check engine light JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 62 of 2199

BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front±end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear-end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
WJFRONT AXLE - 186FBI 3 - 17
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 97 of 2199

peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
3 - 52 REAR AXLE - 198RBIWJ
REAR AXLE - 198RBI (Continued)
Page 120 of 2199

(7) Check rotating torque with an inch pound
torque wrench (Fig. 44). The rotating torque of the
pinion gear should be, the reading recorded during
removal plus an additional 0.56 N´m (5 in. lbs.).
(8) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
align.
(9) Install rear brake calipers and rotors (Refer to
5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS
- INSTALLATION).
(10) Add gear lubricant, if necessary.
(11) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(12) Remove supports and lower vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove fill hole plug from the differential
housing cover.
(3) Remove differential housing cover and drain
fluid.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with flushing oil, light
engine oil or lint free cloth.
NOTE: Do not use water, steam, kerosene or gaso-
line for cleaning.
(5) Remove axle shafts.(6)
Note the reference letters stamped on the bearing
caps and housing machined sealing surface (Fig. 45).
(7) Loosen the differential bearing cap bolts.
(8) Position Spreader W-129-B with Adapter Kit
6987B on differential locating holes (Fig. 46). Install
holddown clamps and tighten the turnbuckle finger-
tight.
Fig. 44 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
Fig. 45 BEARING CAP REFERENCE
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
Fig. 46 SPREADER LOCATION
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - DOWEL
3 - SAFETY HOLD DOWN
4 - SPREADER
5 - TURNBUCKLE
WJREAR AXLE - 198RBI 3 - 75
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER (Continued)
Page 137 of 2199

and therefore creates pressure in the pump. The tun-
ing of the front and rear axle orifices and valves
inside the gerotor pump is unique and each system
includes a torque-limiting pressure relief valve to
protect the clutch pack, which also facilitates vehicle
control under extreme side-to-side traction varia-
tions. The resulting pressure is applied to the clutch
pack and the transfer of torque is completed.
Under conditions in which opposite wheels are on
surfaces with widely different friction characteristics,
Vari-loktdelivers far more torque to the wheel on
the higher traction surface than do conventional
Trac-loktsystems. Because conventional Trac-lokt
differentials are initially pre-loaded to assure torque
transfer, normal driving (where inner and outer
wheel speeds differ during cornering, etc.) produces
torque transfer during even slight side-to-side speed
variations. Since these devices rely on friction from
this preload to transfer torque, normal use tends to
cause wear that reduces the ability of the differential
to transfer torque over time. By design, the Vari-lokt
system is less subject to wear, remaining more con-
sistent over time in its ability to transfer torque. The
coupling assembly is serviced as a unit. From a ser-
vice standpoint the coupling also benefits from using
the same lubricant supply as the ring and pinion
gears.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears, or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
3 - 92 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 160 of 2199

NOTE: If more than 380 N´m (280 ft. lbs.) torque is
required to crush the collapsible spacer, the spacer
is defective and must be replaced.
(7) Check rotating torque with an inch pound
torque wrench (Fig. 44). The rotating torque of the
pinion gear should be, the reading recorded during
removal plus an additional 0.56 N´m (5 in. lbs.).
(8)
Install propeller shaft with reference marks align.
(9) Install rear brake rotors and calipers.
(10) Add gear lubricant, if necessary.
(11) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(12) Remove supports and lower vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove fill hole plug from the differential
housing cover.
(3) Remove differential housing cover and drain
fluid.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with flushing oil, light
engine oil or lint free cloth.
NOTE: Do not use water, steam, kerosene or gaso-
line for cleaning.
(5) Remove axle shafts.(6)
Note the reference letters stamped on the bearing
caps and housing machined sealing surface (Fig. 45).
(7) Loosen the differential bearing cap bolts.
(8) Position Spreader W-129-B with Adapter Kit
6987B on differential locating holes (Fig. 46). Install
holddown clamps and tighten the turnbuckle finger-
tight.
