Brake line JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 183 of 2199

ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the steering column opening cover
(Fig. 2)(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER - REMOV-
AL).
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
adjustable pedal switch.
(3) Remove the switch from the steering column
opening cover by squeezing the retaining clips
together and pushing the switch outwards (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the switch to the steering column open-
ing cover by pushing the switch inwards seating the
retaining clips to the steering column opening cover
(Fig. 3).
(2) Reconnect the electrical connector to the
adjustable pedal switch.
(3) Install the steering column opening cover (Fig.
2)(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTAL-
LATION).
BRAKE LINES
DESCRIPTION
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes,
rear brakes and at the rear axle junction block. Dou-
ble walled steel tubing is used. Double inverted style
and ISO style flares are used on the brake lines.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE HOSES
AND LINES
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front and rear
brakes and at the rear axle junction block. Inspect
the hoses whenever the brake system is serviced, at
every engine oil change, or whenever the vehicle is in
for service.
Inspect the hoses for surface cracking, scuffing, or
worn spots. Replace any brake hose immediately if
the fabric casing of the hose is exposed due to cracks
or abrasions.
Also check brake hose installation. Faulty installa-
tion can result in kinked, twisted hoses, or contact
with the wheels and tires or other chassis compo-
nents. All of these conditions can lead to scuffing,
cracking and eventual failure.
The steel brake lines should be inspected periodi-
cally for evidence of corrosion, twists, kinks, leaks, or
other damage. Heavily corroded lines will eventually
rust through causing leaks. In any case, corroded or
damaged brake lines should be replaced.
Factory replacement brake lines and hoses are rec-
ommended to ensure quality, correct length and supe-
rior fatigue life. Care should be taken to make sure
that brake line and hose mating surfaces are clean
and free from nicks and burrs. Also remember that
right and left brake hoses are not interchangeable.
Use new copper gaskets at all caliper connections.
Be sure brake line connections are properly made
(not cross threaded) and tightened to recommended
torque.
Fig. 2 STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER
REMOVAL/INSTALL
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP PAD
2 - STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER
3 - SCREW (3)
Fig. 3 ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
