ECO mode JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1605 of 2199
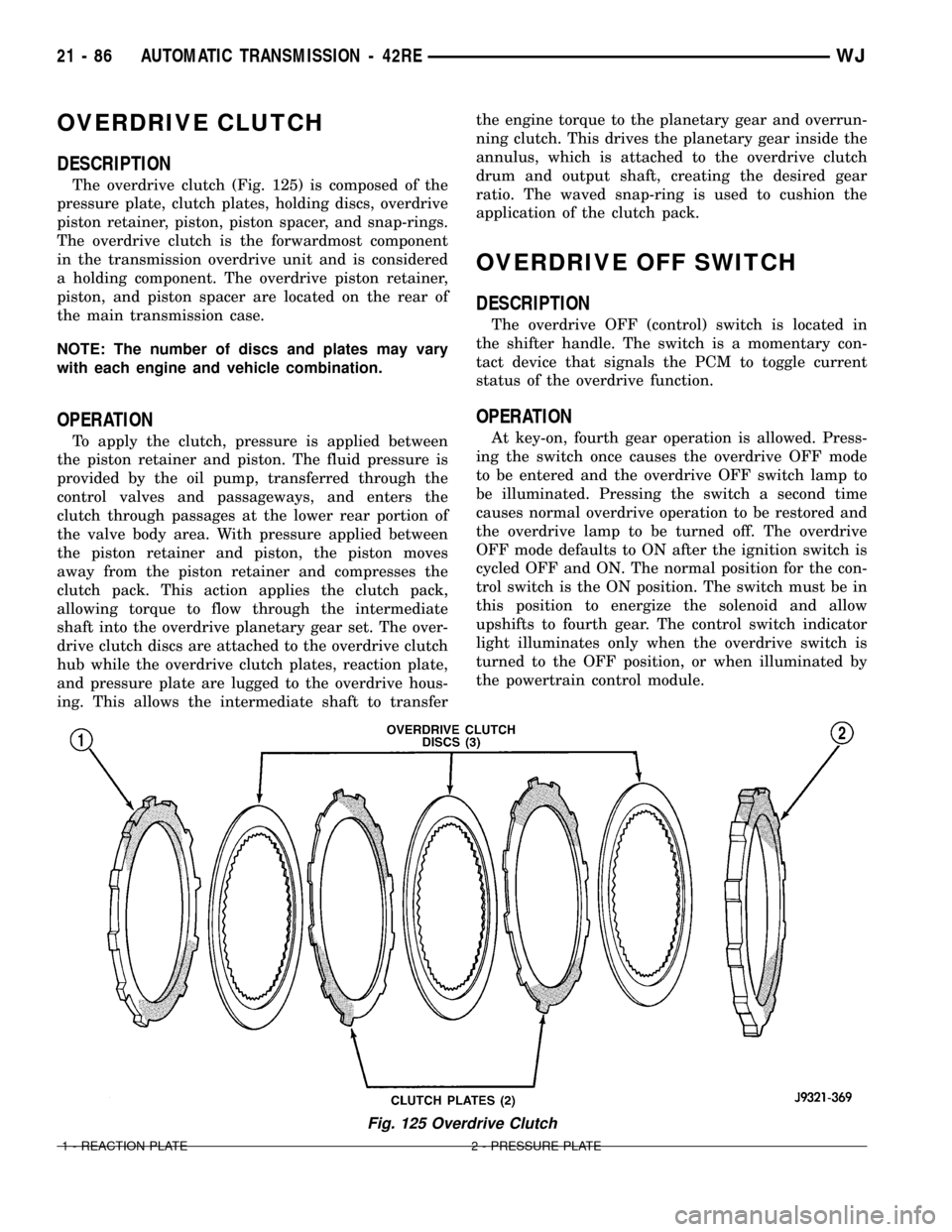
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive clutch (Fig. 125) is composed of the
pressure plate, clutch plates, holding discs, overdrive
piston retainer, piston, piston spacer, and snap-rings.