Fig. 44 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
Fig. 45 BEARING CAP REFERENCE
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
Fig. 46 SPREADER LOCATION
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - DOWEL
3 - SAFETY HOLD DOWN
4 - SPREADER
5 - TURNBUCKLE
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 115
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER (Continued)
Page 178 of 2199

(2) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(3) Inspect brake fluid level and condition. Note
that the brake reservoir fluid level will decrease in
proportion to normal lining wear.Also note that
brake fluid tends to darken over time. This is
normal and should not be mistaken for contam-
ination.
(a) If fluid level is abnormally low, look for evi-
dence of leaks at calipers, brake lines, master cyl-
inder, and HCU.
(b) If fluid appears contaminated, drain out a
sample to examine. System will have to be flushed
if fluid is separated into layers, or contains a sub-
stance other than brake fluid. The system seals,
cups, hoses, master cylinder, and HCU will also
have to be replaced after flushing. Use clean brake
fluid to flush the system.
(4) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and lever. Also
note if vehicle was being operated with parking
brake partially applied.
(5) Check brake pedal operation. Verify that pedal
does not bind and has adequate free play. If pedal
lacks free play, check pedal and power booster for
being loose or for bind condition. Do not road test
until condition is corrected.
(6) Check booster vacuum check valve and hose.
(7) If components checked appear OK, road test
the vehicle.
ROAD TESTING
(1) If complaint involved low brake pedal, pump
pedal and note if it comes back up to normal height.
(2) Check brake pedal response with transmission
in neutral and engine running. Pedal should remain
firm under constant foot pressure.
(3) During road test, make normal and firm brake
stops in 25-40 mph range. Note faulty brake opera-
tion such as low pedal, hard pedal, fade, pedal pulsa-
tion, pull, grab, drag, noise, etc.
(4) Attempt to stop the vehicle with the parking
brake only (do not exceed 25 mph) and note grab,
drag, noise, etc.
PEDAL FALLS AWAY
A brake pedal that falls away under steady foot
pressure is generally the result of a system leak. The
leak point could be at a brake line, fitting, hose, or
caliper. If leakage is severe, fluid will be evident at
or around the leaking component.Internal leakage (seal by-pass) in the master cylin-
der caused by worn or damaged piston cups, may
also be the problem cause.
An internal leak in the ABS system may also be
the problem with no visual fluid leak.
LOW PEDAL
If a low pedal is experienced, pump the pedal sev-
eral times. If the pedal comes back up, the most
likely causes are worn linings, rotors, or calipers are
not sliding on the slide pins. The proper course of
action is to inspect and replace all worn component.
SPONGY PEDAL
A spongy pedal is most often caused by air in the
system. However substandard brake hoses can cause
a spongy pedal. The proper course of action is to
bleed the system, and replace substandard quality
brake hoses if suspected.
HARD PEDAL OR HIGH PEDAL EFFORT
A hard pedal or high pedal effort may be due to
lining that is water soaked, contaminated, glazed, or
badly worn. The power booster, check valve, check
valve seal/grommet or vacuum leak could also cause
a hard pedal or high pedal effort.
PEDAL PULSATION
Pedal pulsation is caused by components that are
loose, or beyond tolerance limits.
The primary cause of pulsation are disc brake
rotors with excessive lateral runout or thickness vari-
ation. Other causes are loose wheel bearings or cali-
pers and worn, damaged tires.
NOTE: Some pedal pulsation may be felt during
ABS activation.
BRAKE DRAG
Brake drag occurs when the lining is in constant
contact with the rotor or drum. Drag can occur at one
wheel, all wheels, fronts only, or rears only.
Drag is a product of incomplete brake release.
Drag can be minor or severe enough to overheat the
linings, rotors and park brake drums.
Minor drag will usually cause slight surface charring
of the lining. It can also generate hard spots in rotors
and park brake drums from the overheat-cool down pro-
cess. In most cases, the rotors, wheels and tires are
quite warm to the touch after the vehicle is stopped.
