Prop JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1237 of 2199

PDC LOWER COVER INSTALLATION
(1) Align the PDC housing lower cover on the bot-
tom of the PDC.
(2) Evenly press the lower cover into place until
latches are fully engaged.
(3) Where the right headlamp and dash harness
enters the PDC, tape the harness securely to the
trough formation on the PDC lower cover.
(4) Install the PDC in its mounting location on the
battery support.
(5) Install the battery wire harness over the two
PDC B+ terminal studs. Torque the nuts to 11.3 N´m
(100 in. lbs.).
(6) Install the battery. Refer to Battery System for
the procedure.
(7) Install the PDC cover.
INSTALLATION
The Power Distribution Center (PDC) main hous-
ing unit, the PDC fuse wedges and the PDC bus bars
cannot be repaired and are only serviced as a unit
with the right headlamp and dash wire harness. If
the PDC main housing unit, the fuse wedges or the
bus bars are faulty or damaged, the entire PDC and
right headlamp and dash wire harness unit must be
replaced.
(1) Position the PDC and the right headlamp and
dash wire harness unit in the engine compartment.
(2) Engage the PDC housing mounts with the
stanchions of the battery support and push the unit
downward until the mount latches fully engage the
mounting tabs on the stanchions.
(3) Install the two-holed eyelet of the battery wire
harness PDC take outs onto the two PDC B(+) termi-
nal studs.
(4) Install and tighten the nuts that secure the
eyelet of the battery wire harness PDC take outs to
the B(+) terminal studs. Tighten the nuts to 11.3
N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(5) Engage each of the retainers that secure the
right headlamp and dash wire harness to the vehicle
body and chassis components. Refer toConnector
Locationsin Wiring Diagrams for the location of
more information on the right headlamp and dash
wire harness retainer locations.
(6) Install all of the fasteners that secure each of
the right headlamp and dash wire harness ground
eyelets to the vehicle body and chassis components.
Refer toConnector Locationsin Wiring Diagrams
for the location of more information on the ground
eyelet locations.
(7) Reconnect each of the right headlamp and dash
wire harness connectors. Refer toConnector Loca-
tionsin Wiring Diagrams for the location of more
information on the right headlamp and dash wire
harness connector locations. For connectors securedwith screws, tighten the screws to 4.3 N´m (38 in.
lbs.).
(8) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION - FRONT POWER OUTLET
An accessory power outlet is standard equipment
on this model. The power outlet is installed in the
instrument panel center lower bezel, which is located
near the bottom of the instrument panel center stack
area, below the heater and air conditioner controls.
The power outlet base is secured by a snap fit within
the center lower bezel. A hinged door with an over-
center spring flips closed to conceal and protect the
power outlet base when the power outlet is not being
used, and flips open below the center lower bezel
while the power outlet is in use.
The power outlet receptacle unit and the power
outlet door are each available for service replace-
ment.
OPERATION - FRONT POWER OUTLET
The power outlet base or receptacle shell is con-
nected to ground, and an insulated contact in the
bottom of the shell is connected to battery current.
The power outlet receives battery voltage from a fuse
in the junction block at all times.
While the power outlet is very similar to a cigar
lighter base unit, it does not include the two small
spring-clip retainers inside the bottom of the recepta-
cle shell that are used to secure the cigar lighter
heating element to the insulated contact.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toHorn/Ci-
gar Lighter/Power Outletin Wiring Diagrams.
WARNING: REFER TO RESTRAINTS BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the junction block.
If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the shorted cir-
cuit or component as required and replace the faulty
fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
in the junction block. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK,
repair the open fused B(+) circuit to the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) fuse as required.
(3) Open the power outlet door. Check for continu-
ity between the inside circumference of the power
8W - 97 - 12 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONWJ
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (Continued)
Page 1239 of 2199

The cigar lighter relay cannot be repaired or
adjusted and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the
relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are
produced when the coil is de-energized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET
RELAY
The power outlet / cigar lighter relay (Fig. 16) is
located in the junction block, below the driver side
end of the instrument panel in the passenger com-
partment. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
Horn/Cigar Lighter/Power Outletin Wiring Dia-
grams.
WARNING: REFER TO RESTRAINTS BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Remove the power outlet / cigar lighter relay
from the junction block. Refer to the procedure in
this group.