1 - RETAINING CLIPS
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
5 - 8 BRAKES - BASEWJ
Page 184 of 2199
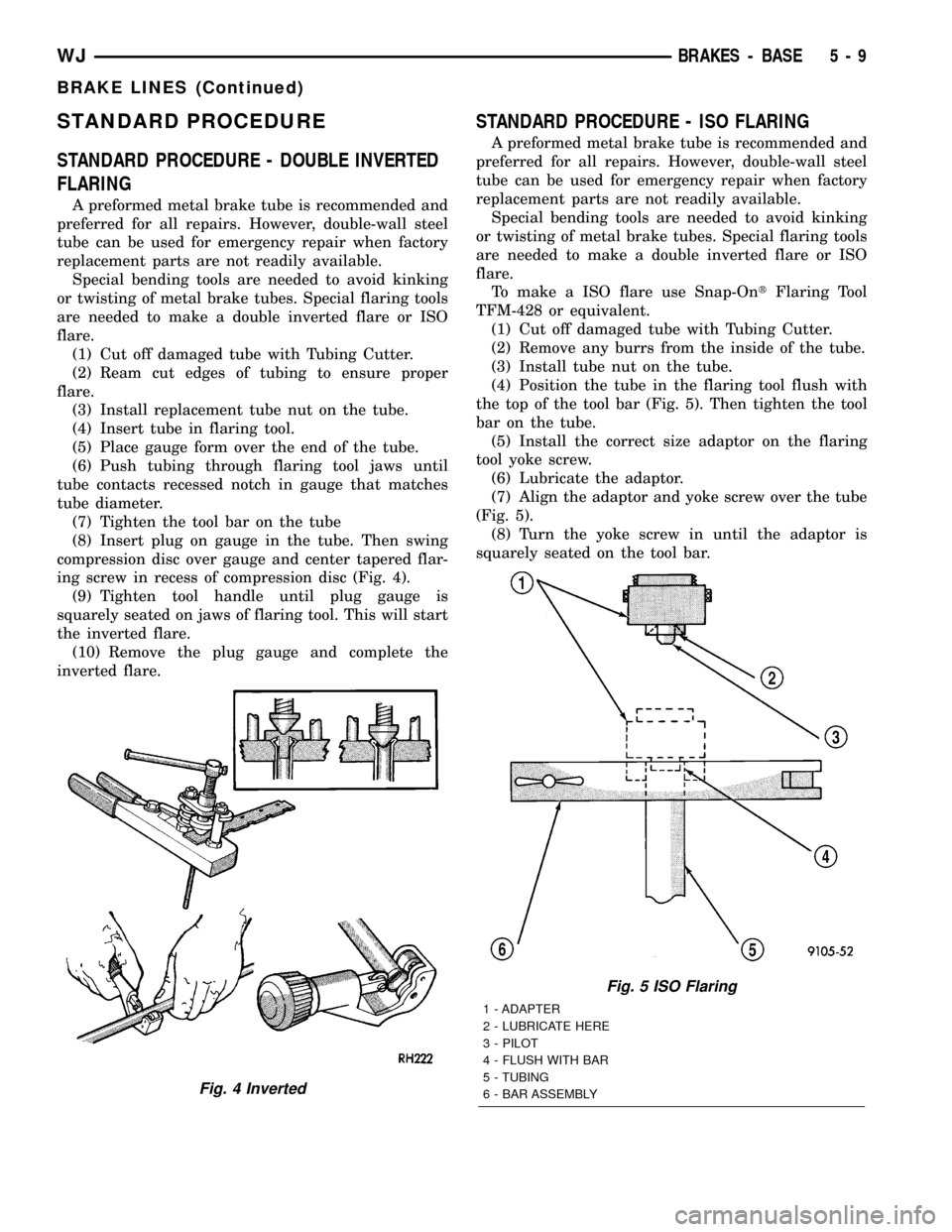
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DOUBLE INVERTED
FLARING
A preformed metal brake tube is recommended and
preferred for all repairs. However, double-wall steel
tube can be used for emergency repair when factory
replacement parts are not readily available.
Special bending tools are needed to avoid kinking
or twisting of metal brake tubes. Special flaring tools
are needed to make a double inverted flare or ISO
flare.
(1) Cut off damaged tube with Tubing Cutter.
(2) Ream cut edges of tubing to ensure proper
flare.
(3) Install replacement tube nut on the tube.
(4) Insert tube in flaring tool.
(5) Place gauge form over the end of the tube.
(6) Push tubing through flaring tool jaws until
tube contacts recessed notch in gauge that matches
tube diameter.
(7) Tighten the tool bar on the tube
(8) Insert plug on gauge in the tube. Then swing
compression disc over gauge and center tapered flar-
ing screw in recess of compression disc (Fig. 4).
(9) Tighten tool handle until plug gauge is
squarely seated on jaws of flaring tool. This will start
the inverted flare.
(10) Remove the plug gauge and complete the
inverted flare.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ISO FLARING
A preformed metal brake tube is recommended and
preferred for all repairs. However, double-wall steel
tube can be used for emergency repair when factory
replacement parts are not readily available.
Special bending tools are needed to avoid kinking
or twisting of metal brake tubes. Special flaring tools
are needed to make a double inverted flare or ISO
flare.
To make a ISO flare use Snap-OntFlaring Tool
TFM-428 or equivalent.
(1) Cut off damaged tube with Tubing Cutter.
(2) Remove any burrs from the inside of the tube.
(3) Install tube nut on the tube.
(4) Position the tube in the flaring tool flush with
the top of the tool bar (Fig. 5). Then tighten the tool
bar on the tube.
(5) Install the correct size adaptor on the flaring
tool yoke screw.
(6) Lubricate the adaptor.
(7) Align the adaptor and yoke screw over the tube
(Fig. 5).
(8) Turn the yoke screw in until the adaptor is
squarely seated on the tool bar.
Fig. 4 Inverted
Fig. 5 ISO Flaring
1 - ADAPTER
2 - LUBRICATE HERE
3 - PILOT
4 - FLUSH WITH BAR
5 - TUBING
6 - BAR ASSEMBLY
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 9
BRAKE LINES (Continued)
Page 194 of 2199

(4) Remove caliper piston dust boot with a suitable
pry tool (Fig. 34) and discard.
(5) Remove piston seal from the caliper (Fig.
35)and discard.
CAUTION: Do not scratch the piston bore while
removing the seal.
(6) Remove caliper slide pin bushings (Fig. 36).
(7) Remove caliper bleed screw.