The overdrive clutch is the forwardmost component
in the transmission overdrive unit and is considered
a holding component. The overdrive piston retainer,
piston, and piston spacer are located on the rear of
the main transmission case.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the piston retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through passages at the lower rear portion of
the valve body area. With pressure applied between
the piston retainer and piston, the piston moves
away from the piston retainer and compresses the
clutch pack. This action applies the clutch pack,
allowing torque to flow through the intermediate
shaft into the overdrive planetary gear set. The over-
drive clutch discs are attached to the overdrive clutch
hub while the overdrive clutch plates, reaction plate,
and pressure plate are lugged to the overdrive hous-
ing. This allows the intermediate shaft to transferthe engine torque to the planetary gear and overrun-
ning clutch. This drives the planetary gear inside the
annulus, which is attached to the overdrive clutch
drum and output shaft, creating the desired gear
ratio. The waved snap-ring is used to cushion the
application of the clutch pack.
OVERDRIVE OFF SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive OFF (control) switch is located in
the shifter handle. The switch is a momentary con-
tact device that signals the PCM to toggle current
status of the overdrive function.
OPERATION
At key-on, fourth gear operation is allowed. Press-
ing the switch once causes the overdrive OFF mode
to be entered and the overdrive OFF switch lamp to
be illuminated. Pressing the switch a second time
causes normal overdrive operation to be restored and
the overdrive lamp to be turned off. The overdrive
OFF mode defaults to ON after the ignition switch is
cycled OFF and ON. The normal position for the con-
trol switch is the ON position. The switch must be in
this position to energize the solenoid and allow
upshifts to fourth gear. The control switch indicator
light illuminates only when the overdrive switch is
turned to the OFF position, or when illuminated by
the powertrain control module.
Fig. 125 Overdrive Clutch
1 - REACTION PLATE 2 - PRESSURE PLATE
21 - 86 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
Page 1698 of 2199
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan
sealing surface (Fig. 1). Refer to this information
when ordering replacement parts. A label is attached
to the transmission case above the stamped numbers.
The label gives additional information which may
also be necessary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS The 545RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime............................1.50:1
3rd .................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
5th .................................0.67:1
Reverse..............................3.00:1
OPERATION
The 545RFE offers full electronic control of all auto-
matic up and downshifts, and features real-time adap-
tive closed-loop shift and pressure control. Electronic
shift and torque converter clutch controls help protect
the transmission from damage due to high tempera-
tures, which can occur under severe operating condi-
tions. By altering shift schedules, line pressure, and
converter clutch control, these controls reduce heat gen-
eration and increase transmission cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses,
the transmission includes a dual-stage transmission
fluid pump with electronic output pressure control.
Under most driving conditions, pump output pres-
sure greatly exceeds that which is needed to keep the
clutches applied. The 545RFE pump-pressure controlsystem monitors input torque and adjusts the pump
pressure accordingly. The primary stage of the pump
works continuously; the second stage is bypassed
when demand is low. The control system also moni-
tors input and output speed and, if incipient clutch
slip is observed, the pressure control solenoid duty
cycle is varied, increasing pressure in proportion to
demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly
allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to
reduce slippage. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce
internal friction. The 545RFE is packaged in a one-
piece die-cast aluminum case. To reduce NVH, the
case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiffness.
It is also designed to maximize the benefit of the
structural dust cover that connects the bottom of the
bell housing to the engine bedplate, enhancing over-
all power train stiffness. Dual filters protect the
pump and other components. A pump return filter is
added to the customary main sump filter. Indepen-
dent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample
pressure for normal transmission operation even if
the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due
to extremely low temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without elec-
tronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK,
REVERSE, NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears,
based solely on driver shift lever selection. This
design allows the vehicle to be driven (in ªlimp-inº
mode) in the event of a electronic control system fail-
ure, or a situation that the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to
the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a
545RFE automatic transmission, check for Diagnos-
tic Trouble Codes with the DRBTscan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Fig. 1 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 179
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1773 of 2199

OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Input and Output Speed Sensors are two-wire
magnetic pickup devices that generate AC signals as
rotation occurs. They are mounted in the left side of
the transmission case and are considered primary
inputs to the Transmission Control Module (TCM).
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil, an AC
voltage is generated and sent to the TCM. The TCM
interprets this information as input shaft rpm.
The Output Speed Sensor generates an AC signal
in a similar fashion, though its coil is excited by rota-
tion of the rear planetary carrier lugs. The TCM
interprets this information as output shaft rpm.
The TCM compares the input and output speed
signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The TCM also compares the input speed signal and
the engine speed signal to determine the following:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable fluid catch pan under the
transmission.
(3) Remove the wiring connector from the output
speed sensor (Fig. 96).