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform the Relay Circuit Test that
follows. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) of
the junction block is connected to battery voltage and
should be hot at all times. Check for battery voltage
at the fused B(+) circuit cavity in the junction block
receptacle for the cigar lighter relay. If OK, go to
Step 2. If not OK, repair the fused B(+) circuit to the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) fuse as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the fused B(+) fuse in the junction block that feeds
the cigar lighter when the relay is energized by the
ignition switch. There should be continuity between
the junction block cavity for relay terminal 87 and
the fused B(+) fuse in the junction block at all times.
If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open fused
B(+) circuit to the junction block fuse as required.
(4) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It receives battery
feed to energize the cigar lighter relay when the igni-
tion switch is in the Accessory or On positions. Turn
the ignition switch to the On position. Check for bat-
tery voltage at the fused ignition switch output (acc/
run) circuit cavity for relay terminal 85 in the
junction block receptacle for the cigar lighter relay. If
OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the open fused
ignition switch output (acc/run) circuit to the ignition
switch as required.
(5) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. The junction block
cavity for this terminal should have continuity to
Fig. 16 Accessory Relay
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
8W - 97 - 14 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONWJ
POWER OUTLET RELAY (Continued)
Page 1240 of 2199

ground at all times. If not OK, repair the open
ground circuit to ground as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the steering column opening cover
from the instrument panel. Refer toSteering Col-
umn Opening Coverin Body for the procedure.
(3) The power outlet / cigar lighter relay is located
on the left side of the combination flasher in the
junction block.
(4) Remove the power outlet / cigar lighter relay
from the junction block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the power outlet / cigar lighter relay in
the proper receptacle in the junction block.
(2) Align the power outlet / cigar lighter relay ter-
minals with the terminal cavities in the junction
block receptacle.
(3) Push in firmly on the power outlet / cigar
lighter relay until the terminals are fully seated in
the terminal cavities in the junction block receptacle.
(4) Install the steering column opening cover onto
the instrument panel. Refer toSteering Column
Opening Coverin Body for the procedure.
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
IOD WIRE HARNESS
CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) connector that is located in a molded
connector receptacle on the lower rear surface of the
Junction Block (JB) housing (Fig. 17). The JB is con-
cealed above the molded plastic instrument panel
fuse cover. Integral latches molded into the fuse
cover secure it the JB, the Body Control Module
(BCM) and the 16-way data link connector tab of the
instrument panel steering column support bracket.
The fuse cover can be pulled downward to disengage
the latches and provide service access to all of the
fuses, relays and wire harness connectors of the JB.
Refer toInstrument Panel Fuse Coverin the
index of this service manual for the location of addi-
tional service information covering the fuse cover.
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw identifies a normal con-
dition where power is being drained from the battery
with the ignition switch in the Off position. The IOD
connector feeds the memory and sleep mode func-
tions for some of the electronic modules in the vehicleas well as various other accessories that require bat-
tery current when the ignition switch is in the Off
position, including the clock.
The IOD connector can be used by the vehicle
owner as a convenient means of reducing battery
depletion when a vehicle is to be stored for periods
not to exceed about twenty days (short-term storage).
Simply disconnect the IOD connector from the JB
receptacle. However, it must be remembered that dis-
connecting the IOD connector will not eliminate IOD,
but only reduce this normal condition. When a vehi-
cle will not be used for more than twenty days, but
less than thirty days, remove the IOD fuse from the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). If a vehicle will be
stored for more than about thirty days, the battery
negative cable should be disconnected to eliminate
normal IOD; and, the battery should be tested and
recharged at regular intervals during the vehicle
storage period to prevent the battery from becoming
discharged or damaged. Refer toIgnition-Off Draw
Fig. 17 Ignition-Off Draw Connector
1 - SNAP CLIPS
2 - SCREW
3 - CONNECTOR
4 - LEFT BODY WIRE HARNESS
5 - IOD CONNECTOR
6 - FUSED B+ CONNECTOR
7 - RIGHT BODY WIRE HARNESS
8 - SCREW
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - JUNCTION BLOCK
WJ8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 15
POWER OUTLET RELAY (Continued)
Page 1251 of 2199
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise, the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
REMOVAL).
(3) Secure the throttle in the wide-open position.
(4) Disconnect the ignition coil.