CLEANING - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
Clean the caliper components with clean brake
fluid or brake clean only. Wipe the caliper and piston
dry with lint free towels or use low pressure com-
pressed air.
CAUTION: Do not use gasoline, kerosene, paint
thinner, or similar solvents. These products may
leave a residue that could damage the piston and
seal.
INSPECTION - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
The piston is made from a phenolic resin (plastic
material) and should be smooth and clean.
The piston must be replaced if cracked or scored.
Do not attempt to restore a scored piston surface by
sanding or polishing.
CAUTION: If the caliper piston is replaced, install
the same type of piston in the caliper. Never inter-
change phenolic resin and steel caliper pistons.
The pistons, seals, seal grooves, caliper bore and
piston tolerances are different.
The bore can belightlypolished with a brake
hone to remove very minor surface imperfections
(Fig. 37). The caliper should be replaced if the bore is
severely corroded, rusted, scored, or if polishing
would increase bore diameter more than 0.025 mm
(0.001 inch).
Fig. 34 Caliper Piston Dust
1 - PISTON DUST BOOT
2 - CALIPER
Fig. 35 Piston Seal Removal
1 - CALIPER
2 - PISTON BORE
3 - PISTON SEAL
Fig. 36 Slide Pin And Bushing
1 - BUSHING
2 - CALIPER SLIDE PIN
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 19
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS (Continued)
Page 200 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER CYLINDER
BLEEDING PROCEDURE
A new master cylinder should be bled before instal-
lation on the vehicle. Required bleeding tools include
bleed tubes and a wood dowel to stroke the pistons.
Bleed tubes can be fabricated from brake line.
(1) Mount master cylinder in vise with brass jaws.
(2) Attach bleed tubes to cylinder outlet ports.
Then position each tube end into the bottom of the
reservoir (Fig. 50).
(3) Fill reservoir with fresh brake fluid.
(4) Press cylinder pistons inward with wood dowel.
Then release pistons and allow them to return under
spring pressure. Continue bleeding operations until
air bubbles are no longer visible in fluid.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the wire connector from the brake fluid
level sensor.
(2) Remove brake lines from master cylinder.
(3) Remove nuts that attach master cylinder to
booster studs (Fig. 51).
(4) Remove master cylinder from booster.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Bleed new master cylinder on bench before
installation, refer to Service Procedures.
(1) Have an assistant depress the brake pedal
while guiding the master cylinder on the booster rod
and mounting studs.
CAUTION: Do not depress brake pedal too hard and
ensure the booster rod is in the master cylinder pis-
ton or booster/master cylinder damage will occur.(2) Install master cylinder mounting nuts and
tighten nuts to 25 N´m (18 lb. lbs.).
NOTE: Use original or factory replacement nuts only.
(3) Install brake lines and tighten to 16 N´m (144
in. lbs.).
(4) Install fluid level sensor connector.
(5) Fill and bleed brake system.
PEDAL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - STANDARD PEDAL
A suspended-type brake pedal is used, the pedal
pivots on a shaft mounted in the pedal support
bracket. The bracket is attached to the dash panel.
The brake pedal assembly and pedal pad are the
only serviceable component.
DESCRIPTION - ADJUSTABLE PEDALS
The Adjustable Pedals System (APS) is designed to
enable the fore and aft repositioning of the brake and
accelerator pedals. This results in improved ergonom-
ics in relation to the steering wheel for taller and
shorter drivers. Being able to adjust the pedal posi-
Fig. 50 Master Cylinder Bleeding
1 - BLEEDING TUBES
2 - RESERVOIR
Fig. 51 Master Cylinder Mounting
1 - MOUNTING NUT
2 - SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - MOUNTING NUT
4 - BRAKE LINES
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 25
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 207 of 2199

Measure rotor thickness a minimum of six points
around the rotor face. Position the micrometer approx-
imately 19 mm (3/4 in.) from the rotor outer circumfer-
ence for each measurement (Fig. 62).
Thickness should not vary by more than 0.0127 mm
(0.0005 in.) from point to point on the rotor. Refinish or
replace the rotor if necessary.
NOTE: A hub mounted on-vehicle lathe is recom-
mended. This type of lathe trues the rotor to the vehi-
cles hub/bearing.
