Prop JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 140 of 2199
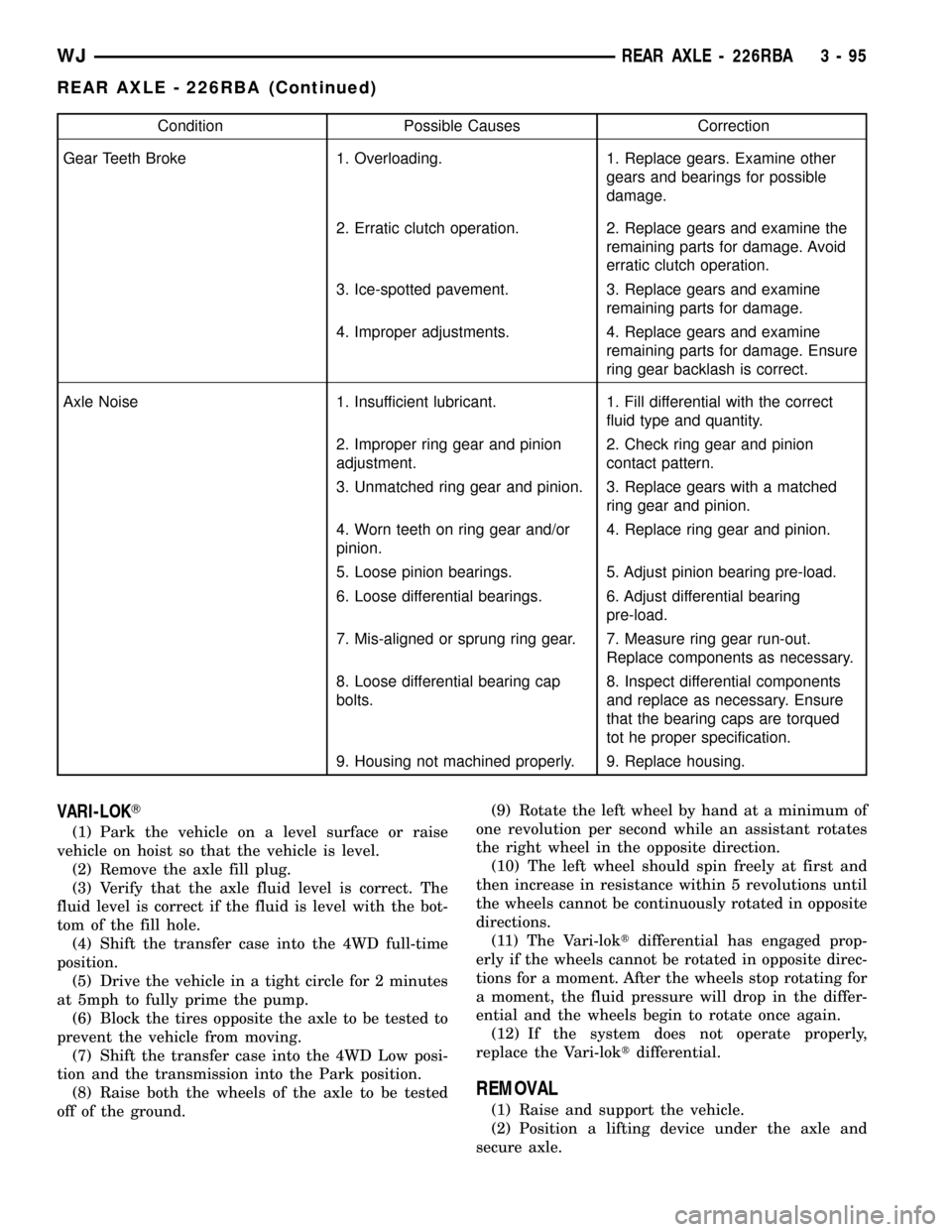
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
VARI-LOKT
(1) Park the vehicle on a level surface or raise
vehicle on hoist so that the vehicle is level.
(2) Remove the axle fill plug.
(3) Verify that the axle fluid level is correct. The
fluid level is correct if the fluid is level with the bot-
tom of the fill hole.
(4) Shift the transfer case into the 4WD full-time
position.
(5) Drive the vehicle in a tight circle for 2 minutes
at 5mph to fully prime the pump.
(6) Block the tires opposite the axle to be tested to
prevent the vehicle from moving.
(7) Shift the transfer case into the 4WD Low posi-
tion and the transmission into the Park position.
(8) Raise both the wheels of the axle to be tested
off of the ground.(9) Rotate the left wheel by hand at a minimum of
one revolution per second while an assistant rotates
the right wheel in the opposite direction.
(10) The left wheel should spin freely at first and
then increase in resistance within 5 revolutions until
the wheels cannot be continuously rotated in opposite
directions.
(11) The Vari-loktdifferential has engaged prop-
erly if the wheels cannot be rotated in opposite direc-
tions for a moment. After the wheels stop rotating for
a moment, the fluid pressure will drop in the differ-
ential and the wheels begin to rotate once again.
(12) If the system does not operate properly,
replace the Vari-loktdifferential.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lifting device under the axle and
secure axle.
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 95
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 141 of 2199