(4) Remove the bolt holding the output speed sen-
sor to the transmission case.
(5) Remove the output speed sensor from the
transmission case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the output speed sensor into the trans-
mission case.
(2) Install the bolt to hold the output speed sensor
into the transmission case. Tighten the bolt to 11.9
N´m (105 in.lbs.).
(3) Install the wiring connector onto the output
speed sensor
(4) Verify the transmission fluid level. Add fluid as
necessary.
(5) Lower vehicle.
OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive OFF (control) switch is located in
the shifter handle. The switch is a momentary con-
tact device that signals the PCM to toggle current
status of the overdrive function.
OPERATION
At key-on, fourth and fifth gear operation is
allowed. Pressing the switch once causes the over-
drive OFF mode to be entered and the overdrive OFF
switch lamp to be illuminated. Pressing the switch a
second time causes normal overdrive operation to be
restored and the overdrive lamp to be turned off. The
overdrive OFF mode defaults to ON after the ignition
switch is cycled OFF and ON. The normal position
for the control switch is the ON position. The switch
must be in this position to energize the solenoids and
allow upshifts to fourth and fifth gears. The control
switch indicator light illuminates only when the over-
drive switch is turned to the OFF position, or when
illuminated by the transmission control module.
Fig. 96 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
21 - 254 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1789 of 2199

(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized
by the TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal oper-
ating mode.
OPERATION
When the relay is ªoffº, no power is supplied to the
solenoid pack and the transmission is in ªlimp-inº
mode. After a controller reset, the TCM energizes the
relay. Prior to this, the TCM verifies that the con-
tacts are open by checking for no voltage at the
switched battery terminals. After this is verified, the
voltage at the solenoid pack pressure switches is
checked. After the relay is energized, the TCM mon-
itors the terminals to verify that the voltage is
greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is part of
the solenoid module, which is mounted to the top of
the valve body inside the transmission.
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has five
switch contact pins that:
²Determine shift lever position
²Supply ground to the Starter Relay in Park and
Neutral only.
²Supply +12 V to the backup lamps in Reverse
only.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transmission
temperature to the TCM and PCM.
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) communi-
cates shift lever position to the TCM as a combina-
tion of open and closed switches. Each shift lever
position has an assigned combination of switch states
(open/closed) that the TCM receives from four sense
circuits. The TCM interprets this information and
determines the appropriate transmission gear posi-
tion and shift schedule.
There are many possible combinations of open and
closed switches (codes). Seven of these possible codes
are related to gear position and five are recognized
as ªbetween gearº codes. This results in many codes
which shouldnever occur. These are called
ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result in a DTC,
and the TCM will then determine the shift lever
position based on pressure switch data. This allows
reasonably normal transmission operation with a
TRS failure.
GEAR C5 C4 C3 C2 C1
ParkCL OP OP CL CL
Temp 1CL OP OP CL OP
ReverseOP OP OP CL OP
Temp 2OP OP CL CL OP
Neutral 1OP OP CL CL CL
Neutral 2OP CL CL CL CL
Temp 3OP CL CL CL OP
DriveOP CL CL OP OP
Temp 4OP CL OP OP OP
Manual 2CL CL OP OP OP
Temp 5CL OP OP OP OP
Manual 1CL OP CL OP OP
Fig. 117 Checking Torque Converter Seating-Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 270 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1865 of 2199
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRES
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
²Rapid acceleration
²Severe brake applications
²High speed driving
²Excessive speeds on turns
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
Radial-ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation.(Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE),
This will help to achieve a greater tread life.