(5) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(6) Record the compression pressure on the third
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the
correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing)
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM HOT COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn OFF the
engine.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
Perform the test procedure on each cylinder accord-
ing to the tester manufacturer's instructions. While
testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through
the throttle body, tailpipe or oil filler cap opening.
Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART .
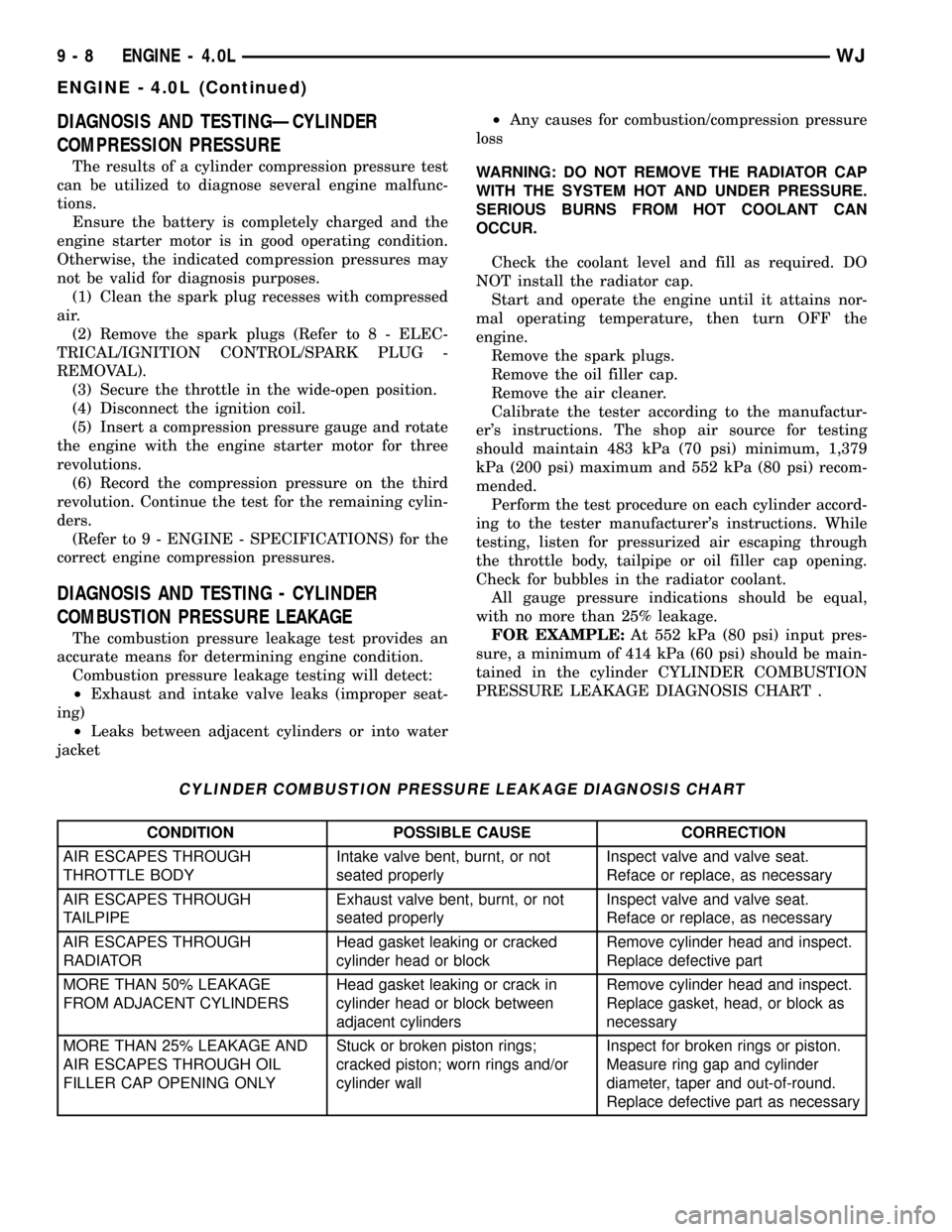
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLYStuck or broken piston rings;
cracked piston; worn rings and/or
cylinder wallInspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
9 - 8 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1252 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐREAR SEAL AREA
LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs, oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as outlined in (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICA-
TION - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks or
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is specially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled. Refer to the service DiagnosisÐMechani-
cal, under the Oil Leak row, for components
inspections on possible causes and corrections.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL
SEAL - REAR - REMOVAL), for proper replacement
procedures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANT
MopartGasket Sealant is a slow drying, perma-
nently soft sealer. This material is recommended for
sealing threaded fittings and gaskets against leakage
of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 9
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1254 of 2199

CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 40É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 3).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 4).CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Mark the hinge locations on the hood panel for
alignment reference during installation. Remove the
engine compartment lamp. Remove the hood.
