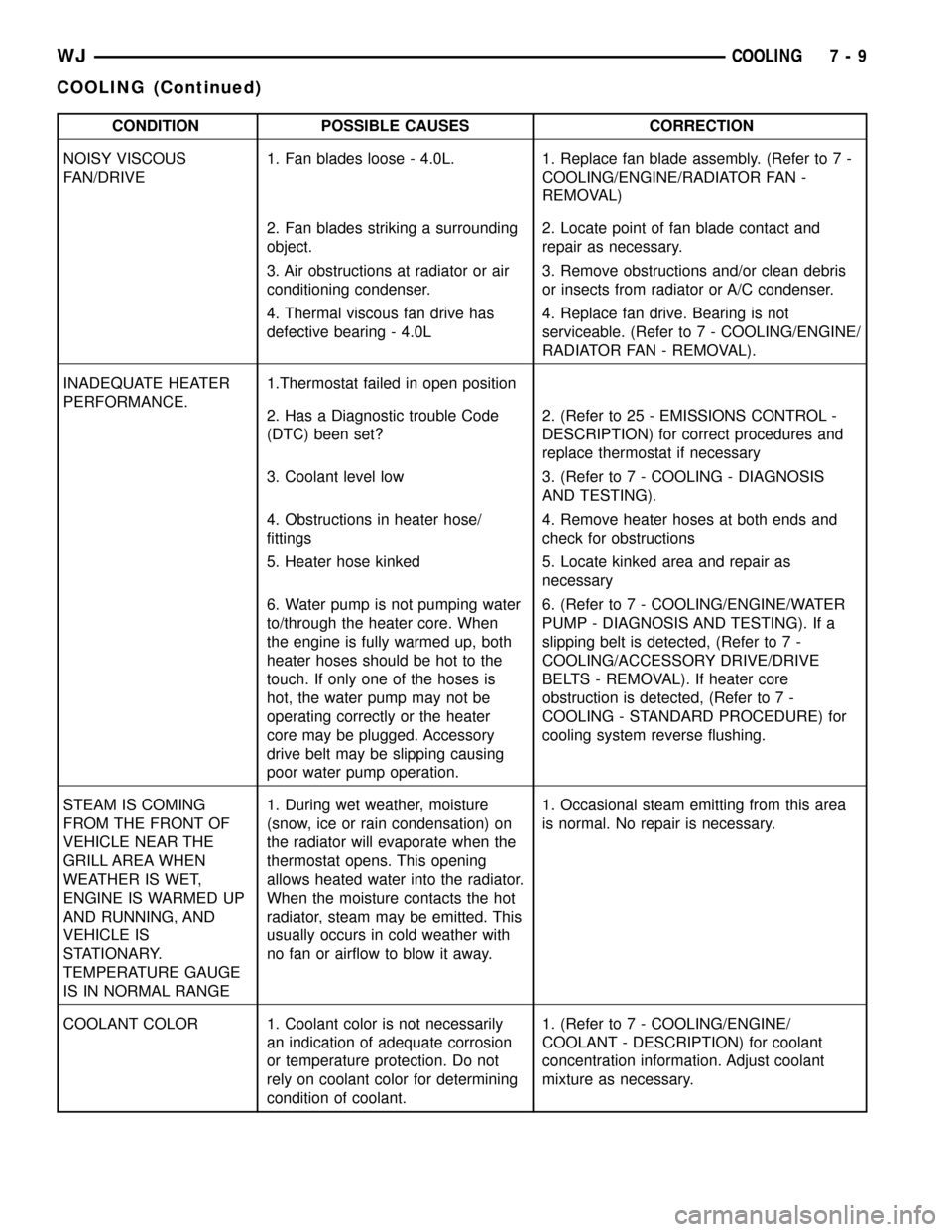
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VISCOUS
FAN/DRIVE1. Fan blades loose - 4.0L. 1. Replace fan blade assembly. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
REMOVAL)
2. Fan blades striking a surrounding
object.2. Locate point of fan blade contact and
repair as necessary.
3. Air obstructions at radiator or air
conditioning condenser.3. Remove obstructions and/or clean debris
or insects from radiator or A/C condenser.