Severe drag can char the brake lining all the way
through. It can also distort and score rotors to the
point of replacement. The wheels, tires and brake
components will be extremely hot. In severe cases,
the lining may generate smoke as it chars from over-
heating.
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 3
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 199 of 2199

OPERATION
The master cylinder bore contains a primary and
secondary piston. The primary piston supplies
hydraulic pressure to the front brakes. The secondary
piston supplies hydraulic pressure to the rear brakes.
The master cylinder reservoir stores reserve brake
fluid for the hydraulic brake circuits.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MASTER
CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER
NOTE: Inspect and repair any external fluid leaks
before performing test.
(1) Start engine and check booster vacuum hose
connections. A hissing noise indicates vacuum leak.
Correct any vacuum leak before proceeding.
(2)
Stop engine and shift transmission into Neutral.
(3) Pump brake pedal until all vacuum reserve in
booster is depleted.
(4) Press and hold brake pedal under light foot
pressure. The pedal should hold firm, if the pedal
falls away the master cylinder or HCU may be faulty
(internal leakage).
(5) Start engine and note pedal action. It should
fall away slightly under light foot pressure then hold
firm. If no pedal action is discernible, power booster,
vacuum supply, or vacuum check valve is faulty. Pro-
ceed to the POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST.
(6) If the POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
passes, rebuild booster vacuum reserve as follows:
Release brake pedal. Increase engine speed to 1500
rpm, close the throttle and turn off the engine.
(7) Wait a minimum of 90 seconds and try brake
action again. Booster should provide two or more vac-
uum assisted pedal applications. If vacuum assist is
not provided, some component of the booster is faulty.
POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
(1) Connect vacuum gauge to booster check valve
with short length of hose and T-fitting (Fig. 48).
(2) Start and run engine at curb idle speed for one
minute.
(3) Observe the vacuum supply. If vacuum supply
is not adequate, repair vacuum supply.
(4) Clamp hose shut between vacuum source and
check valve.
(5) Stop engine and observe vacuum gauge.
(6) If vacuum drops more than one inch HG (33
millibars) within 15 seconds, booster diaphragm,
check valve or check valve seal/grommet is faulty.
POWER BOOSTER CHECK VALVE TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose from check valve.
(2)
Remove check valve and valve seal from booster.
(3) Use a hand operated vacuum pump for test.(4) Apply 51-67 kPa (15-20 in.) vacuum at large
end of check valve (Fig. 49).
(5) Vacuum should hold steady. If gauge on pump
indicates vacuum loss the check valve and seal
should be replaced.
Fig. 48 Typical Booster Vacuum Test Connections
1 - TEE FITTING
2 - SHORT CONNECTING HOSE
3 - CHECK VALVE
4 - CHECK VALVE HOSE
5 - CLAMP TOOL
6 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
7 - VACUUM GAUGE
Fig. 49 Vacuum Check Valve And Seal
1 - BOOSTER CHECK VALVE
2 - APPLY TEST VACUUM HERE
3 - VALVE SEAL
5 - 24 BRAKES - BASEWJ
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 206 of 2199

REMOVAL
(1) Remove the master cylinder.
(2) Disconnect vacuum hose at booster check valve.
(3) Remove retainer clip (Fig. 60) that holds
booster push rod on pedal pin. Then slide push rod
off pin.
(4) Remove four nuts (Fig. 61) that attach booster
to dash panel.
(5) In engine compartment, slide booster forward,
tilt it upward slightly, and remove it from engine
compartment.
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of grommet that secures check
valve in booster. Replace grommet if cut, torn, or
loose.
(2) Install new booster dash seal.
(3) Align and position booster on engine compart-
ment side of dash panel.
(4) Inside passenger compartment:
(a) Lubricate pedal pin Mopar multi-mileage
grease.
(b) Install booster attaching nuts on studs.
Tighten attaching nuts to 39 N´m (29 ft. lbs.).
(c) Slide booster push rod on pedal pin. Then
secure rod to pin with retainer clip.
(5) In engine compartment, attach vacuum hose to
booster check valve.(6) Install the master cylinder with new gasket
and nuts.