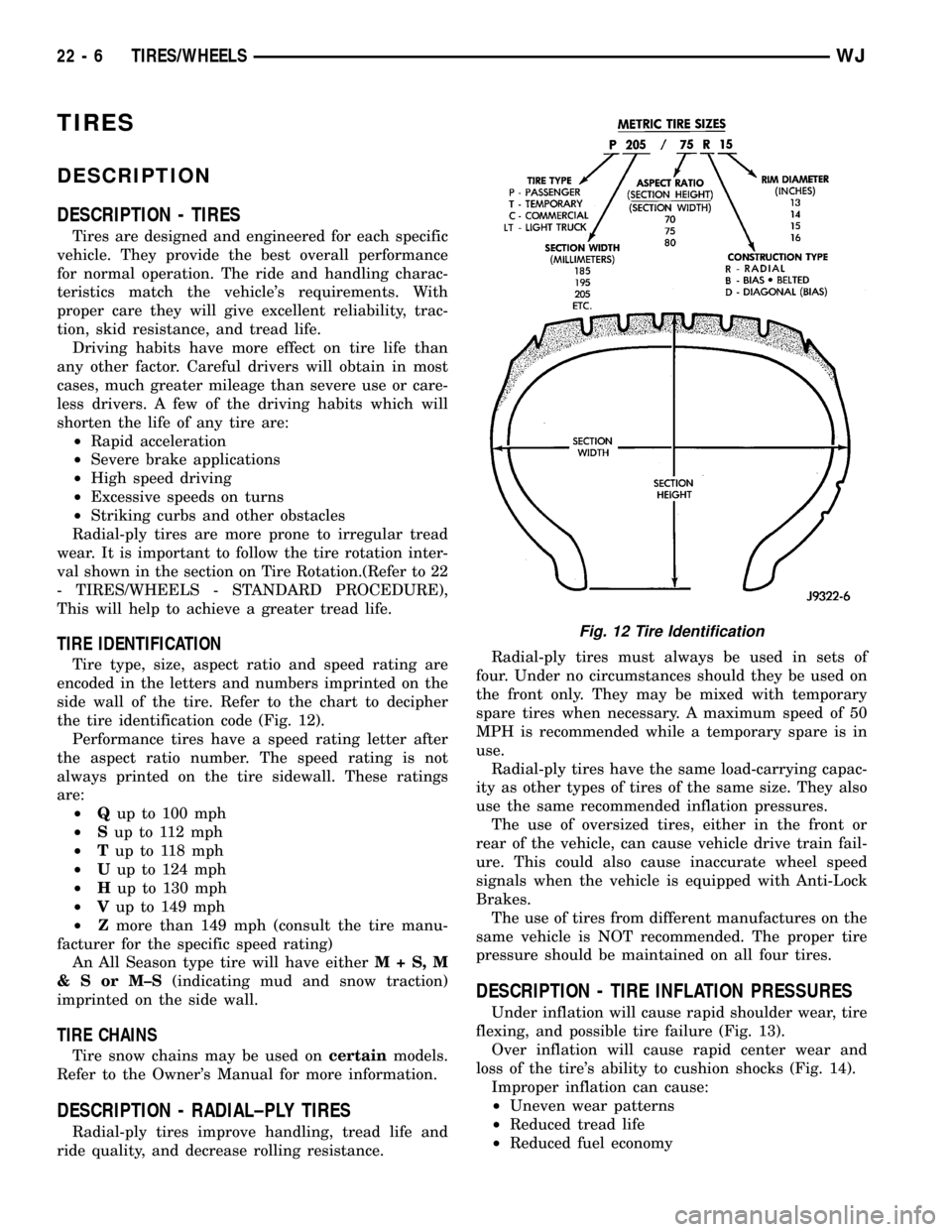
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 12).
Performance tires have a speed rating letter after
the aspect ratio number. The speed rating is not
always printed on the tire sidewall. These ratings
are:
²Qup to 100 mph
²Sup to 112 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manu-
facturer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorM±S(indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used oncertainmodels.
Refer to the Owner's Manual for more information.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL±PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the
same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire
pressure should be maintained on all four tires.
DESCRIPTION - TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
Under inflation will cause rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and possible tire failure (Fig. 13).
Over inflation will cause rapid center wear and
loss of the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 14).
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
Fig. 12 Tire Identification
22 - 6 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 1869 of 2199

SPARE TIRE
DESCRIPTION - SPARE / TEMPORARY TIRE
The temporary spare tire is designed for emer-
gency use only. The original tire should be repaired
or replaced at the first opportunity, then reinstalled.
Do not exceed speeds of 50 M.P.H. when using the
temporary spare tire. Refer to Owner's Manual for
complete details.
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION
The rim size is on the vehicle safety certification
label located on the drivers door shut face. The size
of the rim is determined by the drivetrain package.
Original equipment wheels/rims are designed for
operation up to the specified maximum vehicle capac-
ity.
All models use stamped steel, cast aluminum or
forged aluminum wheels. Every wheel has raised sec-
tions between the rim flanges and rim drop well
called safety humps (Fig. 18) .
Initial inflation of the tire forces the bead over
these raised sections. In case of rapid loss of air pres-
sure, the raised sections help hold the tire on the
wheel.