CAUTION: For vehicles equipped with the Quadra-
Drive System, consisting of the NV-247 transfer case
and a Vari-Lok differential in the front and rear axles,
the following steps must be done prior to the use of a
hub mounted on-vehicle brake lathe. Disconnect the
driveshaft (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/
PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL)
from the respective axle on which the brake rotors are
being machined. Temporarily remove both brake cali-
pers (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL) from the axle
while disc rotor machining is in process. Both steps
will prevent unnecessary loads to the hub mounted
on-vehicle lathe and speed machining times. Install a
thread lock material to the driveshaft attaching bolts
when reinstalling (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
INSTALLATION).
Front rotors and hub/bearings are matched mounted
for minimum lateral runout. Before removing the rotor,
mark the rotor and hub/bearing to maintain original
orientation.
FRONT ROTOR LATERAL RUNOUT
Check rotor lateral runout whenever pedal pulsation,
or rapid, uneven brake lining wear has occurred.
The rotor must be securely clamped to the hub to
ensure an accurate runout measurement. Secure therotor with a minimum of 3 lug nuts and large diameter
flat washers on each stud.
Use a dial indicator to check lateral runout (Fig. 63).
Maximum allowable rotor lateral runout is 0.05 mm
(0.002 in.).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR DISC
BRAKE ROTOR
ROTOR MINIMUM THICKNESS
Minimum usable thickness of the rear disc brake
rotor is 8.5 mm (0.335 in.). The thickness specification
is located on the center section of the rotor.
Never resurface a rotor if machining would cause
thickness to fall below this limit.
Measure rotor thickness at the center of the brake
shoe contact surface. Replace the rotor if worn below
minimum thickness, or if refinishing would reduce
thickness below the allowable minimum.
REAR ROTOR THICKNESS VARIATION
Variations in rotor thickness will cause pedal pulsa-
tion, noise and shudder.
Measure rotor thickness at a minimum of six points
around the rotor face. Position the micrometer approxi-
mately 19 mm (3/4 in.) from the rotor outer circumfer-
ence for each measurement (Fig. 62).
Thickness should not vary by more than 0.0127 mm
(0.0005 in.) from point to point on the rotor. Refinish or
replace the rotor if necessary.
REAR ROTOR LATERAL RUNOUT
Check rotor lateral runout whenever diagnosis indi-
cates pedal pulsation and rapid, uneven brake lining
wear.
The rotor must be securely clamped to the hub to
ensure an accurate runout measurement. Secure the
rotor with the wheel nuts and 4 or 5 large diameter flat
washers on each stud.
Use a dial indicator to check lateral runout (Fig. 63).
Maximum allowable lateral runout is 0.76 mm (0.003 in.).
Fig. 62 Measuring Rotor Thickness Variation
1 - MICROMETER
2 - ROTOR
Fig. 63 Checking Rotor Lateral Runout
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
5 - 32 BRAKES - BASEWJ
ROTORS (Continued)
2002 WJ Service Manual
Publication No. 81-370-02064
02WJ5-32 June, 2002
Page 208 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - DISC ROTOR
MACHINING
CAUTION: For vehicles equipped with the Quadra-
Drive System, consisting of the NV-247 transfer case
and a Vari-Lok differential in the front and rear axles,
the following steps must be done prior to the use of a
hub mounted on-vehicle brake lathe. Disconnect the
driveshaft (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/
PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL)
from the respective axle on which the brake rotors are
being machined. Temporarily remove both brake cali-
pers (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL) from the axle
while disc rotor machining is in process. Both steps
will prevent unnecessary loads to the hub mounted
on-vehicle lathe and speed machining times. Install a
thread lock material to the driveshaft attaching bolts
when reinstalling (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
INSTALLATION).
NOTE: A hub mounted on-vehicle lathe is recom-
mended. This type of lathe trues the rotor to the vehi-
cles hub/bearing.
The disc brake rotor can be machined if scored or
worn. The lathe must machine both sides of the rotor
simultaneously with dual cutter heads. The rotor
mounting surface must be clean before placing on the
lathe. Equipment capable of machining only one side at
a time may produce a tapered rotor.
CAUTION: Brake rotors that do not meet minimum
thickness specifications before or after machining
must be replaced.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE ROTOR
NOTE: Front rotors and hub/bearings are matched
mounted for minimum lateral runout. Before removing
the rotor, mark the rotor and hub/bearing to maintain
original orientation.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the caliper anchor bolts (Fig. 64) and
remove the caliper and anchor as an assembly from the
steering knuckle.
(4) Secure caliper anchor assembly to nearby suspen-
sion part with a wire.Do not allow brake hose to
support caliper weight.