CAUTION: The master cylinder installation proce-
dure must be perform as written or damage to the
booster/master cylinder may occur.
(7) Fill and bleed brake system.
ROTORS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FRONT DISC
BRAKE ROTOR
ROTOR MINIMUM THICKNESS
Rotor minimum usable thickness is 24.5 mm (0.964
in.). Do not resurface a rotor if machining would
cause thickness to fall below this limit.
Measure rotor thickness at the center of the brake
shoe contact surface. Replace the rotor if worn below
minimum thickness, or if refinishing would reduce
thickness below the allowable minimum.
FRONT ROTOR THICKNESS VARIATION
Variations in rotor thickness will cause pedal pul-
sation, noise and shudder.
Fig. 60 Retainer Clip
1 - RETAINER CLIP
2 - PUSH ROD
3 - PEDAL PIN
Fig. 61 Power Brake Booster Mounting
1 - BOOSTER
2 - DASH PANEL
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 31
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER (Continued)
Page 230 of 2199
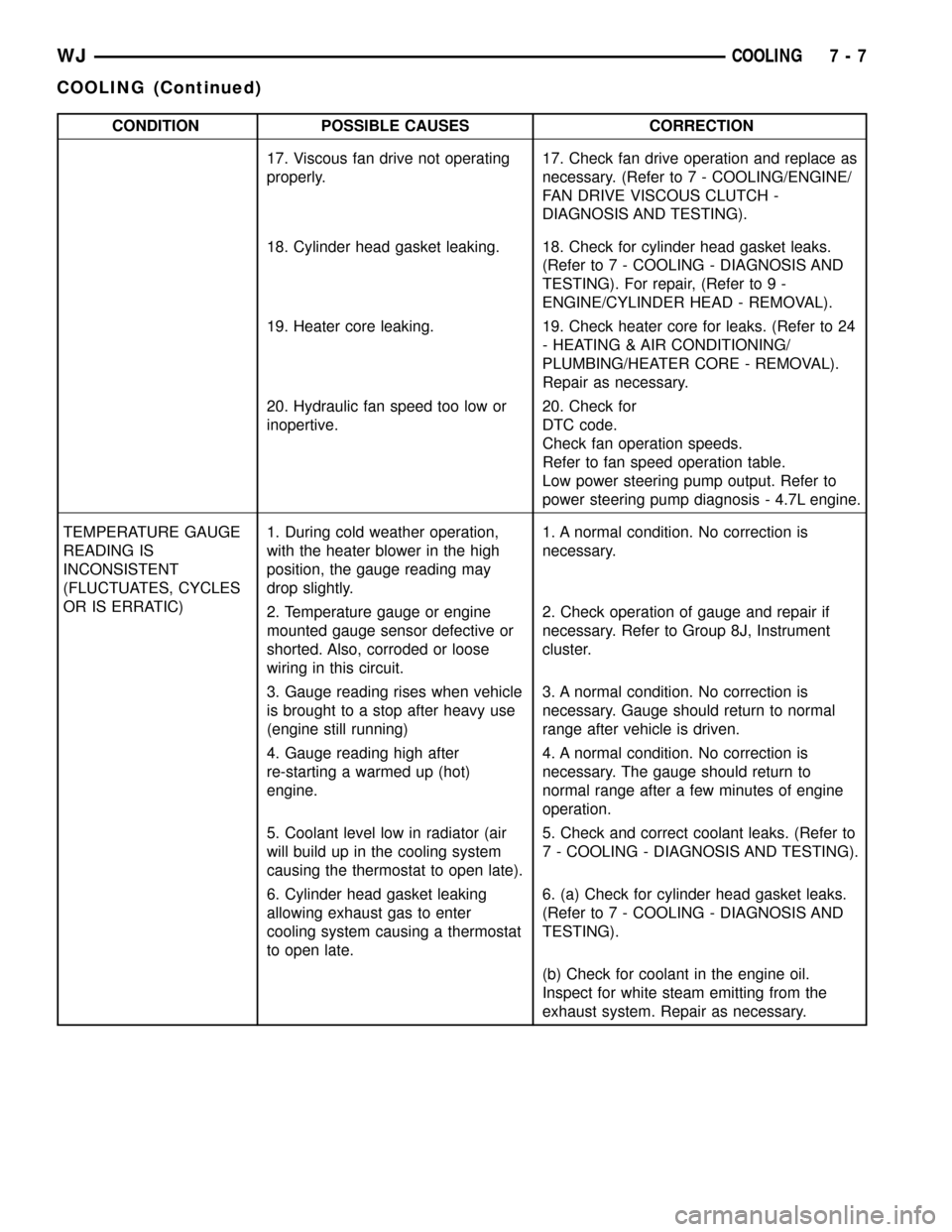
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
17. Viscous fan drive not operating
properly.17. Check fan drive operation and replace as
necessary. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
18. Cylinder head gasket leaking. 18. Check for cylinder head gasket leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). For repair, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
19. Heater core leaking. 19. Check heater core for leaks. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/HEATER CORE - REMOVAL).