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
applications. All aluminum and some steel wheels
have wheel stud nuts with an enlarged nose. This
enlarged nose is necessary to ensure proper retentionof the wheels. Do not use replacement studs or nuts
with a different design or lesser quality.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION
Inspect wheels for:
²Excessive run out
²Dents or cracks
²Damaged wheel lug nut holes
²Air Leaks from any area or surface of the rim
NOTE: Do not attempt to repair a wheel by hammer-
ing, heating or welding.
If a wheel is damaged an original equipment
replacement wheel should be used. When obtaining
replacement wheels, they should be equivalent in
load carrying capacity. The diameter, width, offset,
pilot hole and bolt circle of the wheel should be the
same as the original wheel.
WARNING: FAILURE TO USE EQUIVALENT
REPLACEMENT WHEELS MAY ADVERSELY
AFFECT THE SAFETY AND HANDLING OF THE
VEHICLE. USED WHEELS ARE NOT RECOM-
MENDED. THE SERVICE HISTORY OF THE WHEEL
MAY HAVE INCLUDED SEVERE TREATMENT OR
VERY HIGH MILEAGE. THE RIM COULD FAIL WITH-
OUT WARNING.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
REPLACEMENT
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
applications. They must be replaced with equivalent
parts. Do not use replacement parts of lesser quality
or a substitute design. All aluminum and some steel
wheels have wheel stud nuts which feature an
enlarged nose. This enlarged nose is necessary to
ensure proper retention of the aluminum wheels.
NOTE: Do not use chrome plated lug nuts with
chrome plated wheels.
Before installing the wheel, be sure to remove any
build up of corrosion on the wheel mounting surfaces.
Ensure wheels are installed with good metal-to-metal
contact. Improper installation could cause loosening
of wheel nuts. This could affect the safety and han-
dling of your vehicle.
To install the wheel, first position it properly on
the mounting surface. All wheel nuts should then be
tightened just snug. Gradually tighten them in
sequence to the proper torque specification.Never
use oil or grease on studs or nuts.
Wheels must be replaced if they have:
²Excessive runout
Fig. 18 Safety Rim
1 - FLANGE
2 - RIDGE
3 - WELL
22 - 10 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 1969 of 2199

SUNROOF
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
SUNROOF
DESCRIPTION.........................96
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUNROOF......96
DRAIN TUBE
REMOVAL............................100
INSTALLATION........................100
CONTROL MODULE
REMOVAL............................101
INSTALLATION........................101
DRIVE MOTOR
REMOVAL............................101
INSTALLATION........................101
WIND DEFLECTOR
REMOVAL............................102INSTALLATION........................102
GLASS PANEL
REMOVAL............................102
INSTALLATION........................103
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENTS - FIT.................103
ADJUSTMENT - TIMING...............103
SUNSHADE
REMOVAL............................103
INSTALLATION........................103
HOUSING ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL............................104
INSTALLATION........................104
SUNROOF
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: Keep fingers and other body parts out
of sunroof opening at all times.
The sunroof features a power sliding glass panel
and a sunshade which can be manually positioned
anywhere along its travel, rearward of glass panel
front edge.
The sunroof is electrically operated from a switch
located on the mini overhead console. To operate the
sunroof the ignition switch must be in the On/Run
position. The sunroof has both manual and Express
Open modes of operation when opening. To open the
sunroof in the Express Open mode, the switch is
pressed rearward for less than1 second.This causes
the sunroof glass to automatically retract and stop at
a position slightly forward of full open that reduces
low speed wind buffeting. The sunroof can also be
opened manually by pressing and holding the switch
rearward. Once the switch is held reward for more
than1 second,the glass will retract in the manual
mode. Releasing the switch at any time during travel
will cause the sunroof to stop at the current position.
To close the sunroof from an open position, the
switch must be pushed forward and held until the
sunroof glass comes to a complete stop. Releasing the
switch at any time in this mode will cause the sun-
roof to stop at the current position.
To vent the sunroof from the closed position, the
switch is pushed forward and held. Releasing theswitch at any time during travel will cause the sun-
roof to stop at the current vent position. To reach the
fully vented position, continue to hold the switch for-
ward until vent motion stops. To close the sunroof
from the vent position, push and hold the switch
rearward until the glass comes to a complete stop.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUNROOF
CAUTION: The sunroof motor is only to be powered
through the vehicle battery and vehicle wire har-
ness. Applying power to the sunroof motor leads
will cause failure of the sunroof control unit.