(5) Mark the rotor and hub/bearing to maintain orig-
inal orientation. Remove retainers securing rotor to hub
studs.
(6) Remove rotor from hub/bearing.
REMOVAL - REAR DISC BRAKE ROTOR
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the caliper anchor bolts (Fig. 65).
(4) Remove caliper and anchor as an assembly.(5) Secure caliper anchor assembly to nearby suspen-
sion part with wire.Do not allow brake hose to sup-
port caliper weight.
(6) Remove retainers securing rotor to axle studs.
(7) Remove rotor off axle studs.
Fig. 64 Caliper Anchor Bolts
1 - KNUCKLE
2 - ANCHOR
3 - ANCHOR BOLTS
4 - ROTOR
Fig. 65 Caliper Anchor Bolts
1 - ROTOR
2 - ANCHOR
3 - ANCHOR BOLTS
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 33
ROTORS (Continued)
2002 WJ Service Manual
Publication No. 81-370-02064
02WJ5-33 June, 2002
Page 217 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES
The ABS brake system performs several self-tests
every time the ignition switch is turned on and the
vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the systems
input and output circuits to verify the system is oper-
ating correctly. If the on board diagnostic system
senses that a circuit is malfunctioning the system
will set a trouble code in its memory.
NOTE: An audible noise may be heard during the
self-test. This noise should be considered normal.
NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the ABS system. For additional informa-
tion refer to the Electrical section. For test proce-
dures refer to the Chassis Diagnostic Manual.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM
ABS system bleeding requires conventional bleed-
ing methods plus use of the DRB scan tool. The pro-cedure involves performing a base brake bleeding,
followed by use of the scan tool to cycle and bleed the
HCU pump and solenoids. A second base brake bleed-
ing procedure is then required to remove any air
remaining in the system.
(1) Perform base brake bleeding. (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR (Refer to
5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Connect scan tool to the Data Link Connector.
(3) Select ANTILOCK BRAKES, followed by MIS-
CELLANEOUS, then ABS BRAKES. Follow the
instructions displayed. When scan tool displays TEST
COMPLETE, disconnect scan tool and proceed.
(4) Perform base brake bleeding a second time.
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
OR (Refer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(5) Top off master cylinder fluid level and verify
proper brake operation before moving vehicle.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
G-Sensor Bolt 5.6 Ð 50
Hydraulic Control Unit/Controller
Antilock Brakes
Mounting Bolts12 9 125
Hydraulic Control Unit/Controller
Antilock Brakes
Brake Lines16 Ð 144
Hydraulic Control Unit/Controller
Antilock Brakes
CAB Screws1.8 Ð 16
Wheel Speed Sensors
Front Sensor Bolt12-14 106-124 Ð
Wheel Speed Sensors
Rear Sensor Bolt12-14 106-124 Ð
5 - 42 BRAKES - ABSWJ
BRAKES - ABS (Continued)
Page 220 of 2199

(3) Connect the harness to the switch. Be sure the
harness connector is firmly seated.
(4) Place the carpet in position and fold the rear
seat back down.
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
A wheel speed sensor is used at each wheel. The
front sensors are mounted to the steering knuckles.The rear sensors are mounted at the outboard end of
the axle. Tone wheels are mounted to the outboard
ends of the front and rear axle shafts. The gear type
tone wheel serves as the trigger mechanism for each
sensor.
OPERATION
The sensors convert wheel speed into a small digi-
tal signal. The CAB sends 12 volts to the sensors.
The sensor has an internal magneto resistance
bridge that alters the voltage and amperage of the
signal circuit. This voltage and amperage is changed
by magnetic induction when the toothed tone wheel
passes the wheel speed sensor. This digital signal is
sent to the CAB. The CAB measures the voltage and
amperage of the digital signal for each wheel.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and fold the rear seat forward. Then
move the carpeting aside for access to the rear sensor
connectors.
(2) Disconnect the rear sensor wire at the harness
connectors (Fig. 7).
(3) Push the sensor wires and grommets through
the floorpan holes.
(4) Raise and support the vehicle.
(5) Disengage the sensor wire from the axle and
the chassis brackets and from the brake line retain-
ers.
(6) Remove the sensor mounting bolt from the rear
brake backing plate. (Fig. 8).
(7) Remove the sensor from the backing plate.