4. Thermal viscous fan drive has
defective bearing - 4.0L4. Replace fan drive. Bearing is not
serviceable. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
INADEQUATE HEATER
PERFORMANCE.1.Thermostat failed in open position
2. Has a Diagnostic trouble Code
(DTC) been set?2. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL -
DESCRIPTION) for correct procedures and
replace thermostat if necessary
3. Coolant level low 3. (Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
4. Obstructions in heater hose/
fittings4. Remove heater hoses at both ends and
check for obstructions
5. Heater hose kinked 5. Locate kinked area and repair as
necessary
6. Water pump is not pumping water
to/through the heater core. When
the engine is fully warmed up, both
heater hoses should be hot to the
touch. If only one of the hoses is
hot, the water pump may not be
operating correctly or the heater
core may be plugged. Accessory
drive belt may be slipping causing
poor water pump operation.6. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/WATER
PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). If a
slipping belt is detected, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE
BELTS - REMOVAL). If heater core
obstruction is detected, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE) for
cooling system reverse flushing.
STEAM IS COMING
FROM THE FRONT OF
VEHICLE NEAR THE
GRILL AREA WHEN
WEATHER IS WET,
ENGINE IS WARMED UP
AND RUNNING, AND
VEHICLE IS
STATIONARY.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
IS IN NORMAL RANGE1. During wet weather, moisture
(snow, ice or rain condensation) on
the radiator will evaporate when the
thermostat opens. This opening
allows heated water into the radiator.
When the moisture contacts the hot
radiator, steam may be emitted. This
usually occurs in cold weather with
no fan or airflow to blow it away.1. Occasional steam emitting from this area
is normal. No repair is necessary.
COOLANT COLOR 1. Coolant color is not necessarily
an indication of adequate corrosion
or temperature protection. Do not
rely on coolant color for determining
condition of coolant.1. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
COOLANT - DESCRIPTION) for coolant
concentration information. Adjust coolant
mixture as necessary.
WJCOOLING 7 - 9
COOLING (Continued)
Page 233 of 2199
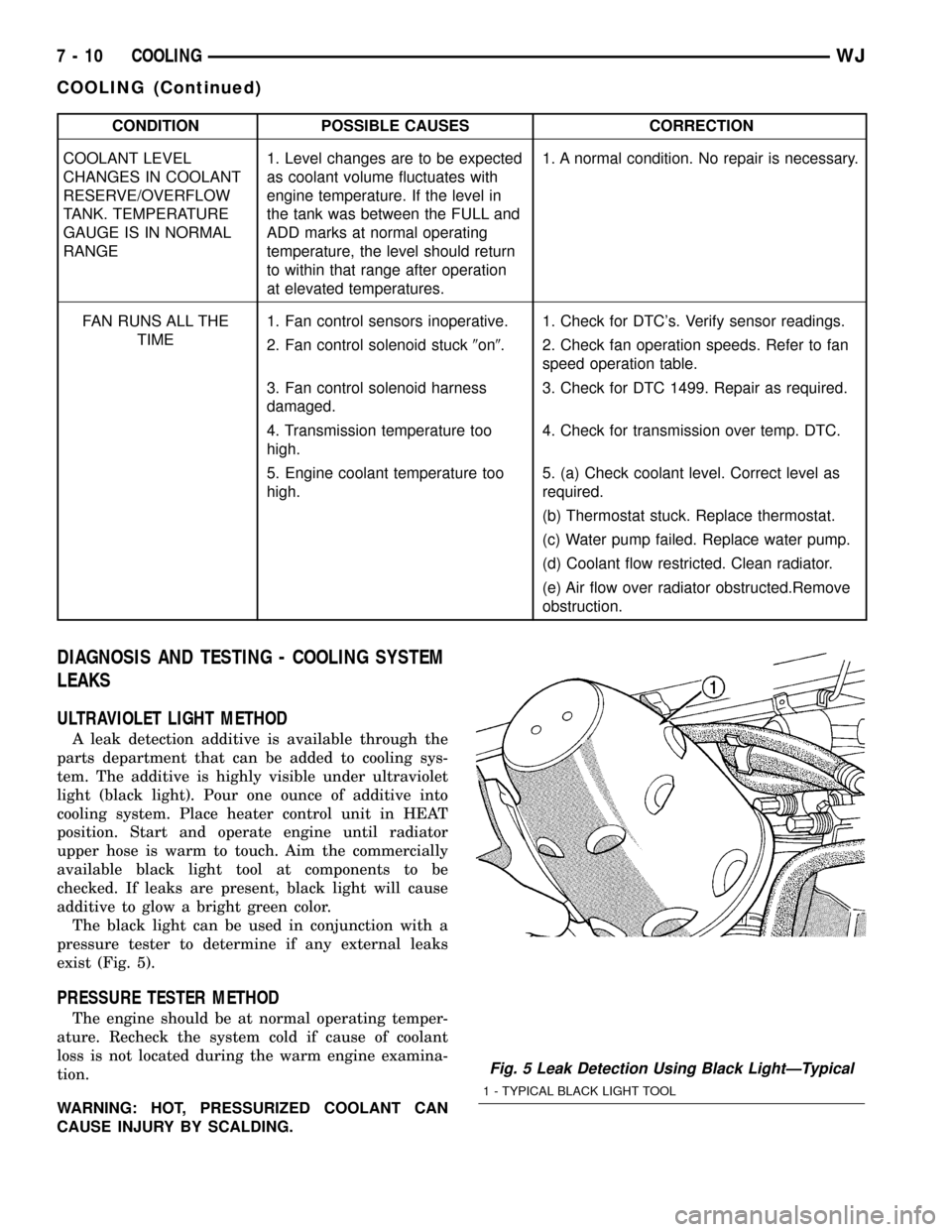
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
COOLANT LEVEL
CHANGES IN COOLANT
RESERVE/OVERFLOW
TANK. TEMPERATURE
GAUGE IS IN NORMAL
RANGE1. Level changes are to be expected
as coolant volume fluctuates with
engine temperature. If the level in
the tank was between the FULL and
ADD marks at normal operating
temperature, the level should return
to within that range after operation
at elevated temperatures.1. A normal condition. No repair is necessary.
FAN RUNS ALL THE
TIME1. Fan control sensors inoperative. 1. Check for DTC's. Verify sensor readings.
2. Fan control solenoid stuck9on9. 2. Check fan operation speeds. Refer to fan
speed operation table.
3. Fan control solenoid harness
damaged.3. Check for DTC 1499. Repair as required.
4. Transmission temperature too
high.4. Check for transmission over temp. DTC.
5. Engine coolant temperature too
high.5. (a) Check coolant level. Correct level as
required.
(b) Thermostat stuck. Replace thermostat.
(c) Water pump failed. Replace water pump.
(d) Coolant flow restricted. Clean radiator.
(e) Air flow over radiator obstructed.Remove
obstruction.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be added to cooling sys-
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate engine until radiator
upper hose is warm to touch. Aim the commercially
available black light tool at components to be
checked. If leaks are present, black light will cause
additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks
exist (Fig. 5).
PRESSURE TESTER METHOD
The engine should be at normal operating temper-
ature. Recheck the system cold if cause of coolant
loss is not located during the warm engine examina-
tion.
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING.
Fig. 5 Leak Detection Using Black LightÐTypical
1 - TYPICAL BLACK LIGHT TOOL
7 - 10 COOLINGWJ
COOLING (Continued)
Page 247 of 2199

ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLANT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLANT.......25