Repair as necessary.
20. Hydraulic fan speed too low or
inopertive.20. Check for
DTC code.
Check fan operation speeds.
Refer to fan speed operation table.
Low power steering pump output. Refer to
power steering pump diagnosis - 4.7L engine.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READING IS
INCONSISTENT
(FLUCTUATES, CYCLES
OR IS ERRATIC)1. During cold weather operation,
with the heater blower in the high
position, the gauge reading may
drop slightly.1. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary.
2. Temperature gauge or engine
mounted gauge sensor defective or
shorted. Also, corroded or loose
wiring in this circuit.2. Check operation of gauge and repair if
necessary. Refer to Group 8J, Instrument
cluster.
3. Gauge reading rises when vehicle
is brought to a stop after heavy use
(engine still running)3. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary. Gauge should return to normal
range after vehicle is driven.
4. Gauge reading high after
re-starting a warmed up (hot)
engine.4. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary. The gauge should return to
normal range after a few minutes of engine
operation.
5. Coolant level low in radiator (air
will build up in the cooling system
causing the thermostat to open late).5. Check and correct coolant leaks. (Refer to
7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Cylinder head gasket leaking
allowing exhaust gas to enter
cooling system causing a thermostat
to open late.6. (a) Check for cylinder head gasket leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(b) Check for coolant in the engine oil.
Inspect for white steam emitting from the
exhaust system. Repair as necessary.
WJCOOLING 7 - 7
COOLING (Continued)
Page 233 of 2199
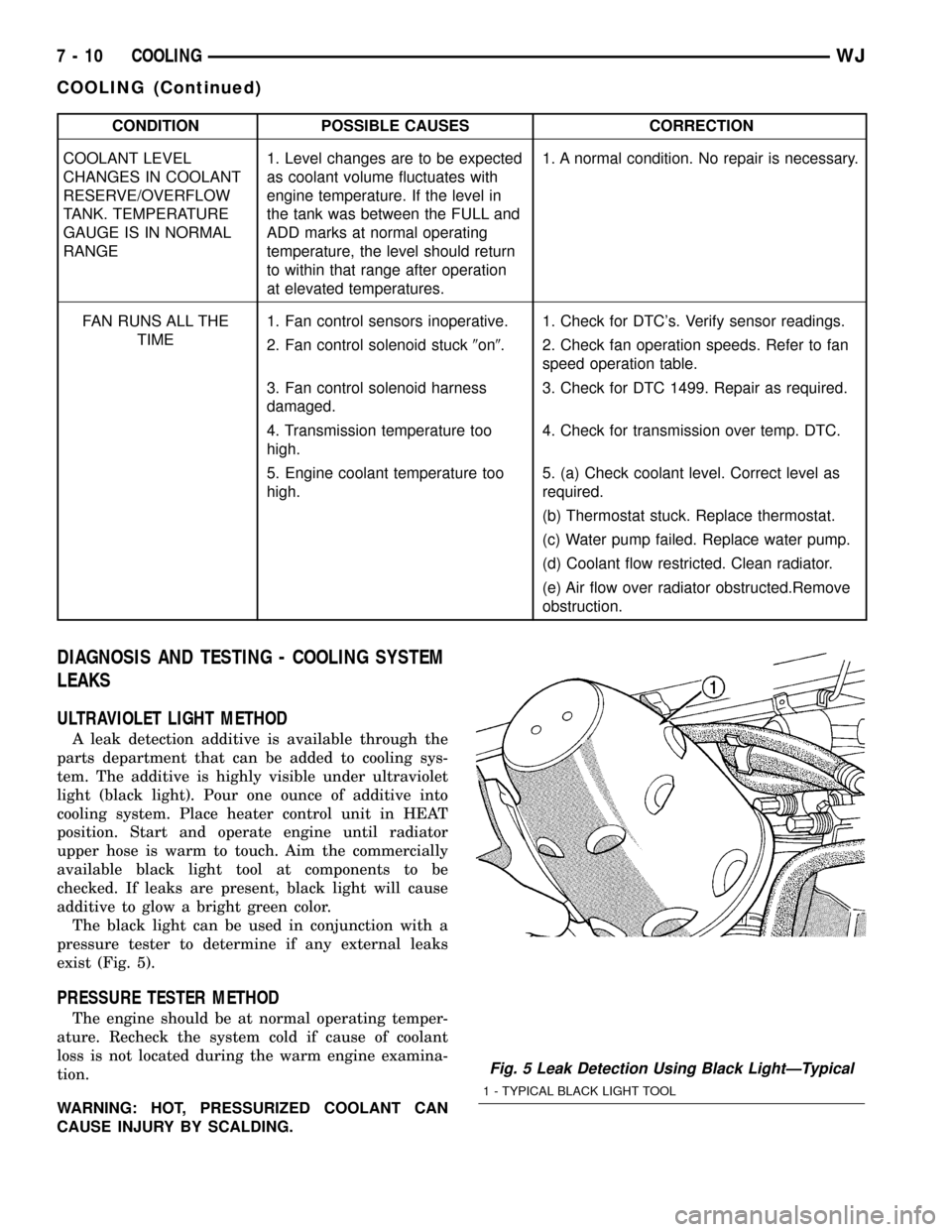
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