Fig. 5 G-Switch Mounting
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS
2 - CONNECTOR
3 - G-SWITCH
Fig. 6 G-Switch
1 - SWITCH PART NUMBER
2 - ARROW INDICATES FRONT OF SWITCH FOR PROPER
MOUNTING
Fig. 7 Rear Sensor Connector
1 - RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 - LEFT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - G-SWITCH SENSOR
4 - PARKING BRAKE CABLES
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 45
G-SWITCH (Continued)
Page 221 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Insert the sensor through the backing plate
(Fig. 9).
(2) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242tto
the original sensor bolt. Use a new bolt if the original
is worn or damaged.
(3) Tighten the sensor bolt to 12-14 N´m (106-124
in. lbs.).
(4) Secure the sensor wire in the brackets and the
retainers on the rear brake lines. Verify that the sen-
sor wire is secure and clear of the rotating compo-
nents.
(5) Route the sensor wires to the rear seat area.
(6) Feed the sensor wires the through floorpan
access hole and seat the sensor grommets into the
floorpan.
(7) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.(8) Fold the rear seat and carpet forward for
access to the sensor wires and connectors.
(9) Connect the sensor wires to the harness con-
nectors.
(10) Reposition the carpet and fold the rear seat
down.
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL
UNIT)
DESCRIPTION
The HCU consists of a valve body, pump motor,
and wire harness.
OPERATION
Accumulators in the valve body store extra fluid
released to the system for ABS mode operation. The
pump is used to clear the accumulator of brake fluid
and is operated by a DC type motor. The motor is
controlled by the CAB.
The valves modulate brake pressure during
antilock braking and are controlled by the CAB.
The HCU provides three channel pressure control
to the front and rear brakes. One channel controls
the rear wheel brakes in tandem. The two remaining
channels control the front wheel brakes individually.
During antilock braking, the solenoid valves are
opened and closed as needed. The valves are not
static. They are cycled rapidly and continuously to
modulate pressure and control wheel slip and decel-
eration.
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
During antilock braking, solenoid valve pressure
modulation occurs in three stages, pressure increase,
pressure hold, and pressure decrease. The valves are
all contained in the valve body portion of the HCU.
PRESSURE DECREASE
The outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is
closed during the pressure decrease cycle.
A pressure decrease cycle is initiated when speed
sensor signals indicate high wheel slip at one or
more wheels. At this point, the CAB closes the inlet
then opens the outlet valve, which also opens the
return circuit to the accumulators. Fluid pressure is
allowed to bleed off (decrease) as needed to prevent
wheel lock.
Once the period of high wheel slip has ended, the
CAB closes the outlet valve and begins a pressure
increase or hold cycle as needed.
Fig. 8 Sensor Mounting Bolt
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLT
Fig. 9 Wheel Speed Sensor
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 - BACKING PLATE
5 - 46 BRAKES - ABSWJ
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
Page 222 of 2199

PRESSURE HOLD
Both solenoid valves are closed in the pressure
hold cycle. Fluid apply pressure in the control chan-
nel is maintained at a constant rate. The CAB main-
tains the hold cycle until sensor inputs indicate a
pressure change is necessary.
PRESSURE INCREASE
The inlet valve is open and the outlet valve is
closed during the pressure increase cycle. The pres-
sure increase cycle is used to counteract unequal
wheel speeds. This cycle controls re-application of
fluid apply pressure due to changing road surfaces or
wheel speed.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the negative battery cable from the
battery.
(2) Remove the air cleaner housing,(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(3) Pull the CAB harness connector release up and
remove connector (Fig. 10).(4) Remove the brake lines from the HCU.
(5) Remove the HCU/CAB side mounting bolt and
the two rear mounting bolts. (Fig. 11).
(6) Remove the HCU/CAB assembly from the vehi-
cle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install HCU/CAB assembly into the mounting
bracket and tighten mounting bolts to 12 N´m (9 ft.
lbs.).
(2) Install the brake lines to the HCU and tighten
to 16 N´m (12 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install CAB harness connector and push down
connector release.
(4) Install air cleaner housing,(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install negative battery cable to the battery.
(6) Bleed base and ABS brake systems,(Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR (Refer to
5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 10 CAB Connector Release
1 - CONNECTOR RELEASE
2 - CAB
Fig. 11 HCU/CAB Assembly
1 - SIDE MOUNTING BOLT
2 - REAR MOUNTING BOLTS
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 47
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT) (Continued)