(3) Remove the wheels and tires.
(4) Remove brake calipers and rotors.
(5) Disconnect parking brake cables from brackets
and lever.
(6) Remove wheel speed sensors.
(7) Remove brake hose at the axle junction block.
Do not disconnect the brake hydraulic lines at the
calipers.
(8) Disconnect the vent hose from the axle shaft
tube.
(9) Mark propeller shaft and yokes for installation
reference.
(10) Remove propeller shaft.
(11) Disconnect stabilizer bar links.
(12) Remove upper suspension arm rear axle ball
joint nut.
(13) Separate rear axle ball joint from the upper
suspension arm with Remover 8278 (Fig. 4).
(14) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle.
(15) Disconnect track bar.
(16) Disconnect lower suspension arms from the
axle brackets.
(17) Separate the axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The weight of the vehicle must be sup-
ported by the springs before suspension arms and
track bar fasteners are tightened. If springs are notat their normal ride position, vehicle ride height and
handling could be affected.
(1) Raise axle with lift and align coil springs.
(2) Install lower suspension arms in axle brackets.
Install nuts and bolts, do not tighten bolts at this
time.
(3) Install upper suspension arm on rear axle ball
joint.
(4) Install rear axle ball joint nut and tighten to
122 N´m (90 ft.lbs.) (Fig. 5).
(5) Install track bar and attachment bolts, do not
tighten bolts at this time.
(6) Install shock absorbers and tighten nuts to 60
N´m (44 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install stabilizer bar links and tighten nuts to
36 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install wheel speed sensors.
(9) Connect parking brake cable to brackets and
lever.
(10) Install brake rotors and calipers.
(11) Install the brake hose to the axle junction
block.
(12) Install axle vent hose.
(13) Align propeller shaft and pinion yoke refer-
ence marks. Install U-joint straps and nuts tighten to
19 N´m (14 ft. lbs.).
(14) Install the wheels and tires.
(15) Add gear lubricant, if necessary.
(16) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
(17) Tighten lower suspension arm bolts to 177
N´m (130 ft. lbs.).
(18) Tighten track bar bolts to 100 N´m (74 ft.
lbs.).
Fig. 4 REAR BALL JOINT
1 - REMOVER
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - BALL JOINT STUD
Fig. 5 REAR BALL JOINT NUT
1 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
2 - REAR AXLE BALL JOINT
3 - REAR AXLE
3 - 96 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 144 of 2199