DESCRIPTION - HOAT COOLANT.........25
OPERATION...........................26
COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION.........................27
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................28
REMOVAL.............................29
CLEANING............................30
INSTALLATION.........................30
RADIATOR FAN - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................31
REMOVAL.............................31
CLEANING............................32
INSPECTION..........................32
INSTALLATION.........................32
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.7L ENGINE............32
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.0L ENGINE............32
OPERATION...........................33
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE BLOCK
HEATER ............................33
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐ4.7L ENGINE...............33
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE...............34
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATIONÐ4.7L ENGINE...........34
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE...........34
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE...............35
REMOVALÐ4.7L ENGINE...............36
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE...........36
INSTALLATIONÐ4.7L ENGINE...........36
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.7L ENGINE............36
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.0L ENGINE............37
OPERATION...........................37DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐTHERMOSTAT . . . 37
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE...............38
REMOVALÐ4.7L ENGINE...............38
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE...........38
INSTALLATIONÐ4.7L ENGINE...........39
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................40
OPERATION...........................40
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐVISCOUS FAN
DRIVE..............................40
PWM FAN CONTROL MODULE - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................41
REMOVAL.............................41
INSTALLATION.........................42
RADIATOR - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION.........................42
REMOVAL.............................42
CLEANING............................43
INSPECTION..........................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
RADIATOR - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................44
REMOVAL.............................44
CLEANING............................46
INSPECTION..........................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
RADIATOR FAN MOTOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐELECTRIC
COOLING FAN........................47
WATER PUMP - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONÐWATER PUMP...........47
DESCRIPTIONÐWATER PUMP BYPASS....47
OPERATION
OPERATIONÐWATER PUMP............47
OPERATIONÐWATER PUMP BYPASS.....48
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐWATER PUMP . . . 48
REMOVAL.............................49
CLEANING............................49
INSPECTION..........................49
INSTALLATION.........................49
WATER PUMP - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................50
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐWATER PUMP . . . 50
REMOVAL.............................51
CLEANING............................52
7 - 24 ENGINEWJ
Page 248 of 2199

INSPECTION..........................52
INSTALLATION.........................52
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................53
OPERATION...........................53
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐRADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP......................53CLEANING............................53
INSPECTION..........................54
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
REMOVAL.............................54
INSTALLATION.........................54
COOLANT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLANT
ETHYLENE-GLYCOL MIXTURES
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethyl-
ene-glycol.