Before beginning sunroof diagnostics verify that all
other power accessories are in proper operating con-
dition. Refer to Sunroof Diagnostic Chart for possible
causes. If not, a common electrical problem may
exist. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams, of this
publication for circuit, splice and component descrip-
tions. Check the condition of the circuit protection
(20 amp high current fuse (battery feed) located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Check the
cover of the PDC for location of the fuse. Check for
correct operation of the sunroof delay relay. Inspect
all wiring connector pins for proper engagement and
continuity. Check for battery voltage at battery and
ignition pins of the power sunroof express module
wiring connector. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Dia-
grams, for circuit information. The controller will not
operate at less than 10 volts. Check the ground at
the sunroof express module.
Before beginning diagnosis for wind noise or water
leaks, verify that the problem was not caused by
23 - 96 SUNROOFWJ
Page 2078 of 2199

HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS.......................1
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................1
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................1
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................2
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................2DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE.......................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE.......................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT.......................6
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE................7
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS..............8
CONTROLS.............................9
DISTRIBUTION..........................36
PLUMBING.............................51
HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS
To maintain the performance level of the heating-
air conditioning system, the engine cooling system
must be properly maintained. The use of a bug
screen is not recommended. Any obstructions in front
of the radiator or condenser will reduce the perfor-
mance of the air conditioning and engine cooling sys-
tems.
The engine cooling system includes the heater core
and the heater hoses. Refer to Cooling for more infor-
mation before opening, or attempting any service to
the engine cooling system.
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER
A manual temperature control type heating-air
conditioning system is standard factory-installed
equipment on this model. An electronically controlled
Automatic Zone Control (AZC) type heating-air con-
ditioning system is an available factory-installed
option.
All vehicles are equipped with a common HVAC
housing assembly (Fig. 1). The system combines air
conditioning, heating, and ventilating capabilities in
a single unit housing mounted under the instrument
panel.DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT
The two refrigerant system service ports are used
to charge, recover/recycle, evacuate, and test the air
conditioning refrigerant system. Unique service port
coupler sizes are used on the R-134a system to
ensure that the refrigerant system is not accidentally
contaminated by the use of the wrong refrigerant
(R-12), or refrigerant system service equipment.
Fig. 1 Blend-Air HVAC System - (typical)
1 - Blend Door
2 - Expansion Valve
3 - Evaporator Core
4 - Blower Assembly
5 - Recirculation Door
6 - Evaporator Probe
7 - Heater Core
8 - Heat/Defrost Door
9 - Panel/Defrost Door
WJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1
Page 2080 of 2199
However, evaporator capacity used to reduce the
amount of moisture in the air is not wasted. Wring-
ing some of the moisture out of the air entering the
vehicle adds to the comfort of the passengers.
Although, an owner may expect too much from their
air conditioning system on humid days. A perfor-
mance test is the best way to determine whether the
system is performing up to standard. This test also
provides valuable clues as to the possible cause of
trouble with the air conditioning system.