COOLANT LEVEL
CHANGES IN COOLANT
RESERVE/OVERFLOW
TANK. TEMPERATURE
GAUGE IS IN NORMAL
RANGE1. Level changes are to be expected
as coolant volume fluctuates with
engine temperature. If the level in
the tank was between the FULL and
ADD marks at normal operating
temperature, the level should return
to within that range after operation
at elevated temperatures.1. A normal condition. No repair is necessary.
FAN RUNS ALL THE
TIME1. Fan control sensors inoperative. 1. Check for DTC's. Verify sensor readings.
2. Fan control solenoid stuck9on9. 2. Check fan operation speeds. Refer to fan
speed operation table.
3. Fan control solenoid harness
damaged.3. Check for DTC 1499. Repair as required.
4. Transmission temperature too
high.4. Check for transmission over temp. DTC.
5. Engine coolant temperature too
high.5. (a) Check coolant level. Correct level as
required.
(b) Thermostat stuck. Replace thermostat.
(c) Water pump failed. Replace water pump.
(d) Coolant flow restricted. Clean radiator.
(e) Air flow over radiator obstructed.Remove
obstruction.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be added to cooling sys-
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate engine until radiator
upper hose is warm to touch. Aim the commercially
available black light tool at components to be
checked. If leaks are present, black light will cause
additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks
exist (Fig. 5).
PRESSURE TESTER METHOD
The engine should be at normal operating temper-
ature. Recheck the system cold if cause of coolant
loss is not located during the warm engine examina-
tion.
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING.
Fig. 5 Leak Detection Using Black LightÐTypical
1 - TYPICAL BLACK LIGHT TOOL
7 - 10 COOLINGWJ
COOLING (Continued)