(3) Remove the radiator drain cock and radiator
cap to drain the coolant. DO NOT waste usable cool-
ant. If the solution is clean, drain the coolant into a
clean container for reuse.
(4) Remove the upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose.
(5) Remove the lower radiator hose.
(6) Remove upper radiator support retaining bolts
and remove radiator support.
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
Fig. 4 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 11
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1262 of 2199

(2) Lift cover up and position to the side.
(3) Remove air cleaner element.
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
(1) Clean inside of air cleaner housing before
installing new element.
(2) Install air cleaner element into housing.
(3) Latch clips and clamp cover down to secure. Be
sure air cleaner cover is properly seated to air
cleaner housing.
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL - 4.0L
(1) Disconnect air cleaner cover-to-air duct clamp
(Fig. 6).
(2) Disconnect air duct at housing.
(3)Each of the 3 air cleaner housing mount-
ing bolts is attached with 2 nuts (an upper nut
and lower nut). DO NOT REMOVE BOLTS. To
prevent stripping bolts, only remove lower
nuts. The lower housing nuts are located under
left front inner fender (Fig. 6).
(a) To gain access to lower nuts, raise vehicle.
(b) Remove clips retaining rubber inner fender
shield.
(c) Pry back shield enough to gain access to
lower nuts.
(d) Remove 3 nuts.
(e) Remove air cleaner assembly from vehicle.
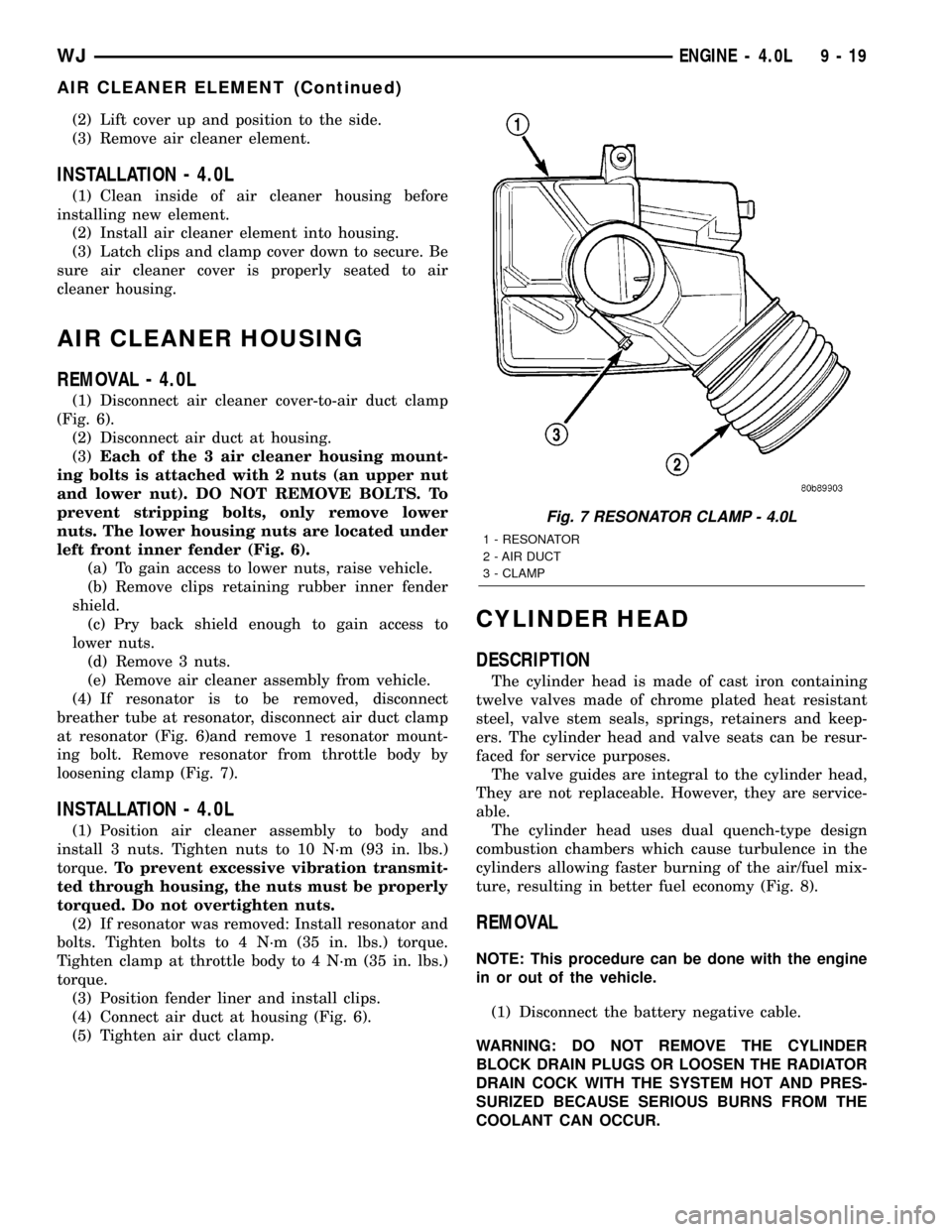
(4) If resonator is to be removed, disconnect
breather tube at resonator, disconnect air duct clamp
at resonator (Fig. 6)and remove 1 resonator mount-
ing bolt. Remove resonator from throttle body by
loosening clamp (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
(1) Position air cleaner assembly to body and
install 3 nuts. Tighten nuts to 10 N´m (93 in. lbs.)
torque.To prevent excessive vibration transmit-
ted through housing, the nuts must be properly
torqued. Do not overtighten nuts.
(2) If resonator was removed: Install resonator and
bolts. Tighten bolts to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
Tighten clamp at throttle body to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Position fender liner and install clips.
(4) Connect air duct at housing (Fig. 6).
(5) Tighten air duct clamp.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head is made of cast iron containing
twelve valves made of chrome plated heat resistant
steel, valve stem seals, springs, retainers and keep-
ers. The cylinder head and valve seats can be resur-
faced for service purposes.
The valve guides are integral to the cylinder head,
They are not replaceable. However, they are service-