If the vehicle has the optional Automatic Zone Control
(AZC) system, and has intermittent operational prob-
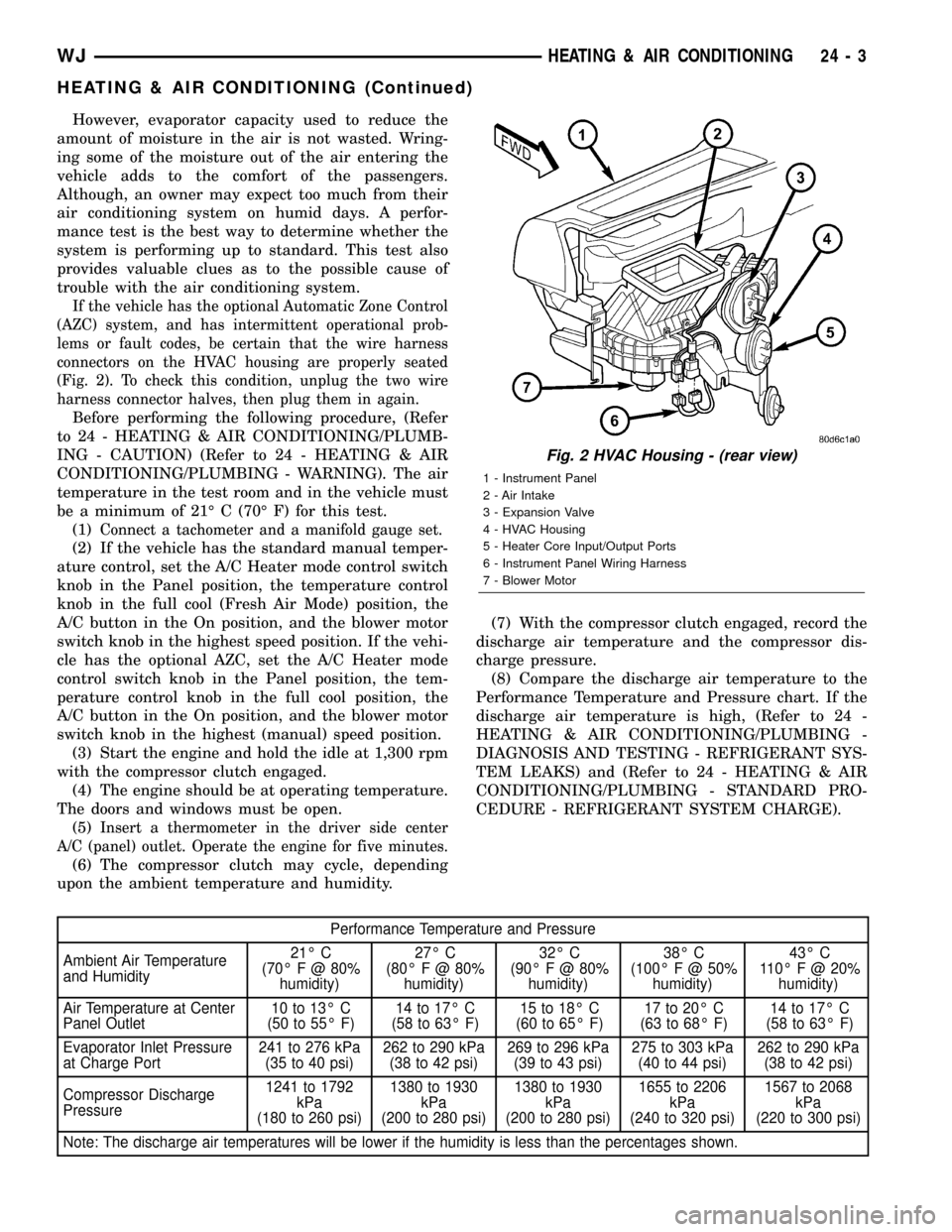
lems or fault codes, be certain that the wire harness
connectors on the HVAC housing are properly seated
(Fig. 2). To check this condition, unplug the two wire
harness connector halves, then plug them in again.
Before performing the following procedure, (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING - CAUTION) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING). The air
temperature in the test room and in the vehicle must
be a minimum of 21É C (70É F) for this test.
(1)
Connect a tachometer and a manifold gauge set.
(2) If the vehicle has the standard manual temper-
ature control, set the A/C Heater mode control switch
knob in the Panel position, the temperature control
knob in the full cool (Fresh Air Mode) position, the
A/C button in the On position, and the blower motor
switch knob in the highest speed position. If the vehi-
cle has the optional AZC, set the A/C Heater mode
control switch knob in the Panel position, the tem-
perature control knob in the full cool position, the
A/C button in the On position, and the blower motor
switch knob in the highest (manual) speed position.
(3) Start the engine and hold the idle at 1,300 rpm
with the compressor clutch engaged.
(4) The engine should be at operating temperature.
The doors and windows must be open.
(5)
Insert a thermometer in the driver side center
A/C (panel) outlet. Operate the engine for five minutes.
(6) The compressor clutch may cycle, depending
upon the ambient temperature and humidity.(7) With the compressor clutch engaged, record the
discharge air temperature and the compressor dis-
charge pressure.
(8) Compare the discharge air temperature to the
Performance Temperature and Pressure chart. If the
discharge air temperature is high, (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM LEAKS) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE).