The required ethylene-glycol (antifreeze) and water
mixture depends upon the climate and vehicle oper-
ating conditions. The recommended mixture of 50/50
ethylene-glycol and water will provide protection
against freezing to -37 deg. C (-35 deg. F). The anti-
freeze concentrationmust alwaysbe a minimum of
44 percent, year-round in all climates.If percentage
is lower than 44 percent, engine parts may be
eroded by cavitation, and cooling system com-
ponents may be severely damaged by corrosion.
Maximum protection against freezing is provided
with a 68 percent antifreeze concentration, which
prevents freezing down to -67.7 deg. C (-90 deg. F). A
higher percentage will freeze at a warmer tempera-
ture. Also, a higher percentage of antifreeze can
cause the engine to overheat because the specific
heat of antifreeze is lower than that of water.
Use of 100 percent ethylene-glycol will cause for-
mation of additive deposits in the system, as the cor-
rosion inhibitive additives in ethylene-glycol require
the presence of water to dissolve. The deposits act as
insulation, causing temperatures to rise to as high as
149 deg. C (300) deg. F). This temperature is hot
enough to melt plastic and soften solder. The
increased temperature can result in engine detona-
tion. In addition, 100 percent ethylene-glycol freezes
at 22 deg. C (-8 deg. F ).
PROPYLENE-GLYCOL MIXTURES
It's overall effective temperature range is smaller
than that of ethylene-glycol. The freeze point of 50/50
propylene-glycol and water is -32 deg. C (-26 deg. F).
5 deg. C higher than ethylene-glycol's freeze point.
The boiling point (protection against summer boil-
over) of propylene-glycol is 125 deg. C (257 deg. F )at 96.5 kPa (14 psi), compared to 128 deg. C (263
deg. F) for ethylene-glycol. Use of propylene-glycol
can result in boil-over or freeze-up on a cooling sys-
tem designed for ethylene-glycol. Propylene glycol
also has poorer heat transfer characteristics than
ethylene glycol. This can increase cylinder head tem-
peratures under certain conditions.
Propylene-glycol/ethylene-glycol Mixtures can
cause the destabilization of various corrosion inhibi-
tors, causing damage to the various cooling system
components. Also, once ethylene-glycol and propy-
lene-glycol based coolants are mixed in the vehicle,
conventional methods of determining freeze point will
not be accurate. Both the refractive index and spe-
cific gravity differ between ethylene glycol and propy-
lene glycol.
DESCRIPTION - HOAT COOLANT
WARNING: ANTIFREEZE IS AN ETHYLENE GLYCOL
BASE COOLANT AND IS HARMFUL IF SWAL-
LOWED OR INHALED. IF SWALLOWED, DRINK
TWO GLASSES OF WATER AND INDUCE VOMIT-
ING. IF INHALED, MOVE TO FRESH AIR AREA.
SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATELY. DO NOT
STORE IN OPEN OR UNMARKED CONTAINERS.
WASH SKIN AND CLOTHING THOROUGHLY AFTER
COMING IN CONTACT WITH ETHYLENE GLYCOL.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN. DISPOSE OF
GLYCOL BASE COOLANT PROPERLY, CONTACT
YOUR DEALER OR GOVERNMENT AGENCY FOR
LOCATION OF COLLECTION CENTER IN YOUR
AREA. DO NOT OPEN A COOLING SYSTEM WHEN
THE ENGINE IS AT OPERATING TEMPERATURE OR
HOT UNDER PRESSURE, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT. AVOID RADIATOR COOLING FAN WHEN
ENGINE COMPARTMENT RELATED SERVICE IS
PERFORMED, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: Use of Propylene Glycol based coolants
is not recommended, as they provide less freeze
protection and less corrosion protection.