NOTE: Arbor Discs 6927A has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.
(5) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(6) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in axle housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the rearward surface of the pinion
height block (Fig. 8). Hold scooter block in place and
zero the dial indicator face to the pointer. Tighten
dial indicator face lock screw.
(7) With scooter block still in position against the
pinion height block, slowly slide the dial indicator
probe over the edge of the pinion height block.
(8) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 11). When the dial probe contacts the arbor bar,
the dial pointer will turn clockwise. Bring dial
pointer back to zero against the arbor bar, do not
turn dial face. Continue moving the dial probe to the
crest of the arbor bar and record the highest reading.
If the dial indicator can not achieve the zero reading,
the rear bearing cup or the pinion depth gauge set is
not installed correctly.
(9) Select a depth shim equal to the dial indicator
reading plus the pinion depth variance number
etched in the face of the pinion (Fig. 6). For example,
if the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD & GEAR
BACKLASH
Differential side bearing preload and gear backlash
is achieved by selective shims positioned behind the
differential side bearing cones. The proper shim
thickness can be determined using slip-fit Dummy
Bearings 6929-A in place of the differential side bear-
ings and a Dial Indicator C-3339. Before proceeding
with the differential bearing preload and gear back-
lash measurements, measure the pinion gear depth
and prepare the pinion for installation. Establishing
proper pinion gear depth is essential to establishing
gear backlash and tooth contact patterns. After the
overall shim thickness to take up differential side
play is measured, the pinion is installed, and the
gear backlash shim thickness is measured. The over-
all shim thickness is the total of the dial indicator
reading and the preload specification added together.
The gear backlash measurement determines the
thickness of the shim used on the ring gear side of
the differential case. Subtract the gear backlash shim
thickness from the total overall shim thickness and
select that amount for the pinion gear side of the dif-
ferential (Fig. 12). Differential shim measurements
are performed with the spreader W-129-B removed.
SHIM SELECTION
NOTE: It is difficult to salvage the differential side
bearings during the removal procedure. Install
replacement bearings if necessary.
(1) Remove differential side bearings from differ-
ential case.
Fig. 10 GAUGE TOOLS IN HOUSING
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 11 PINION GEAR DEPTH MEASUREMENT
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 99
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 147 of 2199

(14) Remove differential case and dummy bearings
from the housing.
(15) Install the pinion gear in the housing. Install
the pinion yoke and establish the correct pinion
rotating torque.
(16) Install differential case and Dummy Bearings
6929-A in the housing.
(17) Install a single dummy shim in the ring gear
side. Install bearing caps and tighten bolts snug.
(18) Seat ring gear side dummy bearing (Fig. 16).
(19) Position the dial indicator plunger on a flat
surface between the ring gear bolt heads. (Fig. 17).
(20) Push and hold differential case toward pinion
gear and zero dial indicator (Fig. 20).
(21) Push and hold differential case to ring gear
side of the housing and record dial indicator reading
(Fig. 21). Add Dummy Shim thickness to this read-
ing. This will be the total shim thickness to achieve
zero backlash.
(22) Subtract 0.152 mm (0.006 in.) from the dial
indicator reading to compensate for backlash between
ring and pinion gears. This total is the thickness
shim required to achieve proper backlash.(23) Subtract backlash shim thickness from the
total preload shim thickness. The remainder is the
shim thickness required on the pinion side of the
housing.
(24) Rotate dial indicator out of the way on pilot
stud.
(25) Remove differential case and dummy bearings
from the housing.
(26) Install side bearings and cups on differential
case.
(27) Install spreader W-129-B, utilizing some items
from Adapter Set 6987, on the housing and spread
axle opening enough to receive differential case.
(28) Place the bearing preload shims in the hous-
ing against the axle tubes.
(29) Install differential case into the housing.
(30) Remove spreader from housing.
(31) Rotate the differential case several times to
seat the side bearings.
Fig. 20 ZERO DIAL INDICATOR
1 - DIAL INDICATOR FACE
2 - FORCE DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO PINION GEAR SIDE
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - HOUSING
5 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 21 DIFFERENTIAL CASE RING GEAR SIDE
1 - READ DIAL INDICATOR
2 - FORCE DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO RING GEAR SIDE
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
3 - 102 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 148 of 2199