able.
The cylinder head uses dual quench-type design
combustion chambers which cause turbulence in the
cylinders allowing faster burning of the air/fuel mix-
ture, resulting in better fuel economy (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure can be done with the engine
in or out of the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAIN COCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE
COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
Fig. 7 RESONATOR CLAMP - 4.0L
1 - RESONATOR
2 - AIR DUCT
3 - CLAMP
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 19
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT (Continued)
Page 1263 of 2199

(2) Drain the coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE) and disconnect the hoses
at the engine thermostat housing and the water
pump inlet. DO NOT waste reusable coolant. If the
solution is clean and is being drained only to service
the engine or cooling system, drain the coolant into a
clean container for reuse.
(3) Remove the air cleaner assembly (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the capscrews, bridge and pivot assem-
blies and rocker arms (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD/ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER ASSY -
REMOVAL).
(6) Remove the push rods.Retain the push rods,
bridges, pivots and rocker arms in the same
order as removed.
(7) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the A/C compressor mounting bolts
and secure the compressor to the side.
(9) Remove the power steering pump and bracket
from the intake manifold and water pump. Set the
pump and bracket aside. DO NOT disconnect the
hoses.
(10) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release
procedure. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Disconnect the fuel supply line at the fuel rail.(12) Remove the intake and exhaust manifolds
from the engine cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove the coil rail (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/COIL RAIL - REMOV-
AL).
(14) Remove spark plugs (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG - REMOV-
AL).
(15) Disconnect the temperature sending unit wire
connector.
(16) Remove the engine cylinder head bolts. Bolt
No.14 cannot be removed until the head is moved for-
ward (Fig. 9). Pull bolt No.14 out as far as it will go
and then suspend the bolt in this position (tape
around the bolt).
(17) Remove the engine cylinder head and gasket
(Fig. 9).
(18) If this was the first time the bolts were
removed, put a paint dab on the top of the bolt. If the
bolts have a paint dab on the top of the bolt or it
isn't known if they were used before, discard the
bolts.
(19) Stuff clean lint free shop towels into the cyl-
inder bores.