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine metal, in
the cylinder head area near the exhaust valves and
engine block. Then coolant carries the heat to the
radiator where the tube/fin radiator can transfer the
heat to the air.
WJENGINE 7 - 25
Page 251 of 2199

²Fan control valve
²Two stage G-rotor hydraulic drive
The hydraulic fan and drive is not serviceable.
Therefore any failure of the fan blade, hydraulic fan
drive or fan shroud requires replacement of the fan
module because the fan blade and hydraulic fan drive
are matched and balanced as a system and servicing
either separately would disrupt this balance.
For hydraulic fluid routing information refer to
(Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not attempt to service the hydraulic
cooling fan or fan drive separately replace the cooling
module as an assembly. Failure to do so may cause
severe damage to the hydraulic cooling fan assembly.
OPERATION
The hydraulic radiator cooling fan used on the
Grand Cherokee with the 4.7L engine replaces both
the electric fan and the engine driven mechanical
fan. The use of this hydraulic fan provides the 4.7L
equipped Grand Cherokee with heavy trailer tow
capability while at the same time reducing unneces-
sary power drain on both the engine and the vehicles
electrical system.
HYDRAULIC FAN STRATEGY
The hydraulic radiator cooling fan is controlled by
the JTEC. A PWM (Pulse With Modulated) signal
from the JTEC controls the fan from 0 to 100% of the
available fan speed. There are four inputs to the
JTEC that determine what speed percentage of fan is
required by the vehicle. These inputs are:
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Transmission Oil Temperature
²Battery Temperature
²A/C System Pressure
By monitoring these four parameters, the JTEC
can determine if cooling airflow is required. If airflow
is required, the JTEC will slowly ramp up (speed up)
the fan speed until the parameter(s) are under con-
trol. Once the temperature or pressure is reduced to
within operating parameters the fan will ramp up,
ramp down, or hold its speed to maintain the temper-
ature / pressure requirements.
NOTE: Even if the JTEC is not requesting fan on
operation the fan blade will usually spin between
100 and 500 RPM when the vehicle is at idle. This is
due to a controlled minimum oil flow requirement
through the fan drive motor.
ACTIVATING THE HYDRAULIC FAN WITH THE DRB
Under the Engine Systems test heading, there is a
subheading. ªHydraulic fan solenoid testº, that has
the selections, on /off. Activating the fan with the
DRB will run the fan at 100% duty cycle, which will
help troubleshoot any system problems, and also help
with the deaeration procedure.
NOTE: Engine must be running to activate the fan
with the DRB.
RADIATOR COOLING FAN HYDRAULIC FLUID PATH
Hydraulic fluid is pumped through the power
steering pump, from the pump the fluid travels
though a high pressure delivery line to the fan drive
motor. As fluid is diverted through the G-rotors, rota-
tional motion is created as fluid moves from the high-
pressure (inlet) side of the motor to the low-pressure
(outlet) side. Fluid exiting the drive motor is divided
into two paths. Path one continues through a high
pressure delivery line to the vehicles steering gear to
provide steering assist. and path two sends fluid
back to the power steering pump through a low pres-
sure line. Fluid exits the steering gear under low
pressure and travels through a low pressure line to
the power steering fluid cooler to be cooled before
being returned back the the power steering fluid res-
ervoir (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 HYDRAULIC RADIATOR COOLING FAN AND
FAN DRIVE
1 - POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
2 - RADIATOR
3 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE FROM STEERING GEAR PUMP TO
HYDRAULIC FAN MOTOR
4 - HYDRAULIC FAN MOTOR
5 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE FROM HYDRAULIC FAN MOTOR TO
STEERING GEAR
6 - FAN SHROUD
7 - 28 ENGINEWJ
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 258 of 2199

(2) Insert block heater assembly with element loop
pointing at twelve o'clock (Fig. 19).
(3) With block heater fully seated, tighten center
screw to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is
used to sense engine coolant temperature. The sensor
protrudes into an engine water jacket.
The ECT sensor is a two-wire Negative Thermal
Coefficient (NTC) sensor. Meaning, as engine coolant
temperature increases, resistance (voltage) in the
sensor decreases. As temperature decreases, resis-
tance (voltage) in the sensor increases.
OPERATION
At key-on, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
sends out a regulated 5 volt signal to the ECT sensor.