(32) Position the indicator plunger against a ring
gear tooth (Fig. 22).
(33) Push and hold ring gear upward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate.
(34) Zero dial indicator face to pointer.
(35) Push and hold ring gear downward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate. Dial indicator
reading should be between 0.076 mm (0.003 in.) and
0.15 mm (0.006 in.). If backlash is not within specifi-
cations transfer the necessary amount of shim thick-
ness from one side of the housing to the other (Fig.
23).
(36) Verify differential case and ring gear runout
by measuring ring to pinion gear backlash at eight
locations around the ring gear. Readings should not
vary more than 0.05 mm (0.002 in.). If readings vary
more than specified, the ring gear or the differential
case is defective.
After the proper backlash is achieved, perform
Gear Contact Pattern procedure.
GEAR CONTACT PATTERN
The ring gear and pinion teeth contact patterns
will show if the pinion depth is correct in the axle
housing. It will also show if the ring gear backlashhas been adjusted correctly. The backlash can be
adjusted within specifications to achieve desired
tooth contact patterns.
(1) Apply a thin coat of hydrated ferric oxide or
equivalent to the drive and coast side of the ring gear
teeth.
(2) Wrap, twist and hold a shop towel around the
pinion yoke to increase the turning resistance of the
pinion. This will provide a more distinct contact pat-
tern.
(3) With a boxed end wrench on a ring gear bolt,
rotate the differential case one complete revolution in
both directions while a load is being applied from
shop towel.
The areas on the ring gear teeth with the greatest
degree of contact against the pinion teeth will squee-
gee the compound to the areas with the least amount
of contact. Note and compare patterns on the ring
gear teeth to Gear Tooth Contact Patterns chart (Fig.
24) and adjust pinion depth and gear backlash as
necessary.
Fig. 22 RING GEAR BACKLASH
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 23 BACKLASH SHIM
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 103
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 156 of 2199

(7) Press metal retaining ring onto axle shaft with
Installer 7913 and a press (Fig. 30).
(8) Install axle in vehicle.
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Remove rear brake calipers and rotors.
(4) Mark propeller shaft and pinion yoke for
installation reference.
(5) Remove the propeller shaft from the yoke.
(6) Rotate pinion gear three or four times and ver-
ify that pinion rotates smoothly.
(7) Record torque necessary to rotate the pinion
gear with a inch pound dial-type torque wrench.
(8) Using a short piece of pipe and Spanner
Wrench 6958 to hold the pinion yoke and remove pin-
ion nut and washer (Fig. 31).
(9) Remove pinion companion flange with Remover
C-452 and Flange Wrench C-3281. (Fig. 32)
Fig. 30 BEARING RETAINING RING
1 - PRESS
2 - AXLE
3 - AXLE BEARING
4 - INSTALLER
5 - METAL RETAINING RING
Fig. 31 Pinion Yoke Holder
1 - PIPE
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - SPANNER WRENCH
4 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
Fig. 32 Pinion Yoke Remover
1 - FLANGE WRENCH
2 - YOKE
3 - YOKE PULLER
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 111
AXLE BEARINGS/SEALS (Continued)
Page 157 of 2199

(10) Remove pinion seal with Remover 7794-A and
a slide hammer (Fig. 33).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal. Install seal with an appropriate in
installer (Fig. 34).
(2) Install yoke on the pinion gear with Installer
C-3718 and Spanner Wrench 6958 (Fig. 35).
(3) Install anewnut on the pinion gear.Tighten
the nut only enough to remove the shaft end
play.
CAUTION: Do not exceed the minimum tightening
torque 298 N´m (220 ft. lbs.) when installing the pin-
ion yoke retaining nut at this point. Damage to col-
lapsible spacer or bearings may result.(4) Rotate the pinion a minimum of ten times and
verify pinion rotates smoothly. Rotate the pinion
shaft using an inch pound torque wrench. Rotating
torque should be equal to the reading recorded dur-
ing removal, plus 0.56 N´m (5 in. lbs.) (Fig. 36).
Fig. 33 Pinion Seal Remover
1 - REMOVER
2 - SLIDE HAMMER
3 - PINION SEAL
Fig. 34 PINION SEAL INSTALLER
1 - HANDLE
2 - INSTALLER
Fig. 35 PINION YOKE INSTALLER
1 - INSTALLER
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
4 - SPANNER WRENCH
Fig. 36 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - 112 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
PINION SEAL (Continued)
Page 158 of 2199