NOTE: If the valves, springs, or seals are to be
inspected/replaced at this time, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST
VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE) for
proper inspection procedures.
Fig. 8 Cylinder Head 4.0L Engine
1 - CYLINDER HEAD BOLTS
2 - CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
3 - CYLINDER HEAD
Fig. 9 Engine Cylinder
1 - CYLINDER HEAD BOLTS
2 - CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
3 - CYLINDER HEAD
9 - 20 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1269 of 2199

(5) Position the valve spring and retainer on the
engine cylinder head and compress the valve spring
with Valve Spring Compressor Tool MD-998772A.
(6) Install the valve locks and release the tool.
(7) Tap the valve spring from side to side with a
hammer to ensure that the spring is properly seated
at the engine cylinder head. Also tap the top of the
retainer to seat the valve locks.
(8) Install the engine cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The rocker arms are made of stamped steel and
have a operational ratio of 1.6:1 (Fig. 21).
OPERATION
When the push rods are forced upward by the cam-
shaft lobes the push rod presses upward on the
rocker arms, the rocker arms pivot, forcing down-
ward pressure on the valves forcing the valves to
move downward and off from their seats.
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure can be done with the engine
in or out of the vehicle.
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Check for rocker arm bridges which are caus-
ing misalignment of the rocker arm to valve tip area.
(3) Remove the capscrews at each bridge and pivot
assembly (Fig. 22). Alternately loosen the capscrews
one turn at a time to avoid damaging the bridges.
(4) Remove the bridges, pivots and corresponding
pairs of rocker arms (Fig. 22). Place them on a bench
in the same order as removed.
(5) Remove the push rods and place them on a
bench in the same order as removed.
CLEANING
Clean all the components with cleaning solvent.
Use compressed air to blow out the oil passages in
the rocker arms and push rods.
Fig. 20 Valve and Valve Components
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
Fig. 21 Rocker ArmsÐTypical
1 - CAPSCREWS
2 - BRIDGE
3 - PIVOT ASSEMBLY
4 - PUSH RODS
5 - ROCKER ARMS
9 - 26 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1272 of 2199

(2) Remove cap screws, bridge and pivot assem-
blies and rocker arms (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD/ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER ASSY -
REMOVAL) for access to each valve spring to be
removed.
(3) Remove push rods.Retain the push rods,
bridges, pivots and rocker arms in the same
order and position as removed.
(4) Inspect the springs and retainer for cracks and
possible signs of weakening.
(5) Remove the spark plug(s) adjacent to the cylin-
der(s) below the valve springs to be removed.
(6) Connect an air hose to the adapter and apply
air pressure slowly. Maintain at least 621 kPa (90
psi) of air pressure in the cylinder to hold the valves
against their seats. For vehicles equipped with an air
conditioner, use a flexible air adaptor when servicing
the No.1 cylinder.
(7) Tap the retainer or tip with a rawhide hammer
to loosen the lock from the retainer. Use Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A to compress the spring
and remove the locks (Fig. 27).
(8) Remove valve spring and retainer (Fig. 27).
(9) Remove valve stem oil seals (Fig. 27). Note the
valve seals are different for intake and exhaust
valves. The top of each seal is marked either INT
(intake/black in color) or EXH (exhaust/brown in
color). DO NOT mix the seals.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: This procedure can be done with the engine
cylinder head installed on the block.
CAUTION: Install oil seals carefully to prevent dam-
age from the sharp edges of the valve spring lock
grove.
(1) Lightly push the valve seal over the valve stem
and valve guide boss. Be sure the seal is completely
seated on the valve guide boss.
(2) Install valve spring and retainer (Fig. 28).
(3) Compress the valve spring with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A and insert the valve
locks. Release the spring tension and remove the
tool. Tap the spring from side-to-side to ensure that
the spring is seated properly on the engine cylinder
head.(4) Release air pressure and disconnect the air
hose. Remove the adaptor from the spark plug hole
and install the spark plug.
(5) Repeat the procedures for each remaining valve
spring to be removed.
(6) Install the push rods. Ensure the bottom end of
each rod is centered in the plunger cap seat of the
hydraulic valve tappet.
(7) Install the rocker arms, pivots and bridge
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER
ARM / ADJUSTER ASSY - INSTALLATION) at their
original location.
(8) Install the engine cylinder head cover (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 27 Valve and Valve Components
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 29
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)