The PCM then monitors the signal as it passes
through the ECT sensor to the sensor ground (sensor
return).
When the engine is cold, the PCM will operate in
Open Loop cycle. It will demand slightly richer air-
fuel mixtures and higher idle speeds. This is done
until normal operating temperatures are reached.
The PCM uses inputs from the ECT sensor for the
following calculations:
²for engine coolant temperature gauge operation
through CCD or PCI (J1850) communications
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance curves
²ASD relay shut-down times
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor key-on steps
²Pulse-width prime-shot during cranking
²O2 sensor closed loop times
²Purge solenoid on/off times
²EGR solenoid on/off times (if equipped)
²Leak Detection Pump operation (if equipped)
²Radiator fan relay on/off times (if equipped)
²Target idle speed
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. COOLING SYSTEM
MUST BE PARTIALLY DRAINED BEFORE REMOV-
ING THE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT)
SENSOR. REFER TO GROUP 7, COOLING.
(1) Partially drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 18 Drain Plug
1 - COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - BLOCK DRAIN PLUG
Fig. 19 Engine Block Heater
1 - ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
WJENGINE 7 - 35
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER (Continued)
Page 263 of 2199

FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH
- 4.0L
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: Engines equipped with serpentine drive
belts have reverse rotating fans and viscous fan
drives. They are marked with the word REVERSE to
designate their usage. Installation of the wrong fan
or viscous fan drive can result in engine overheat-
ing.
CAUTION: If the viscous fan drive is replaced
because of mechanical damage, the cooling fan
blades should also be inspected. Inspect for fatigue
cracks, loose blades, or loose rivets that could
have resulted from excessive vibration. Replace fan
blade assembly if any of these conditions are
found. Also inspect water pump bearing and shaft
assembly for any related damage due to a viscous
fan drive malfunction.
The thermal viscous fan drive (Fig. 27) is a sili-
cone-fluid-filled coupling used to connect the fan
blades to the water pump shaft. The coupling allows
the fan to be driven in a normal manner. This is
done at low engine speeds while limiting the top
speed of the fan to a predetermined maximum level
at higher engine speeds.
An electrical cooling fan located in the fan shroud
aids in low speed cooling, It is designed to augment
the viscous fan, However, it does not replace the vis-
cous fan.
OPERATION
A thermostatic bimetallic spring coil is located on
the front face of the viscous fan drive unit (Fig. 27).
This spring coil reacts to the temperature of the radi-
ator discharge air. It engages the viscous fan drive
for higher fan speed if the air temperature from the
radiator rises above a certain point. Until additional
engine cooling is necessary,the fan will remain at
a reduced rpm regardless of engine speed. Nor-
mally less than three hundred (300) rpm.
Only when sufficient heat is present, will the vis-
cous fan drive engage. This is when the air flowing
through the radiator core causes a reaction to the
bimetallic coil. It then increases fan speed to provide
the necessary additional engine cooling.
Once the engine has cooled, the radiator discharge
temperature will drop. The bimetallic coil again
reacts and the fan speed is reduced to the previous
disengaged speed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐVISCOUS FAN
DRIVE
If the fan assembly free-wheels without drag (the
fan blades will revolve more than five turns when
spun by hand), replace the fan drive. This spin test
must be performed when the engine is cool.
For the following test, the cooling system must be
in good condition. It also will ensure against exces-
sively high coolant temperature.
WARNING: BE SURE THAT THERE IS ADEQUATE
FAN BLADE CLEARANCE BEFORE DRILLING.
(1) Drill a 3.18-mm (1/8-in) diameter hole in the
top center of the fan shroud.
(2) Obtain a dial thermometer with an 8 inch stem
(or equivalent). It should have a range of -18É to
105ÉC (0É to 220É F). Insert thermometer through the
hole in the shroud. Be sure that there is adequate
clearance from the fan blades.
(3) Connect a tachometer and an engine ignition
timing light (timing light is to be used as a strobe
light).
(4) Block the air flow through the radiator. Secure
a sheet of plastic in front of the radiator (or air con-
ditioner condenser). Use tape at the top to secure the
plastic and be sure that the air flow is blocked.
(5) Be sure that the air conditioner (if equipped) is
turned off.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO
NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
Fig. 27 Viscous Fan Drive
1 - VISCOUS FAN DRIVE
2 - THERMOSTATIC SPRING
3 - MOUNTING NUT TO WATER PUMP HUB
7 - 40 ENGINEWJ