Performance Temperature and Pressure
Ambient Air Temperature
and Humidity21É C
(70É F @ 80%
humidity)27É C
(80É F @ 80%
humidity)32É C
(90É F @ 80%
humidity)38É C
(100ÉF@50%
humidity)43É C
110É F @ 20%
humidity)
Air Temperature at Center
Panel Outlet10 to 13É C
(50 to 55É F)14 to 17É C
(58 to 63É F)15 to 18É C
(60 to 65É F)17 to 20É C
(63 to 68É F)14 to 17É C
(58 to 63É F)
Evaporator Inlet Pressure
at Charge Port241 to 276 kPa
(35 to 40 psi)262 to 290 kPa
(38 to 42 psi)269 to 296 kPa
(39 to 43 psi)275 to 303 kPa
(40 to 44 psi)262 to 290 kPa
(38 to 42 psi)
Compressor Discharge
Pressure1241 to 1792
kPa
(180 to 260 psi)1380 to 1930
kPa
(200 to 280 psi)1380 to 1930
kPa
(200 to 280 psi)1655 to 2206
kPa
(240 to 320 psi)1567 to 2068
kPa
(220 to 300 psi)
Note: The discharge air temperatures will be lower if the humidity is less than the percentages shown.
Fig. 2 HVAC Housing - (rear view)
1 - Instrument Panel
2 - Air Intake
3 - Expansion Valve
4 - HVAC Housing
5 - Heater Core Input/Output Ports
6 - Instrument Panel Wiring Harness
7 - Blower Motor
WJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 3
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2090 of 2199

A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch assembly consists of a sta-
tionary electromagnetic coil, a hub bearing and pul-
ley assembly, and a clutch plate (Fig. 4). The
electromagnetic coil unit and the hub bearing and
pulley assembly are each retained on the nose of the
compressor front housing with snap rings. The clutch
plate is keyed to the compressor shaft and secured
with a bolt.
OPERATION
The compressor clutch components provide the
means to engage and disengage the compressor from
the engine serpentine accessory drive belt. When the
clutch coil is energized, it magnetically draws the
clutch into contact with the pulley and drives the
compressor shaft. When the coil is not energized, the
pulley freewheels on the clutch hub bearing, which is
part of the pulley. The compressor clutch and coil are
the only serviced parts on the compressor.
The compressor clutch engagement is controlled by
several components: the a/c switch on the a/c heater
control panel, the Automatic Zone Control (AZC) con-
trol module (if the vehicle is so equipped), the evap-
orator probe, the a/c high pressure transducer, the
a/c compressor clutch relay, the body control module
(BCM) and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The PCM may delay compressor clutch engagement
for up to thirty seconds. Refer to Electronic Control
Modules for more information on the PCM controls.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring diagrams. The battery must be
fully-charged before performing the following tests.
Refer to Battery for more information.
(1) Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale) in
series with the clutch coil terminal. Use a voltmeter
(0 to 20 volt scale) with clip-type leads for measuring
the voltage across the battery and the compressor
clutch coil.
(2) With the a/c heater mode control switch in any
a/c mode, the a/c heater control a/c switch in the ON
position, and the blower motor switch in the lowest
speed position, start the engine and run it at normal
idle.
(3) The compressor clutch coil voltage should read
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage. If there is
voltage at the clutch coil, but the reading is not
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage, test the clutch
coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop and repair
as required. If there is no voltage reading at the
clutch coil, use a DRBIIItscan tool and the appro-
priate diagnostic information for testing of the com-
pressor clutch circuit. The following components
must be checked and repaired as required before you
can complete testing of the clutch coil:
²Fuses in the junction block and the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC)
²A/C heater mode control switch
²A/C compressor clutch relay
²A/C high pressure transducer
²A/C evaporator probe
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Body Control Module (BCM)
(4) The compressor clutch coil is acceptable if the
current draw measured at the clutch coil is 2.0 to 3.9
amperes with the electrical system voltage at 11.5 to
12.5 volts. This should only be checked with the work
area temperature at 21É C (70É F). If system voltage
is more than 12.5 volts, add electrical loads by turn-
ing on electrical accessories until the system voltage
drops below 12.5 volts.
(a) If the clutch coil current reading is four
amperes or more, the coil is shorted and should be
replaced.
(b) If the clutch coil current reading is zero, the
coil is open and should be replaced.
Fig. 4 COMPRESSOR CLUTCH - TYPICAL
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - SHAFT KEY
3 - PULLEY
4 - COIL
5 - CLUTCH SHIMS
6 - SNAP RING
7 - SNAP RING
WJCONTROLS 24 - 13