(5) If rotating torque is low, use Wrench 6958 to
hold the pinion yoke (Fig. 37) and tighten the pinion
shaft nut in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.) increments until
rotating torque is achieved.
CAUTION: If the maximum tightening torque is
reached prior to reaching the required rotating
torque, the collapsible spacer may have been dam-
aged. Replace the collapsible spacer.
(6) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(7) Fill differential with gear lubricant.
(8) Install the brake rotors and calipers.
(9) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(10) Lower the vehicle.
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Remove rear brake calipers and rotors.
(4) Mark propeller shaft and pinion yoke for
installation reference and remove propeller shaft.
(5) Rotate pinion gear a minimum of ten times and
verify pinion rotates smoothly.
(6) Record rotate torque of the pinion gear, with an
inch pound torque wrench.
(7) Hold pinion yoke with Spanner Wrench 6958
and remove pinion nut and washer (Fig. 38).
(8) Remove pinion yoke with Remover C-452 and
Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 39).
Fig. 37 PINION SHAFT NUT
1 - SPANNER WRENCH
2 - PIPE
3 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 38 PINION YOKE HOLDER
1 - 1 in. PIPE
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - SPANNER WRENCH
4 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
Fig. 39 PINION YOKE PULLER
1 - WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - PULLER
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 113
PINION SEAL (Continued)
Page 159 of 2199

(9) Remove pinion shaft seal with Remover 7794-A
and slide hammer (Fig. 40).
(10)
Remove front pinion bearing using a pair of pick
tools to pull the bearing off the pinion gear shaft.
NOTE: If the pinion bearing becomes bound on the
pinion shaft, lightly tap the end of the shaft with a
rawhide/rubber mallet.
(11) Remove the collapsible spacer.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install anewcollapsible spacer on pinion
shaft.
(2) Install pinion front bearing on the pinion shaft.
(3) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal and install seal with an appropriate
installer (Fig. 41).
(4) Install yoke with Installer C-3718 and Spanner
Wrench 6958 (Fig. 42).(5) Install yoke washer andnewnut on the pinion
gear. Tighten the nut to 271 N´m (200 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Never loosen pinion gear nut to decrease
pinion rotating torque and never exceed specified pre-
load torque. If preload torque or rotating torque is
exceeded a new collapsible spacer must be installed.
(6) Using yoke with Spanner Wrench 6958 and a
torque wrench set at 380 N´m (280 ft. lbs.), (Fig. 43)
slowly tighten the nut in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.) incre-
ments until the rotating torque is achieved. Measure
the rotating torque frequently to avoid over crushing
the collapsible spacer (Fig. 44).
Fig. 43 PINION NUT
1 - SPANNER WRENCH
2 - PIPE
3 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 40 PINION SEAL REMOVER
1 - REMOVER
2 - SLIDE HAMMER
3 - PINION SEAL
Fig. 41 PINION SEAL INSTALLER
1 - HANDLE
2 - INSTALLER
Fig. 42 Pinion Yoke Installer
1 - INSTALLER
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
4 - SPANNER WRENCH
3 - 114 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER (Continued)
Page 160 of 2199

NOTE: If more than 380 N´m (280 ft. lbs.) torque is
required to crush the collapsible spacer, the spacer
is defective and must be replaced.
(7) Check rotating torque with an inch pound
torque wrench (Fig. 44). The rotating torque of the
pinion gear should be, the reading recorded during
removal plus an additional 0.56 N´m (5 in. lbs.).
(8)
Install propeller shaft with reference marks align.
(9) Install rear brake rotors and calipers.
(10) Add gear lubricant, if necessary.
(11) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(12) Remove supports and lower vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove fill hole plug from the differential
housing cover.
(3) Remove differential housing cover and drain
fluid.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with flushing oil, light
engine oil or lint free cloth.
NOTE: Do not use water, steam, kerosene or gaso-
line for cleaning.
(5) Remove axle shafts.(6)
Note the reference letters stamped on the bearing
caps and housing machined sealing surface (Fig. 45).
(7) Loosen the differential bearing cap bolts.
(8) Position Spreader W-129-B with Adapter Kit
6987B on differential locating holes (Fig. 46). Install
holddown clamps and tighten the turnbuckle finger-
tight.
Fig. 44 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
Fig. 45 BEARING CAP REFERENCE
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
Fig. 46 SPREADER LOCATION
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - DOWEL
3 - SAFETY HOLD DOWN
4 - SPREADER
5 - TURNBUCKLE
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 115
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER (Continued)